Advanced Hyperpolarized 13C Metabolic Imaging Protocol for Patients with Gliomas: A Comprehensive Multimodal MRI Approach
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject Population
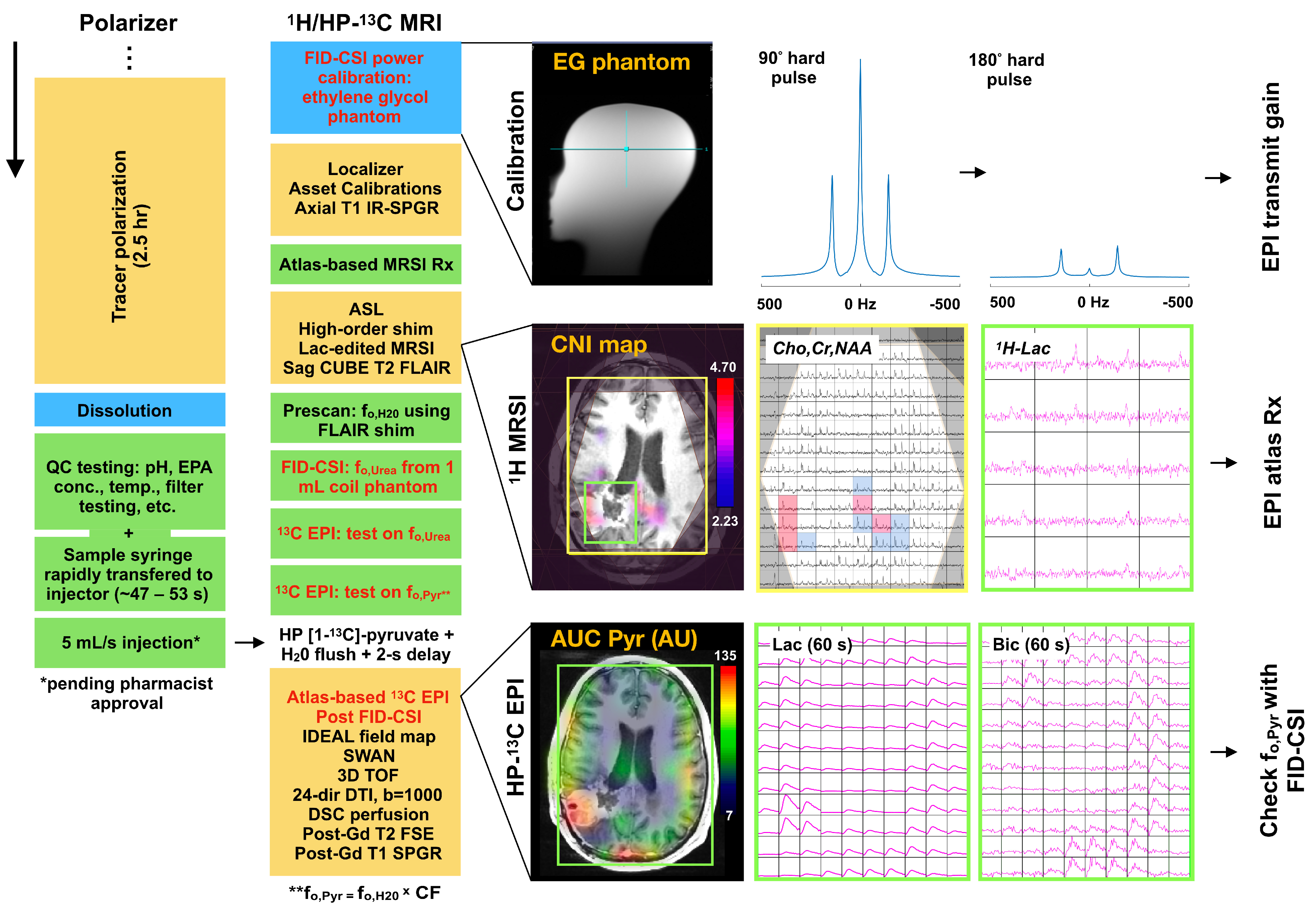
2.2. 1H/HP-13C MRI Protocol Overview
2.3. Tracer Polarization, QC & Injection
2.4. HP-13C EPI Data Acquisition
2.5. Data Post-Processing
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Data Overiew
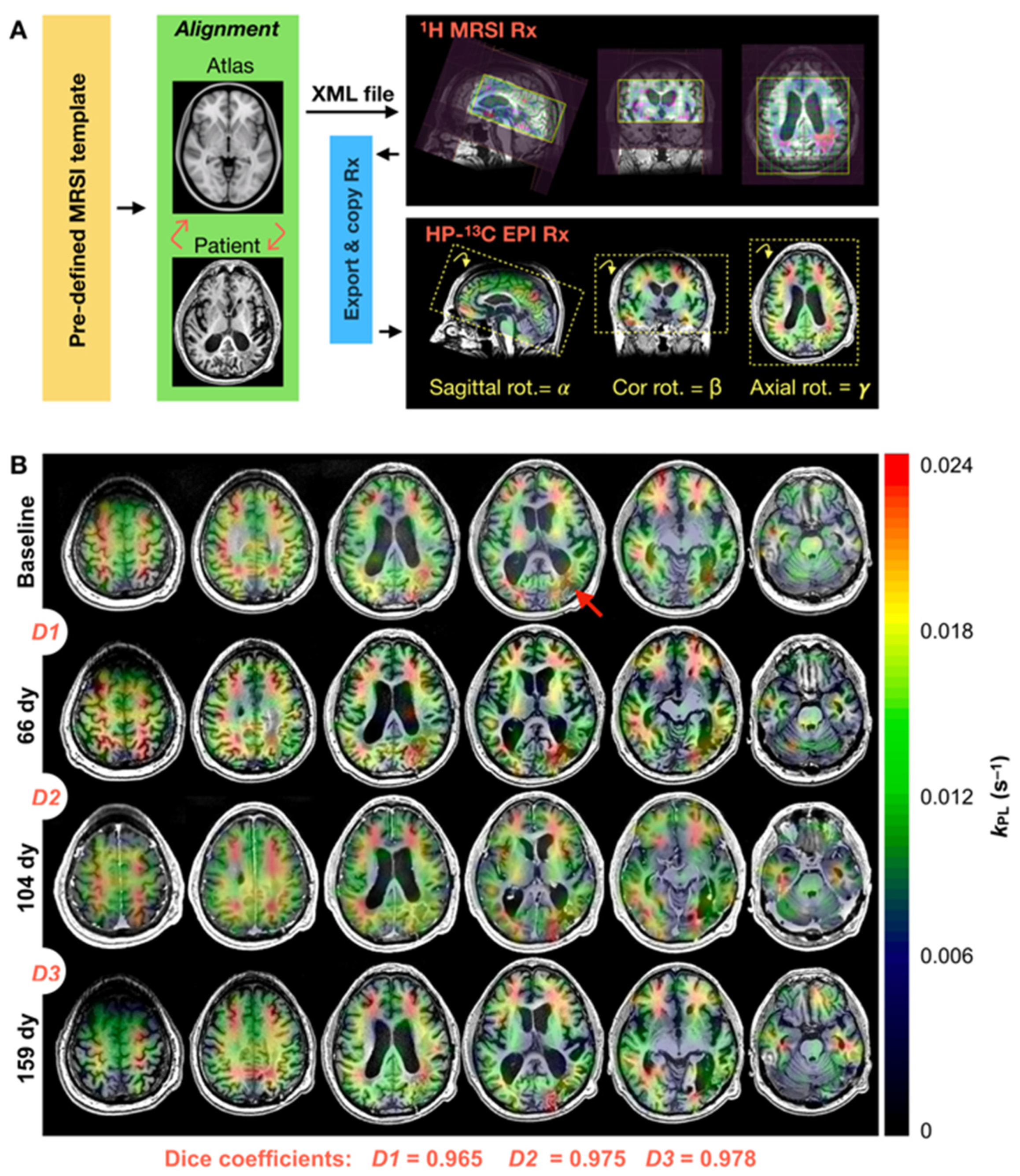
3.2. Serial Atlas-Based HP-13C EPI
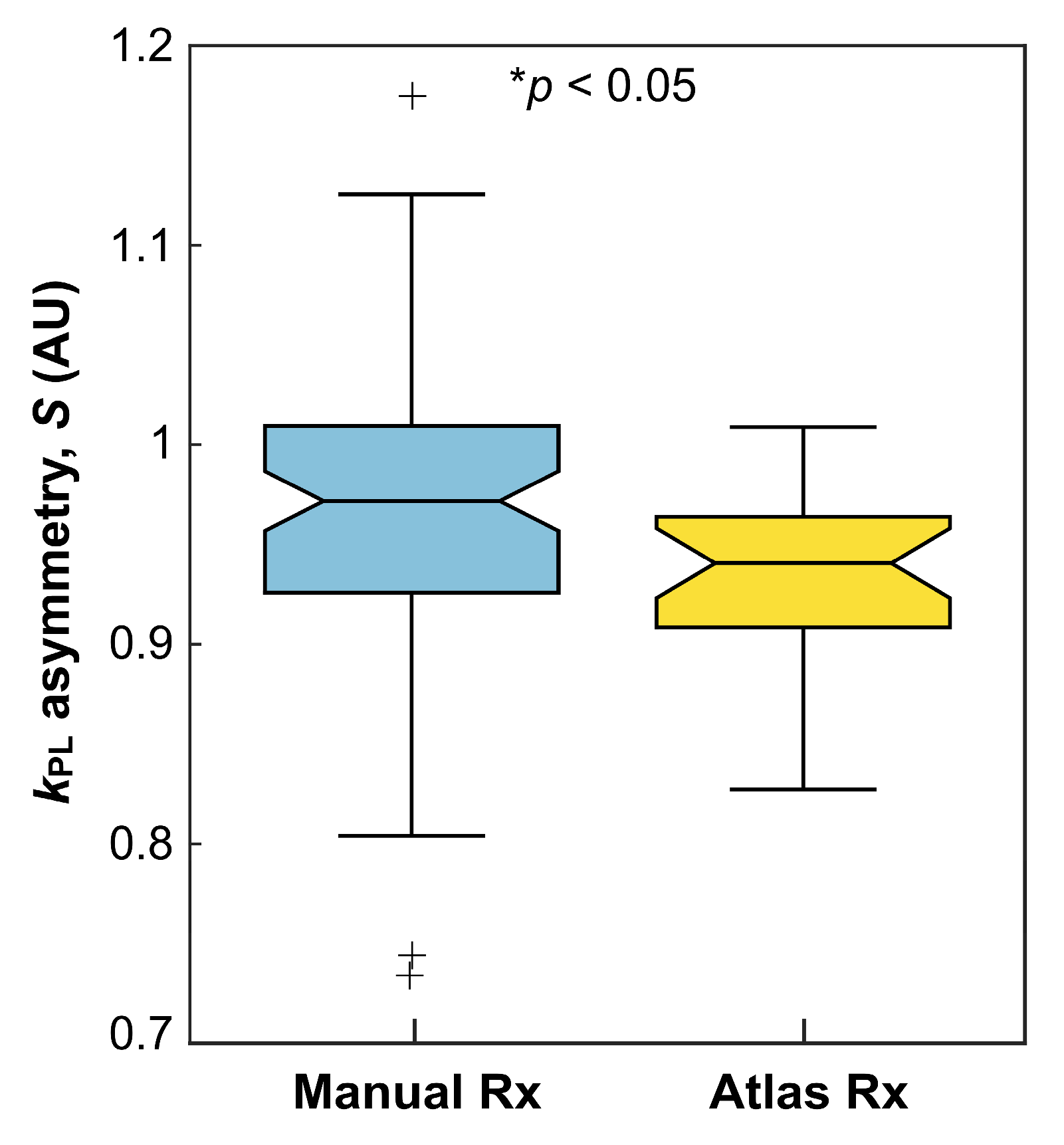
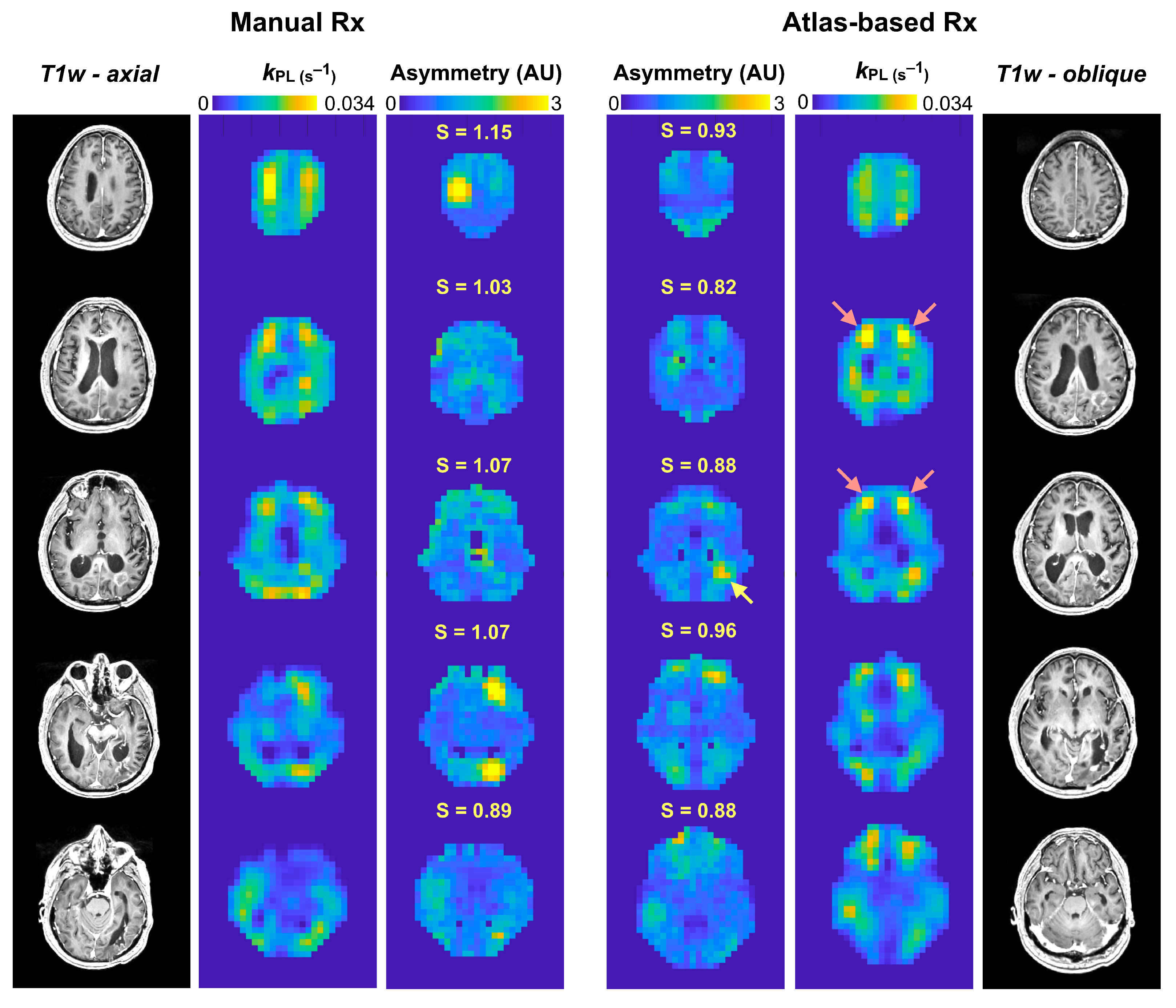
3.3. Asymmetry in EPI Kinetics
3.4. Referencing [13C]-Pyruvate fo
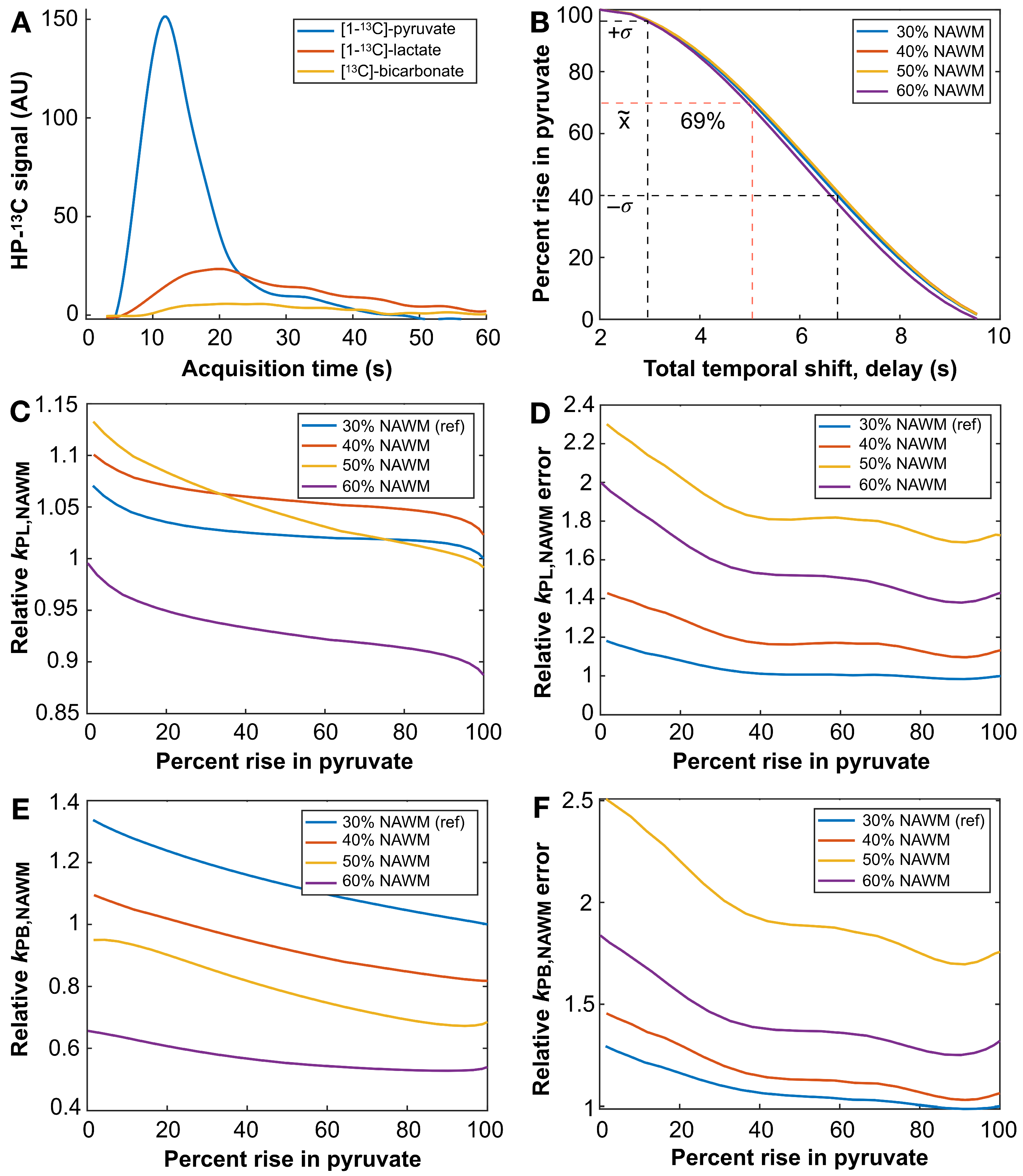
3.5. HP-13C EPI Acquisition Delay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warburg, O. On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science 1956, 124, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Zadeh, G. Metabolic reprogramming in glioblastoma: The influence of cancer metabolism on epigenetics and unanswered questions. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Fridlund, B.; Gram, A.; Hansson, G.; Hansson, L.; Lerche, M.H.; Servin, R.; Thaning, M.; Golman, K. Increase in signal-to-noise ratio of >10,000 times in liquid-state NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10158–10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Gordon, J.W.; Carvajal, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Bok, R.; Van Criekinge, M.; Ferrone, M.; Slater, J.B.; Xu, D.; et al. Development of methods and feasibility of using hyperpolarized carbon-13 imaging data for evaluating brain metabolism in patient studies. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miloushev, V.Z.; Granlund, K.L.; Boltyanskiy, R.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Brennan, C.W.; Tabar, V.; Yang, T.J.; Holodny, A.I.; et al. Metabolic imaging of the human brain with hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate demonstrates 13C-lactate production in brain tumor patients. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3755–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autry, A.W.; Gordon, J.W.; Chen, H.Y.; LaFontaine, M.; Bok, R.; Van Kriekinge, M.; Slater, J.B.; Carvajal, L.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Chang, S.M.; et al. Characterization of serial hyperpolarized-13C metabolic imaging in patients with glioma. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 27, 102323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Patel, T.R.; Pinho, M.C.; Choi, C.; Harrison, C.E.; Baxter, J.D.; Derner, K.; Pena, S.; Liticker, J.; Raza, J.; et al. Preoperative imaging of glioblastoma patients using hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate: Potential role in clinical decision making. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccagna, F.; McLean, M.A.; Grist, J.T.; Kaggie, J.; Mair, R.; Riemer, F.; Woitek, R.; Bill, A.B.; Deen, S.; Daniels, C.J.; et al. Imaging glioblastoma metabolism by using hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate demonstrates heterogeneity in lactate labeling: A proof of principle study. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2022, 4, e210076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autry, A.W.; Vaziri, S.; LaFontaine, M.; Gordon, J.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Kim, Y.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Molinaro, A.; Clarke, J.L.; Bush, N.A.O.; et al. Multi-parametric hyperpolarized 13C/1H imaging reveals Warburg-related metabolic dysfunction and associated regional heterogeneity in high-grade human gliomas. NeuroImage Clin. 2023, 39, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cruz, L.C.H.; Rodriguez, I.; Domingues, R.C.; Gasparetto, E.L.; Sorensen, A.G. Pseudoprogression and pseudoresponse: Imaging challenges in the assessment of posttreatment glioma. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S. Neuroimaging in neuro-oncology. Neurotherapeutic 2009, 6, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, W.; Li, Y.; Crane, J.C.; Nelson, S.J. A fully automated atlas based method for prescribing 3D PRESS MR spectroscopic imaging: Towards robust and reproduceable metabolite measurements in human brain. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Autry, A.W.; Park, I.; Van Criekinge, M.; Mammoli, D.; Milshteyn, E.; Bok, R.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; et al. Translation of carbon-13 EPI for hyperpolarized MR molecular imaging of prostate and brain cancer patients. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 2702–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grist, J.T.; Hansen, E.S.S.; Sanchez-Heredia, J.D.; McLean, M.A.; Tougaard, R.; Riemer, F.; Schulte, R.F.; Kaggie, J.D.; Ardenkjaer, J.H.; Lautsen, C.; et al. Creating a clinical platform for carbon-13 studies using sodium-23 and proton resonances. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.; Chen, A.P.; Zierhut, M.L.; Ozturk-Isik, E.; Vigneron, D.B.; Nelson, S.J. Implementation of 3T lactate-edited 3D 1H MR spectroscopic imaging with flyback echo-planar readout for gliomas patients. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingson, B.M.; Chung, C.; Pope, W.B.; Boxerman, J.L.; Kaufmann, T.J. Pseudoprogression, radionecrosis, inflammation or true tumor progression? Challenges associated with glioblastoma response assessment in an evolving therapeutic landscape. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 134, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenburger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Vigneron, D.B.; Xu, D. Current human brain applications and challenges of dynamic hyperpolarized carbon-13 labeled pyruvate MR metabolic imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 4225–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathy, S.; Crawford, F.W.; Lamborn, K.R.; Pirzkal, A.; Chang, S.M.; Cha, S.M.; Nelson, S.J. Evaluation of MR markers that predict survival in patients with newly diagnosed GBM prior to adjuvant therapy. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2009, 91, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autry, A.W.; Gordon, J.W.; Carvajal, L.; Mareyam, A.; Chen, H.Y.; Park, I.; Mammoli, D.; Vareth, M.; Chang, S.M.; Wald, L.L.; et al. Comparison between 8- and 32-channel phased-array receive coils for in vivo hyperpolarized 13C imaging of the human brain. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sanchez-Heredia, J.D.; Olin, R.B.; Hansen, E.S.S.; Laustsen, C.; Zhurbenko, V.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.K. A cryogenic 14-channel 13C receiver array for 3T human head imaging. Magn. Reason. Med. 2023, 89, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabner, G.; Janke, A.L.; Budge, M.M.; Smith, D.; Pruessner, J.; Collins, D.L. Symmetric atlasing and model based segmentation: An application to the hippocampus in older adults. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 2006, 9, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reeder, S.B.; Pineda, A.R.; Wen, Z.; Shimakawa, A.; Yu, H.; Brittain, J.H.; Gold, G.E.; Beaulieu, C.H.; Pelc, N.J. Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL): Application with fast spin-echo imaging. Magn. Reason. Med. 2005, 54, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, J.C. The Choleski Decomposition. In Compact Numerical Methods for Computers: Linear Algebra and Function Minimization, 2nd ed.; Adam Hilger: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Chapter 7; pp. 84–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Ohliger, M.; Tang, S.; Cao, P.; Carvajal, L.; Autry, A.W.; Li, Y.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Chang, S.M.; et al. Coil combination methods for multi-channel hyperpolarized-13C imaging data from human studies. J. Magn. Reson. 2019, 301, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Autry, A.W.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.; Chang, S.M.; Li, Y.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Brender, J.R.; Krishna, M.C.; Xu, D.; et al. Denoising of hyperpolarized-13C MR images of the human brain using patch-based higher-order singular value decomposition. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 86, 2497–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, S.; Autry, A.W.; LaFontaine, M.; Kim, Y.; Gordon, J.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Hu, J.Y.; Lupo, J.M.; Chang, S.M.; Clarke, J.L.; et al. Assessment of higher-order singular value decomposition denoising methods on dynamic hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRI data from patients with glioma. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 36, 103155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, P.E.Z.; Chen, H.Y.; Gordon, J.W.; Korn, N.; Maidens, J.; Arcak, M.; Tang, S.; Criekinge, M.; Carvajal, L.; Mammoli, D.; et al. Investigation of analysis methods for hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate metabolic MRI in prostate cancer patients. NMR Biomed. 