Sarcopenia in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Background
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection Criteria and Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Included Studies
3.2. Patient and Study Characteristics
3.3. Outcomes
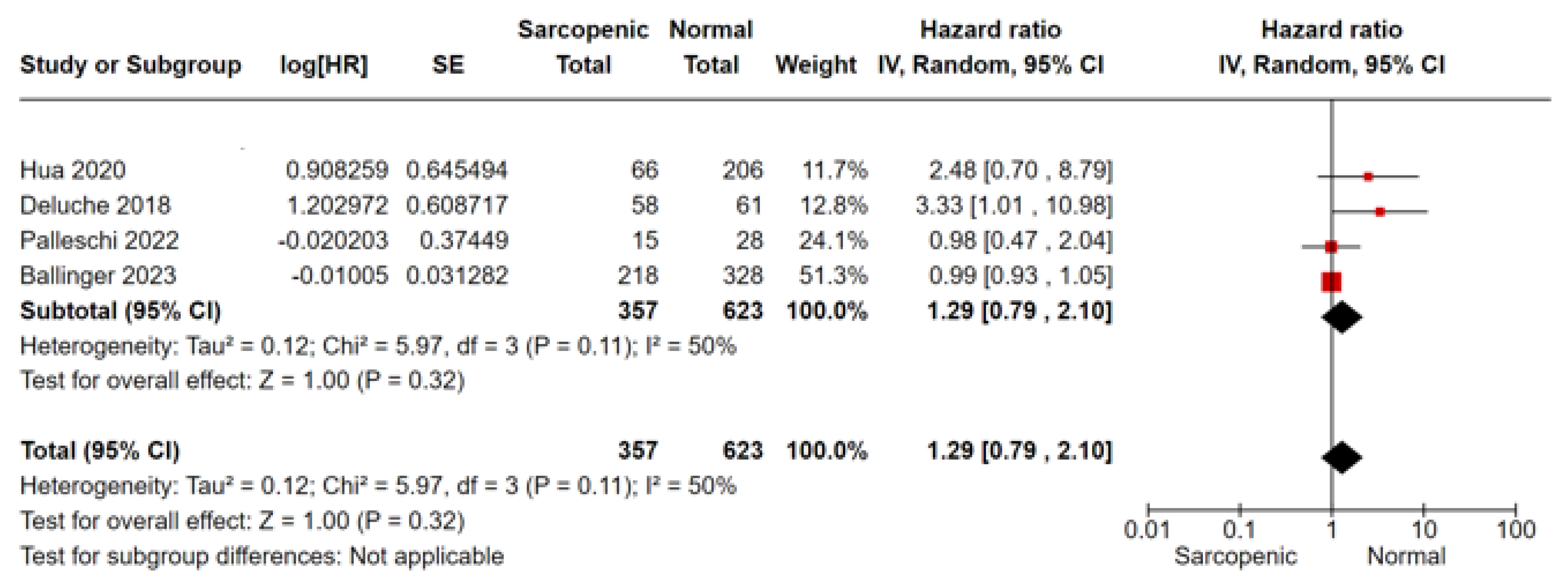
3.3.1. Survival Analysis
3.3.2. Response
3.3.3. Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Gray, R.; Braybrooke, J.; Davies, C.; Taylor, C.; McGale, P.; Peto, R.; Pritchard, K.I.; Bergh, J.; Dowsett, M.; et al. 20-Year Risks of Breast-Cancer Recurrence after Stopping Endocrine Therapy at 5 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argilés, J.M.; Busquets, S.; Stemmler, B.; López-Soriano, F.J. Cancer cachexia: Understanding the molecular basis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilmi, M.; Jouinot, A.; Burns, R.; Pigneur, F.; Mounier, R.; Gondin, J.; Neuzillet, C.; Goldwasser, F. Body composition and sarcopenia: The next-generation of personalized oncology and pharmacology? Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 196, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boshier, P.R.; Heneghan, R.; Markar, S.R.; Baracos, V.E.; Low, D. Assessment of body composition and sarcopenia in patients with esophageal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis. Esophagus 2018, 31, doy047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarajah, S.K.; Bundred, J.; Tan, B.H.L. Body composition assessment and sarcopenia in patients with gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintziras, I.; Miligkos, M.; Wächter, S.; Manoharan, J.; Maurer, E.; Bartsch, D.K. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity are significantly associated with poorer overall survival in patients with pancreatic cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 59, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhang, F.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z. Can sarcopenia be a predictor of prognosis for patients with non-metastatic colorectal cancer? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2018, 33, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.-Y.; Hou, L.; Zha, P.; Huang, K.-L.; Peng, L. Sarcopenia is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor of non-small cell lung cancer after surgical resection: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.; Jeong, C.; Kwon, K.A.; Yoon, T.I.; Yi, O.; Kim, K.W.; Yang, S.-O.; Lee, J. Artificial intelligence for predicting five-year survival in stage IV metastatic breast cancer patients: A focus on sarcopenia and other host factors. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzoi, M.A.; Vandeputte, C.; Eiger, D.; Caparica, R.; Brandão, M.; De Angelis, C.; Hendlisz, A.; Awada, A.; Piccart, M.; de Azambuja, E. Computed tomography-based analyses of baseline body composition parameters and changes in breast cancer patients under treatment with CDK 4/6 inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 181, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villaseñor, A.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Baumgartner, K.; Baumgartner, R.; Bernstein, L.; McTiernan, A.; Neuhouser, M.L. Prevalence and prognostic effect of sarcopenia in breast cancer survivors: The HEAL Study. J. Cancer Surviv. 