Outcome of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab Combination Therapy in High-Risk Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Best Tumor Responses
3.3. Disease Control Rate
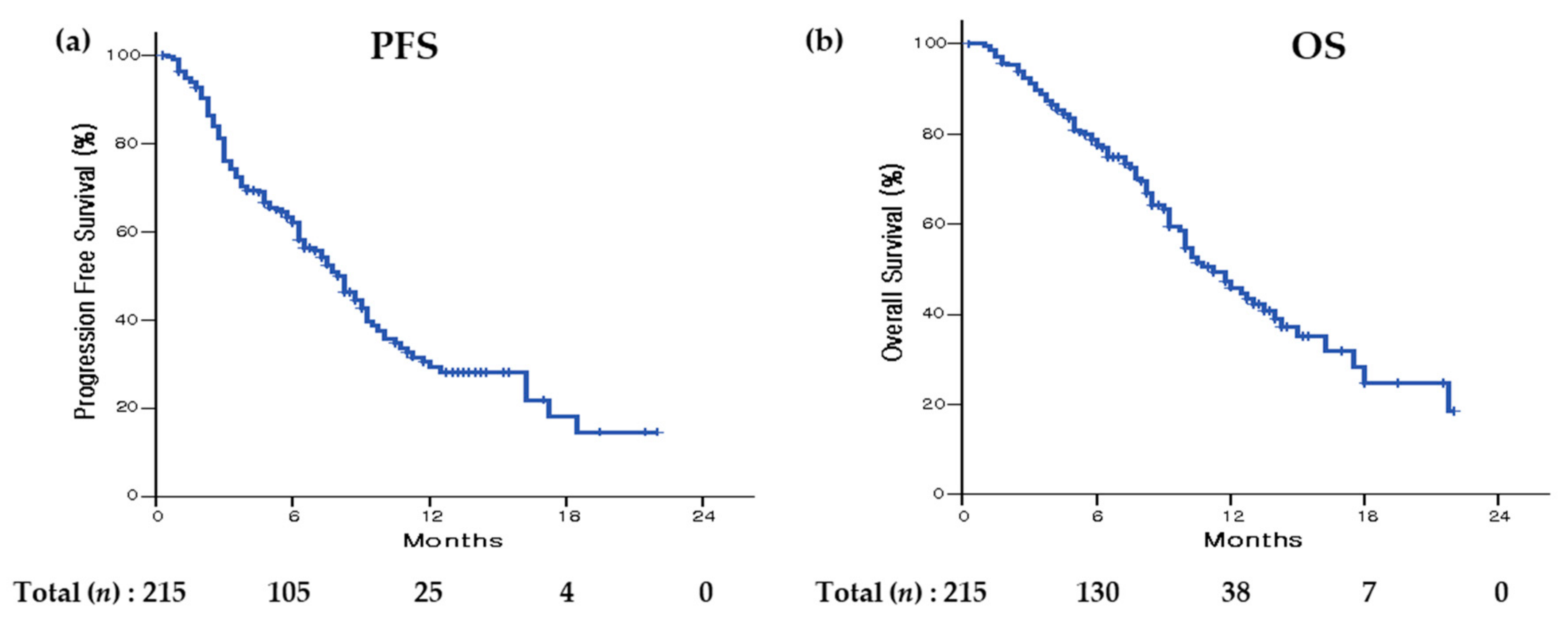
3.4. Progression-Free Survival
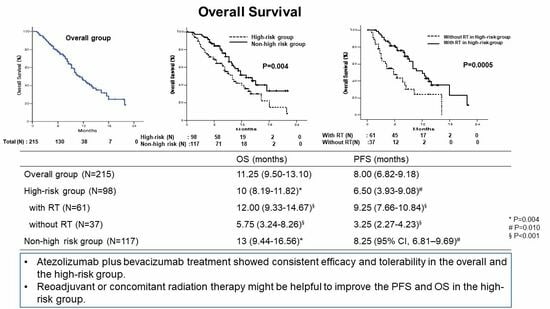
3.5. Overall Survival
3.6. Adverse Events
3.7. Outcome after ATE + BEV Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Bsc, M.F.B.; Me, J.F.; Soerjomataram, M.I.; et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.G.; Farinati, F.; Ciccarese, F.; Pecorelli, A.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Di Marco, M.; Benvegnù, L.; Caturelli, E.; Zoli, M.; Borzio, F.; et al. Prognosis of untreated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 61, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Lau, G.; Kudo, M.; Chan, S.L.; Kelley, R.K.; Furuse, J.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Kang, Y.-K.; Dao, T.V.; Toni, E.N.D.; et al. Tremelimumab plus Durvalumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.L.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Lim, H.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; et al. Updated efficacy and safety data from IMbrave150: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs. sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, I.; Sanchiz, L.; Legidos-García, M.E.; Murillo-Llorente, M.T.; Pérez-Bermejo, M. Atezolizumab and Bevacizumab Combination Therapy in the Treatment of Advanced Hepatocellular Cancer. Cancers 2023, 16, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Huang, W.-T.; Lee, M.-Y.; Tsao, C.-J.; Feng, Y.-H. Bevacizumab and Atezolizumab for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Real-world Data in Taiwan-Tainan Medical Oncology Group H01 Trial. In Vivo 2023, 37, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, M.; Inoue, M.; Ogasawara, S.; Maruta, S.; Okubo, T.; Itokawa, N.; Iino, Y.; Obu, M.; Haga, Y.; Seki, A.; et al. Clinical effects and emerging issues of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma from Japanese real-world practice. Cancer 2023, 129, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Krishna, V.; Kumar, K.; Sharma, M.; Patodiya, B.; Khan, A.; Shaik, S.; Pasumarthy, A.; Chhabra, P.; Kumar Da, P.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Atezolizumab-Bevacizumab in Real World: The First Indian Experience. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2023, 13, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhampalwar, S.; Choudhary, N.S.; Saraf, N.; Bhangui, P.; Soin, A.S. Atezolizumab and Bevacizumab for Treatment of Patients with Unresectable/Non-transplantable Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Real-World Single Center Experience from North India. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2024, 14, 101219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, R.; Ma, H.; Zuo, S. Efficacy and safety of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in the real world: A single-arm meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.; Kudo, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Breder, Y.; Cheng, A.L.; et al. Updated efficacy and safety by risk status in patients (pts) receiving atezolizumab (atezo) + bevacizumab (bev) vs. sorafenib (sor) as first-line treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Cancer Res. 2021, 81, CT009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Liver Cancer Association. 