National Multicenter Study on the Comparison of Robotic and Open Thymectomy for Thymic Neoplasms in Myasthenic Patients: Surgical, Neurological and Oncological Outcomes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Surgical Results
3.2. Oncological Results
3.3. Neurological Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marulli, G.; Comacchio, G.M.; Schiavon, M.; Rebusso, A.; Mammana, M.; Zampieri, D.; Perissinotto, E.; Rea, F. Comparing robotic and trans-sternal thymectomy for early-stage thymoma: A propensity score-matching study. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 54, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Asaf, B.B.; Pulle, M.V.; Puri, H.V.; Sethi, N.; Bishnoi, S. Myasthenia is a poor prognostic factor for perioperative outcomes after robotic thymectomy for thymoma. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 59, 807–813. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Swierzy, M.; Rückert, R.I.; Rückert, J.C. Robotic thymectomy for myasthenia gravis. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2014, 24, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, G.I.; Kaminski, H.J.; Aban, I.B.; Minisman, G.; Kuo, H.C.; Marx, A.; Ströbel, P.; Mazia, C.; Oger, J.; Cea, J.G.; et al. Randomized Trial of Thymectomy in Myasthenia Gravis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, J.; Javidfar, J.; Newmark, A.; Lavelle, M.; Bacchetta, M.; Gorenstein, L.; D’Ovidio, F.; Ginsburg, M.E.; Sonett, J.R. Minimally invasive thymectomy and open thymectomy: Outcome analysis of 263 patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 94, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marulli, G.; Maessen, J.; Melfi, F.; Schmid, T.A.; Keijzers, M.; Fanucchi, O.; Augustin, F.; Comacchio, G.M.; Mussi, A.; Hochstenbag, M.; et al. Multi-institutional European experience of robotic thymectomy for thymoma. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 5, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, M.; Galetta, D.; Borri, A.; Tessitore, A.; Romano, R.; Brambilla, D.; Maisonneuve, P.; Spaggiari, L. Robotic-assisted thymectomy for early-stage thymoma: A propensity-score matched analysis. J. Robot. Surg. 2018, 12, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilshire, C.L.; Blitz, S.L.; Fuller, C.C.; Rückert, J.C.; Li, F.; Cerfolio, R.J.; Ghanim, A.F.; Onaitis, M.W.; Sarkaria, I.S.; Wigle, D.A.; et al. Minimally invasive thymectomy for myasthenia gravis favours a left-sided approach and low severity class. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 60, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaoka, A.; Yamakawa, Y.; Niwa, H.; Fukai, I.; Kondo, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Fujii, Y.; Monden, Y. Extended thymectomy for myasthenia gravis patients: A 20-year review. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1996, 62, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneuertz, P.J.; Kamel, M.K.; Stiles, B.M.; Lee, B.E.; Rahouma, M.; Nasar, A.; Altorki, N.K.; Port, J.L. Robotic Thymectomy Is Feasible for Large Thymomas: A Propensity-Matched Comparison. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, N.; Ruffini, E.; Marx, A.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Peters, S.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Thymic epithelial tumours: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26 (Suppl. S5), v40–v55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Thymomas and Thymic Carcinomas; Version 1.2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/thymic.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Sugarbaker, D.J. Thoracoscopy in the management of anterior mediastinal masses. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1993, 56, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romano, G.; Zirafa, C.C.; Ceccarelli, I.; Guida, M.; Davini, F.; Maestri, M.; Morganti, R.; Ricciardi, R.; Hung Key, T.; Melfi, F. Robotic thymectomy for thymoma in patients with myasthenia gravis: Neurological and oncological outcomes. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 60, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaretzki, A., 3rd; Barohn, R.J.; Ernstoff, R.M.; Kaminski, H.J.; Keesey, J.C.; Penn, A.S.; Sanders, D.B. Myasthenia gravis: Recommendations for clinical research standards. Task Force of the Medical Scientific Advisory Board of the Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America. Neurology 2000, 55, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Weksler, B.; Tavares, J.; Newhook, T.E.; Greenleaf, C.E.; Diehl, J.T. Robot-assisted thymectomy is superior to transsternal thymectomy. Surg. Endosc. 