Obesity and Inflammatory Factors in the Progression of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Review
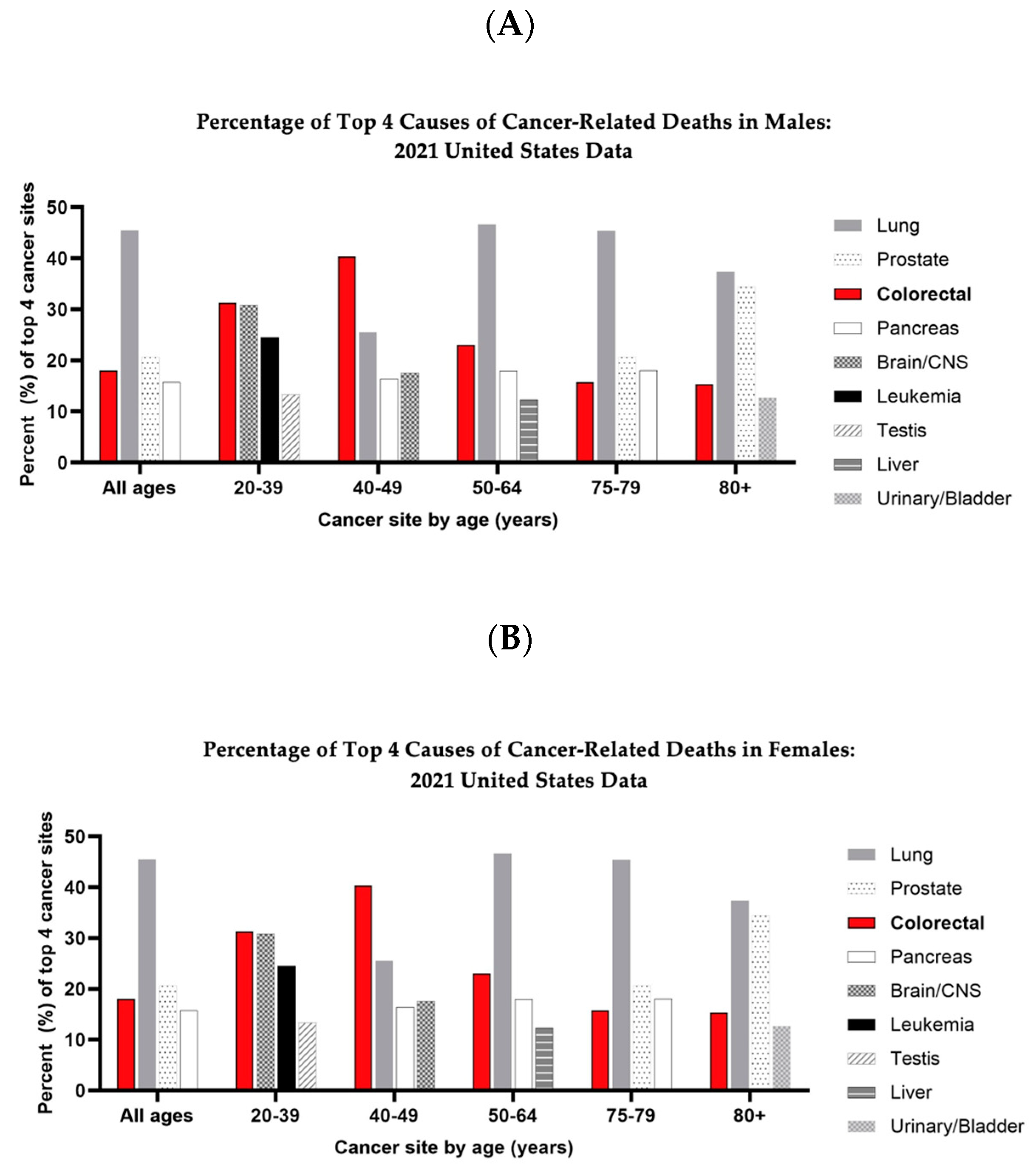
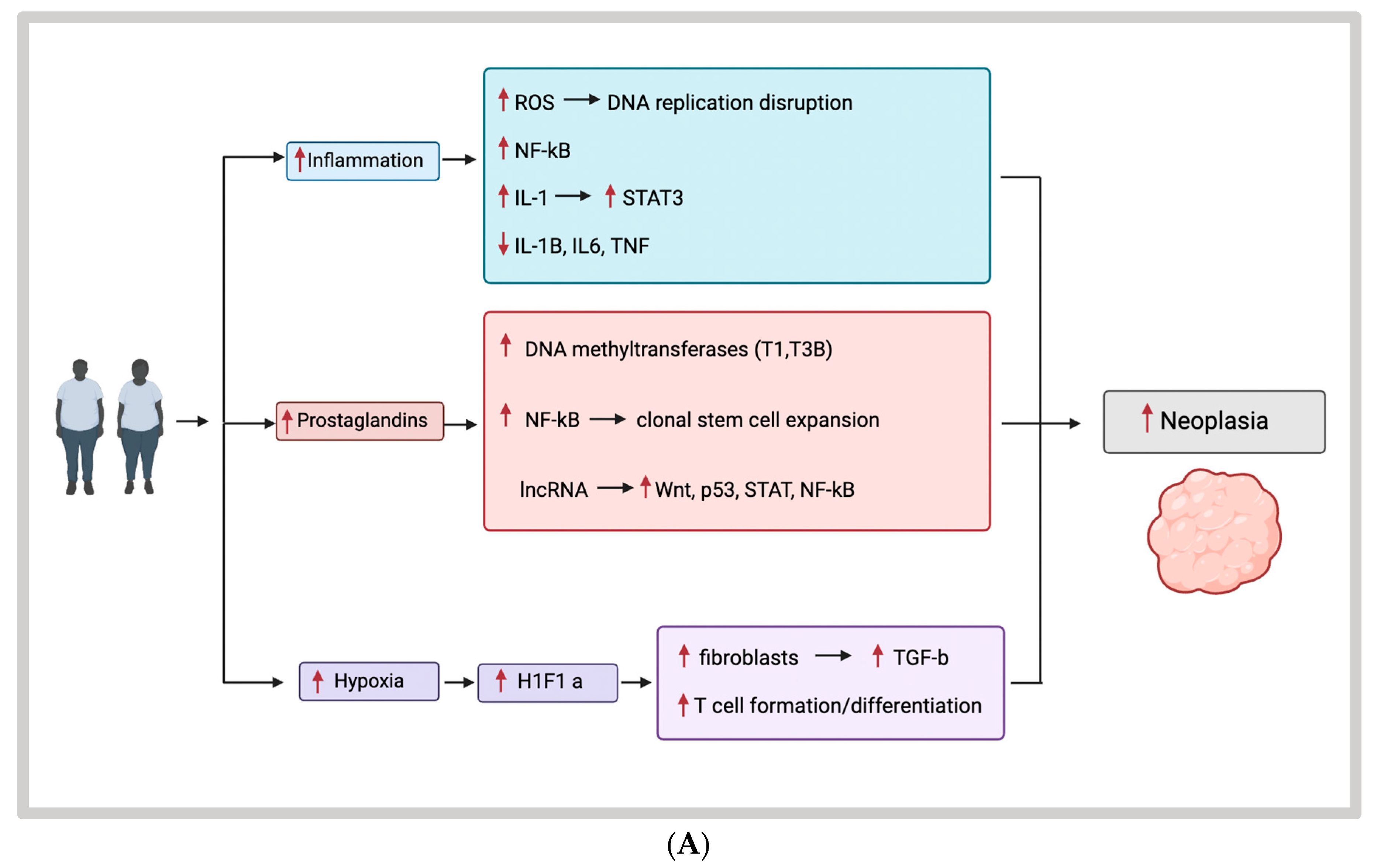
3.1. Obesity, Inflammation, and EOCRC
3.2. Obesity Hormones and Their Mechanisms
3.2.1. Obesity and the Tumor Microenvironment
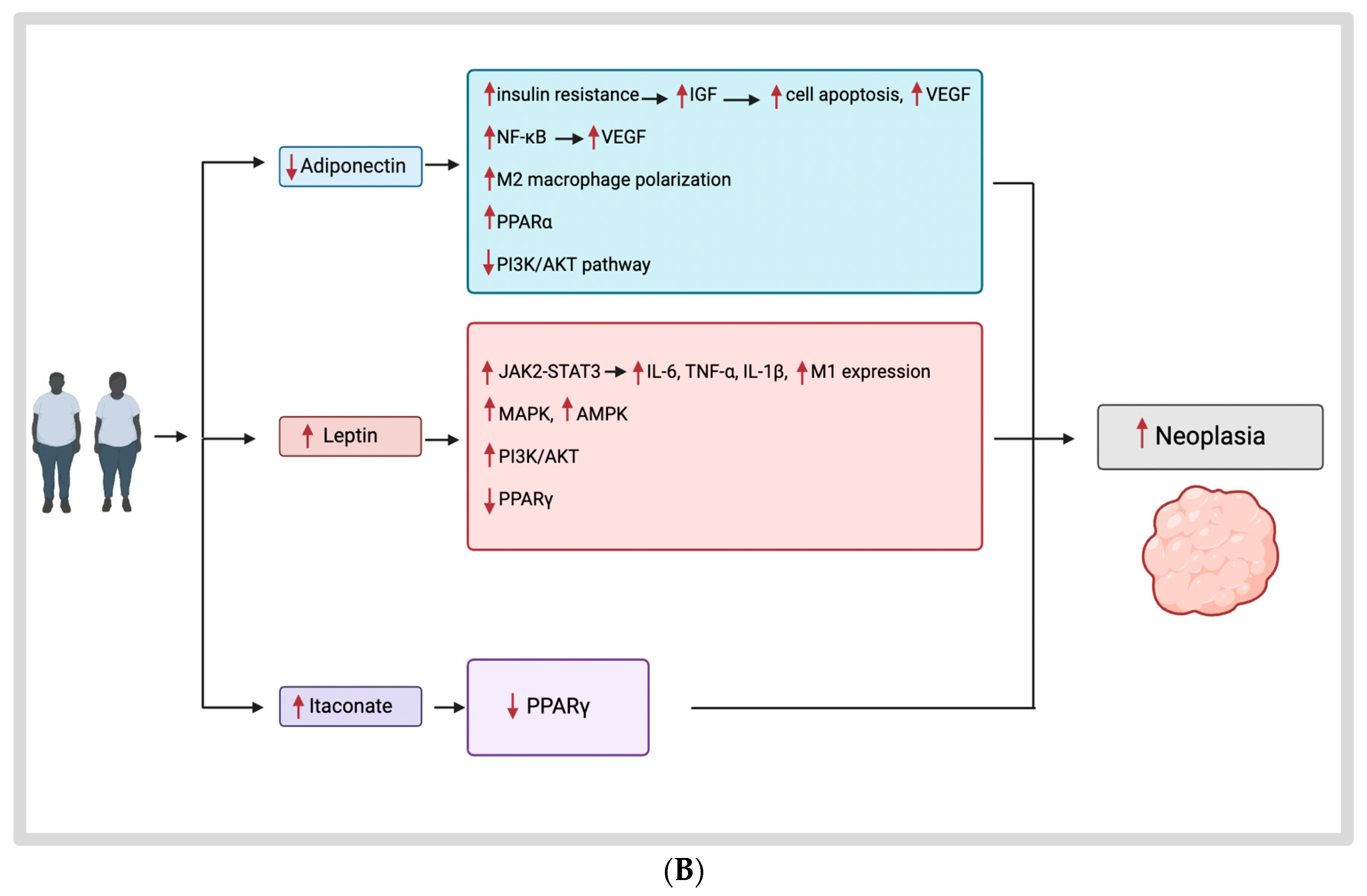
3.2.2. Adiponectin
3.2.3. Leptin
3.3. Itaconate
3.4. Microbiome
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaander, M.C.W.; Zauber, A.G.; Syngal, S.; Blaser, M.J.; Sung, J.J.; You, Y.N.; Kuipers, E.J. Young-onset colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.M.D.; Fontham, E.T.H.; Church, T.R.; Flowers, C.R.; Guerra, C.E.; LaMonte, S.J.; Etzioni, R.; McKenna, M.T.; Oeffinger, K.C.; Shih, Y.T.; et al. Colorectal cancer screening for average-risk adults: 2018 guideline update from the American Cancer Society. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 250–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Abnet, C.C.; Neale, R.E.; Vignat, J.; Giovannucci, E.L.; McGlynn, K.A.; Bray, F. Global Burden of 5 Major Types of Gastrointestinal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 335–349.e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, S.K.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Hursting, S.D. The World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research Third Expert Report on Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Cancer: Impact and Future Directions. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou, M.; Rouland, A.; Martel, M.; Loffroy, R.; Barkun, A.N.; Chapelle, N. Review article: Obesity and colorectal cancer. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 56, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaguera, D.; Fernández-Barrés, S.; Gracia-Lavedán, E.; Vendrell, E.; Azpiri, M.; Ruiz-Moreno, E.; Martín, V.; Gómez-Acebo, I.; Obón, M.; Molinuevo, A.; et al. Consumption of ultra-processed foods and drinks and colorectal, breast, and prostate cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, K.L.; Frugé, A.D.; Heslin, M.J.; Lipke, E.A.; Greene, M.W. Diet as a Risk Factor for Early-Onset Colorectal Adenoma and Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 896330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyaz, S.; Mana, M.D.; Roper, J.; Kedrin, D.; Saadatpour, A.; Hong, S.J.; Bauer-Rowe, K.E.; Xifaras, M.E.; Akkad, A.; Arias, E.; et al. High-fat diet enhances stemness and tumorigenicity of intestinal progenitors. Nature 2016, 531, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.H.; Wu, K.; Ng, K.; Zauber, A.G.; Nguyen, L.H.; Song, M.; He, X.; Fuchs, C.S.; Ogino, S.; Willett, W.C.; et al. Association of Obesity With Risk of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Among Women. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, M.J.; Dunne, M.R.; Donohoe, C.L.; Reynolds, J.V. Obesity-associated cancer: An immunological perspective. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Lyon, C.J.; Bergin, S.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Hsueh, W.A. Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheurlen, K.M.; Snook, D.L.; Alfieri, T.; Littlefield, A.B.; George, J.B.; Seraphine, C.; Cook, C.N.; Rochet, A.; Gaskins, J.T.; Galandiuk, S. Obesity hormones and itaconate mediating inflammation in human colon cancer cells—Another lead to early-onset colon cancer? Heliyon 2023, 9, e13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheurlen, K.M. The Role of Obesity in Macrophage-Mediated Mechanisms Promoting Early-Onset Colon Cancer. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, D.; Welch, B.S.; Rehman, A. Pathophysiology of Obesity. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kothari, N.; Teer, J.K.; Abbott, A.M.; Srikumar, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yoder, S.J.; Brohl, A.S.; Kim, R.D.; Reed, D.R.; Shibata, D. Increased incidence of FBXW7 and POLE proofreading domain mutations in young adult colorectal cancers. Cancer 2016, 122, 2828–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirzin, S.; Marisa, L.; Guimbaud, R.; De Reynies, A.; Legrain, M.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Cordelier, P.; Pradère, B.; Bonnet, D.; Meggetto, F.; et al. Sporadic early-onset colorectal cancer is a specific sub-type of cancer: A morphological, molecular and genetics study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Greten, F.R. The inflammatory pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Miki, C.; Okugawa, Y.; Toiyama, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M. Decreased expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 predicts poor prognosis following curative resection of colorectal cancer. Dis. Colon. Rectum 2008, 51, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachiya, K.; Masuya, M.; Kuroda, N.; Yoneda, M.; Tsuboi, J.; Nagaharu, K.; Nishimura, K.; Shiotani, T.; Ohishi, K.; Tawara, I.; et al. Irbesartan, an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker, inhibits colitis-associated tumourigenesis by blocking the MCP-1/CCR2 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meira, L.B.; Bugni, J.M.; Green, S.L.; Lee, C.W.; Pang, B.; Borenshtein, D.; Rickman, B.H.; Rogers, A.B.; Moroski-Erkul, C.A.; McFaline, J.L.; et al. DNA damage induced by chronic inflammation contributes to colon carcinogenesis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2516–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckmann, L.; Nebelsiek, T.; Fingerle, A.A.; Dann, S.M.; Mages, J.; Lang, R.; Robine, S.; Kagnoff, M.F.; Schmid, R.M.; Karin, M.; et al. Opposing functions of IKKbeta during acute and chronic intestinal inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15058–15063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greten, F.R.; Eckmann, L.; Greten, T.F.; Park, J.M.; Li, Z.W.; Egan, L.J.; Kagnoff, M.F.; Karin, M. IKKbeta links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell 2004, 118, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaked, H.; Hofseth, L.J.; Chumanevich, A.; Chumanevich, A.A.