Evaluation of the Prognostic Value of Pretherapeutic Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Predicting Soft Tissue Sarcoma Radiation Response: A Retrospective Study from a Large Institutional Sarcoma Imaging Database
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Acquisition Technique
2.3. Image Post-Processing and Analysis
Functional MRI Analysis
2.4. Radiotherapy
2.5. Histopathological Analysis
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Population
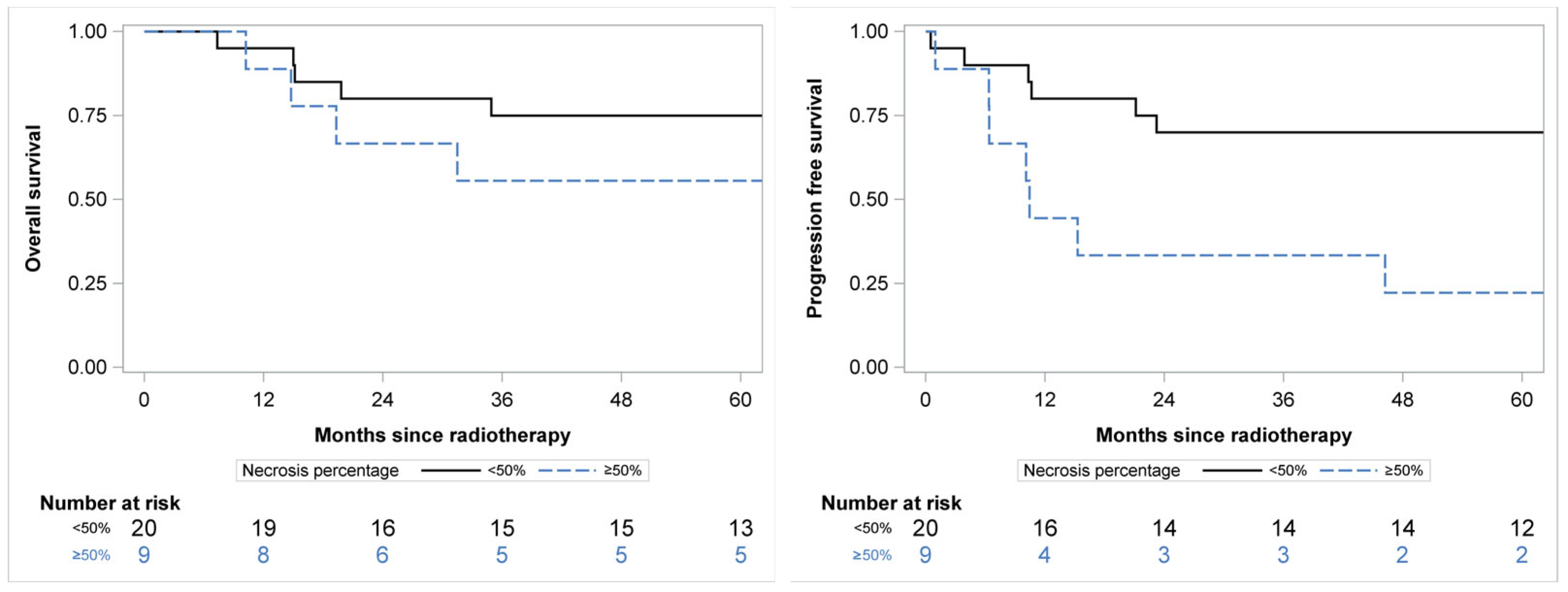
3.2. Clinical Outcome
3.3. DWI and Histopathological Analysis
3.4. DCE Perfusion and Histopathological Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.H.; Ro, J.Y. The 2020 WHO Classification of Tumors of Bone: An Updated Review. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2021, 28, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, B.; Davis, A.M.; Turcotte, R.; Bell, R.; Catton, C.; Chabot, P.; Wunder, J.; Kandel, R.; Goddard, K.; Sadura, A.; et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: A randomised trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 2235–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansu, J.; Groenewegen, J.; van Coevorden, F.; van Houdt, W.; van Akkooi, A.C.J.; van Boven, H.; van de Sande, M.; Verheij, M.; Haas, R.L. Time dependent dynamics of wound complications after preoperative radiotherapy in Extremity Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Absi, E.; Farrokhyar, F.; Sharma, R.; Whelan, K.; Corbett, T.; Patel, M.; Ghert, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of oncologic outcomes of pre- versus postoperative radiation in localized resectable soft-tissue sarcoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Eisenberg, B.L.; Kane, J.M.; Li, X.A.; Lucas, D.; Petersen, I.A.; DeLaney, T.F.; Freeman, C.R.; Finkelstein, S.E.; et al. Significant Reduction of Late Toxicities in Patients With Extremity Sarcoma Treated With Image-Guided Radiation Therapy to a Reduced Target Volume: Results of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group RTOG-0630 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, I.M.; Hornick, J.L.; Barysauskas, C.M.; Raut, C.P.; Patel, S.A.; Royce, T.J.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Baldini, E.H. Histologic Appearance After Preoperative Radiation Therapy for Soft Tissue Sarcoma: Assessment of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group Response Score. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvalot, S.; Wunder, J.; Gronchi, A.; Broto, J.M.; Turcotte, R.; Rastrelli, M.; Papai, Z.; Radaelli, S.; Lindner, L.H.; Shumelinsky, F.; et al. Complete pathological response to neoadjuvant treatment is associated with better survival outcomes in patients with soft tissue sarcoma: Results of a retrospective multicenter study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 