Electroporation in Translational Medicine: From Veterinary Experience to Human Oncology
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
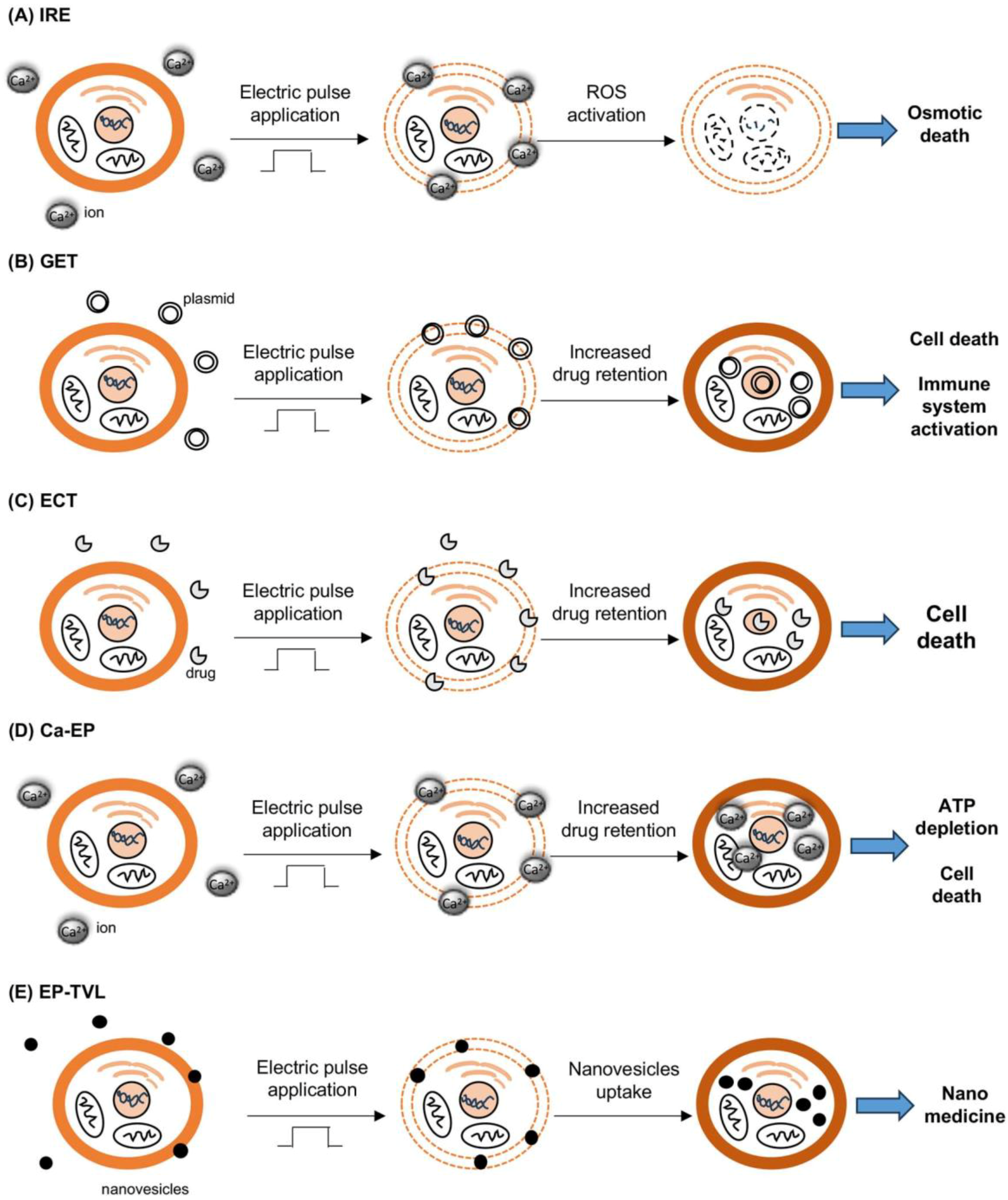
2. Different Electroporation Techniques
3. Translational Use of EP in Veterinary Oncology and Humans
3.1. Irreversible Electroporation (IRE)
3.2. Gene Electrotransfer (GET)
3.3. Electrochemotherapy (ECT)
3.3.1. Clinical Electrochemotherapy Protocols in Veterinary Oncology
- The only standardized and approved protocols for human cancer treatment are those for the palliative care of cutaneous cancer metastases or for the treatment of primary skin tumors. There are many investigations of the treatment of visceral cancer through endoscopy or laparoscopy, but they are not yet approved standard approaches. On the other hand, in veterinary oncology, ECT has been adopted as a first-line treatment of solid tumors and for the treatment of selected visceral neoplasms, to the point that such therapies are reimbursed by veterinary insurance schemes.
- Although human ECT is habitually performed under local anesthesia, veterinary ECT is performed with the patients under heavy sedation or general anesthesia.
