Role of Systemic Therapy in Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma: Where Do We Stand and Where Are We Heading?
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Current Standard of Care for Management of Localized RCC
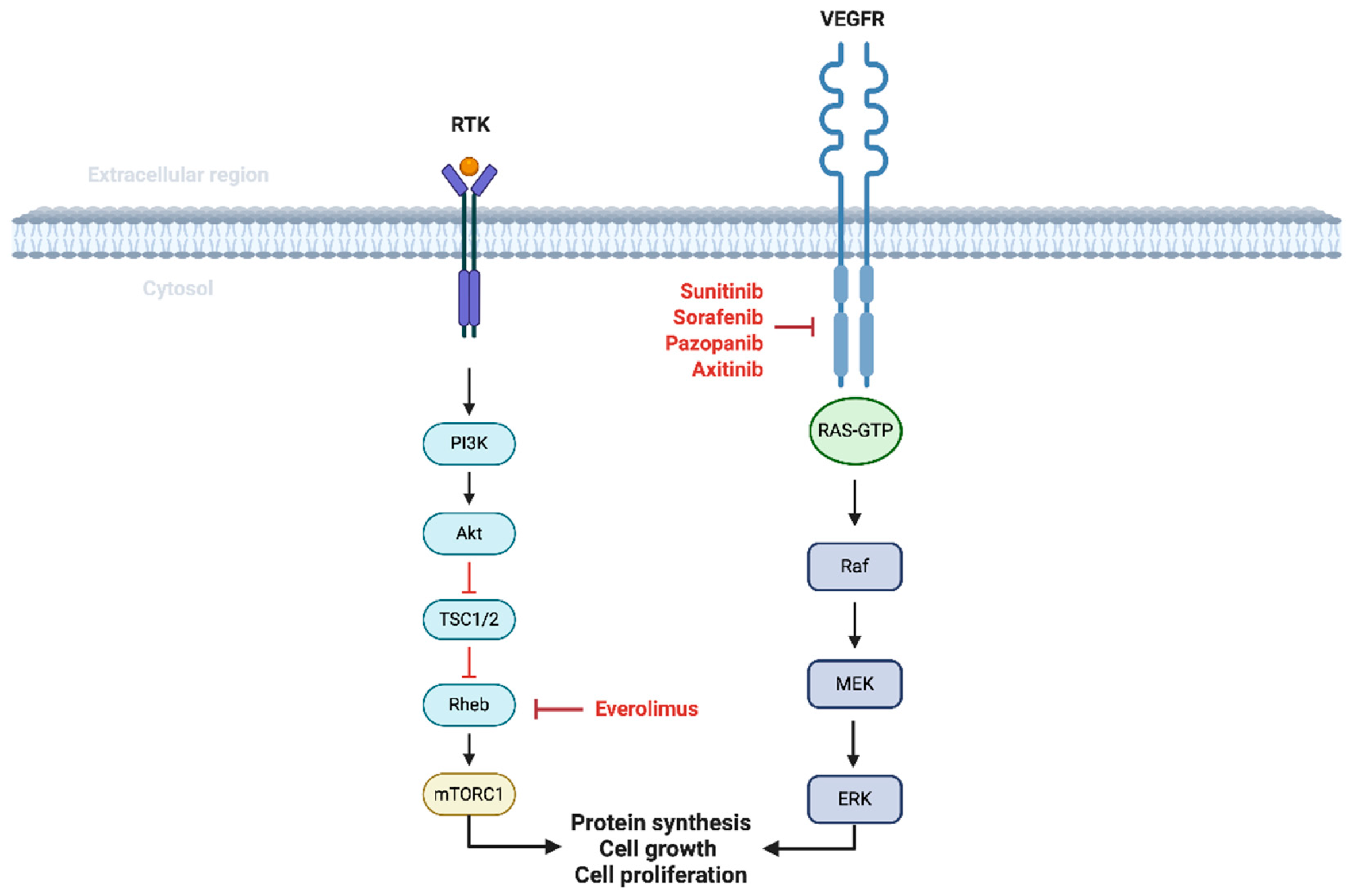
4. Changing Landscape in the Management of Localized RCC
4.1. Studies on Adjuvant Therapy in Localized RCC
4.1.1. Immunotherapy as an Adjuvant Therapy
4.1.2. Targeted Therapy in the Adjuvant Setting
4.2. Perioperative and Neoadjuvant Therapy in Localized RCC
4.2.1. Immunotherapy in the Neoadjuvant Setting
4.2.2. Targeted Therapy with or Without Immunotherapy in the Neoadjuvant Setting
4.3. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cancer Stat Facts: Kidney and Renal Pelvis Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/kidrp.html (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Janzen, N.K.; Kim, H.L.; Figlin, R.A.; Belldegrun, A.S. Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 30, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitanio, U.; Bensalah, K.; Bex, A.; Boorjian, S.A.; Bray, F.; Coleman, J.; Gore, J.L.; Sun, M.; Wood, C.; Russo, P. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.L.; Kim, W.Y. Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Review. Jama 2024, 332, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Jonasch, E.; Agarwal, N.; Alva, A.; Bagshaw, H.; Baine, M.; Beckermann, K.; Carlo, M.I.; Choueiri, T.K.; Costello, B.A.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Kidney Cancer, Version 2.2024. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2024, 22, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Tomczak, P.; Park, S.H.; Venugopal, B.; Ferguson, T.; Symeonides, S.N.; Hajek, J.; Gurney, H.; Chang, Y.H.; Lee, J.L.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as post-nephrectomy adjuvant therapy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-564): 30-month follow-up analysis of a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Uzzo, R.; Karam, J.A.; A Master, V.; Donskov, F.; Suarez, C.; Albiges, L.; Rini, B.; Tomita, Y.; Kann, A.G.; et al. Adjuvant atezolizumab versus placebo for patients with renal cell carcinoma at increased risk of recurrence following resection (IMmotion010): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Russo, P.; Grünwald, V.; Tomita, Y.; Zurawski, B.; Parikh, O.; Buti, S.; Barthélémy, P.; Goh, J.C.; Ye, D.; et al. Adjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus placebo for localised renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy (CheckMate 914): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Bex, A.; Russo, P.; Tomita, Y.; Cutuli, H.J.; Rojas, C.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Schinzari, G.; Melichar, B.; Barthélémy, P.; et al. Adjuvant Nivolumab for Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma at High Risk of Recurrence After Nephrectomy: Part B of the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase III CheckMate 914 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveros, C.; Huang, E.; Ranganathan, S.; Klaassen, Z.; Rini, B.; Wallis, C.J.D.; Satkunasivam, R. Adjuvant immunotherapy in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BJU Int. 2023, 131, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnarra, J.; Tory, K.; Weng, Y.; Schmidt, L.; Wei, M.; Li, H.; Latif, F.; Liu, S.; Chen, F.; Duh, F.M.; et al. Mutations of the VHL tumour suppressor gene in renal carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 1994, 7, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, M.; Kondo, K.; Yang, H.; Kim, W.; Valiando, J.; Ohh, M.; Salic, A.; Asara, J.M.; Lane, W.S.