2166–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canter, R.J.; Martinez, S.R.; Tamurian, R.M.; Wilton, M.; Li, C.S.; Ryu, J.; Mak, W.; Monsky, W.L.; Borys, D. Radiographic and histologic response to neoadjuvant radiotherapy in patients with soft tissue sarcoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 2578–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Grange, F.; Cassoni, A.M.; Seddon, B.M. Tumour volume changes following pre-operative radiotherapy in borderline resectable limb and trunk soft tissue sarcoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 40, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, Y.; Ngan, S.; Clark, J.C.; Akiyama, T.; Choong, P.F. The significance of size change of soft tissue sarcoma during preoperative radiotherapy. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 36, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delisca, G.O.; Alamanda, V.K.; Archer, K.R.; Song, Y.; Schwartz, H.S.; Holt, G.E. Tumor size increase following preoperative radiation of soft tissue sarcomas does not affect prognosis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messiou, C.; Bonvalot, S.; Gronchi, A.; Vanel, D.; Meyer, M.; Robinson, P.; Morosi, C.; Bloem, J.L.; Terrier, P.H.; Lazar, A.; et al. Evaluation of response after pre-operative radiotherapy in soft tissue sarcomas; the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group (EORTC-STBSG) and Imaging Group recommendations for radiological examination and reporting with an emphasis on Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 56, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielack, S.S.; Kempf-Bielack, B.; Delling, G.; Exner, G.U.; Flege, S.; Helmke, K.; Kotz, R.; Salzer-Kuntschik, M.; Werner, M.; Winkelmann, W.; et al. Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picci, P.; Bohling, T.; Bacci, G.; Ferrari, S.; Sangiorgi, L.; Mercuri, M.; Ruggieri, P.; Manfrini, M.; Ferraro, A.; Casadei, R.; et al. Chemotherapy-induced tumor necrosis as a prognostic factor in localized Ewing’s sarcoma of the extremities. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 15, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnapauff, D.; Zeile, M.; Niederhagen, M.B.; Fleige, B.; Tunn, P.U.; Hamm, B.; Dudeck, O. Diffusion-weighted echo-planar Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the assessment of tumor cellularity in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 29, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatos, T.; Ahlawat, S.; Montgomery, E.; Chalian, M.; Jacobs, M.A.; Fayad, L.M. Multiparametric Assessment of Treatment Response in High-Grade Soft-Tissue Sarcomas with Anatomic and Functional MR Imaging Sequences. Radiology 2016, 278, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kransdorf, M.J.; Murphey, M.D. Radiologic evaluation of soft-tissue masses: A current perspective. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsdottir, H.; Wejde, J.; Bauer, H.C. Pre-operative radiotherapy in soft tissue tumors. Assessment of response by static post-contrast MR imaging compared to histopathology. Acta Radiol. 2001, 42, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Erlemann, R.; Sciuk, J.; Bosse, A.; Ritter, J.; Kusnierz-Glaz, C.R.; Peters, P.E.; Wuisman, P. Response of osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma to preoperative chemotherapy: Assessment with dynamic and static MR imaging and skeletal scintigraphy. Radiology 1990, 175, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favinger, J.L.; Hippe, D.S.; Davidson, D.J.; Elojeimy, S.; Roth, E.S.; Lindberg, A.W.; Ha, A.S. Soft Tissue Sarcoma Response to Two Cycles of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Multireader Analysis of MRI Findings and Agreement with RECIST Criteria and Change in SUVmax. Acad. Radiol. 2018, 25, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudeck, O.; Zeile, M.; Pink, D.; Pech, M.; Tunn, P.U.; Reichardt, P.; Ludwig, W.D.; Hamm, B. Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging allows monitoring of anticancer treatment effects in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 27, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, B.D.; Hanna, S.L.; Fairclough, D.L.; Gronemeyer, S.A. Pediatric musculoskeletal tumors: Use of dynamic, contrast-enhanced MR imaging to monitor response to chemotherapy. Radiology 1992, 184, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsky, W.L.; Jin, B.; Molloy, C.; Canter, R.J.; Li, C.S.; Lin, T.C.; Borys, D.; Mack, W.; Kim, I.; Buonocore, M.H.; et al. Semi-automated volumetric quantification of tumor necrosis in soft tissue sarcoma using contrast-enhanced MRI. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 4951–4961. [Google Scholar]
- van Rijswijk, C.S.; Geirnaerdt, M.J.; Hogendoorn, P.C.; Peterse, J.L.; van Coevorden, F.; Taminiau, A.H.; Tollenaar, R.A.; Kroon, B.B.; Bloem, J.L. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging in monitoring response to isolated limb perfusion in high-grade soft tissue sarcoma: Initial results. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winfield, J.M.; Miah, A.B.; Strauss, D.; Thway, K.; Collins, D.J.; de Souza, N.M.; Leach, M.O.; Morgan, V.A.; Giles, S.L.; Moskovic, E.; et al. Utility of Multi-Parametric Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Characterization and Radiotherapy Response Assessment in Soft-Tissue Sarcomas and Correlation with Histopathology. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsdottir, H.; Karlsson, M.; Wejde, J.; Bauer, H.C. Diffusion-weighted MRI of soft tissue tumours. Eur. Radiol. 2004, 14, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonarelli, C.; Teixeira, P.A.; Hossu, G.; Meyer, J.B.; Chen, B.; Gay, F.; Blum, A. Impact of ROI Positioning and Lesion Morphology on Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Analysis for the Differentiation Between Benign and Malignant Nonfatty Soft-Tissue Lesions. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, W106–W113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwee, T.C.; Galban, C.J.; Tsien, C.; Junck, L.; Sundgren, P.C.; Ivancevic, M.K.; Johnson, T.D.; Meyer, C.R.; Rehemtulla, A.; Ross, B.D.; et al. Comparison of Apparent Diffusion Coefficients and distributed diffusion coefficients in high-grade gliomas. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 31, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vreeze, R.S.; de Jong, D.; Haas, R.L.; Stewart, F.; van Coevorden, F. Effectiveness of radiotherapy in myxoid sarcomas is associated with a dense vascular pattern. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 72, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latour, L.L.; Svoboda, K.; Mitra, P.P.; Sotak, C.H. Time-dependent diffusion of water in a biological model system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, S.; Nishimura, H.; Uchida, M.; Sakoda, J.; Tonan, T.; Hiraoka, K.; Nagata, K.; Akiba, J.; Abe, T.; Hayabuchi, N. Diffusion-weighted imaging of soft tissue tumors: Usefulness of the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient for differential diagnosis. Radiat. Med. 2008, 26, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, G.J. Analysis of MR diffusion weighted images. Br. J. Radiol. 2004, 77, S176–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Raghunand, N.; Karczmar, G.S.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. MRI of the tumor microenvironment. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 16, 430–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardelmann, E.; Haas, R.L.; Bovee, J.V.; Terrier, P.; Lazar, A.; Messiou, C.; LePechoux, C.; Hartmann, W.; Collin, F.; Fisher, C.; et al. Evaluation of response after neoadjuvant treatment in soft tissue sarcomas; the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group (EORTC-STBSG) recommendations for pathological examination and reporting. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 53, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Grande, F.; Subhawong, T.; Weber, K.; Aro, M.; Mugera, C.; Fayad, L.M. Detection of soft-tissue sarcoma recurrence: Added value of functional MR imaging techniques at 3.0 T. Radiology 2014, 271, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.M.; Joodi, R.; Madhuranthakam, A.J.; Oz, O.K.; Sharma, R.; Chhabra, A. Current utilities of imaging in grading musculoskeletal soft tissue sarcomas. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, P.A.; Gay, F.; Chen, B.; Zins, M.; Sirveaux, F.; Felblinger, J.; Blum, A. Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the initial characterization of non-fatty soft tissue tumors: Correlation between T2 signal intensity and ADC values. Skelet. Radiol. 