Infectious Complications in Patients with B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated with Bispecific Antibodies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
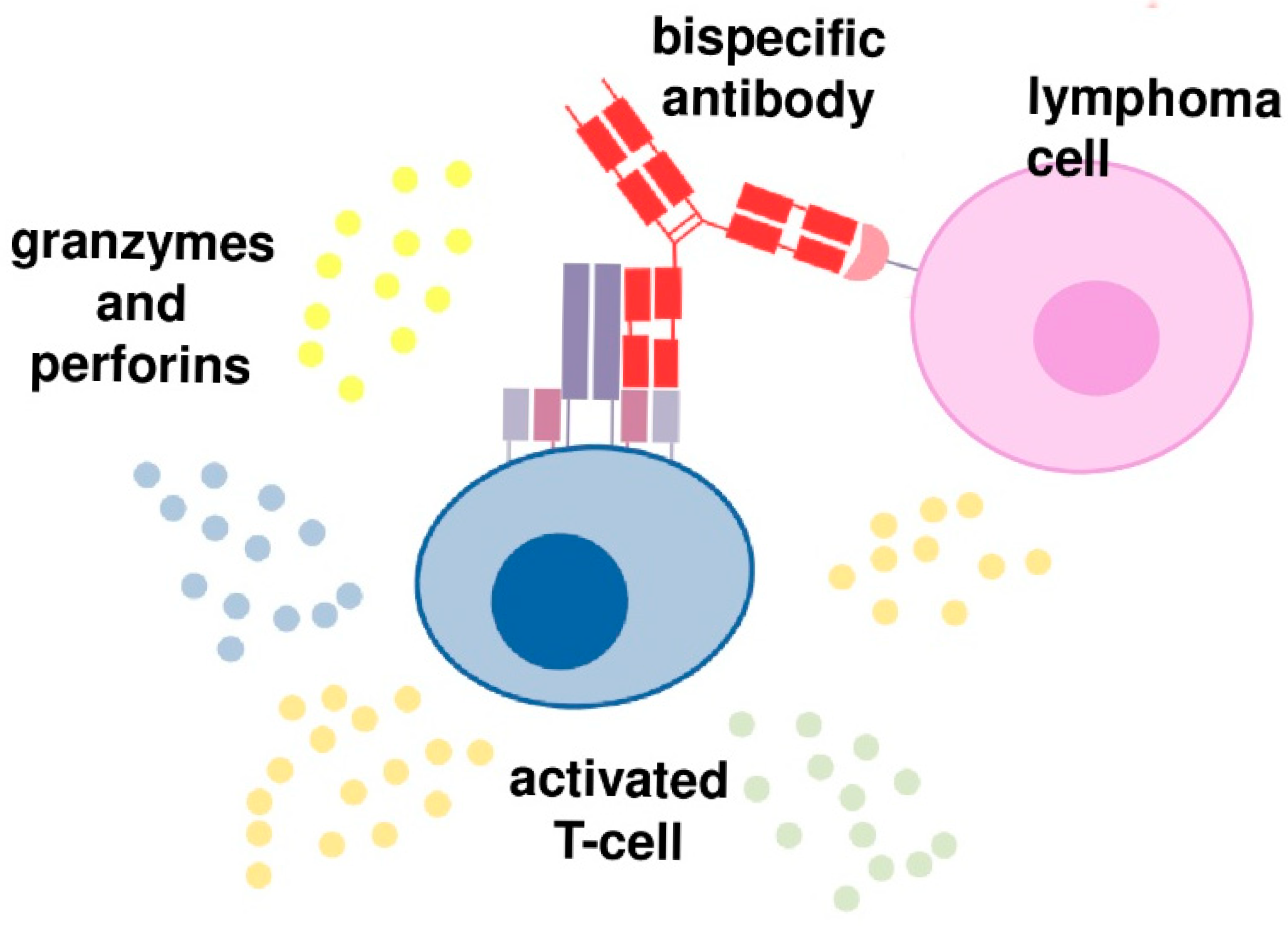
2. BsABs in Patients with B-Cell Malignancies
3. Other Bispecific Antibodies
4. Adverse Events During BsABs Treatment
5. Infectious Complications of BsABs
6. Mosunetuzumab
7. Glofitamab
8. Epcoritamab
9. Odronextamab
10. Other Bispecific Antibodies
11. Differences in Infections Between Plasma Cell Myeloma and Lymphoma Patients Treated with Bispecific Antibodies
12. Discussion
13. Recommendations on Infection Prophylaxis and Treatment
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Omer, M.H.; Shafqat, A.; Ahmad, O.; Alkattan, K.; Yaqinuddin, A.; Damlaj, M. Bispecific Antibodies in Hematological Malignancies: A Scoping Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISCT Leads Global Scientific Consortia to Respond to Recent FDA Report on Risk of T-Cell Malignancy in Patients Following CAR T-Cell Immunotherapies. Available online: https://www.isctglobal.org/telegrafthub/blogs/lauren-reville/2024/01/09/isct-leads-global-scientific-consortia-to-respond- (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Castaneda-Puglianini, O.; Chavez, J.C. Bispecific Antibodies for Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas and Multiple Myeloma. Drugs Context 2021, 10, 2021-2-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavarozzi, R.; Manzato, E. The Role of Bispecific Antibodies in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: From Structure to Prospective Clinical Use. Antibodies 2022, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. FDA Grants Accelerated Approval to Tarlatamab-Dlle for Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Abou Dalle, I.; Dulery, R.; Moukalled, N.; Ricard, L.; Stocker, N.; El-Cheikh, J.; Mohty, M.; Bazarbachi, A. Bi- and Tri-Specific Antibodies in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Current Data and Perspectives. Blood Cancer J. 2024, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizamuddin, I.A.; Bartlett, N.L. Bispecific Antibodies in Follicular Lymphoma. Haematologica 2024, 110, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atallah-Yunes, S.A.; Robertson, M.J. Current and Emerging Monoclonal Antibodies, Antibody-Drug Conjugates, and Bispecific Antibodies in Treatment of Lymphoma. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2022, 17, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez, M.P.; Bonifant, C.L.; Gottschalk, S. Redirecting T Cells to Hematological Malignancies with Bispecific Antibodies. Blood 2018, 131, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falchi, L.; Vardhana, S.A.; Salles, G.A. Bispecific Antibodies for the Treatment of B-Cell Lymphoma: Promises, Unknowns, and Opportunities. Blood 2023, 141, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejeune, M.; Köse, M.C.; Duray, E.; Einsele, H.; Beguin, Y.; Caers, J. Bispecific, T-Cell-Recruiting Antibodies in B-Cell Malignancies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Galisteo, A.; Álvarez-Vallina, L.; Sanz, L. Bi- and Trispecific Immune Cell Engagers for Immunotherapy of Hematological Malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, V.S.; Davies, A.J. Bispecific Antibodies in Indolent B-Cell Lymphomas. Front. Immunol. 2024, 14, 1295599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budde, L.E.; Assouline, S.; Sehn, L.H.; Schuster, S.J.; Yoon, S.