Antitumor Effect of mTOR1/2 Dual Inhibitor AZD8055 in Canine Pulmonary Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture
2.2. In Vitro Sensitivity Assay of mTOR Inhibitors
2.3. Western Blotting
2.4. Oral Administration of AZD8055 to the Tumor Xenograft Model
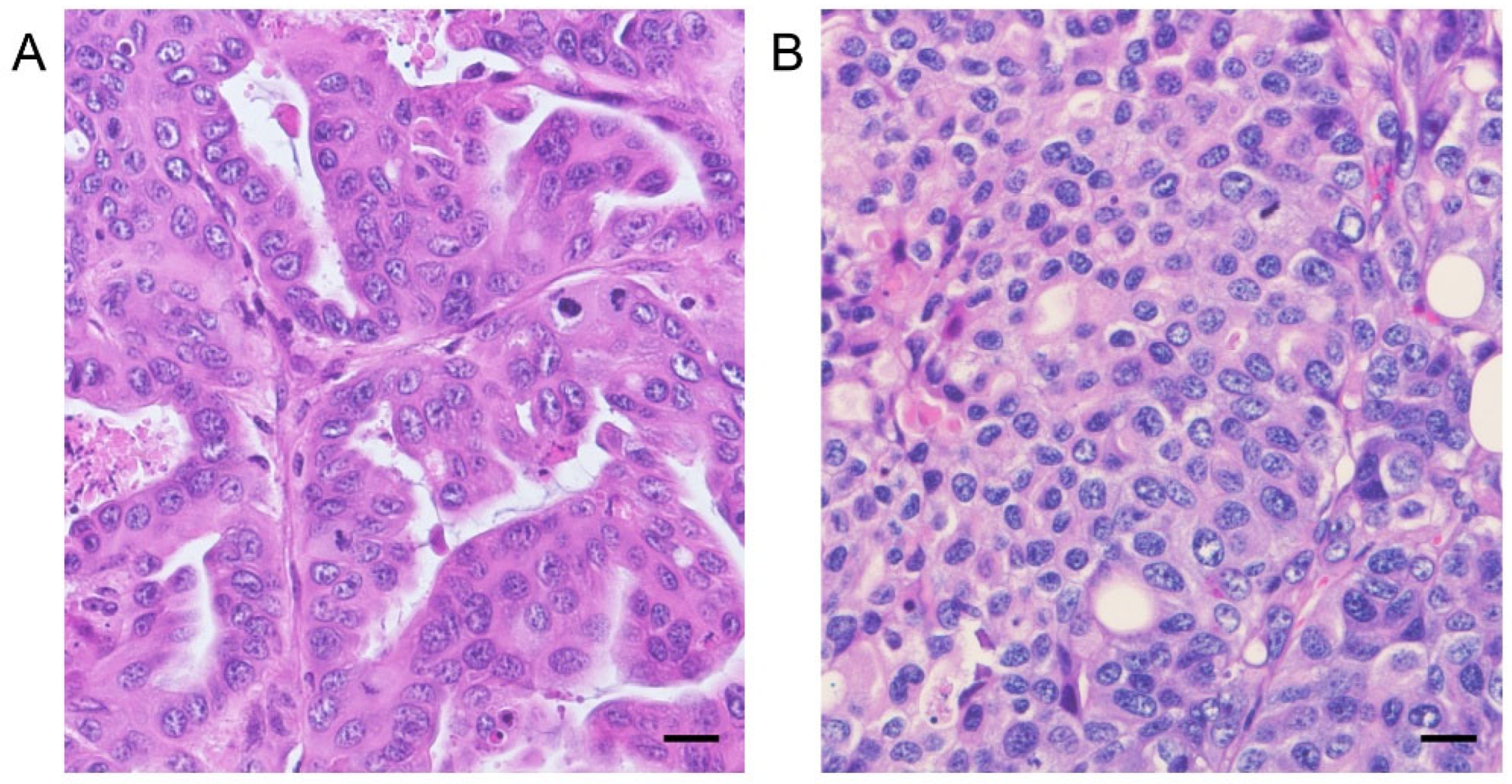
2.5. Histopathology
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of TTF-1 Expression of Canine PC Cell Lines
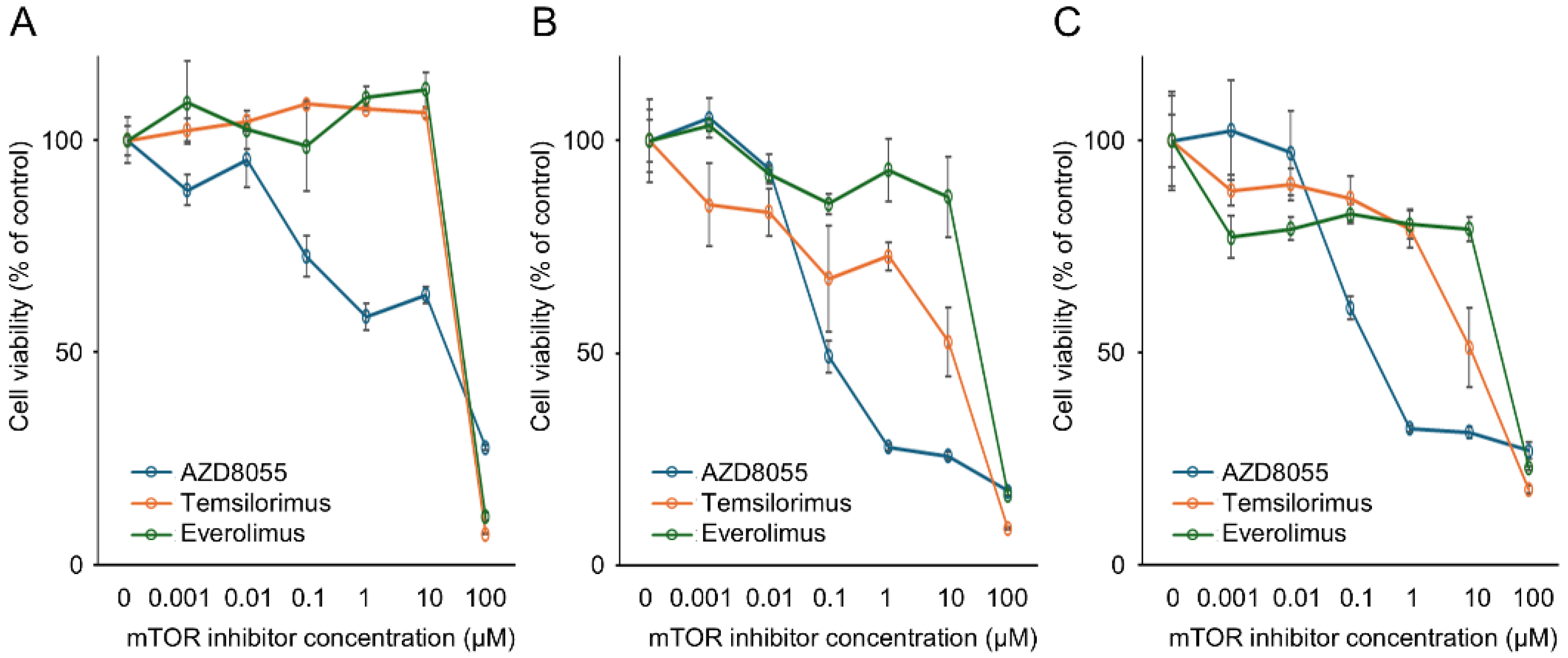
3.2. In Vitro Antitumor Effects of mTOR Inhibitors on the Proliferation of Canine PC Cell Lines
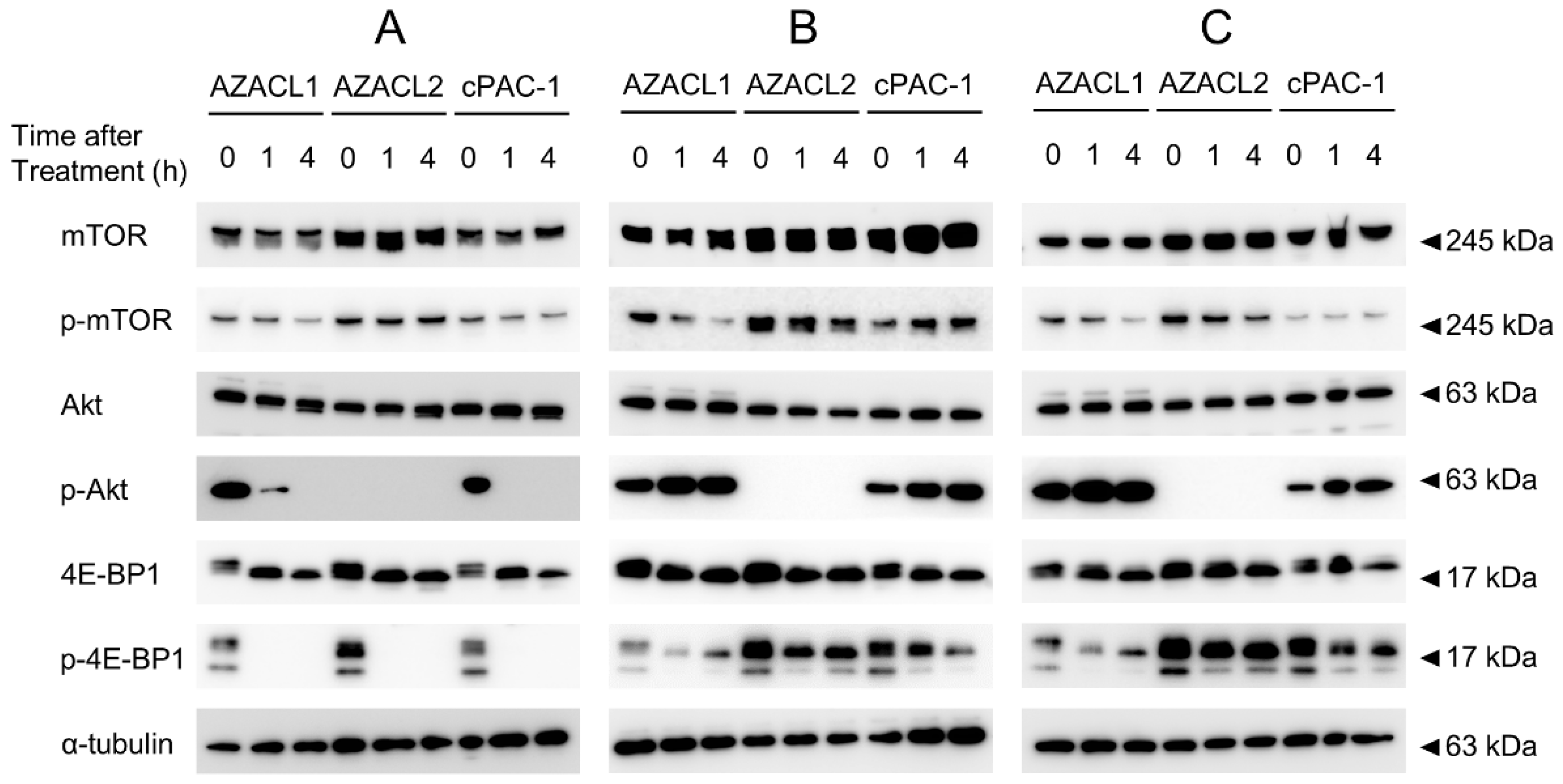
3.3. mTOR1/2 Inhibition AZD8055 Strongly Suppresses Phosphorylation of mTOR Signal Compared with mTOR1 Inhibitors Everolimus and Temsirolimus
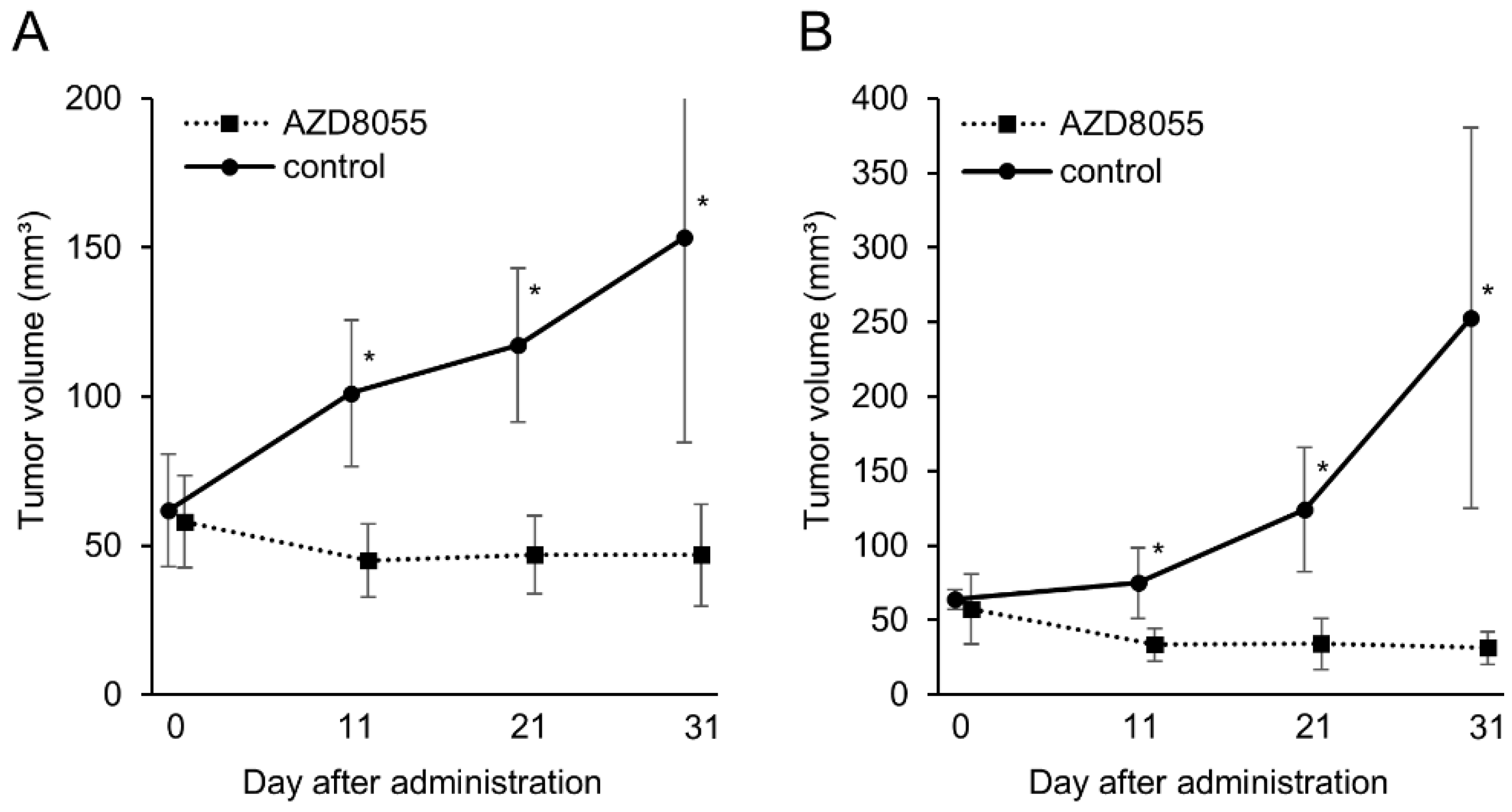
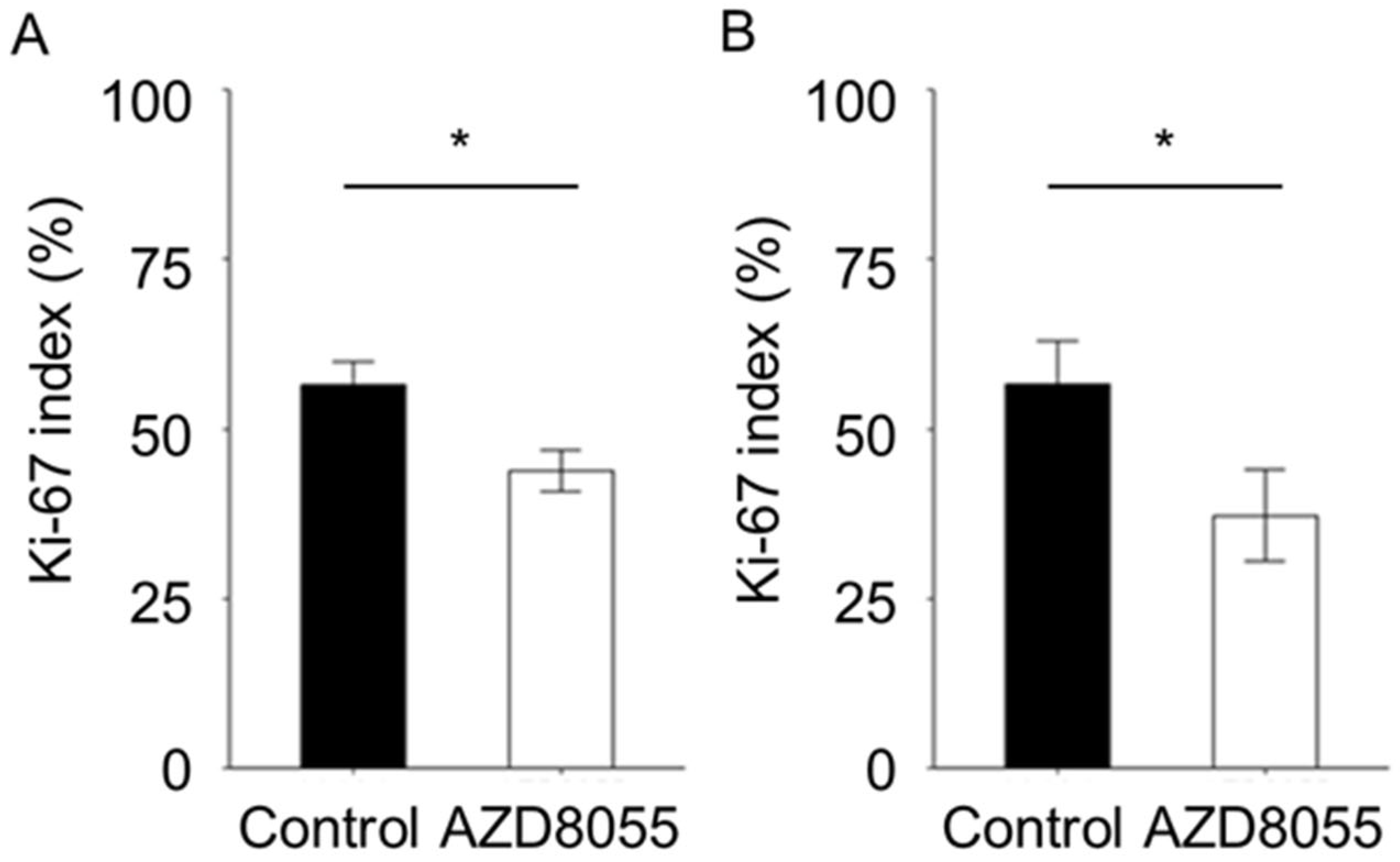
3.4. In Vivo Antitumor Effects of AZD8055 in Xenograft Mice Injected with PC Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Form |
| PC | Pulmonary carcinoma |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PKB; AKT | Protein kinase B |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| mTORC1 | mTOR complex 1 |
| mTORC2 | mTOR complex 2 |
| TTF-1 | Thyroid transcription factor 1 |
References
