Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Extracranial Oligometastatic Disease from Head and Neck Primary Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Review
2.2. Appraisal
2.3. Endpoints and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Demographics
3.2. Study Quality
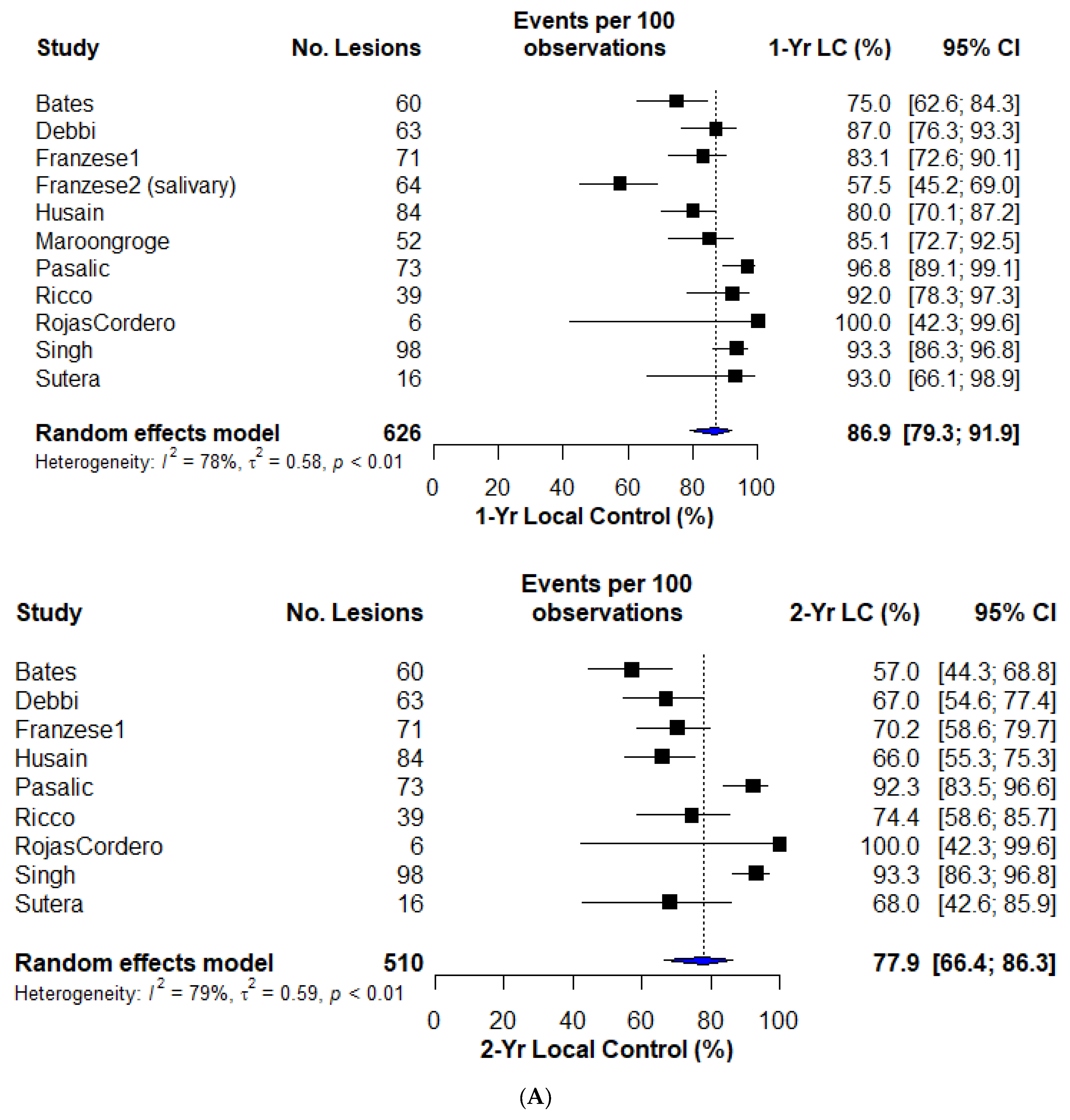
3.3. Local Control
3.4. Progression-Free Survival
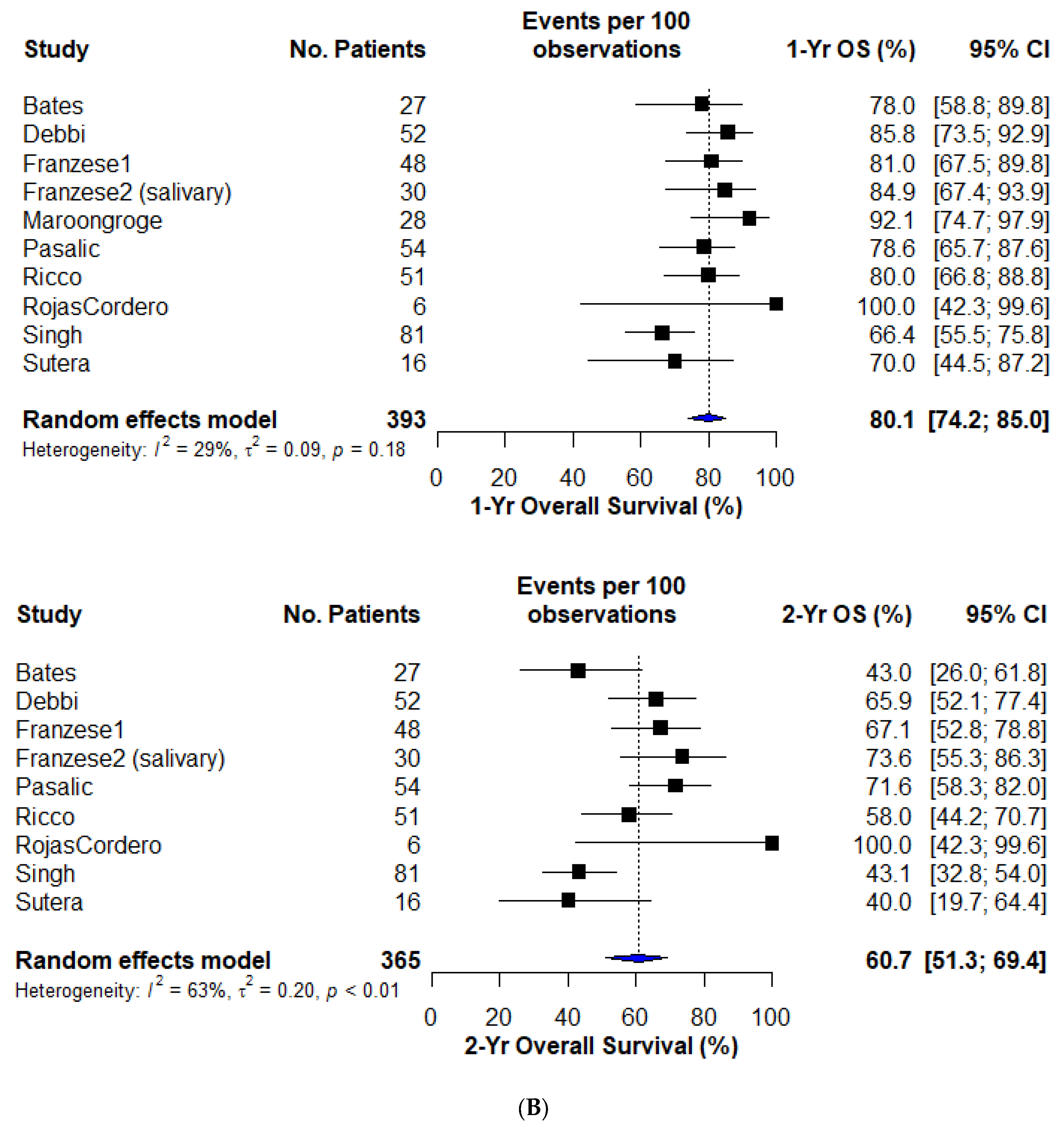
3.5. Overall Survival
3.6. Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Future Directions
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Search Strategy
Appendix A.1.1. PubMed
Appendix A.1.2. EMBASE
References
- Lewis, S.L.; Porceddu, S.; Nakamura, N.; Palma, D.A.; Lo, S.S.; Hoskin, P.; Moghanaki, D.; Chmura, S.J.; Salama, J.K. Definitive Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) for Extracranial Oligometastases: An International Survey of >1000 Radiation Oncologists. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 40, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.; Jiang, W.; Liu, M.; Bergman, A.; Schellenberg, D.; Mou, B.; Alexander, A.; Carolan, H.; Hsu, F.; Miller, S.; et al. Treatment With Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Up to 5 Oligometastases in Patients With Cancer: Primary Toxic Effect Results of the Nonrandomized Phase 2 SABR-5 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.M.; Chen, Y.; Zaric, G.S.; Senan, S.; Olson, R.A.; Harrow, S.; John-Baptiste, A.; Gaede, S.; Mulroy, L.A.; Schellenberg, D.; et al. Is SABR Cost-Effective in Oligometastatic Cancer? An Economic Analysis of the SABR-COMET Randomized Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, A.S.; Helou, J.; Bezjak, A.; Wong, R.; Dawson, L.A.; Ringash, J.; Fazelzad, R.; Liu, Z.; Olson, R.; Palma, D.; et al. Health related quality of life outcomes following stereotactic body radiotherapy in patients with oligo-metastatic disease: A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2022, 173, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Louie, A.V.; Higginson, D.S.; Palma, D.A.; Colaco, R.; Sahgal, A. Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in the Management of Oligometastatic Disease. Clin. Oncol. R. Coll. Radiol. 2020, 32, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Weinreb, I.; Hope, A.; Massey, C.; Waldron, J.N.; Kim, J.; Bayley, A.J.; Cummings, B.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Natural course of distant metastases following radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy in HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeman, J.E.; Li, J.G.; Pei, X.; Venigalla, P.; Zumsteg, Z.S.; Katsoulakis, E.; Lupovitch, E.; McBride, S.M.; Tsai, C.J.; Boyle, J.O.; et al. Patterns of Treatment Failure and Postrecurrence Outcomes Among Patients with Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma after Chemoradiotherapy Using Modern Radiation Techniques. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahig, H.; Huang, S.H.; O’Sullivan, B. Oligometastatic Head and Neck Cancer: Challenges and Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for the Comprehensive Treatment of Oligometastatic Cancers: Long-Term Results of the SABR-COMET Phase II Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2830–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, E.R.; Diakos, E.; Khalid-Raja, M.; Mehanna, H. Resection of subsequent pulmonary metastases from treated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2015, 40, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.E.; De Leo, A.N.; Morris, C.G.; Amdur, R.J.; Dagan, R. Oligometastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with stereotactic body ablative radiotherapy: Single-institution outcomes. Head Neck 2019, 41, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, P.; Greto, D.; Desideri, I.; Loi, M.; Di Cataldo, V.; Orlandi, E.; Iacovelli, N.A.; Becherini, C.; Visani, L.; Salvestrini, V.; et al. Clinical outcome of stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung-only oligometastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Is the deferral of systemic therapy a potential goal? Oral Oncol. 