2018, 31, e3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden random field model and the expectation maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2001, 20, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E.T.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, C.P.; Feng, J.; Joliot, M. Automated anatomical labelling atlas 3. NeuroImage 2020, 206, 116189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menze, B.H.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.; Burren, Y.; Porz, N.; Slotboom, J.; Wiest, R.; et al. The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1993–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogeweg, L.; Sanchez, C.I.; Maduskar, P.; Philipsen, R.H.H.M.; van Ginneken, B. Fast and effective quantification of symmetry in medical images for pathological detection: Application to chest radiography. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 2242–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.W.; Autry, A.W.; Tang, S.; Graham, J.Y.; Bok, R.A.; Zhu, X.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Li, Y.; Ohliger, M.A.; Abraham, M.R.; et al. A variable resolution approach for improved acquisition of hyperpolarized 13C metabolic MRI. Magn. Reason. Med. 2020, 84, 2943–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Kim, Y.; Autry, A.W.; Frost, M.M.; Bok, R.A.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Vigneron, D.B.; et al. Kinetic analysis of multi-resolution hyperpolarized 13 C human brain MRI to study cerebral metabolism. Magn. Reason. Med. 2022, 88, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Vaziri, S.; Bogh, N.; Kim, Y.; Autry, A.W.; Bok, R.A.; Li, Y.; Laustsen, C.; Xu, D.; Larson, P.E.Z.; et al. Investigating cerebral perfusion with high resolution hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 90, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenck, J.F. The role of magnetic susceptibility in magnetic resonance imaging: MRI magnetic compatibility of first and second kinds. Med. Phys. 1996, 23, 815–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autry, A.W.; Park, I.; Kline, C.; Chen, H.Y.; Gordon, J.W.; Raber, S.; Hoffman, C.; Kim, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Vigneron, D.B.; et al. Pilot study of hyperpolarized 13C metabolic imaging in pediatric patients with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma and other CNS cancers. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Keshari, K.R.; Cunningham, C.H. Slowing T1 relaxation of hyperpolarized [2-13C]pyruvate with deuterium enrichment. Proc. Int. Soc. Magn. Res. Med. 2021, 31, Abstract 3803. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, S.J.; Li, Y.; Park, I.; Chang, S.M. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Glioblastoma; Iv, M., Wintermark, M., Massoud, T.F., Eds.; Glioblastoma: State-of-the-Art Clinical Neuroimaging; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2019; Chapter 15; pp. 193–218. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, C.; Ganji, S.K.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Rakheja, D.; Kovacs, Z.; Yang, X.L.; Mashimo, T.; Raisanen, J.M.; Marin-Valencia, I.; et al. 2-hydroxyglutarate detection by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in IDH-mutated patients with gliomas. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autry, A.W.; LaFontaine, M.; Jalbert, L.; Philips, E.; Phillips, J.J.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.; Berger, M.S.; Chang, S.M.; Li, Y. Spectroscopic imaging of D-2-hydroxyglutarate and other metabolites in pre-surgical patients with IDH-mutant lower-grade gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2022, 159, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, B.T.; Chen, H.Y.; Gordon, J.W.; Mammoli, D.; Sriram, R.; Autry, A.W.; Le Page, L.M.; Chaumeil, M.; Shin, P.; Slater, J.; et al. First hyperpolarized [2-13C]pyruvate MR studies of human brain metabolism. J. Magn. Reson. 2019, 309, 106617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.T.; Kim, Y.; Gordon, J.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Autry, A.W.; Lee, P.M.; Hu, J.Y.; Tan, C.T.; Suszczynski, C.; Chang, S.M.; et al. Hyperpolarized [2-13C]pyruvate MR molecular imaging with whole brain coverage. NeuroImage 2023, 280, 120350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Tsang, M.; Subbaraj, L.; Cleveland, J.; Chen, L.; Lu, M.; Sharma, J.; Vigneron, D.B.; Kurhanewicz, J.; LaFontaine, M.; et al. Tumor metabolism and neurocognition in CNS lymphoma. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feichtinger, R.G.; Weis, S.; Johannes, A.M.; Zimmermann, F.A.; Bogner, B.; Sperl, W.; Kofler, B. Alterations of oxidative phosphorylation in meningiomas and peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy-Kanniappan, S. Tumor glycolysis as a target for cancer therapy: Progress and prospects. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sushentsev, N.; McLean, M.A.; Warren, A.Y.; Benjamin, A.J.V.; Brodie, C.; Frary, A.; Gill, A.B.; Jones, J.; Kaggie, J.D.; Lamb, B.W.; et al. Hyperpolarized 13C-MRI identifies the emergence of a glycolytic cell population within intermediate-risk human prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Aggarwal, R.; Bok, R.A.; Ohliger, M.A.; Zhu, Z.; Lee, P.; Gordon, J.W.; van Criekinge, M.; Carvajal, L.; Slater, J.B.; et al. Hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate MRI detects real-time metabolic flux in prostate cancer metastases to bone and liver: A clinical feasibility study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020, 23, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.M.; Chen, H.Y.; Gordon, J.W.; Wang, Z.J.; Bok, R.; Hashoian, R.; Kim, Y.; Liu, X.; Nickles, T.; Cheung, K.; et al. Whole-abdomen metabolic imaging of healthy volunteers using hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 1792–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Meng, M.V.; Slater, J.B.; Gordon, J.W.; Vigneron, D.B.; Stohr, B.A.