- Rinaldi, V.; Finotello, R.; Boari, A.; Cabibbo, E.; Crisi, P.E. Vinorelbine as first-line treatment in stage IV canine primary pulmonary carcinoma. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuten, D.J. Tumors in Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 467–498. [Google Scholar]
- Polton, G.; Finotello, R.; Sabattini, S.; Rossi, F.; Laganga, P.; Vasconi, M.E.; Barbanera, A.; Stiborova, K.; Rohrer Bley, C.; Marconato, L. Survival analysis of dogs with advanced primary lung carcinoma treated by metronomic cyclophosphamide, piroxicam, and thalidomide. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2018, 16, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouda, R.M.; Miller, M.E.; Chon, E.; Stein, T.J. Clinical effects of vinorelbine administration in the management of various malignant tumor types in dogs: 58 cases (1997–2012). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 246, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Abbas, H.A.; Negrao, M.V.; Ramineni, M.; Hu, X.; Hubert, S.M.; Fujimoto, J.; Reuben, A.; Varghese, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. The histologic phenotype of lung cancers is associated with transcriptomic features rather than genomic characteristics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Thoracic Tumours; International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization [distributor]: Lyon, France, 2021; pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Martini, M.; De Santis, M.C.; Braccini, L.; Gulluni, F.; Hirsch, E. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An updated review. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Tao, T.; Li, H.; Zhu, X. mTOR signaling pathway and mTOR inhibitors in cancer: Progress and challenges. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Luo, T.; Jiang, Y. Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuten, T.K.; Dean, G.A.; Thamm, D.H. Review: The PI3K-AKT-mTOR signal transduction pathway in canine cancer. Vet. Pathol. 2024, 61, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michishita, M.; Ochiai, K.; Nakahira, R.; Azakami, D.; Machida, Y.; Nagashima, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Ishiwata, T. mTOR Pathway as a potential therapeutic target for cancer stem cells in canine mammary carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, M.; Ochiai, K.; Michishita, M.; Morimatsu, M.; Sakai, H.; Kinoshita, N.; Sakaue, M.; Onozawa, E.; Azakami, D.