Induction of Multiple Alternative Mitogenic Signaling Pathways Accompanies the Emergence of Drug-Tolerant Cancer Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Development of Features of Drug Tolerance in PC9 and SKMEL28 Cells
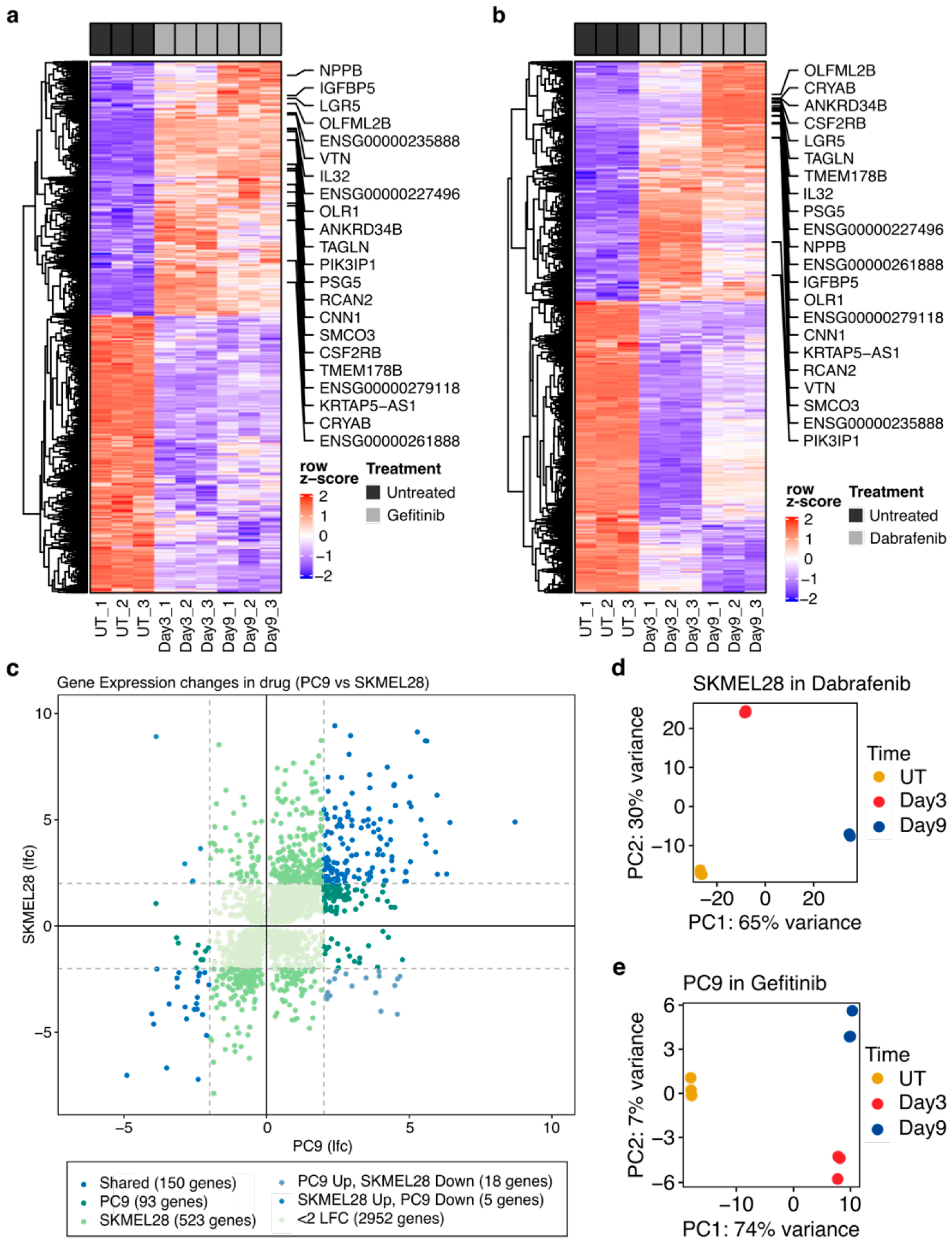
2.2. Numerous Transcriptional Alterations Are Shared between EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer Cells during EGFR Inhibition and BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Cells during BRAF Inhibition
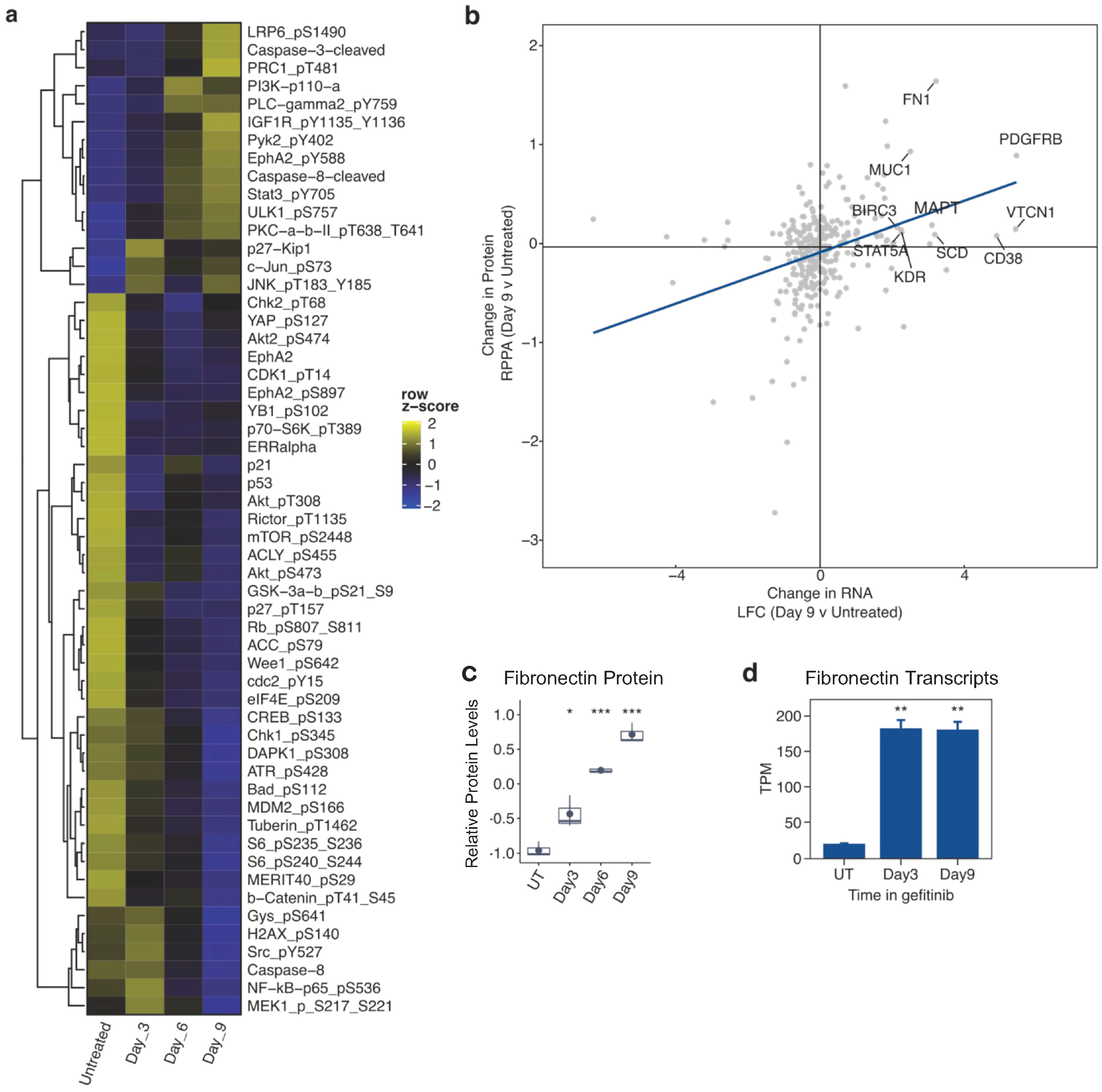
2.3. Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Alterations Accompany the Development of Drug Tolerance
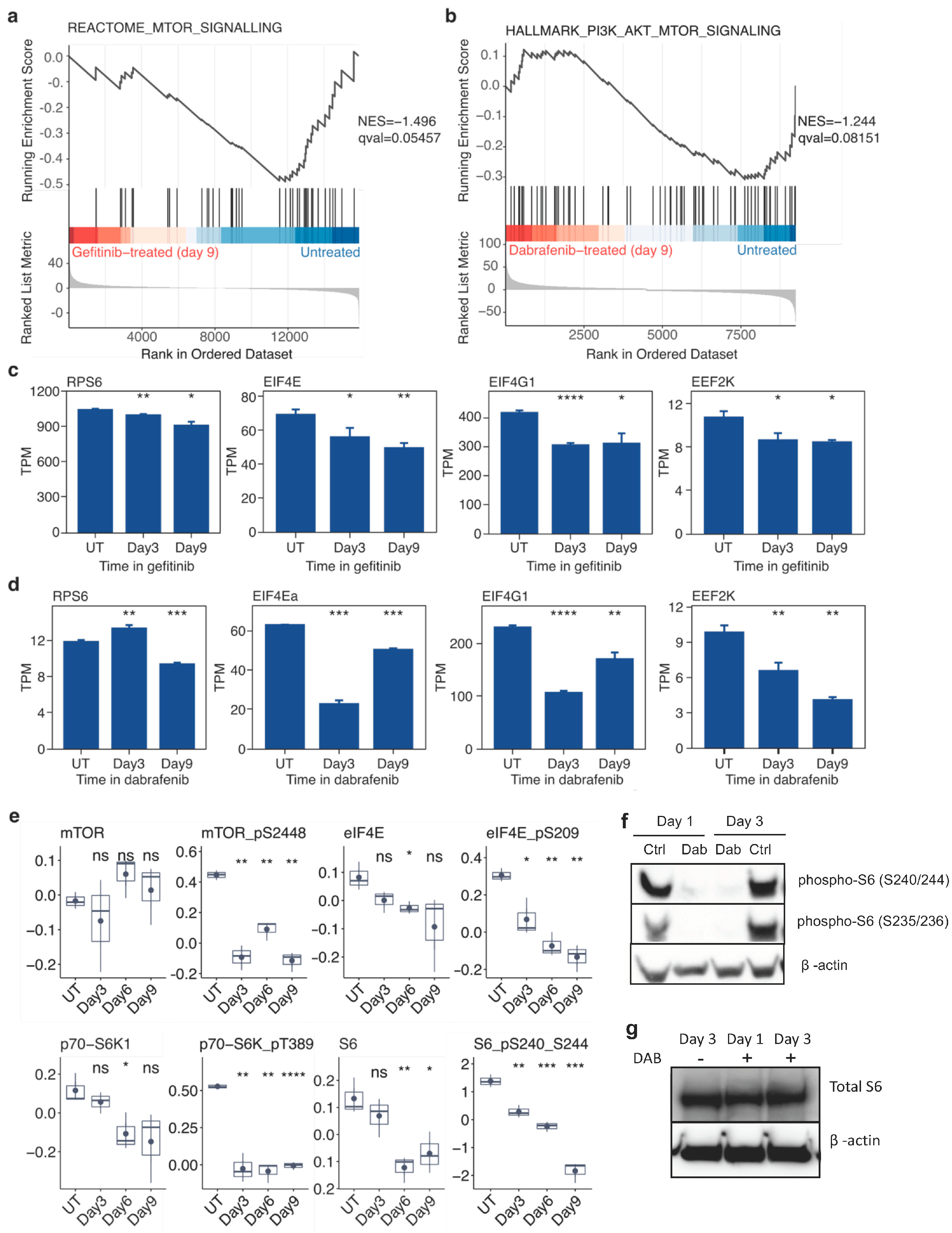
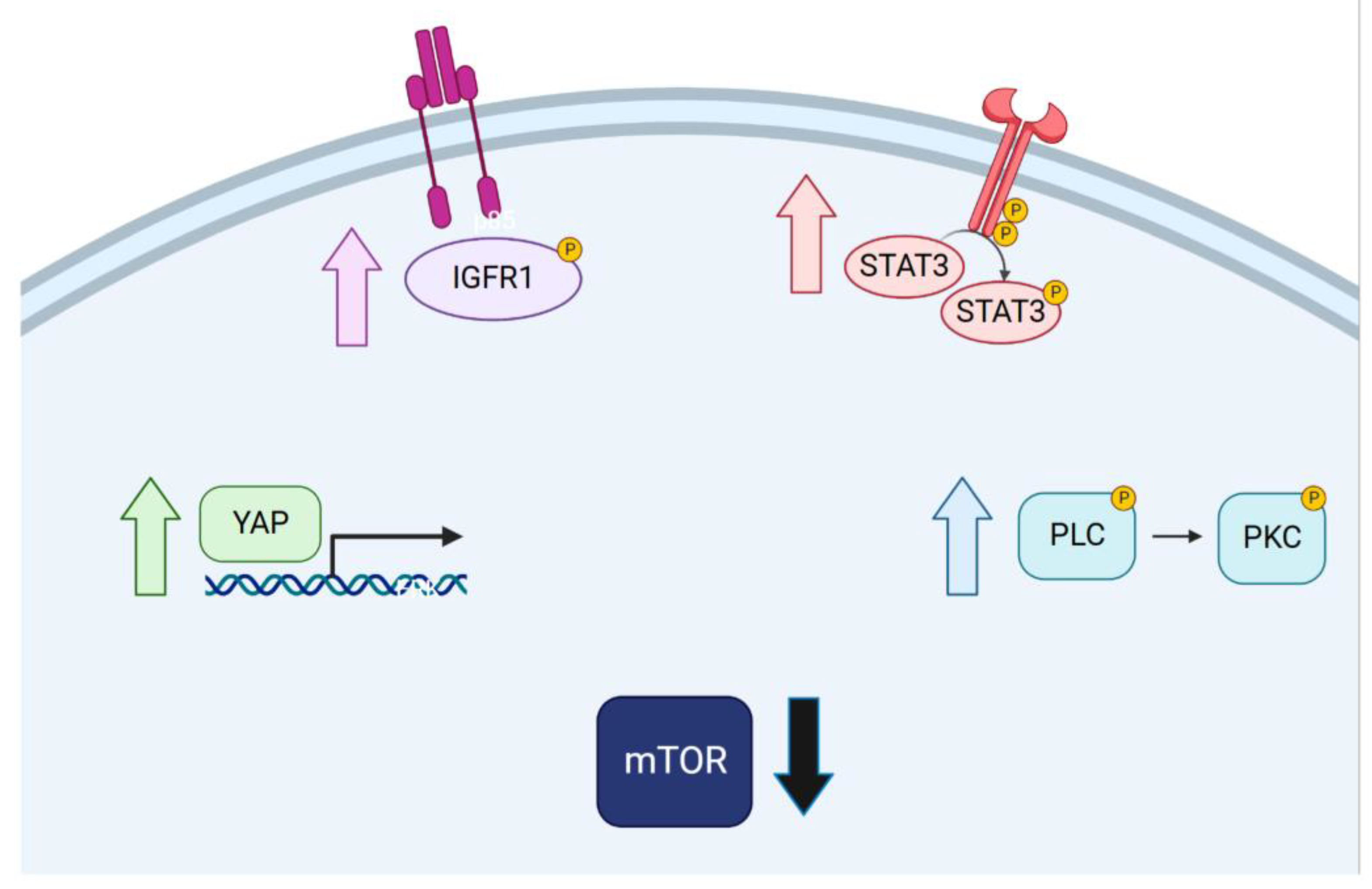
2.4. Targeted Inhibition of Mutationally Activated Oncogenes Induces Sustained mTOR-Pathway Suppression
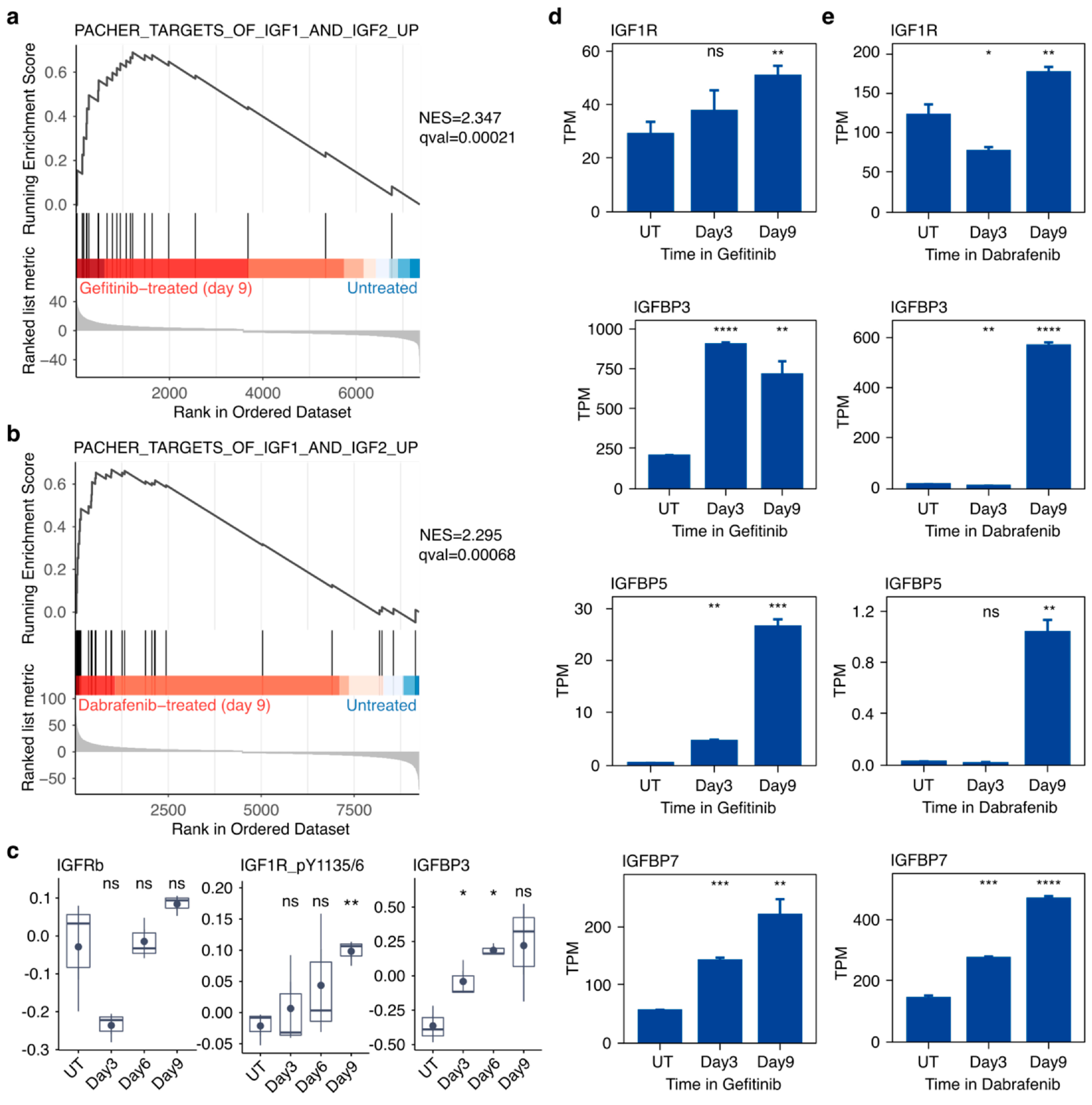
2.5. Targeted Inhibition of Mutationally Activated Oncogenes Induces IGF-Pathway Activation
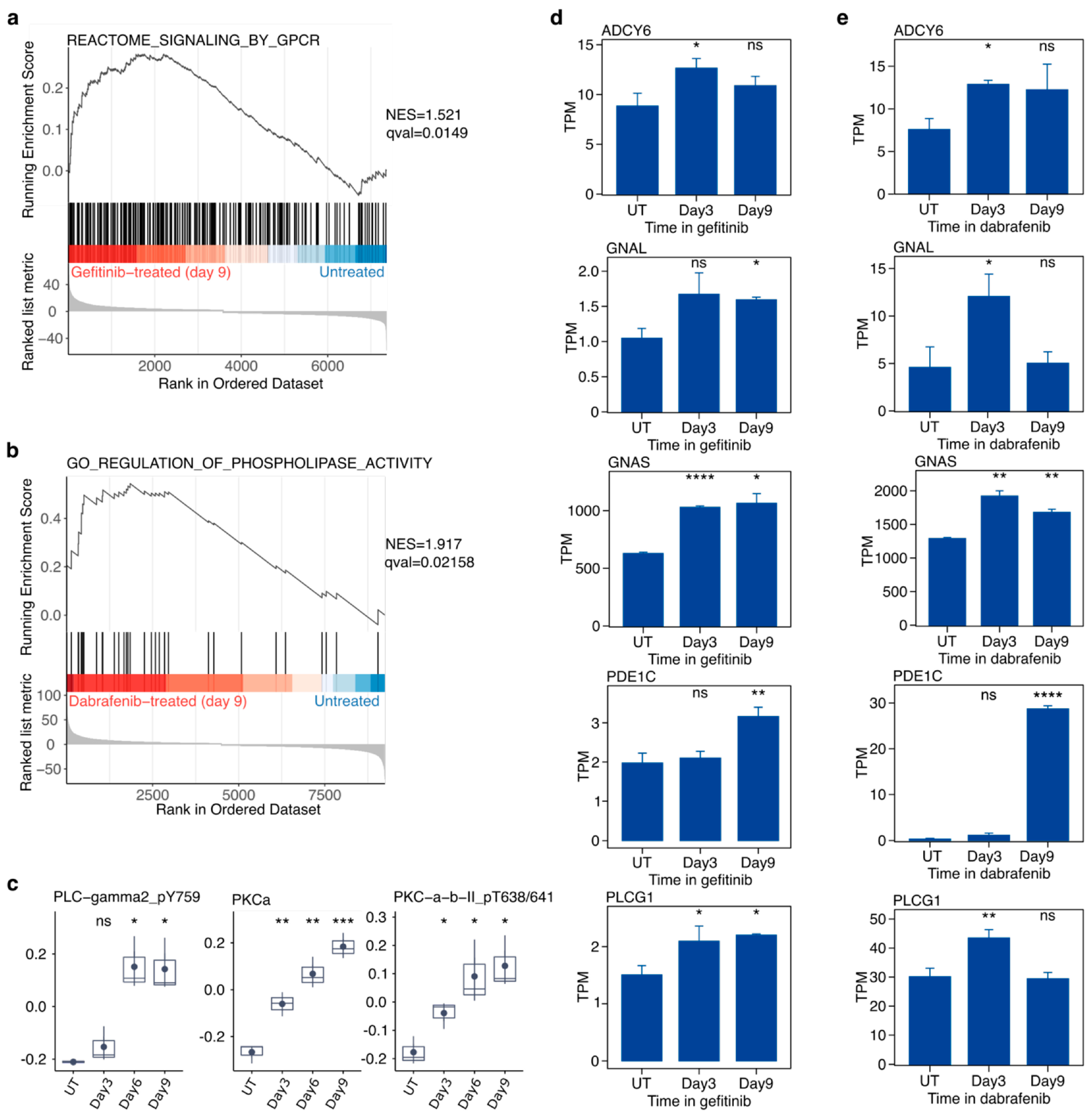
2.6. Targeted Inhibition of Mutationally Activated Oncogenes Induces PLC/PKC Signaling
2.7. Targeted Inhibition of Mutationally Activated Oncogenes Induces STAT3 Activation and YAP Activation
2.8. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals Simultaneous Up-Regulation of Markers of Multiple Alternate Mitogenic Signaling Pathways
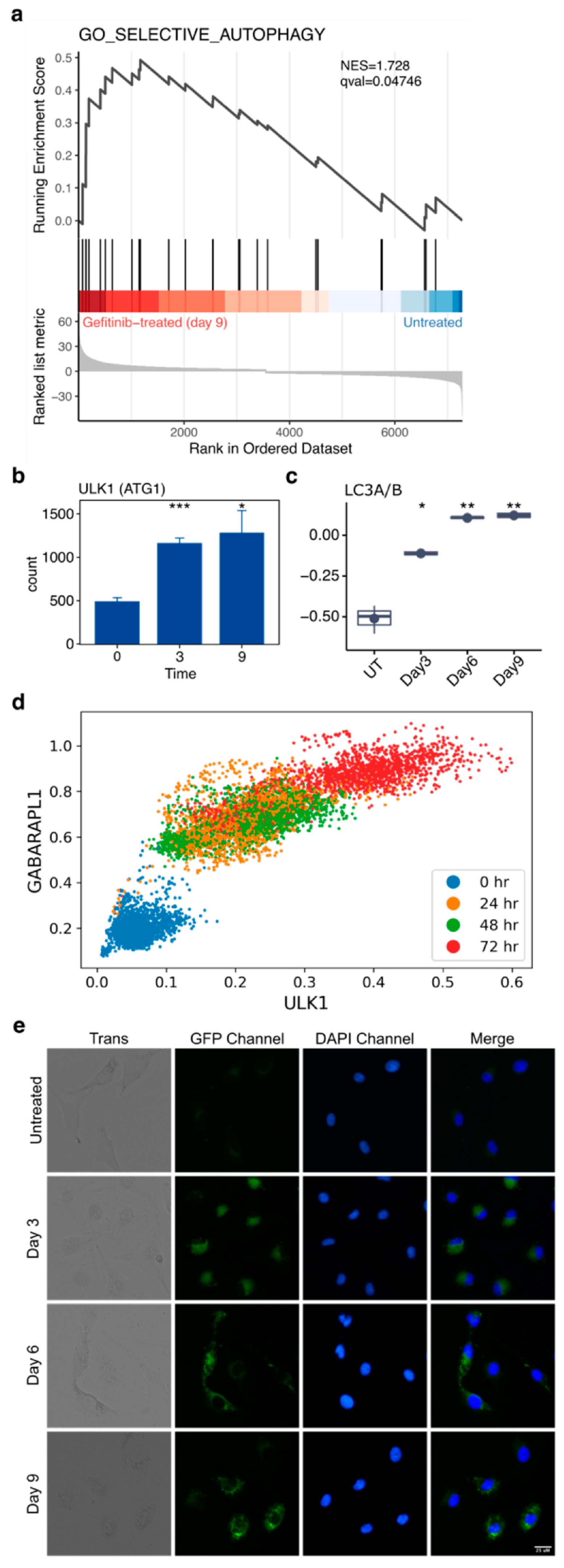
2.9. Autophagy Accompanies the Development of Drug Tolerance and Can Be Disrupted with Hydroxychloroquine to Reduce the Number of Drug-Tolerant Cells
2.10. Disruption of ATG5 Results in Decreased Autophagic Flux but Does Not Enhance Gefitinib Killing of PC9 Cells
2.11. Pharmacologic but Not Genetic Inhibition of BCL-XL Results in Increased Gefitinib Efficacy
