Impact of Low Muscle Mass on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Liver-Directed Therapies: Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.4. Assessment of Methodological Quality
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
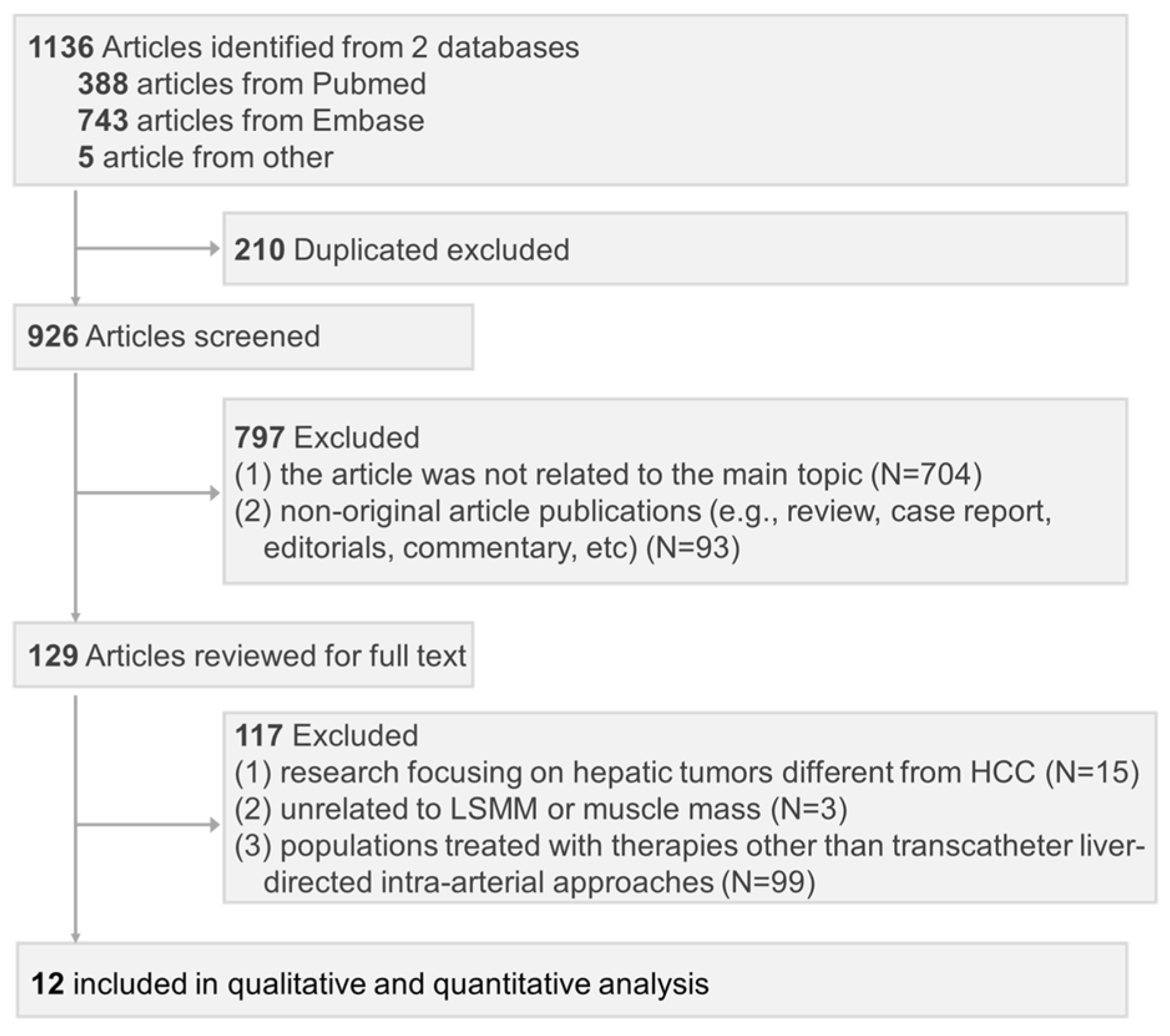
3.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
3.2. Study Description
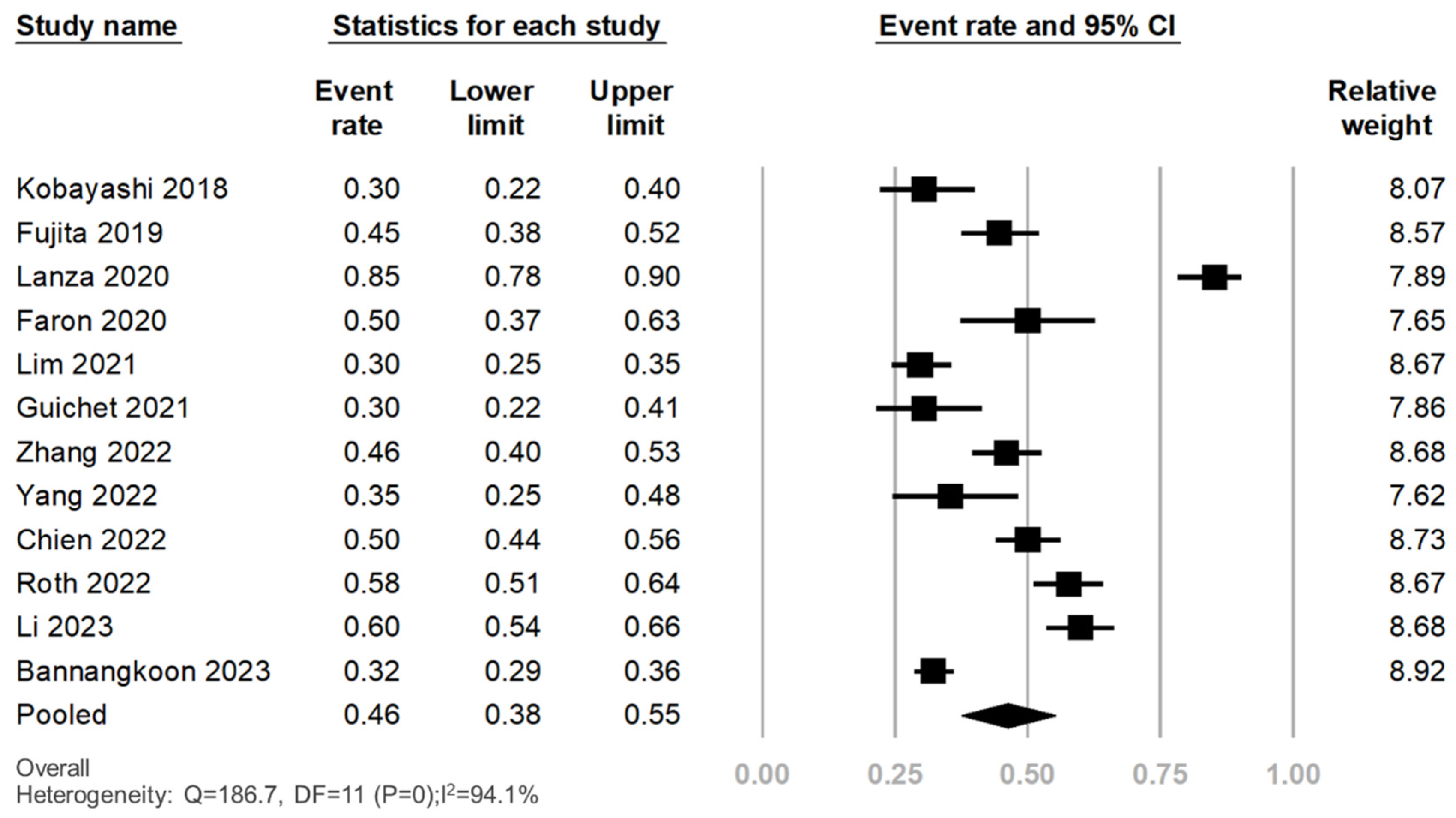
3.3. Prevalence of LSMM in Patients with HCC Treated with Transcatheter Liver-Directed Intra-Arterial Therapies
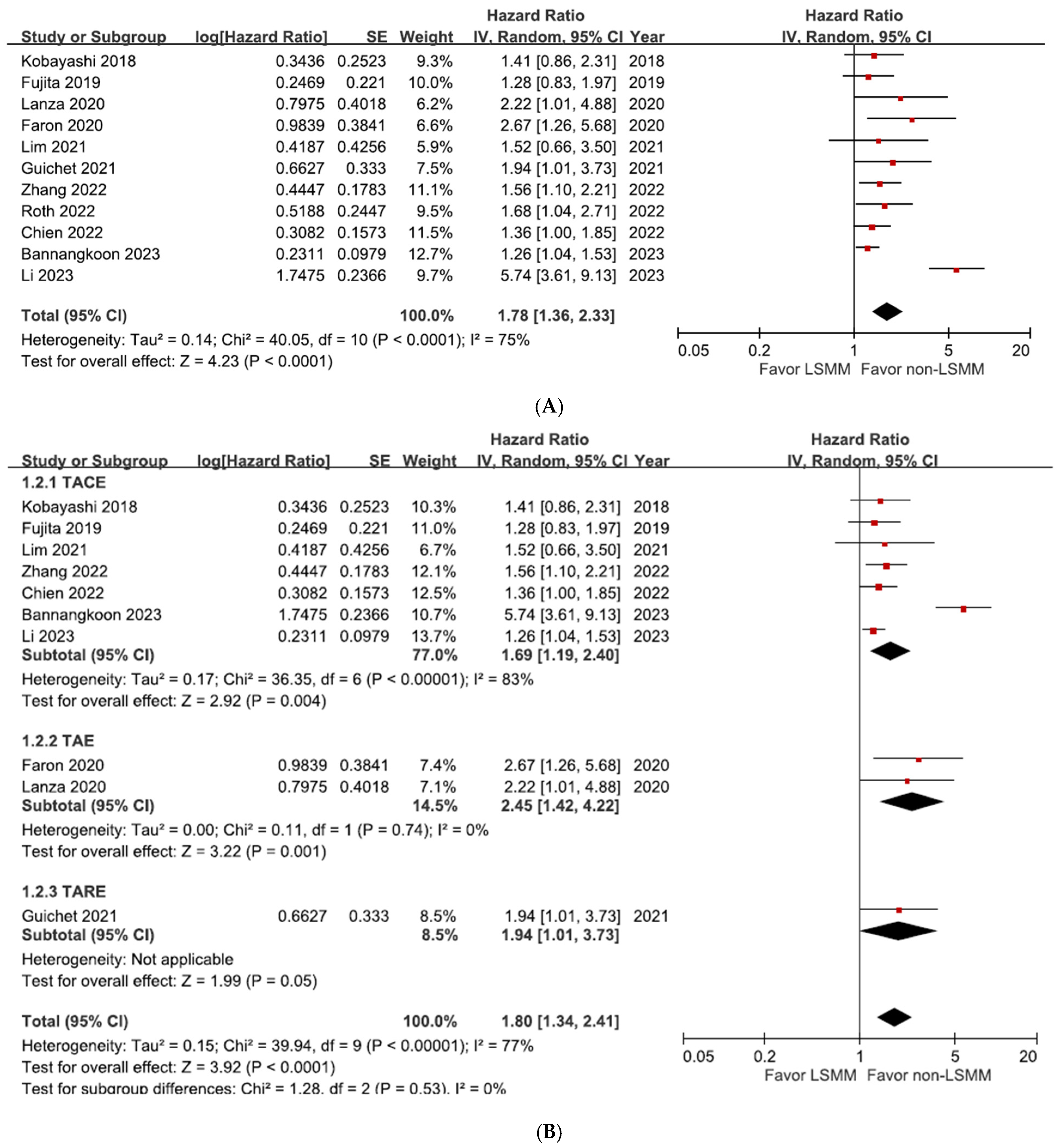
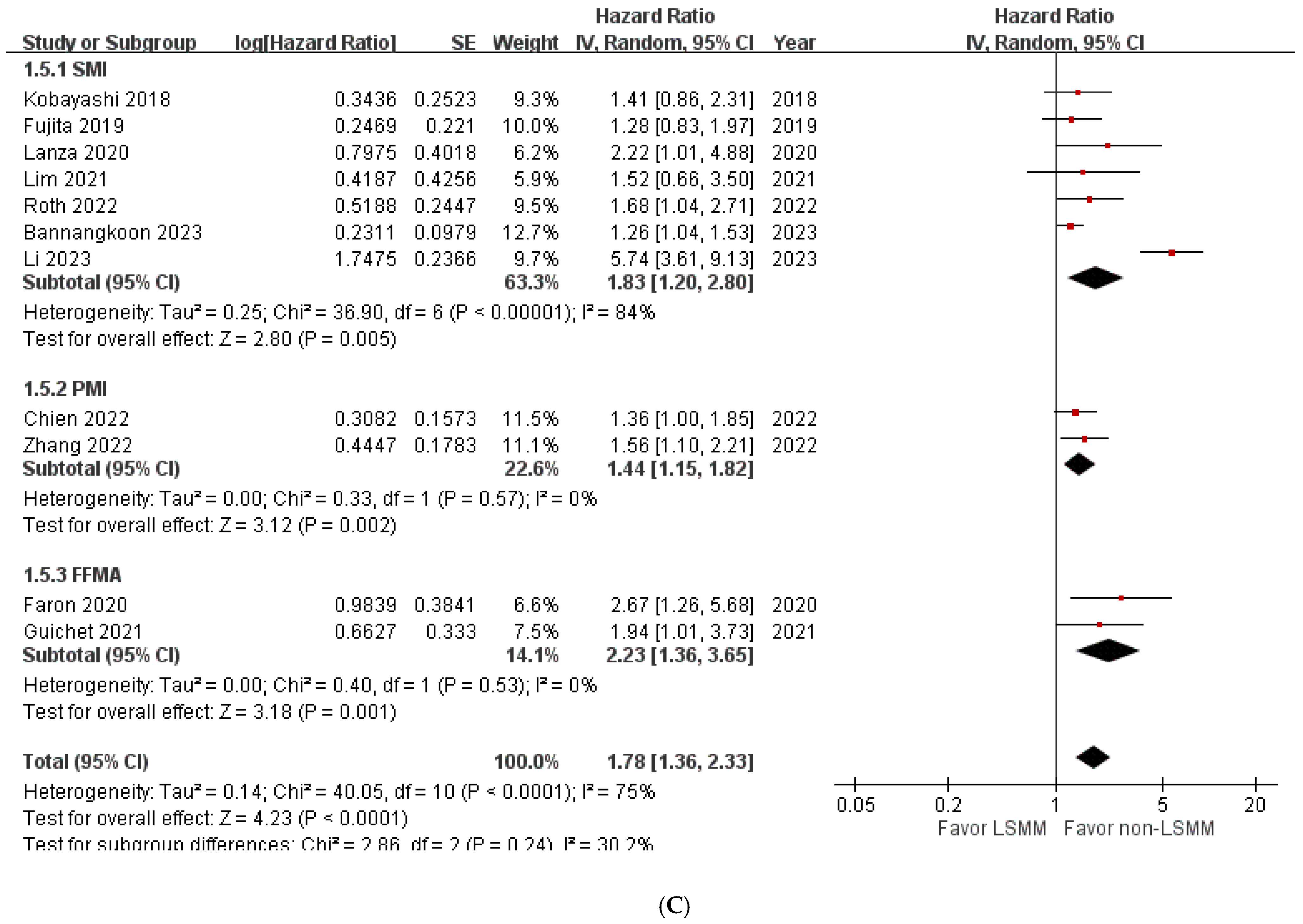
3.4. Overall Survival in Patients with HCC Treated with Transcatheter Liver-Directed Intra-Arterial Therapies with and without LSMM
3.5. Publication Bias and Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.G.; Moscatelli, A.; Pellegatta, G.; Vitale, A.; Farinati, F.; Ciccarese, F.; Piscaglia, F.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Di Marco, M.; Caturelli, E.; et al. Application of the Intermediate-Stage Subclassification to Patients with Untreated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.-M.; Ngan, H.; Tso, W.-K.; Liu, C.-L.; Lam, C.-M.; Poon, R.T.-P.; Fan, S.-T.; Wong, J. Randomized controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Real, M.I.; Montaña, X.; Planas, R.; Coll, S.; Aponte, J.; Ayuso, C.; Sala, M.; Muchart, J.; Solà, R.; et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.T.; Do, R.K.; Gonen, M.; Covey, A.M.