Multivariate Framework of Metabolism in Advanced Prostate Cancer Using Whole Abdominal and Pelvic Hyperpolarized 13C MRI—A Correlative Study with Clinical Outcomes
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Demographics
2.2. Hyperpolarization Methods
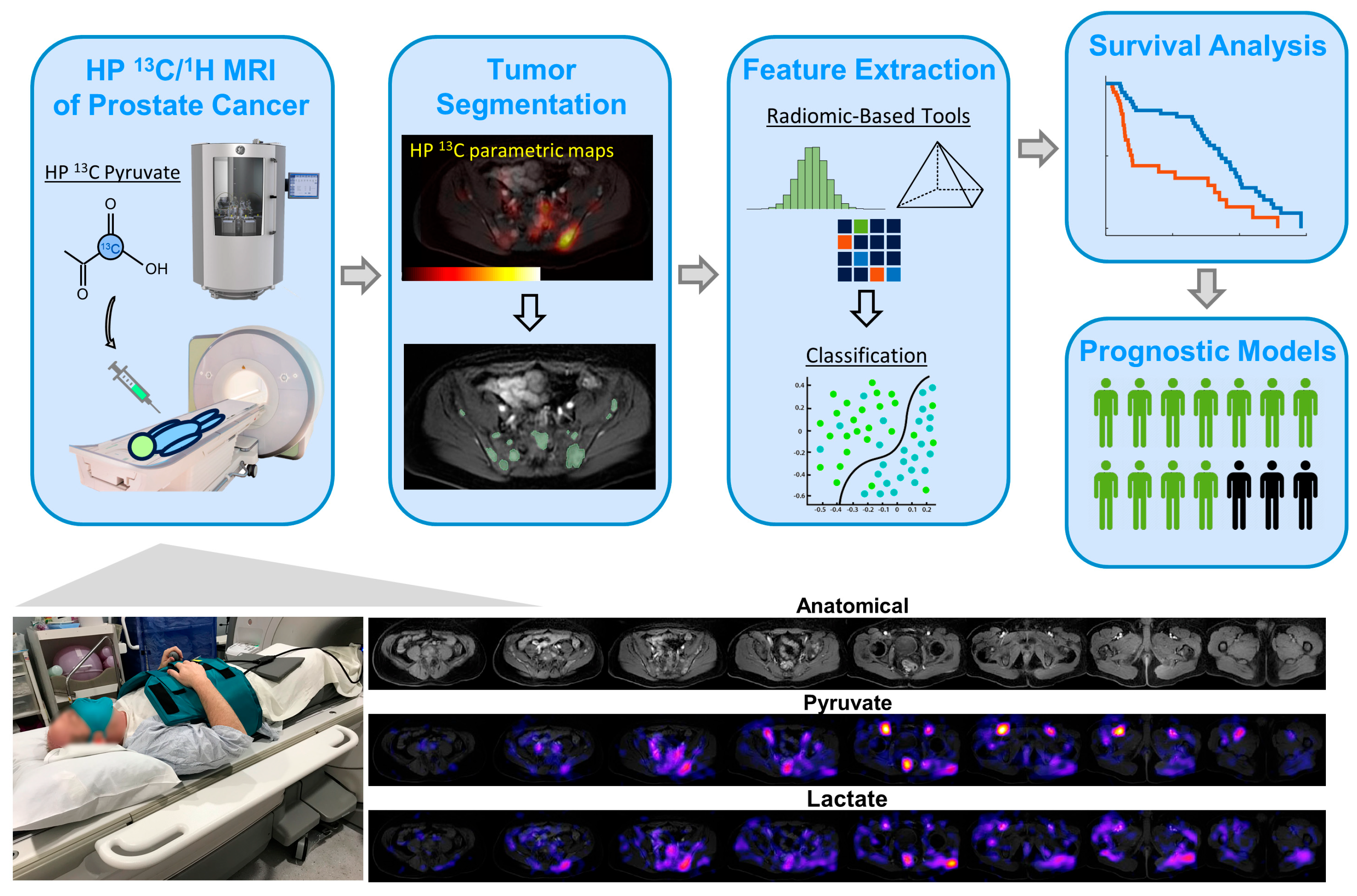
2.3. Hyperpolarized 13C MRI Exam of Abdomen/Pelvis—Planning and Execution
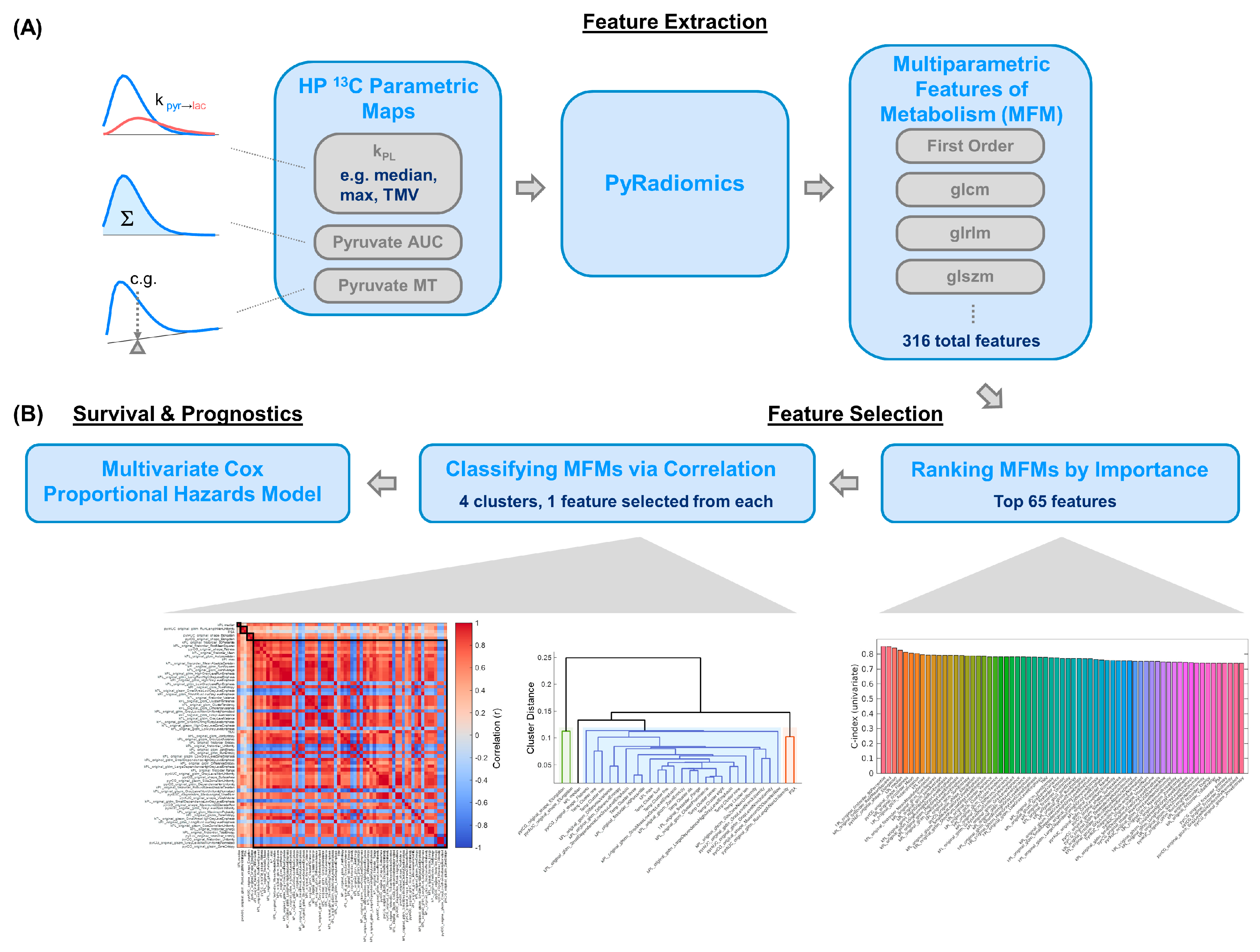
2.4. Multiparametric Feature Extraction and Analysis
2.5. Survival Analyses Using Uni- and Multivariate Models
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
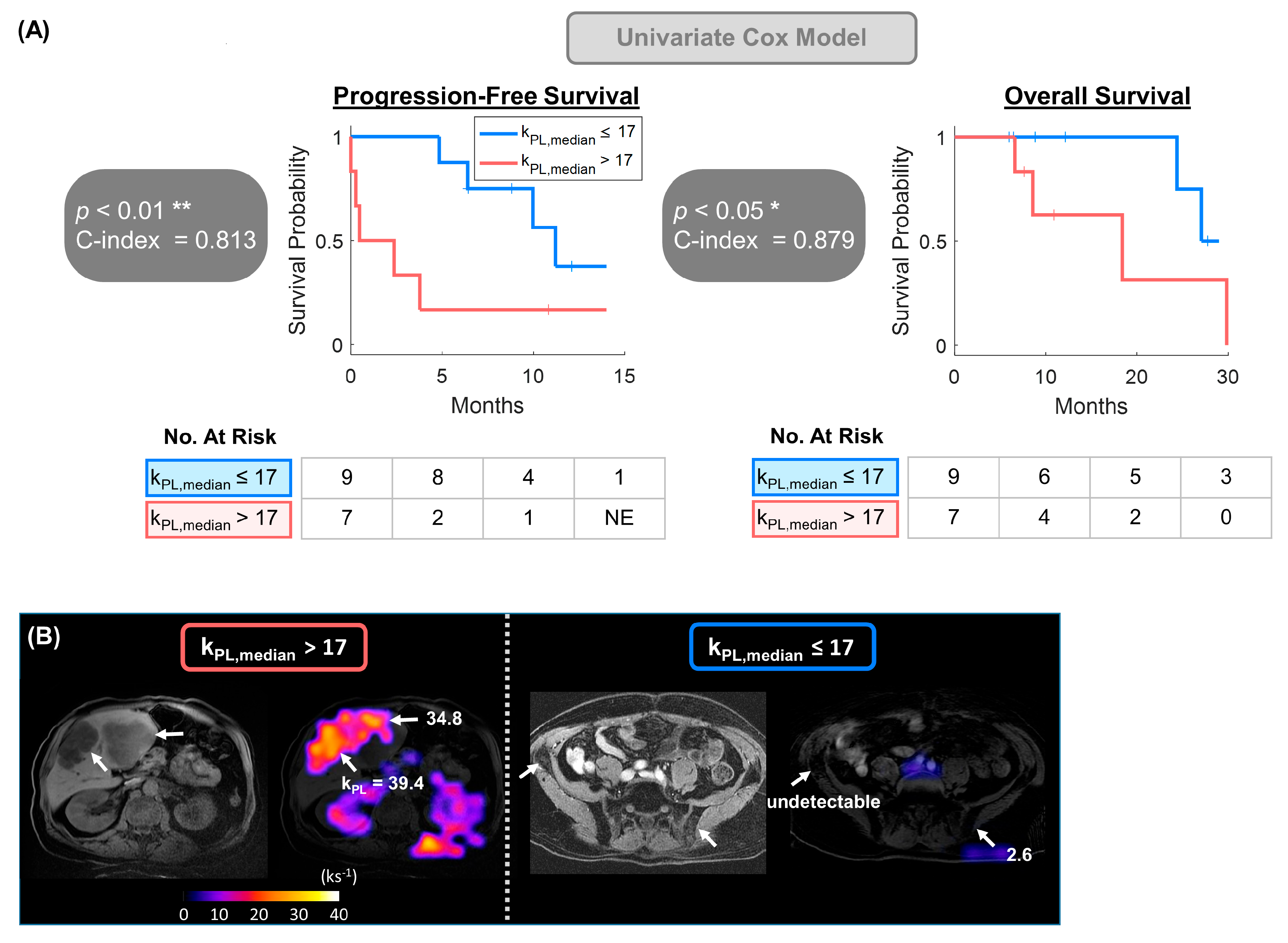
3.2. Univariate Model Detected Significant Correlation Between kPL and Clinical Endpoints
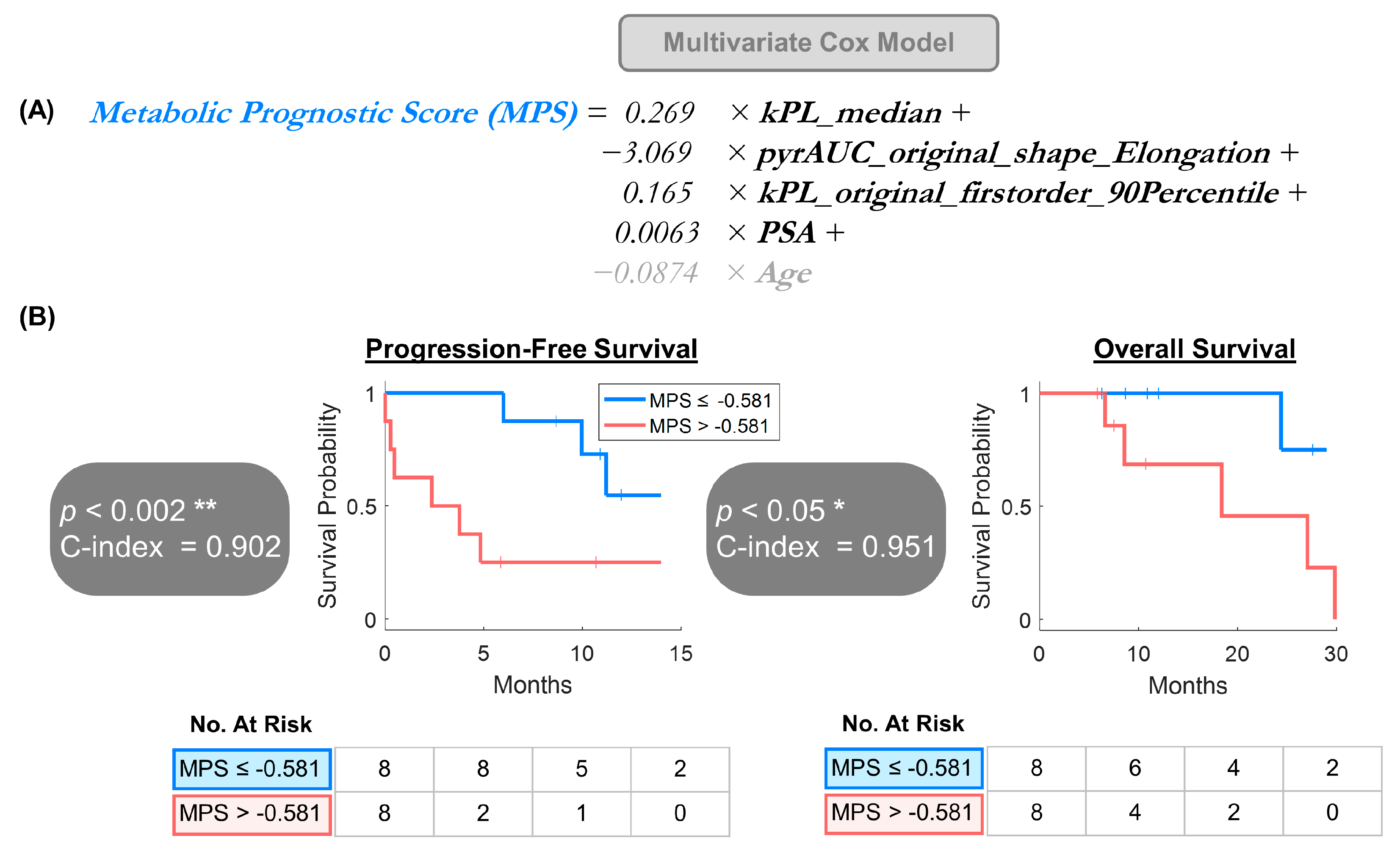
3.3. Multivariate Model Offered a Provisional Approach for Larger Future Datasets
−3.069 × pyrAUC_original_shape_Elongation +
0.165 × kPL_original_firstorder_90Percentile +
0.0063 × PSA +
−0.0874 × Age
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MFM | Multiparametric Features of Metabolism |
| HP 13C MRI | Hyperpolarized 13C MRI |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PSA | Prostate-specific antigen |
References
- Fizazi, K.; Foulon, S.; Carles, J.; Roubaud, G.; McDermott, R.; Flechon, A.; Tombal, B.; Supiot, S.; Berthold, D.; Ronchin, P.; et al. Abiraterone plus prednisone added to androgen deprivation therapy and docetaxel in de novo metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (PEACE-1): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study with a 2 × 2 factorial design. Lancet 2022, 399, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bono, J.; Kang, J.; Hussain, M. Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, O.; de Bono, J.; Chi, K.N.; Fizazi, K.; Herrmann, K.; Rahbar, K.; Tagawa, S.T.; Nordquist, L.T.; Vaishampayan, N.; El-Haddad, G.; et al. Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kurhanewicz, J.; Vigneron, D.B.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Bankson, J.A.; Brindle, K.; Cunningham, C.H.; Gallagher, F.A.; Keshari, K.R.; Kjaer, A.; Laustsen, C.; et al. Hyperpolarized (13)C MRI: Path to Clinical Translation in Oncology. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Z.J.; Ohliger, M.A.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Gordon, J.W.; Bok, R.A.; Slater, J.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Hess, C.P.