Induction of the Inflammasome Pathway by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Provides an Actionable Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Tumor Animal Models
2.3. HCC Patient Study and ATLAS Database Information
2.4. RNA Isolation and Gene Array
2.5. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.6. Cell Culture and Biochemical Analysis
2.7. Cytokine Array and ELISA
2.8. Three-Dimensional Tumor Liver Spheroid Generation
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
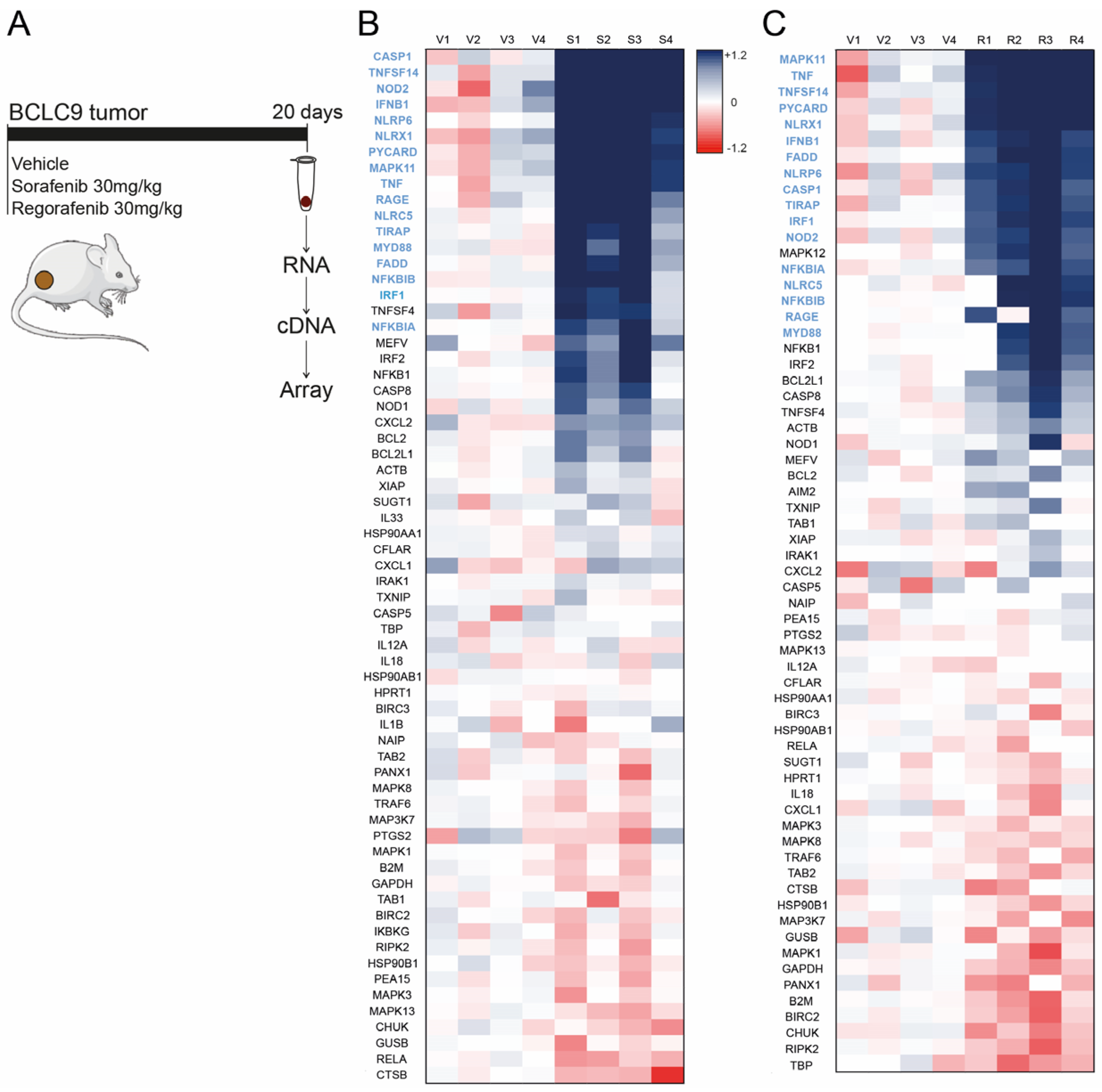
3.1. Sorafenib and Regorafenib Induction of Inflammasome-Related Genes Is Similar, Exhibiting Analogous Transcriptomic Signature
3.2. Transcriptional Increase of Inflammasome-Related Genes Is Associated with Poorer Prognosis Only for Male Liver Cancer Patients, According to Database Results
3.3. Sorafenib and Regorafenib-Treated HCC Patients Exhibit Transcriptomic Induction of the Inflammasome Pathway
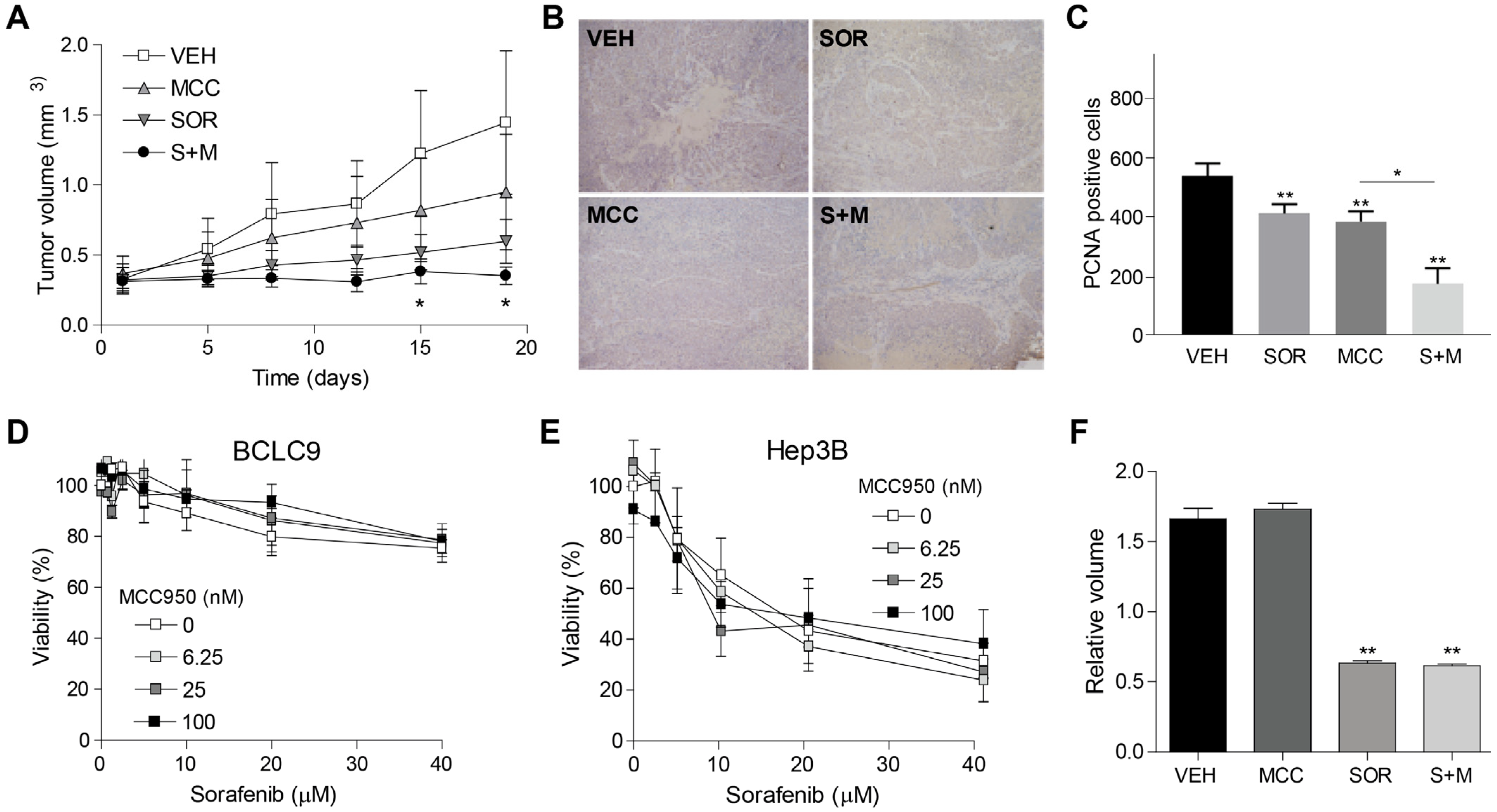
3.4. Inflammasome Inhibition Potentiates Sorafenib Efficacy in a Murine Subcutaneous Model of Human HCC
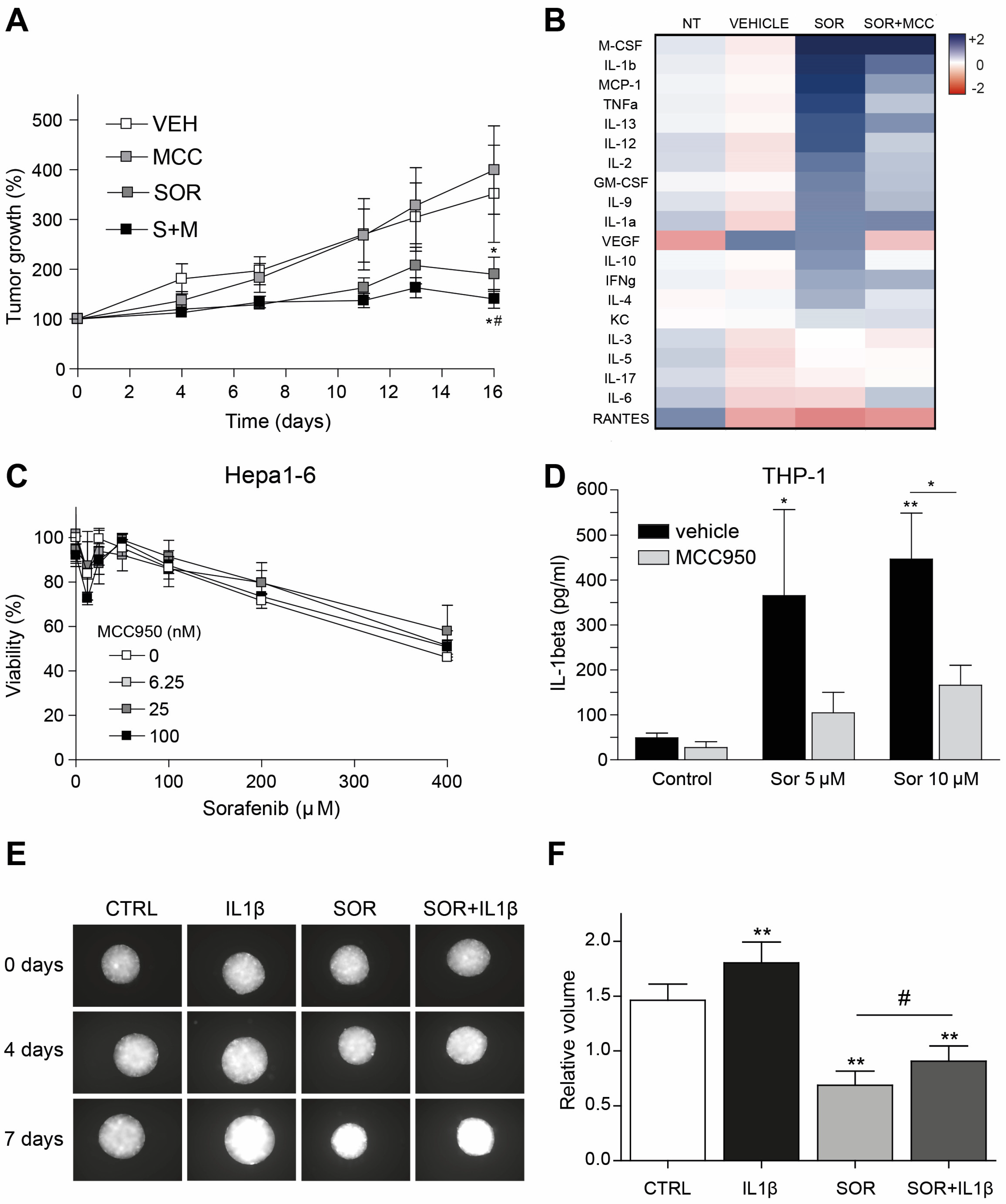
3.5. Inflammasome Inhibition on Tumor Microenvironment Increases Sorafenib Efficacy in a Syngeneic Mouse Model
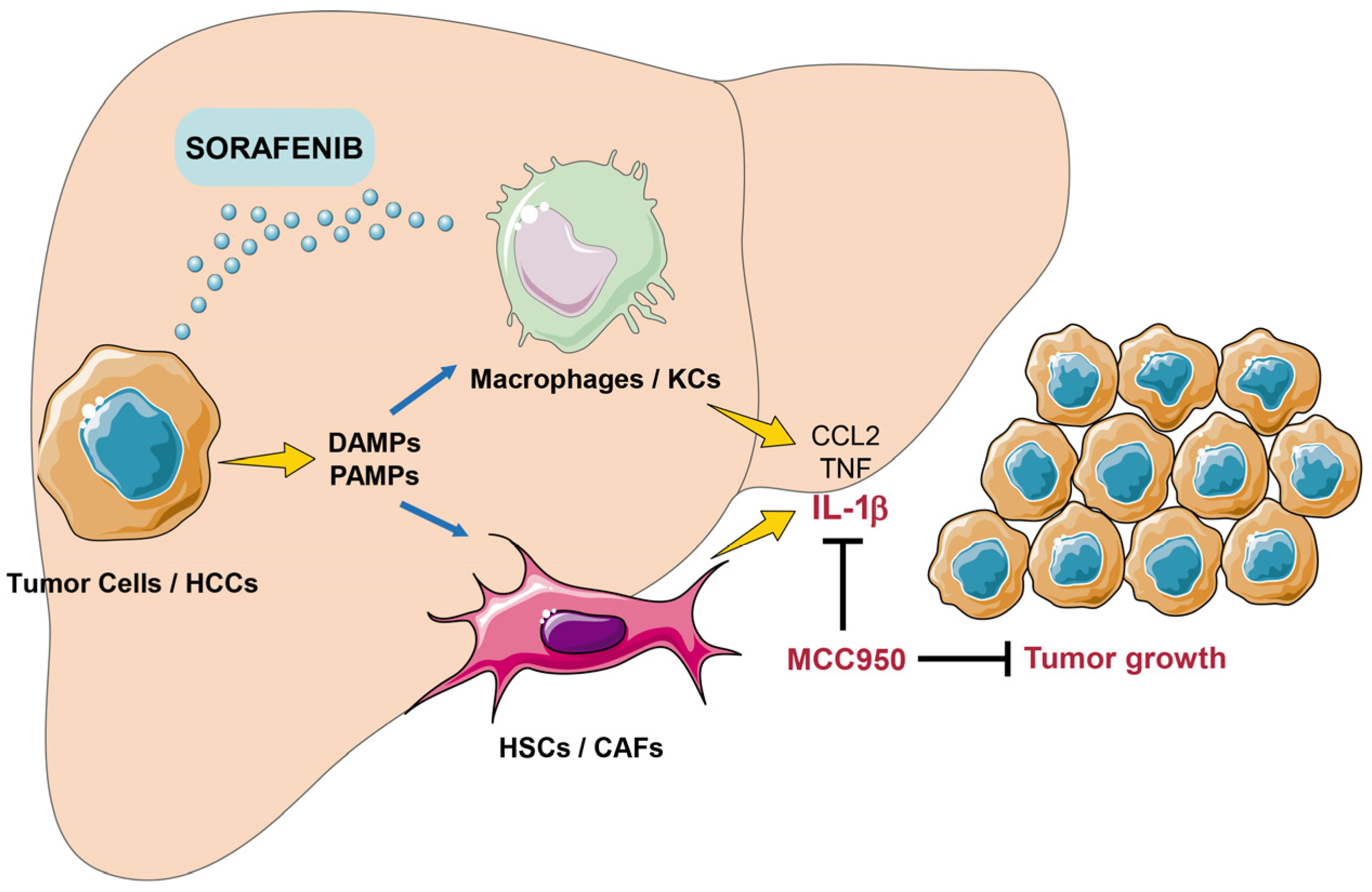
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cucarull, B.; Tutusaus, A.; Rider, P.; Hernáez-Alsina, T.; Cuño, C.; García de Frutos, P.; Colell, A.; Marí, M.; Morales, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Molecular Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Advances. Cancers 2022, 14, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutusaus, A.; Stefanovic, M.; Boix, L.; Cucarull, B.; Zamora, A.; Blasco, L.; de Frutos, P.G.; Reig, M.