-S.; Yoon, D.H.; Matasar, M.J.; Bosch, F.; Kim, W.S.; Nastoupil, L.J.; et al. Single-Agent Mosunetuzumab Shows Durable Complete Responses in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas: Phase I Dose-Escalation Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budde, L.E.; Olszewski, A.J.; Assouline, S.; Lossos, I.S.; Diefenbach, C.; Kamdar, M.; Ghosh, N.; Modi, D.; Sabry, W.; Naik, S.; et al. Mosunetuzumab with Polatuzumab Vedotin in Relapsed or Refractory Aggressive Large B Cell Lymphoma: A Phase 1b/2 Trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linton, K.M.; Vitolo, U.; Jurczak, W.; Lugtenburg, P.J.; Gyan, E.; Sureda, A.; Christensen, J.H.; Hess, B.; Tilly, H.; Cordoba, R.; et al. Epcoritamab Monotherapy in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma (EPCORE NHL-1): A Phase 2 Cohort of a Single-Arm, Multicentre Study. Lancet Haematol. 2024, 11, e593–e605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, M.J.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Bachy, E.; Corradini, P.; Iacoboni, G.; Khan, C.; Wróbel, T.; Offner, F.; Trněný, M.; et al. Glofitamab for Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2220–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.S.; Ku, M.; Hertzberg, M.; Huang, H.-Q.; Fox, C.P.; Zhang, H.; Yoon, D.H.; Kim, W.-S.; Abdulhaq, H.; Townsend, W.; et al. Glofitamab plus Gemcitabine and Oxaliplatin (GemOx) versus Rituximab-GemOx for Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (STARGLO): A Global Phase 3, Randomised, Open-Label Trial. Lancet 2024, 404, 1940–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplon, H.; Crescioli, S.; Chenoweth, A.; Visweswaraiah, J.; Reichert, J.M. Antibodies to Watch in 2023. mAbs 2022, 15, 2153410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.Gov. Home. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- Korfi, K.; Christiansen, A.; Jiang, Z.; Wilson, S.; Tracy, S.; Blank, A.; Herter, S.; Dimier, N.; Gomes, B.; Umana, P.; et al. Englumafusp Alfa (CD19-4-1BBL) and Glofitamab Combination in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (R/R NHL): Biomarker Results from a Phase I Dose-Escalation Trial. Blood 2023, 142, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.; Dickinson, M.J.; Gritti, G.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Townsend, W.; Bosch, F.; Bartlett, N.L.; Cartron, G.; Ghesquieres, H.; Houot, R.; et al. Englumafusp Alfa (CD19-4-1BBL) Combined with Glofitamab Is Safe and Efficacious in Patients with r/r B-NHL: Extended Follow up Analysis of the Dose-Escalation Part of Phase 1 Trial BP41072. Blood 2024, 144, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.; Gouni, S.; Pulles, A.; Strati, P.; Minnema, M.C.; Budde, L.E. Bispecific Antibody Use in Patients with Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2024, 44, e433516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvaris, R.; Ong, J.; Gregory, G.P. Bispecific Antibodies: A Review of Development, Clinical Efficacy and Toxicity in B-Cell Lymphomas. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangolo, A.; Amoozgar, B.; Mansour, C.; Zhang, L.; Gill, S.; Ip, A.; Cho, C. Comprehensive Review of Early and Late Toxicities in CAR T-Cell Therapy and Bispecific Antibody Treatments for Hematologic Malignancies. Cancers 2025, 17, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabkowska, A.; Domka, K.; Firczuk, M. Advancements in Cancer Immunotherapies Targeting CD20: From Pioneering Monoclonal Antibodies to Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1363102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crombie, J.L.; Graff, T.; Falchi, L.; Karimi, Y.H.; Bannerji, R.; Nastoupil, L.; Thieblemont, C.; Ursu, R.; Bartlett, N.; Nachar, V.; et al. Consensus Recommendations on the Management of Toxicity Associated with CD3×CD20 Bispecific Antibody Therapy. Blood 2024, 143, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Kothari, J. Supportive Care Measures for Bispecific T-Cell Engager Therapies in Haematological Malignancies. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2024, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafei, H.; Rezvani, K. Mitigating Infection Risks: The Promise and Challenge of Bispecific Antibodies in Haematological Malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 205, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tix, T.; Alhomoud, M.; Shouval, R.; Iacoboni, G.; Cliff, E.R.S.; Hansen, D.K.; Usmani, S.Z.; Salles, G.; Perales, M.-A.; Santos, D.M.C.D.; et al. Non-Relapse Mortality with Bispecific Antibodies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis in Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma. Mol. Ther. 2025, 33, 3163–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matasar, M.; Bartlett, N.L.; Shadman, M.; Budde, L.E.; Flinn, I.; Gregory, G.P.; Kim, W.S.; Hess, G.; El-Sharkawi, D.; Diefenbach, C.S.; et al. Mosunetuzumab Safety Profile in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Clinical Management Experience from a Pivotal Phase I/II Trial. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2024, 24, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budde, L.E.; Assouline, S.; Sehn, L.H.; Schuster, S.J.; Yoon, S.-S.; Yoon, D.H.; Matasar, M.J.; Bosch, F.; Kim, W.S.; Nastoupil, L.J.; et al. Durable Responses with Mosunetuzumab in Relapsed/Refractory Indolent and Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Extended Follow-Up of a Phase I/II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2250–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehn, L.H.; Bartlett, N.L.; Matasar, M.J.; Schuster, S.J.; Assouline, S.E.; Giri, P.; Kuruvilla, J.; Shadman, M.; Cheah, C.Y.; Dietrich, S.; et al. Long-Term 3-Year Follow-up of Mosunetuzumab in Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma after ≥2 Prior Therapies. Blood 2025, 145, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munakata, W.; Izutsu, K.; Mishima, Y.; Nagai, H.; Ishihara, Y.; Suzumiya, J.; Kanakura, Y.; Nanki, T.; Miyake, T.; Kawasaki, A.; et al. Dose-Escalation Part of Phase I Study of Single-Agent Mosunetuzumab in Japanese Patients with Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 53, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszewski, A.J.; Phillips, T.J.; Hoffmann, M.S.; Armand, P.; Kim, T.M.; Yoon, D.H.; Mehta, A.; Greil, R.; Westin, J.; Lossos, I.S.; et al. Mosunetuzumab in Combination with CHOP in Previously Untreated DLBCL: Safety and Efficacy Results from a Phase 2 Study. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 6055–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, M.; Morschhauser, F.; Iacoboni, G.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Offner, F.C.; Sureda, A.; Salles, G.; Martínez-Lopez, J.; Crump, M.; Thomas, D.N.; et al. Glofitamab, a Novel, Bivalent CD20-Targeting T-Cell–Engaging Bispecific Antibody, Induces Durable Complete Remissions in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphoma: A Phase I Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thieblemont, C.; Phillips, T.; Ghesquieres, H.; Cheah, C.Y.; Clausen, M.R.; Cunningham, D.; Do, Y.R.; Feldman, T.; Gasiorowski, R.; Jurczak, W.; et al. Epcoritamab, a Novel, Subcutaneous CD3xCD20 Bispecific T-Cell-Engaging Antibody, in Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Dose Expansion in a Phase