- Veterinary ECT can be palliative, adjuvant or neoadjuvant and can be administered concurrently with surgery (intraoperative ECT). Additionally, ECT guided by ultrasound is gaining importance in veterinary oncology for treating deep tumors that are not easily reachable by surgery or that are at an advanced stage.
3.3.2. Clinical Outcome in Solid Tumors
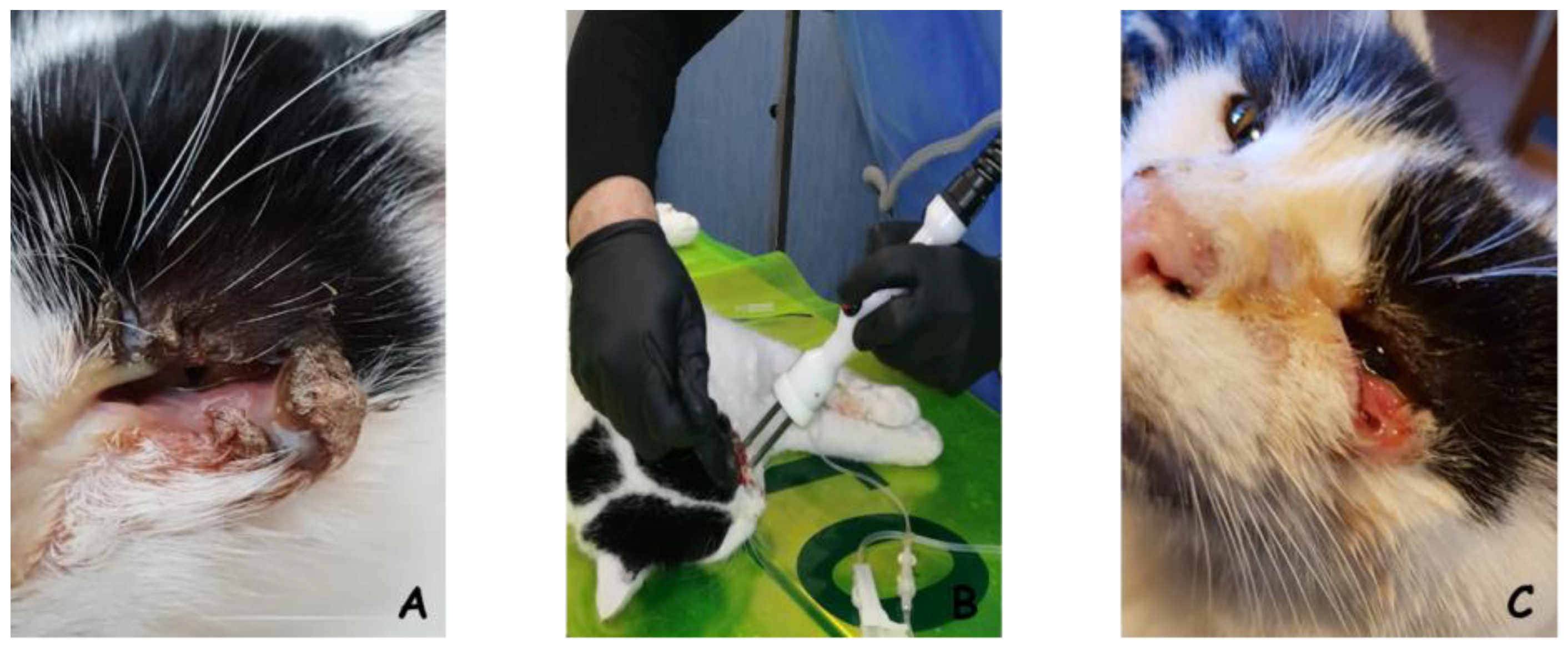
Feline and Canine Soft Tissue Sarcoma (STS)
Epithelial Tumors
Melanoma
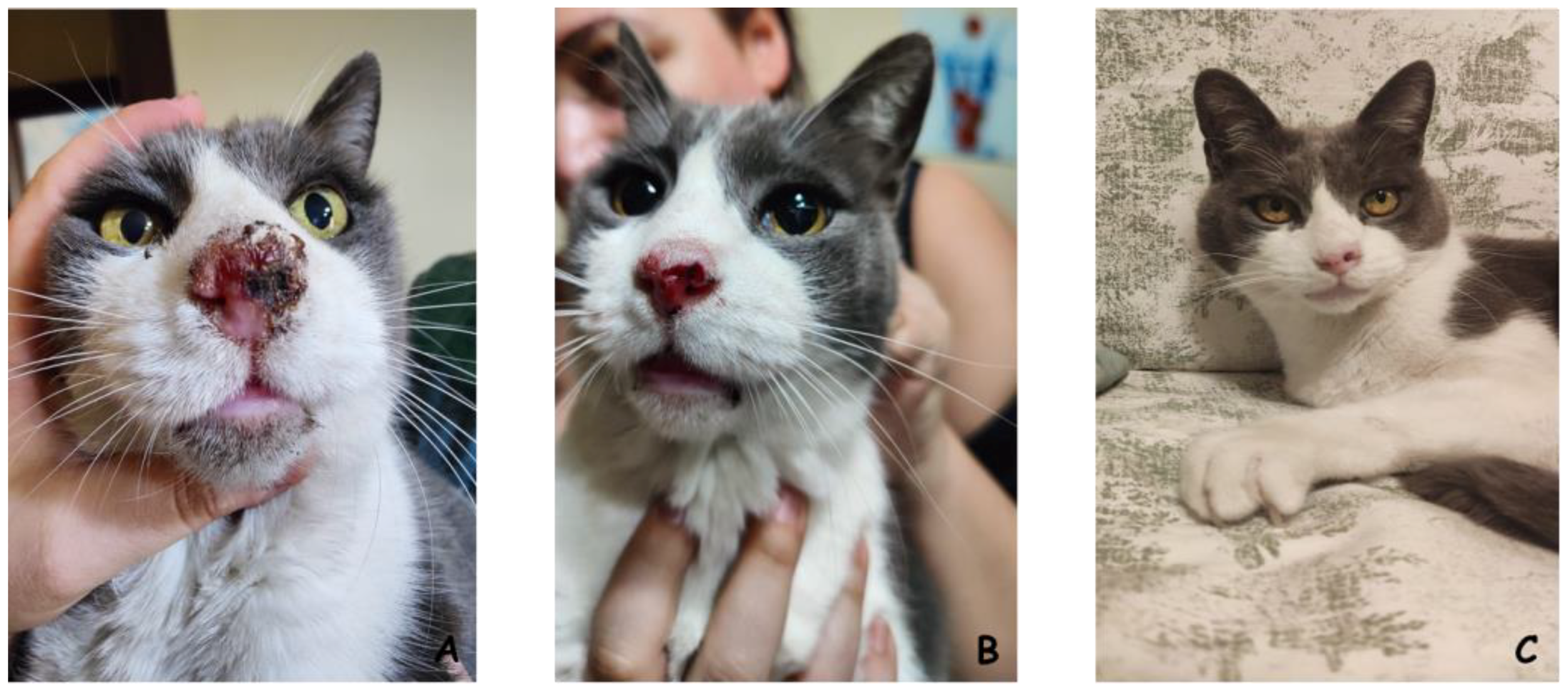
3.4. ECT Clinical Trials in Humans
3.5. Calcium–EP
3.6. EP–TVL
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balantič, K.; Miklavčič, D.; Križaj, I.; Kramar, P. The good and the bad of cell membrane electroporation. Acta Chim. Slov. 2021, 68, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aycock, K.N.; Davalos, R.V. Irreversible Electroporation: Background, Theory, and Review of Recent Developments in Clinical Oncology. Bioelectricity 2019, 1, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Melillo, A.; Quagliuolo, L.; Boccellino, M.; Vincenzi, B.; Pasquali, P.; Baldi, A. Definition of novel electrochemotherapy parameters and validation of their in vitro and in vivo effectiveness. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davalos, R.V.; Mir, L.M.; Rubinsky, B. Tissue Ablation with Irreversible Electroporation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Fan, Q.; Ji, Z.; Qiu, X.; Li, Z. The Effects of Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) on Nerves. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maor, E.; Ivorra, A.; Leor, J.; Rubinsky, B. The Effect of Irreversible Electroporation on Blood Vessels. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 6, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Zhong, Z. Research frontiers of electroporation-based applications in cancer treatment: A bibliometric analysis. Biomed. Tech. 2023, 68, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Baldi, A. Electrochemotherapy in Veterinary Oncology: State-of-the-Art and Perspectives. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2019, 49, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, B.; Jarm, T.; Snoj, M.; Sersa, G.; Miklavcic, D. Antitumor effectiveness of electrochemotherapy: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 39, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groselj, A.; Kranjc, S.; Bosnjak, M.; Krzan, M.; Kosjek, T.; Prevc, A.; Cemazar, M.; Sersa, G. Vascularization of the tumours affects the pharmacokinetics of bleomycin and the effectiveness of electrochemotherapy. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 123, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunikowska, J.; Rembiałkowska, N.; Michel, O.; Mączyńska, J.; Antończyk, A.; Prządka, P.; Kiełbowicz, Z.; Kulbacka, J. Electrochemotherapy with Bleomycin Supported by NIRF Imaging with Indocyanine Green (ICG)—In Vitro and In Vivo Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groselj, A.; Bosnjak, M.; Strojan, P.; Krzan, M.; Cemazar, M.; Sersa, G. Efficiency of electrochemotherapy with reduced bleomycin dose in the treatment of nonmelanoma head and neck skin cancer: Preliminary results. Head Neck 2017, 40, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlasa, W.; Kiełbik, A.; Szewczyk, A.; Novickij, V.; Tarek, M.; Łapińska, Z.; Saczko, J.; Kulbacka, J.; Rembiałkowska, N. Atorvastatin Modulates the Efficacy of Electroporation and Calcium Electrochemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, S.K.; Vissing, M.; Gehl, J. A Comprehensive Review of Calcium Electroporation—A Novel Cancer Treatment Modality. Cancers 2020, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frandsen, S.K.; Gehl, J. A Review on Differences in Effects on Normal and Malignant Cells and Tissues to Electroporation-Based Therapies: A Focus on Calcium Electroporation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818788077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilushkina, A.A.; Emene, C.C.; Barlev, N.A.; Gomzikova, M.O. Strategies for Engineering of Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, R.; Alberti, A.; Castellani, D.; Yee, C.H.; Zhang, K.; Poon, D.M.C.; Chiu, P.K.; Campi, R.; Resta, G.R.; Dibilio, E.; et al. Oncological results and cancer control definition in focal therapy for Prostate Cancer: A systematic review. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Geboers, B.; Scheltema, M.J.; Blazevski, A.; Katelaris, A.; Doan, P.; Ali, I.; Agrawal, S.; Barreto, D.; Matthews, J.; Haynes, A.M.; et al. Median 4-year outcomes of salvage irreversible electroporation for localized radio-recurrent prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2023, 131 (Suppl. S4), 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, K.; Philips, P.P.; Egger, M.E.; Scoggins, C.R.; McMasters, K.M.; Martin, R.C.G., 2nd. Multi-institutional review of adverse events associated with irreversible electroporation in the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Surgery 2023, 175, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmer, F.E.F.; Geboers, B.; Scheffer, H.J.; Bakker, J.; Ruarus, A.H.; Dijkstra, M.; van der Lei, S.; Boon, R.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; van den Bemd, B.A.T.; et al. Tissue Resistance Decrease during Irreversible Electroporation of Pancreatic Cancer as a Biomarker for the Adaptive Immune Response and Survival. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2023, 34, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühling, P.; Stillström, D.; Holmquist, F.; Nilsson, A.; Fredman, J. Irreversible electroporation of hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal cancer liver metastases: A nationwide multicenter study with short- and long-term follow-up. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 49, 107046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Chen, G.; Hu, X.; Zheng, J.; Xue, Z.; He, X.; et al. Novel irreversible electroporation ablation (Nano-knife) versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of solid liver tumors: A comparative, randomized, multicenter clinical study. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 945123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, R.E.; Singh, R.; Hatcher, H.C.; Kock, N.D.; Torti, S.V.; Davalos, R.V. Treatment of Breast Cancer through the Application of Irreversible Electroporation Using a Novel Minimally Invasive Single Needle Electrode. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 123, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmeisl, J.H., Jr.; Garcia, P.A.; Pancotto, T.E.; Robertson, J.L.; Henao-Guerrero, N.; Neal, R.E., 2nd; Ellis, T.L.; Davalos, R.V. Safety and feasibility of the NanoKnife system for irreversible electroporation ablative treatment of canine spontaneous intracranial gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 1008–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latouche, E.L.; Arena, C.B.; Ivey, J.W.; Garcia, P.A.; Pancotto, T.E.; Pavlisko, N.; Verbridge, S.S.; Davalos, R.V.; Rossmeisl, J.H. High-Frequency Irreversible Electroporation for Intracranial Meningioma: A Feasibility Study in a Spontaneous Canine Tumor Model. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818785285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie Butty, E.; Forsyth, B.; Labato, M.A. Irreversible Electroporation Balloon Therapy for Palliative Treatment of Obstructive Urethral Transitional Cell Carcinoma in Dogs. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2022, 58, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, B.R.; O’Brien, T.J.; Lorenzo, M.F.; Coutermarsh-Ott, S.L.; Barry, S.L.; Stadler, K.; Muro, N.; Meyerhoeffer, M.; Allen, I.C.; Davalos, R.V.; et al. High-Frequency Irreversible Electroporation for Treatment of Primary Liver Cancer: A Proof-of-Principle Study in Canine Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, J.A.; Malone, R.W.; Williams, P.; Chong, W.; Acsadi, G.; Jani, A.; Felgner, P.L. Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle in vivo. Science 1990, 247, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flingai, S.; Czerwonko, M.; Goodman, J.; Kudchodkar, S.B.; Muthumani, K.; Weiner, D.B. Synthetic DNA vaccines: Improved vaccine potency by electroporation and co-delivered genetic adjuvants. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, D.J. Viral and non-viral methods for gene transfer into skeletal muscle. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2006, 9, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Gregoveric, P.; Biankinship, M.J.; Chamberlain, J.S. Viral vectors for gene transfer to striated muscle. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2004, 6, 491–498. [Google Scholar]