2019, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbi, K.; Loganadane, G.; To, N.H.; Kinj, R.; Husain, Z.A.; Chapet, S.; Nguyen, N.P.; Barillot, I.; Benezery, K.; Belkacemi, Y.; et al. Curative intent Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy (SABR) for treatment of lung oligometastases from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): A multi-institutional retrospective study. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20210033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohopolski, M.J.; Horne, Z.; Clump, D.; Burton, S.A.; Heron, D.E. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Pulmonary Oligometastases Arising from Non-lung Primaries in Patients Without Extrapulmonary Disease. Cureus 2018, 10, e2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzese, C.; Badalamenti, M.; Teriaca, A.; De Virgilio, A.; Mercante, G.; Cavina, R.; Ferrari, D.; Santoro, A.; Spriano, G.; Scorsetti, M. Metastasis-directed stereotactic body radiation therapy in the management of oligometastatic head and neck cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzese, C.; Ingargiola, R.; Tomatis, S.; Iacovelli, N.A.; Beltramo, G.; Franco, P.; Bonomo, P.; Zanetti, I.B.; Argenone, A.; Cante, D.; et al. Metastatic salivary gland carcinoma: A role for stereotactic body radiation therapy? A study of AIRO-Head and Neck working group. Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.C.; Ayala-Peacock, D.N.; Lee, J.; Blackstock, A.W.; Okunieff, P.; Sung, M.W.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Kao, J.; Urbanic, J.J.; Milano, M.T.; et al. Classification for long-term survival in oligometastatic patients treated with ablative radiotherapy: A multi-institutional pooled analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, Z.A.; Chen, H.; Biswas, T.; Dagan, R.; Erler, D.; Foote, M.C.; Louie, A.V.; Redmond, K.J.; Ricardi, U.; Sahgal, A.; et al. Outcomes for Oligometastatic Head and Neck Cancer Undergoing SBRT: Results from an International Multi-Institutional Consortium. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 111, e370–e371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroongroge, S.; Sosa, A.; Rhines, L.; Amini, B.; Phan, J.; Ghia, A. Stereotactic Spinal Radiosurgery (SSRS) for Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, E53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasalic, D.; Betancourt-Cuellar, S.L.; Taku, N.; Ludmir, E.B.; Lu, Y.; Allen, P.K.; Tang, C.; Antonoff, M.B.; Fuller, C.D.; Rosenthal, D.I.; et al. Outcomes and toxicities following stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for pulmonary metastases in patients with primary head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1939–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricco, A.; Davis, J.; Rate, W.; Yang, J.; Perry, D.; Pablo, J.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Sharma, S.; Sundararaman, S.; Kolker, J.; et al. Lung metastases treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: The RSSearch® patient Registry’s experience. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas Cordero, J.V.; Sancho Pardo, G.; Majercakova, K.; Gallego Franco, P.; Carrasco de Fez, P.; Soto Cambres, A.M.; Balart Serra, J.; Farré Bernadó, N. PO-1253 Lung metastases from different primary tumors treated with Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 170, S1057–S1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Jenkins, J.; Davis, J.; Song, S.; Sharma, S.; Vargo, J.A. A multi-institutional analysis of outcomes following stereotactic body radiation therapy for management of metastases from squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. J. Radiosurgery SBRT 2022, 8, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutera, P.; Clump, D.A.; Kalash, R.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Mihai, A.; Wang, H.; Petro, D.P.; Burton, S.A.; Heron, D.E. Initial Results of a Multicenter Phase 2 Trial of Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy for Oligometastatic Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 103, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Niibe, Y.; Aoki, M.; Shintani, T.; Yamada, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Yamashita, H.; Ozaki, M.; Manabe, Y.; Onishi, H.; et al. Analyses of the local control of pulmonary Oligometastases after stereotactic body radiotherapy and the impact of local control on survival. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaorsky, N.G.; Lehrer, E.J.; Kothari, G.; Louie, A.V.; Siva, S. Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy for oligometastatic renal cell carcinoma (SABR ORCA): A meta-analysis of 28 studies. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 2, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Moideen, N.; Bratti, V.F.; Moraes, F.Y. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in metachronous oligometastatic prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis on the current prospective evidence. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20200496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, A.B.; Senan, S.; Palma, D.A.; Riquet, M.; Ahn, Y.C.; Ricardi, U.; Congedo, M.T.; Gomez, D.R.; Wright, G.M.; Melloni, G.; et al. An individual patient data metaanalysis of outcomes and prognostic factors after treatment of oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2014, 15, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viani, G.A.; Gouveia, A.G.; Louie, A.V.; Korzeniowski, M.; Pavoni, J.F.; Hamamura, A.C.; Moraes, F.Y. Stereotactic body radiotherapy to treat breast cancer oligometastases: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2021, 164, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battermann, J.J.; Breur, K.; Hart, G.A.; van Peperzeel, H.A. Observations on pulmonary metastases in patients after single doses and multiple fractions of fast neutrons and cobalt-60 gamma rays. Eur. J. Cancer 1981, 17, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN. NCCN Guidelines Version 1.2023—Very Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/head-and-neck.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2023.).
- Burtness, B.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Psyrri, A.; Basté, N.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, Å.; et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 394, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rischin, D.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Psyrri, A.; Braña, I.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, Å.; et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Health-related quality-of-life results from KEYNOTE-048. Oral Oncol. 2022, 128, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deek, M.P.; Van der Eecken, K.; Sutera, P.; Deek, R.A.; Fonteyne, V.; Mendes, A.A.; Decaestecker, K.; Kiess, A.P.; Lumen, N.; Phillips, R.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes and Genetic Predictors of Response to Metastasis-Directed Therapy Versus Observation in Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: Analysis of STOMP and ORIOLE Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3377–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.R.