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Wang, Z.J. Metabolic imaging with hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate magnetic resonance imaging in patients with renal tumors-Initial experience. Cancer 2021, 127, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursprung, S.; Woitek, R.; McLean, M.; Priest, A.N.; Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Brodie, C.R.; Gill, A.B.; Gehrung, M.; Beer, L.; Riddick, A.C.P.; et al. Hyperpolarized 13C-Pyruvate Metabolism as a Surrogate for Tumor Grade and Poor Outcome in Renal Cell Carcinoma—A Proof of Principle Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stodkilde-Jorgensen, H.; Laustsen, C.; Hansen, E.S.S.S.; Schulte, R.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Comment, A.; Frokiaer, J.; Ringgaard, S.; Bertelsen, L.B.; Ladekarl, M.; et al. Pilot study experiences with hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRI in Pancreatic Cancer Patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 647–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient ID | Age | Sex | Diagnosis | Disease State | Treatment before First Scan | No. of Study Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-01 | 62 | M | GBM | newly Dx | Sx | 11 |
| P-02 | 47 | M | G2AIDH+ | recurrent | Sx | 2 |
| P-03 | 59 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 3 |
| P-04 | 55 | M | GBM | newly Dx | Sx | 3 |
| P-05 | 45 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, CCNU, afatinib, abemaciclib | 2 |
| P-06 | 52 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 3 |
| P-07 | 55 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 1 |
| P-08 | 45 | F | GBM | newly Dx | Sx | 1 |
| P-09 | 48 | M | GBM | newly Dx | Sx, RT, TMZ, nivolumab, Optune | 1 |
| P-10 | 61 | M | GBM | newly Dx | Sx, RT, TMZ | 1 |
| P-11 | 62 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, vaccine trial, TMZ, oliparib, everolimus | 2 |
| P-12 | 69 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 5 |
| P-13 | 55 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 3 |
| P-14 | 55 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 3 |
| P-15 | 51 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, Toca 511, bevacizumab | 1 |
| P-16 | 57 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, afatinib, olaparib | 4 |
| P-17 | 58 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, optune | 2 |
| P-18 | 44 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 1 |
| P-19 | 44 | F | GBM | newly Dx | Sx, RT, TMZ, Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor | 1 |
| P-20 | 45 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, nivolumab, Poliovirus | 3 |
| P-21 | 40 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 4 |
| P-22 | 55 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 5 |
| P-23 | 58 | M | GBM | newly Dx | Biopsy | 2 |
| P-24 | 64 | M | GBM | newly Dx | Sx | 1 |
