CT-Based Radiomics for a priori Predicting Response to Chemoradiation in Locally Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Image Acquisition
2.3. Radiomic Features
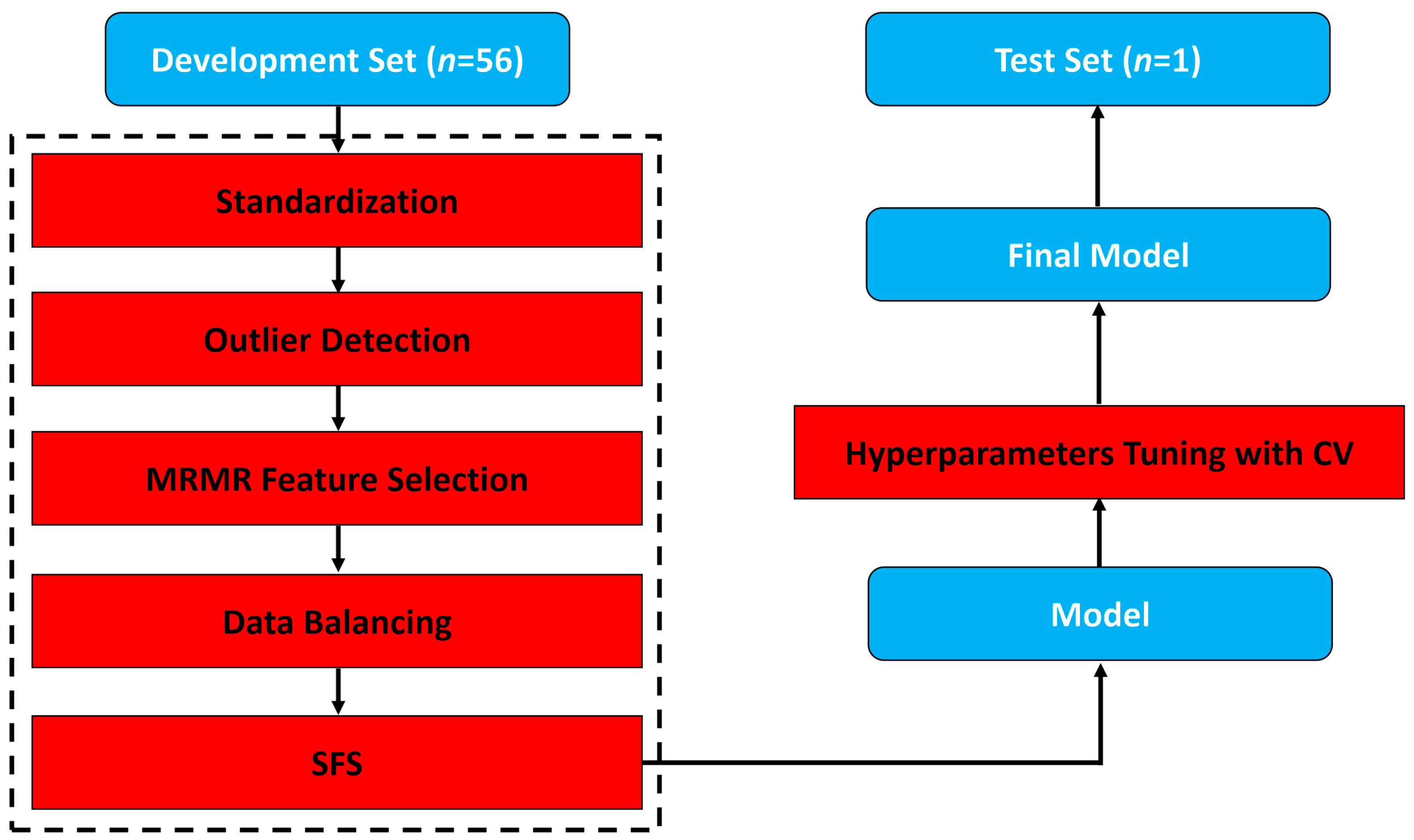
2.4. Model Building and Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
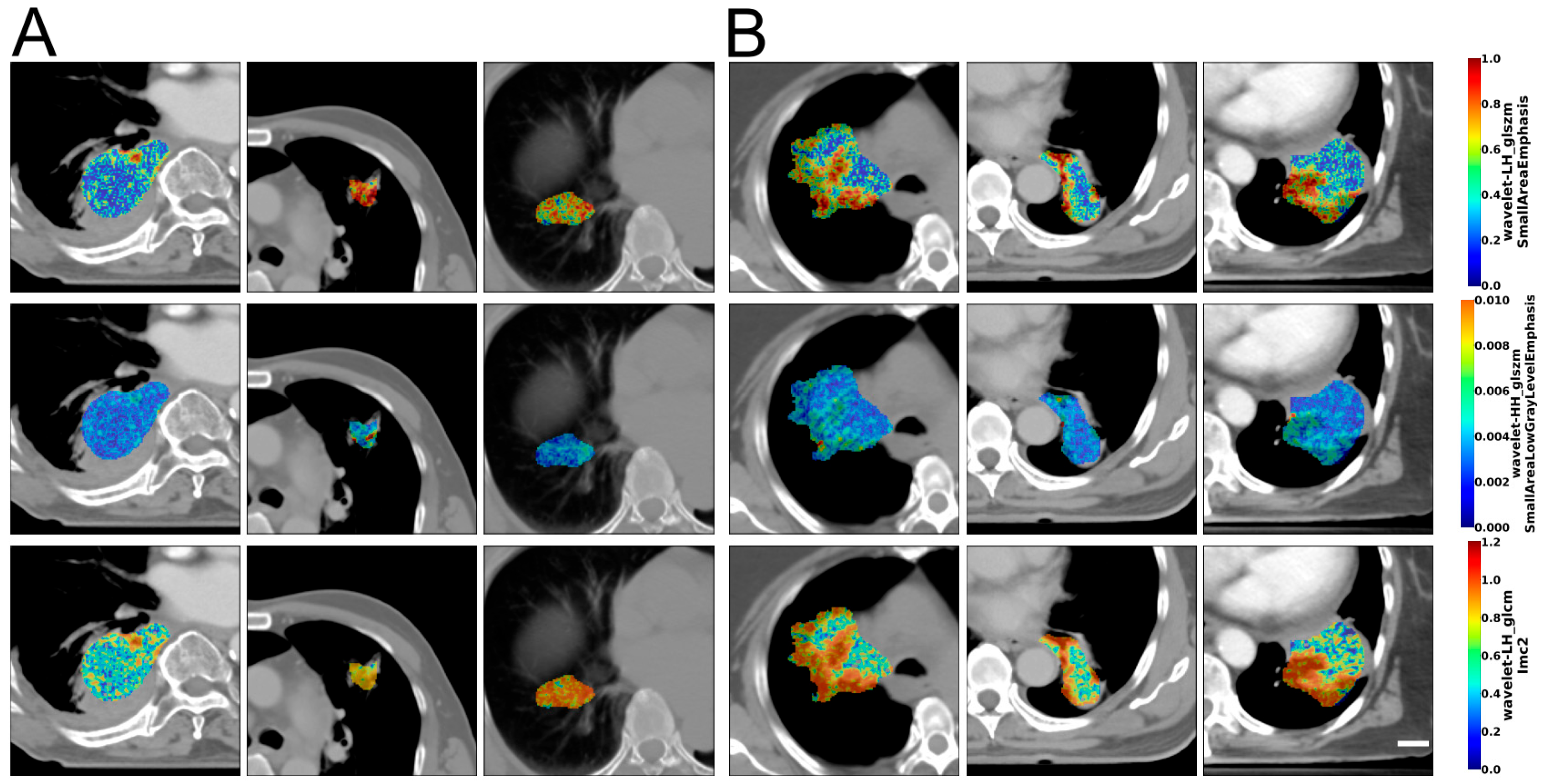
3.2. Image Analysis and Data Classification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| US | Ultrasound |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| PD-L1 | Programmed cell death ligand-1 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ALK-1 | Activin receptor-like kinase-1 |
| SEER | Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results |
| RECIST | Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors |
| kVp | Kilovoltage peak |
| GLCM | Gray-level co-occurrence matrix |
| GRLM | Gray-level run length matrix |
| GLSZM | Gray-level size zone matrix |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| NGTDM | Neighboring gray tone difference matrix |
| GLDM | Gray-level dependence matrix |
| LOOCV | Leave-one-out cross-validation |
| LOO | Leave one out |
| MRMR | Minimal redundancy–maximal relevance |
| SMOTE | Synthetic minority oversampling technique |
| SFS | Forward-sequential feature selection |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbors |
| SVM-Linear | Linear support vector machines |
| SVM-RBF | Support vector machines—radial basis function |
| RF | Random forest |
| XGBoost | Extreme gradient boosting |
| IMC2 | Informational Measure of Correlation 2 |
| AU | Arbitrary unit |
| pCR | Pathological complete response |
| MRD | Microscopic residual disease |
| GRD | Gross residual disease |
| IBSI | Image biomarkers standardization initiative |
| RTOG | Radiation therapy oncology group |
| CCRT | Chemoradiotherapy |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| MITK | Medical Imaging Interaction Toolkit |
| SERA | Standardized Environment for Radiomics Analysis |
| CaPTK | Cancer Imaging Phenomics Toolkit |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganti, A.K.; Klein, A.B.; Cotarla, I.; Seal, B.; Chou, E. Update of Incidence, Prevalence, Survival, and Initial Treatment in Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer in the US. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezjak, A.; Temin, S.; Franklin, G.; Giaccone, G.; Govindan, R.; Johnson, M.L.; Rimner, A.; Schneider, B.J.; Strawn, J.; Azzoli, C.G. Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation Oncology Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2100–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiaoit, K.; DiCenzo, D.; Fatima, K.; Bhardwaj, D.; Sannachi, L.; Gangeh, M.; Sadeghi-Naini, A.; Dasgupta, A.; Kolios, M.C.; Trudeau, M.; et al. Quantitative Ultrasound Radiomics for Therapy Response Monitoring in Patients with Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Multi-Institutional Study Results. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiCenzo, D.; Quiaoit, K.; Fatima, K.; Bhardwaj, D.; Sannachi, L.; Gangeh, M.; Sadeghi-Naini, A.; Dasgupta, A.; Kolios, M.C.; Trudeau, M.; et al. Quantitative Ultrasound Radiomics in Predicting Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Results from Multi-Institutional Study. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 5798–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravanelli, M.; Farina, D.; Morassi, M.; Roca, E.; Cavalleri, G.; Tassi, G.; Maroldi, R. Texture Analysis of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) on Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography: Prediction of the Response to the First-Line Chemotherapy. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 3450–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, M.M. Texture Analysis Using Gray Level Run Lengths. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1975, 4, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, B.V.; Holder, E.B. Image Characterizations Based on Joint Gray Level—Run Length Distributions. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1991, 12, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.; Sehgal, C.M.; Greenleaf, J.F. Use of Gray Value Distribution of Run Lengths for Texture Analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1990, 11, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X. Texture Information in Run-Length Matrices. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1998, 7, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibault, G.; Angulo, J.; Meyer, F. Advanced Statistical Matrices for Texture Characterization: Application to Cell Classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amadasun, M.; King, R. Textural Features Corresponding to Textural Properties. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1989, 19, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wee, W.G. Neighboring Gray Level Dependence Matrix for Texture Classification. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1983, 23, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Long, F.; Ding, C. Feature Selection Based on Mutual Information Criteria of Max-Dependency, Max-Relevance, and Min-Redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.T.; Ting, K.M.; Zhou, Z.-H. Isolation Forest. In Proceedings of the 2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Pisa, Italy, 15–19 December 2008; pp. 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique 2011. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, W.J., Jr.; Paulus, R.; Langer, C.J.; Komaki, R.; Lee, J.S.; Hauser, S.; Movsas, B.; Wasserman, T.; Rosenthal, S.A.; Gore, E.; et al. Sequential vs Concurrent Chemoradiation for Stage III Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Randomized Phase III Trial RTOG 9410. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, G.J.R.; O’Brien, M.E.; Siddique, M.; Chicklore, S.; Loi, H.Y.; Sharma, B.; Punwani, R.; Bassett, P.; Goh, V.; Chua, S. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Erlotinib: Heterogeneity of 18F-FDG Uptake at PET—Association with Treatment Response and Prognosis. Radiology 2015, 276, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Sun, X.; Sun, L.; Maxim, P.G.; Xing, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Wan, H.; Zhao, X.; Xing, L.; et al. Early Change in Metabolic Tumor Heterogeneity during Chemoradiotherapy and Its Prognostic Value for Patients with Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetan, M.R.; Gleeson, F.V. Radiomics in Predicting Treatment Response in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coroller, T.P.; Agrawal, V.; Narayan, V.; Hou, Y.; Grossmann, P.; Lee, S.W.; Mak, R.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Radiomic Phenotype Features Predict Pathological Response in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2016, 119, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coroller, T.P.; Agrawal, V.; Huynh, E.; Narayan, V.; Lee, S.W.; Mak, R.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Radiomic-Based Pathological Response Prediction from Primary Tumors and Lymph Nodes in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2017, 12, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.Y.; Ahn, Y.C.; Lee, K.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, J.; Shim, Y.M.; Han, J.; Choi, Y.-L. Quantitative CT Variables Enabling Response Prediction in Neoadjuvant Therapy with EGFR-TKIs: Are They Different from Those in Neoadjuvant Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Xia, W.; Zhang, R.; Wei, H.; Feng, J.; Zhao, X.; Jian, J.; Gao, X.; et al. CT-Based Radiomics Signatures Can Predict the Tumor Response of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with First-Line Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, L.A.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, L.; Matney, J.E.; Choi, H.; Kry, S.F.; Martel, M.K.; Stingo, F.; Liao, Z.; Gomez, D.; et al. NSCLC Tumor Shrinkage Prediction Using Quantitative Image Features. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. Off. J. Comput. Med. Imaging Soc. 2016, 49, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramella, S.; Fiore, M.; Greco, C.; Cordelli, E.; Sicilia, R.; Merone, M.; Molfese, E.; Miele, M.; Cornacchione, P.; Ippolito, E.; et al. A Radiomic Approach for Adaptive Radiotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-Based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Varghese, B.; Hwang, D.; Cen, S.; Lei, X.; Desai, B.; Azadikhah, A.; Oberai, A.; Duddalwar, V. Benchmarking Various Radiomic Toolkit Features While Applying the Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative toward Clinical Translation of Radiomic Analysis. J. Digit. Imaging 2021, 34, 1156–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yolchuyeva, S.; Giacomazzi, E.; Tonneau, M.; Lamaze, F.; Orain, M.; Coulombe, F.; Malo, J.; Belkaid, W.; Routy, B.; Joubert, P.; et al. Imaging-Based Biomarkers Predict Programmed Death-Ligand 1 and Survival Outcomes in Advanced NSCLC Treated with Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab: A Multi-Institutional Study. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2023, 4, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Miguel-Perez, D.; Ak, M.; Mamindla, P.; Russo, A.; Zenkin, S.; Ak, N.; Peddagangireddy, V.; Lara-Mejia, L.; Gunasekaran, M.; Cardona, A.F.; et al. Validation of a Multiomic Model of Plasma Extracellular Vesicle PD-L1 and Radiomics for Prediction of Response to Immunotherapy in NSCLC. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, J.; Haakensen, V.D.; Bar, J.; Belmans, F.; Corsi, A.; Flechet, M.; Libert, L.; Meca, C.C.; Tsoutzidis, N.; Chander, P.; et al. 1240MO Quantitative Radiomics for the Detection of Symptomatic Pneumonitis Following Chemoradiotherapy in Patients with Stage III Unresectable NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, S794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | N = 57 |
|---|---|
| Median age, years (range) | 66 (41–81) |
| Sex, no. (%) | |
| Male | 24 (42%) |
| Female | 33 (58%) |
| Smoking status, no. (%) | |
| Never smoked | 6 (11%) |
| Current/former smoker | 47 (83%) |
| Exposed to second-hand smoke | 4 (7%) |
| Disease stage, no. (%) | |
| 3A | 24 (42%) |
| 3B | 27 (47%) |
| 3C | 5 (9%) |
| 4A | 1 (2%) |
| Median initial tumor size, mm (IQR) | 35 (26–60) |
| Median residual tumor size, mm (IQR) | 31 (20–42) |
| PD-L1 expression level, no. (%) | |
| <1% | 15 (26%) |
| 1–49% | 13 (23%) |
| ≥50% | 27 (47%) |
| Not reported | 2 (4%) |
| EGFR (%) | |
| Negative | 27 (47%) |
| Positive | 13 (23%) |
| Indeterminate | 15 (26%) |
| Not reported | 2 (4%) |
| ALK-1 (%) | |
| Negative | 36 (63%) |
| Positive | 4 (7%) |
| Not reported | 17 (30%) |
| Radiotherapy dose fractionation, cGy/# of fractions (%) | |
| 6000/30 | 37 (65%) |
| 6600/33 | 19 (33%) |
| 4500/25 + SBRT boost | 1 (2%) |
| Concurrent chemotherapy regimen (%) | |
| Cisplatin, etoposide | 16 (28%) |
| Carboplatin, paclitaxel | 7 (12%) |
| Carboplatin, pemetrexed | 12 (21%) |
| Cisplatin, pemetrexed | 22 (39%) |
| Response group based on RECIST 1.1, no. (%) | |
| Non-responder (stable/progressive disease) | 37 (65%) |
| Responder (partial/complete) | 20 (35%) |