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Vigneron, D.B. Hyperpolarized (13)C MRI: State of the Art and Future Directions. Radiology 2019, 291, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brindle, K.M.; Bohndiek, S.E.; Gallagher, F.A.; Kettunen, M.I. Tumor imaging using hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aggarwal, R.; Vigneron, D.B.; Kurhanewicz, J. Hyperpolarized 1-[(13)C]-Pyruvate Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detects an Early Metabolic Response to Androgen Ablation Therapy in Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 1028–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, H.Y.; Aggarwal, R.; Bok, R.A.; Ohliger, M.A.; Zhu, Z.; Lee, P.; Gordon, J.W.; van Criekinge, M.; Carvajal, L.; Slater, J.B.; et al. Hyperpolarized (13)C-pyruvate MRI detects real-time metabolic flux in prostate cancer metastases to bone and liver: A clinical feasibility study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020, 23, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chowdhury, R.; Mueller, C.A.; Smith, L.; Gong, F.; Papoutsaki, M.V.; Rogers, H.; Syer, T.; Singh, S.; Brembilla, G.; Retter, A.; et al. Quantification of Prostate Cancer Metabolism Using 3D Multiecho bSSFP and Hyperpolarized [1-(13) C] Pyruvate: Metabolism Differs Between Tumors of the Same Gleason Grade. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 2022, 57, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kouchkovsky, I.; Nguyen, H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Liu, X.; Qin, H.; Stohr, B.A.; Santos, R.D.; Ohliger, M.A.; Wang, Z.J.; Bok, R.A.; et al. Dual Hyperpolarized [1-13C] Pyruvate and [13C] Urea Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Prostate Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Open 2024, 21, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granlund, K.L.; Tee, S.S.; Vargas, H.A.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Reznik, E.; Fine, S.; Laudone, V.; Eastham, J.A.; Touijer, K.A.; Reuter, V.E.; et al. Hyperpolarized MRI of Human Prostate Cancer Reveals Increased Lactate with Tumor Grade Driven by Monocarboxylate Transporter 1. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 105–114.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nelson, S.J.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Vigneron, D.B.; Larson, P.E.; Harzstark, A.L.; Ferrone, M.; van Criekinge, M.; Chang, J.W.; Bok, R.; Park, I.; et al. Metabolic imaging of patients with prostate cancer using hyperpolarized [1-(1)(3)C]pyruvate. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 198ra08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sushentsev, N.; Hamm, G.; Flint, L.; Birtles, D.; Zakirov, A.; Richings, J.; Ling, S.; Tan, J.Y.; McLean, M.A.; Ayyappan, V.; et al. Metabolic imaging across scales reveals distinct prostate cancer phenotypes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sushentsev, N.; McLean, M.A.; Warren, A.Y.; Benjamin, A.J.; Brodie, C.; Frary, A.; Gill, A.B.; Jones, J.; Kaggie, J.D.; Lamb, B.W.; et al. Hyperpolarised 13C-MRI identifies the emergence of a glycolytic cell population within intermediate-risk human prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 466. [Google Scholar]
- Bankson, J.; Larson, P.E. Analysis and visualization of hyperpolarized 13C MR data. In Advances in Magnetic Resonance Technology and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 3, pp. 129–155. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, P.E.Z.; Bernard, J.M.L.; Bankson, J.A.; Bogh, N.; Bok, R.A.; Chen, A.P.; Cunningham, C.H.; Gordon, J.; Hövener, J.-B.; Laustsen, C.; et al. Current methods for hyperpolarized [1-(13)C]pyruvate MRI human studies. Magn. Reson. Med. 2024, 91, 2204–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liberini, V.; Laudicella, R.; Balma, M.; Nicolotti, D.G.; Buschiazzo, A.; Grimaldi, S.; Lorenzon, L.; Bianchi, A.; Peano, S.; Bartolotta, T.V.; et al. Radiomics and artificial intelligence in prostate cancer: New tools for molecular hybrid imaging and theragnostics. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2022, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in medical imaging-“how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Into Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, B. Understanding Sources of Variation to Improve the Reproducibility of Radiomics. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 633176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Du, L.X.; Yuan, J.P.; Gan, M.; Li, Z.G.; Wang, P.; Hou, Z.J.; Wang, C. A comparative study between deep learning and radiomics models in grading liver tumors using hepatobiliary phase contrast-enhanced MR images. BMC Med. Imaging 2022, 22, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tagliafico, A.S.; Piana, M.; Schenone, D.; Lai, R.; Massone, A.M.; Houssami, N. Overview of radiomics in breast cancer diagnosis and prognostication. Breast 2020, 49, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lovinfosse, P.; Polus, M.; Van Daele, D.; Martinive, P.; Daenen, F.; Hatt, M.; Visvikis, D.; Koopmansch, B.; Lambert, F.; Coimbra, C.; et al. FDG PET/CT radiomics for predicting the outcome of locally advanced rectal cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.; Choi, W.H.; Joo, M.W.; Ha, S.; Chung, Y.