Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Biomarker Predictors of Oral Mucositis Severity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Submitted to Combined Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategies
2.3. Study Selection and Data Collection Process
2.4. Study Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
3. Results
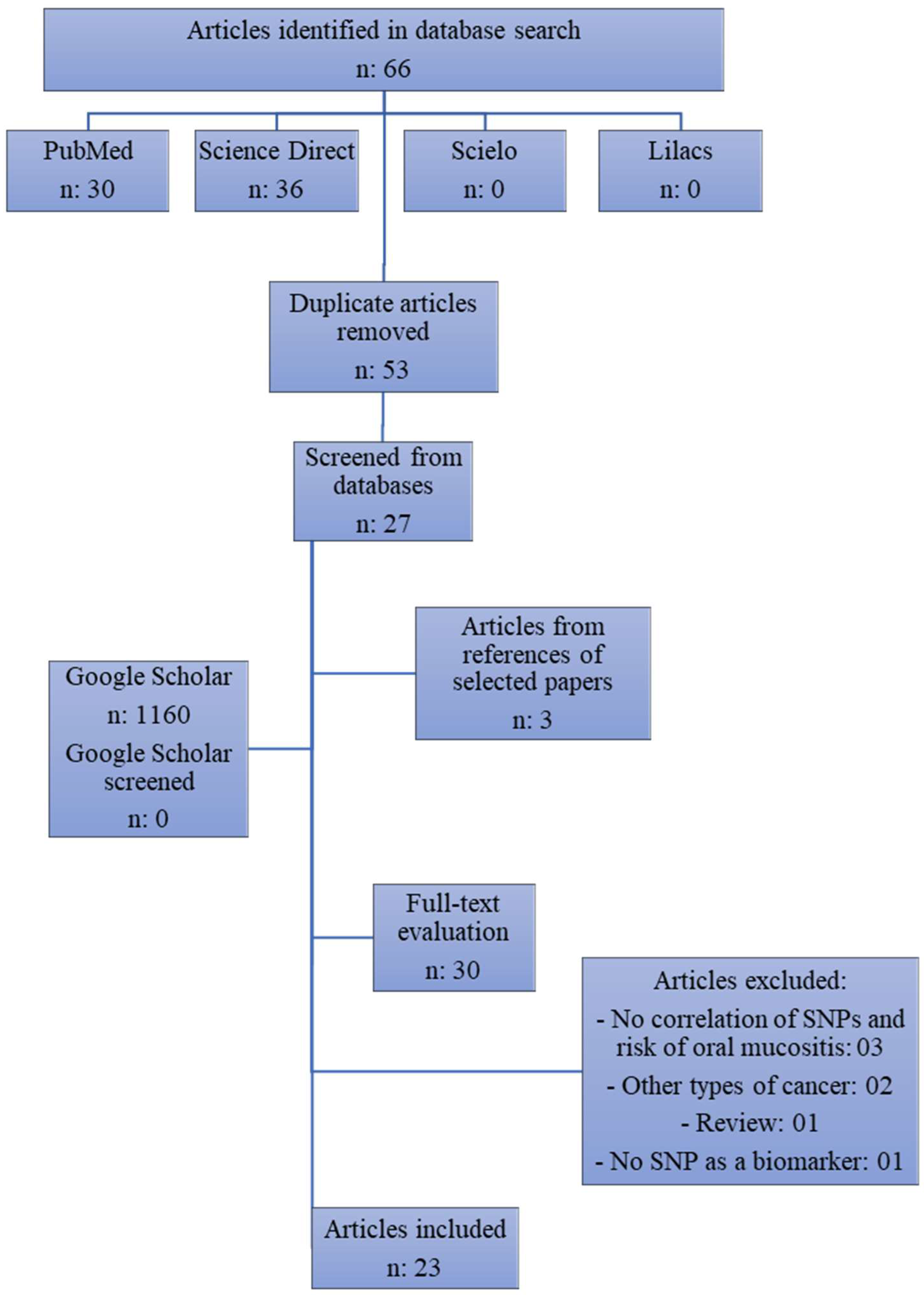
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
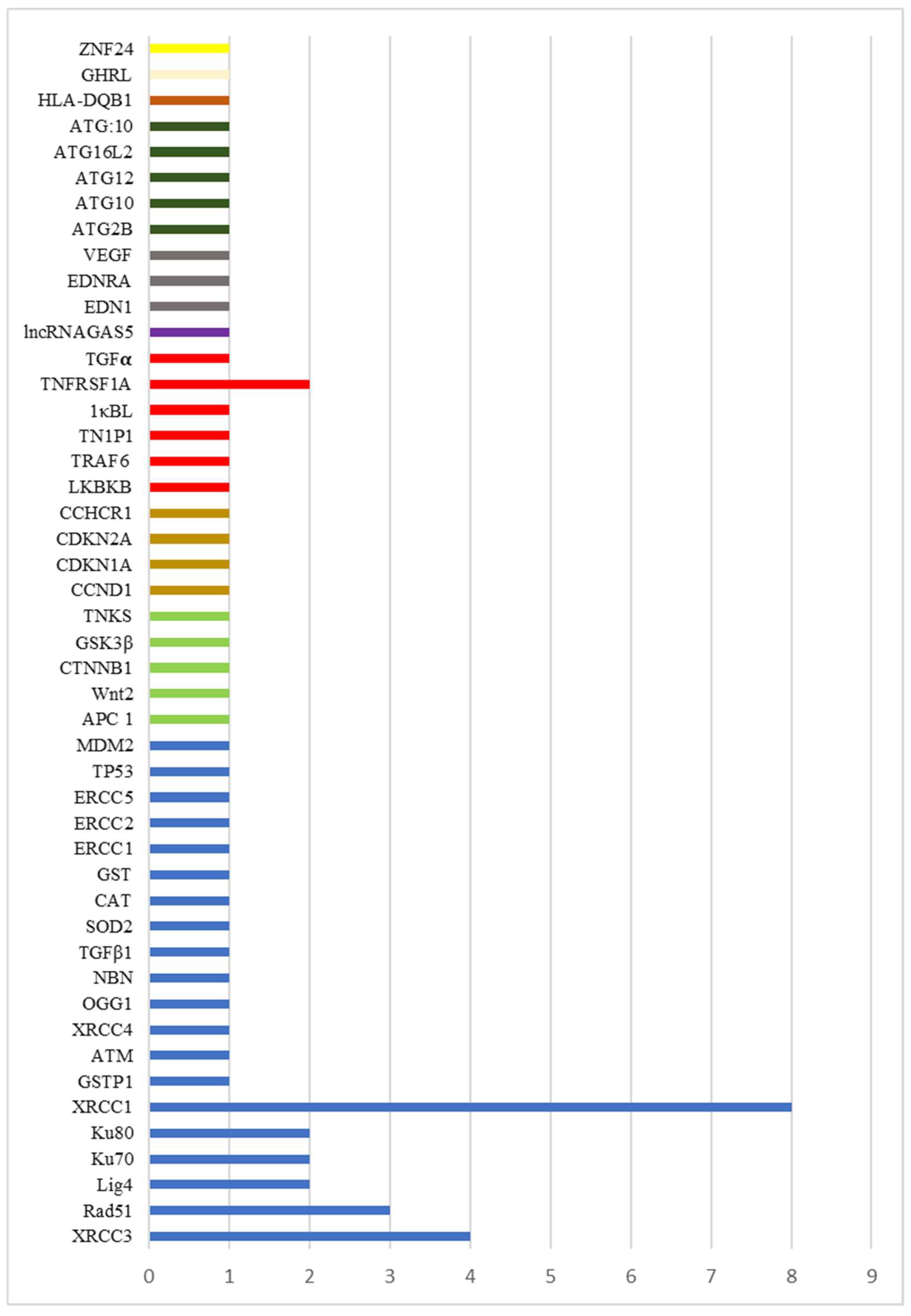
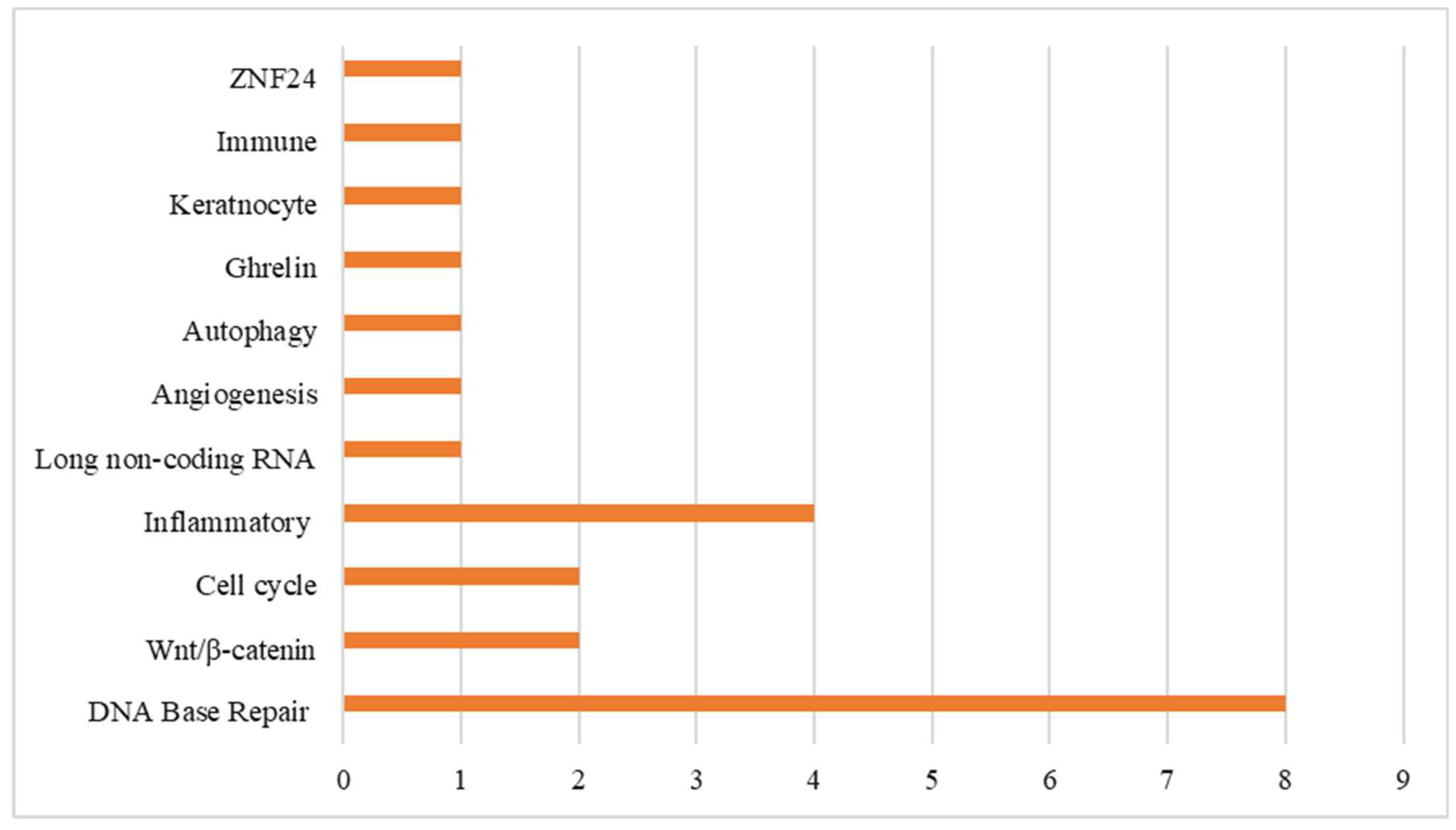
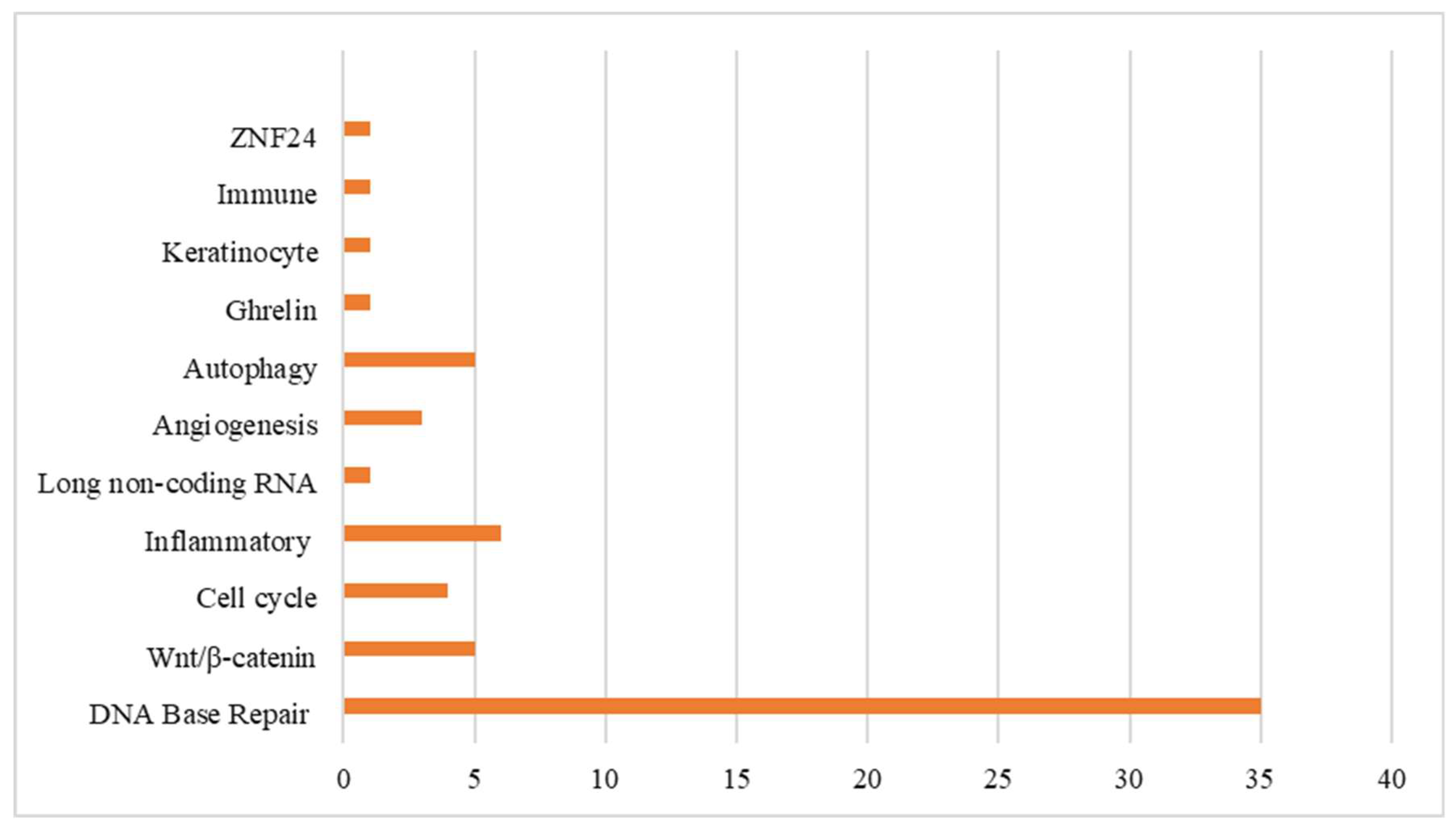
3.3. Synthesis of Results
3.3.1. Mucositis SNP-Associated Non-Proinflammatory Mediator-Regulated Genes
3.3.2. Mucositis SNP-Associated Proinflammatory Mediator-Regulated Genes
3.4. Study Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mody, M.; Rocco, J.; Yom, S.; Haddad, R.; Saba, N. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, G.; Fisher, S.; Hong, W.; Hilman, R.; Spaulding, M.; Laramore, G. Induction chemotherapy plus radiation compared with surgery plus radiation in patients with advanced laryngeal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pignon, J.; Maillard, E.; Bourhis, J. Meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer (MACH-NC): An update on 93 randomised trials and 17,346 patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 92, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elting, L.S.; Cooksley, C.D.; Chambers, M.S.; Garden, A.S. Risk, outcomes, and costs of radiation-induced oral mucositis among patients with head-and-neck malignancies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.A.; Ridner, S.; Wells, N.; Dietrich, M. Quality of life research in head and neck cancer: A review of the current state of the science. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2007, 62, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonis, S.T. The pathobiology of mucositis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Sonis, S.T. Mucositis. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normando, A.G.C.; Rocha, C.L.; de Toledo, I.P.; de Souza Figueiredo, P.T.; dos Reis, P.E.D.; De Luca Canto, G.; Guerra, E.N.S. Biomarkers in the assessment of oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Support. Care Cancer 2017, 25, 2969–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruglyak, L.; Nickerson, D.A. Variation is the spice of life. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulow, C.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Aloamidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Br. Med. J. 