The Therapeutic Efficacy and Mechanism of Action of Gnetin C, a Natural Compound from the Melinjo Plant, in a Preclinical Mouse Model of Advanced Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Cell Culture
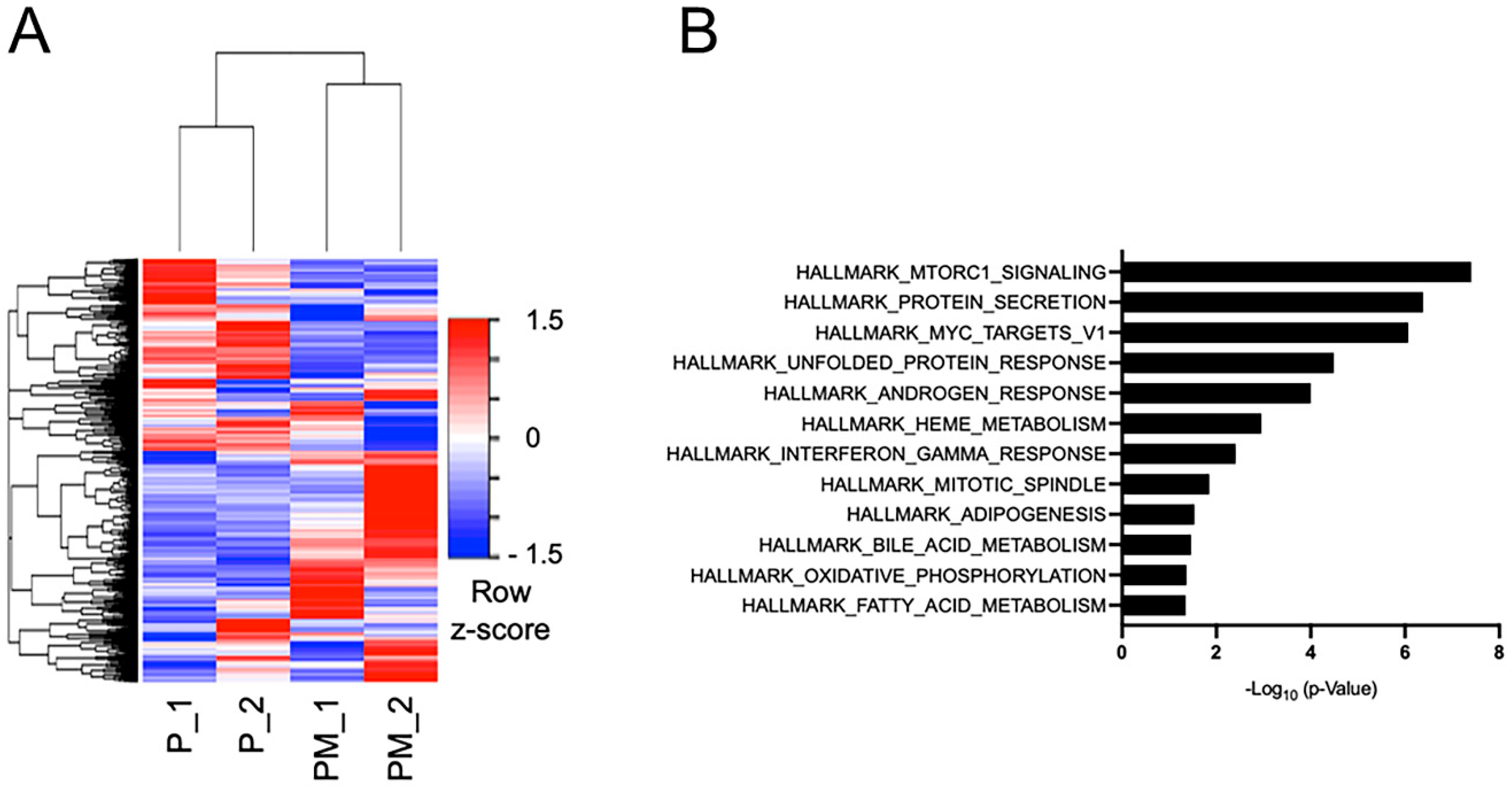
2.2. RNA Sequencing
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
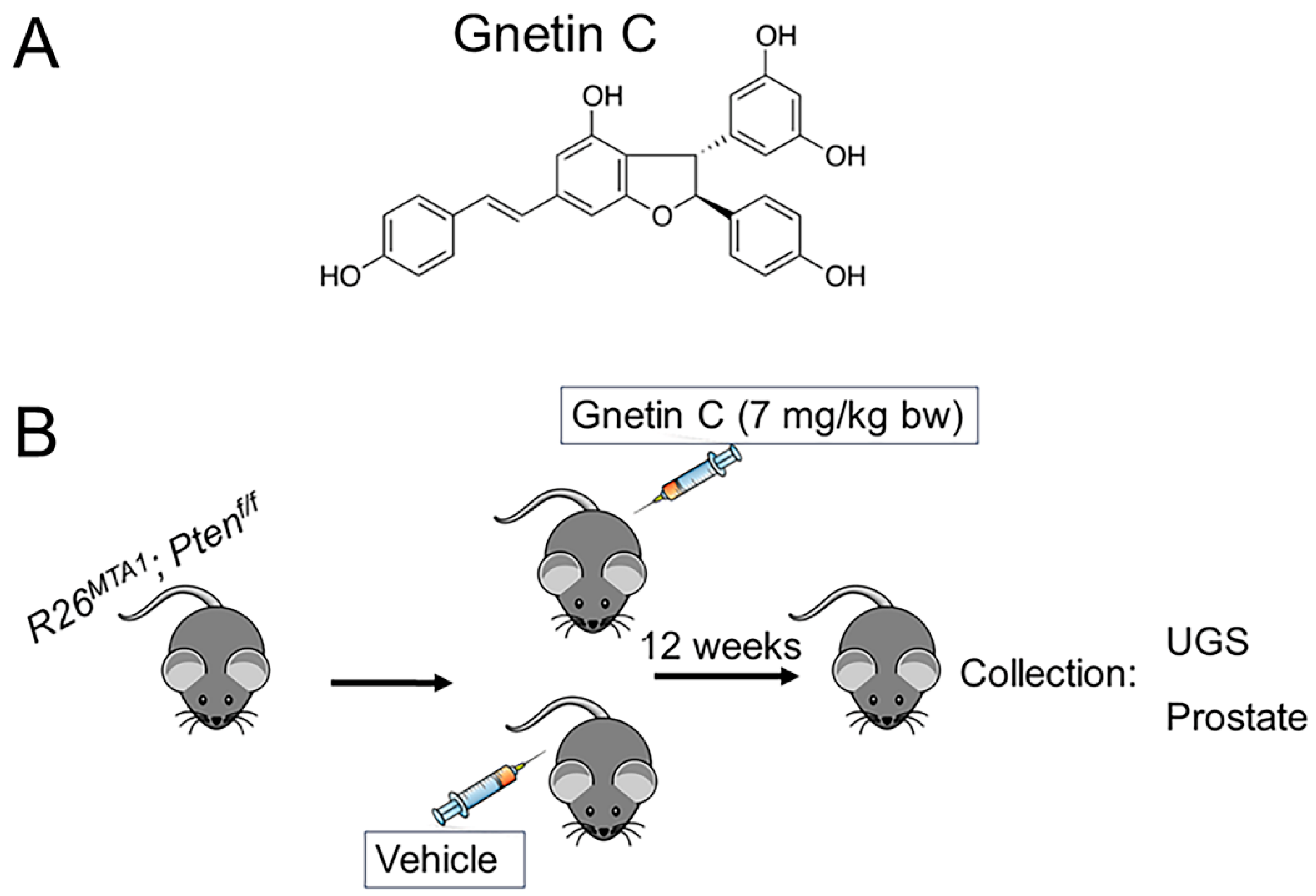
2.4. Animals and Study Design
2.5. Histology and Immunohistochemistry Analyses of Prostate Tissues
2.6. ELISA
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
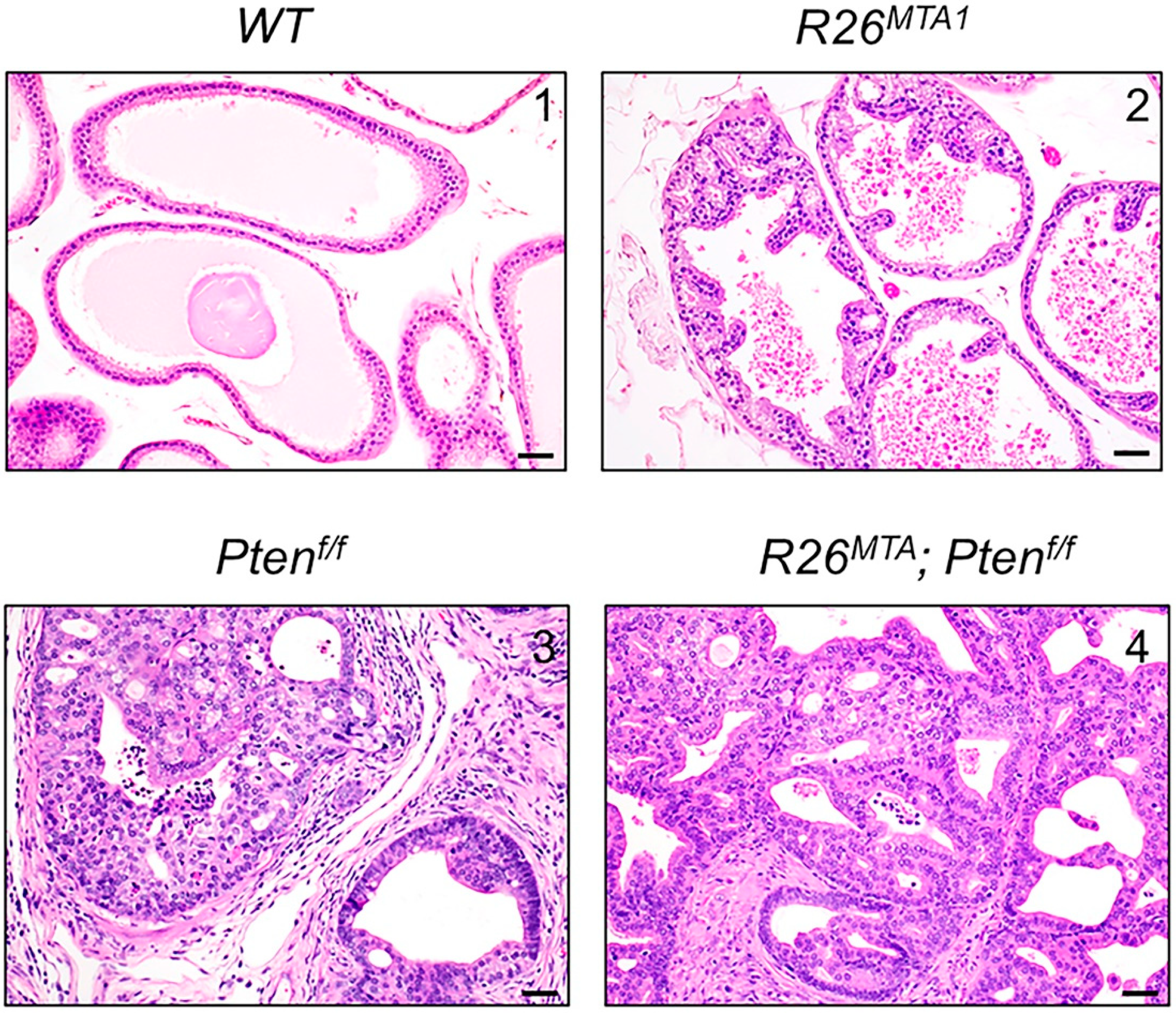
3.1. Prostate-Specific MTA1 Overexpression Makes Ptenf/f Mice Progress with Invasive Adenocarcinoma
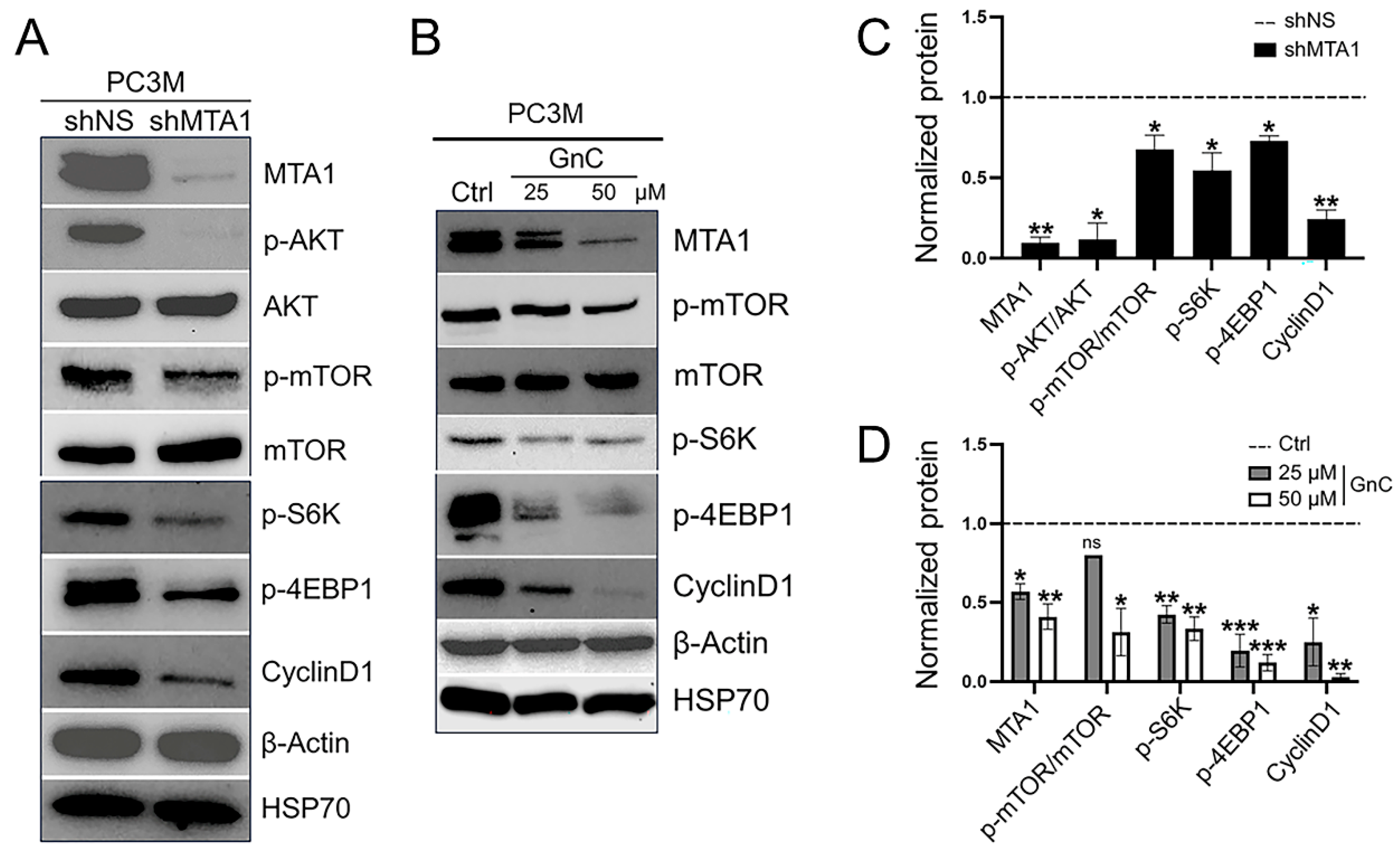
3.2. Inhibition of MTA1/mTOR Pathway by Gnetin C in Cell Culture
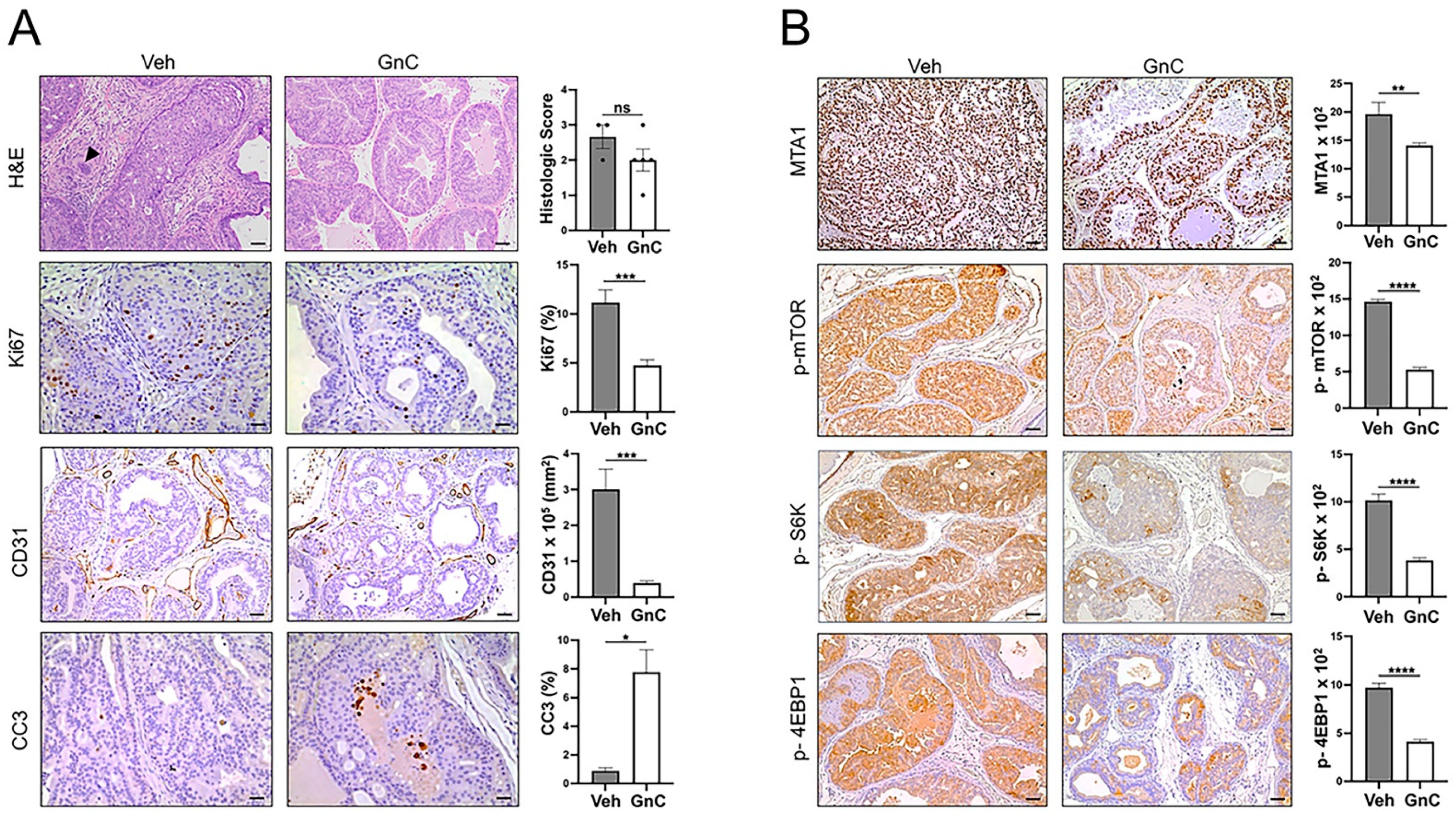
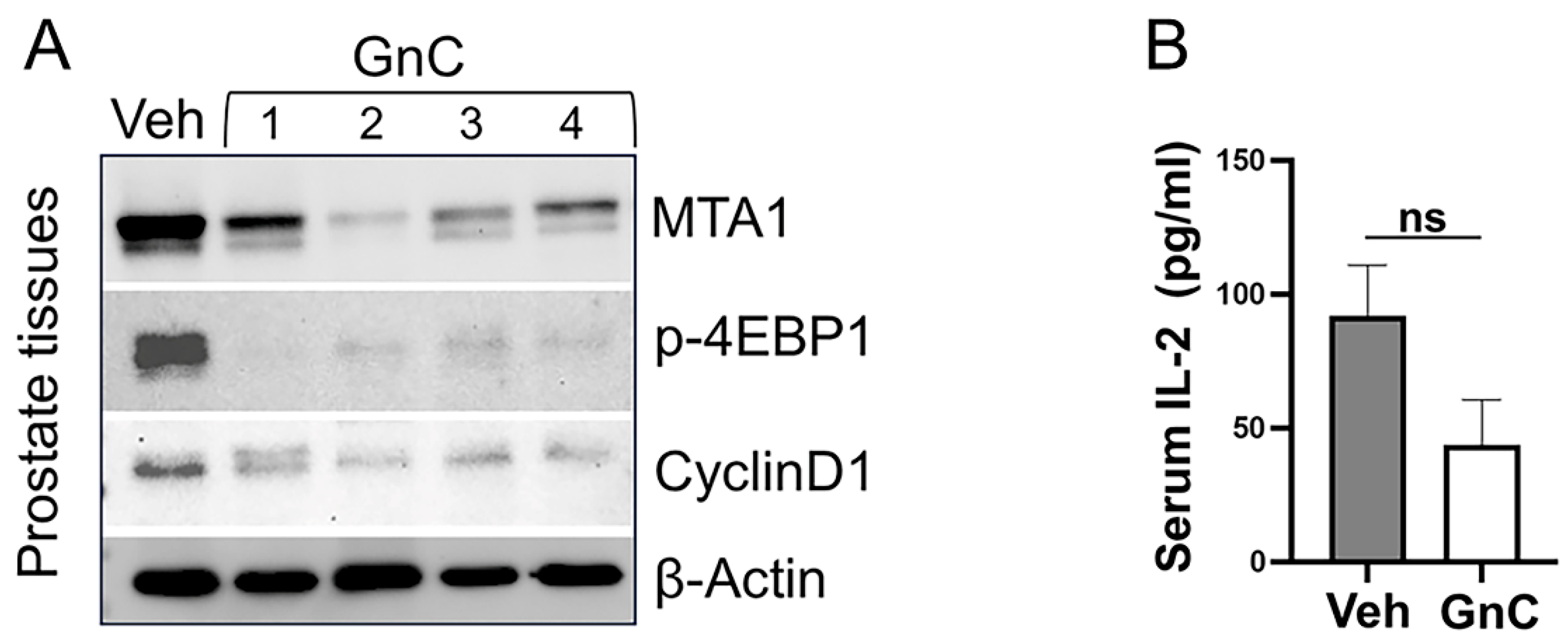
3.3. Gnetin C Treatment Diminishes Adenocarcinoma Progression in R26MTA1; Ptenf/f Mice
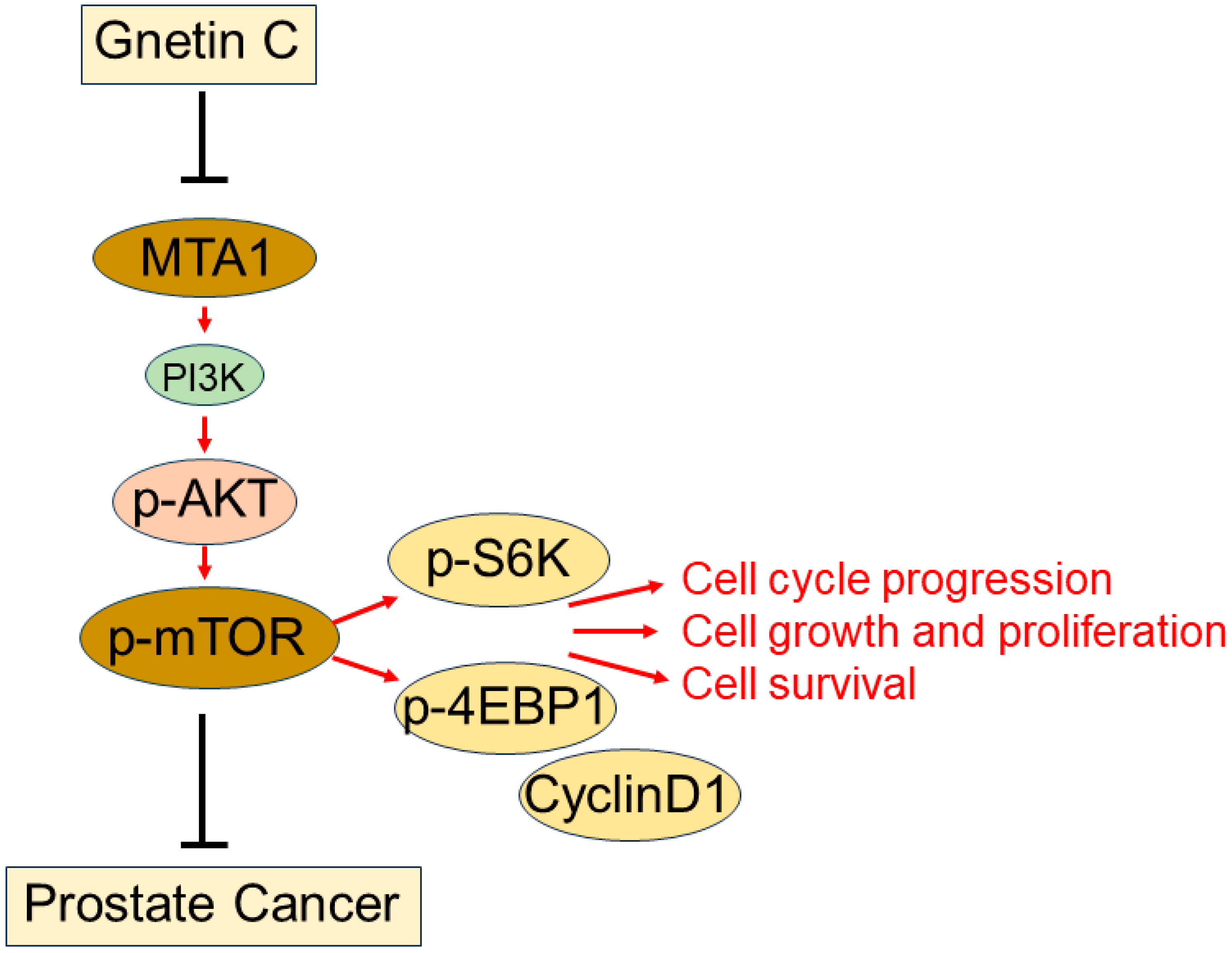
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene (protein kinase B) |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| AR | Androgen receptor |
| bw | Body weight |
| CC3 | Cleaved caspase 3 |
| CD31 | Cluster of differentiation 31 |
| CRPC | Castration-resistant prostate cancer |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Ctrl | Control |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| f/f | Pten gene flanked by two loxP sites in each allele |
| GnC | gnetin C |
| GRCm39 | Genome reference consortium mouse build 39 |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HED | Human equivalent dose |
| HSP70 | Heat shock protein 70 |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IL-2 | Interleukin 2 |
| i.p. | Intraperitoneal |
| Ki67 | Cellular protein marker of proliferation |
| LIU | Long Island University |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| ns | Non-significant |
| NS | Non-silenced |
| OE | Overexpression |