2012, 26, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueckert, J.; Swierzy, M.; Badakhshi, H.; Meisel, A.; Ismail, M. Robotic-assisted thymectomy: Surgical procedure and results. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 63, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Keijzers, M.; de Baets, M.; Hochstenbag, M.; Abdul-Hamid, M.; Zur Hausen, A.; van der Linden, M.; Kuks, J.; Verschuuren, J.; Kessels, F.; Dingemans, A.M.; et al. Robotic thymectomy in patients with myasthenia gravies: Neurological and surgical outcomes. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 48, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evoli, A.; Meacci, E. An update on thymectomy in myasthenia gravis. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.D. History of Thymectomy for Myasthenia Gravis. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2019, 29, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.M.; Herbert, M.A.; Sobhani, N.C.; Tavakolian, P.; Duncan, A.; Bruns, M.; Korngut, K.; Williams, J.; Prince, S.L.; Huber, L.; et al. Comparative clinical outcomes of thymectomy for myasthenia gravis performed by extended transsternal and minimally invasive approaches. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 87, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, X.J.; Ma, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.F. Thoracoscopic thymectomy for myasthenia gravis with and without thymoma: A single-centre experience. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 93, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, Y.; Ulas, A.B.; Mutlu, V.; Colak, A.; Eroglu, A. Thymectomy in Myasthenia Gravis. Eurasian J. Med. 2017, 49, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, I.; Hashizume, M.; Shimada, M.; Tomikawa, M.; Tomiyasu, M.; Suemitsu, R.; Sugimachi, K. Thoracoscopic thymomectomy with the da Vinci computer-enhanced surgical system. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2001, 122, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marulli, G.; Rea, F.; Melfi, F.; Schmid, T.A.; Ismail, M.; Fanucchi, O.; Augustin, F.; Swierzy, M.; Di Chiara, F.; Mussi, A.; et al. Robot-aided thoracoscopic thymectomy for early-stage thymoma: A multicenter European study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 144, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.J.; Hurd, J.; Shah, S.A.; Liou, D.; Wang, H.; Backhus, L.M.; Lui, N.S.; D’Amico, T.A.; Shrager, J.B.; Berry, M.F. A