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C.; Marí, M.; et al. Antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins determine sorafenib/regorafenib resistance and BH3-mimetic efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16701–16717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucarull, B.; Tutusaus, A.; Subías, M.; Stefanovic, M.; Hernáez-Alsina, T.; Boix, L.; Reig, M.; García de Frutos, P.; Marí, M.; Colell, A.; et al. Regorafenib Alteration of the BCL-xL/MCL-1 Ratio Provides a Therapeutic Opportunity for BH3-Mimetics in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Models. Cancers 2020, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, M.; Torres, F.; Rodriguez-Lope, C.; Forner, A.; LLarch, N.; Rimola, J.; Darnell, A.; Ríos, J.; Ayuso, C.; Bruix, J. Early dermatologic adverse events predict better outcome in HCC patients treated with sorafenib. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimola, J.; Díaz-González, Á.; Darnell, A.; Varela, M.; Pons, F.; Hernandez-Guerra, M.; Delgado, M.; Castroagudin, J.; Matilla, A.; Sangro, B.; et al. Complete response under sorafenib in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Relationship with dermatologic adverse events. Hepatology 2018, 67, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, F.; Alencar, R.S.M.; Volt, F.; Sartori, G.; Dode, A.; Kikuchi, L.; Tani, C.M.; Chagas, A.L.; Pfiffer, T.; Hoff, P.; et al. The Impact of Early Dermatologic Events in the Survival of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-González, Á.; Sanduzzi-Zamparelli, M.; Sapena, V.; Torres, F.; LLarch, N.; Iserte, G.; Forner, A.; da Fonseca, L.; Ríos, J.; Bruix, J.; et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The critical role of dermatological events in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Callaway, J.B.; Ting, J.P.-Y. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, W.-C.; Jha, S.; Linhoff, M.W.; Ting, J.P.-Y. The NLR gene family: From discovery to present day. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.R.; Kanneganti, T.-D. NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer and metabolic diseases. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho Ribeiro, M.; Szabo, G. Role of the Inflammasome in Liver Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaul, S.; Leszczynska, A.; Alegre, F.; Kaufmann, B.; Johnson, C.D.; Adams, L.A.; Wree, A.; Damm, G.; Seehofer, D.; Calvente, C.J.; et al. Hepatocyte pyroptosis and release of inflammasome particles induce stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boaru, S.G.; Borkham-Kamphorst, E.; Tihaa, L.; Haas, U.; Weiskirchen, R. Expression analysis of inflammasomes in experimental models of inflammatory and fibrotic liver disease. J. Inflamm. 2012, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrasek, J.; Bala, S.; Csak, T.; Lippai, D.; Kodys, K.; Menashy, V.; Barrieau, M.; Min, S.-Y.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Szabo, G. IL-1 receptor antagonist ameliorates inflammasome-dependent alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3476–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Pras, E.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Gracia-Sancho, J.; Pérez-Del-Pulgar, S. Cell Death in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancers 2021, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.-L.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Shen, J.-L.; Cheng, H. Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatocellular carcinoma: A double-edged sword. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, L.; Shang, R.; Zhou, P. The role of pyroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Oncol. 2023, 46, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Apetoh, L.; Tesniere, A.; Aymeric, L.; Ma, Y.; Ortiz, C.; Vermaelen, K.; Panaretakis, T.; Mignot, G.; Ullrich, E.; et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in dendritic cells induces IL-1beta-dependent adaptive immunity against tumors. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupaul-Chicoine, J.; Arabzadeh, A.; Dagenais, M.; Douglas, T.; Champagne, C.; Morizot, A.; Rodrigue-Gervais, I.G.; Breton, V.; Colpitts, S.L.; Beauchemin, N.; et al. The Nlrp3 Inflammasome Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Metastatic Growth in the Liver by Promoting Natural Killer Cell Tumoricidal Activity. Immunity 2015, 43, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hage, C.; Hoves, S.; Strauss, L.; Bissinger, S.; Prinz, Y.; Pöschinger, T.; Kiessling, F.; Ries, C.H. Sorafenib Induces Pyroptosis in Macrophages and Triggers Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1280–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, R.