Correlation of Increased Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 with Mortality and Dependence on Treatment in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Longitudinal Cohort Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Determination of sTNF-R1 and CRP Levels
2.3. Outcome
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CARLA | CARdiovascular Living and Ageing |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CRP | C-reactive Protein |
| EQD2 | Equivalent Dose in 2 Gray |
| GTV | Gross Tumor Volume |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| LC | Lung Cancer |
| NSCLC | Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| PTV | Planning Target Volume |
| IP-10 | Interferon Gamma-induced Protein-10 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| SBRT | Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy |
| sTNF-R | Soluble TNF Receptor |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| TNF-R | Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor |
| TNM | Tumor Node Metastasis |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, M.J. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2006. Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2006/ (accessed on 4 December 2009).
- Gomes, M.; Teixeira, A.L.; Coelho, A.; Araújo, A.; Medeiros, R. The Role of Inflammation in Lung Cancer. In Inflammation and Cancer; Aggarwal, B.B., Sung, B., Gupta, S.C., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bremnes, R.M.; Al-Shibli, K.; Donnem, T.; Sirera, R.; Al-Saad, S.; Andersen, S.; Stenvold, H.; Camps, C.; Busund, L. The Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Chronic Inflammation at the Tumor Site on Cancer Development, Progression, and Prognosis: Emphasis on Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuzzi, G.; Galeone, C.; Gisabella, M.; Duranti, L.; Taverna, F.; Suatoni, P.; Morelli, D.; Pastorino, U. Baseline C-Reactive Protein Level Predicts Survival of Early-Stage Lung Cancer: Evidence from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tumori J. 2016, 102, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loo, G.; Bertrand, M.J.M. Death by TNF: A road to inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarosz-Griffiths, H.H.; Holbrook, J.; Lara-Reyna, S.; McDermott, M.F. TNF receptor signalling in autoinflammatory diseases. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalliolias, G.D.; Ivashkiv, L.B. TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Scheurich, P. Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, S. Role of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) in host defence against tuberculosis: Implications for immunotherapies targeting TNF. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62 (Suppl. S2), ii37–ii42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertazza, L.; Mocellin, S. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) biology and cell death. Front Biosci. 2008, 13, 2736–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. The paradox of pro-inflammatory cytokines in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.; Blaser, H.