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchini, C.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N. Assessing the quality of studies in meta-analyses: Advantages and limitations of the Newcastle Ottawa Scale. World J. Meta-Anal. 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werbrouck, J.; De Ruyck, K.; Duprez, F.; Veldeman, L.; Claes, K.; Van Eijkeren, M.; Boterberg, T.; Willems, P.; Vral, A.; De Neve, W.; et al. Acute Normal Tissue Reactions in Head-and-Neck Cancer Patients Treated With IMRT: Influence of Dose and Association with Genetic Polymorphisms in DNA DSB Repair Genes. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 73, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratesi, N.; Mangoni, M.; Mancini, I.; Paiar, F.; Simi, L.; Livi, L.; Cassani, S.; Buglione, M.; Grisanti, S.; Almici, C.; et al. Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms in the XRCC1 and RAD51 genes and clinical radiosensitivity in head and neck câncer. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 99, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; You, Y.; Lin, C.; Zheng, M.; Hong, C.; Chen, J.; Li, D.; Au, W.W.; Chen, Z. XRCC1 codon 399Gln polymorphism is associated with radiotherapy-induced acute dermatitis and mucositis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, G.H.; Manjunath, V.B.; Mumbrekar, K.D.; Negi, H.; Fernandes, D.J.; Sharan, K.; Banerjee, S.; Sadashiva, S.R.B. Polymorphisms in Radio-Responsive Genes and Its Association with Acute Toxicity among Head and Neck Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Yin, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Yuan, H.; Yang, G.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms of Wnt/β-catenin pathway genes are associated with the efficacy and toxicities of radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 82528–82537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Yin, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Yuan, H.; Yang, G.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms of long non-coding RNA GAS5 predict platinum-based concurrent chemoradiotherapy response in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 62286–62297. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Li, G.; Hua, L.; Chen, S.; Huang, H. Association between XRCC1 single-nucleotide polymorphism and acute radiation reaction in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma A cohort study. Medicine 2017, 96, e8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Huang, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, L.; Gong, X.; Huang, M.; Jiang, C.; Liao, Y.; Huang, L.; Yang, G.; et al. The impacts of single nucleotide polymorphisms in genes of cell cycle and NF-κB pathways on the efficacy and acute toxicities of radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25334–25344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Z.; Niu, X.; Chen, Y.; Ou, X.; Zhao, G.; Liu, Q.; Tu, W.; Hu, C.; Kong, L.; Liu, Y. Predictive single nucleotide polymorphism markers for acute oral mucositis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with radiotherapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 63026–63037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.L.; Liu, R.; Huang, L.H.; Zou, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.J.; Meng, X.G.; Yang, J.K.; Li, H.; et al. Impact of polymorphisms in angiogenesis-related genes on clinical outcomes of radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Gibby, C.C.; Melkonian, S.C.; Wang, J.; Yu, R.K.; Shelburne, S.A.; Lu, C.; Gunn, G.B.; Chambers, M.S.; Hanna, E.Y.; Yeung, S.C.J. Identifying novel genes and biological processes relevant to the development of cancer therapy-induced mucositis: An informative gene network analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchiellini, D.; Etienne-Grimaldi, M.C.; Bensadoun, R.J.; Benezery, K.; Dassonville, O.; Poissonnet, G.; Llorca, L.; Ebran, N.; Formento, P.; Château, Y.; et al. Candidate apoptotic and DNA repair gene approach confirms involvement of ERCC1, ERCC5, TP53 and MDM2 in radiation-induced toxicity in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2017, 67, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.S.; Gandhi, A.K.; Rastogi, M.; Khurana, R.; Hadi, R.; Sahni, K.; Mishra, S.P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bhatt, M.L.B.; Parmar, D. Evaluation of XRCC1 Gene Polymorphism as a Biomarker in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemoradiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 101, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, A.; Homa-Mlak, I.; Mlak, R.; Gołębiowski, P.; Mazurek, M.; Ciesielka, M.; Małecka-Massalska, T. Polymorphism of regulatory region of GHRL gene (-2531C>T) as a promising predictive factor for radiotherapy-induced oral mucositis in patients with head neck cancer. Head Neck 2018, 40, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, A.; Powrózek, T.; Homa-Mlak, I.; Mlak, R.; Ciesielka, M.; Gołębiowski, P.; Małecka-Massalska, T. Polymorphism of Promoter Region of TNFRSF1A Gene (−610 T > G) as a Novel Predictive Factor for Radiotherapy Induced Oral Mucositis in HNC Patients. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2018, 24, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, G.; Aguín, S.; Cruz, R.; Barros, F.; Giráldez, J.; Bernárdez, B.; López-López, R.; Carracedo, Á.n.g.e.l.; Lamas, M. Association of GSTP1 and ERCC1 polymorphisms with toxicity in locally advanced head and neck cancer platinum-based chemoradiotherapy treatment. Head Neck 2019, 41, 2704–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Potentially functional variants of autophagy-related genes are associated with the efficacy and toxicity of radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Mathew, D.; Ghoshal, S.; Pal, A. XRCC1 (rs25487) polymorphism is associated with severe oral mucositis and poor treatment response after radiotherapy for oropharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Cancer 2019, 3, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlak, R.; Powrózek, T.; Brzozowska, A.; Homa-Mlak, I.; Mazurek, M.; Gołębiowski, P.; Korzeb, D.; Rahnama-Hezavah, M.; Małecka-Massalska, T. Polymorphism of TNFRSF1 A may act as a predictor of severe radiation-induced oral mucositis and a prognosis factor in patients with head and neck cancer. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020, 130, 283–291.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlak, R.; Powrózek, T.; Brzozowska, A.; Homa-Mlak, I.; Mazurek, M.; Gołębiowski, P.; Sobieszek, G.; Małecka-Massalska, T. The relationship between TNF-α gene promoter polymorphism (−1211 T>C), the plasma concentration of TNF-α, and risk of oral mucositis and shortening of overall survival in patients subjected to intensity-modulated radiation therapy due to head and neck cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.W.; Wang, T.M.; Zhang, J.B.; Li, X.Z.; He, Y.Q.; Xiao, R.; Xue, W.Q.; Zheng, X.H.; Zhang, P.F.; Zhang, S.D.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies genetic susceptibility loci and pathways of radiation-induced acute oral mucositis. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raturi, V.; Hojo, H.; Bhatt, M.L.B.; Suhel, M.; Wu, C.T.; Bei, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Okumura, M.; Zhang, H.; Parmar, D.; et al. Prospective evaluation of XRCC-1 Arg194Trp polymorphism as bio-predictor for clinical outcome in locally advanced laryngeal cancer undergoing cisplatin-based chemoradiation. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, C. Associations of GWAS-Indentified risk loci with progression, efficacy and toxicity of radiotherapy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with radiotherapy. Pharmacogenomics Pers. Med. 2021, 14, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, D.E.; Keefe, D.M.S. New frontiers in mucositis. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2012, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinausero, M.; Aprile, G.; Ermacora, P.; Basile, D.; Vitale, M.; Fanotto, V.; Parisi, G.; Calvetti, L.; Sonis, S. New frontiers in the pathobiology and treatment of cancer regimen-related mucosal injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossi, P.; Bergamini, C.; Miceli, R.; Cova, A.; Orlandi, E.; Resteghini, C.; Locati, L.; Alfieri, S.; Imbimbo, M.; Granata, R.; et al. Salivary Cytokine Levels and Oral Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Treated with Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalliolias, G.D.; Ivashkiv, L.B. TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhou, P. DNA damage response signaling pathways and targets for radiotherapy sensitization in cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Country | Year | Primary Sites | Possible Treatments | Number of Patients (n) | Dose (Gy) | Genes Accessed by the Studies | Sample | Type of Study | Main Conclusions | Mucositis as One of the Primary End Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Werbrouk et al. [13] | Belgium | 2009 | Head and Neck | RT/RT + CT/Surgery + RT | 88 | 66–70 | DNA DSB repair genes XRCC3, Rad51, Lig4, Ku70, Ku80 | Blood | Cohort | - Association was found between the presence of the XRCC3c.562-14 A>G (rs1415120657) polymorphism and the risk of severe acute mucositis (adjusted OR = 1.96; p = 0.178). - One variant allele of Rad51c.-3392 was associated with a small increase in the risk for severe mucositis after RT (adjusted OR = 1.21; p = 0.728). - A negative but not significant association was found for Ku70c.-1310 SNP. | Yes |
| Patresi et al. [14] | Italy | 2011 | Head and Neck | RT/RT + CT | 101 | 54–70 | XRCC1 c.1196A>G, XRCC3 c.722C>T, RAD51 (c.-3429G>C, c.-3392G>T), and GSTP1 c.313A>G. | Blood | Cohort | - Risk of mucositis was increased in patients with XRCC1-399Gln allele genotypes both in the chemoradiotherapy (p = 0.035, HR = 1.72, CI = 1.03–2.86) and radiotherapy alone (p = 0.049, HR = 2.50, CI = 0.97–6.47) groups. | Yes |
