Bevacizumab Treatment for Patients with NF2-Related Schwannomatosis: A Single Center Experience
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Treatment Protocol and Outcomes
2.3. Clinical Assessment
2.4. Radiological Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
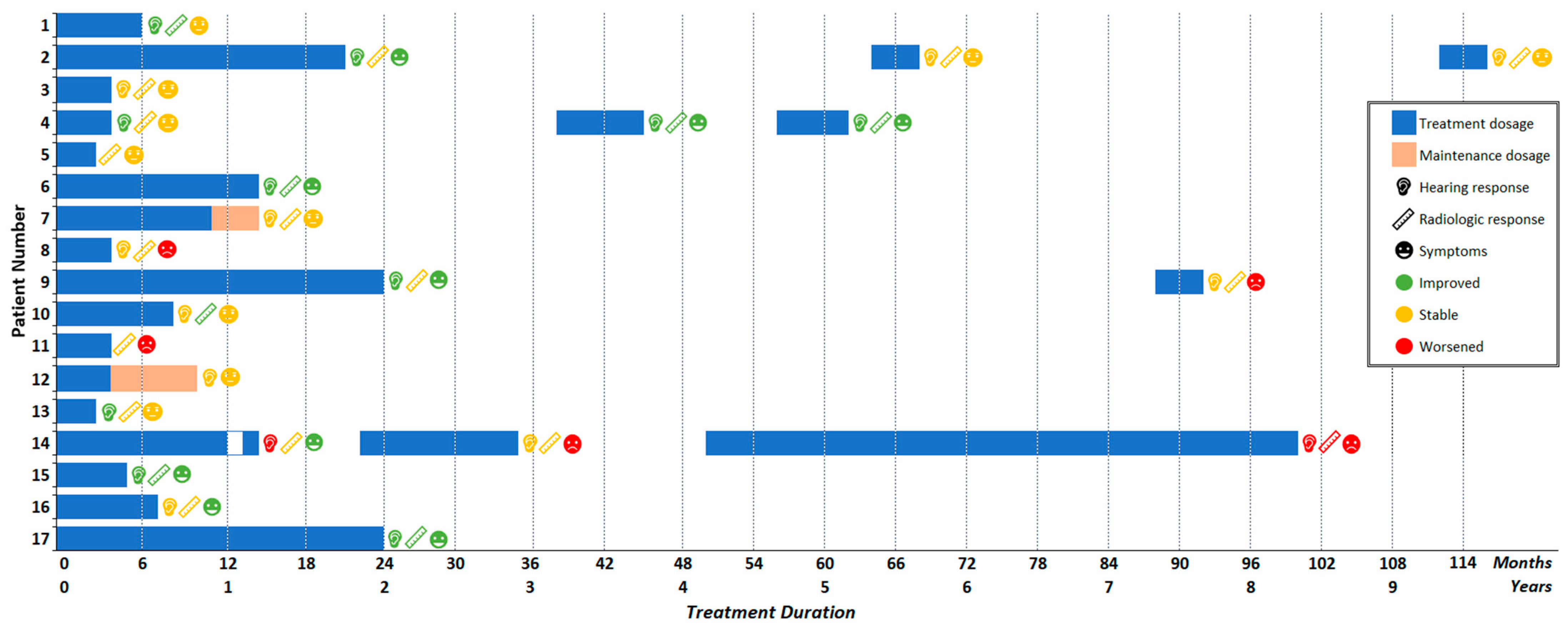
3.2. Bevacizumab Treatment
3.3. Adverse Events
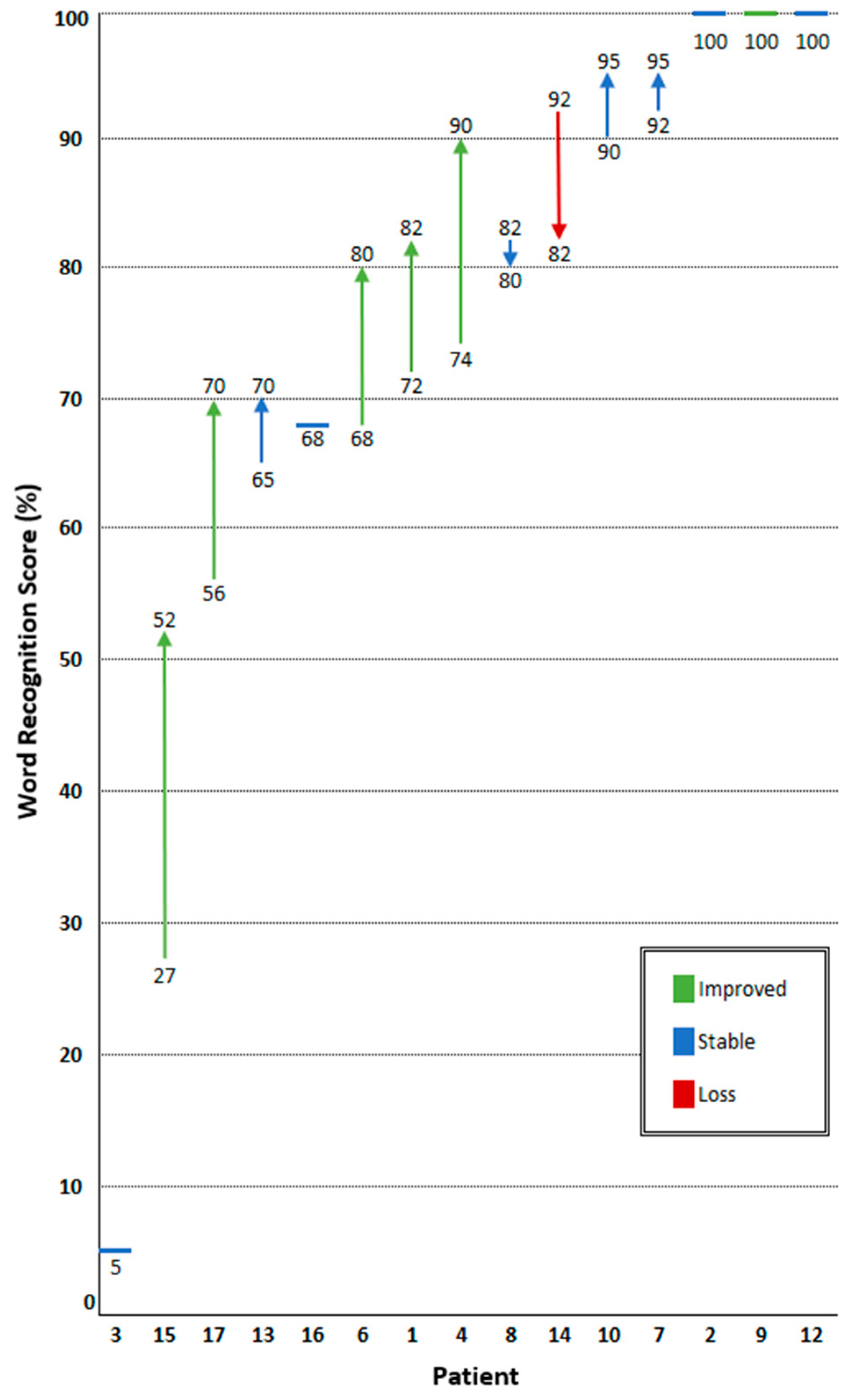
3.4. Hearing Response
3.5. Radiologic Response
3.6. Symptomatic Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, D. Chapter 5—Neurofibromatosis type 2. In Neurocutaneous Syndromes; Islam, M.P., Roach, E.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 132, pp. 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Asthagiri, A.R.; Parry, D.M.; Butman, J.A.; Kim, H.J.; Tsilou, E.T.; Zhuang, Z.; Lonser, R.R. Neurofibromatosis type 2. Lancet 2009, 373, 1974–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.; Huson, S.; Donnai, D.; Neary, W.; Blair, V.; Newton, V.; Harris, R. A Clinical Study of Type 2 Neurofibromatosis. QJM Int. J. Med. 1992, 84, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D. Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2): A clinical and molecular review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2009, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeley, J.O.; Evans, D.G.; Adler, J.; Brackmann, D.; Chen, R.; Ferner, R.E.; Hanemann, C.O.; Harris, G.; Huson, S.M.; Jacob, A.; et al. Consensus recommendations for current treatments and accelerating clinical trials for patients with neurofibromatosis type 2. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2012, 158A, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldbrunner, R.; Weller, M.; Regis, J.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Stavrinou, P.; Reuss, D.; Evans, D.G.; Lefranc, F.; Sallabanda, K.; Falini, A.; et al. EANO guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of vestibular schwannoma. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniakas, A.; Saliba, I. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 Vestibular Schwannoma Treatment: A Review of the Literature, Trends, and Outcomes. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, U.; Maayan, O.; An, A.; Lavieri, M.E.T.; Guadix, S.W.; DeRosa, A.P.; Christos, P.J.; Pannullo, S.; Stieg, P.E.; Brandmaier, A.