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J.; Blumenschein, G.R., Jr.; Hernandez, M.; Lee, J.J.; Ye, R.; Palma, D.A.; Louie, A.V.; Camidge, D.R.; et al. Local Consolidative Therapy Vs. Maintenance Therapy or Observation for Patients With Oligometastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Long-Term Results of a Multi-Institutional, Phase II, Randomized Study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.; Yang, J.T.; Guttmann, D.M.; Shaverdian, N.; Shepherd, A.F.; Eng, J.; Gelblum, D.; Xu, A.J.; Namakydoust, A.; Iqbal, A.; et al. Consolidative Use of Radiotherapy to Block (CURB) Oligoprogression—Interim Analysis of the First Randomized Study of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Patients with Oligoprogressive Metastatic Cancers of the Lung and Breast. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 111, 1325–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkidou, A.; Macmillan, T.; Grzeda, M.T.; Peacock, J.; Summers, J.; Eddy, S.; Coker, B.; Patrick, H.; Powell, H.; Berry, L.; et al. Stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy in patients with oligometastatic cancers: A prospective, registry-based, single-arm, observational, evaluation study. Lancet. Oncol. 2021, 22, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Patients with Rare Oligometastatic Cancers (OligoRARE). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04498767 (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Correa, R.J.M.; Schneiders, F.; Haasbeek, C.J.A.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Lock, M.; Yaremko, B.P.; Bauman, G.S.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 4-10 oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-10): Study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.; Yang, J.T.; Guttmann, D.M.; Shaverdian, N.; Eng, J.; Yeh, R.; Girshman, J.; Das, J.; Gelblum, D.; Xu, A.J.; et al. Final Analysis of Consolidative Use of Radiotherapy to Block (CURB) Oligoprogression Trial—A Randomized Study of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Oligoprogressive Metastatic Lung and Breast Cancers. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroese, T.E.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Nilsson, M.; Lordick, F.; Guckenberger, M.; Ruurda, J.P.; D’Ugo, D.; Haustermans, K.; van Cutsem, E.; van Hillegersberg, R.; et al. Definition of oligometastatic esophagogastric cancer and impact of local oligometastasis-directed treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 166, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guckenberger, M.; Lievens, Y.; Bouma, A.B.; Collette, L.; Dekker, A.; deSouza, N.M.; Dingemans, A.C.; Fournier, B.; Hurkmans, C.; Lecouvet, F.E.; et al. Characterisation and classification of oligometastatic disease: A European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer consensus recommendation. Lancet. Oncol. 2020, 21, e18–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.G.; Wang, W.; Shokri, T.; Ducic, Y. Treatment of Oligometastatic Disease in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E1476–E1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckham, T.H.; Leeman, J.E.; Xie, P.; Li, X.; Goldman, D.A.; Zhang, Z.; Sherman, E.; McBride, S.; Riaz, N.; Lee, N.; et al. Long-term survival in patients with metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with metastasis-directed therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmann, T.; Höfler, D.; Hecht, M.; Semrau, S.; Haderlein, M.; Filimonova, I.; Frey, B.; Bert, C.; Lettmaier, S.; Mantsopoulos, K.; et al. Oligometastatic head and neck cancer: Which patients benefit from radical local treatment of all tumour sites? Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, D.; Wirth, M.; Piontek, G.; Knopf, A.; Straube, C.; Pigorsch, S.; Combs, S.E.; Pickhard, A. Improved overall survival in head and neck cancer patients after specific therapy of distant metastases. Eur. Arch. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2018, 275, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardinois, I.; Dequanter, D.; Lechien, J.R.; Bouland, C.; Javadian, R.; Rodriguez, A.; Loeb, I.; Journe, F.; Saussez, S. Survival and treatment outcome of head and neck cancer patients with pulmonary oligometastases. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2021, 46, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bai, Y.; Wu, M.; Shen, L.; Shi, F.; Sun, X.; Lin, C.; Chang, B.; Pan, C.; Li, Z.; et al. Combined CT-guided radiofrequency ablation with systemic chemotherapy improves the survival for nasopharyngeal carcinoma with oligometastasis in liver: Propensity score matching analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 52132–52141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.M.; Lee, D.Y.; Shimunov, D.; Carmona, R.; Barsky, A.R.; Sun, L.; Cohen, R.B.; Bauml, J.M.; Brody, R.M.; Basu, D.; et al. Definitive tumor directed therapy confers a survival advantage for metachronous oligometastatic HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer following trans-oral robotic surgery. Oral Oncol. 2021, 121, 105509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonia, D.R.; Rajappa, S.K.; Dewan, A.K.; Sehrawat, A.; Agrawal, C.; Venkata Pradeep Babu, K. Exploring an Unfathomed Entiry: A Pooled Analysis of Solitory Skeletal Muscle Metastasis from Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2022, 21, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, S.; Sherman, E.; Tsai, C.J.; Baxi, S.; Aghalar, J.; Eng, J.; Zhi, W.I.; McFarland, D.; Michel, L.S.; Young, R.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Nivolumab With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Versus Nivolumab Alone in Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatten, S.J., Jr.; Lehrer, E.J.; Liao, J.; Sha, C.M.; Trifiletti, D.M.; Siva, S.; McBride, S.M.; Palma, D.; Holder, S.L.; Zaorsky, N.G. A Patient-Level Data Meta-analysis of the Abscopal Effect. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 7, 100909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Jiang, W.; Mou, B.; Lund, C.R.; Liu, M.; Bergman, A.M.; Schellenberg, D.; Alexander, A.S.; Carolan, H.; Atrchian, S.; et al. Progression-Free Survival and Local Control After SABR for up to 5 Oligometastases: An Analysis From the Population-Based Phase 2 SABR-5 Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; Bressel, M.; Mai, T.; Le, H.; Vinod, S.; de Silva, H.; Macdonald, S.; Skala, M.; Hardcastle, N.; Rezo, A.; et al. Single-Fraction vs Multifraction Stereotactic Ablative Body Radiotherapy for Pulmonary Oligometastases (SAFRON II): The Trans Tasman Radiation Oncology Group 13.01 Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol 2021, 7, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.A.; Bell, J.B.; Kim, T.; Agulnik, M.; Chandler, J.P.; Mittal, B.B.; Kruser, T.J. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases from primary head and neck carcinomas: A retrospective analysis. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 134, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, R.; Liu, Y.P.; Huang, P.Y.; Zou, X.; Sun, R.; He, Y.X.; Wu, Y.S.; Shen, G.P.; Zhang, H.D.; Duan, C.Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Locoregional Radiotherapy With Chemotherapy vs. Chemotherapy Alone in De Novo Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Multicenter Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, T.D.; Marchiano, E.; Chin, O.Y.; Kilic, S.; Eloy, J.A.; Baredes, S.; Park, R.C. Utility of Surgery/Radiotherapy in Distant Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Population-Based Approach. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 154, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumsteg, Z.S.; Luu, M.; Yoshida, E.J.; Kim, S.; Tighiouart, M.; David, J.M.; Shiao, S.L.; Mita, A.C.; Scher, K.S.; Sherman, E.J.; et al. Combined high-intensity local treatment and systemic therapy in metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: An analysis of the National Cancer Data Base. Cancer 2017, 123, 4583–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabarriti, R.; Baliga, S.; Ohri, N.; Guha, C.; Kalnicki, S.; Garg, M.K. Radiation therapy for patients with newly diagnosed metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2019, 41, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.C.; James, N.D.; Brawley, C.D.; Clarke, N.W.; Hoyle, A.P.; Ali, A.; Ritchie, A.W.S.; Attard, G.; Chowdhury, S.; Cross, W.; et al. Radiotherapy to the primary tumour for newly diagnosed, metastatic prostate cancer (STAMPEDE): A randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 2353–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badwe, R.; Hawaldar, R.; Nair, N.; Kaushik, R.; Parmar, V.; Siddique, S.; Budrukkar, A.; Mittra, I.; Gupta, S. Locoregional treatment versus no treatment of the primary tumour in metastatic breast cancer: An open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2015, 16, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrials.gov. A Randomized Phase III Trial of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Patients With Up to 10 Oligometastases and a Synchronous Primary Tumor. (SABR-SYNC). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05717166 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Steven, J.; Chmura, K.A.W.; Woodward, W.A.; Borges, V.F.; Salama, J.K.; Al-Hallaq, H.A.; Matuszak, M.; Milano, M.T.; Jaskowiak, N.T.; Bandos, H.; et al. NRG-BR002: A phase IIR/III trial of standard of care systemic therapy with or without stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) and/or surgical resection (SR) for newly oligometastatic breast cancer (NCT02364557). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffin, A.T.; Li, H.; Vujanovic, L.; Zandberg, D.P.; Ferris, R.L.; Bruno, T.C. Improving head and neck cancer therapies by immunomodulation of the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Camrelizumab Plus Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy vs Camrelizumab Alone for Oligometastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT04944914 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Sari, S.Y.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Aktas, B.Y.; Aksoy, S.; Gullu, I.; Cengiz, M.; Ozyigit, G.; Yazici, G. Results of concurrent radiotherapy and immunotherapy in recurrent and metastatic head and neck cancer: A single-center experience. Oral Oncol. 2022, 124, 105658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahig, H.; Aubin, F.; Nguyen-Tan, P.F.; Souliere, D.; Palma, D.A.; Charpentier, D.; Debenham, B.J.; Jamal, R.; Sultanem, K.; Ballivy, O.; et al. Initial analyses of a phase I/II trial of durvalumab (D) plus tremelimumab (T) and stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for oligometastatic head and neck carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GORTEC. NCT03070366: Stereotactic Radiotherapy Combined With Chemotherapy or Not for Treatment of Oligometastases in HNSCC (OMET). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03070366 (accessed on 10 October 2023.).