| P-25 | 62 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, nivolumab/placebo trial | 1 |
| P-26 | 56 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, CCNU, bevacizumab | 1 |
| P-27 | 32 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, bevacizumab, afatinib, olaparib | 1 |
| P-28 | 68 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 1 |
| P-29 | 40 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, CCNU, afatinib, abemaciclib | 1 |
| P-30 | 68 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, CCNU, everolimus, dasatinib | 2 |
| P-31 | 40 | F | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, DC Vax trial, CCNU, bevacizumab, pembrolizumab | 1 |
| P-32 | 66 | M | GBM | newly Dx | Sx | 1 |
| P-33 | 62 | F | GBM | newly Dx | Sx, RT, TMZ, Optune | 1 |
| P-34 | 57 | M | GBM | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 2 |
| P-35 | 28 | F | G4AIDH+ | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ | 7 |
| P-36 | 39 | M | G4AIDH+ | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, bevacizumab | 3 |
| P-37 | 33 | M | G4AIDH+ | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, Optune, olaparib, abemaciclib | 5 |
| P-38 | 41 | F | G4AIDH+ | newly Dx | Sx | 1 |
| P-39 | 50 | M | G3OIDH+ | recurrent | Sx, RT, TMZ, CCNU | 2 |
| P-40 | 50 | F | G2OIDH+ | newly Dx | Sx | 2 |
| P-41 | 46 | F | G2OIDH+ | recurrent | Sx | 2 |
| P-42 | 39 | F | G2AIDH+ | recurrent | Sx | 1 |
| Sequence | TE (ms) | TR/TI (ms) | rBW (kHz) | SBW (Hz)/pts | Freq | Phase | Freq. Dir. | FOV (cm) | Flip Angle (deg) | Slice/Space (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Localizer | Min | Min | 62.5 | 288 | 192 | 36.0 | 5.0 | |||
| Asset calibration | 0.5 | 1.4 | 62.5 | A/P | 32.0 | 6.4 | ||||
| Asset calibration for MRSI | 1.6 | 150 | 62.5 | 128 | 128 | A/P | 30.0 | 20 | 5.0/5.0 | |
| Ax T1 IR-SPGR | 3.2 | 8.2/450 | 31.25 | 256 | 256 | A/P | 25.6 | 12 | 1.5 | |
| ASL | 62.5 | 512 | 8 | R/L | 25.6 | 4.0 | ||||
| High-order shim (MRSI) | 7.0 | 1558 | 64 | A/P | 24.0 | 60 | 5.8 | |||
| Lac-edited MRSI | 144 | 1279 | 988/ 712 | 18 | 18 | R/L | 18.0 | 1.0 | ||
| Sag CUBE T2 FLAIR | 86 | 5650/ 1668 | 83.33 | 256 | 224 | S/I | 25.6 | 1.2 | ||
| HP-13C EPI | 21.7 | 62.5 | ~20 | 16 | 16 | R/L | 24.0 | 20 (Pyr) 30 (Lac) 30 (Bic) | 15.0 | |
| 13C FID-CSI | 3000 | 5000/ 2048 | NA | NA | A/P | 20.0 | 100 | |||
| IDEAL field map | Min Full | 125 | 256 | 128 | A/P | 34.0 | 4 | 3.0 | ||
| SWAN | 25.0 | 39.4 | 50.0 | 512 | 300 | A/P | 24.0 | 10 | 2.8 | |
| 3D TOF | 2 | 30.0 | 41.67 | 224 | 160 | A/P | 22.0 | 20 | 1.2 | |
| DTI TOPUP (prescan) | 62 | 7500 | 128 | 128 | R/L | 24.0 | 2.0 | |||
| 24-dir DTI, b = 1000 | 62 | 7500 | 128 | 128 | R/L | 24.0 | 2.0 | |||
| DSC TOPUP (prescan) | 25 | 1500 | 100 | 100 | R/L | 25.6 | 30 | 3.5 | ||
| DSC Perfusion | 25 | 1500 | 100 | 100 | R/L | 25.6 | 30 | 3.5 | ||
| Post-Gd T2 FSE | 110 | 8835 | 41.67 | 384 | 224 | A/P | 24.0 | 30 | 3.0 | |
| post-Gd T1 IR-SPGR | 3.2 | 8.2/450 | 31.25 | 256 | 256 | A/P | 25.6 | 12 | 1.5 |