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: Live or let die. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprang, S.R. The divergent receptors for TNF. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1990, 15, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelavarthi, K.K.; Hunt, J.S. Analysis of p60 and p80 tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor messenger RNA and protein in human placentas. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kartikasari, A.E.R.; Cassar, E.; Razqan, M.A.M.; Szydzik, C.; Huertas, C.S.; Mitchell, A.; Plebanski, M. Elevation of circulating TNF receptor 2 in cancer: A systematic meta-analysis for its potential as a diagnostic cancer biomarker. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 918254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossus, L.; Becker, S.; Rinaldi, S.; Lukanova, A.; Tjønneland, A.; Olsen, A.; Overvad, K.; Chabbert-Buffet, N.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, soluble TNF receptors and endometrial cancer risk: The EPIC study. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2032–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielczarek-Palacz, A.; Kondera-Anasz, Z.; Sikora, J. Higher serum levels of tumour necrosis factor and its soluble receptors are associated with ovarian tumours. Arch. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Chen, Q.Q.; Cao, J.; Xu, L.Q.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, L.X. Expression of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 in human non-small cell lung cancer and its role as a potential prognostic biomarker. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, K.; Guo, G.; Beckley, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Sharma, M.; Habib, A.A. Tumor necrosis factor in lung cancer: Complex roles in biology and resistance to treatment. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.A.; Kallakury, B.V.; Ambros, R.A.; Ross, J.S. Prognostic significance of tumor necrosis factors and their receptors in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 1998, 83, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, V.; Spreafico, A.; Floriani, I.; Colombo, B.; Ludovini, V.; Pistola, L.; Bellezza, G.; Viganò, M.G.; Villa, E.; Corti, A. Prognostic value of circulating chromogranin A and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 2007, 110, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiser, K.H.; Kluttig, A.; Schumann, B.; Swenne, C.A.; Kors, J.A.; Kuss, O.; Haerting, J.; Schmidt, H.; Thiery, J.; Werdan, K. Cardiovascular diseases, risk factors and short-term heart rate variability in an elderly general population: The CARLA study 2002–2006. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 24, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiser, K.H.; Kluttig, A.; Schumann, B.; Kors, J.A.; Swenne, C.A.; Kuss, O.; Werdan, K.; Haerting, J. Cardiovascular disease, risk factors and heart rate variability in the elderly general population: Design and objectives of the CARdiovascular disease, Living and Ageing in Halle (CARLA) Study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2005, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.; Imai, K.; King, G.; Stuart, E.; Whitworth, A.; Greifer, N. Package ‘MatchIt’. Version. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-hub.io/web/packages/MatchIt/MatchIt.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Bates, D.; Sarkar, D.; Bates, M.D.; Matrix, L. The lme4 package. R Package Version 2007, 2, 74. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Derin, D.; Soydinç, H.O.; Guney, N.; Tas, F.; Camlica, H.; Duranyildiz, D.; Yasasever, V.; Topuz, E. Serum levels of apoptosis biomarkers, survivin and TNF-alpha in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2008, 59, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvillard, L.; Ortega-Deballon, P.; Bourredjem, A.; Scherrer, M.-L.; Mantion, G.; Delhorme, J.-B.; Deguelte-Lardière, S.; Petit, J.-M.; Claire Bonithon-Kopp for the AGARIC Study Group. A case–control study of pre-operative levels of serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and other potential inflammatory markers in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kędziora, S.; Słotwiński, R.; Olszewski, W.L.; Zaleska, M.; Lech, G.; Słodkowski, M.; Krasnodębski, I.W. Programmed death of leukocytes through Fas and TNFR1 in malnourished patients with pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterol. Rev./Przegl. Gastroenterol. 2011, 6, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, M.S.; Bou-Anak, S.; Burgett, M.E.; Sarmey, N.; Khosla, D.; Dahiya, S.; Weil, R.J.; Bae, E.; Huang, P.; McGraw, M.; et al. Correlation of higher levels of soluble TNF-R1 with a shorter survival, independent of age, in recurrent glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 131, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; MacManus, M.; Kron, T.; Best, N.; Smith, J.; Lobachevsky, P.; Ball, D.; Martin, O. A Pattern of Early Radiation-Induced Inflammatory Cytokine Expression Is Associated with Lung Toxicity in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovo, M.; Giaj-Levra, N.; Furlan, C.; Bortolin, M.T.; Muraro, E.; Polesel, J.; Minatel, E.; Tedeschi, R.; Filippi, A.R.; Alongi, F.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy and intensity modulated radiation therapy induce different plasmatic cytokine changes in non-small cell lung cancer patients: A pilot study. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 18, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Demaria, S.; Formenti, S. Radiation as an immunological adjuvant: Current evidence on dose and fractionation. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolin, M.; Trovo, M.; Furlan, C.; Bidoli, E.; Basaglia, G.; Avanzo, M.; Minatel, E.; Gobitti, C.; Franchin, G.; De Paoli, P.; et al. Multiplexed Plasma Cytokine Chemokine and Growth Factor Profiling in Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, S811–S812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
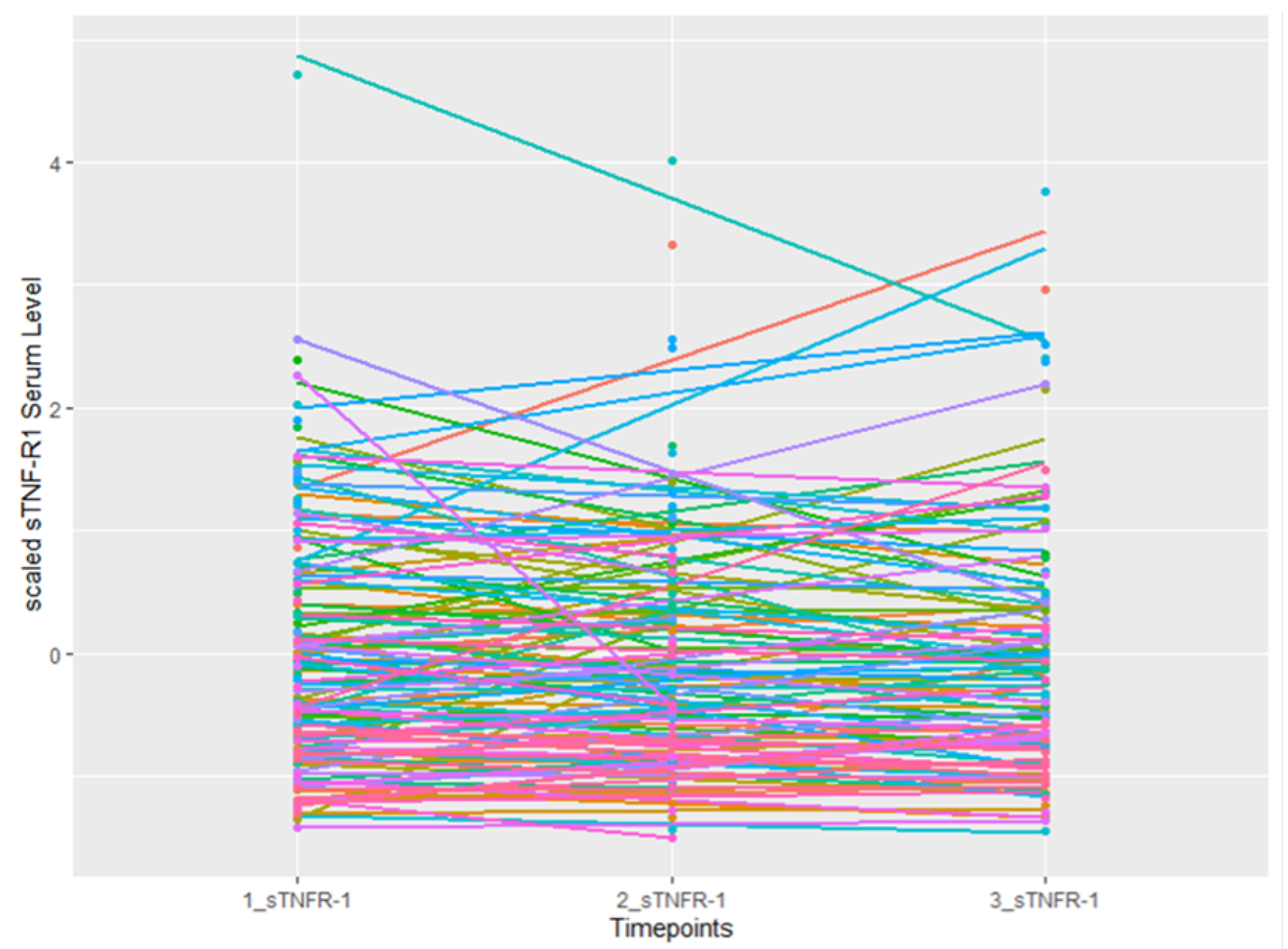
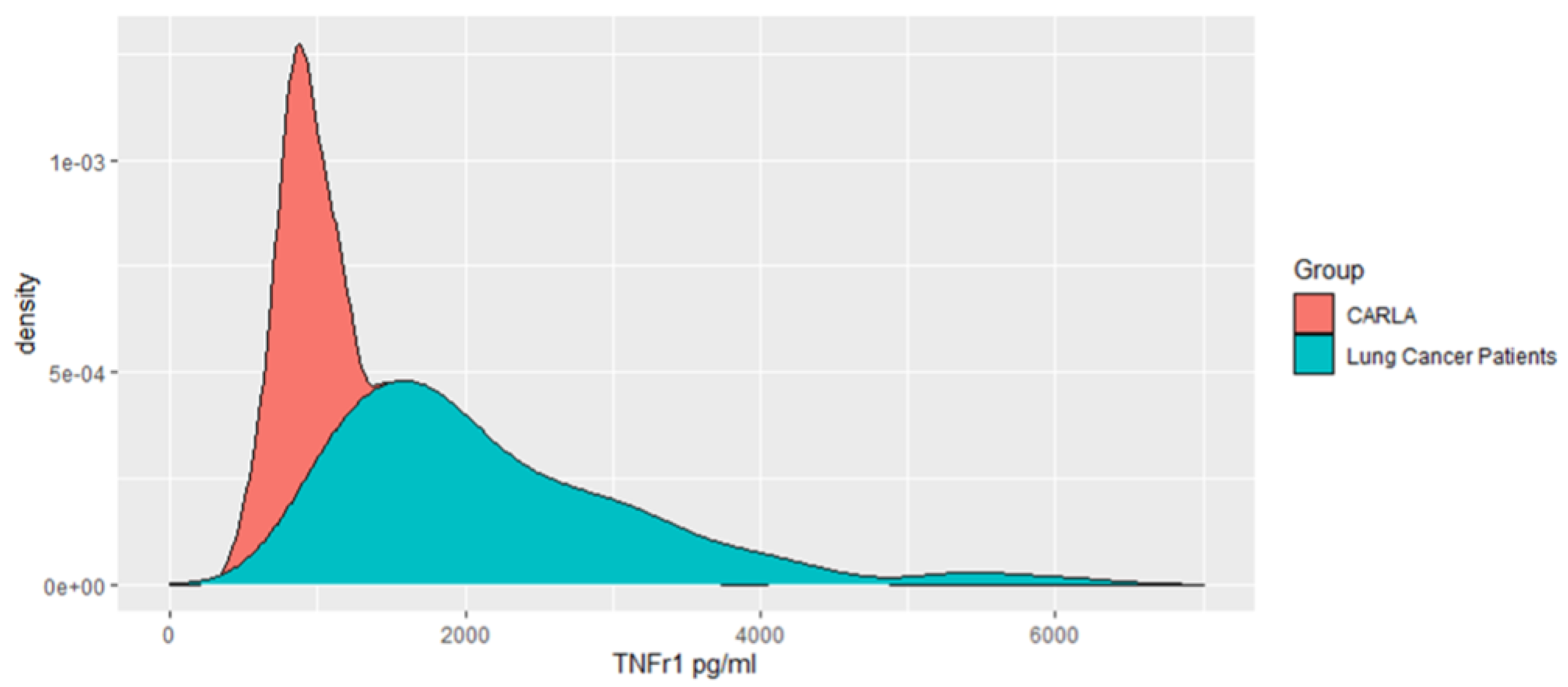
| Patient Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Age (years), mean | 68.18 (10) |
| Sex (female) | 60 (45%) |