- Schertzer, J.D.; Plant, D.R.; Lynch, G.S. Optimizing plasmid-based gene transfer for investigating skeletal muscle structure and function. Mol. Ther. 2005, 13, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, J.M.; Wells, D.J. Electroporation for gene transfer to skeletal muscles: Current status. BioDrugs 2004, 18, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peri, D.; Deville, M.; Poignard, C.; Signori, E.; Natalini, R. Numerical optimization of plasmid DNA delivery combined with hyaluronidase injection for electroporation protocol. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 186, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schertzer, J.D.; Lynch, G.S. Plasmid-based gene transfer in mouse skeletal muscle by electroporation. Meth. Mol. Biol. 2008, 433, 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lavigne, M.D.; Yates, L.; Coxhead, P.; Górecki, D.C. Nuclear-targeted chimeric vector enhancing nonviral gene transfer into skeletal muscle of Fabry mice in vivo. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedzinski, E.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Olson, D.C.; Parker, E.A.; Park, H.; Udove, J.A.; Scollay, R.; McMahon, B.M.; Bennett, M.J. Enhanced systemic transgene expression after nonviral salivary gland transfection using a novel endonuclease inhibitor/DNA formulation. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 2133–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- DiFranco, M.; Quinonez, M.; Capote, J.; Vergara, J. DNA transfection of mammalian skeletal muscles using in vivo electroporation. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 32, 1520. [Google Scholar]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Scimeca, M.; Amadio, B.; Cortese, G.; Fanciulli, M.; Vincenzi, B.; De Luca, A.; Baldi, A. Definition of a Novel Plasmid-Based Gene Transfection Protocol of Mammalian Skeletal Muscles by Means of In Vivo Electroporation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 521, 6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlin, D.; Cemazar, M.; Cör, A.; Sersa, G.; Pogacnik, A.; Tozon, N. Electrogene therapy with interleukin-12 in canine mast cell tumors. Radiol. Oncol. 2011, 45, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cemazar, M.; Ambrozic Avgustin, J.; Pavlin, D.; Sersa, G.; Poli, A.; Krhac Levacic, A. Efficacy and safety of electrochemotherapy combined with peritumoral IL-12 gene electrotransfer of canine mast cell tumours. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2016, 15, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, C.; Svara, T.; Rocchigiani, G.; Millanta, F.; Pavlin, D.; Cemazar, M.; Lampreht Tratar, U.; Sersa, G.; Tozon, N.; Poli, A. Effects of Electrochemotherapy with Cisplatin and Peritumoral IL-12 Gene Electrotransfer on Canine Mast Cell Tumors: A Histopathologic and Immunohistochemical Study. Radiol. Oncol. 2017, 51, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglietti, F.; Michinski, S.; Emanuela, S.; Tellado, M.; Marshall, G. Electrochemotherapy immune response enhancement by gene electrotransfer using IL-2 and IL-12 genes in canine patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 61, S210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milevoj, N.; Tratar, U.L.; Nemec, A.; Brožič, A.; Žnidar, K.; Serša, G.; Čemažar, M.; Tozon, N. A combination of electrochemotherapy, gene electrotransfer of plasmid encoding canine IL-12 and cytoreductive surgery in the treatment of canine oral malignant melanoma. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 122, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellado, M.; De Robertis, M.; Montagna, D.; Giovannini, D.; Salgado, S.; Michinski, S.; Signori, E.; Maglietti, F. Electrochemotherapy Plus IL-2+IL-12 Gene Electrotransfer in Spontaneous Inoperable Stage III-IV Canine Oral Malignant Melanoma. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavazza, A.; Lubas, G.; Fridman, A.; Peruzzi, D.; Impellizeri, J.A.; Luberto, L.; Marra, E.; Roscilli, G.; Ciliberto, G.; Aurisicchio, L. Safety and efficacy of a genetic vaccine targeting telomerase plus chemotherapy for the therapy of canine B-cell lymphoma. Hum. Gene Ther. 2013, 24, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impellizeri, J.A.; Gavazza, A.; Greissworth, E.; Crispo, A.; Montella, M.; Ciliberto, G.; Lubas, G.; Aurisicchio, L. Tel-eVax: A genetic vaccine targeting telomerase for treatment of canine lymphoma. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacobino, D.; Camerino, M.; Riccardo, F.; Cavallo, F.; Tarone, L.; Martano, M.; Dentini, A.; Iussich, S.; Lardone, E.; Franci, P.; et al. Difference in outcome between curative intent vs marginal excision as a first treatment in dogs with oral malignant melanoma and the impact of adjuvant CSPG4-DNA electrovaccination: A retrospective study on 155 cases. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2021, 19, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardo, F.; Tarone, L.; Camerino, M.; Giacobino, D.; Iussich, S.; Barutello, G.; Arigoni, M.; Conti, L.; Bolli, E.; Quaglino, E.; et al. Antigen mimicry as an effective strategy to induce CSPG4-targeted immunity in dogs with oral melanoma: A veterinary trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, K.; Egberink, H.; Möstl, K.; Addie, D.; Belák, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Frymus, T.; Lloret, A.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Marsilio, F.; et al. Feline Injection-Site Sarcoma and Other Adverse Reactions to Vaccination in Cats. Viruses 2023, 15, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobromylskyj, M. Feline Soft Tissue Sarcomas: A Review of the Classification and Histological Grading, with Comparison to Human and Canine. Animals 2022, 12, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Baldi, A.; Vincenzi, B.; Bongiorni, F.; Bellelli, C.; Citro, G.; Porrello, A. Intraoperative versus postoperative electrochemotherapy in high grade soft tissue sarcomas: A preliminary study in a spontaneous feline model. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Vincenzi, B.; Citro, G.; Santini, D.; Dotsinsky, I.; Mudrov, N.; Montesarchio, V.; Laieta, M.T.; Esposito, V.; Baldi, A. Adjuvant electrochemotherapy for the treatment of incompletely excised spontaneous canine sarcomas. In Vivo 2007, 21, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Renaud, S.M.; Buglioni, S.; Carocci, F.; Dragonetti, E.; Murace, R.; Cardelli, P.; Vincenzi, B.; Baldi, A.; Citro, G. Electrochemotherapy with cisplatin enhances local control after surgical ablation of fibrosarcoma in cats: An approach to improve the therapeutic index of highly toxic chemotherapy drugs. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrigiani, F.; Pierini, A.; Lowe, R.; Simčič, P.; Lubas, G. Soft tissue sarcoma in dogs: A treatment review and a novel approach using electrochemotherapy in a case series. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2019, 17, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Vincenzi, B.; Amadio, B.; Baldi, A. Adjuvant electrochemotherapy with bleomycin and cisplatin combination for canine soft tissue sarcomas: A study of 30 cases. Open Vet. J. 2019, 9, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Vincenzi, B.; Carocci, F.; Bonichi, C.; Menicagli, F.; Baldi, A. Combination of bleomycin and cisplatin as adjuvant electrochemotherapy protocol for the treatment of incompletely excised feline injection-site sarcomas: A retrospective study. Open Vet. J. 2020, 10, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winge, M.C.G.; Kellman, L.N.; Guo, K.; Tang, J.Y.; Swetter, S.M.; Aasi, S.Z.; Sarin, K.Y.; Chang, A.L.S.; Khavari, P.A. Advances in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millanta, F.; Parisi, F.; Poli, A.; Sorelli, V.; Abramo, F. Auricular Non-Epithelial Tumors with Solar Elastosis in Cats: A Possible UV-Induced Pathogenesis. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Vincenzi, B.; Citro, G.; Tonini, G.; Dotsinsky, I.; Mudrov, N.; Baldi, A. Electrochemotherapy for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma in cats: A preliminary report. Vet. J. 2009, 179, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozon, N.; Pavlin, D.; Sersa, G.; Dolinsek, T.; Cemazar, M. Electrochemotherapy with intravenous bleomycin injection: An observational study in superficial squamous cell carcinoma in cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2014, 16, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Pizzuto, M.; Filipponi, M.; Romani, L.; Vincenzi, B.; Menicagli, F.; Lanza, A.; De Girolamo, R.; Lomonaco, R.; Fanciulli, M.; et al. Electroporation Enhances Bleomycin Efficacy in Cats with Periocular Carcinoma and Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Anjos, D.S.; Sierra, O.R.; Spugnini, E.P.; De Nardi, A.B.; Fonseca-Alves, C.E. Comparison of two different doses of bleomycin in electrochemotherapy protocols for feline cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma nonsegregated from ultraviolet light exposure. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simčič, P.; Pierini, A.; Lubas, G.; Lowe, R.; Granziera, V.; Tornago, R.; Valentini, F.; Alterio, G.; Cochi, M.; Rangel, M.M.M.; et al. A Retrospective Multicentric Study of Electrochemotherapy in the Treatment of Feline Nasal Planum Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellado, M.; Michinski, S.; Impellizeri, J.A.; Marshall, G.; Signori, E.; Maglietti, F. Electrochemotherapy using thin-needle electrode improves recovery in feline nasal planum squamous cell carcinoma—A translational model. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022, 5, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simčič, P.; Lowe, R.; Granziera, V.; Pierini, A.; Torrigiani, F.; Lubas, G. Electrochemotherapy in treatment of canine oral non-tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma. A case series report. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2020, 18, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Anjos, D.; Bueno, C.; Mattos-Junior, E.; De Nardi, A.B.; Fonseca-Alves, C.E. VEGF Expression, Cellular Infiltration, and Intratumoral Collagen Levels after Electroporation-Based Treatment of Dogs with Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Life 2021, 11, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozon, N.; Kodre, V.; Sersa, G.; Cemazar, M. Effective treatment of perianal tumors in dogs with electrochemotherapy. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Dotsinsky, I.; Mudrov, N.; Cardosi, G.; Citro, G.; D’Avino, A.; Baldi, A. Biphasic pulses enhance bleomycin efficacy in a spontaneous canine perianal tumors model. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 26, 483–487. [Google Scholar]
- Valenti, P.; Menicagli, F.; Baldi, A.; Barella, G.; Catalucci, C.; Attorri, V.; Spugnini, E.P. Evaluation of electrochemotherapy in the management of apocrine gland anal sac adenocarcinomas in dogs: A retrospective study. Open Vet. J. 2021, 11, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Dragonetti, E.; Vincenzi, B.; Onori, N.; Citro, G.; Baldi, A. Pulse-mediated chemotherapy enhances local control and survival in a spontaneous canine model of primary mucosal melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2006, 16, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellado, M.N.; Maglietti, F.H.; Michinski, S.D.; Marshall, G.R.; Signori, E. Electrochemotherapy in treatment of canine oral malignant melanoma and factors influencing treatment outcome. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 54, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Scacco, L.; Bolaffio, C.; Baldi, A. Electrochemotherapy for the treatment of cutaneous solid tumors in equids: A retrospective study. Open Vet. J. 2021, 11, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricotti, F.; Giuliodori, K.; Cataldi, I.; Campanati, A.; Ganzetti, G.; Ricotti, G.; Offidani, A. Electrochemotherapy: An effective local treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous melanoma metastases. Dermatol. Ther. 2014, 27, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunte, C.; Letulé, V.; Gehl, J.; Dahlstroem, K.; Curatolo, P.; Rotunno, R.; Muir, T.; Occhini, A.; Bertino, G.; Powell, B.; et al. Electrochemotherapy in the treatment of metastatic malignant melanoma: A prospective cohort study by InspECT. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk Hansen, H.; Bourke, M.; Stigaard, T.; Clover, J.; Buckley, M.; O’Riordain, M.; Winter, D.C.; Hjorth Johannesen, H.; Hansen, R.H.; Heebøll, H.; et al. Electrochemotherapy for Colorectal Cancer Using Endoscopic Electroporation: A Phase 1 Clinical Study. Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E124–E132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeland, C.; Baeksgaard, L.; Johannesen, H.H.; Löfgren, J.; Plaschke, C.C.; Svendsen, L.B.; Gehl, J.; Achiam, M.P. Endoscopic electrochemotherapy for esophageal cancer: A phase I clinical study. Endosc. Int. Open. 2018, 6, E727–E734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehl, J.; Sersa, G.; Garbay, J.; Soden, D.; Rudolf, Z.; Marty, M.; O’Sullivan, G.; Geertsen, P.F.; Mir, L.M. Results of the ESOPE (European Standard Operating Procedures on Electrochemotherapy) study: Efficient, highly tolerable and simple palliative treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases from cancers of any histology. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 464s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehl, J.; Sersa, G.; Matthiessen, L.W.; Muir, T.; Soden, D.; Occhini, A.; Quaglino, P.; Curatolo, P.; Campana, L.G.; Kunte, C.; et al. Updated standard operating procedures for electrochemotherapy of cutaneous tumours and skin metastases. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, H.; Matthiessen, L.W.; Wooler, G.; Gehl, J. Calcium electroporation for treatment of cutaneous metastases; a randomized double-blinded phase II study, comparing the effect of calcium electroporation with electrochemotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2017, 57, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaschke, C.C.; Gehl, J.; Johannesen, H.H.; Fischer, B.M.; Kjaer, A.; Lomholt, A.F.; Wessel, I. Calcium electroporation for recurrent head and neck cancer: A clinical phase I study. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2019, 4, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galant, L.; Delverdier, M.; Lucas, M.N.; Raymond-Letron, I.; Teissie, J.; Tamzali, Y. Calcium electroporation: The bioelectrochemical treatment of spontaneous equine skin tumors results in a local necrosis. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 129, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, S.K.; Gehl, J.; Tramm, T.; Thoefner, M.S. Calcium Electroporation of Equine Sarcoids. Animals 2020, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri Kenari, A.; Cheng, L.; Hill, A.F. Methods for loading therapeutics into extracellular vesicles and generating extracellular vesicles mimetic-nanovesicles. Methods 2020, 177, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hao, M.; Li, W.; Mao, X.; Mo, L.; Yang, C.; Ding, X.; et al. Encapsulation of Nano-Bortezomib in Apoptotic Stem Cell-Derived Vesicles for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. Small 2023, 19, e2301748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Logozzi, M.; Di Raimo, R.; Mizzoni, D.; Fais, S. A Role of Tumor-Released Exosomes in Paracrine Dissemination and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logozzi, M.; Spugnini, E.P.; Mizzoni, D.; Di Raimo, R.; Fais, S. Extracellular acidity and increased exosome release as key phenotypes of malignant tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, T.; Zhang, X.; Bie, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Hakeem, A.; Hu, J.; Gan, L.; Santos, H.A.; et al. Tumor exosome-based nanoparticles are efficient drug carriers for chemotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulin, C.; Crupi, M.J.F.; Ilkow, C.S.; Bell, J.C.; Boulton, S. Extracellular Vesicles and Viruses: Two Intertwined Entities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Qi, Y.X.; Zhu, C.H.; Li, A.; Pei, D.D. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for treatment of bone loss within periodontitis in pre-clinical animal models: A meta-analysis. BMC Oral. Health 2023, 23, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Manrique, P.; Matos, M.; Gutiérrez, G.; Pazos, C.; Blanco-López, M.C. Therapeutic biomaterials based on extracellular vesicles: Classification of bio-engineering and mimetic preparation routes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1422676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, G.; Cauda, V. Biomimicking Extracellular Vesicles with Fully Artificial Ones: A Rational Design of EV-BIOMIMETICS toward Effective Theranostic Tools in Nanomedicine. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 5924–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, S.; Di Martino, D.; Cerri, S.; Genta, I.; Dorati, R.; Bertino, G.; Benazzo, M.; Conti, B. Investigation and Comparison of Active and Passive Encapsulation Methods for Loading Proteins into Liposomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghayari, S. Electroporation combined with intelligent drug delivery promising new and clean approach to cancer treatment. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Title | Phase Study | Treatment Modality | Clinical Trials.gov Identifiers/References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bleomycin with or without Electroporation Therapy in Patients with Stage III or Stage IV Melanoma | I | Electroporation plus bleomycin | NCT00006035 |
| Electrochemotherapy: An Effective Local Treatment of Cutaneous and Subcutaneous Melanoma Metastases | I | Electroporation with Cliniporator plus bleomycin | Ricotti et al., 2014 [74] |
| Electrochemotherapy in the Treatment of Metastatic Malignant Melanoma: A Prospective Cohort Study by InspECT | Electroporation plus bleomycin | Kunte et al., 2017 [75] | |
| ECT-Pembrolizumab in Patients with Unresectable Melanoma with Superficial or Superficial and Visceral Metastases | II | Electroporation with Cliniporator plus Pembrolizumab and bleomycin | NCT03448666 |
| Electrochemotherapy for Colorectal Cancer Using Endoscopic Electroporation: A Phase 1 Clinical Study | I | Electroporation plus bleomycin | Hansen et al., 2020 [76] |
| Neoadjuvant Electrochemotherapy for Colorectal Cancer—a Randomized Controlled Trial | II | Electroporation plus bleomycin | NCT04816045 |
| Electrochemotherapy of Gynecological Cancer (GynECT) | II | Electroporation plus bleomycin or cisplatin | NCT04760327 |
| Electrochemotherapy of Posterior Resection Surface for Lowering Disease Recurrence Rate in Pancreatic Cancer (PanECT Study) | I/II | Electroporation with Cliniporator Vitae plus bleomycin | NCT04281290 |
| Endoscopic-assisted Electrochemotherapy in addition to Neoadjuvant Treatment of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer | II | Electroporation with EndoVE plus bleomycin | NCT03040180 |
| Treatment of Primary Liver Tumors with Electrochemotherapy (ECT-HCC) | I/II | Electroporation with Cliniporator Vitae plus bleomycin | NCT02291133 |
| Electrochemotherapy for Non-curable Gastric Cancer | I | Electroporation plus bleomycin | NCT0413907 |
| Electrochemotherapy on Head and Neck Cancer | II | Electroporation with Cliniporator plus bleomycin | NCT02549742 |
| Electrochemotherapy for Chest Wall Recurrence of Breast Cancer: Present Challenges and Future Prospects | II | Electroporation with Cliniporator plus bleomycin | NCT000744653 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spugnini, E.P.; Condello, M.; Crispi, S.; Baldi, A. Electroporation in Translational Medicine: From Veterinary Experience to Human Oncology. Cancers 2024, 16, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051067
Spugnini EP, Condello M, Crispi S, Baldi A. Electroporation in Translational Medicine: From Veterinary Experience to Human Oncology. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051067
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpugnini, Enrico P., Maria Condello, Stefania Crispi, and Alfonso Baldi. 2024. "Electroporation in Translational Medicine: From Veterinary Experience to Human Oncology" Cancers 16, no. 5: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051067
APA StyleSpugnini, E. P., Condello, M., Crispi, S., & Baldi, A. (2024). Electroporation in Translational Medicine: From Veterinary Experience to Human Oncology. Cancers, 16(5), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051067










