Current Treatment Options for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Focus on Cell-Based Immunotherapy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Demographics
1.2. Staging
1.3. Risk Factors
1.4. Molecular Pathology
1.5. RCC Immunogenicity
1.6. RCC Tumour Microenvironment (TME)
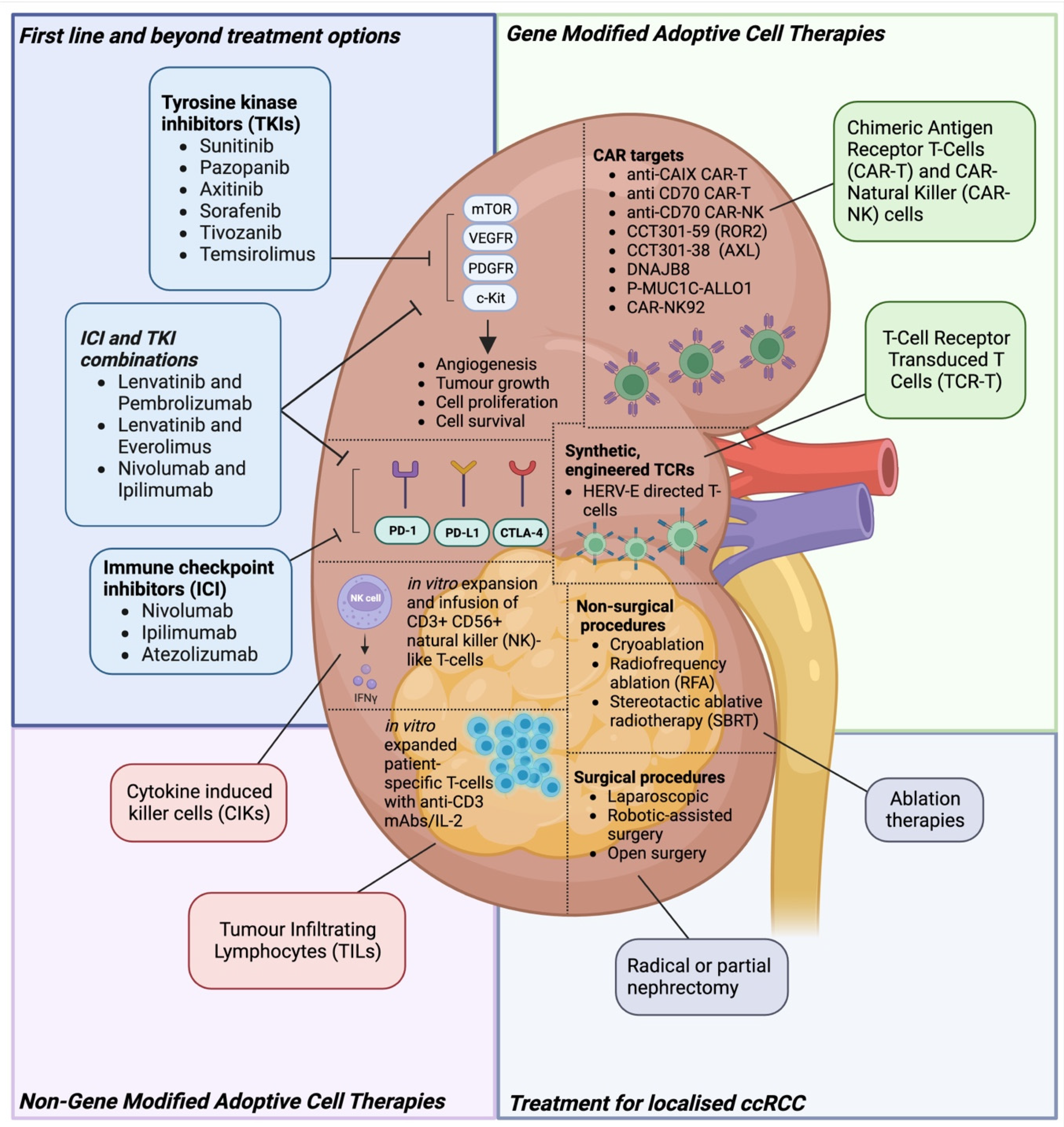
2. Drug Treatments
2.1. Treatment for Localised ccRCC
2.2. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI)-Based Treatment for mRCC in the First Line
2.3. TKI-Based Treatment for mRCC beyond 1st Line
2.4. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICI) for mRCC in the 1st Line and beyond
2.5. ICI and TKI Combinations for mRCC in the 1st Line and beyond
3. Non-Gene-Modified Cell Therapies
3.1. Cytokine Induced Killer Cells (CIKs)
3.1.1. Biology and Background
3.1.2. CIKs for mRCC
3.1.3. Combinatorial Approaches: CIKs + Dendritic Cells (DCs-CIKs)
3.1.4. Combinatorial Approaches: CIKs +/ Dendritic Cells +/ TKI +/ ICIs
3.1.5. Future Directions for CIK Therapy
3.2. Tumour Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs)
3.2.1. Biology and Background
3.2.2. TILs for mRCC
3.2.3. Future Directions for TIL Therapy for mRCC
4. Gene-Modified Adoptive Cell Therapies
4.1. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cells (CAR-Ts) and NK Cells (CAR-NKs)
4.1.1. CAR-T Biology, Background, Targets
4.1.2. Carboxy-Anhydrase-IX (CAIX) Biology
4.1.3. CAIX-Directed CAR-T Therapy
4.1.4. Allogeneic Approaches to CAIX-Directed CAR Therapy, including NK Cells
4.1.5. CD70 Biology
4.1.6. CD70-Directed CAR-T Therapy
4.1.7. Allogeneic Approaches to CD70-Directed CAR Therapy, including NK Cells
4.1.8. AXL & ROR2 Biology
4.1.9. AXL, ROR2-Directed CAR-T Therapy
4.1.10. DNAJB8 Biology
4.1.11. DNAJB8-Directed CAR-T Therapy
4.1.12. P-MUC1C-ALLO1
4.1.13. C-Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition Factor (c-met)
4.1.14. Epidermal Growth Factor (EGFR) Specific CAR-NK92
4.2. T-Cell Receptor Transduced T-Cells (TCR-Ts)
4.2.1. TCR-T Biology, Background, Targets
4.2.2. HERV-E-Directed TCR-T Therapy
5. Future Perspective of Cell Therapy against RCC
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Cancer Incidence Statistics. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/kidney-cancer/incidence (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Cancer of the Kidney and Renal Pelvis—Cancer Stat Facts. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/kidrp.html (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Motzer, R.J.; Bander, N.H.; Nanus, D.M. Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, H.; Amin, M.B.; Berney, D.M.; Compérat, E.M.; Gill, A.J.; Hartmann, A.; Menon, S.; Raspollini, M.R.; Rubin, M.A.; Srigley, J.R.; et al. The 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs—Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahunt, B.; Eble, J.N.; Samaratunga, H.; Thunders, M.; Yaxley, J.W.; Egevad, L. Staging of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Current Progress and Potential Advances. Pathology 2021, 53, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitanio, U.; Bensalah, K.; Bex, A.; Boorjian, S.A.; Bray, F.; Coleman, J.; Gore, J.L.; Sun, M.; Wood, C.; Russo, P. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, T.; Kadomoto, S.; Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A. Epidemiology and Prevention of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonasch, E.; Walker, C.L.; Rathmell, W.K. Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Ontogeny and Mechanisms of Lethality. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarelli, G.; Loizzo, D.; Franzin, R.; Battaglia, S.; Ferro, M.; Cantiello, F.; Castellano, G.; Bettocchi, C.; Ditonno, P.; Battaglia, M. Metabolomic Insights into Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Biomarker Discovery in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Yoshizato, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Maekawa, S.; Okuno, Y.; Kamura, T.; Shimamura, T.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Nagae, G.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Integrated Molecular Analysis of Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.M.; Rathmell, W.K.; de Cubas, A.A. Immunogenicity in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Shifting Focus to Alternative Sources of Tumour-Specific Antigens. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.C.; Beckermann, K.E.; Bortone, D.S.; Cubas, A.A.D.; Bixby, L.M.; Lee, S.J.; Panda, A.; Ganesan, S.; Bhanot, G.; Wallen, E.M.; et al. Endogenous Retroviral Signatures Predict Immunotherapy Response in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 128, 4804–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyerer, V.; Strissel, P.L.; Stöhr, C.; Eckstein, M.; Wach, S.; Taubert, H.; Brandl, L.; Geppert, C.I.; Wullich, B.; Cynis, H.; et al. Endogenous Retroviral–K Envelope Is a Novel Tumor Antigen and Prognostic Indicator of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 657187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricketts, C.J.; De Cubas, A.A.; Fan, H.; Smith, C.C.; Lang, M.; Reznik, E.; Bowlby, R.; Gibb, E.A.; Akbani, R.; Beroukhim, R.; et al. The Cancer Genome Atlas Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 313–326.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, D.A.; Street, K.; Burke, K.P.; Cookmeyer, D.L.; Denize, T.; Pedersen, C.B.; Gohil, S.H.; Schindler, N.; Pomerance, L.; Hirsch, L.; et al. Progressive Immune Dysfunction with Advancing Disease Stage in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 632–648.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Lu, J.; Liu, W.-R.; Anwaier, A.; Wu, Y.; Tian, X.; Su, J.-Q.; Qu, Y.-Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Heterogeneity in Tertiary Lymphoid Structures Predicts Distinct Prognosis and Immune Microenvironment Characterizations of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komohara, Y.; Hasita, H.; Ohnishi, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Suzu, S.; Eto, M.; Takeya, M. Macrophage Infiltration and Its Prognostic Relevance in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungberg, B.; Albiges, L.; Abu-Ghanem, Y.; Bedke, J.; Capitanio, U.; Dabestani, S.; Fernández-Pello, S.; Giles, R.H.; Hofmann, F.; Hora, M.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2022 Update. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, A.J.; Chetner, M.P.; Rourke, K.; Gleave, M.E.; Signaevsky, M.; Palmer, B.; Kuan, J.; Brock, G.B.; Tanguay, S. Guidelines for the Surveillance of Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma Based on the Patterns of Relapse after Nephrectomy. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonasch, E.; Gao, J.; Rathmell, W.K. Renal Cell Carcinoma. BMJ 2014, 349, g4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Tomczak, P.; Park, S.H.; Venugopal, B.; Ferguson, T.; Chang, Y.-H.; Hajek, J.; Symeonides, S.N.; Lee, J.L.; Sarwar, N.; et al. Adjuvant Pembrolizumab after Nephrectomy in Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Russo, P.; Grünwald, V.; Tomita, Y.; Zurawski, B.; Parikh, O.; Buti, S.; Barthélémy, P.; Goh, J.C.; Ye, D.; et al. Adjuvant Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Placebo for Localised Renal Cell Carcinoma after Nephrectomy (CheckMate 914): A Double-Blind, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Uzzo, R.; Karam, J.A.; Master, V.A.; Donskov, F.; Suarez, C.; Albiges, L.; Rini, B.; Tomita, Y.; Kann, A.G.; et al. Adjuvant Atezolizumab versus Placebo for Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma at Increased Risk of Recurrence Following Resection (IMmotion010): A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaf, M.; Kim, S.E.; Harshman, L.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Master, V.A.; Signoretti, S.; Cole, S.; Moon, H.; Adra, N.; Singer, E.A.; et al. LBA67 Phase III Randomized Study Comparing Perioperative Nivolumab (Nivo) versus Observation in Patients (Pts) with Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) Undergoing Nephrectomy (PROSPER, ECOG-ACRIN EA8143), a National Clinical Trials Network Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1432–S1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, G.; Fisher, R.I.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Sznol, M.; Parkinson, D.R.; Louie, A.C. Results of Treatment of 255 Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Who Received High-Dose Recombinant Interleukin-2 Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; Michaelson, M.D.; Bukowski, R.M.; Oudard, S.; Negrier, S.; Szczylik, C.; Pili, R.; Bjarnason, G.A.; et al. Overall Survival and Updated Results for Sunitinib Compared with Interferon Alfa in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3584–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, C.N.; Davis, I.D.; Mardiak, J.; Szczylik, C.; Lee, E.; Wagstaff, J.; Barrios, C.H.; Salman, P.; Gladkov, O.A.; Kavina, A.; et al. Pazopanib in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Results of a Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, R.C.; Farrell, A.T.; Saber, H.; Tang, S.; Williams, G.; Jee, J.M.; Liang, C.; Booth, B.; Chidambaram, N.; Morse, D.; et al. Sorafenib for the Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7271–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudier, B.; Szczylik, C.; Hutson, T.E.; Demkow, T.; Staehler, M.; Rolland, F.; Negrier, S.; Laferriere, N.; Scheuring, U.J.; Cella, D.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of First-Line Treatment with Sorafenib Versus Interferon Alfa-2a in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudier, B.; Eisen, T.; Stadler, W.M.; Szczylik, C.; Oudard, S.; Siebels, M.; Negrier, S.; Chevreau, C.; Solska, E.; Desai, A.A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Clear-Cell Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudier, B.; Pluzanska, A.; Koralewski, P.; Ravaud, A.; Bracarda, S.; Szczylik, C.; Chevreau, C.; Filipek, M.; Melichar, B.; Bajetta, E.; et al. Bevacizumab plus Interferon Alfa-2a for Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Randomised, Double-Blind Phase III Trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudes, G.; Carducci, M.; Tomczak, P.; Dutcher, J.; Figlin, R.; Kapoor, A.; Staroslawska, E.; Sosman, J.; McDermott, D.; Bodrogi, I.; et al. Temsirolimus, Interferon Alfa, or Both for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2271–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Nosov, D.; Eisen, T.; Bondarenko, I.; Lesovoy, V.; Lipatov, O.; Tomczak, P.; Lyulko, O.; Alyasova, A.; Harza, M.; et al. Tivozanib Versus Sorafenib as Initial Targeted Therapy for Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Results from a Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Hessel, C.; Halabi, S.; Sanford, B.; Michaelson, M.D.; Hahn, O.; Walsh, M.; Olencki, T.; Picus, J.; Small, E.J.; et al. Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib as Initial Therapy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma of Intermediate or Poor Risk (Alliance A031203 CABOSUN Randomised Trial): Progression-Free Survival by Independent Review and Overall Survival Update. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 94, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Escudier, B.; Tomczak, P.; Kaprin, A.; Szczylik, C.; Hutson, T.E.; Michaelson, M.D.; Gorbunova, V.A.; Gore, M.E.; Rusakov, I.G.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Axitinib versus Sorafenib in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (AXIS): A Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; Oudard, S.; Hutson, T.E.; Porta, C.; Bracarda, S.; Grünwald, V.; Thompson, J.A.; Figlin, R.A.; Hollaender, N.; et al. Efficacy of Everolimus in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Phase III Trial. Lancet 2008, 372, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Glen, H.; Michaelson, M.D.; Molina, A.; Eisen, T.; Jassem, J.; Zolnierek, J.; Maroto, J.P.; Mellado, B.; et al. Lenvatinib, Everolimus, and the Combination in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Randomised, Phase 2, Open-Label, Multicentre Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Escudier, B.; Powles, T.; Tannir, N.M.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Rini, B.I.; Hammers, H.J.; Donskov, F.; Roth, B.J.; Peltola, K.; et al. Cabozantinib versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (METEOR): Final Results from a Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; Tykodi, S.S.; Sosman, J.A.; Procopio, G.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Arén Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiges, L.; Tannir, N.M.; Burotto, M.; McDermott, D.