-A. SPECT/CT Radiomics for Differentiating between Enchondroma and Grade I Chondrosarcoma. Tomography 2023, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, G.J.R.; Azad, G.; Owczarczyk, K.; Siddique, M.; Goh, V. Challenges and Promises of PET Radiomics. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 102, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Spetsieris, P.G.; Eidelberg, D.; Ma, Y. Radiomics and supervised machine learning in the diagnosis of parkinsonism with FDG PET: Promises and challenges. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindle, K.M. Imaging cancer metabolism using magnetic resonance. npj Imaging 2024, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autry, A.W.; Gordon, J.W.; Chen, H.Y.; LaFontaine, M.; Bok, R.; Van Criekinge, M.; Slater, J.B.; Carvajal, L.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Chang, S.M.; et al. Characterization of serial hyperpolarized (13)C metabolic imaging in patients with glioma. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 27, 102323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, P.M.; Chen, H.Y.; Gordon, J.W.; Wang, Z.J.; Bok, R.; Hashoian, R.; Kim, Y.; Liu, X.; Nickles, T.; Cheung, K.; et al. Whole-Abdomen Metabolic Imaging of Healthy Volunteers Using Hyperpolarized [1-(13) C]pyruvate MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 2022, 56, 1792–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grist, J.T.; Hansen, E.S.S.; Sanchez-Heredia, J.D.; McLean, M.A.; Tougaard, R.; Riemer, F.; Schulte, R.F.; Kaggie, J.D.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Laustsen, C.; et al. Creating a clinical platform for carbon-13 studies using the sodium-23 and proton resonances. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gordon, J.W.; Vigneron, D.B.; Larson, P.E. Development of a symmetric echo planar imaging framework for clinical translation of rapid dynamic hyperpolarized (13) C imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bok, R.; Lee, J.; Sriram, R.; Keshari, K.; Sukumar, S.; Daneshmandi, S.; Korenchan, D.E.; Flavell, R.R.; Vigneron, D.B.; Kurhanewicz, J.; et al. The Role of Lactate Metabolism in Prostate Cancer Progression and Metastases Revealed by Dual-Agent Hyperpolarized (13)C MRSI. Cancers 2019, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, E104–E107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, P.E.Z.; Chen, H.Y.; Gordon, J.W.; Korn, N.; Maidens, J.; Arcak, M.; Tang, S.; Criekinge, M.; Carvajal, L.; Mammoli, D.; et al. Investigation of analysis methods for hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate metabolic MRI in prostate cancer patients. NMR Biomed. 