2018 Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut Liver 2019, 13, 227–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Izaki, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Mayahara, H.; Morita, Y.; Yoden, E.; Matsumoto, S.; Soejima, T.; Sugimura, K. Prospective trial of combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for portal vein tumor thrombus in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 57, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Park, W.; Lim, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, B.C.; Paik, S.W.; Kho, K.C.; Kim, T.H.; Ahn, Y.C.; Huh, S.J. Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for portal vein thrombosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2005, 103, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.I.; Park, H.C.; Lim, D.H.; Park, W.; Yoo, B.C.; Paik, S.W.; Koh, K.C.; Lee, J.H. Prognostic index for portal vein tumor thrombosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with radiation therapy. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2011, 26, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hou, J.-Z.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, M.-S. Influence of tumor thrombus location on the outcome of external-beam radiation therapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Xiang, Y.-J.; Yu, H.-M.; Cheng, Y.-Q.; Liu, Z.-H.; Zhong, J.-Y.; Feng, S.; Ni, Q.-Z.; Zhu, H.-F.; Pan, W.-W.; et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy combined with systemic atezolizumab and bevacizumab in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic portal vein tumor thrombus: A preliminary multicenter single-arm prospective study. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1107542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzar, G.S.; De, B.S.; Abana, C.O.; Lee, S.S.; Javle, M.; Kaseb, A.O.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Cao, H.S.T.; Koong, A.C.; Smith, G.L.; et al. Outcomes and Toxicities of Modern Combined Modality Therapy with Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Radiation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones-Pauley, M.; Victor, D.W., 3rd; Kodali, S. Pushing the limits of treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2024, 29, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiniker, S.M.; Chen, D.S.; Reddy, S.; Chang, D.T.; Jones, J.C.; Mollick, J.A.; Swetter, S.M.; Knox, S.J. A systemic complete response of metastatic melanoma to local radiation and immunotherapy. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 5, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Barker, C.A.; Yamada, Y.; Yuan, J.; Kitano, S.; Mu, Z.; Rasalan, T.; Adamow, M.; Ritter, E.; et al. Immunologic correlates of the abscopal effect in a patient with melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynders, K.; Illidge, T.; Siva, S.; Chang, J.Y.; De Ruysscher, D. The abscopal effect of local radiotherapy: Using immunotherapy to make a rare event clinically relevant. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, E.B.; Demaria, S.; Schiff, P.B.; Chachoua, A.; Formenti, S.C. An abscopal response to radiation and ipilimumab in a patient with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, E.D.M.; Schoenhals, J.E.B.; Tang, C.; Micevic, G.B.; Gomez, D.R.; Chang, J.Y.; Welsh, J.W. Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy Combined with Immunotherapy for Solid Tumors. Cancer J. 2016, 22, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, X.; Pan, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L. Optimizing the Treatment Schedule of Radiotherapy Combined with Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Immunotherapy in Metastatic Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 638873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngwa, W.; Irabor, O.C.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Hesser, J.; Demaria, S.; Formenti, S.C. Using immunotherapy to boost the abscopal effect. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Sun, Z.-J. Turning cold tumors into hot tumors by improving T-cell infiltration. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5365–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, K.; Wang, K.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Shi, M.; Liang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Low-dose radiotherapy combined with dual PD-L1 and VEGFA blockade elicits antitumor response in hepatocellular carcinoma mediated by activated intratumoral CD8+ exhausted-like T cells. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajiri, K.; Tsukada, K.; Tokimitsu, Y.; Motofuji, Y.; Kawai, K.; Muraishi, N.; Murayama, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Yasuda, I. Objective Response and Progression-Free Survival Contribute to Prolong Overall Survival in Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab Treatment for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncology 2024, 102, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessio, A.; Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; Nishida, N.; Schönlein, M.; von Felden, J.; Schulze, K.; Wege, H.; Gaillard, V.E.; Saeed, A.; Wietharn, B.; et al. Preliminary evidence of safety and tolerability of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh A and B cirrhosis: A real-world study. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.Y.; Heo, J.; Yoon, K.T.; Kim, G.H.; Kang, D.H.; Song, G.A.; Cho, M. Clinical course of sorafenib treatment in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cools-Lartigue, J.; Spicer, J.; Najmeh, S.; Ferri, L. Neutrophil extracellular traps in cancer progression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 4179–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.G.; Kim, C.; Yoon, S.E.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, S.J.; Kang, B.; Kim, H.R.; Park, S.-H.; Shin, E.-C.; Kim, Y.-Y.; et al. Hyperprogressive disease during PD-1 blockade in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Yu, J.I.; Park, H.C.; Yoo, G.S.; Choi, C.; Hong, J.Y.; Lim, H.Y.; Lee, J.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, J.E.; et al. Incorporating sarcopenia and inflammation with radiation therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with nivolumab. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.; Yoo, C.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.; Lee, M.A.