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Porta, C.; Powles, T.; Donskov, F.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib for First-Line Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Extended 4-Year Follow-up of the Phase III CheckMate 214 Trial. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e001079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.; Alekseev, B.; Rha, S.-Y.; Porta, C.; Eto, M.; Powles, T.; Grünwald, V.; Hutson, T.E.; Kopyltsov, E.; Méndez-Vidal, M.J.; et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Eto, M.; Motzer, R.; De Giorgi, U.; Buchler, T.; Basappa, N.S.; Méndez-Vidal, M.J.; Tjulandin, S.; Hoon Park, S.; Melichar, B.; et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab versus Sunitinib as First-Line Treatment of Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (CLEAR): Extended Follow-up from the Phase 3, Randomised, Open-Label Study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Powles, T.; Burotto, M.; Escudier, B.; Bourlon, M.T.; Shah, A.Y.; Suárez, C.; Hamzaj, A.; Porta, C.; Hocking, C.M.; et al. Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib in First-Line Treatment for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (CheckMate 9ER): Long-Term Follow-up Results from an Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Plimack, E.R.; Soulières, D.; Waddell, T.; Stus, V.; Gafanov, R.; Nosov, D.; Pouliot, F.; Melichar, B.; Vynnychenko, I.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib Monotherapy as First-Line Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (KEYNOTE-426): Extended Follow-up from a Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Powles, T.B.; Albiges, L.; Burotto, M.; Szczylik, C.; Zurawski, B.; Riuz, E.Y.; Maruzzo, M.; Zaizar, A.S.; Fein, L.E.; et al. LBA8 Phase III Study of Cabozantinib (C) in Combination with Nivolumab (N) and Ipilimumab (I) in Previously Untreated Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (aRCC) of IMDC Intermediate or Poor Risk (COSMIC-313). Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1430–S1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Powles, T.; Albiges, L.; Burotto, M.; Szczylik, C.; Zurawski, B.; Yanez Ruiz, E.; Maruzzo, M.; Suarez Zaizar, A.; Fein, L.E.; et al. Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Powles, T.; Atkins, M.B.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; Alekseev, B.Y.; Lee, J.-L.; Suarez, C.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; De Giorgi, U.; et al. Final Overall Survival and Molecular Analysis in IMmotion151, a Phase 3 Trial Comparing Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab vs. Sunitinib in Patients with Previously Untreated Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pievani, A.; Borleri, G.; Pende, D.; Moretta, L.; Rambaldi, A.; Golay, J.; Introna, M. Dual-Functional Capability of CD3+CD56+ CIK Cells, a T-Cell Subset That Acquires NK Function and Retains TCR-Mediated Specific Cytotoxicity. Blood 2011, 118, 3301–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Wolf, I.G.; Negrin, R.S.; Kiem, H.P.; Blume, K.G.; Weissman, I.L. Use of a SCID Mouse/Human Lymphoma Model to Evaluate Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells with Potent Antitumor Cell Activity. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyle, C.; Bangs, C.D.; Chang, P.; Kamel, O.; Mehta, B.; Negrin, R.S. Expansion of Philadelphia Chromosome–Negative CD3+CD56+ Cytotoxic Cells from Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients: In Vitro and In Vivo Efficacy in Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease Mice. Blood 1998, 92, 3318–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.G.H. Ten-Year Update of the International Registry on Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells in Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 9291–9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verneris, M.R.; Karami, M.; Baker, J.; Jayaswal, A.; Negrin, R.S. Role of NKG2D Signaling in the Cytotoxicity of Activated and Expanded CD8+ T Cells. Blood 2004, 103, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Qi, X.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Wei, S.; Hao, X.; Ren, X. Randomized Study of Autologous Cytokine-Induced Killer Cell Immunotherapy in Metastatic Renal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.-C.; Fan, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, K.-C.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Chen, M.-X.; et al. Autologous CIK Cell Immunotherapy in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma after Radical Nephrectomy. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 195691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Yang, T.; He, C.; Song, Y.; Gao, Q. Association of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Efficacy of Cytokine-Induced Killer Cell Immunotherapy in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients. J. Immunother. 2014, 37, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wei, J.; Liu, L.; Yin, Y.; Gu, Y.; Shu, Y. The Effects of Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells for the Treatment of Patients with Solid Tumors: A Clinical Retrospective Study. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Zhang, L.; Jin, L.; Ye, J.; Guan, Z.; Chen, R.; Guo, T. Immunotherapy with Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2010, 25, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Märten, A.; Ziske, C.; Schöttker, B.; Renoth, S.; Weineck, S.; Buttgereit, P.; Schakowski, F.; von Rücker, A.; Sauerbruch, T.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.G.H. Interactions Between Dendritic Cells and Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells Lead to an Activation of Both Populations. J. Immunother. 2001, 24, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Gao, X.; Pu, X.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, J. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Postoperative Tumor Lysate-Pulsed Dendritic Cells and Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells Immunotherapy in Patients with Localized and Locally Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Chin. Med. J. 2012, 125, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Yang, S.; Xie, T.; Huang, L.; Yue, D.; Xu, L.; Wang, L.; et al. Cytokine Induced Killer Cell-Based Immunotherapies in Patients with Different Stages of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2015, 362, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Tan, J.