2.12. Drug-Tolerant Cells Show Significant Gene Expression Changes Affecting AXL/GAS6, Enzymes That Utilize Glutathione as a Co-Factor, and Low-Fidelity Polymerases
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Methods
5.1. Cell Culture
5.2. Drug Co-Treatment Studies
5.3. RNA Preparation and Bulk RNA-Seq
5.4. Bulk RNA-Seq Data Analysis and Visualization
5.5. Single-Cell RNA-Seq
5.6. scRNA-Seq Data Pre-Processing
5.7. scRNA-Seq Analysis
5.8. Reverse Phase Protein Array Analysis
5.9. Antibodies and Immunoblotting
5.10. CRISPR Studies
5.11. Visualizing Autophagy and Senescence
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, S.V.; Lee, D.Y.; Li, B.; Quinlan, M.P.; Takahashi, F.; Maheswaran, S.; McDermott, U.; Azizian, N.; Zou, L.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 2010, 141, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, S.M.; Dunagin, M.C.; Torborg, S.R.; Torre, E.A.; Emert, B.; Krepler, C.; Beqiri, M.; Sproesser, K.; Brafford, P.A.; Xiao, M.; et al. Rare cell variability and drug-induced reprogramming as a mode of cancer drug resistance. Nature 2017, 546, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Benelli, M.; Karthaus, W.R.; Hoover, E.; Chen, C.C.; Wongvipat, J.; Ku, S.Y.; Gao, D.; Cao, Z.; et al. SOX2 promotes lineage plasticity and antiandrogen resistance in TP53- and RB1-deficient prostate cancer. Science 2017, 355, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.A.; Jen, J.; Jiang, S.; Sayad, A.; Mer, A.S.; Brown, K.R.; Nixon, A.M.L.; Dhabaria, A.; Tang, K.H.; Venet, D.; et al. Ontogeny and Vulnerabilities of Drug-Tolerant Persisters in HER2+ Breast Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 1022–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy, C.; Li, M.; Teater, M.; Meydan, C.; Garrett-Bakelman, F.E.; Lee, T.C.; Chin, C.R.; Durmaz, C.; Kawabata, K.C.; Dhimolea, E.; et al. Chemotherapy Induces Senescence-Like Resilient Cells Capable of Initiating AML Recurrence. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1542–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesch, A.; Vultur, A.; Bogeski, I.; Wang, H.; Zimmermann, K.M.; Speicher, D.; Korbel, C.; Laschke, M.W.; Gimotty, P.A.; Philipp, S.E.; et al. Overcoming intrinsic multidrug resistance in melanoma by blocking the mitochondrial respiratory chain of slow-cycling JARID1B(high) cells. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanos, H.F.; Hata, A.N. Emerging Insights into Targeted Therapy-Tolerant Persister Cells in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Somwar, R.; Politi, K.; Balak, M.; Chmielecki, J.; Jiang, X.; Pao, W. Induction of BIM is essential for apoptosis triggered by EGFR kinase inhibitors in mutant EGFR-dependent lung adenocarcinomas. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi-Sichani, M.; Becker, V.; Izar, B.; Baker, G.J.; Lin, J.R.; Boswell, S.A.; Shah, P.; Rotem, A.; Garraway, L.A.; Sorger, P.K. Adaptive resistance of melanoma cells to RAF inhibition via reversible induction of a slowly dividing de-differentiated state. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2017, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, D.R.; Garbett, S.P.; Frick, P.L.; Quaranta, V. Fractional proliferation: A method to deconvolve cell population dynamics from single-cell data. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tian, C.; Hoffman, T.E.; Jacobsen, N.K.; Spencer, S.L. Melanoma subpopulations that rapidly escape MAPK pathway inhibition incur DNA damage and rely on stress