- Faraji, F.; Eisele, D.W.; Fakhry, C. Emerging insights into recurrent and metastatic human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2017, 2, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Population | Patients with metastatic (synchronous or metachronous) cancers from head and neck primaries (mucosal or parotid) with less than or equal to 5 total lesions to any anatomic site in the body (excluding the brain) |
| Intervention | Stereotactic radiation therapy, defined as highly conformal, image-guided, high dose-per-fraction (>=6 Gy/fraction, total BED >= 48 Gy) external beam radiation therapy delivered with ablative intent |
| Control | Multiple-arm studies in which one or more arms involved stereotactic radiation or no control group |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: local control at 1 and 2 years. Secondary outcomes: overall survival at 1 and 2 years; progression-free survival at 1 and 2 years; any toxicity |
| Study Design | Prospective or retrospective studies with greater than 5 head and neck cancer patients |
| Study | Pts/ Lesions | Design | OM HNC Definition | Sites Treated | Age (Med) | Performance Status | RT Dose | BED10 (Min–Max) | Median Follow-Up | LC | OS | Toxicity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12M | 24M | 12M | 24M | |||||||||||
| Bates [13] | 27/60 | Retro | 1–5 mets, mixed histology; (22 metachronous, 5 synchronous; OP:5) | Mixed sites; 59% lung only | 65 (20–76) | - | 35/5# to 50/5# | 59.5–100 Gy | 19.2 mos | 75.0% | 57.0% | 78.0% | 43.0% | NR |
| Bonomo [14] | 27/28 | Retro | 1–5 mets, HNSCC; <5cm max dim, (de novo:22; OP:6) | Lung only | 67 (37–85) | ECOG 0–2 | 26Gy/1# to 54Gy/3# | 93.6–151.2 | 22.0 mos | NR | NR | NR | NR median OS of 47mos | 14.8% Gr1–2 |
| Debbi [15] | 52/63 | Multi-institutional/Retro | 1–2 mets, HNSCC; all metachronous, <5 cm max dim | Lung only | 65.5 (50–83) | ECOG 0–2 | 60Gy/3# | 180 Gy | 45.3 mos | 87.0% | 67.0% | 85.8% | 65.9% | 2% Gr2 2% Gr3 |
| Dohopolski [16] | 17/NR | Retro | 1–5 mets, mixed histology, majority metachronous | Lung only | 68 IQR (69–75) | - | Mixed: 60/3# to 48/4# | 105.6–180 Gy | 29.5 mos | HR | HR | - | ||
| Franzese [17] | 48/71 | Retro | 1–5 mets, mixed histology; metachronous: 42; OP: 6 | Mixed sites; 59% lung | 70.5 (32–83) | ECOG 0–1 | 21Gy/3# to 75Gy/8# | 35.7–145.3 Gy | 20.2 mos | 83.1% | 70.2% | 81.0% | 67.1% | 1.7% Gr2 |
| Franzese [18] | 30/64 | Retro | 1–3 mets, salivary gland primary | Mixed sites; 53% lung | 56.5 (25–82) | - | 20/1# to 54/5# | 60–115.5 Gy | 29.2 mos | 57.5% | 84.9% | 73.6% | NR | |
| Hong [19] | 34/NR | Multi-institutional/Retro | 1–5 mets, NS | NR | 62.7 IQR: (54–71) * | - | 24Gy/3# to 50Gy/10# | 43.2–75.0 Gy | 26.2 mos | HR | HR | NR | ||
| Husain [20] (ABS) | 42/84 | Multi-institutional/Retro | <=5 extracranial mets; HNC mixed histology; metachronous: 31; synchronous: 11 | Mixed site; 50% lung | 64 (NR) | - | 20–28/1# to 50 Gy/10 (median BED = 100) | 60–100 Gy (median BED = 100) | 18.2 mos | 80% | 66% | 4.7% Gr 3 pneumontiis | ||
| Maroongroge [21] (ABS) | 28/52 | Retro | Limited spine mets, mixed histology; | Spine only | – | - | - | - | 51.7 mos | 85.1% | 92.1% | NR | ||
| Pasalic [22] | 54/73 | Retro | 1–3 mets, mixed histology; majority metachronous (nonoligo patients also reported) | Lung only | 65 (26–93) | - | Range from 50/4# to 70/10# | Range from 112.50 to 119.0 Gy | 20 mos | 96.8% | 92.3% | 78.6% | 71.6% | 6.2% Gr2 |
| Ricco [23] | 51/39 ** | Multi-institutional database/Retro | 1–3 mets, mixed histology | Lung only | 69 (18–93) | KPS 90 (25–100) | Median: 50 Gy/3# | Median: 50 Gy/3# | 13.0 mos | 92.0% | 74.4% | 80.0% | 58.0% | NR |
| Rojas Cordero [24] (ABS) | 6/6 | Retro | 1–4, mixed histology; <5 cm max dim | Lung only | 75 (24–94) | - | 50 Gy/5# to 55/5# | 100.0–1115.5 Gy | 42.0 mos | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | NR |
| Singh [25] | 81/98 | Registry/Retro | HNC OMD–NS | Mixed site; 53% lung | 68 (NR) | KPS 90 | 20 Gy/1# to 60 Gy/5 | Median BED: 37.5–180 Gy med: 92.2 Gy | NR | 93.3% | 93.3% | 66.4% | 43.1% | 17.3% Gr 1–2, no Gr3+ no Gr 3 |