2012, 6, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shachar, S.S.; Deal, A.M.; Weinberg, M.; Williams, G.R.; Nyrop, K.A.; Popuri, K.; Choi, S.K.; Muss, H.B. Body composition as a predictor of toxicity in patients receiving anthracycline and taxane-based chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3537–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caan, B.J.; Cespedes Feliciano, E.M.; Prado, C.M.; Alexeeff, S.; Kroenke, C.H. Association of muscle and adiposity measured by computed tomography with survival in patients with nonmetastatic breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluche, E.; Leobon, S.; Desport, J.C.; Venat-Bouvet, L.; Usseglio, J.; Tubiana-Mathieu, N. Impact of body composition on outcome in patients with early breast cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2018, 26, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Deng, J.-P.; Long, Z.-Q.; Zhang, W.-W.; Huang, X.; Wen, W.; Guo, L.; He, Z.-Y.; Lin, H.-X. Prognostic significance of the skeletal muscle index and an inflammation biomarker in patients with breast cancer who underwent postoperative adjuvant radiotherapy. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2020, 44, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, E.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Xi, K.; Fang, Q. Association of body composition with clinical outcome in Chinese women diagnosed with breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 957527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.C.; Segal, R.J.; McKenzie, D.C.; Vallerand, J.R.; Morielli, A.R.; Mackey, J.R.; Gelmon, K.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Reid, R.D.; Courneya, K.S. Impact of resistance and aerobic exercise on sarcopenia and dynapenia in breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 158, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.M.; Baracos, V.E.; McCargar, L.J.; Reiman, T.; Mourtzakis, M.; Tonkin, K.; Mackey, J.R.; Koski, S.; Pituskin, E.; Sawyer, M.B. Sarcopenia as a determinant of chemotherapy toxicity and time to tumor progression in metastatic breast cancer patients receiving capecitabine treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2920–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.W.; Park, H.S.; Ko, Y.; Sung, Y.S.; Shim, B.Y.; Suh, Y.J.; Kim, H.A. Intermuscular fat density as a novel prognostic factor in breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 189, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Deng, J.-P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.-W.; Sun, J.-Y.; Chi, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.-G.; He, Z.-Y. Prognostic significance of the skeletal muscle index and systemic inflammatory index in patients with lymph node-positive breast cancer after radical mastectomy. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleschi, M.; Iamurri, A.P.; Scarpi, E.; Mariotti, M.; Maltoni, R.; Mannozzi, F.; Barone, D.; Paganelli, G.; Casi, M.; Giampalma, E.; et al. Computed tomography-based analyses of body mass composition in HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer patients undergoing first line treatment with pertuzumab and trastuzumab. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballinger, T.J.; Marques, H.S.; Xue, G.; Hoffman, R.; Gatsonis, C.; Zhao, F.; Miller, K.D.; Sparano, J.; Connolly, R.M. Impact of Muscle Measures on Outcome in Patients Receiving Endocrine Therapy for Metastatic Breast Cancer: Analysis of ECOG-ACRIN E2112. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2023, 21, 915–923.