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, I.; Oh, S.; Hwang, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in Korean patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Michitaka, K.; Kumada, T.; Izumi, N.; Kadoya, M.; Kokudo, N.; Kubo, S.; Matsuyama, Y.; Nakashima, O.; Sakamoto, M.; et al. Validation and Potential of Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Prognostication in a Nationwide Survey of 46,681 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients in Japan: The Need for a More Detailed Evaluation of Hepatic Function. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Belle, S.J.-P.; Cocquyt, V. Impact of haemoglobin levels on the outcome of cancers treated with chemotherapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2003, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wei, S.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Cao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, P. The prognostic impact of decreased pretreatment haemoglobin level on the survival of patients with lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svaton, M.; Zemanova, M.; Skrickova, J.; Jakubikova, L.; Kolek, V.; Kultan, J.; Koubkova, L.; Bejckova, A.; Salajka, F.; Hrnciarik, M.; et al. Chronic Inflammation as a Potential Predictive Factor of Nivolumab Therapy in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2018, 38, 6771–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, S.; Peng, S.; Liu, Y.; Xing, S.; He, X.; Chen, H. Prognostic nomogram for patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma incorporating hematological biomarkers and clinical characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watine, J.; Bouarioua, N. Anemia as an independent prognostic factor for survival in patients with cancer. Cancer 2002, 94, 2793–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, W.J.; Greer, B.E.; Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Campos, S.M.; Cho, K.R.; Chon, H.S.; Chu, C.; Cohn, D.; Crispens, M.A.; Dizon, D.S.; et al. Vulvar Cancer, Version 1.2017, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc Netw. 2017, 15, 92–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; He, R.; Long, H.; Guo, B.; Jia, Q.; Qin, D.; Liu, S.-Q.; Wang, Z.; Xiang, T.; Zhang, J.; et al. Late-stage tumors induce anemia and immunosuppressive extramedullary erythroid progenitor cells. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, B.L.; Sharma, P.; Das, R. Anemia in malignancies: Pathogenetic and diagnostic considerations. Hematology 2015, 20, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höckel, M.; Vaupel, P. Tumor hypoxia: Definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, F.; Eralp, Y.; Basaran, M.; Sakar, B.; Alici, S.; Argon, A.; Bulutlar, G.; Camlica, H.; Aydiner, A.; Topuz, E. Anemia in oncology practice: Relation to diseases and their therapies. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 25, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Oncology meets immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedge, P.S.; Wallin, J.J.; Mancao, C. Predictive markers of anti-VEGF and emerging role of angiogenesis inhibitors as immunotherapeutics. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Wallin, J.J.; Bendell, J.C.; Funke, R.; Sznol, M.; Korski, K.; Jones, S.; Hernandez, G.; Mier, J.; He, X.; Hodi, F.S.; et al. Atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab enhances antigen-specific T-cell migration in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, S.; Duda, D.G.; Xu, L.; Munn, L.L.; Boucher, Y.