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Diverging inflammasome signals in tumorigenesis and potential targeting. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Qin, W.; Lei, L.; Jiang, J.; Hu, J. The role of pyroptosis in cancer: Pro-cancer or pro-“host”? Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanovic, M.; Tutusaus, A.; Martinez-Nieto, G.A.; Bárcena, C.; de Gregorio, E.; Moutinho, C.; Barbero-Camps, E.; Villanueva, A.; Colell, A.; Marí, M.; et al. Targeting glucosylceramide synthase upregulation reverts sorafenib resistance in experimental hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8253–8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mingo, Á.; de Gregorio, E.; Moles, A.; Tarrats, N.; Tutusaus, A.; Colell, A.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C.; Morales, A.; Marí, M. Cysteine cathepsins control hepatic NF-κB-dependent inflammation via sirtuin-1 regulation. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bárcena, C.; Stefanovic, M.; Tutusaus, A.; Martinez-Nieto, G.A.; Martinez, L.; García-Ruiz, C.; de Mingo, A.; Caballeria, J.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C.; Marí, M.; et al. Angiogenin secretion from hepatoma cells activates hepatic stellate cells to amplify a self-sustained cycle promoting liver cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armengol, C.; Tarafa, G.; Boix, L.; Solé, M.; Queralt, R.; Costa, D.; Bachs, O.; Bruix, J.; Capellá, G. Orthotopic implantation of human hepatocellular carcinoma in mice: Analysis of tumor progression and establishment of the BCLC-9 cell line. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 2150–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucarull, B.; Tutusaus, A.; Hernáez-Alsina, T.; García de Frutos, P.; Reig, M.; Colell, A.; Marí, M.; Morales, A. Antioxidants Threaten Multikinase Inhibitor Efficacy against Liver Cancer by Blocking Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Takano, S.; Noguchi, T.; Kagi, T.; Komatsu, R.; Tan, M.; Hirata, Y.; Matsuzawa, A. The NLRP3 Inflammasome Works as a Sensor for Detecting Hypoactivity of the Mitochondrial Src Family Kinases. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imano, H.; Kato, R.; Ijiri, Y.; Hayashi, T. Activation of inflammasomes by tyrosine kinase inhibitors of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor: Implications for VEGFR TKIs-induced immune related adverse events. Toxicol. In Vitro 2021, 71, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, R.; Ijiri, Y. Regorafenib and reactive metabolite of sunitinib activate inflammasomes: Implications for multi tyrosine kinase inhibitor-Iiduced immune related adverse events. Pharmazie 2022, 77, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyr, B.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P. Sex Differences in the Inflammatory Profile in the Brain of Young and Aged Mice. Cells 2023, 12, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, M.; Csak, T.; Szabo, G. High fat diet feeding results in gender specific steatohepatitis and inflammasome activation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8525–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, R.C.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Chae, J.J.; Higgins, S.C.; Muñoz-Planillo, R.; Inserra, M.C.; Vetter, I.; Dungan, L.S.; Monks, B.G.; Stutz, A.; et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Peng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, C. Estrogen plays an important role by influencing the NLRP3 inflammasome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Shi, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Wang, K.; Shao, F. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature 2017, 547, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, C.; Dubyak, G.R. Chemotherapy engages multiple pathways leading to IL-1β production by myeloid leukocytes. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e27499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Tran, L.T.; Magun, E.A.; Magun, B.E.; Wood, L.J. Production of IL-1β by bone marrow-derived macrophages in response to chemotherapeutic drugs: Synergistic effects of doxorubicin and vincristine. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mridha, A.R.; Wree, A.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Yeh, M.M.; Johnson, C.D.; Van Rooyen, D.M.; Haczeyni, F.; Teoh, N.C.-H.; Savard, C.; Ioannou, G.N.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces liver inflammation and fibrosis in experimental NASH in mice. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirre-Lizaso, A.; Huici-Izagirre, M.; Urretabizkaia-Garmendia, J.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Banales, J.M.; Perugorria, M.J. Targeting the Heterogeneous Tumour-Associated Macrophages in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Feng, S.-R.; Chen, J.-F.; Li, X.-G.; Shi, Y.-H.; Tang, Z.; Liu, W.-R.; Zhang, X.; Huang, A.; Luo, X.-M.; et al. Inhibition of autophagy in macrophage promotes IL-1β-mediated hepatocellular carcinoma progression via inflammasome accumulation and self-recruitment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Liu, M.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Xie, M.; Ji, X.; et al. IL-1β-Induced Elevation of Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis Through Up-regulating Programmed Death Ligand 1 and Colony-Stimulating Factor 1. Hepatology 2021, 74, 3174–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Huang, C.-X.; Qu, C.; Li, P.-L.; Wu, X.-N.; Yao, W.; Shen, C.; Huang, R.; Wan, C.-C.; Jian, Z.-W.; et al. Targeting ferroptosis-elicited inflammation suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and enhances sorafenib efficacy. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, H.V.; Dwivedi, D.K.; Khan, S.; Jena, G. Mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated hepatic stellate cell activation: Therapeutic potential for liver fibrosis. Genes. Dis. 2023, 10, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affo, S.; Filliol, A.; Gores, G.J.; Schwabe, R.F. Fibroblasts in liver cancer: Functions and therapeutic translation. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Tartaglia, N.; Villani, R.; Serviddio, G.; Ramai, D.; Mohan, B.P.; Chandan, S.; El Aziz, M.A.A.; Evangelista, J.; Cotsoglou, C.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 2379–2387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tutusaus, A.; Sanduzzi-Zamparelli, M.; Boix, L.; Rider, P.; Subías, S.; García de Frutos, P.; Colell, A.; Marí, M.; Reig, M.; Morales, A. Induction of the Inflammasome Pathway by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Provides an Actionable Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081491
Tutusaus A, Sanduzzi-Zamparelli M, Boix L, Rider P, Subías S, García de Frutos P, Colell A, Marí M, Reig M, Morales A. Induction of the Inflammasome Pathway by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Provides an Actionable Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2024; 16(8):1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081491
Chicago/Turabian StyleTutusaus, Anna, Marco Sanduzzi-Zamparelli, Loreto Boix, Patricia Rider, Silvia Subías, Pablo García de Frutos, Anna Colell, Montserrat Marí, María Reig, and Albert Morales. 2024. "Induction of the Inflammasome Pathway by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Provides an Actionable Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 16, no. 8: 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081491
APA StyleTutusaus, A., Sanduzzi-Zamparelli, M., Boix, L., Rider, P., Subías, S., García de Frutos, P., Colell, A., Marí, M., Reig, M., & Morales, A. (2024). Induction of the Inflammasome Pathway by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Provides an Actionable Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 16(8), 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081491