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Fabbro, E.; Parsons, H.; Warneke, C.L.; Pulivarthi, K.; Litton, J.K.; Dev, R.; Palla, S.L.; Brewster, A.; Bruera, E. The Relationship Between Body Composition and Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Women with Operable Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2012, 17, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheean, P.; Gomez-Perez, S.; Joyce, C.; O’connor, P.; Bojko, M.; Smith, A.; Vasilopoulos, V.; Rao, R.; Sclamberg, J.; Robinson, P. Myosteatosis at diagnosis is adversely associated with 2-year survival in women with estrogen receptor-negative metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 190, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sudo, M.; Imai, S. Sarcopenia as a risk factor of severe laboratory adverse events in breast cancer patients receiving perioperative epirubicin plus cyclophosphamide therapy. Support Care Cancer. 2020, 28, 4249–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellieni, A.; Fusco, D.; Sanchez, A.M.; Franceschini, G.; Di Capua, B.; Allocca, E.; Di Stasio, E.; Marazzi, F.; Tagliaferri, L.; Masetti, R.; et al. Different Impact of Definitions of Sarcopenia in Defining Frailty Status in a Population of Older Women with Early Breast Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delrieu, L.; Martin, A.; Touillaud, M.; Pérol, O.; Morelle, M.; Febvey-Combes, O.; Freyssenet, D.; Friedenreich, C.; Dufresne, A.; Bachelot, T.; et al. Sarcopenia and serum biomarkers of oxidative stress after a 6-month physical activity intervention in women with metastatic breast cancer: Results from the ABLE feasibility trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 188, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluche, E.; Lachatre, D.; Di Palma, M.; Simon, H.; Tissot, V.; Vansteene, D.; Meingan, P.; Mohebi, A.; Lenczner, G.; Pigneur, F.; et al. Is sarcopenia a missed factor in the management of patients with metastatic breast cancer? Breast 2021, 61, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.K.; Park, S.; Park, C.; Doorenbos, A.; Go, J.; Kim, S. Hematologic toxicities, sarcopenia, and body composition change in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Support. Care Cancer 2023, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleixo, G.F.P.; Williams, G.R.; Nyrop, K.A.; Muss, H.B.; Shachar, S.S. Muscle composition and outcomes in patients with breast cancer: Meta-analysis and systematic review. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 177, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-M.; Dou, Q.-L.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, A.S.K.; Zhang, W.-W. Sarcopenia as a predictor of mortality in women with breast cancer: A meta-analysis and systematic review. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.C.; Heymsfield, S.B. Bioelectrical impedance analysis for diagnosing sarcopenia and cachexia: What are we really estimating? J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.R.; Rier, H.N.; McDonald, A.; Shachar, S.S. Sarcopenia & aging in cancer. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2019, 10, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argilés, J.M.; Busquets, S.; Stemmler, B.; López-Soriano, F.J. Cachexia and sarcopenia: Mechanisms and potential targets for intervention. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 22, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, A.-L.; Hu, H.-Y.; Rong, Y.-D.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.-X.; Zhou, X.-Z. A study on relationship between elderly sarcopenia and inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2017, 22, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feliciano, E.M.C.; Kroenke, C.H.