| p-AKTS473 | Phosphorylation of serine 473 in C-terminus of AKT |
| p-4EBP1 | Phosphorylated eukaryotic translational initiation factor 4E (elF4E)-binding protein 1 |
| p-S6K | Phosphorylated p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase |
| p-mTOR | Phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin |
| Pb-Cre+ | Probasin promoter directing expression of epithelial Cre recombinase |
| PC3M | Human prostate cancer cell line |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PIN | Prostate intraepithelial neoplasia |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| Pten+/f | Pten heterozygous mice |
| Ptenf/f | Pten homozygous, Pten-null |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| RPMI-1640 | Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 cell culture media |
| R26 | Rosa26 loci in the mouse genome |
| SEM | Standard error of mean |
| shMTA1 | short hairpin MTA1 |
| shNS | short hairpin non-silence |
| UGS | Urogenital system |
| WT | Wild-type |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.N.; Brattain, M.; Ghosh, P.M.; Troyer, D.A.; Prihoda, T.; Bedolla, R.; Kreisberg, J.I. Immunohistochemical demonstration of phospho-Akt in high Gleason grade prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paweletz, C.P.; Charboneau, L.; Bichsel, V.E.; Simone, N.L.; Chen, T.; Gillespie, J.W.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Roth, M.J.; Petricoin, I.E.; Liotta, L.A. Reverse phase protein microarrays which capture disease progression show activation of pro-survival pathways at the cancer invasion front. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Cardiff, R.D.; Desai, N.; Banach-Petrosky, W.A.; Parsons, R.; Shen, M.M.; Abate-Shen, C. Cooperativity of Nkx3.1 and Pten loss of function in a mouse model of prostate carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2884–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, S. Cotargeting survival signaling pathways