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. HIFα targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: Implications for O2 sensing. Science 2001, 292, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonasch, E.; Slack, R.S.; Geynisman, D.M.; Hasanov, E.; Milowsky, M.I.; Rathmell, W.K.; Stovall, S.; Juarez, D.; Gilchrist, T.R.; Pruitt, L.; et al. Phase II study of two weeks on, one week off sunitinib scheduling in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.V.; Tran, C.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Welsbie, D.S.; Chan, E.; Fueger, B.; Czernin, J.; Sawyers, C.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor determines sensitivity to inhibitors of mTOR in kidney cancer. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, N.B.; Manola, J.; Uzzo, R.G.; Flaherty, K.T.; Wood, C.G.; Kane, C.; Jewett, M.; Dutcher, J.P.; Atkins, M.B.; Pins, M.; et al. Adjuvant sunitinib or sorafenib for high-risk, non-metastatic renal-cell carcinoma (ECOG-ACRIN E2805): A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 2008–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.W.; Tangen, C.; Heath, E.I.; Stein, M.N.; Meng, M.; Alva, A.S.; Pal, S.K.; Puzanov, I.; Clark, J.I.; Chouieri, T.K.; et al. EVEREST: Everolimus for renal cancer ensuing surgical therapy—A phase III study (SWOG S0931, NCT01120249). Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, LBA4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, T.; Frangou, E.; Oza, B.; Ritchie, A.W.; Smith, B.; Kaplan, R.; Davis, I.D.; Stockler, M.R.; Albiges, L.; Escudier, B.; et al. Adjuvant Sorafenib for Renal Cell Carcinoma at Intermediate or High Risk of Relapse: Results from the SORCE Randomized Phase III Intergroup Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4064–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Marconi, L.; Eisen, T.; Escudier, B.; Giles, R.H.; Haas, N.B.; Harshman, L.C.; Quinn, D.I.; Larkin, J.; Pal, S.K.; et al. Adjuvant Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-targeted Therapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veldt, A.A.; Meijerink, M.R.; Eertwegh, A.J.v.D.; Bex, A.; de Gast, G.; Haanen, J.B.; Boven, E. Sunitinib for treatment of advanced renal cell cancer: Primary tumor response. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaf, M.E.; Kim, S.E.; Master, V.; McDermott, D.F.; Harshman, L.C.; Cole, S.M.; Drake, C.G.; Signoretti, S.; Akgul, M.; Baniak, N.; et al. Perioperative nivolumab versus observation in patients with renal cell carcinoma undergoing nephrectomy (PROSPER ECOG-ACRIN EA8143): An open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 1038–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bex, A.; van Thienen, J.V.; Schrier, M.; Graafland, N.; Kuusk, T.; Hendricksen, K.; Lagerveld, B.; Zondervan, P.; A van Moorselaar, J.; Blank, C.; et al. A Phase II, single-arm trial of neoadjuvant axitinib plus avelumab in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma who are at high risk of relapse after nephrectomy (NEOAVAX). Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 2203–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, K.; Campbell, S.; Nguyen, M.; Rathi, N.; Wang, L.; Rini, B.I.; Ornstein, M.C.; McKay, R.R.; Derweesh, I.H. Phase II study of axitinib prior to partial nephrectomy to preserve renal function: An interim analysis of the PADRES clinical trial. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G.; Kong, W.; Cheoklong, N.; Tricard, T.; Wu, X.; Zhai, W.; et al. Neoadjuvant toripalimab combined with axitinib in patients with locally advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A single-arm, phase II trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberstein, J.L.; Millard, F.; Mehrazin, R.; Kopp, R.; Bazzi, W.; DiBlasio, C.J.; Patterson, A.L.; Downs, T.M.; Yunus, F.; Kane, C.J.; et al. Feasibility and efficacy of neoadjuvant sunitinib before nephron-sparing surgery. BJU Int. 2010, 106, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaud, A.; Motzer, R.J.; Pandha, H.S.; George, D.J.; Pantuck, A.J.; Patel, A.; Chang, Y.-H.; Escudier, B.; Donskov, F.; Magheli, A.; et al. Adjuvant Sunitinib in High-Risk Renal-Cell Carcinoma after Nephrectomy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Haas, N.B.; Donskov, F.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Varlamov, S.; Kopyltsov, E.; Lee, J.L.; Melichar, B.; Rini, B.I.; Choueiri, T.K.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Adjuvant Pazopanib Versus Placebo After Nephrectomy in Patients with Localized or Locally Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3916–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross-Goupil, M.; Kwon, T.; Eto, M.; Ye, D.; Miyake, H.; Seo, S.; Byun, S.-S.; Lee, J.; Master, V.; Jin, J.; et al. Axitinib versus placebo as an adjuvant treatment of renal cell carcinoma: Results from the phase III, randomized ATLAS trial. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamie, K.; Donin, N.M.; Klöpfer, P.; Bevan, P.; Fall, B.; Wilhelm, O.; Storkel, S.; Said, J.; Gambla, M.; Hawkins, R.E.; et al. Adjuvant Weekly Girentuximab Following Nephrectomy for High-Risk Renal Cell Carcinoma: The ARISER Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, J.A.; Devine, C.E.; Urbauer, D.L.; Lozano, M.; Maity, T.; Ahrar, K.; Tamboli, P.; Tannir, N.M.; Wood, C.G. Phase 2 trial of neoadjuvant axitinib in patients with locally advanced nonmetastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Plimack, E.R.; Takagi, T.; Elson, P.; Wood, L.S.; Dreicer, R.; Gilligan, T.; Garcia, J.; Zhang, Z.; Kaouk, J.; et al. A Phase II Study of Pazopanib in Patients with Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma to Optimize Preservation of Renal Parenchyma. J. Urol. 2015, 194, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Deng, J.; Ji, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, H. Sorafenib neoadjuvant therapy in the treatment of high-risk renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hatiboglu, G.; Hohenfellner, M.; Arslan, A.; Hadaschik, B.; Teber, D.; Radtke, J.P.; Hallscheidt, P.; Tolstov, Y.; Roth, W.; Grüllich, C.; et al. Effective downsizing but enhanced intratumoral heterogeneity following neoadjuvant sorafenib in patients with non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2017, 402, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebacle, C.; Bensalah, K.; Bernhard, J.; Albiges, L.; Laguerre, B.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Baumert, H.; Lang, H.; Tricard, T.; Duclos, B.; et al. Evaluation of axitinib to downstage cT2a renal tumours and allow partial nephrectomy: A phase II study. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo, M.I.; Attalla, K.; Mazaheri, Y.; Gupta, S.; Yildirim, O.; Murray, S.J.; Coskey, D.T.; Kotecha, R.; Lee, C.H.; Feldman, D.R.; et al. Phase II Study of Neoadjuvant Nivolumab in Patients with Locally Advanced Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Undergoing Nephrectomy. Eur. Urol. 2022, 81, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| RCC Stage | Description | TNM | Primary Management | Secondary Management | Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage I | Tumor < 7 cm and has not spread outside of the kidney | T1, N0, M0 | Partial nephrectomy (preferred), ablative techniques, radical nephrectomy, or active surveillance | Surveillance | Active surveillance:
|
| Stage II | Tumor > 7 cm and has not spread outside of the kidney | T2, N0, M0 | Partial nephrectomy or radical nephrectomy | Non-clear cell: surveillance. Clear cell: surveillance or adjuvant pembrolizumab (category 1) |
|
| Stage III | Cancer has spread to adjacent tissue, may involve lymph nodes, and no distant metastasis | T3, N0, M0 or T1-T3, N1, M0 | Radical nephrectomy or partial nephrectomy (if indicated) | Non-clear cell: surveillance or clinical trial. Clear cell: adjuvant pembrolizumab (category 1) or surveillance |
|
| Trial Name | Year | Design | Number of Participants | Intervention | Type | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECOG-ACRIN E2805 [15] | 2016 | Randomized, phase III | 1943 | Sunitinib, sorafenib | Adjuvant | Median DFS was 5.8 years for sunitinib, 6.1 years for sorafenib, and 6.6 years for placebo |
| S-TRAC [25] | 2016 | Randomized, phase III | 615 | Sunitinib | Adjuvant | Median DFS was 6.8 years for sunitinib and 5.6 years for placebo |
| PROTECT [26] | 2017 | Randomized, phase III | 1538 | Pazopanib | Adjuvant | Median DFS was 54 months for the placebo and not attained for the pazopanib group |
| ATLAS [27] | 2018 | Randomized, phase III | 724 | Axitinib | Adjuvant | No difference in DFS [hazard ratio (HR) = 0.870; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.660–1.147, p = 0.321] |
| ARISER [28] | 2017 | Randomized, phase III | 864 | Girentuximab | Adjuvant | Median DFS was 71.4 months forgirentuximab and not reached for placebo |
| SORCE [17] | 2020 | Randomized, phase III | 1711 | Sorafenib | Adjuvant | Ten-year DFS rate was 53% for 3-year sorafenib, 55% for 1-year sorafenib and 54% for placebo |
| EVEREST [16] | 2022 | Randomized, phase III | 1499 | Everolimus | Adjuvant | 6-year RFS estimate was 64% for Everolimus and 61% for placebo |
| IMmotion010 [7] | 2022 | Randomized, phase III | 778 | Atezolizumab | Adjuvant | Median DFSl was 57.2 months for atezolizumab and 49.5 months for placebo |
| CheckMate 914 (Part A) [8] | 2023 | Randomized, phase III | 816 | Nivolumab, ipilimumab | Adjuvant | Median DFS was not reached for nivolumab plus ipilimumab and was 50.7 months for placebo |
| CheckMate 914 (Part B) [9] | 2025 | Randomized, phase III | 825 | Nivolumab | Adjuvant | Median DFS was not reached in either arm, DFS probabilities were 83.3% in nivolumab and 78.2% in placebo (at 12 months) |
| Keynote 564 [6] | 2022 | Randomized, phase III | 994 | Pembrolizumab | Adjuvant | DFS at 24 months was 77.3% for Pembrolizumab and 68.1% for placebo |
| Silberstein et al. [24] | 2010 | Retrospective | 12 | Sunitinib | Neoadjuvant | All patients had a decrease in size with a mean reduction in maximum diameter of 1.5 cm (21.1%) |
| Karam et al. [29] | 2014 | Phase II | 24 | Axitinib | Neoadjuvant | The median reduction in renal tumor diameter was 28.3% |
| Rini et al. [30] | 2015 | Phase II | 25 | Pazopanib | Neoadjuvant | R.E.N.A.L. score decreased in 71% of tumors and 92% had a reduction in tumor volume |
| Zhang et al. [31] | 2015 | Retrospective | 18 | Sorafenib | Neoadjuvant | Tumor size decreased from 7.8 cm to 6.2 cm and the median value of average tumor CT value decreased from 61 HU to 52 HU |