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Prado, C.M.; Bradshaw, P.T.; Kwan, M.L.; Xiao, J.; Alexeeff, S.; Corley, D.; Weltzien, E.; et al. Association of Systemic Inflammation and Sarcopenia with Survival in Nonmetastatic Colorectal Cancer: Results From the C SCANS Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, e172319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, a Regulator and Therapeutic Agent on Breast Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.H.; Birdsell, L.A.; Martin, L.; Baracos, V.E.; Fearon, K.C. Sarcopenia in an overweight or obese patient is an adverse prognostic factor in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6973–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; McCargar, L.J.; Reiman, T.; Sawyer, M.B.; Martin, L.; Baracos, V.E. Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieli-Conwright, C.M.; Courneya, K.S.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Sami, N.; Lee, K.; Sweeney, F.C.; Stewart, C.; Buchanan, T.A.; Spicer, D.; Tripathy, D.; et al. Aerobic and resistance exercise improves physical fitness, bone health, and quality of life in overweight and obese breast cancer survivors: A randomized controlled trial 11 Medical and Health Sciences 1117 Public Health and Health Services. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzuca, F.; Roberto, M.; Botticelli, A.; Arrivi, G.; Sarfati, E.; Schipilliti, F.M.; Crimini, E.; Di Girolamo, M.; Muscaritoli, M.; Marchetti, P. Effect of nutritional support with highly purified, whey proteins for malnutrition and sarcopenia in patients affected with stage II-III colorectal or breast cancer: A blind, placebo controlled, randomized clinical trial. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1534735419866920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballinger, T.J.; Thompson, W.R.; Guise, T.A. The bone–muscle connection in breast cancer: Implications and therapeutic strategies to preserve musculoskeletal health. Breast Cancer Res. 2022, 24, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, D.; Locquet, M.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Lengelé, L.; Bruyère, O. Malnutrition as a Strong Predictor of the Onset of Sarcopenia. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.-H.; Chen, W.-M.; Chen, M.-C.; Shia, B.-C.; Wu, S.-Y. The Impact of Sarcopenia Onset Prior to Cancer Diagnosis on Cancer Survival: A National Population-Based Cohort Study Using Propensity Score Matching. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscaritoli, M.; Bar-Sela, G.; Battisti, N.M.L.; Belev, B.; Contreras-Martínez, J.; Cortesi, E.; de Brito-Ashurst, I.; Prado, C.M.; Ravasco, P.; Yalcin, S. Oncology-Led Early Identification of Nutritional Risk: A Pragmatic, Evidence-Based Protocol (PRONTO). Cancers 2023, 15, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscaritoli, M.; Modena, A.; Valerio, M.; Marchetti, P.; Magarotto, R.; Quadrini, S.; Narducci, F.; Tonini, G.; Grassani, T.; Cavanna, L.; et al. The Impact of NUTRItional Status at First Medical Oncology Visit on Clinical Outcomes: The NUTRIONCO Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| First Author, Year of Publication | Type of the Study | Nation | Follow-Up Period | Patients (N), Disease Setting, and Breast Cancer Subtypes | Median (Range)/Mean (SD) Age, Years | Treatments | Sarcopenia Definition (cm2/m2) | Patients with Sarcopenia (N, %) | Measured Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Villasenor 2012 et al. [14] | Prospective | US | 9.6 years | 471, stage I–IIIA | 56 (29.4–85.8) in sarcopenic and 63.9 (39.6–87.8) in non-sarcopenic patients | Adjuvant RT +/− CT/HT | LMI < 5.45 Kg/m2 | 75 (16) | 5 y-OS, BCSS |