I/II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2238–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thieblemont, C.; Karimi, Y.H.; Ghesquieres, H.; Cheah, C.Y.; Clausen, M.R.; Cunningham, D.; Jurczak, W.; Do, Y.R.; Gasiorowski, R.; Lewis, D.J.; et al. Epcoritamab in Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma: 2-Year Follow-up from the Pivotal EPCORE NHL-1 Trial. Leukemia 2024, 38, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, Y.; Abrisqueta, P.; de Vos, S.; Nijland, M.; Offner, F.; Osei-Bonsu, K.; Rana, A.; Archer, K.G.; Song, Y.; Cordoba, R.; et al. Epcoritamab + R-DHAX/C in Transplant-Eligible Patients (Pts) with High-Risk Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 7032. Available online: https://ascopubs.org/doi/10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.7032 (accessed on 30 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Vermaat, J.S.P.; Brody, J.; Duras, J.; Karimi, Y.; Cheah, C.Y.; Darrah, J.; Musuraca, G.; Morschhauser, F.; Hoehn, D.; Rana, A.; et al. Results from the Epcore NHL-2 Trial Arm 8: Epcoritamab SC + R-Mini-CHOP Leads to High Complete Metabolic Response Rates in Patients with Previously Untreated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Ineligible for Full-Dose R-CHOP. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2024, 30, S357–S358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, J.D.; Jørgensen, J.; Belada, D.; Costello, R.; Trněný, M.; Vitolo, U.; Lewis, D.J.; Karimi, Y.H.; Sureda, A.; André, M.; et al. Epcoritamab plus GemOx in Transplant-Ineligible Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL: Results from the EPCORE NHL-2 Trial. Blood 2025, 145, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lori, L.A.; Falchi, L.; Vermaat, J.S.; Musuraca, G.; Belada, D.; Nijland, M.; Christensen, J.H.; Offner, F.; Hoehn, D.; Marek, J.; et al. Epcoritamab with Rituximab + Lenalidomide (R2) in Previously Untreated (1L) Follicular Lymphoma (FL) and Epcoritamab Maintenance in FL: EPCORE NHL-2 Arms 6 and 7. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 7014. Available online: https://ascopubs.org/doi/10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.7014 (accessed on 30 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Sureda, A.; Falchi, L.; Leppa, S.; Vermaat, J.; Holte, H.; Hutchings, M.; Lugtenburg, P.; de Vos, S.; Abrisqueta, P.; Nijland, M.; et al. S222: Epcoritamab with rituximab + lenalidomide (r2) provides durable responses in patients with high-risk follicular lymphoma, regardless of pod24 status. HemaSphere 2023, 7, e5547136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, L.; Sureda Balari, A.; Leppä, S.; Vermaat, J.S.P.; Nijland, M.; Christensen, J.H.; de Vos, S.; Holte, H.; Merryman, R.W.; Lugtenburg, P.; et al. Fixed-Duration Epcoritamab + R2 Drives Deep and Durable Responses in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: 2-Year Follow-up from Arm 2 of the Epcore NHL-2 Trial. Blood 2024, 144, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerji, R.; Arnason, J.E.; Advani, R.H.; Brown, J.R.; Allan, J.N.; Ansell, S.M.; Barnes, J.A.; O’Brien, S.M.; Chávez, J.C.; Duell, J.; et al. Odronextamab, a Human CD20×CD3 Bispecific Antibody in Patients with CD20-Positive B-Cell Malignancies (ELM-1): Results from the Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Cohort in a Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 1 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2022, 9, e327–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topp, M.S.; Matasar, M.; Allan, J.N.; Ansell, S.M.; Barnes, J.A.; Arnason, J.E.; Michot, J.