2016, 45, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rijswijk, C.S.; Kunz, P.; Hogendoorn, P.C.; Taminiau, A.H.; Doornbos, J.; Bloem, J.L. Diffusion-weighted MRI in the characterization of soft-tissue tumors. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 15, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Hegde, S.; DeNardo, D.G. Tumor-associated fibrosis as a regulator of tumor immunity and response to immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazikhanlou-Sani, K.; Firoozabadi, S.M.; Agha-Ghazvini, L.; Mahmoodzadeh, H. Evaluation of Soft Tissue Sarcoma Tumors Electrical Conductivity Anisotropy Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging for Numerical Modeling on Electroporation. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2016, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hagmann, P.; Jonasson, L.; Maeder, P.; Thiran, J.P.; Wedeen, V.J.; Meuli, R. Understanding diffusion MR imaging techniques: From scalar diffusion-weighted imaging to diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Radiographics 2006, 26 (Suppl. S1), S205–S223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Jee, W.H.; Whang, S.; Jung, C.K.; Chung, Y.G.; Cho, S.G. Differentiation of soft-tissue lymphoma from undifferentiated sarcoma: Apparent diffusion coefficient histogram analysis. Acta Radiol. 2021, 62, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bihan, D.; Mangin, J.F.; Poupon, C.; Clark, C.A.; Pappata, S.; Molko, N.; Chabriat, H. Diffusion tensor imaging: Concepts and applications. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 13, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steven, A.J.; Zhuo, J.; Melhem, E.R. Diffusion kurtosis imaging: An emerging technique for evaluating the microstructural environment of the brain. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, W26–W33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, C.; Ding, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z. Distinguishing soft tissue sarcomas of different histologic grades based on quantitative MR assessment of intratumoral heterogeneity. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 118, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, S.; Gurney-Champion, O.J.; Klaassen, R.; Thoeny, H.C. Deep learning how to fit an intravoxel incoherent motion model to diffusion-weighted MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Zhong, X.; Li, N.; Van Dams, R.; Lewis, J.; Sung, K.; Raldow, A.C.; Jin, J.; Qi, X.S. Deep learning-based radiomic features for improving neoadjuvant chemoradiation response prediction in locally advanced rectal cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 075001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
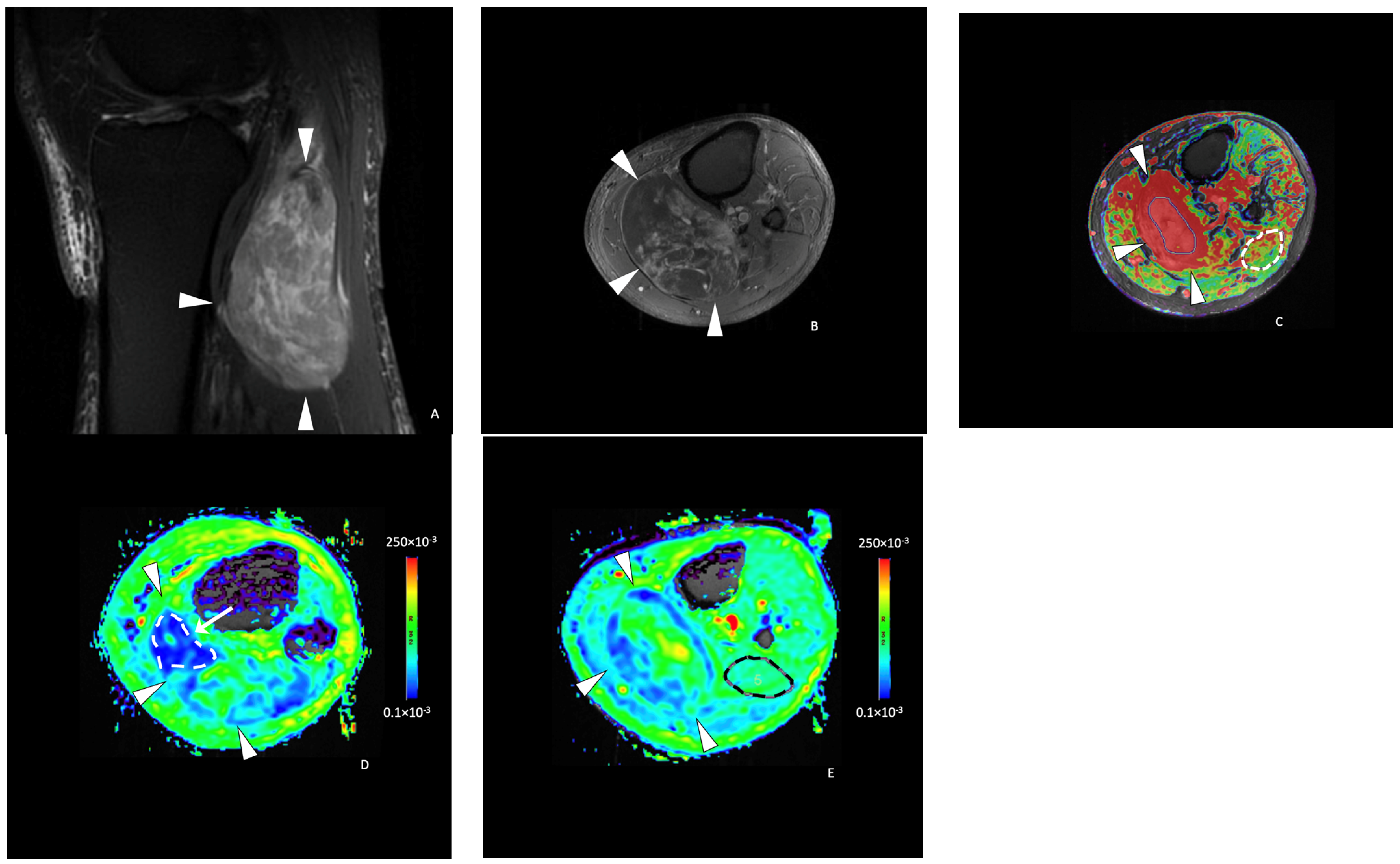




| Necrosis Percentage <50% (n = 20) | Necrosis Percentage ≥50% (n = 9) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD (range) | 59 ± 19 (19–83) | 64 ± 10 (46–84) | 0.65 |