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Normalization of the vasculature for treatment of cancer and other diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 1071–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motz, G.T.; Santoro, S.P.; Wang, L.P.; Garrabrant, T.; Lastra, R.R.; Hagemann, I.S.; Lal, P.; Feldman, M.D.; Benecia, F.; Coukos, G. Tumor endothelium FasL establishes a selective immune barrier promoting tolerance in tumors. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voron, T.; Colussi, O.; Marcheteau, E.; Pernot, S.; Nizard, M.; Pointet, A.L.; Latreche, S.; Bergaya, S.; Benhamouda, N.; Tonchot, C.; et al. VEGF-A modulates expression of inhibitory checkpoints on CD8+ T cells in tumors. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Nagaraj, S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat.Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, C.L.; Lynn, K.D.; Toombs, J.E.; Dineen, S.P.; Udugamasooriya, D.G.; Brekken, R.A. Cytokine levels correlate with immune cell infiltration after anti-VEGF therapy in preclinical mouse models of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciabene, A.; Peng, X.; Hagemann, I.S.; Balint, K.; Barchetti, A.; Wang, L.P.; Gimotty, P.A.; Gilks, C.B.; Lal, P.; Zhang, L.; et al. Tumour hypoxia promotes tolerance and angiogenesis via CCL28 and T(reg) cells. Nature 2011, 475, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, T.; Ran, S.; Ishida, T.; Nadaf, S.; Kerr, L.; Carbone, D.P.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Vascular endothelial growth factor affects dendritic cell maturation through the inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B activation in hemopoietic progenitor cells. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Chen, H.L.; Girgis, K.R.; Cunningham, H.T.; Meny, G.M.; Nadaf, S.; Kavanaugh, D.; Carbone, D.P. Production of vascular endothelial growth factor by human tumors inhibits the functional maturation of dendritic cells. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; Lawrence, D.; Lezcano, C.; Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Sasada, T.; Zeng, W.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Atkins, M.B.; Ibrahim, N.; et al. Bevacizumab plus ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Total (n = 215) n (%) or Median (Range) | High-Risk (n = 98) n (%) or Median (Range) | Non-High-Risk (n = 117) n (%) or Median (Range) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age in years | 63 (39–92) | 60.5 (39–92) | 66 (43–86) | 0.011 |
| Male sex | 182 (84.7) | 84 (85.7) | 98 (83.8) | 0.692 |
| Etiology | 0.296 | |||
| Hepatitis B | 119 (55.3) | 58 (59.2) | 61 (52.1) | |
| Hepatitis C | 33 (15.3) | 10 (10.2) | 23 (19.7) | |
| Hepatitis B + hepatitis C coinfection | 2 (0.9) | 1 (1.0) | 1 (0.9) | |
| Non-viral | 61 (28.4) | 29 (29.6) | 32 (27.4) | |
| ECOG performance status score | 0.073 | |||
| 0 | 143 (66.5) | 59 (60.2) | 84 (71.8) | |
| 1 | 72 (33.5) | 39 (39.8) | 33 (28.2) | |
| Child–Pugh classification | <0.001 | |||
| A5 | 154 (71.6) | 53 (54.1) | 101 (86.3) | |
| A6 | 32 (14.9) | 26 (26.5) | 6 (5.1) | |
| B7 | 24 (11.2) | 15 (15.3) | 9 (7.7) | |
| B8 | 4 (1.9) | 3 (3.1) | 1 (0.9) | |
| B9 | 1 (0.5) | 1 (1.0) | 0 (0) | |
| Ascites | 20 (9.3) | 16 (16.3) | 4 (3.4) | 0.002 |
| Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage | <0.001 | |||
| A | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| B | 29 (13.5) | 4 (4.1) | 25 (21.4) | |
| C | 186 (86.5) | 94 (95.9) | 92 (78.6) | |