-M.; Wu, W.-Z.; Qiu, Y.-M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, T.-Z.; Sun, X.-H.; Zhuo, W.-L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.-P. Adjuvant Dendritic Cells Vaccine Combined with Cytokine-Induced-Killer Cell Therapy after Renal Cell Carcinoma Surgery. J. BUON Off. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2015, 20, 505–513. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.-J.; Pan, Q.-Z.; Ding, Y.; Zeng, J.; Dong, P.; Zhao, J.-J.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; He, J.; et al. The Efficacy and Safety of the Combination of Axitinib and Pembrolizumab-Activated Autologous DC-CIK Cell Immunotherapy for Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Phase 2 Study. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2021, 10, e1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiong, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, H.; Ning, K.; Peng, Y.; Yu, C.; Ding, Y.; Weng, D.; Xia, J.; et al. Neoadjuvant Combination of Pazopanib or Axitinib and Programmed Cell Death Protein-1-Activated Dendritic Cell-Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells Immunotherapy May Facilitate Surgery in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Li, T.; Song, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, B.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, Y.; Xu, B.; Guo, J.; Qin, P.; et al. High Complete Response Rate in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Receiving Autologous Cytokine-Induced Killer Cell Therapy Plus Anti-Programmed Death-1 Agent: A Single-Center Study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 779248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Sharma, A.; Weiher, H.; Schmid, M.; Kristiansen, G.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.G.H. Anti-CD40 Predominates over Anti-CTLA-4 to Provide Enhanced Antitumor Response of DC-CIK Cells in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 925633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Yang, H.; Wei, Y. Combined Induction with Anti-PD-1 and Anti-CTLA-4 Antibodies Provides Synergistic Antitumor Effects in DC-CIK Cells in Renal Carcinoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Dehno, M.N.; Li, Y.; Weiher, H.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.G.H. Increase in Efficacy of Checkpoint Inhibition by Cytokine-Induced-Killer Cells as a Combination Immunotherapy for Renal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeel, L.C.; Schmeel, F.C.; Coch, C.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.G.H. Cytokine-Induced Killer (CIK) Cells in Cancer Immunotherapy: Report of the International Registry on CIK Cells (IRCC). J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser, M.J.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Itzhaki, O.; Treves, A.J.; Zippel, D.B.; Levy, D.; Kubi, A.; Shoshani, N.; Zikich, D.; Ohayon, Y.; et al. Adoptive Transfer of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma: Intent-to-Treat Analysis and Efficacy after Failure to Prior Immunotherapies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4792–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Yang, J.C.; Sherry, R.M.; Kammula, U.S.; Hughes, M.S.; Phan, G.Q.; Citrin, D.E.; Restifo, N.P.; Robbins, P.F.; Wunderlich, J.R.; et al. Durable Complete Responses in Heavily Pretreated Patients with Metastatic Melanoma Using T-Cell Transfer Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4550–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figlin, R.A.; Thompson, J.A.; Bukowski, R.M.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Novick, A.C.; Lange, P.; Steinberg, G.D.; Belldegrun, A.S. Multicenter, Randomized, Phase III Trial of CD8+ Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Combination with Recombinant Interleukin-2 in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markel, G.; Cohen-Sinai, T.; Besser, M.J.; Oved, K.; Itzhaki, O.; Seidman, R.; Fridman, E.; Treves, A.J.; Keisari, Y.; Dotan, Z.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of Adoptive Cell Therapy for Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andersen, R.; Westergaard, M.C.W.; Kjeldsen, J.W.; Müller, A.; Pedersen, N.W.; Hadrup, S.R.; Met, Ö.; Seliger, B.; Kromann-Andersen, B.; Hasselager, T.; et al. T-Cell Responses in the Microenvironment of Primary Renal Cell Carcinoma—Implications for Adoptive Cell Therapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Theodoropoulos, J.; Huuhtanen, J.; Bhattacharya, D.; Järvinen, P.; Tornberg, S.; Nísen, H.; Mirtti, T.; Uski, I.; Kumari, A.; et al. Immunologic Characterization and T Cell Receptor Repertoires of Expanded Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. Commun. 2023, 3, 1260–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldan, V.; Griffiths, R.; Hawkins, R.E.; Gilham, D.E. Efficient and Reproducible Generation of Tumour-Infiltrating Lymphocytes for Renal Cell Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillebroer, A.B.; Mulders, P.F.A.; Boerman, O.C.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Oosterwijk, E. Carbonic Anhydrase IX in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Implications for Prognosis, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, C.H.J.; Klaver, Y.; Gratama, J.W.; Sleijfer, S.; Debets, R. Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (mRCC) with CAIX CAR-Engineered T-Cells–a Completed Study Overview. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, C.H.; Sleijfer, S.; van Steenbergen, S.; van Elzakker, P.; van Krimpen, B.; Groot, C.; Vulto, A.; den Bakker, M.; Oosterwijk, E.; Debets, R.; et al. Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma with CAIX CAR-Engineered T Cells: Clinical Evaluation and Management of On-Target Toxicity. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, E.R.; Chang, D.-K.; Sun, J.; Sui, J.; Freeman, G.J.; Signoretti, S.; Zhu, Q.; Marasco, W.A. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Secreting Anti-PD-L1 Antibodies More Effectively Regress Renal Cell Carcinoma in a Humanized Mouse Model. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34341–34355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Buck, A.; Grimaud, M.; Culhane, A.C.; Kodangattil, S.; Razimbaud, C.; Bonal, D.M.