| Male Female | 10 (50%) 10 (50%) | 4 (44.4%) 5 (55.6%) | 1 |
| Histologic diagnosis | NC | ||
| - Myxoid fibrosarcoma | 3 (15%) | 2 (22.2%) | |
| - Undifferentiated sarcoma | 4 (20%) | 1 (11.1%) | |
| - Liposarcoma | 2 (10%) | 2 (22.2%) | |
| - Myxofibrosarcoma | 3 (15%) | 0 | |
| - Dedifferentiated liposarcoma | 1 (5%) | 1 (11.1%) | |
| - Spindle cell sarcoma | 1 (5%) | 2 (22.2%) | |
| - Unclassified pleomorphic sarcoma | 2 (10%) | 0 | |
| - Leiomyosarcoma | 1 (5%) | 0 | |
| - Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor | 1 (5%) | 0 | |
| - Pleomorphic liposarcoma | 1 (5%) | 0 | |
| - Pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma | 0 | 1 (11.1%) | |
| - Synovial sarcoma | 1 (5%) | 0 | |
| FNCLCC grade | 0.844 | ||
| 1 | 7 (35%) | 2 (22.2%) | |
| 2 | 11 (55%) | 6 (66.7%) | |
| 3 | 2 (10%) | 1 (11.1%) |
| Cellularity percentage, median (IQR) | 20 (40–50) |
| Necrosis percentage, median (IQR) <50% ≥50% | 20 (0–60) 20 (69.0%) 9 (31.0%) |
| Fibrosis grade I grade II grade III | 6 (21%) 11 (38%) 12 (41%) |
| ADC, median (IQR) | 134.3 (101.7–167.9) |
| Tumor-to-muscle ADC ratio, median (IQR) | 1.00 (0.77–1.55) |
| AUC, median (IQR) | 70.108 (34.778–158.224) |
| Tumor-to-muscle AUC ratio, median (IQR) | 6.12 (3.52–7.24) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vogin, G.; Lepage, M.; Salleron, J.; Cuenin, M.; Blum, A.; Gondim Teixeira, P.A. Evaluation of the Prognostic Value of Pretherapeutic Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Predicting Soft Tissue Sarcoma Radiation Response: A Retrospective Study from a Large Institutional Sarcoma Imaging Database. Cancers 2024, 16, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050878
Vogin G, Lepage M, Salleron J, Cuenin M, Blum A, Gondim Teixeira PA. Evaluation of the Prognostic Value of Pretherapeutic Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Predicting Soft Tissue Sarcoma Radiation Response: A Retrospective Study from a Large Institutional Sarcoma Imaging Database. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050878
Chicago/Turabian StyleVogin, Guillaume, Matthias Lepage, Julia Salleron, Mathilde Cuenin, Alain Blum, and Pedro Augusto Gondim Teixeira. 2024. "Evaluation of the Prognostic Value of Pretherapeutic Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Predicting Soft Tissue Sarcoma Radiation Response: A Retrospective Study from a Large Institutional Sarcoma Imaging Database" Cancers 16, no. 5: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050878
APA StyleVogin, G., Lepage, M., Salleron, J., Cuenin, M., Blum, A., & Gondim Teixeira, P. A. (2024). Evaluation of the Prognostic Value of Pretherapeutic Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Predicting Soft Tissue Sarcoma Radiation Response: A Retrospective Study from a Large Institutional Sarcoma Imaging Database. Cancers, 16(5), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050878