| Alpha-fetoprotein, ng/mL | 190.8 (1.3–121,000) | 610.1 (1.3–121,000) | 81 (1.3–100,000) | <0.001 |
| Alpha-fetoprotein > 400 ng/mL | 90 (41.9) | 52 (53.1) | 38 (32.5) | 0.002 |
| DCP, mAU/ml | 748 (13–615,936) | 3722 (14.45–615,936) | 184 (13–239,099) | <0.001 |
| Macrovascular invasion | 108 (50.2) | 81 (82.7) | 27 (23.1) | <0.001 |
| Vp4 portal vein thrombus, | 70 (32.6) | 70 (71.4) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| Bile duct invasion | 23 (10.7) | 23 (23.5) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| Liver infiltration > 50% | 48 (22.3) | 48 (49.0) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 129 (60.0) | 55 (56.1) | 74 (63.2) | 0.288 |
| Prior local therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma | 140 (65.1) | 41 (41.8) | 99 (84.6) | <0.001 |
| Neoadjuvant or concomitant radiation therapy | 128 (59.5) | 61 (62.2) | 67 (57.3) | 0.459 |
| Varices | ||||
| Present at baseline | 108 (50.2) | 59 (60.2) | 49 (41.9) | 0.007 |
| Treated at baseline | 15 (7.0) | 12 (12.2) | 3 (2.6) | 0.006 |
| WBC (/mm3) | 5760 (1390–27,540) | 6265 (1690–27,540) | 5300 (1390–25,440) | 0.009 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 12.7 (6.5–20.5) | 12.4 (6.9–17.6) | 13 (6.5–20.5) | 0.023 |
| AST (U/L) | 50 (16–550) | 65.5 (16–550) | 37 (16–331) | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 29 (6–349) | 35 (9–281) | 26 (6–349) | 0.002 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.9 (2.1–5.0) | 3.7 (2.5–4.6) | 4.1 (2.1–5.0) | <0.001 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.9 (0.25–6.60) | 1.0 (0.3–6.6) | 0.8 (0.3–2.5) | 0.002 |
| Prothrombin time (INR) | 1.12 (0.88–1.74) | 1.14 (0.93–1.74) | 1.10 (0.88–1.64) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio | 3.06 (0.25–19.73) | 3.73 (1.38–19.73) | 2.72 (0.25–12.96) | 0.036 |
| ≤2.25 | 64 (29.9) | 22 (22.7) | 42 (35.9) | |
| >2.25 | 150 (70.1) | 75 (77.3) | 75 (64.1) | |
| ALBI grade | <0.001 | |||
| 1 | 99 (46) | 27 (27.6) | 72 (61.5) | |
| 2 | 109 (50.7) | 67 (68.4) | 42 (35.9) | |
| 3 | 7 (3.3) | 4 (4.1) | 3 (2.6) |
| Subgroup | Events/Patients | Median OS, Months (95% CI) | p-Value * | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All patients | 92/215 | 11.25 (9.50–13.10) | ||
| Age, years < 65 | 48/113 | 11.25(8.18–14.32) | 0.777 | |
| ≥65 | 44/102 | 11.75 (9.69–13.81) | ||
| Sex | 0.815 | |||
| Male | 74/182 | 11.25 (9.25–13.25) | ||
| Female | 18/33 | 13 (8.41–17.59) | ||
| Etiology | 0.617 | |||
| Hepatitis B | 54/119 | 10.75 (8.13–13.37) | ||
| Hepatitis C | 9/33 | 14.25 (9.23–19.27) | ||
| Hepatitis B + hepatitis C | 0/2 | - | ||
| Non-viral | 29/61 | 9.75 (8.55–10.95) | ||
| ECOG performance status | 0.169 | |||
| 0 | 58/143 | 12.75 (9.94–15.56) | ||
| 1 | 34/72 | 10 (7.82–12.18) | ||
| Child–Pugh score | <0.001 | 0.408 | ||
| 5A | 50/154 | 14.00 (10.41–17.59) | ||
| 6A | 21/32 | 6.50 (5.14–7.86) | ||
| 7B | 17/24 | 8.00 (2.07–13.93) | ||
| 8B | 4/4 | 5.75 (0–13.10) | ||
| 9B | 0/1 | - | ||
| Ascites | 0.001 | 0.079 | ||
| Absent at baseline | 78/195 | 11.75 (9.13–14.37) | ||
| Present at baseline | 14/20 | 7.25 (2.96–11.54) | ||
| Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage | 0.204 | |||
| B | 6/29 | 14.25 (-) | ||
| C | 86/186 | 10.50 (8.83–12.17) | ||
| Alpha-fetoprotein at baseline | 0.172 | |||
| ≤400 ng/mL | 46/125 | 12.00 (9.32–14.68) | ||
| >400 ng/ml | 46/90 | 10.00 (8.02–11.98) | ||