in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3003–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorning, B.Y.; Dass, M.S.; Smalley, M.J.; Pearson, H.B. The PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway and Prostate Cancer: At the Crossroads of AR, MAPK, and WNT Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinkade, C.W.; Castillo-Martin, M.; Puzio-Kuter, A.; Yan, J.; Foster, T.H.; Gao, H.; Sun, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Gerald, W.L.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; et al. Targeting AKT/mTOR and ERK MAPK signaling inhibits hormone-refractory prostate cancer in a preclinical mouse model. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3051–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, S.J.; Zhou, X.; Ivanovic, M.; Gailey, M.P.; Dhar, S.; Zhang, L.; He, Z.; Penman, A.D.; Vijayakumar, S.; Levenson, A.S. Nuclear MTA1 overexpression is associated with aggressive prostate cancer, recurrence and metastasis in African Americans. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, M.D.; Kuefer, R.; Varambally, S.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Shapiro, G.I.; Gschwend, J.E.; Hautmann, R.E.; Sanda, M.G.; Giehl, K.; et al. The role of metastasis-associated protein 1 in prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, S.; Kumar, A.; Zhang, L.; Rimando, A.M.; Lage, J.M.; Lewin, J.R.; Atfi, A.; Zhang, X.; Levenson, A.S. Dietary pterostilbene is a novel MTA1-targeted chemopreventive and therapeutic agent in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18469–18484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, S.; Kumar, A.; Li, K.; Tzivion, G.; Levenson, A.S. Resveratrol regulates PTEN/Akt pathway through inhibition of MTA1/HDAC unit of the NuRD complex in prostate cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemani, R.; Patel, I.; Inamdar, N.; Campanelli, G.; Donovan, V.; Kumar, A.; Levenson, A.S. Dietary Pterostilbene for MTA1-Targeted Interception in High-Risk