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Zhu, Z.; Wei, K.; et al. Anti-CAIX BBζ CAR4/8 T Cells Exhibit Superior Efficacy in a ccRCC Mouse Model. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 24, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Buck, A.; Grimaud, M.; Kodangattil, S.; Razimbaud, C.; Fayed, A.; Chang, M.; Culhane, A.; Braun, D.A.; Choueiri, T.K.; et al. Abstract 62: Development of Dual-Targeted Fine-Tuned Immune Restoring (DFIR) CAR T Cell Therapy for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC). Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, J.; Lu, M.; Liu, H.; Miao, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, G.; Zheng, J.; Pei, D.; Zhang, Q. CAIX-Specific CAR-T Cells and Sunitinib Show Synergistic Effects Against Metastatic Renal Cancer Models. J. Immunother. 2020, 43, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.S.; Zea, A.H.; Rini, B.I.; Ireland, J.L.; Elson, P.; Cohen, P.; Golshayan, A.; Rayman, P.A.; Wood, L.; Garcia, J.; et al. Sunitinib Mediates Reversal of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Accumulation in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2148–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finke, J.H.; Rini, B.; Ireland, J.; Rayman, P.; Richmond, A.; Golshayan, A.; Wood, L.; Elson, P.; Garcia, J.; Dreicer, R.; et al. Sunitinib Reverses Type-1 Immune Suppression and Decreases T-Regulatory Cells in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6674–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.H.; Maki, G.; Klingemann, H.G. Characterization of a Human Cell Line (NK-92) with Phenotypical and Functional Characteristics of Activated Natural Killer Cells. Leukemia 1994, 8, 652–658. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, S.; Meagher, R.; Swearingen, M.; Myint, H.; Rich, E.; Martinson, J.; Klingemann, H. Infusion of the Allogeneic Cell Line NK-92 in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Cancer or Melanoma: A Phase I Trial. Cytotherapy 2008, 10, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.; Ding, J.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Lu, M.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Q.; et al. Bortezomib Improves Adoptive Carbonic Anhydrase IX-specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor-modified NK92 Cell Therapy in Mouse Models of Human Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3714–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, A.; Yokoyama, H.; Smith, A.; Berg, M.; Childs, R. Bortezomib Treatment and Regulatory T-Cell Depletion Enhance the Antitumor Effects of Adoptively Infused NK Cells. Blood 2009, 113, 6120–6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denoeud, J.; Moser, M. Role of CD27/CD70 Pathway of Activation in Immunity and Tolerance. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, J.; Hendriks, J.; Xiao, Y. CD27 and CD70 in T Cell and B Cell Activation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2005, 17, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.-L.; Gordon, K.A.; Toki, B.E.; Yamane, A.K.; Hering, M.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Petroziello, J.M.; Ryan, M.C.; Smith, L.; Simon, R.; et al. Lymphocyte Activation Antigen CD70 Expressed by Renal Cell Carcinoma Is a Potential Therapeutic Target for Anti-CD70 Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tran, B.; Haanen, J.; Hurwitz, M.; Sacher, A.; Agarwal, N.; Tannir, N.; Budde, E.; Harrison, S.; Klobuch, S.; et al. 558 CTX130 Allogeneic CRISPR-Cas9–Engineered Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells in Patients with Advanced Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Results from the Phase 1 COBALT-RCC Study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srour, S.; Kotecha, R.; Curti, B.; Chahoud, J.; Drakaki, A.; Tang, L.; Goyal, L.; Prashad, S.; Szenes, V.; Norwood, K.; et al. Abstract CT011: A Phase 1 Multicenter Study (TRAVERSE) Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of ALLO-316 Following Conditioning Regimen in Pts with Advanced or Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC). Cancer Res. 2023, 83, CT011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Chang, J.-W.; Krueger, J.; Lahr, W.S.; Pomeroy, E.; Walsh, M.; Khamhoung, A.; Johnson, J.; Franco, C.; Swiech, L.; et al. Engineering CD70-Directed CAR-NK Cells for the Treatment of Hematological and Solid Malignancies. Blood 2021, 138, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, B.; Choi, E.; Picarella, D.; Moore, F.; Nunez, A.; Moreno, H.; Marques, M.; Barandiaran, A.; Walsh, M.; Pradhan, K.; et al. Abstract 2898: CAT-248, an Allogeneic CD70-Directed CAR-NK Cell Therapy Effectively Controls CD70-Positive Tumor Xenografts. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, R.; Ma, B.; Li, X.; Yen, H.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Krasnoperov, V.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, X.; Bove, A.M.; et al. Axl Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Siemann, D.W. Gas6/Axl Signaling Pathway in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Cancers 2020, 12, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, T.M.; Brannon, A.R.; Gordan, J.D.; Mikels, A.J.; Mitchell, C.; Chen, S.; Espinosa, I.; van de Rijn, M.; Pruthi, R.; Wallen, E.; et al. Ror2, a Developmentally Regulated Kinase, Promotes Tumor Growth Potential in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2513–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanghai PerHum Therapeutics Co., Ltd. A Dose Escalation and Dose Expansion Trial to Assess the Safety, Tolerability and Anti-Tumor Activity of Autologous T Cell Modified Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) CCT 301-38 or CCT 301-59 in Patients with Recurrent or Refractory Stage IV Renal Cell Carcinoma. 2021. Available online: www.Clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Watanabe, Y.; Tsukahara, T.; Murata, K.; Hamada, S.; Kubo, T.; Kanaseki, T.; Hirohashi, Y.; Emori, M.; Teramoto, A.; Nakatsugawa, M.; et al. Development of CAR-T Cells Specifically Targeting Cancer Stem Cell Antigen DNAJB8 against Solid Tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poseida Therapeutics, Inc. A Phase 1 Dose Escalation and Expanded Cohort Study of P-MUC1C-ALLO1 in Adult Subjects with Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. 