| Sutera [26] | 16/16 | Phase II –single-arm | 1–5 mets, mixed histology; | Mixed site | 66.4 IQR: (59.5–74.6) | KPS 90 (60–100) | 41–54 Gy in 3–5 # | 97.0–104.0 Gy | 41.3 mos | 93.0% | 68.0% | 70.0% | 40.0% | 7.5% Gr2 2.0% Gr3 |
| Yamamoto [27] | NR/126 | Multi-institutional database/Retro | 1–5 mets, NR | Lung only | 72 (63–78) * | ECOG 0–3 | NR | BED > 75 Gy | HR | HR | NR | |||
| Series | Design | Metastasis-Directed Therapy Utilized | Number Patients/ Lesions | Demographics | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vincent [45] | Retrospective review | Surgical metastasectomy | 81/81 | Single distant metastasis | 5-year OS: 40% |
| Young [10] | Systematic review and meta-analysis of retrospective studies | Surgical metastasectomy of lung metastases | 11 studies; 387/NR | Lung-only oligometastasis, 1–6 nodules resected per patient (286 with single) | 5-year OS: 29.1% |
| Beckham [46] | Retrospective single-institution | MDT included surgery, RT, RFA—most (74) received no treatment | 104 */248 (30 underwent MDT) | Mixed cohort of OM and PM, with mixed treatment | 5-year OS in patients receiving MDT = 31% |
| Weissman [47] | Retrospective single-institution | 90% SBRT, 25% surgery, 3% RFA | 40/75 | 1–7 mets, lung in 58%; 68% metachronous | LC1 = 90%, LC3 = 85% (no difference between modality) |
| Shulz [48] | Retrospective review with propensity-matched cohort | SBRT and or surgery (radiation dose/fractionation not detailed) | 37/64 | Limited metastatic disease from HNSCC | Significantly higher OS (23.97 months vs. 7.07 months) for patients receiving MDT |
| Lardinois [49] | Retrospective single-institution | Surgery (26), radiation (dose/technique not specified) (10), chemotherapy (47), supportive care (17) | 100/123 | Majority lung metastases, <5, 94% metachronous | RFS–OS and OS were significantly better than patients without specific treatment (respectively, p = 0.02 and p = 0.002) |
| Li [50] | Retrospective single-institution; Propensity-matched | Chemo + RFA | 37/66 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma with <=3 liver metastases; 22 metachronous; 15 synchronous | Median OS 32.5 months vs. 18.8 months (chemo-only matched cohort). 29.5% 5-year OS in chemo + RFA group |
| Wright [51] | Retrospective single-institution | Metastatic patients presenting after surgery treated with surgery or RT 14 additional OM patients treated with systemic therapy | 12/16 | <5 metastasis, with most having 1 or 2 | Significantly better OS in patients treated with MDT than systemic therapy alone (not reached vs. 40.7 months) |
| Poonia [52] | Retrospective single-institution | Skeletal muscle metastases treated with surgery/RT/chemo | 6/6 * | Mixed cohort of OM and PM, with mixed treatment | Limited sample of rare entity limits findings |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mutsaers, A.; Akingbade, A.; Louie, A.V.; Id Said, B.; Zhang, L.; Poon, I.; Smoragiewicz, M.; Eskander, A.; Karam, I. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Extracranial Oligometastatic Disease from Head and Neck Primary Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050851
Mutsaers A, Akingbade A, Louie AV, Id Said B, Zhang L, Poon I, Smoragiewicz M, Eskander A, Karam I. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Extracranial Oligometastatic Disease from Head and Neck Primary Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050851
Chicago/Turabian StyleMutsaers, Adam, Aquila Akingbade, Alexander V. Louie, Badr Id Said, Liying Zhang, Ian Poon, Martin Smoragiewicz, Antoine Eskander, and Irene Karam. 2024. "Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Extracranial Oligometastatic Disease from Head and Neck Primary Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 5: 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050851
APA StyleMutsaers, A., Akingbade, A., Louie, A. V., Id Said, B., Zhang, L., Poon, I., Smoragiewicz, M., Eskander, A., & Karam, I. (2024). Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Extracranial Oligometastatic Disease from Head and Neck Primary Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(5), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050851