Premalignant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2022, 15, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parupathi, P.; Campanelli, G.; Deabel, R.A.; Puaar, A.; Devarakonda, L.S.; Kumar, A.; Levenson, A.S. Gnetin C Intercepts MTA1-Associated Neoplastic Progression in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.D. PTEN-PI3K pathway alterations in advanced prostate cancer and clinical implications. Prostate 2022, 82 (Suppl. S1), S60–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braglia, L.; Zavatti, M.; Vinceti, M.; Martelli, A.M.; Marmiroli, S. Deregulated PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in prostate cancer: Still a potential druggable target? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asensi, M.; Ortega, A.; Mena, S.; Feddi, F.; Estrela, J.M. Natural polyphenols in cancer therapy. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2011, 48, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudzinska, A.; Juchaniuk, P.; Oberda, J.; Wisniewska, J.; Wojdan, W.; Szklener, K.; Mandziuk, S. Phytochemicals in Cancer Treatment and Cancer Prevention-Review on Epidemiological Data and Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swetha, M.; Keerthana, C.K.; Rayginia, T.P.; Anto, R.J. Cancer Chemoprevention: A Strategic Approach Using Phytochemicals. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 809308. [Google Scholar]
- Tewari, D.; Patni, P.; Bishayee, A.; Sah, A.N.; Bishayee, A. Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in cancer: A novel therapeutic strategy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanankutty, A. Inhibitory Potential of Dietary Nutraceuticals on Cellular PI3K/Akt Signaling: Implications in Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 1816–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanankutty, A. Phytochemicals as PI3K/Akt/mTOR Inhibitors and Their Role in Breast Cancer Treatment. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenson, A.S. Metastasis-associated protein 1-mediated antitumor and anticancer activity of dietary stilbenes for prostate cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 80, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadkari, K.; Kolhatkar, U.; Hemani, R.; Campanelli, G.; Cai, Q.; Kumar, A.; Levenson, A.S. Therapeutic Potential of Gnetin C in Prostate Cancer: A Pre-Clinical Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Dholakia, K.; Sikorska, G.; Martinez, L.A.; Levenson, A.S. MTA1-Dependent Anticancer Activity of Gnetin C in Prostate Cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, H.; Hikami, S.; Iizuna, S.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Asama, T.; Ota, H.; Kimura, Y.; Tatefuji, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Higaki, K. Pharmacokinetics and safety of resveratrol derivatives in humans after oral administration of melinjo (Gnetum gnemon L.) seed extract powder. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, J.L.; Elbadry, M.I.; Taniwaki, M.; Harada, K.; Trung, L.Q.; Nakagawa, N.; Takami, A.; Ishiyama, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Takenaka, K.; et al. The simultaneous inhibition of the mTOR and MAPK pathways with Gnetin-C induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Lett. 2017, 400, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagami, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Espinoza, J.L.; Vu Quang, L.; Enomoto, M.; Takasugi, S.; Nakamura, A.; Nakayama, T.; Tani, H.; Hanamura, I.; et al. Immunomodulatory and Metabolic Changes after Gnetin-C Supplementation in Humans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Kanai, Y.; Katagiri, M.; Watanabe, T.; Mori, A.; Ikuta, T.; Tani, H.; Fukushima, S.; Tatefuji, T.; Shirasawa, T. Melinjo (Gnetum gnemon L.) Seed Extract Decreases Serum Uric Acid Levels in Nonobese Japanese Males: A Randomized Controlled Study. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 589169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, J.L.; An, D.T.; Trung, L.Q.; Yamada, K.; Nakao, S.; Takami, A. Stilbene derivatives from melinjo extract have antioxidant and immune modulatory effects in healthy individuals. Integr. Mol. Med. 2015, 2, 405–413. [Google Scholar]