| Li H et al. [15] | China | 2013 | Nasopharynx | RT/RT + CT | 114 | 66–70 | XRCC1 (194Arg/Trp and 399Arg/Gln) | Blood | Cohort | - XRCC1 399Arg/Gln was associated with higher incidence of grade 3 oral mucosa toxicity, OR = 2.11 (95% CI: 0.951–4.66), p = 0.065. | Yes |
| Venkatesh et al. [16] | India | 2014 | Head and Neck | RT + CT | 183 | 60–70 | ATM, XRCC1, XRCC3, XRCC4, Ku70, Ku80, LIG4, OGG1, NBN, RAD51, TGFb1, SOD2, CAT, GST | Blood | Cohort | - There was no association of NBN (rs1805794) polymorphism in univariate and multivariate analysis with severe mucositis. | Yes |
| Yu J et al. [17] | China | 2016 | Nasopharynx | RT/RT + CT | 188 | 66–70 | 7 SNPS Wnt/β-Catenin | Blood | Cohort | - APC rs454886 polymorphism (minor A allele) was associated with acute grade 3–4 radiation-induced oral mucositis in additive (p = 0.045) and recessive models (p = 0.038) after adjustment for BMI. | Yes |
| Guo Z et al. [18] | China | 2017 | Nasopharynx | RT + CT | 505 | 68–72 | lncRNA GAS5 | Blood | Cohort | - Slight relationship was found in the discovery stage between severe oral mucositis and rs2067079, as well as rs6790 (p = 0.049). - Patients of rs2067079 TT genotype receiving DP for IC regimen (TT vs. CC, OR = 3.031, p = 0.047) or CCRT regimen (TT vs. CC, OR = 21.882, p = 0.043) were subjected to high risk of oral mucositis. | Yes |
| Chen H et al. [19] | China | 2017 | Nasopharynx | RT/RT + CT | 114 | 70–76 | Base repair XRCC1 Codon 399 SNP | Blood | Cohort | - The injury degree of acute radiation oral mucositis showed no significant difference (p = 0.449, 95% CI: 0.691–2.304). | Yes |
| Guo C et al. [20] | China | 2017 | Nasopharynx | RT/RT + CT | 154 | 66–70 | 3 SNPS Cell cycle/5 SNPS NF-κB | Blood | Cohort | - CCND1 rs9344 was related to grade 3–4 acute radiation-induced oral mucositis in recessive model among patients <51 years old. | Yes |
| Le Z et al. [21] | China | 2017 | Nasopharynx | RT/RT + CT | 24 | 66–70.4 | Genome-wide screening | Blood | Cohort | - The SNP rs11081899-A in ZN24 was significantly associated with an enhanced risk of severe mucositis (OR = 14.631, 95% CI = 2.61–105.46, p = 1.2 × 10−4). | |
| Ma W et al. [22] | China | 2017 | Nasopharynx | RT/RT + CT | 180 | 66–77 | Angiogenesis-related genes 3 SNPS EDN1/3 SNPS EDNRA/2 SNPS VEGF | Blood | Cohort | - GT genotype in EDN1 rs1800541 was significantly associated with an elevated risk of developing grade 3+ oral mucositis (p = 0.038). | Yes |
| Reyes-Gibbi C [23] | USA | 2017 | Head and Neck | RT/RT + CT/Surgery + RT | NI | NI | Informative gene network analysis | x | X | - SNP in RB1 (rs2227311, p-value = 0.034, OR = 0.67) showed a protective effect for oral mucositis. | Yes |