| DCP at baseline (mAU/mL) | 0.023 | 0.034 | ||
| ≤2000 | 43/123 | 12.75 (10.31–15.19) | ||
| >2000 | 47/88 | 8.50 (6.69–10.31) | ||
| Macrovascular invasion at baseline | 0.085 | |||
| No | 37/107 | 13.00 (9.87–16.19) | ||
| Yes | 55/108 | 10.00 (8.78–11.22) | ||
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 0.500 | |||
| No | 33/86 | 11.75 (9.16–14.34) | ||
| Yes | 59/129 | 10.75 (7.37–14.13) | ||
| Vp4 portal vein thrombus | 0.001 | 0.710 | ||
| No | 52/145 | 14.00 (10.90–17.10) | ||
| Yes | 40/70 | 9.25 (7.76–10.74) | ||
| Bile duct invasion | 0.014 | 0.034 | ||
| No | 76/192 | 11.75 (9.49–14.01) | ||
| Yes | 16/23 | 8.25 (3.44–13.06) | ||
| Liver infiltration > 50% | 0.002 | 0.923 | ||
| No | 61/167 | 12.00 (9.74–14.26) | ||
| Yes | 31/48 | 8.25 (5.39–11.11) | ||
| Prior local therapy | 0.007 | 0.751 | ||
| No | 38/75 | 9.75 (7.60–11.90) | ||
| Yes | 54/140 | 12.75 (9.47–15.53) | ||
| Neoadjuvant or concomitant radiation therapy | 0.305 | |||
| No | 35/87 | 10.50 (7.60–13.40) | ||
| Yes | 57/128 | 12.00 (8.76–15.24) | ||
| Hb (g/dL) | 0.001 | 0.013 | ||
| ≤12.5 | 57/99 | 9.25 (7.65–10.85) | ||
| >12.5 | 35/116 | 14.00 (9.57–18.43) | ||
| AST (U/L) | 0.001 | 0.490 | ||
| ≤40 | 26/81 | 15.00 (8.73–21.27) | ||
| >40 | 66/134 | 10.00 (8.38–11.62) | ||
| Varices | 0.004 | 0.504 | ||
| Absent at baseline | 35/107 | 16.25 (10.92–21.58) | ||
| Present at baseline | 60/108 | 10.00 (9.02–10.98) | ||
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio | 0.001 | 0.017 | ||
| ≤2.25 | 18/64 | 18.00 (10.38–25.62) | ||
| >2.25 | 74/150 | 10.00 (8.64–11.36) | ||
| ALBI grade | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 1 | 23/99 | 17.50 (13.34–21.66) | ||
| 2 | 62/109 | 8.25 (7.48–9.02) | ||
| 3 | 7/7 | 5.00 (0.00–13.34) |
| Subgroup | Events/Patients | Median OS, Months (95% CI) | p-Value * | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All patients | 54/98 | 10 (8.19–11.82) | ||
| Age, years < 65 | 30/60 | 10 (5.27–14.73) | 0.326 | |
| ≥65 | 24/38 | 10 (7.00–13.00) | ||
| Sex | 0.416 | |||
| Male | 45/84 | 9.25 (7.78–10.72) | ||
| Female | 9/14 | 10.25 (5.68–14.82) | ||
| Etiology | 0.161 | |||
| Hepatitis B | 33/58 | 10.25 (6.21–14.29) | ||
| Hepatitis C | 3/10 | 21.75 (-) | ||
| Hepatitis B + hepatitis C | 0/1 | - | ||
| Non-viral | 18/29 | 8.25 (5.13–11.37) | ||
| ECOG performance status | 0.187 | |||
| 0 | 31/59 | 10.00 (7.84–12.16) | ||
| 1 | 23/39 | 8.50 (4.07–12.93) | ||
| Child–Pugh score | 0.012 | 0.516 | ||
| 5A | 23/53 | 13.50 (9.08–17.92) | ||
| 6A | 17/26 | 6.50 (4.74–8.26) | ||
| 7B | 11/15 | 5.75 (1.32–10.18) | ||
| 8B | 3/3 | 9.00 (3.80–14.20) | ||
| 9B | 0/1 | - | ||
| Ascites | 0.239 | |||
| Absent at baseline | 43/82 | 10.00 (7.88–12.12) | ||
| Present at baseline | 11/16 | 7.75 (0.70–14.80) | ||
| Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage | 0.316 | |||
| B | 3/4 | 4.00 (1.80–6.20) | ||
| C | 51/94 | 10.00 (8.23–11.77) | ||
| Alpha-fetoprotein at baseline | 0.833 | |||
| ≤400 ng/mL | 26/46 | 10.00 (6.73–13.27) | ||
| >400 ng/ml | 28/52 | 8.50 (6.37–10.63) | ||
| DCP at baseline (mAU/mL) | 0.282 | |||
| ≤2000 | 19/39 | 12.00 (8.90–15.10) | ||
| >2000 | 33/56 | 8.25 (6.30–10.20) | ||
| Macrovascular invasion at baseline | 0.104 | |||
| No | 11/17 | 4.25 (0.08–8.42) | ||
| Yes | 43/81 | 10.00 (8.03–11.97) | ||
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 0.801 | |||
| No | 25/43 | 9.00 (7.08–10.92) | ||