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. In vitro anticancer effects of alpelisib against PIK3CA-mutated canine hemangiosarcoma cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 47, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.R.; Michael, H.T.; Halsey, C.H.; Peer, C.J.; Adhikari, A.; Dwyer, J.E.; Hoover, S.B.; El Meskini, R.; Kozlov, S.; Weaver Ohler, Z.; et al. Synergistic targeted inhibition of MEK and dual PI3K/mTOR diminishes viability and inhibits tumor growth of canine melanoma underscoring its utility as a preclinical model for human mucosal melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.; Poon, A.C.; Tam, P.M.; Mutsaers, A.J. Investigation of the effects of mTOR inhibitors rapamycin and everolimus in combination with carboplatin on canine malignant melanoma cells. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chresta, C.M.; Davies, B.R.; Hickson, I.; Harding, T.; Cosulich, S.; Critchlow, S.E.; Vincent, J.P.; Ellston, R.; Jones, D.; Sini, P.; et al. AZD8055 Is a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable ATP-competitive mammalian target of rapamycin kinase inhibitor with In vitro and In vivo antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.P.; Kang, S.A.; Rameseder, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ottina, K.A.; Lim, D.; Peterson, T.R.; Choi, Y.; Gray, N.S.; Yaffe, M.B.; et