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Guma, M.; Shenouda, S.; Clevers, H.; et al. Chronic epithelial NF-κB activation accelerates APC loss and intestinal tumor initiation through iNOS up-regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14007–14012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrieva-Posocco, O.; Dzutsev, A.; Posocco, D.F.; Hou, V.; Yuan, W.; Thovarai, V.; Mufazalov, I.A.; Gunzer, M.; Shilovskiy, I.P.; Khaitov, M.R.; et al. Cell-Type-Specific Responses to Interleukin-1 Control Microbial Invasion and Tumor-Elicited Inflammation in Colorectal Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 166–180.e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Su, X.; Dai, L.; Chen, N.; Fang, C.; Dong, Z.; Fu, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; et al. Temporal DNA methylation pattern and targeted therapy in colitis-associated cancer. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackstadt, R.; van Hooff, S.R.; Leach, J.D.; Cortes-Lavaud, X.; Lohuis, J.O.; Ridgway, R.A.; Wouters, V.M.; Roper, J.; Kendall, T.J.; Roxburgh, C.S.; et al. Epithelial NOTCH Signaling Rewires the Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal Cancer to Drive Poor-Prognosis Subtypes and Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 319–336.e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Nicolas, A.; Petrocelli, V.; Pesic, M.; Mahmoud, A.; Michels, B.E.; Etlioglu, E.; Yepes, D.; Häupl, B.; Ziegler, P.K.; et al. AKT-dependent NOTCH3 activation drives tumor progression in a model of mesenchymal colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; DuBois, R.N. Role of prostanoids in gastrointestinal cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2732–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tołoczko-Iwaniuk, N.; Dziemiańczyk-Pakieła, D.; Nowaszewska, B.K.; Celińska-Janowicz, K.; Miltyk, W. Celecoxib in Cancer Therapy and Prevention—Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, J.C.; Elliott, F.; Macrae, F.; Mecklin, J.P.; Möslein, G.; McRonald, F.E.; Bertario, L.; Evans, D.G.; Gerdes, A.M.; Ho, J.W.C.; et al. Cancer Prevention with Resistant Starch in Lynch Syndrome Patients in the CAPP2-Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial: Planned 10-Year Follow-up. Cancer Prev. Res. 2022, 15, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, J.; Sheth, H.; Elliott, F.; Reed, L.; Macrae, F.; Mecklin, J.P.; Möslein, G.; McRonald, F.E.; Bertario, L.; Evans, D.G.; et al. Cancer prevention with aspirin in hereditary colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome), 10-year follow-up and registry-based 20-year data in the CAPP2 study: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, Z.; Bei, B.