| Classifier | Recall (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy (%) | Balanced Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | NPV (%) | F1-Score (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | 78 | 50 | 68 | 64 | 74 | 56 | 53 | 0.66 |
| KNN k = 1 | 84 | 70 | 80 | 77 | 84 | 70 | 84 | 0.77 |
| KNN k = 3 | 81 | 70 | 77 | 76 | 83 | 67 | 68 | 0.78 |
| KNN k = 5 | 76 | 60 | 70 | 68 | 78 | 57 | 59 | 0.69 |
| SVM-Linear | 78 | 65 | 74 | 72 | 81 | 62 | 63 | 0.71 |
| Random Forest | 68 | 55 | 63 | 61 | 74 | 48 | 51 | 0.65 |
| XGBoost | 68 | 55 | 63 | 61 | 74 | 48 | 51 | 0.65 |
| Classifier | Recall (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy (%) | Balanced Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | NPV (%) | F1-Score (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | 87 ± 5 | 78 ± 7 | 82 ± 3 | 83 ± 3 | 81 ± 5 | 87 ± 4 | 81 ± 4 | 0.86 ± 0.04 |
| KNN k = 1 | 84 ± 6 | 93 ± 4 | 88 ± 3 | 88 ± 3 | 93 ± 4 | 87 ± 4 | 89 ± 3 | 0.88 ± 0.03 |
| KNN k = 3 | 81 ± 5 | 94 ± 4 | 88 ± 4 | 88 ± 4 | 94 ± 4 | 84 ± 4 | 89 ± 3 | 0.92 ± 0.04 |
| KNN k = 5 | 78 ± 7 | 94 ± 5 | 86 ± 3 | 86 ± 3 | 94 ± 5 | 83 ± 5 | 87 ± 3 | 0.91 ± 0.04 |
| SVM-Linear | 86 ± 6 | 78 ± 8 | 82 ± 3 | 82 ± 3 | 82 ± 6 | 86 ± 4 | 81 ± 4 | 0.78 ± 0.17 |
| Random Forest | 82 ± 6 | 87 ± 7 | 85 ± 5 | 85 ± 5 | 88 ± 6 | 84 ± 4 | 85 ± 5 | 0.91 ± 0.03 |
| XGBoost | 80 ± 7 | 86 ± 7 | 83 ± 5 | 83 ± 5 | 87 ± 6 | 82 ± 5 | 83 ± 5 | 0.89 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, E.Z.; Osapoetra, L.O.; Cheung, P.; Poon, I.; Louie, A.V.; Tsao, M.; Ung, Y.; Cunha, M.T.; Menjak, I.B.; Czarnota, G.J. CT-Based Radiomics for a priori Predicting Response to Chemoradiation in Locally Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142386
Chung EZ, Osapoetra LO, Cheung P, Poon I, Louie AV, Tsao M, Ung Y, Cunha MT, Menjak IB, Czarnota GJ. CT-Based Radiomics for a priori Predicting Response to Chemoradiation in Locally Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(14):2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142386
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Erika Z., Laurentius O. Osapoetra, Patrick Cheung, Ian Poon, Alexander V. Louie, May Tsao, Yee Ung, Mateus T. Cunha, Ines B. Menjak, and Gregory J. Czarnota. 2025. "CT-Based Radiomics for a priori Predicting Response to Chemoradiation in Locally Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 14: 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142386
APA StyleChung, E. Z., Osapoetra, L. O., Cheung, P., Poon, I., Louie, A. V., Tsao, M., Ung, Y., Cunha, M. T., Menjak, I. B., & Czarnota, G. J. (2025). CT-Based Radiomics for a priori Predicting Response to Chemoradiation in Locally Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 17(14), 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142386