| Yes | 29/55 | 10.00 (5.13–14.87) | ||
| Vp4 portal vein thrombus | 0.328 | |||
| No | 14/28 | 14.00 (6.45–21.55) | ||
| Yes | 40/70 | 9.25 (7.76–10.74) | ||
| Bile duct invasion | 0.165 | |||
| No | 38/75 | 10.00 (7.83–12.17) | ||
| Yes | 16/23 | 8.25 (3.44–13.06) | ||
| Liver infiltration over 50% | 0.127 | |||
| No | 23/50 | 10.25 (6.52–13.98) | ||
| Yes | 31/48 | 8.25 (5.39–11.11) | ||
| Prior local therapy | 0.272 | |||
| No | 30/57 | 10.00 (5.88–14.12) | ||
| Yes | 24/41 | 10.00 (6.63–13.37) | ||
| Neoadjuvant or concomitant radiation therapy | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| No | 24/37 | 5.75 (3.24–8.26) | ||
| Yes | 30/61 | 12.00 (9.33–14.67) | ||
| Varices | 0.514 | |||
| Absent at baseline | 17/39 | 16.25 (-) | ||
| Present at baseline | 37/59 | 10.00 (8.34–11.66) | ||
| Hb (g/dL) | 0.016 | 0.057 | ||
| ≤12.5 | 34/50 | 8.00 (6.12–9.88) | ||
| >12.5 | 20/48 | 14.00 (10.37–17.63) | ||
| AST (U/L) | 0.752 | |||
| ≤40 | 9/14 | 9.25 (6.88–11.62) | ||
| >40 | 45/84 | 10.00 (7.38–12.62) | ||
| Varix | 0.514 | |||
| Absent | 17/39 | 16.25 (-) | ||
| Present | 37/59 | 10.00 (8.34–11.66) | ||
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio | 0.009 | 0.163 | ||
| ≤2.25 | 7/22 | 18.00 (9.77–26.23) | ||
| >2.25 | 47/75 | 8.25 (5.69–10.81) | ||
| ALBI grade | <0.001 | 0.007 | ||
| 1 | 9/27 | 16.25 (12.00–20.50) | ||
| 2 | 41/67 | 8.25 (6.18–10.32) | ||
| 3 | 4/4 | 1.75 (0–5.91) |
| Adverse Event | Total (n = 215), n (%) | High-Risk (n = 98), n (%) | Non-High-Risk (n = 117), n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any adverse event | 177 (82.3) | 79 (80.6) | 98 (83.8) | 0.593 |
| Grade 3 or 4 adverse event | 37 (17.2) | 24 (24.5) | 13 (11.1) | 0.019 |
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | 13 (6.04) | 12 (12.24) | 1 (0.85) | <0.001 |
| Temporary discontinuation | 25 (11.6) | 13 (13.2) | 12 (10.2) | 0.519 |
| Permanent discontinuation | 13 (6.0) | 7 (7.1) | 6 (5.1) | 0.549 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, S.Y.; Woo, H.Y.; Heo, J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, Y.J.; Yi, K.Y.; Lee, Y.R.; Park, S.Y.; Chung, W.J.; Jang, B.K.; et al. Outcome of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab Combination Therapy in High-Risk Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040838
Hwang SY, Woo HY, Heo J, Kim HJ, Park YJ, Yi KY, Lee YR, Park SY, Chung WJ, Jang BK, et al. Outcome of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab Combination Therapy in High-Risk Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2024; 16(4):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040838
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Sang Youn, Hyun Young Woo, Jeong Heo, Hyung Jun Kim, Young Joo Park, Ki Youn Yi, Yu Rim Lee, Soo Young Park, Woo Jin Chung, Byoung Kuk Jang, and et al. 2024. "Outcome of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab Combination Therapy in High-Risk Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 16, no. 4: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040838
APA StyleHwang, S. Y., Woo, H. Y., Heo, J., Kim, H. J., Park, Y. J., Yi, K. Y., Lee, Y. R., Park, S. Y., Chung, W. J., Jang, B. K., & Tak, W. Y. (2024). Outcome of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab Combination Therapy in High-Risk Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 16(4), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040838