national analysis of open versus minimally invasive thymectomy for stage I to III thymoma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 160, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buentzel, J.; Straube, C.; Heinz, J.; Roever, C.; Beham, A.; Emmert, A.; Hinterthaner, M.; Danner, B.C.; Emmert, A. Thymectomy via open surgery or robotic video assisted thoracic surgery: Can a recommendation already be made? Medicine 2017, 96, e7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, K.E.; Kreaden, U.S.; Hebert, A.E.; Eaton, D.; Redmond, K.C. A systematic review of robotic versus open and video assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) approaches for thymectomy. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 8, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Samarasinghe, Y.; Patel, J.; Khondker, A.; McKechnie, T.; Samarasinghe, N.; Finley, C.; Hanna, W.; Shargall, Y.; Agzarian, J. The short and long-term effects of open vs minimally invasive thymectomy in myasthenia gravis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 3321–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, H. Chylothorax after thoracoscopic extended thymectomy: A case report and literatures review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, E639–E642. [Google Scholar]
- Salfity, H.V.; Timsina, L.; Ceppa, D.P.; Birdas, T.J. Minimally invasive surgery in the management of resectable thymoma: A retrospective analysis from the National Cancer Database. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 6353–6362. [Google Scholar]
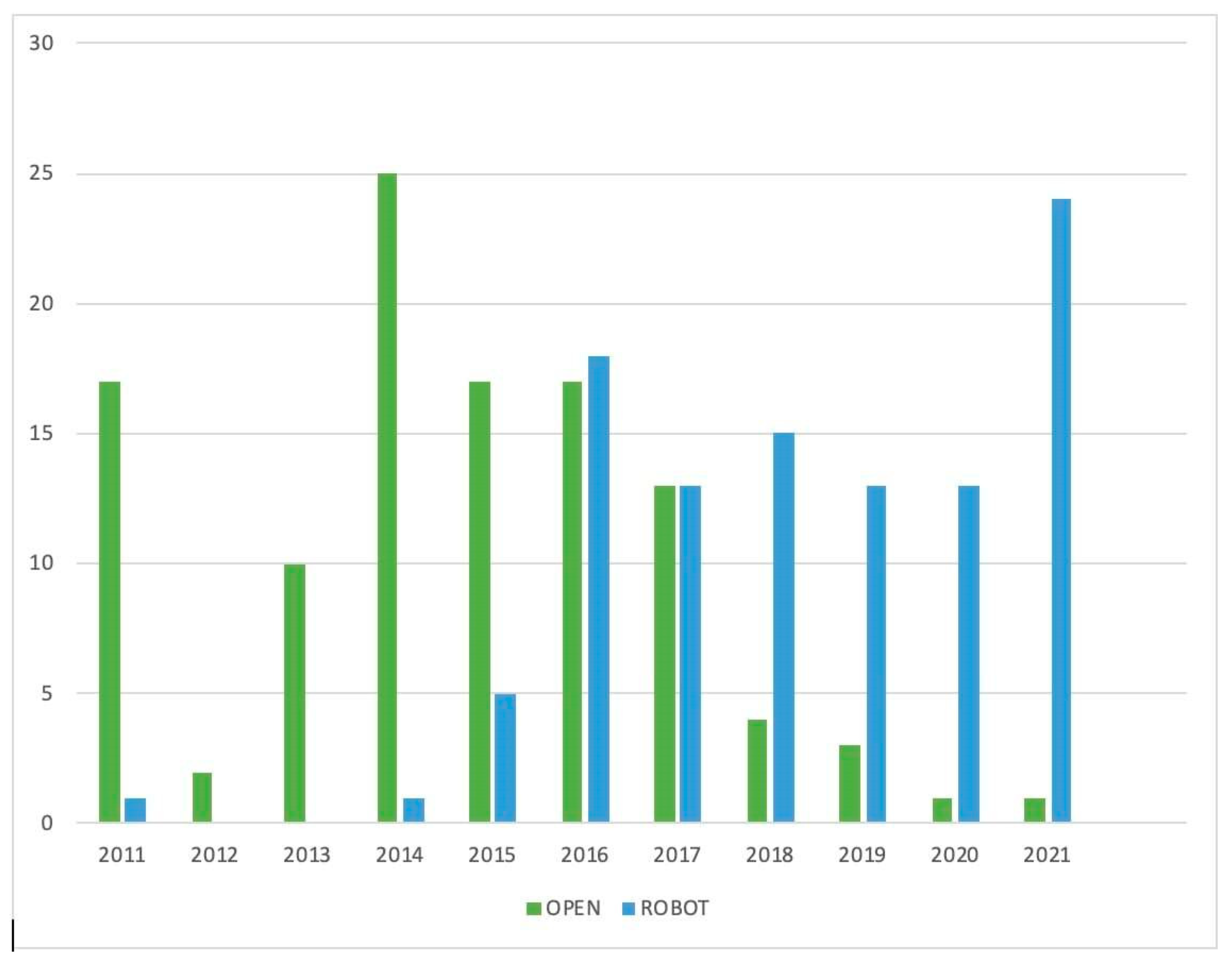
| All Patients n = 213 | Open Surgery n = 110 (51.6%) | Robotic Surgery n = 103 (48.4%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 98 (46%) | 50 (45.5%) | 48 (46.6%) |
| Female | 115 (54%) | 60 (54.5%) | 55 (53.4%) |
| Age (years) | 55 (14.7) | 55.2 (13.9) | 55 (15.6) |
| Steroid at operation time (mg) | 32.8 (22.3) | 34.1 (20.5) | 31.3 (24.2) |
| Pyridostigmine at operation time (mg) | 134.1 (101.1) | 141.5 (97.6) | 125.8 (104.7) |
| All Patients n = 213 | Open Surgery n = 110 (51.6%) | Robotic Surgery n = 103 (48.4%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operative time (minutes) | 127.8 (57.1) | 110 (42) | 146 (62) | <0.001 |
| Extubation day | ||||