- Bitting, R.L.; Armstrong, A.J. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, R83–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrard, R.M.; Maitland, N.J. Regulation of protein kinase B activity by PTEN and SHIP2 in human prostate-derived cell lines. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, N.; Sonenberg, N. Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1926–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, Q.; Jin, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wong, L.L.; Yang, W.; et al. Overexpressed Cyclin D1 and CDK4 proteins are responsible for the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor in breast cancer that can be reversed by PI3K/mTOR inhibitors. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Ross, K.N.; Balk, S.P. Androgens induce prostate cancer cell proliferation through mammalian target of rapamycin activation and post-transcriptional increases in cyclin D proteins. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7783–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recchia, A.G.; Musti, A.M.; Lanzino, M.; Panno, M.L.; Turano, E.; Zumpano, R.; Belfiore, A.; Ando, S.; Maggiolini, M. A cross-talk between the androgen receptor and the epidermal growth factor receptor leads to p38MAPK-dependent activation of mTOR and cyclinD1 expression in prostate and lung cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Flynn, D.C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, X.S.; Walker, V.; Liu, K.J.; Shi, X.; Jiang, B.H. G1 cell cycle progression and the expression of G1 cyclins are regulated by PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K1 signaling in human ovarian cancer cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, C281–C291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelloo, S.; Sanders, J.; Nevedomskaya, E.; de Jong, J.; Peters, D.; van Leenders, G.J.; Jenster, G.; Bergman, A.M.; Zwart, W. mTOR pathway activation is a favorable prognostic factor in human prostate adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32916–32924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, P.C.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Gupta, R.; Dreicer, R.; Klein, E.A.; Garcia, J.A. Association of mTOR Pathway Markers and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Intermediate-/High-risk Prostate Cancer: Long-Term Analysis. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2019, 17, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerusalem, G.; Rorive, A.; Collignon, J. Use of mTOR inhibitors in the treatment of breast cancer: An evaluation of factors that influence patient outcomes. Breast Cancer 2014, 6, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Battelli, C.; Cho, D.C. mTOR inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma. Therapy 2011, 8, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, H.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Luo, T.; Jiang, Y. Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlind, M.P.; Hsieh, A.C. PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling in prostate cancer progression and androgen deprivation therapy resistance. Asian J. Androl. 2014, 16, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Netto, G.J.; Rudek, M.A.; Halabi, S.; Wood, D.P.; Creel, P.A.; Mundy, K.; Davis, S.L.; Wang, T.; Albadine, R.; et al. A pharmacodynamic study of rapamycin in men with intermediate- to high-risk localized prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 3057–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Kong, X.; Liu, T.; Zhou, L.; Wu, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Yao, S.; Ding, Y.; et al. Metastasis-associated protein 1, modulated by miR-30c, promotes endometrial cancer progression through AKT/mTOR/4E-BP1 pathway. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 154, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, G.; Deabel, R.A.; Puaar, A.; Devarakonda, L.S.; Parupathi, P.; Zhang, J.; Waxner, N.; Yang, C.; Kumar, A.; Levenson, A.S. Molecular Efficacy of Gnetin C as Dual-Targeted Therapy for Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2300479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campanelli, G.; Francois, E.; Parupathi, P.; Devarakonda, L.S.; Yang, C.; Kumar, A.; Levenson, A.S. The Therapeutic Efficacy and Mechanism of Action of Gnetin C, a Natural Compound from the Melinjo Plant, in a Preclinical Mouse Model of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071344
Campanelli G, Francois E, Parupathi P, Devarakonda LS, Yang C, Kumar A, Levenson AS. The Therapeutic Efficacy and Mechanism of Action of Gnetin C, a Natural Compound from the Melinjo Plant, in a Preclinical Mouse Model of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(7):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071344
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampanelli, Gisella, Ekniel Francois, Prashanth Parupathi, Lakshmi Sirisha Devarakonda, Ching Yang, Avinash Kumar, and Anait S. Levenson. 2024. "The Therapeutic Efficacy and Mechanism of Action of Gnetin C, a Natural Compound from the Melinjo Plant, in a Preclinical Mouse Model of Advanced Prostate Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 7: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071344
APA StyleCampanelli, G., Francois, E., Parupathi, P., Devarakonda, L. S., Yang, C., Kumar, A., & Levenson, A. S. (2024). The Therapeutic Efficacy and Mechanism of Action of Gnetin C, a Natural Compound from the Melinjo Plant, in a Preclinical Mouse Model of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 16(7), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071344