signalling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, Y.; Tsabar, M.; Cuoco, M.S.; Amir-Zilberstein, L.; Cabanos, H.F.; Hutter, J.C.; Hu, B.; Thakore, P.I.; Tabaka, M.; Fulco, C.P.; et al. Cycling cancer persister cells arise from lineages with distinct programs. Nature 2021, 596, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarangelo, T.; Sisinni, L.; Trino, S.; Calice, G.; Simeon, V.; Landriscina, M. IL6/STAT3 axis mediates resistance to BRAF inhibitors in thyroid carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 433, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Zhuang, G.; Cao, Y.; Du, P.; Kim, H.J.; Settleman, J. Drug resistance via feedback activation of Stat3 in oncogene-addicted cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoof, S.; Mulford, I.J.; Frisco-Cabanos, H.; Nangia, V.; Timonina, D.; Labrot, E.; Hafeez, N.; Bilton, S.J.; Drier, Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Targeting FGFR overcomes EMT-mediated resistance in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6399–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, H.; Yamada, T.; Wang, R.; Tanimura, K.; Adachi, Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Tanimoto, A.; Takeuchi, S.; Araujo, L.H.; Boroni, M.; et al. AXL confers intrinsic resistance to osimertinib and advances the emergence of tolerant cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.N.; Bhatt, R.; Rotow, J.; Rohrberg, J.; Olivas, V.; Wang, V.E.; Hemmati, G.; Martins, M.M.; Maynard, A.; Kuhn, J.; et al. Aurora kinase A drives the evolution of resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauthe, M.; Orhon, I.; Rocchi, C.; Zhou, X.; Luhr, M.; Hijlkema, K.J.; Coppes, R.P.; Engedal, N.; Mari, M.; Reggiori, F. Chloroquine inhibits autophagic flux by decreasing autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1435–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wible, D.J.; Chao, H.P.; Tang, D.G.; Bratton, S.B. ATG5 