| Patient | Exam No. | Atlas-Based Rx | Manual Rx | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kPL,NAWM (s−1) | kPB,NAWM (s−1) | kPL,NAWM (s−1) | kPB,NAWM (s−1) | ||
| P-01 | 1 | 0.015 ± 0.001 | 0.0026 ± 0.0007 | 0.015 ± 0.001 | 0.0026 ± 0.0008 |
| 2 | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.0028 ± 0.0007 | |||
| 3 | 0.017 ± 0.001 | 0.0034 ± 0.0010 | |||
| 4 | 0.016 ± 0.002 | 0.0027 ± 0.0013 | |||
| P-02 | 1 | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.0038 ± 0.0012 | 0.017 ± 0.001 | 0.0048 ± 0.0010 |
| P-03 | 1 | 0.013 ± 0.002 | 0.0014 ± 0.0013 | 0.014 ± 0.002 | 0.0017 ± 0.0015 |
| 2 | 0.014 ± 0.001 | 0.0020 ± 0.0008 | 0.013 ± 0.001 | 0.0017 ± 0.0014 | |
| Patient | Scan Interval (Days) | EPI Volumetric Coverage Overlap (Dice Coefficient) |
|---|---|---|
| P-01 | 66 | 0.965 |
| 38 | 0.975 | |
| 55 | 0.978 | |
| P-03 | 37 | 0.991 |
| 62 | 0.977 | |
| P-04 | 56 | 0.980 |
| P-05 | 57 | 0.972 |
| Summary (mean ± SD) | 53 ± 11 | 0.977 ± 0.008 |
| Parameter | Methodological Comparison (No. of Exams), Mean ± SD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atlas-based Rx (n = 26) | Manual Rx (n = 78) | ||
| Hemispheric asymmetry, kPL (S) | 0.939 ± 0.039 | 0.970 ± 0.074 | <0.05 |
| H20 reference (n = 43) | [13C]-urea reference (n = 61) | ||
| |foffset,Pyr| (Hz) | 4.1 ± 3.7 | 9.9 ± 10.7 | <0.001 |
| 2 s delay (n = 29) | 5 s delay (n = 75) | ||
| InflowPyr (%) | 87 ± 19 | 61 ± 29 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Autry, A.W.; Vaziri, S.; Gordon, J.W.; Chen, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Dang, D.; LaFontaine, M.; Noeske, R.; Bok, R.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; et al. Advanced Hyperpolarized 13C Metabolic Imaging Protocol for Patients with Gliomas: A Comprehensive Multimodal MRI Approach. Cancers 2024, 16, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020354
Autry AW, Vaziri S, Gordon JW, Chen H-Y, Kim Y, Dang D, LaFontaine M, Noeske R, Bok R, Villanueva-Meyer JE, et al. Advanced Hyperpolarized 13C Metabolic Imaging Protocol for Patients with Gliomas: A Comprehensive Multimodal MRI Approach. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020354
Chicago/Turabian StyleAutry, Adam W., Sana Vaziri, Jeremy W. Gordon, Hsin-Yu Chen, Yaewon Kim, Duy Dang, Marisa LaFontaine, Ralph Noeske, Robert Bok, Javier E. Villanueva-Meyer, and et al. 2024. "Advanced Hyperpolarized 13C Metabolic Imaging Protocol for Patients with Gliomas: A Comprehensive Multimodal MRI Approach" Cancers 16, no. 2: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020354
APA StyleAutry, A. W., Vaziri, S., Gordon, J. W., Chen, H.-Y., Kim, Y., Dang, D., LaFontaine, M., Noeske, R., Bok, R., Villanueva-Meyer, J. E., Clarke, J. L., Oberheim Bush, N. A., Chang, S. M., Xu, D., Lupo, J. M., Larson, P. E. Z., Vigneron, D. B., & Li, Y. (2024). Advanced Hyperpolarized 13C Metabolic Imaging Protocol for Patients with Gliomas: A Comprehensive Multimodal MRI Approach. Cancers, 16(2), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020354