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Jarnagin, W.R.; D’angelica, M.I.; Allen, P.J.; Erinjeri, J.P.; et al. Randomized Trial of Hepatic Artery Embolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Doxorubicin-Eluting Microspheres Compared with Embolization with Microspheres Alone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, L.; Yakoub, D.; Picado, O.; Ripat, C.; Pendola, F.; Sharma, R.; ElTawil, R.; Kwon, D.; Venkat, S.; Portelance, L.; et al. Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Radioembolization Versus Chemoembolization: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, G.; Serenari, M.; Renzulli, M.; Alemanni, L.V.; Rossini, B.; Pettinari, I.; Dajti, E.; Ravaioli, F.; Golfieri, R.; Cescon, M.; et al. Clinical impact of sarcopenia assessment in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing treatments. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, P.; Silletta, M.; De Vincentis, A.; Prinzi, F.L.; Terracciani, F.; Di Fazio, G.; Flagiello, V.; Gentilucci, U.V.; Incalzi, R.A.; Picardi, A. Sarcopenia in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Pathogenesis and Management. Chemotherapy 2022, 67, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.L. Cancer cachexia: Pathophysiology and association with cancer-related pain. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 971295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.R.; Dunne, R.F.; Giri, S.; Shachar, S.S.; Caan, B.J. Sarcopenia in the Older Adult with Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2068–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.