| Borchiellini et al. [24] | France | 2017 | Head and Neck | RT/RT + CT | 122 | 60–70 | ERCC1/ERCC2/XRCC1/M2M | Diagnostic biopsy | Cohort | - G allele of MDM2 309 (genotypes TG or GG) or the Thr allele of ERCC1 251 (genotypes Lys/Thr and Thr/Thr) were associated with a higher risk of acute G3-4 DMEX. | No |
| Nanda S et al. [25] | India | 2018 | Oral cavity, pharynx, larynx | RT + CT | 101 | 66–70 | Base repair XRCC1 Arg194Trp | Blood | Cohort | - Polymorphic variant had higher grade > 2 oral mucositis, 35.8% vs. 16.0% (OR: 2.91; 95% CI 1.13–7.46; p = 0.023). | Yes |
| Brzozowska et al. [26] | Poland | 2018 | Head and Neck | RT/RT + CT/Surgery + RT | 65 | 60–70 | GHRL | Blood | Cohort | - AA genotype was associated with 7-fold decrease in the risk of occurrence of intensified oral mucositis (grades 2 and 3) in the sixth week of RT. | Yes |
| Brzozowska et al. [27] | Poland | 2018 | Head and Neck | RT/RT + CT | 58 | 66–70 | TNFRSF1A | Blood | Cohort | - TT or GT genotype demonstrated higher risk of manifestation of grade 3 mucositis toxicity in 5th week of RT (p = 0.041; OR = 9.240; 95% CI: 1.101–77.581) compared to GG carriers. | Yes |
| Duran G et al. [28] | Spain | 2019 | Oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, unknown primary | RT + CT | 110 | 50–76 | ABCC1 | Blood | Cohort | - For rs1045642, patients with the variant T/T genotype showed higher acute mucositis than C/C or C/T genotype patients (47.1% vs. 24.1%; OR: 3.42; 95% CI: 1.04–11.21; p = 0.042 in a recessive model). | Yes |
| Yang Z et al. [29] | China | 2019 | Nasopharynx | RT/RT + CT | 468 | 66–70 | Autophagy genes (ATG) | Blood | Cohort | - ATG10 rs10514231 and ATG16L2 rs10898880 were significantly associated with the occurrence of grade 3–4 oral mucositis. | Yes |
| Gupta A et al. [30] | India | 2019 | Oropharynx | RT/RT + CT | 179 | 66 | XRCC1/XRCC3/XRCC4/XRCC6/ERCC4/Lig4/ATM | Blood | Cohort | - Homozygous AA genotype of XRCC1 (rs25487) and certain clinical characteristics are likely to develop severe acute mucositis (p = 0.024). | Yes |
| Mlak R et al. [31] | Poland | 2020 | Head and Neck | RT/RT + CT | 60 | 54–70 | (_135 T>C, rs767455) of TNFRSF1 A | Blood | Cohort | - SNP (_135 T>C) of the TNFRSF1 A gene may act as a predictor of OM occurrence in patients with HNC treated with IMRT. | Yes |
| Mlak R et al. [32] | Poland | 2020 | Head and Neck | RT/RT + CT | 62 | 66–70 | TNF⍺ rs1799964 (-1211 T>C) | Blood | Cohort | - CC genotype was related to over 7-fold (OR = 7.33, 95% CI 1.120–44.96, p = 0.031) and 23-fold (OR = 23.15, 95% CI 1.24– 432.14, p = 0.035) higher risk of 3rd-degree OM development after the 5th and 7th week of RTH, respectively. | Yes |