| OP | 206 (96.7%) | 104 (94.5%) | 102 (99%) | 0.578 |
| I POD | 3 (1.4%) | 2 (1.8%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Complications | 37 (17.4%) | 22 (20%) | 15 (14.6%) | 0.038 |
| Need of transfusion | 5 (2.3%) | 4 (3.6%) | 1 (1%) | 0.199 |
| Hospitalization days | 6.5 (5.5) | 7.5 (6) | 5.5 (4.8) | 0.006 |
| Chest tube days | 3.4 (3.5) | 3.3 (2) | 3.5 (4.6) | 0.634 |
| Postoperative complications | ||||
| Anemia requiring | 5 (2.3%) | 4 (3.6%) | 1 (1%) | |
| blood transfusion | ||||
| Arrhythmias | 8 (3.8%) | 5 (4.5%) | 3 (2.9%) | |
| Chylothorax | 3 (1.4%) | 0 | 3 (2.9%) | |
| Exacerbation/myasthenic crisis | 6 (2.8%) | 3 (2.7%) | 3 (2.9%) | |
| Neuromyotonia | 1 (0.5%) | 1 (0.9%) | 0 | |
| Thoracic complications (pneumothorax, pleural effusion) | 6 (2.8%) | 5 (4.5%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Myocardial infarction | 1 (0.5%) | 1 (0.9%) | 0 |
| All Patients n = 213 | Open Surgery n = 110 (51.6%) | Robotic Surgery n = 103 (48.4%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masaoka–Koga stage | ||||
| I | 58 (27.2%) | 12 (10.9%) | 46 (44.7%) | 0.604 |
| II | 131 (61.5%) | 82 (74.6%) | 49 (47.5%) | |
| III | 20 (9.4%) | 13 (11.8%) | 7 (6.8%) | |
| IV | 4 (1.9%) | 3 (2.7%) | 1 (1%) | |
| WHO | ||||
| A | 31 (14.6%) | 20 (18.2%) | 11 (10.7%) | 0.075 |
| AB | 36 (16.9%) | 21 (19.1%) | 15 (14.6%) | |
| B1 | 34 (15.9%) | 12 (10.2%) | 22 (21.4%) | |
| B2 | 85 (39.9%) | 47 (42.8%) | 38 (36.9%) | |
| B3 | 12 (5.6%) | 8 (7.3%) | 4 (3.8%) | |
| C | 2 (1%) | 0 | 2 (1.8%) | |
| Others | 13 (6.1%) | 2 (1.8%) | 11 (10.7%) | |
| Tumor size (cm) | 5.2 (2.6) | 5.6 (2.6) | 3.5 (2.1) | <0.001 |
| R0 | 208 (97.6%) | 107 (97.3%) | 101 (98%) | 0.705 |
| R1 | 5 (2.4%) | 3 (2.7%) | 2 (2%) | |
| Postoperative Radiotherapy | 72 (33.8%) | 51 (46.4%) | 21 (20.4%) | <0.001 |
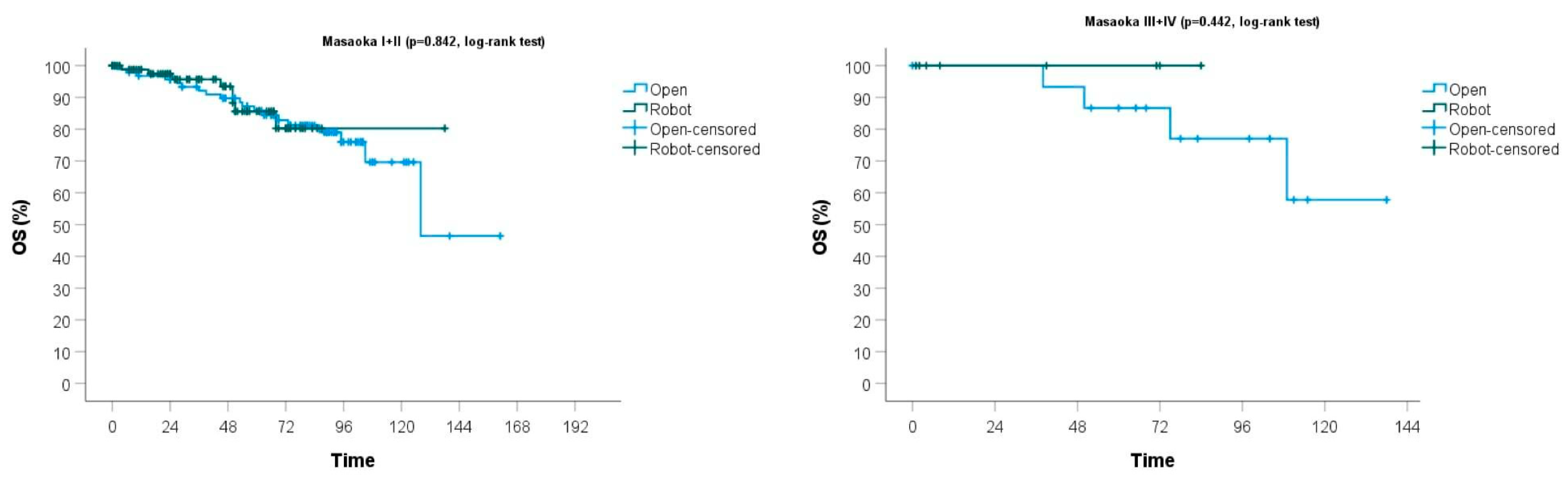
| 3-year OS | 94% | 93% | 95% | |
| 5-year OS | 86% | 86% | 87% |
| All Patients n = 213 | Open Surgery n = 110 (51.6%) | Robotic Surgery n = 103 (48.4%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MFGA-PIS | |||
| CSR | 17 (8%) | 12 (10.9%) | 5 (4.9%) |
| MM | 73 (34.3%) | 47 (42.7%) | 26 (25.2%) |
| PR | 2 (0.9%) | 1 (0.9%) | 1 (0.9%) |
| I | 93 (43.7%) | 63 (57.3%) | 30 (29.1%) |
| U | 30 (14.1%) | 16 (14.5%) | 14 (13.6%) |
| W | 14 (6.6%) | 3 (2.7%) | 11 (10.7%) |
| E | 3 (1.4%) | 2 (1.8%) | 1 (0.9%) |
