Correction: Gresseau et al. A Signaling Crosstalk Links SNAIL to the 37/67 kDa Laminin-1 Receptor Ribosomal Protein SA and Regulates the Acquisition of a Cancer Stem Cell Molecular Signature in U87 Glioblastoma Neurospheres. Cancers 2022, 14, 5944
Error in Figure
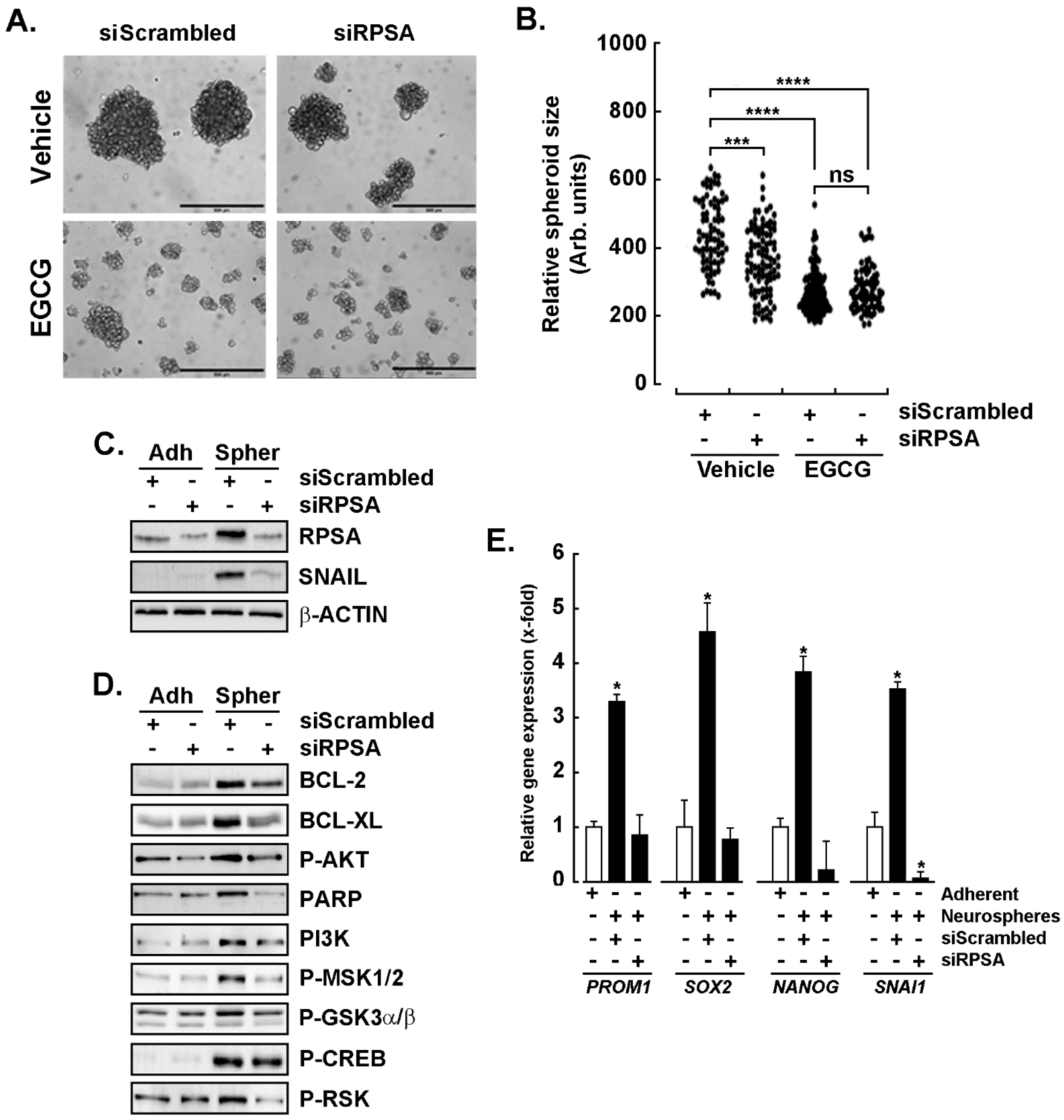
Reference
- Gresseau, L.; Roy, M.-E.; Duhamel, S.; Annabi, B. A signaling crosstalk links SNAIL to the 37/67 kDa laminin-1 receptor ribosomal protein SA and regulates the acquisition of a cancer stem cell molecular signature in U87 glioblastoma neurospheres. Cancers 2022, 14, 5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gresseau, L.; Roy, M.-E.; Duhamel, S.; Annabi, B. Correction: Gresseau et al. A Signaling Crosstalk Links SNAIL to the 37/67 kDa Laminin-1 Receptor Ribosomal Protein SA and Regulates the Acquisition of a Cancer Stem Cell Molecular Signature in U87 Glioblastoma Neurospheres. Cancers 2022, 14, 5944. Cancers 2024, 16, 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051065
Gresseau L, Roy M-E, Duhamel S, Annabi B. Correction: Gresseau et al. A Signaling Crosstalk Links SNAIL to the 37/67 kDa Laminin-1 Receptor Ribosomal Protein SA and Regulates the Acquisition of a Cancer Stem Cell Molecular Signature in U87 Glioblastoma Neurospheres. Cancers 2022, 14, 5944. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051065
Chicago/Turabian StyleGresseau, Loraine, Marie-Eve Roy, Stéphanie Duhamel, and Borhane Annabi. 2024. "Correction: Gresseau et al. A Signaling Crosstalk Links SNAIL to the 37/67 kDa Laminin-1 Receptor Ribosomal Protein SA and Regulates the Acquisition of a Cancer Stem Cell Molecular Signature in U87 Glioblastoma Neurospheres. Cancers 2022, 14, 5944" Cancers 16, no. 5: 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051065
APA StyleGresseau, L., Roy, M.-E., Duhamel, S., & Annabi, B. (2024). Correction: Gresseau et al. A Signaling Crosstalk Links SNAIL to the 37/67 kDa Laminin-1 Receptor Ribosomal Protein SA and Regulates the Acquisition of a Cancer Stem Cell Molecular Signature in U87 Glioblastoma Neurospheres. Cancers 2022, 14, 5944. Cancers, 16(5), 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051065