al. The mTOR-regulated phosphoproteome reveals a mechanism of mTORC1-mediated inhibition of growth factor signaling. Science 2011, 332, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, X.; Molinolo, A.A.; Martin, D.; Vitale-Cross, L.; Nohata, N.; Ando, M.; Wahba, A.; Amornphimoltham, P.; Wu, X.; et al. 4E-BP1 is a tumor suppressor protein reactivated by mTOR inhibition in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, A.Y.; Yoon, S.O.; Kim, S.G.; Roux, P.P.; Blenis, J. Rapamycin differentially inhibits S6Ks and 4E-BP1 to mediate cell-type-specific repression of mRNA translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17414–17419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memmott, R.M.; Dennis, P.A. Akt-dependent and -independent mechanisms of mTOR Regulation in cancer. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.; Qazi, Y.; Wellen, J.R. Strategies for the management of adverse events associated with mTOR inhibitors. Transplant. Rev. 2014, 28, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagashima, T.; Ochiai, K.; Takizawa, Y.; Koike, Y.; Saito, T.; Muramatsu, A.; Azakami, D.; Machida, Y.; Bonkobara, M.; Ishiwata, T.; et al. Antitumor Effect of mTOR1/2 Dual Inhibitor AZD8055 in Canine Pulmonary Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121991
Nagashima T, Ochiai K, Takizawa Y, Koike Y, Saito T, Muramatsu A, Azakami D, Machida Y, Bonkobara M, Ishiwata T, et al. Antitumor Effect of mTOR1/2 Dual Inhibitor AZD8055 in Canine Pulmonary Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(12):1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121991
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagashima, Tomokazu, Kazuhiko Ochiai, Yuka Takizawa, Youta Koike, Takahiro Saito, Asumi Muramatsu, Daigo Azakami, Yukino Machida, Makoto Bonkobara, Toshiyuki Ishiwata, and et al. 2025. "Antitumor Effect of mTOR1/2 Dual Inhibitor AZD8055 in Canine Pulmonary Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 12: 1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121991
APA StyleNagashima, T., Ochiai, K., Takizawa, Y., Koike, Y., Saito, T., Muramatsu, A., Azakami, D., Machida, Y., Bonkobara, M., Ishiwata, T., & Michishita, M. (2025). Antitumor Effect of mTOR1/2 Dual Inhibitor AZD8055 in Canine Pulmonary Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(12), 1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121991