2018, 31, e3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Leijenaar, R.T.; Nalbantov, G.; Carvalho, S.; van Elmpt, W.J.; Troost, E.G.; Boellaard, R.; Aerts, H.J.; Gillies, R.J.; Lambin, P. The effect of SUV discretization in quantitative FDG-PET Radiomics: The need for standardized methodology in tumor texture analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Harrell, F.E.; Califf, R.M., Jr.; Pryor, D.B.; Lee, K.L.; Rosati, R.A. Evaluating the yield of medical tests. JAMA 1982, 247, 2543–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, K.A.; Ghahramani, Z. Bayesian hierarchical clustering. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Bonn, Germany, 7–11 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.Y.; Lu, Y. Decision tree methods: Applications for classification and prediction. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2015, 27, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Karpinski, M.J.; Husing, J.; Claassen, K.; Moller, L.; Kajuter, H.; Oesterling, F.; Grünwald, V.; Umutlu, L.; Kleesiek, J.; Telli, T.; et al. Combining PSMA-PET and PROMISE to re-define disease stage and risk in patients with prostate cancer: A multicentre retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 1188–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, S.; Hadaschik, B.; Gabriel, M.; Herrmann, K.; Eiber, M.; Costa, D. Influence of androgen deprivation therapy on PSMA expression and PSMA-ligand PET imaging of prostate cancer patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGranahan, N.; Swanton, C. Clonal heterogeneity and tumor evolution: Past, present, and the future. Cell 2017, 168, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Lin, P.; Higano, C.S.; Sternberg, C.N.; Sonpavde, G.; Tombal, B.; Templeton, A.; Fizazi, K.; Phung, D.; Wong, E.; et al. Development and validation of a prognostic model for overall survival in chemotherapy-na⟨ve men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2200–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halabi, S.; Yang, Q.; Roy, A.; Luo, B.; Araujo, J.C.; Logothetis, C.; Sternberg, C.N.; Armstrong, A.J.; Carducci, M.A.; Chi, K.N.; et al. External Validation of a Prognostic Model of Overall Survival in Men With Chemotherapy-Naive Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2736–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Zhang, T.; Small, E.J.; Armstrong, A.J. Neuroendocrine prostate cancer: Subtypes, biology, and clinical outcomes. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 2014, 12, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran, H.; Tomlins, S.; Aparicio, A.; Arora, V.; Rickman, D.; Ayala, G.; Huang, J.; True, L.; Gleave, M.E.; Soule, H.; et al. Aggressive Variants of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2846–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, M.C.; Zwart, W.; Roudier, M.P.; True, L.D.; Nelson, W.G.; Epstein, J.; De Marzo, A.M.; Nelson, P.S.; Yegnasubramanian, S. Genomic and phenotypic heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2021, 18, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.R.; Quigley, D.A.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Beer, T.M.; Rettig, M.B.; Reiter, R.E.; Gleave, M.E.; Thomas, G.V.; Foye, A.; et al. Whole-Genome and Transcriptional Analysis of Treatment-Emergent Small-Cell Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer Demonstrates Intraclass Heterogeneity. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2019, 17, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Forkasiewicz, A.; Dorociak, M.; Stach, K.; Szelachowski, P.; Tabola, R.; Augoff, K. The usefulness of lactate dehydrogenase measurements in current oncological practice. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G. The lactate and the lactate dehydrogenase in inflammatory diseases and major risk factors in COVID-19 patients. Inflammation 2022, 45, 2091–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonpavde, G.; Pond, G.R.; Berry, W.R.; de Wit, R.; Armstrong, A.J.; Eisenberger, M.A.; Tannock, I.F. Serum alkaline phosphatase changes predict survival independent of PSA changes in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastasis receiving chemotherapy. Urol. Oncol-Semin. Ori. 2012, 30, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, H.; Yelensky, R.; Frampton, G.M.; Park, K.; Downing, S.R.; MacDonald, T.Y.; Jarosz, M.; Lipson, D.; Tagawa, S.T.; Nanus, D.M.; et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing of advanced prostate cancer identifies potential therapeutic targets and disease heterogeneity. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cooperberg, M.R.; Pasta, D.J.; Elkin, E.P.; Litwin, M.S.; Latini, D.M.; Du Chane, J.; Carroll, P.R. The University of California, San Francisco Cancer of the Prostate Risk Assessment score: A straightforward and reliable preoperative predictor of disease recurrence after radical prostatectomy. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 1938–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cagiannos, I.; Karakiewicz, P.; Eastham, J.A.; Ohori, M.; Rabbani, F.; Gerigk, C.; Reuter, V.; Graefen, M.; Hammerer, P.G.; Erbersdobler, A.; et al. A preoperative nomogram identifying decreased risk of positive pelvic lymph nodes in patients with prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.J. Random Forest for Bioinformatics. In Ensemble Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 307–323. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Narasimhan, B.; Tay, K.; Simon, N.; Qian, J.; Yang, J. glmnet: Lasso and Elastic-Net Regularized Generalized Linear Models. Astrophysics Source Code Library. 2023. ascl: 2308.011. Available online: https://ascl.net/2308.011 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Jeon, H.; Oh, S. Hybrid-Recursive Feature Elimination for Efficient Feature Selection. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircioglu, A. Benchmarking Feature Selection Methods in Radiomics. Investig. Radiol. 2022, 57, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylona, E.; Zaridis, D.I.; Kalantzopoulos, C.; Tachos, N.S.; Regge, D.; Papanikolaou, N.; Tsiknakis, M.; Marias, K.; Fotiadis, D.I. Optimizing radiomics for prostate cancer diagnosis: Feature selection strategies, machine learning classifiers, and MRI sequences. Insights Into Imaging 2024, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tannock, I.F.; Pond, G.R.; Booth, C.M. Biased evaluation in cancer drug trials—How use of progression-free survival as the primary end point can mislead. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 679–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesan, V.; Olivier, T.; Prasad, V. Progression-free survival estimates are shaped by specific censoring rules: Implications for PFS as an endpoint in cancer randomized trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 202, 114022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhani, A.R.; Lecouvet, F.E.; Tunariu, N.; Koh, D.M.; De Keyzer, F.; Collins, D.J.; Sala, E.; Schlemmer, H.P.; Petralia, G.; Vargas, H.A.; et al. METastasis Reporting and Data System for Prostate Cancer: Practical Guidelines for Acquisition, Interpretation, and Reporting of Whole-body Magnetic Resonance Imaging-based Evaluations of Multiorgan Involvement in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Van Nieuwenhove, S.; Van Damme, J.; Padhani, A.R.; Vandecaveye, V.; Tombal, B.; Wuts, J.; Pasoglou, V.; Lecouvet, F.E. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer assessment: Current status and future directions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 2022, 55, 653–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Participants (N = 16) | |