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas in neurofibromatosis type 2 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2022, 156, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.; Halliday, D.; Obholzer, R.; Afridi, S.; Forde, C.; Rutherford, S.A.; Hammerbeck-Ward, C.; Lloyd, S.K.; Freeman, S.M.; Pathmanaban, O.N.; et al. Radiation treatment of benign tumors in NF2-related-schwannomatosis: A national study of 266 irradiated patients showing a significant increase in malignancy/malignant progression. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2023, 5, vdad025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.R.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.O.; Barker, F.G.; Halpin, C.; Padera, T.P.; Tyrrell, A.; Sorensen, A.G.; Jain, R.K.; di Tomaso, E. Hearing Improvement after Bevacizumab in Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeley, J.O.; Ye, X.; Duda, D.G.; Halpin, C.F.; Bergner, A.L.; Muzikansky, A.; Merker, V.L.; Gerstner, E.R.; Fayad, L.M.; Ahlawat, S.; et al. Efficacy and Biomarker Study of Bevacizumab for Hearing Loss Resulting From Neurofibromatosis Type 2–Associated Vestibular Schwannomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponghini, A.P.; Platini, F.; Rondonotti, D.; Soffietti, R. Bevacizumab Treatment for Vestibular Schwannoma in a Patient with Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Hearing Improvement and Tumor Shrinkage. Tumori J. 2015, 101, e167–e170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochart, A.; Gaillard, V.; Baroncini, M.; André, N.; Vannier, J.-P.; Vinchon, M.; Dubrulle, F.; Lejeune, J.-P.; Vincent, C.; Nève, V.; et al. Bevacizumab decreases vestibular schwannomas growth rate in children and teenagers with neurofibromatosis type 2. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 124, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanin, M.C.; Klausen, C.; Caye-Thomasen, P.; Thomsen, C.; Fugleholm, K.; Poulsgaard, L.; Lassen, U.; Mau-Sorensen, M.; Hofland, K.F. The effect of bevacizumab on vestibular schwannoma tumour size and hearing in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 3627–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, K.A.; Golding, J.F.; Axon, P.R.; Afridi, S.; Blesing, C.; Ferner, R.E.; Halliday, D.; Jena, R.; Pretorius, P.M.; UK NF2 Research Group; et al. Bevacizumab in neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) related vestibular schwannomas: A nationally coordinated approach to delivery and prospective evaluation. Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2016, 3, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, V.; Bergner, A.L.; Halpin, C.; Merker, V.L.; Sheridan, M.R.; Widemann, B.C.; Blakeley, J.O.; Plotkin, S.R. Improvement in Patient-reported Hearing After Treatment With Bevacizumab in People With Neurofibromatosis Type 2. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverak, P.; Adams, M.E.; Haines, S.J.; Levine, S.C.; Nascene, D.; Sommer, K.; Dusenbery, K.; Huang, T.C.; Moertel, C. Bevacizumab for Hearing Preservation in Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Emphasis on Patient-Reported Outcomes and Toxicities. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2019, 160, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiranth, S.; Langer, S.W.; Poulsen, H.S.; Urup, T. A systematic review of targeted therapy for vestibular schwannoma in patients with NF2-related schwannomatosis. Neurooncol Adv. 2023, 5, vdad099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, K.A.; Golding, J.F.; Blesing, C.; Evans, D.G.; Ferner, R.E.; Foweraker, K.; Halliday, D.; Jena, R.; McBain, C.; McCabe, M.G.; et al. Toxicity profile of bevacizumab in the UK Neurofibromatosis type 2 cohort. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 131, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.R.; Messiaen, L.; Legius, E.; Pancza, P.; Avery, R.A.; Blakeley, J.O.; Babovic-Vuksanovic, D.; Ferner, R.; Fisher, M.J.; Friedman, J.M.; et al. Updated diagnostic criteria and nomenclature for neurofibromatosis type 2 and schwannomatosis: An international consensus recommendation. Genet. Med. 2022, 24, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE); US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, G.; Robertson, J.H. Hearing Preservation in Unilateral Acoustic Neuroma Surgery. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1988, 97, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium Guidelines for the Evaluation of Hearing Preservation in Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Schwannoma): Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 179–180. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, J.W.; Brackmann, D.E. Facial Nerve Grading System. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1985, 93, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dombi, E.; Ardern-Holmes, S.L.; Babovic-Vuksanovic, D.; Barker, F.G.; Connor, S.; Evans, D.G.; Fisher, M.J.; Goutagny, S.; Harris, G.J.; Jaramillo, D.; et al. Recommendations for imaging tumor response in neurofibromatosis clinical trials. Neurology 2013, 81, S33–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M.L.; Link, M.J. Vestibular Schwannomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1335–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.R.; Halpin, C.; Blakeley, J.O.; Slattery, W.H.; Welling, D.B.; Chang, S.M.; Loeffler, J.S.; Harris, G.J.; Sorensen, A.G.; McKenna, M.J.; et al. Suggested response criteria for phase II antitumor drug studies for neurofibromatosis type 2 related vestibular schwannoma. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 93, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dunn, I.F.; Bi, W.L.; Mukundan, S.; Delman, B.N.; Parish, J.; Atkins, T.; Asher, A.L.; Olson, J.J. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines on the Role of Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Vestibular Schwannomas. Neurosurgery 2018, 82, E32–E34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzaki, J.; Tos, M.; Sanna, M.; Moffat, D.A. New and Modified Reporting Systems from the Consensus Meeting on Systems for Reporting Results in Vestibular Schwannoma. Otol. Neurotol. 2003, 24, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charabi, S.; Thomsen, J.; Mantoni, M.; Charabi, B.; Bjarne, J.R.; Sven Erik, B.R.; Gyldensted, C.; Tos, M. Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Schwannoma): Growth and Surgical and Nonsurgical Consequences of the Wait-And-See Policy. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.R.; Duda, D.G.; Muzikansky, A.; Allen, J.; Blakeley, J.; Rosser, T.; Campian, J.L.; Clapp, D.W.; Fisher, M.J.; Tonsgard, J.; et al. Multicenter, Prospective, Phase II and Biomarker Study of High-Dose Bevacizumab as Induction Therapy in Patients With Neurofibromatosis Type 2 and Progressive Vestibular Schwannoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3446–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slusarz, K.M.; Merker, V.L.; Muzikansky, A.; Francis, S.A.; Plotkin, S.R. Long-term toxicity of bevacizumab therapy in neurofibromatosis 2 patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 73, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.R.; Merker, V.L.; Halpin, C.; Jennings, D.; McKenna, M.J.; Harris, G.J.; Barker, F.G.I. Bevacizumab for Progressive Vestibular Schwannoma in Neurofibromatosis Type 2: A Retrospective Review of 31 Patients. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farschtschi, S.; Kollmann, P.; Dalchow, C.; Stein, A.; Mautner, V.-F. Reduced dosage of bevacizumab in treatment of vestibular schwannomas in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 3857–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killeen, D.E.; Klesse, L.; Tolisano, A.M.; Hunter, J.B.; Kutz, J.W., Jr. Long-Term Effects of Bevacizumab on Vestibular Schwannoma Volume in Neurofibromatosis Type 2 Patients. J. Neurol. Surg B Skull Base 2019, 80, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
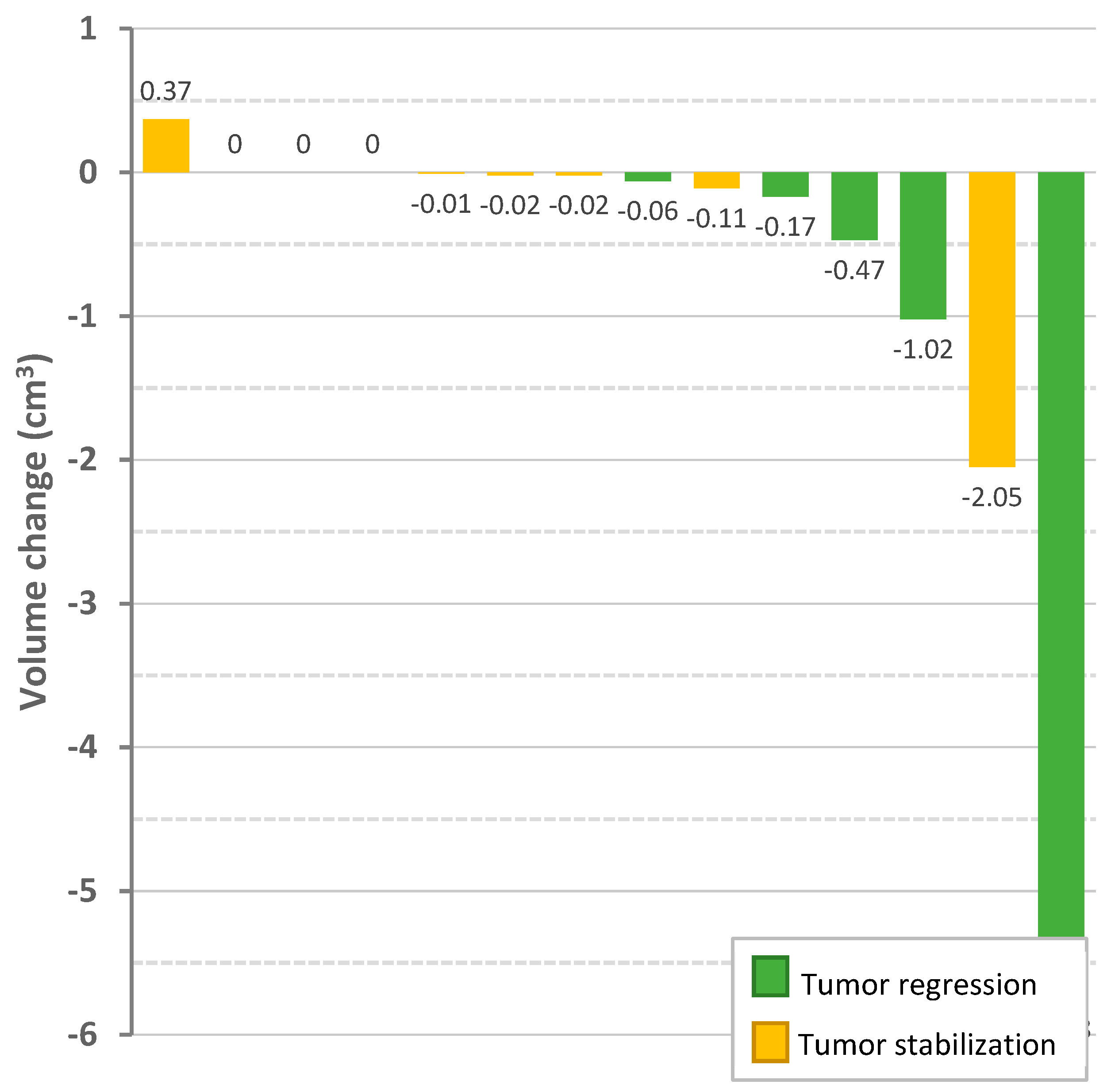
| Patient Characteristics | Patients, n = 17 | |
|---|---|---|
| Alive, n (%) | 16 (94.1) | |
| Age, years, median (range) | Time of diagnosis Start of treatment | 39.1 (16.5–67.3) 48.1 (22.9–70.7) |
| Female, n (%) | 9 female (52.9) | |
| Family history of NF2, n (%) | 2 (11.8) | |
| Previous treatment, yes, n (%) | Total | 11 (64.7) |
| Surgical resection Target vestibular schwannoma Non-target tumor(s) | 10 (58.8) 2 (11.8) 10 (58.8) | |
| Radiotherapy Target vestibular schwannoma Non-target tumor(s) | 3 (17.6) 0 (0.0) 3 (17.6) | |
| NF2 classification, n (%) 1 | Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 | 15 (88.2) 0 (0.0) 2 (11.8) |
| Tumor localization, n (%) | Unilateral vestibular schwannoma Bilateral vestibular schwannoma | 2 (11.8) 15 (88.2) |
| Non-vestibular schwannoma Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system | 12 (70.6) 12 (70.6) 3 (17.6) | |
| Total tumor count, median (range) | 12 (2–40) | |
| Adverse Event 1 | Patients, n (%) | Grade 1, n (%) | Grade 2, n (%) | Grade 3, n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 16 (94.1) | 13 (76.5) | 12 (70.6) | 2 (11.8) |
| Hypertension | 14 (82.4) | 3 (17.6) | 9 (52.9) | 2 (11.8) |
| Fatigue | 5 (29.4) | 5 (29.4) | ||
| Elevated liver enzymes | 3 (17.6) | 3 (17.6) | ||
| Diarrhea | 2 (11.8) | 2 (11.8) | ||
| Dry skin | 2 (11.8) | 2 (11.8) | ||
| Epistaxis | 2 (11.8) | 2 (11.8) | ||
| Headache | 2 (11.8) | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | |
| Hyperkalemia | 2 (11.8) | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | |
| Impaired wound healing | 2 (11.8) | 2 (11.8) | ||
| Infection | 2 (11.8) | 2 (11.8) | ||
| Irregular menses 2 | 2 (22.2) | 1 (11.1) | 1 (11.1) | |
| Myalgia | 2 (11.8) | 2 (11.8) | ||
| Nausea | 2 (11.8) | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | |
| Allergic dermatologic reaction | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | ||