2023. Available online: www.Clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Oh, D.; Henry, J.; Baranda, J.C.; Dumbrava, E.E.; Cohen, E.; Eskew, J.D.; Belani, R.; McCaigue, J.; Namini, H.; Martin, C.; et al. 46P Development of an Allogeneic CAR-T Targeting MUC1-C (MUC1, Cell Surface Associated, C-Terminal) for Epithelial Derived Tumors. Immuno-Oncol. Technol. 2022, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowska, A.; Zhang, Y.; Fritz, J.; Wang, S.; Codde, R.; Argus, E.; Ibitokou, S.; Richardson, V.; Jain, S.; Richter, M.; et al. 120 P-MUC1C-ALLO1: An Allogeneic Car-t for Multiple Solid Tumor Indications. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, A1–A559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, J.; Adachi, K.; Sakoda, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Goto, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Matsuyama, H.; Tamada, K. Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Human Anti-c-Met CAR-T Cells against Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma in an Orthotopic Model. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Tian, K.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Fu, Q.; Chai, D.; Li, H.; Zheng, J. Synergistic Effects of Cabozantinib and EGFR-Specific CAR-NK-92 Cells in Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, e6915912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baulu, E.; Gardet, C.; Chuvin, N.; Depil, S. TCR-Engineered T Cell Therapy in Solid Tumors: State of the Art and Perspectives. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L. The Emerging World of TCR-T Cell Trials Against Cancer: A Systematic Review. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819831068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafer, P.; Kelly, L.M.; Hoyos, V. Cancer Therapy With TCR-Engineered T Cells: Current Strategies, Challenges, and Prospects. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 835762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaventura, P.; Alcazer, V.; Mutez, V.; Tonon, L.; Martin, J.; Chuvin, N.; Michel, E.; Boulos, R.E.; Estornes, Y.; Valladeau-Guilemond, J.; et al. Identification of Shared Tumor Epitopes from Endogenous Retroviruses Inducing High-Avidity Cytotoxic T Cells for Cancer Immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabj3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Harashima, N.; Kajigaya, S.; Yokoyama, H.; Cherkasova, E.; McCoy, J.P.; Hanada, K.; Mena, O.; Kurlander, R.; Abdul, T.; et al. Regression of Human Kidney Cancer Following Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Is Associated with Recognition of an HERV-E Antigen by T Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkasova, E.; Scrivani, C.; Doh, S.; Weisman, Q.; Takahashi, Y.; Harashima, N.; Yokoyama, H.; Srinivasan, R.; Linehan, W.M.; Lerman, M.I.; et al. Detection of an Immunogenic HERV-E Envelope with Selective Expression in Clear Cell Kidney Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2177–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, R.; Barisic, S.; Scurti, G.M.; Cherkasova, E.; Chen, L.; Wood, K.; Highfill, S.L.; Wells, B.; Aue, G.; Shalabi, R. Phase I Results of Human Endogenous Retrovirus Type-E (HERV-E) TCR Transduced T-Cells in Patients (Pts) with Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (mccRCC); American Society of Clinical Oncology: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, M.; Clubb, J.D.; Chen, Y.Y. Engineering CAR-T Cells for Next-Generation Cancer Therapy. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.M.; Engel, N.W.; Uslu, U.; Wellhausen, N.; June, C.H. Next-Generation CAR T Cell Therapies. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juillerat, A.; Tkach, D.; Busser, B.W.; Temburni, S.; Valton, J.; Duclert, A.; Poirot, L.; Depil, S.; Duchateau, P. Modulation of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Surface Expression by a Small Molecule Switch. BMC Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinzing, B.; Krenciute, G. Hypoxia-Inducible CAR Expression: An Answer to the on-Target/off-Tumor Dilemma? Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panowski, S.H.; Srinivasan, S.; Tan, N.; Tacheva-Grigorova, S.K.; Smith, B.; Mak, Y.S.L.; Ning, H.; Villanueva, J.; Wijewarnasuriya, D.; Lang, S.; et al. Preclinical Development and Evaluation of Allogeneic CAR T Cells Targeting CD70 for the Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 2610–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Bai, J.; Gu, J.; Xie, L.; Wu, W. Neoantigen-Targeted TCR-Engineered T Cell Immunotherapy: Current Advances and Challenges. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Tao, H.; Karachi, A.; Long, Y.; Hou, A.Y.; Na, M.; Dyson, K.A.; Grippin, A.J.; Deleyrolle, L.P.; Zhang, W.; et al. CXCR1- or CXCR2-Modified CAR T Cells Co-Opt IL-8 for Maximal Antitumor Efficacy in Solid Tumors. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Sun, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Dong, Y.; Du, G.; Luo, H.; Shi, B.; Jiang, H.; et al. CXCR4-Modified CAR-T Cells Suppresses MDSCs Recruitment via STAT3/NF-κB/SDF-1α Axis to Enhance Efficacy against Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2023, 31, 3193–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-C.S.; Lo, A.; Scholler, J.; Sun, J.; Majumdar, R.S.; Kapoor, V.; Antzis, M.; Cotner, C.E.; Johnson, L.A.; Durham, A.C.; et al. Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein in Tumor Stroma with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Can Inhibit Tumor Growth and Augment Host Immunity without Severe Toxicity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegram, H.J.; Lee, J.C.; Hayman, E.G.; Imperato, G.H.; Tedder, T.F.; Sadelain, M.; Brentjens, R.J. Tumor-Targeted T Cells Modified to Secrete IL-12 Eradicate Systemic Tumors without Need for Prior Conditioning. Blood 2012, 119, 4133–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, N.; Shi, J.; Qin, L.; Chen, A.; Tang, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; He, B.; et al. IL-7 and CCL19-Secreting CAR-T Cell Therapy for Tumors with Positive Glypican-3 or Mesothelin. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Ren, J.; Luo, Y.; Keith, B.; Young, R.M.; Scholler, J.; Zhao, Y.; June, C.H. Augmentation of Antitumor Immunity by Human and Mouse CAR T Cells Secreting IL-18. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenciute, G.; Prinzing, B.L.; Yi, Z.; Wu, M.-F.; Liu, H.; Dotti, G.; Balyasnikova, I.V.; Gottschalk, S. Transgenic Expression of IL15 Improves Antiglioma Activity of IL13Rα2-CAR T Cells but Results in Antigen Loss Variants. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloss, C.C.; Lee, J.; Zhang, A.; Chen, F.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Lacey, S.F.; Maus, M.V.; Fraietta, J.A.; Zhao, Y.; June, C.H. Dominant-Negative TGF-β Receptor Enhances PSMA-Targeted Human CAR T Cell Proliferation and Augments Prostate Cancer Eradication. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2018, 26, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, T.L.; Li, P.J.; Blaeschke, F.; Nies, J.F.; Apathy, R.; Mowery, C.; Yu, R.; Nguyen, M.L.T.; Lee, Y.; Truong, A.; et al. Pooled Knockin Targeting for Genome Engineering of Cellular Immunotherapies. Cell 2020, 181, 728–744.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kverneland, A.H.; Pedersen, M.; Westergaard, M.C.W.; Nielsen, M.; Borch, T.H.; Olsen, L.R.; Aasbjerg, G.; Santegoets, S.J.; van der Burg, S.H.; Milne, K.; et al. Adoptive Cell Therapy in Combination with Checkpoint Inhibitors in Ovarian Cancer. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 2092–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, L.J.; Schumann, K.; Roybal, K.T.; Gate, R.E.; Ye, C.J.; Lim, W.A.; Marson, A. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated PD-1 Disruption Enhances Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Human Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Li, M.; Ye, J.; Zhao, S.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Z. Mesothelin CAR-T Cells Secreting PD-L1 Blocking scFv for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment. Cancer Genet. 2022, 268–269, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klichinsky, M.; Ruella, M.; Shestova, O.; Lu, X.M.; Best, A.; Zeeman, M.; Schmierer, M.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; Anderson, N.R.; Petty, N.E.; et al. Human Chimeric Antigen Receptor Macrophages for Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical Trial | Primary Endpoint | Treatment Description | Condition | Sponsor | Phase | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDA approved combination therapies | ||||||
| FDA approved combination of Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in April 2018 | ||||||
| NCT02231749 (CheckMate 214) | ORR PFS OS | (PD-1 inhibitor+ CTLA-4 inhibitor vs. TKI) Nivolumab + Ipilimumab vs. Sunitinib monotherapy | First-line treatment of intermediate-/poor-risk advanced RCC | Bristol-Myers Squibb | 3 | Active, not recruiting |
| FDA approved combination of Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib in April 2019 | ||||||
| NCT02853331 (Keynote 426) | PFS OS | (PD-1 inhibitor + TKI vs. TKI monotherapy) Pembrolizumab + Axitinib vs. Sunitinib monotherapy | First-line treatment of advanced ccRCC | Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC | 3 | Active, not recruiting |
| FDA approved combination of Avelumab plus Axitinib in May 2019 | ||||||
| NCT02684006 (Javelin 101) | PFS OS | (PD-1 inhibitor + TKI vs. TKI monotherapy) Avelumab + Axitinib and of Sunitinib monotherapy | First-line treatment in patients with advanced RCC | Pfizer | 3 | Active, not recruiting |
| FDA approved combination of Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib Jan 2021 | ||||||
| NCT03141177 (CheckMate 9ER) | PFS | (PD-1 inhibitor +TKI vs. TKI) Nivolumab + Cabozantinib vs. Sunitinib | First-line treatment of advanced or mRCC | Bristol-Myers Squibb | 3 | Active, not recruiting |
| FDA approved combination of Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab in August 2021 | ||||||
| NCT02811861 (CLEAR) | PFS | (TKI+ mTOR inhibitor or PD-1 inhibitor vs. TKI monotherapy) Lenvatinib + Everolimus or Pembrolizumab vs. Sunitinib monotherapy | First-line treatment of advanced RCC | Eisai Inc. | 3 | Active, not recruiting |
| Other TKI and ICI combination therapies | ||||||
| NCT04338269 CONTACT-03 | PFS OS | (ICI+TKI) vs. TKI monotherapy Atezolizumab + Cabozantinib vs. Cabozantinib monotherapy | Advanced RCC | Hoffmann-La Roche | 3 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT03138512 (CheckMate 914) | DFS | (PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy vs. PD-1 inhibtor+ CTLA-4 inhibitor vs. placebo) Nivolumab, Nivolumab + Ipilimumab and Placebo | Localized kidney cancer with removal of part of a kidney | Bristol-Myers Squibb | 3 | Completed |
| NCT03288532 (RAMPART) | DFS OS | (PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy vs. PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy+ CTLA-4 inhibitor) Durvalumab monotherapy or Durvalumab + Tremelimumab | Resected primary RCC at high or intermediate risk of relapse | University College London | 3 | Recruiting |
| NCT05239728 | DFS | (HIF-2α inhibitor+PD-1 inhibitor vs. placebo+PD-1 inhibitor) Belzutifan + Pembrolizumab vs. placebo +Pembrolizumab | Adjuvant treatment of ccRCC post nephrectomy | Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC | 3 | Recruiting |
| NCT04394975 (JS001-036-III-RCC) | PFS | (PD-1 inhibitor +TKI vs. TKI monotherapy) Toripalimab + with Axitinib vs. Sunitinib monotherapy | First-line therapy for advanced RCC | Shanghai Junshi Bioscience Co., Ltd. | 3 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT03937219 (COSMIC-313) | PFS | (TKI+PD-1 inhibitor+ CTLA-4 inhibitor vs. PD-1 inhibitor+ CTLA-4 inhibitor +matched placebo) Cabozantinib + Nivolumab + Ipilimumab vs. Nivolumab and Ipilimumab + matched placebo | Intermediate- or poor-risk advanced or mRCC | Exelixis | 3 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT04736706 NCT05899049 or MK-6482-012 (China extension study) (LIFESPARK-012) | PFS OS | (PD-1 inhibitor +HIF-2α inhibitor+ TKI or PD-1 inhibitor/CTLA-4 inhibitor +TKI vs. PD-1 inhibitor+TKI) Pembrolizumab + Belzutifan + Lenvatinib or Pembrolizumab/Quavonlimab + Lenvatinib vs. Pembrolizumab + Lenvatinib | First-line treatment in participants with advanced ccRCC | Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC | 3 | Recruiting |