| Shachar 2017 et al. [15] | Prospective | US | 1.9 years | 40, MBC, 15 luminal, 14 HER2+, 10 triple negative | 55 (34–80) | CT, TT | SMI ≤ 41 | 23 (48) | Toxicity OS |
| Caan 2018 et al. [16] | Retrospective | US | 6.0 years | 3241, stage II-III | 54 (18–80) | Adjuvant RT +/− CT | SMI < 40 | 1086 (34) | mOS |
| Deluche 2018 et al. [17] | Retrospective | France | 4.3 years | 119 (88 ER+, 11 HER2+), stage I–IIIA | 56 (21–87) | (Neo)adjuvant—CT +/− RT | SMI ≤ 41 | 58 (49) | DFS, OS |
| Hua 2020 et al. [18] | Retrospective | China | 1.5 years | 272 (197 ER+, 98 HER2+), stage I–III | 45 (23–73) | Adjuvant-RT +/− CT | 2 groups: low-SMI: 9.9 (range 5.3–10.6) and high-SMI: 12.5 (range 10.6–28.1) | 66 (24) | OS, RFS |
| Jeon 2021 et al. [22] | Retrospective | Korea | 6.5 years | 479 (300 ER+), stage I–III, 237 luminal, 149 HER2 positive, 93 triple negative | SMI ≤ 41 | 178 (37) | OS, BCSS | ||
| Tang 2022 et al. [23] | Retrospective | China | 5.2 years | 97 (61 ER+, 40 HER2+), stage II–III | 51 (21–87) | Adjuvant-CT | OS | ||
| Palleschi 2022 et al. [24] | Retrospective | Italy | 2.7 years | 25, stage I–III; 18, MBC. All HER2+. | 58 (52–64) | CT +/− anti-HER2 agents | 46 (27–73) | Adjuvant RT +/− CT | PFS, OS, |
| Ballinger 2023 et al. [25] | Prospective, phase III trial | US | Not specified (247 PFS events) | 540 MBC, HR+ HER2− | 63.2 (11.5) | HT+/− entinostat | SMI < 41 | 212 (39) | PFS, OS |
| Del Fabbro 2012 et al. [26] | Retrospective | US | 7.7 years | 129 (96 ER+, 44 HER2+), clinical stage I–III. | NA | Neoadjuvant-CT | SMI ≤ 38.5 | 18 (14) | pCR |
| Prado 2009 et al. [21] | Prospective | Canada | 1 year | 55 (39 ER+, 18 HER2+), MBC | 54.8 (37–80) | CT | SMI ≤ 38.5 | 14 (26) | Toxicity, TTP |
| Ueno 2019 et al. [28] | Retrospective | Japan | 4 years | 82, clinical stage I–III. | 55 (44.3–66) | Neoadjuvant -CT | SMI < 40 | 10 (12) | Toxicity |
| Bellieni 2021 et al. [29] | Retrospective | Italy | 1 year | 96, stage 0–III | 77 (70–89) | Adjuvant-CT | LMI < 5.45 Kg/m2 | 41 (43) | Toxicity |
| Delrieu 2021 et al. [30] | Prospective | France | 6 months | 47 MBC | 55 (10.41) | CT, TT, HT and RT | SMI < 40 | 25 (53) | Toxicity |
| Deluche 2022 et al. [31] | Prospective cross-sectional | France | 6 months | 139, MBC | 61, 2(29.9–97.8) | CT, TT, HT | SMI < 39 | 41 (29) | Toxicity |
| Jang 2023 et al. [32] | Retrospective | Korea | 5 months | 298 stage I–III; luminal:103, HER2+:109, Triple negative:93 | 52.9 (overall SD NA) | Neoadjuvant CT | SMI ≤ 38.5 | 74 (25) | Toxicity (only the hematological) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roberto, M.; Barchiesi, G.; Resuli, B.; Verrico, M.; Speranza, I.; Cristofani, L.; Pediconi, F.; Tomao, F.; Botticelli, A.; Santini, D. Sarcopenia in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030596
Roberto M, Barchiesi G, Resuli B, Verrico M, Speranza I, Cristofani L, Pediconi F, Tomao F, Botticelli A, Santini D. Sarcopenia in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(3):596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030596
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoberto, Michela, Giacomo Barchiesi, Blerina Resuli, Monica Verrico, Iolanda Speranza, Leonardo Cristofani, Federica Pediconi, Federica Tomao, Andrea Botticelli, and Daniele Santini. 2024. "Sarcopenia in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 3: 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030596
APA StyleRoberto, M., Barchiesi, G., Resuli, B., Verrico, M., Speranza, I., Cristofani, L., Pediconi, F., Tomao, F., Botticelli, A., & Santini, D. (2024). Sarcopenia in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(3), 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030596