| Age (years) | 69 ± 10 (52–88) |
| Staging | |
| Local-regionally advanced | |
| T3 | 1 |
| T4 | 2 |
| Metastatic | |
| M1a | 1 |
| M1b | 8 |
| M1c | 4 |
| Hormonal Status | |
| Sensitive | 5 |
| Resistant | 11 |
| Laboratory Markers | |
| PSA | 13.9 (0.05–336.0) |
| LDH | 208 (139–422) |
| ALP | 76 (37–190) |
| Feature | Likelihood p-Values | |
|---|---|---|
| PFS | OS | |
| kPL max | * 0.024 | * 0.031 |
| kPL median | ** 0.008 | * 0.048 |
| kurtosis | * 0.023 | * 0.029 |
| TMV | 0.106 | * 0.028 |
| PSA | 0.194 | 0.412 |
| LDH | 0.601 | 0.342 |
| ALP | 0.853 | 0.821 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.-Y.; de Kouchkovsky, I.; Bok, R.A.; Ohliger, M.A.; Wang, Z.J.; Gebrezgiabhier, D.; Nickles, T.; Carvajal, L.; Gordon, J.W.; Larson, P.E.Z.; et al. Multivariate Framework of Metabolism in Advanced Prostate Cancer Using Whole Abdominal and Pelvic Hyperpolarized 13C MRI—A Correlative Study with Clinical Outcomes. Cancers 2025, 17, 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132211
Chen H-Y, de Kouchkovsky I, Bok RA, Ohliger MA, Wang ZJ, Gebrezgiabhier D, Nickles T, Carvajal L, Gordon JW, Larson PEZ, et al. Multivariate Framework of Metabolism in Advanced Prostate Cancer Using Whole Abdominal and Pelvic Hyperpolarized 13C MRI—A Correlative Study with Clinical Outcomes. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132211
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hsin-Yu, Ivan de Kouchkovsky, Robert A. Bok, Michael A. Ohliger, Zhen J. Wang, Daniel Gebrezgiabhier, Tanner Nickles, Lucas Carvajal, Jeremy W. Gordon, Peder E. Z. Larson, and et al. 2025. "Multivariate Framework of Metabolism in Advanced Prostate Cancer Using Whole Abdominal and Pelvic Hyperpolarized 13C MRI—A Correlative Study with Clinical Outcomes" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132211
APA StyleChen, H.-Y., de Kouchkovsky, I., Bok, R. A., Ohliger, M. A., Wang, Z. J., Gebrezgiabhier, D., Nickles, T., Carvajal, L., Gordon, J. W., Larson, P. E. Z., Kurhanewicz, J., Aggarwal, R., & Vigneron, D. B. (2025). Multivariate Framework of Metabolism in Advanced Prostate Cancer Using Whole Abdominal and Pelvic Hyperpolarized 13C MRI—A Correlative Study with Clinical Outcomes. Cancers, 17(13), 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132211