-M.; Goldschmidt, N.; O’Brien, S.M.; Abadi, U.; et al. Odronextamab Monotherapy in R/R DLBCL after Progression with CAR T-Cell Therapy: Primary Analysis of the ELM-1 Study. Blood 2025, 145, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.S.; Kim, T.M.; Cho, S.-G.; Jarque, I.; Iskierka-Jażdżewska, E.; Poon, L.M.; Prince, H.M.; Zhang, H.; Cao, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. Odronextamab Monotherapy in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma: Primary Efficacy and Safety Analysis in Phase 2 ELM-2 Trial. Nat. Cancer 2025, 6, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.M.; Taszner, M.; Novelli, S.; Cho, S.-G.; Villasboas, J.C.; Merli, M.; Jiménez-Ubieto, A.; Tessoulin, B.; Poon, L.M.; Tucker, D.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Odronextamab in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Riedell, P.A.; Tilly, H.; Ahmed, S.; Michot, J.-M.; Ghesquieres, H.; Schiano de Collela, J.M.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Bouabdallah, K.; Tessoulin, B.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of Plamotamab, an Anti-CD20 x Anti-CD3 Bispecific Antibody, in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: Recommended Dose Safety/Efficacy Update and Escalation Exposure-Response Analysis. Blood 2022, 140, 9470–9472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Qian, Z.; Zhou, K.; Fan, L.; Tan, P.; Giri, P.; Li, Z.; Kenealy, M.; et al. GB261, an Fc-Function Enabled and CD3 Affinity De-Tuned CD20/CD3 Bispecific Antibody, Demonstrated a Highly Advantageous Safety/Efficacy Balance in an Ongoing First-in-Human Dose-Escalation Study in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2023, 142, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morschhauser, F. Englumafusp Alfa (CD19/4-1BBL) Combined with Glofitamab Is Safe and Shows High Efficacy in Patients with R/R Aggressive B-NHL: Final Results of the Dose Escalation Part of Phase 1 Trial BP41072. Available online: https://library.ehaweb.org/eha/2024/eha2024-congress/422341/franck.morschhauser.englumafusp.alfa.28cd19.4-1bbl29.combined.with.glofitamab.is.html?f=menu%3D6%2Abrowseby%3D8%2Asortby%3D2%2Ace_id%3D2552%2Aot_id%3D29171%2Amarker%3D5099%2Afeatured%3D18527 (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Raje, N.; Anderson, K.; Einsele, H.; Efebera, Y.; Gay, F.; Hammond, S.P.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Lonial, S.; Ludwig, H.; Moreau, P.; et al. Monitoring, Prophylaxis, and Treatment of Infections in Patients with MM Receiving Bispecific Antibody Therapy: Consensus Recommendations from an Expert Panel. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, P.; Garfall, A.L.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Nahi, H.; San-Miguel, J.F.; Oriol, A.; Nooka, A.K.; Martin, T.; Rosinol, L.; Chari, A.; et al. Teclistamab in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesokhin, A.M.; Tomasson, M.H.; Arnulf, B.; Bahlis, N.J.; Miles Prince, H.; Niesvizky, R.; Rodrίguez-Otero, P.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Koehne, G.; Touzeau, C.; et al. Elranatamab in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Phase 2 MagnetisMM-3 Trial Results. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2259–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumma, N.; Richter, J.; Jagannath, S.; Lee, H.C.; Hoffman, J.E.; Suvannasankha, A.; Zonder, J.A.; Shah, M.R.; Lentzsch, S.; Baz, R.; et al. Linvoseltamab for Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2702–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, A.; Touzeau, C.; Schinke, C.; Minnema, M.C.; Berdeja, J.G.; Oriol, A.