cancer mutations and alternative mRNA splicing reveal a conjugation switch that regulates ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L1 complex assembly and autophagy. Cell Discov. 2019, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Doornebal, E.J.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Giorgadze, N.; Wentworth, M.; Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg, H.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D.; Tchkonia, T.; Kirkland, J.L. New agents that target senescent cells: The flavone, fisetin, and the BCL-X(L) inhibitors, A1331852 and A1155463. Aging (Albany N. Y.) 2017, 9, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lee, J.C.; Lin, L.; Olivas, V.; Au, V.; LaFramboise, T.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Wang, X.; Levine, A.D.; Rho, J.K.; et al. Activation of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted therapy in lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, A.; Belugali Nataraj, N.; Lee, J.S.; Zhitomirsky, B.; Oren, Y.; Oster, S.; Lindzen, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Will, R.; Ghosh, S.; et al. AXL and Error-Prone DNA Replication Confer Drug Resistance and Offer Strategies to Treat EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2666–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangauer, M.J.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Ryan, M.J.; Bole, D.; Eaton, J.K.; Matov, A.; Galeas, J.; Dhruv, H.D.; Berens, M.E.; Schreiber, S.L.; et al. Drug-tolerant persister cancer cells are vulnerable to GPX4 inhibition. Nature 2017, 551, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Crisafulli, G.; Sogari, A.; Reilly, N.M.; Arena, S.; Lamba, S.; Bartolini, A.; Amodio, V.; Magri, A.; Novara, L.; et