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, N. Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation in Colitis Associated Cancer. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Moyer, M.P.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, N.; et al. Long non-coding RNA CCAL regulates colorectal cancer progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway via suppression of activator protein 2α. Gut 2016, 65, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.L.; Subramanian, M.; Jones, M.F.; Chaudhary, R.; Singh, D.K.; Zong, X.; Gryder, B.; Sindri, S.; Mo, M.; Schetter, A.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA PURPL Suppresses Basal p53 Levels and Promotes Tumorigenicity in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2408–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokavec, M.; Öner, M.G.; Li, H.; Jackstadt, R.; Jiang, L.; Lodygin, D.; Kaller, M.; Horst, D.; Ziegler, P.K.; Schwitalla, S.; et al. Corrigendum. IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Liao, L.; Yin, F.; Kuang, H.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y. LncRNA AB073614 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells via regulating the JAK/STAT3 pathway. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 21, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Shen, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, K.; Ye, Y.; Wang, S. A novel long non-coding RNA lnc-GNAT1-1 is low expressed in colorectal cancer and acts as a tumor suppressor through regulating RKIP-NF-κB-Snail circuit. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurlen, K.M.; Snook, D.L.; Walter, M.N.; Cook, C.N.; Fiechter, C.R.; Pan, J.; Beal, R.J.; Galandiuk, S. Itaconate and leptin affecting PPARγ in M2 macrophages: A potential link to early-onset colorectal cancer. Surgery 2022, 171, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Price, R.L.; Singh, U.P. Adipocyte, Immune Cells, and miRNA Crosstalk: A Novel Regulator of Metabolic Dysfunction and Obesity. Cells 2021, 10, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegaard, J.I.; Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.R.; Goforth, M.H.; Morel, C.R.; Subramanian, V.; Mukundan, L.; Red Eagle, A.; Vats, D.; Brombacher, F.; Ferrante, A.W.; et al. Macrophage-specific PPARgamma controls alternative activation and improves insulin resistance. Nature 2007, 447, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, W.; Kong, W.; Zeng, T. Itaconate: A Potent Macrophage Immunomodulator. Inflammation 2023, 46, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurlen, K.M.; Billeter, A.T.; O’Brien, S.J.; Galandiuk, S. Metabolic dysfunction and early-onset colorectal cancer - how macrophages build the bridge. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 6679–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurlen, K.M.; Chariker, J.H.; Kanaan, Z.; Littlefield, A.B.; George, J.B.; Seraphine, C.; Rochet, A.; Rouchka, E.C.; Galandiuk, S. The NOTCH4-GATA4-IRG1 axis as a novel target in early-onset colorectal cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2022, 67, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramipour, K.; Chamari, K.; Hekmatikar, A.A.; Ziyaiyan, A.; Taherkhani, S.; Elguindy, N.M.; Bragazzi, N.L. Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais, R.; Silaghi, H.; Silaghi, A.C.; Rusu, M.L.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Metabolic syndrome and risk of subsequent colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 5141–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katira, A.; Tan, P.H. Evolving role of adiponectin in cancer-controversies and update. Cancer Biol. Med. 2016, 13, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, E.K.; Giovannucci, E.; Fuchs, C.S.; Willett, W.C.; Mantzoros, C.S. Low plasma adiponectin levels and risk of colorectal cancer in men: A prospective study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 1688–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroni, P.; Palmirotta, R.; Spila, A.; Martini, F.; Raparelli, V.; Fossile, E.; Mariotti, S.; Del Monte, G.; Buonomo, O.; Roselli, M.; et al. Prognostic significance of adiponectin levels in non-metastatic colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 483–489. [Google Scholar]
- Ogino, S.; Shima, K.; Baba, Y.; Nosho, K.; Irahara, N.; Kure, S.; Chen, L.; Toyoda, S.; Kirkner, G.J.; Wang, Y.L.; et al. Colorectal cancer expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG, PPARgamma) is associated with good prognosis. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawi, T.K.; Shaker, O.G.; Ismail, M.F.; Sayed, N.H. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma in Obesity and Colorectal Cancer: The Role of Epigenetics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, K.M.; Gaulke, C.A.; Tsikitis, V.L. Understanding the microbiome: A primer on the role of the microbiome in colorectal neoplasia. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2020, 33, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanapareddy, N.; Legge, R.M.; Jovov, B.; McCoy, A.; Burcal, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Randall, T.A.; Galanko, J.; Benson, A.; Sandler, R.S.; et al. Increased rectal microbial richness is associated with the presence of colorectal adenomas in humans. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1858–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Liang, S.; Jia, H.; Stadlmayr, A.; Tang, L.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xia, H.; Xu, X.; Jie, Z.; et al. Gut microbiome development along the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gong, L.; Ge, C.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Y. The differences in colonic mucosal microbiota between normal individual and colon cancer patients by polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Hold, G.L.; Flint, H.J. The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Lu, N.; Wang, Z.; et al. Dysbiosis signature of fecal microbiota in colorectal cancer patients. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proença, M.A.; Biselli, J.M.; Succi, M.; Severino, F.E.; Berardinelli, G.N.; Caetano, A.; Reis, R.M.; Hughes, D.J.; Silva, A.E. Relationship between Fusobacterium nucleatum, inflammatory mediators and microRNAs in colorectal carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5351–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, L.; Thiele Orberg, E.; Geis, A.L.; Chan, J.L.; Fu, K.; DeStefano Shields, C.E.; Dejea, C.M.; Fathi, P.; Chen, J.; Finard, B.B.; et al. Bacteroides fragilis Toxin Coordinates a Pro-carcinogenic Inflammatory Cascade via Targeting of Colonic Epithelial Cells. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 203–214.e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleij, A.; van Gelder, M.M.; Swinkels, D.W.; Tjalsma, H. Clinical Importance of Streptococcus gallolyticus infection among colorectal cancer patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmerich, S.; Schöller, M.; Duranton, B.; Gossé, F.; Galluser, M.; Klein, J.P.; Raul, F. Promotion of intestinal carcinogenesis by Streptococcus bovis. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huycke, T.; Moore, D.R.; Lightfoot, S.A.; Huycke, M.M. Colon Macrophages Polarized by Commensal Bacteria Cause Colitis and Cancer through the Bystander Effect. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.C.; Yu, J. Gut microbiota in colorectal cancer development and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sánchez, M.A.; Núñez-Sánchez, M.; Balaguer-Román, A.; Oliva-Bolarín, A.; Pujante-Gilabert, G.; Hernández-Agüera, Q.; Mesa-López, M.J.; Egea-Valenzuela, J.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Ruiz-Alcaraz, A.J.; et al. Gut Microbiome Modification through Dietary Intervention in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: Protocol for a Prospective, Interventional, Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial in Patients with Scheduled Surgical Intervention for CRC. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nct. COffee and Metabolites Modulating the Gut MicrobiomE in Colorectal caNCER. 2023. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05692024 (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Nct. Mediterranean Diet and Weight Loss: Targeting the Bile Acid/Gut Microbiome Axis to Reduce Colorectal Cancer. 2021. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04753359 (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Nct. Beans/Bran Enriching Nutritional Eating For Intestinal Health Trial. 2013. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01929122 (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Dai, R.; Kelly, B.N.; Ike, A.; Berger, D.; Chan, A.; Drew, D.A.; Ljungman, D.; Mutiibwa, D.; Ricciardi, R.; Tumusiime, G.; et al. The Impact of the Gut Microbiome, Environment, and Diet in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Development. Cancers 2024, 16, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barot, S.V.; Sangwan, N.; Nair, K.G.; Schmit, S.L.; Xiang, S.; Kamath, S.; Liska, D.; Khorana, A.A. Distinct intratumoral microbiome of young-onset and average-onset colorectal cancer. EBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.F.; Elias-Oliveira, J.; Pereira, Í.S.; Pereira, J.A.; Barbosa, S.C.; Machado, M.S.G.; Carlos, D. Akkermansia muciniphila and Gut Immune System: A Good Friendship That Attenuates Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Obesity, and Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 934695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittayanon, R.; Lau, J.T.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Tse, F.; Yuan, Y.; Surette, M.; Moayyedi, P. Differences in Gut Microbiota in Patients with vs. without Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 930–946.e931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z. Gut microbiome in type 1 diabetes: A comprehensive review. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, A.N.; Scheurlen, K.M.; Macleod, A.; Simon, H.L.; Galandiuk, S. Obesity and Inflammatory Factors in the Progression of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071403
Jones AN, Scheurlen KM, Macleod A, Simon HL, Galandiuk S. Obesity and Inflammatory Factors in the Progression of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(7):1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071403
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Alexandra N., Katharina M. Scheurlen, Anne Macleod, Hillary L. Simon, and Susan Galandiuk. 2024. "Obesity and Inflammatory Factors in the Progression of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 7: 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071403
APA StyleJones, A. N., Scheurlen, K. M., Macleod, A., Simon, H. L., & Galandiuk, S. (2024). Obesity and Inflammatory Factors in the Progression of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 16(7), 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071403