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; Morillo, D.; Martinez-Chamorro, C.; et al. Safety and Activity of Talquetamab in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (MonumenTAL-1): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 1-2 Study. Lancet Haematol. 2025, 12, e269–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, Y.C.; Magen, H.; Gatt, M.; Sebag, M.; Kim, K.; Min, C.-K.; Ocio, E.M.; Yoon, S.-S.; Chu, M.P.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; et al. Talquetamab plus Teclistamab in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblay, N.; Maity, R.; Hasan, F.; Neri, P. Deregulation of Adaptive T Cell Immunity in Multiple Myeloma: Insights into Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Cho, J.; Lee, M.H.; Yoon, S.E.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, S.J. CAR T Cells vs Bispecific Antibody as Third- or Later-Line Large B-Cell Lymphoma Therapy: A Meta-Analysis. Blood 2024, 144, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, G.K.; Maclean, M.; Cliff, E.R.S.; Teh, B.W.; Thursky, K.A.; Slavin, M.A.; Anderson, M.A.; Hawkes, E.A. Infections in Patients with Lymphoma Treated with Bispecific Antibodies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 3555–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minson, A.G.; Dickinson, M.J. New Bispecific Antibodies in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Haematologica 2025, 110, 1483–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhitano, A.P.; Slavin, M.A.; Harrison, S.J.; Teh, B.W. Bispecific Antibody Therapy, Its Use and Risks for Infection: Bridging the Knowledge Gap. Blood Rev. 2021, 49, 100810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacterial: Febrile Neutropenia—Duration of Therapy—New Drugs. Available online: https://www.ecil-leukaemia.com/images/ecil-10/ECIL_10_-_bacterial_group_final_recommendations.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Pagano, L.; Maschmeyer, G.; Lamoth, F.; Blennow, O.; Xhaard, A.; Spadea, M.; Busca, A.; Cordonnier, C.; Maertens, J.; ECIL. Primary Antifungal Prophylaxis in Hematological Malignancies. Updated Clinical Practice Guidelines by the European Conference on Infections in Leukemia (ECIL). Leukemia 2025, 39, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| BsAB | Antibody Platform Technology/Half-Life (Days) | Type of Fc | Epitope of CD20 | Route of Administration, Dosing Protocol | Approval (EMA/FDA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mosunetuzumab | knobs-into-holes/6–11 | IgG1 | Same as rituximab | i.v.; step-up dosing, up to 17 cycles | FL (June 2022/December 2022) |
| epcoritamab | Duobody, Head-to-tail fusion/22 | IgG1 | Same as ofatumumab | s.c. step-up dosing, to disease progression or toxicity | DLBCL (September 2023/May 2023) FL (September 2024/June 2024) |
| glofitamab | Humanized IgG1-based 2 + 1 CrossMab/6–11 | IgG1 | Same as obinutuzumab | i.v.; step-up dosing, up to 12 cycles | DLBCL (July 2023/June 2023) Combined with gemcitabine and oxaliplatin (pending, positive CHMP opinion February 2025/pending) |
| odronextamab | VelociBi/14 | IgG4 | Same as ofatumumab | i.v. step-up dosing, to disease progression or toxicity | DLBCL (August 2024/pending) |
| Clinical Trial Number (Phase) | Study Population/Number of Patients/Median Age (Years) F/M (%) | Number of Previous Lines of Therapy (Median) | Follow-Up (Months) | ORR/CR (%) | Median PFS/OS (Months) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monotherapy (≥2 prior lines of therapy) | ||||||