al. Adaptive mutability of colorectal cancers in response to targeted therapies. Science 2019, 366, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, D.R.; Gui, P.; Mayekar, M.K.; Law, E.K.; Pich, O.; Bailey, C.; Boumelha, J.; Kerr, D.L.; Blakely, C.M.; Manabe, T.; et al. The role of APOBEC3B in lung tumor evolution and targeted cancer therapy resistance. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isozaki, H.; Sakhtemani, R.; Abbasi, A.; Nikpour, N.; Stanzione, M.; Oh, S.; Langenbucher, A.; Monroe, S.; Su, W.; Cabanos, H.F.; et al. Therapy-induced APOBEC3A drives evolution of persistent cancer cells. Nature 2023, 620, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, N.M.G.; Becerra, J.N.; McKinney, B.J.; DiMarco, A.V.; Wu, F.; Fitzgibbon, M.; Alvarez, J.V. APOBEC3 activity promotes the survival and evolution of drug-tolerant persister cells during acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakov, N. Protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms in cancer, tumor promotion and tumor suppression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 48, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, J.; Vultur, A.; Lee, J.T.; Somasundaram, R.; Fukunaga-Kalabis, M.; Cipolla, A.K.; Wubbenhorst, B.; Xu, X.; Gimotty, P.A.; Kee, D.; et al. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and IGF-1R/PI3K. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Tian, Y.; Buettner, R.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Horne, D.; Dellinger, T.H.; Han, E.S.; Jove, R.; et al. Synergistic anti-tumor effect of combined inhibition of EGFR and JAK/STAT3 pathways in human ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurppa, K.J.; Liu, Y.; To, C.; Zhang, T.; Fan, M.; Vajdi, A.; Knelson, E.H.; Xie, Y.; Lim, K.; Cejas, P.; et al. Treatment-Induced Tumor Dormancy through YAP-Mediated Transcriptional Reprogramming of the Apoptotic Pathway. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 104–122.112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.B.; Sun, H.; Robichaux, J.; Pfeifer, M.; McDermott, U.; Travers, J.; Diao, L.; Xi, Y.; Tong, P.; Shen, L.; et al. A YAP/FOXM1 axis mediates EMT-associated EGFR inhibitor resistance and increased expression of spindle assembly checkpoint components. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Song, Y.; Quach, C.; Guo, H.; Jang, G.B.; Maazi, H.; Zhao, S.; Sands, N.A.; Liu, Q.; In, G.K.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of autophagy-lysosomal function in BRAF-driven melanoma progression and chemoresistance. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poojan, S.; Bae, S.H.; Min, J.W.; Lee, E.Y.; Song, Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Sim, H.W.; Kang, E.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, H.O.; et al. Cancer cells undergoing epigenetic transition show short-term resistance and are transformed into cells with medium-term resistance by drug treatment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Lung | Melanoma | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | p-Val | logFC | p-Val | logFC |
| APOBEC3A | 0.38 | 1.47 | 0.13 | 0.59 |
| APOBEC3B | 0.02 | 2.16 | 2 × 10−3 | 0.38 |
| AXL | 0.01 | 0.65 | 9 × 10−5 | 15.98 |
| GAS6 | 2 × 10−3 | 2.36 | 9 × 10−5 | 4.93 |
| GPX4 | 0.06 | 1.30 | 0.09 | 1.28 |
| GSR | 0.08 | 0.79 | 0.02 | 1.43 |
| GSS | 0.94 | 1.01 | 0.02 | 0.61 |
| GSTA4 | 0.00 | 2.51 | 0.00 | 3.60 |
| GSTCD | 0.01 | 0.67 | 0.01 | 0.75 |
| GSTK1 | 0.01 | 2.03 | 0.68 | 0.95 |