| Yang D et al. [33] | China | 2020 | Nasopharynx | RT/RT + CT | 1467 | 68–76 | Genome-wide association study | Blood | Cohort | - The SNP rs117157809 located in TNKS gene was associated with increased risk of oral mucositis (95% CI 2.10–6.57; p = 6.33 × 10−6). | Yes |
| Raturi V et al. [34] | Japan | 2020 | Larynx | RT + CT | 134 | 70 | XRCC1 Arg194Trp | Blood | Cohort | - XRCC-1 Arg194Trp polymorphism is significantly associated with oral mucositis (p = 0.01). | Yes |
| Quinghua L et al. [35] | China | 2021 | Head and Neck | RT/RT + CT | 500 | NI | Genome-wide association study | Blood | Cohort | - SNP rs1265081 in CCHCR1 gene (allele A vs. C: OR = 1.41, 95% CIs = 1.08–1.86, p = 0.012) and rs3135001 (allele T vs. allele C: OR = 0.53, 95% CIs = 0.35–0.79, p = 0.002) were significantly associated with the occurrence of grade 3–4 oral mucositis. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavalieri, R.; de Oliveira, H.F.; Louvain de Souza, T.; Kanashiro, M.M. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Biomarker Predictors of Oral Mucositis Severity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Submitted to Combined Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050949
Cavalieri R, de Oliveira HF, Louvain de Souza T, Kanashiro MM. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Biomarker Predictors of Oral Mucositis Severity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Submitted to Combined Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050949
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavalieri, Ronaldo, Harley Francisco de Oliveira, Thais Louvain de Souza, and Milton Masahiko Kanashiro. 2024. "Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Biomarker Predictors of Oral Mucositis Severity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Submitted to Combined Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review" Cancers 16, no. 5: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050949
APA StyleCavalieri, R., de Oliveira, H. F., Louvain de Souza, T., & Kanashiro, M. M. (2024). Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Biomarker Predictors of Oral Mucositis Severity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Submitted to Combined Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review. Cancers, 16(5), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050949