| mosunetuzumab | NCT02500407/(1/2) | RR FL/90/60/39/61 | 3 | 37.4 | 77.8/60 | 24/NR |
| glofitamab | NCT03075696/(1/2) | RR LBCL/154/66/35/65 | 3 | 12.9 | 52/40 | 4.9/50% 12-month OS: 50% |
| epcoritamab | NCT03625037 (1/2) | RR LBCL/164/64/40/60 | 3 | 25.1 | 63/40.1 | 24-month PFS/OS: 27.8/44.6 CR 65.1/76.2 |
| NCT03625037/(1/2) | RR FL/128/65/38/62 | 3 | 17.4 | 82/62.5 | ND | |
| odronextamab | NCT03888105 (2) | RR FL/128/61/49/51 | 3 | 20.1 | 80/73.4 | 20.7/NR |
| NCT03888105 (1/2) | RR DLBCL 127/67/40/60 | 3 | 29.9 | 52/31.5 | 4.4/9.2 | |
| Combination therapy (≥1 prior lines of therapy) | ||||||
| Glofitamab + GemOx | NCT04408638 STARGLO (3) | RR LBCL 183/68/43/57 | 1 | 20.7 | 69.9/57.4 | 14.4/25.5 |
| Bispecific Antibody | Study | Infection AEs n (%) | Treatment- Related Infection AEs (n; %) | Serious Infection AEs (n; %) | Infection AEs Leading to Treatment Discontinuation (n; %) | Infection AEs Resulting in Death (n; %) | Viral Infection (n; %) | Bacterial Infection (n; %) | Fungal Infection (n; %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epcoritamab monotherapy | EPCORE NHL-1 (FL) | NR | NR | NR | n = 17; 13% (COVID-19: n = 12; 9%), hepatitis E: n = 2; 2%), pneumonia: n = 1; 1%, sepsis from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: n = 1; 1%, sinusitis: n = 1; 1%) | n =8; 6% (COVID-19: n = 6; 5%), pneumonia: n = 1; 1%, sepsis from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: n = 1; 1%) | NR | NR | NR |
| Epcoritamab monotherapy | EPCORE NHL-1 (LBCL) | Grade 3–4: 40 (25.5%) | NR | NR | NR | Treatment-related: n = 2; 1% (COVID-19 pneumonia: n = 1; 1%), bacterial pneumonia: n = 1; 1%), Unrelated to treatment: n = 3; 2% (COVID-19: n = 2; 1%), PML: n = 1; 1%) | NR | NR | NR |
| Epcoritamab in combination (Epcoritamab-GemOx) | EPCORE NHL-2 arm 5 | 72% (COVID-19: 29%, URTI: 14%, pneumonia: 10%, UTI: 10%); Grade 3–4: 21% | NR | 32% | NR | n = 8; 8% * (COVID-19: n = 5; 5%, lung infection: n = 2; 2%, E. coli sepsis: n =1; 1%) | NR | NR | NR |
| Odronextamab | ELM-1 | 71 (49%) (Pneumonia: 15 (10%), URTI: 14 (10%), UTI: 14 (10%), oral candidiasis 8 (6%)); Grade ≥ 3: 33 (23%) (Pneumonia: 12 (8%), URTI: 3 (2%), UTI: 2 (1%)) | NR | Pneumonia: n = 9; 6% | Treatment-related: n = 4; 3% (CMV: n = 1; 1%), toxoplasmosis: n = 1; 1%, pneumonia: n = 2; 1%); treatment-unrelated: n = 2; 1% (neck abscess in a patient with previous spinal surgery: n = 1; 1%, device-related infection: n = 1; 1% | n = 3; 2% (lung infection: n = 1; 1%, pneumonia: n = 1; 1%, COVID-19: n = 1; 1%) | NR | NR | NR |
| Odronextamab | ELM-1 (DLBCL after CAR T) | 30 (50%); Grade ≥ 3: 12 (20%) | NR | NR | n = 3;5% (COVID-19: n = 1; 1.7%, pneumonia: n = 1; 1.7%, device-related infection: n = 1; 1.7%) | n = 2; 3.3% (COVID-19 pneumonia: n = 1; 1.7%, brain herniation in a patient with ongoing COVID-19 infection: n = 1; 1.7%) | n = 18; 30.0% | n = 1; 1.7% | n = 3; 5.0% |
| Odronextamab | ELM-2 (DLBCL) | 82 (64.6%); grade ≥ 3: 49 (38.6%) | grade ≥ 3 TEAEs COVID-19: 13 (10.2%) | NR | n = 6; 5% (COVID-19: n = 1; 1%, CMV reactivation: n = 1; 1%, pulmonary tuberculosis: n = 1; 1%, septic shock: n = 1; 1%, pneumonia: n = 1; 1%, P. jirovecii: n = 1; 1%) | n = 15; 12% (COVID-19: n = 5; 4%, pneumonia: n = 3; 2%, sepsis: n = 3; 2%, P. jirovecii pneumonia: n = 1; 1%, CMV infection: n = 1, 1%, pseudomonal sepsis: n = 1; 1%, CMV pneumonia: n = 1; 1%) | NR | NR | NR |
| Odronextamab | ELM-2 (FL) | 102 (79.7%); Grade ≥ 3: 54 (42.2%) | NR | NR | n = 12; 9% (COVID-19: n = 4; 3.1%, pneumonia: n = 2; 1.6%, COVID-19 pneumonia: n = 2; 1.6%, bronchitis viral: n = 1; 0.8%, pseudomonal pneumonia: n = 1; 0.8%, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: n = 1; 0.8%, sepsis: n = 1; 0.8%) | Treatment-related: n = 4; 3% (pneumonia: n = 1; 1%, PML: n = 1; 1%, pseudomonal pneumonia: n = 1; 1%, COVID-19 pneumonia plus systemic mycosis: n = 1; 1%) | NR | NR | NR |