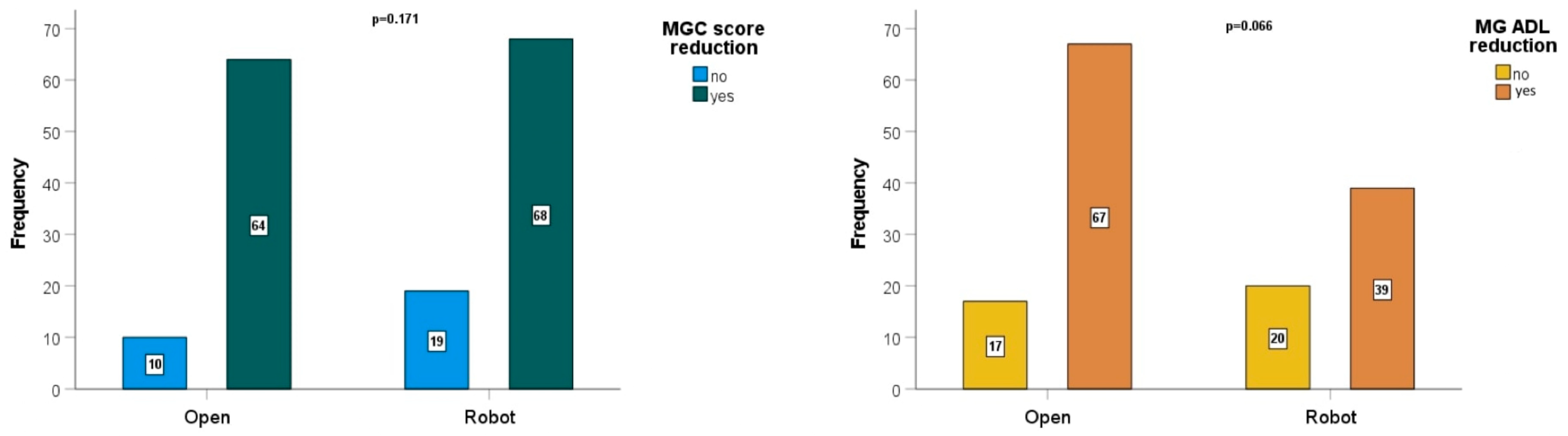
| Preoperative MGC score | 7.1 (8.1) | 7 (8.2) | 7.1 (8.1) |
| Postoperative MGC score | 2.8 (5.5) | 2.8 (5.6) | 2.8 (5.5) |
| Preoperative MG-ADL | 3.8 (3.3) | 3.9 (3.3) | 3.8 (3.3) |
| Median postoperative | |||
| MG-ADL | 1.8 (2.8) | 1.8 (2.9) | 1.8 (2.8) |
| Postoperative reduction of steroid | 117 (54.9%) | 70 (63.6%) | 47 (45.6%) |
| Postoperative reduction of pyridostigmine | 91 (42.7%) | 53 (48.2%) | 38 (36.9%) |
| Postoperative reduction of MG symptoms | 146 (68.5%) | 77 (70%) | 69 (67%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sicolo, E.; Zirafa, C.C.; Romano, G.; Brandolini, J.; De Palma, A.; Bongiolatti, S.; Gallina, F.T.; Ricciardi, S.; Maestri, M.; Guida, M.; et al. National Multicenter Study on the Comparison of Robotic and Open Thymectomy for Thymic Neoplasms in Myasthenic Patients: Surgical, Neurological and Oncological Outcomes. Cancers 2024, 16, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020406
Sicolo E, Zirafa CC, Romano G, Brandolini J, De Palma A, Bongiolatti S, Gallina FT, Ricciardi S, Maestri M, Guida M, et al. National Multicenter Study on the Comparison of Robotic and Open Thymectomy for Thymic Neoplasms in Myasthenic Patients: Surgical, Neurological and Oncological Outcomes. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020406
Chicago/Turabian StyleSicolo, Elisa, Carmelina Cristina Zirafa, Gaetano Romano, Jury Brandolini, Angela De Palma, Stefano Bongiolatti, Filippo Tommaso Gallina, Sara Ricciardi, Michelangelo Maestri, Melania Guida, and et al. 2024. "National Multicenter Study on the Comparison of Robotic and Open Thymectomy for Thymic Neoplasms in Myasthenic Patients: Surgical, Neurological and Oncological Outcomes" Cancers 16, no. 2: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020406
APA StyleSicolo, E., Zirafa, C. C., Romano, G., Brandolini, J., De Palma, A., Bongiolatti, S., Gallina, F. T., Ricciardi, S., Maestri, M., Guida, M., Morganti, R., Carleo, G., Mugnaini, G., Tajè, R., Calabró, F., Lenzini, A., Davini, F., Cardillo, G., Facciolo, F., ... Melfi, F. (2024). National Multicenter Study on the Comparison of Robotic and Open Thymectomy for Thymic Neoplasms in Myasthenic Patients: Surgical, Neurological and Oncological Outcomes. Cancers, 16(2), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020406