| 1st sTNF-RI (pg/mL), mean | 2081.62 (844) |
| CRP (mg/L), mean | 53.8 (68) |
| Adjuvant chemotherapy | 65 (52%) |
| Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) | 33 (32%) |
| Type of treatment (palliative) | 48 (36%) |
| TNM stage I | 19 (15%) |
| TNM stage II | 13 (10%) |
| TNM stage III | 47 (36%) |
| TNM stage IV | 51 (39%) |
| Gross tumor volume (GTV) (ccm) | 106.3 (266) |
| Planning target volume (PTV) dose (Gy) | 62.0 (24) |
| 2nd sTNF-RI (pg/mL), mean | 2228.24 (917) |
| 3rd sTNF-RI (pg/mL), mean | 2298.40 (1026) |
| Status (Dead) | 54 (41%) |
| Adjusted -Estimates * (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.211 (−1.754–2.305) | 0.79 |
| Standardized mean of sTNFR-1 at first measurement | −0.0460 (−0.3–0.2) | 0.67 |
| Age (in years) | 0.008 (−0.013–0.029) | 0.45 |
| Sex (female) | 0.0988 (−343–0.555) | 0.67 |
| Chemotherapy vs no chemotherapy | 0.203 (−0.22–0.63) | 0.34 |
| TNM stage II vs. I | −0.17 (−1.040–0.69) | 0.69 |
| TNM stage III vs. I | −0.18 (−0.98–0.62) | 0.65 |
| TNM stage IV vs. I | −0.29 (−1.11–0.54) | 0.49 |
| Log (CRP) (mg/L) | −0.01 (−0.15–0.12) | 0.84 |
| Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) vs. no SBRT | 0.95 (0.33–1.58) | 0.003 |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) Model 1 | Adjusted HR (95% CI) Model 2 | Adjusted HR (95% CI) Model 3 with CRP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized baseline sTNF-RI (pg/mL) | 1.38 (1.1–1.8) | 1.16 (0.8–1.5) | 1.16 (0.9–1.6) |
| Standardized change in sTNF-RI (pg/mL/day) | 1.22 (0.9–1.7) | 2.60 (1.4–4.7) | 2.60 (1.4–4.7) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, L.; Bedir, A.; Kraus, F.B.; Ostheimer, C.; Vordermark, D.; Mikolajczyk, R.; Seliger, B.; Medenwald, D. Correlation of Increased Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 with Mortality and Dependence on Treatment in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030525
Hassan L, Bedir A, Kraus FB, Ostheimer C, Vordermark D, Mikolajczyk R, Seliger B, Medenwald D. Correlation of Increased Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 with Mortality and Dependence on Treatment in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Cancers. 2024; 16(3):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030525
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Lamiaa, Ahmed Bedir, Frank Bernhard Kraus, Christian Ostheimer, Dirk Vordermark, Rafael Mikolajczyk, Barbara Seliger, and Daniel Medenwald. 2024. "Correlation of Increased Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 with Mortality and Dependence on Treatment in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Longitudinal Cohort Study" Cancers 16, no. 3: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030525
APA StyleHassan, L., Bedir, A., Kraus, F. B., Ostheimer, C., Vordermark, D., Mikolajczyk, R., Seliger, B., & Medenwald, D. (2024). Correlation of Increased Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 with Mortality and Dependence on Treatment in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Cancers, 16(3), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030525