| Mosunetuzumab | NCT02500407 cohort B (safety population) | NR | NR | Grade ≥ 3 pneumonia: n = 5; 2.5%); urinary tract infection grade ≥ 3: n = 5; 2.5% | NR | Chronic active Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infection and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) due to infection: n = 1, sepsis: n = 1, Candida sp. Infection: n = 1, pneumonia: n = 1 | Chronic active Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infection: n = 1 | NR | Candida sp. Infection: n = 1 |
| Mosunetuzumab | NCT02500407 | 102 (46.8%) | NR | n = 37; 17.0% (the most common of which was pneumonia: n = 9; 3.2%) | n = 25; 11.5%) | NR | Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infection: n = 1 | NR | NR |
| Mosunetuzumab | JO40295 | NR | NR | 0 | In 1 case due to grade 3 hemorrhagic cystitis and grade 3 pyelonephritis due to adenovirus infection | NR | n = 3; 13.0% Herpes zoster infection; n = 1 gastroenteritis in the course of Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection reactivation; n = 1 grade 3 hemorrhagic cystitis and grade 3 pyelonephritis due to adenovirus infection | NR | NR |
| Mosunetuzumab | NCT03671018 (R/R LBCL) | 39.2% | n = 17; 14.2% | 8.3% | Pneumonia: n = 1 | Pneumonia with concomitant exacerbation of heart failure: n = 1; 0.8%); COVID-19: n = 2; 1.7% | COVID-19: n = 10; 8.3), CMV infection: n = 1; 0.8%, EBV infection: n = 1; 0.8%; Herpes simplex infection: n = 1; 0.8%, hepatitis B virus reactivation: n = 1; 0.8% | NR | Candida infection: n = 2; 1.7%, bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: n = 1; 0.8%, fungal infection: n = 1; 0.8% |
| Mosunetuzumab | NCT03677141 (DLBCL) | 21 (52.5%) | NR | n = 9; 22.5% | NR | Pneumonia due to SARS-CoV-2 infection: n =1 | Herpes zoster: n = 5; 12.5% | NR | oral candidiasis: n = 3; 7.5% |
| Glofitamab | NCT03075696 (MCL) | 59 (38%) | NR | n = 23; 15.0% | NR | NR | COVID-19: n = 14; 9% | sepsis: n = 6; 4.0% | NR |
| Glofitamab | NP30179 | 88 (51.5%) | NR | 17.5% | n = 2; 1.2% | n = 2; 1.2% | Grade 3 CMV chorioretinitis: n = 1; 1.2% | sepsis and colitis: n = 1; 1.2% | NR |
| Glofitamab | STARGLO | 57.2% | NR | 23.3% | COVID-19 infection: n = 22; 12.2% | COVID-19: n = 9; 3.9% | COVID-19 infection: n = 33; 18.3% | NR | NR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szymczyk, A.; Drozd-Sokołowska, J.; Hus, I. Infectious Complications in Patients with B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated with Bispecific Antibodies. Cancers 2025, 17, 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152426
Szymczyk A, Drozd-Sokołowska J, Hus I. Infectious Complications in Patients with B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated with Bispecific Antibodies. Cancers. 2025; 17(15):2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152426
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzymczyk, Agnieszka, Joanna Drozd-Sokołowska, and Iwona Hus. 2025. "Infectious Complications in Patients with B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated with Bispecific Antibodies" Cancers 17, no. 15: 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152426
APA StyleSzymczyk, A., Drozd-Sokołowska, J., & Hus, I. (2025). Infectious Complications in Patients with B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated with Bispecific Antibodies. Cancers, 17(15), 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152426