| NCT03873402 CA209-8Y8 | PFS ORR | (PD-1 inhibitor + CTLA-4 inhibitor vs. PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy) Nivolumab + Ipilimumab vs. Nivolumab monotherapy | Untreated kidney cancer that has spread | Bristol-Myers Squibb | 3b | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT03793166 (PDIGREE) | OS | (PD-1 inhibitor+ CTLA-4 inhibitor followed by PD-1 inhibitor or PD-1 inhibitor + TKI) Nivolumab and Ipilimumab Followed by Nivolumab or Nivolumab with Cabozantinib | Advanced kidney cancer | National Cancer Institute (NCI) | 3 | Recruiting |
| NCT05219318 | DP | PD-1/PD-L1 ICI + VEGFR-TKI | First-line ICI for mRCC | University Hospital, Bordeaux | 3 | Recruiting |
| NCT03260894 (KEYNOTE-679/ECHO-302) | ORR | (PD-1 inhibitor + IDO1 selective inhibitor vs. TKI) Pembrolizumab+Epacadostat vs. Sunitinib or Pazopanib | First-line treatment for mRCC | Incyte Corporation | 3 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT05678673 | PFS ORR | (TKI+ PD-1 inhibitor vs. TKI) XL092 + Nivolumab vs. Sunitinib | Unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic nccRCC who have not received prior systemic anticancer therapy | Exelixis | 3 | Recruiting |
| NCT05043090 | PFS | Savolitinib + Durvalumab vs. Sunitinib | MET-driven unresectable and locally advanced or metastatic PRCC | AstraZeneca | 3 | Recruiting |
| NCT01668784 (CheckMate 025) | OS | (PD-1 inhibitor vs. mTOR inhibitor) Nivolumab vs. Everolimus | Advanced or mRCC after failure of one or two regimens of anti-angiogenic therapy | Bristol-Myers Squibb | 3 | Completed |
| NCT01865747 (METEOR) | PFS | (TKI vs. mTOR inhibitor) Cabozantinib (XL184) vs. Everolimus (Afinitor) | mRCC after prior VEGF-targeted therapy | Exelixis | 3 | Completed |
| NCT01030783 | PFS | (TKI vs. TKI) Tivozanib vs. Sorafenib | First targeted therapy in recurrent or mRCC | AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 3 | Completed |
| NCT02420821 (IMmotion 151) | DP PFS OS | (ICI+VEGF inhibitor vs. TKI) Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab vs. Sunitinib | Untreated advanced RCC | Hoffmann-La Roche | 3 | Completed |
| CA045002 NCT03729245 (PIVOT 09) | ORR OS | (IL-2 pro-drug + PD-1 inhibitor vs. TKI monotherapy) Bempegaldesleukin+ Nivolumab vs. (Sunitinib or Cabozantinib) | Previously untreated advanced RCC | Nektar Therapeutics | 3 | Terminated |
| NCT04523272 (TQB2450-III-07) | PFS | (PD-1 inhibitor+ TKI vs. TKI) TQB2450 + Anlotinib vs. Sunitinib | Advanced RCC | Chia Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. | 3 | Unknown |
| Clinical Trial | Primary Endpoint | Description | Condition | Company | Phase | Target Antigen | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAR T therapy targeting CD70 | |||||||
| NCT04696731 | DLT | Allogeneic ALLO-316 | Advanced or metastatic ccRCC | Allogene Therapeutics | 1 | CD70 | Recruiting |
| NCT04438083 | ORR DLT | CTX130 | Relapsed or refractory RCC | CRISPR Therapeutics AG | 1 | CD70 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT06010875 NCT05468190 | Safety evaluation and tolerability | CD70-targeting CAR-T cells | Advanced/metastatic solid tumours | Chongqing Precision Biotech Co., Ltd. | 1 | CD70 | Recruiting |
| NCT05420545 NCT05420519 | Safety evaluation and tolerability | CAR-T | Advanced/solid tumours including RCC | Chongqing Precision Biotech Co., Ltd. | 1 | CD70 | Recruiting |
| NCT05518253 | Safety evaluation and tolerability | CAR-T | Advanced/solid tumours including RCC | Weijia Fang, MD | 1 | CD70 | Recruiting |
| NCT05795595 | DLT ORR | Allogeneic CTX131 | Relapsed or refractory solid tumours including ccRCC | CRISPR Therapeutics AG | 1/2 | CD70 | Recruiting |
| CAR NK cell therapy | |||||||
| NCT05703854 | Safety evaluation and optimal cell dose | CAR.70-engineered IL15-transduced Cord Blood-derived NK Cells in Conjunction with Lymphodepleting Chemotherapy | Advanced RCC | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | 1/2 | CD70 | Recruiting |
| CAR PBL therapy | |||||||
| NCT02830724 | Safety evaluation RR | PBL Transduced with a CD70-Binding CAR | RCC | National Cancer Institute (NCI) | 1/2 | CD70 | Recruiting |
| CAR T therapy with different target antigen | |||||||
| NCT03393936 | Safety evaluation ORR | Autologous CCT301-38 or CCT 301-59 T cells | Relapsed and refractory stage IV mRCC | Shanghai PerHum Therapeutics Co., Ltd. | 1/2 | ROR2 | Unknown |
| NCT01218867 | Safety evaluation | Anti-VEGFR2 gene modified tumour white blood cells | mRCC | National Cancer Institute (NCI) | 1/2 | VEGFR2 | Terminated |
| NCT03638206 | Safety evaluation | Autologous CAR-T/TCR-T cell immunotherapy | Different malignancies including RCC | Shenzhen BinDeBio Ltd. | 1/2 | c-MET | Unknown |
| NCT04969354 | Safety evaluation ORR CR PR SD PD | CAR T cells targeting CAIX | Advanced RCC | The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University | 1 | CAIX | Recruiting |
| NCT05239143 | MTD RP2D DLT ORR | P-MUC1C-ALLO1 allogeneic CAR-T cells | Advanced or metastatic solid tumours | Poseida Therapeutics, Inc. | 1 | Mucin 1 cell surface-associated C-terminal | Recruiting |
| NCT05672459 | ORR | Autologous HLA-G- Targeted CAR-T Cells IVS-3001 | Previously treated advanced HLA-G-positive solid tumours | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | 1/2 | Human leukocyte antigen (HLA-G) | Recruiting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, A.; Mehra, V.; Chhetri, J.; Ali, S.; Tran, M.; Roddie, C. Current Treatment Options for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Focus on Cell-Based Immunotherapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061209
Hwang A, Mehra V, Chhetri J, Ali S, Tran M, Roddie C. Current Treatment Options for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Focus on Cell-Based Immunotherapy. Cancers. 2024; 16(6):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061209
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Angela, Vedika Mehra, Jyoti Chhetri, Samira Ali, Maxine Tran, and Claire Roddie. 2024. "Current Treatment Options for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Focus on Cell-Based Immunotherapy" Cancers 16, no. 6: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061209
APA StyleHwang, A., Mehra, V., Chhetri, J., Ali, S., Tran, M., & Roddie, C. (2024). Current Treatment Options for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Focus on Cell-Based Immunotherapy. Cancers, 16(6), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061209