| GSTM1 | 1 × 10−3 | 4.93 | 0.25 | 0.63 |
| GSTM2 | 9 × 10−5 | 4.86 | 0.09 | 1.27 |
| GSTM3 | 0.01 | 2.67 | 0.01 | 1.63 |
| GSTM4 | 1 × 10−3 | 7.18 | 0.02 | 0.65 |
| GSTO1 | 0.17 | 0.83 | 1 × 10−3 | 0.19 |
| GSTO2 | 0.14 | 0.65 | 0.04 | 2.16 |
| GSTP1 | 0.13 | 1.22 | 0.69 | 0.95 |
| GSTZ1 | 0.18 | 1.25 | 0.64 | 1.09 |
| MGST1 | 0.34 | 0.89 | 0.33 | 0.89 |
| MGST2 | 0.82 | 1.04 | 0.00 | 0.23 |
| MGST3 | 0.04 | 1.73 | 0.29 | 0.86 |
| POLE | 0.05 | 0.72 | 2 × 10−3 | 0.27 |
| POLE2 | 0.01 | 0.56 | 4 × 10−3 | 0.34 |
| POLE3 | 4 × 10−3 | 0.62 | 0.11 | 1.24 |
| POLE4 | 0.32 | 0.83 | 0.01 | 0.61 |
| POLH | 0.17 | 0.81 | 0.17 | 0.82 |
| POLI | 0.72 | 1.04 | 8 × 10−4 | 2.10 |
| POLK | 0.18 | 0.83 | 0.01 | 1.57 |
| POLQ | 5 × 10−3 | 0.54 | 2 × 10−3 | 0.35 |
| RAD18 | 0.04 | 0.71 | 0.02 | 1.45 |
| REV1 | 0.32 | 0.86 | 0.44 | 1.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Celeste, F.V.; Powers, S. Induction of Multiple Alternative Mitogenic Signaling Pathways Accompanies the Emergence of Drug-Tolerant Cancer Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051001
Celeste FV, Powers S. Induction of Multiple Alternative Mitogenic Signaling Pathways Accompanies the Emergence of Drug-Tolerant Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051001
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeleste, Frank V., and Scott Powers. 2024. "Induction of Multiple Alternative Mitogenic Signaling Pathways Accompanies the Emergence of Drug-Tolerant Cancer Cells" Cancers 16, no. 5: 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051001
APA StyleCeleste, F. V., & Powers, S. (2024). Induction of Multiple Alternative Mitogenic Signaling Pathways Accompanies the Emergence of Drug-Tolerant Cancer Cells. Cancers, 16(5), 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16051001