| Dysphonia | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | ||
| Edema of limbs | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | ||
| Erectile dysfunction | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | ||
| Hyperglycemia | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | ||
| Proteinuria | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | ||
| Thrombocytopenia | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | ||
| Vertigo | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) |
| Radiologic Characteristics | n = | |
|---|---|---|
| First presentation | 16 | |
| Extrameatal extension, n (%) | 13 (81.3) | |
| Extrameatal volume, cm3, median (range) | 2.07 (0.09–24.45) | |
| Start of bevacizumab treatment | 16 | |
| Extrameatal extension, n (%) | 14 (87.5) | |
| Extrameatal volume, cm3, median (range) | 1.24 (0.05–12.67) | |
| Relative change, % (range) | 43 (−61–816) | |
| End of bevacizumab treatment | 16 | |
| Extrameatal extension, n (%) | 13 (81.3) | |
| Extrameatal volume, cm3, median (range) | 1.15 (0.0 1–10.52) | |
| Relative change, % (range) | −12 (−100 1–6) | |
| Most recent radiologic surveillance | 12 | |
| Extrameatal extension, n (%) | 11 (91.7) | |
| Extrameatal volume, cm3, median (range) | 1.52 (0.03–8.25) | |
| Relative change, % (range) | 27 (−22–275) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Douwes, J.P.J.; Hensen, E.F.; Jansen, J.C.; Gelderblom, H.; Schopman, J.E. Bevacizumab Treatment for Patients with NF2-Related Schwannomatosis: A Single Center Experience. Cancers 2024, 16, 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081479
Douwes JPJ, Hensen EF, Jansen JC, Gelderblom H, Schopman JE. Bevacizumab Treatment for Patients with NF2-Related Schwannomatosis: A Single Center Experience. Cancers. 2024; 16(8):1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081479
Chicago/Turabian StyleDouwes, Jules P. J., Erik F. Hensen, Jeroen C. Jansen, Hans Gelderblom, and Josefine E. Schopman. 2024. "Bevacizumab Treatment for Patients with NF2-Related Schwannomatosis: A Single Center Experience" Cancers 16, no. 8: 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081479
APA StyleDouwes, J. P. J., Hensen, E. F., Jansen, J. C., Gelderblom, H., & Schopman, J. E. (2024). Bevacizumab Treatment for Patients with NF2-Related Schwannomatosis: A Single Center Experience. Cancers, 16(8), 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081479