| Hatiboglu et al. [32] | 2017 | Prospective | 12 | Sorafenib | Neoadjuvant | Primary renal tumor diameter changed from 5.4 cm to 4.4 cm for sorafenib group and 10.6 cm to 10.7 cm in placebo group |
| NEOAVAX [21] | 2019 | Phase II | 40 | Axitinib, avelumab | Neoadjuvant | Median tumor size reduction was 20% with 32% experiencing recurrence, median OS was not reached |
| Lebacle et al. [33] | 2019 | Phase II | 18 | Axitinib | Neoadjuvant | Primary tumor diameter had a median size reduction of 17% |
| PADRES [22] | 2023 | Phase II | 26 | Axitinib | Neoadjuvant | Decreased tumor size (7.7 to 6.3 cm) and RENAL score (11 vs. 10, p < 0.001) |
| Carlo et al. [34] | 2023 | Phase II | 18 | Nivolumab | Neoadjuvant | Median RFS at 1 year was 82% (95% CI 65–100%) |
| Huang et al. [23] | 2024 | Phase II | 18 | Toripalimab, axitinib | Neoadjuvant | The objective response rate was 45%, median DFS was not reached, and estimated DFS rates at 1 year and 2 years were 84.7% and 84.7% |
| PROSPER EA8143 [20] | 2024 | Randomized, phase III | 819 | Nivolumab | Neoadjuvant | 33% had RFS in nivolumab versus 33% in surgery only |
| Trial Name | Year | Design | Number of Participants | Intervention | Type | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPARC-1 (NCT04028245) | 2019 | Open-label pilot | Recruiting | Spartalizumab, canakinumab | Neoadjuvant | Pending |
| RAMPART (NCT03288532) | 2021 | Multi-arm multi-stage, phase III | Recruiting | Durvalumab, tremelimumab | Neoadjuvant | Pending |
| LITESPARK-022 (NCT05239728) | 2022 | Randomized, phase III | Recruiting | Pembrolizumab, belzutifan | Adjuvant | Pending |
| NESCIO (NCT05148546) | 2022 | Randomized, phase II | 69 | Nivolumab, ipilimumab, relatlimab | Neoadjuvant | Pending |
| TUOAD-RCC (NCT06584435) | 2022 | Phase II | Recruiting | Teprolizumab | Adjuvant | Pending |
| Narayan et al. (NCT05733715) | 2023 | Randomized pilot | Recruiting | Pembrolizumab, lenvatinib | Neoadjuvant | Pending |
| INTerpath-004 (NCT06307431) | 2024 | Randomized, phase II | Recruiting | V940, pembrolizumab | Adjuvant | Pending |
| MRD GATE RC(NCT03142334) | 2024 | Multicenter open label | Recruiting | Pembrolizumab | Adjuvant | Pending |
| Voss et al. (NCT03005782) | 2025 | Phase II | Recruiting | Cemiplimab, fianlimab | Neoadjuvant | Pending |
| Liu et al. (NCT06574412) | 2025 | Phase II | Pending | Cardonilizumab, renvastinib | Adjuvant and neoadjuvant | Pending |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raghavan, D.; Gibatova, V.; Vojjala, N.; Moka, N.; Yen, A.E. Role of Systemic Therapy in Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma: Where Do We Stand and Where Are We Heading? Cancers 2025, 17, 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101656
Raghavan D, Gibatova V, Vojjala N, Moka N, Yen AE. Role of Systemic Therapy in Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma: Where Do We Stand and Where Are We Heading? Cancers. 2025; 17(10):1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101656
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaghavan, Deepa, Viktoriya Gibatova, Nikhil Vojjala, Nagaishwarya Moka, and Aihua Edward Yen. 2025. "Role of Systemic Therapy in Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma: Where Do We Stand and Where Are We Heading?" Cancers 17, no. 10: 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101656
APA StyleRaghavan, D., Gibatova, V., Vojjala, N., Moka, N., & Yen, A. E. (2025). Role of Systemic Therapy in Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma: Where Do We Stand and Where Are We Heading? Cancers, 17(10), 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101656