-C.; Lai, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lai, E.C.-C.; Hung, M.-J.; Chi, C.-C. Associations of thiazide use with skin cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, T.-P.; Huang, S.-F.; Chan, W.-H.; Pan, K.-T.; Yu, M.-C.; Lee, W.-C.; Tsai, H.-I.; Lin, P.-T.; Chen, H.-Y.; Chen, J.-H.; et al. The combination of sarcopenia and biochemical factors can predict the survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving transarterial chemoembolization. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1005571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faron, A.; Sprinkart, A.M.; Pieper, C.C.; Kuetting, D.L.; Fimmers, R.; Block, W.; Meyer, C.; Thomas, D.; Attenberger, U.; Luetkens, J.A. Yttrium-90 radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: Outcome prediction with MRI derived fat-free muscle area. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 125, 108889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Takahashi, A.; Hayashi, M.; Okai, K.; Abe, K.; Ohira, H. Skeletal muscle volume loss during transarterial chemoembolization predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichet, P.L.; Taslakian, B.; Zhan, C.; Aaltonen, E.; Farquharson, S.; Hickey, R.; Horn, C.J.; Gross, J.S. MRI-Derived Sarcopenia Associated with Increased Mortality Following Yttrium-90 Radioembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kawai, H.; Nakano, O.; Abe, S.; Kamimura, H.; Sakamaki, A.; Kamimura, K.; Tsuchiya, A.; Takamura, M.; Yamagiwa, S.; et al. Rapidly declining skeletal muscle mass predicts poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transcatheter intra-arterial therapies. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, E.; Masetti, C.; Messana, G.; Muglia, R.; Pugliese, N.; Ceriani, R.; Lleo de Nalda, A.; Rimassa, L.; Torzilli, G.; Poretti, D.; et al. Sarcopenia as a predictor of survival in patients undergoing bland transarterial embolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232371. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Kim, K.W.; Ko, Y.; Jang, I.-Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Chung, Y.-H.; Lee, H.C.; Lim, Y.-S.; Kim, K.M.; Shim, J.H.; et al. The role of muscle depletion and visceral adiposity in HCC patients aged 65 and over undergoing TACE. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.; Teyssier, Y.; Benhamou, M.; Abousalihac, M.; Caruso, S.; Sengel, C.; Seror, O.; Ghelfi, J.; Seigneurin, A.; Ganne-Carrie, N.; et al. Impact of sarcopenia on tumor response and survival outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by trans-arterial (chemo)-embolization. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 5324–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Su, T.; Yu, J.; Cao, S.; Wang, H.; Jin, L. CT-based skeletal muscle loss for predicting poor survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma experiencing curative hepatectomy plus adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization: A preliminary retrospective study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Yan, H.-T.; Ding, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Zu, Q.-Q.; Shi, H.-B. Low Psoas-Muscle index is associated with decreased survival in hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transarterial chemoembolization. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hou, J.; Chen, R. Prognostic value of sarcopenic visceral obesity in hepatocellular carcinoma treated with TACE. Medicine 2023, 102, e34292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannangkoon, K.; Hongsakul, K.; Tubtawee, T.; Ina, N.; Chichareon, P. Association of myosteatosis with treatment response and survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing chemoembolization: A retrospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.-C.; Kuo, L.-T.; Shao, S.-C. Ten essential steps for performing a systematic review: A quick tutorial. Dermatol. Sin. 2022, 40, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Shao, S.-C.; Lai, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hung, M.-J.; Liao, S.-C. Prevalence, incidence and mortality of delirium in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2021, 50, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.; Garner, P.; Donegan, S. Interpretation of subgroup analyses in systematic reviews: A tutorial. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 7, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayasu, K.; Arii, S.; Ikai, I.; Omata, M.; Okita, K.; Ichida, T.; Matsuyama, Y.; Nakanuma, Y.; Kojiro, M.; Makuuchi, M.; et al. Prospective Cohort Study of Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma in 8510 Patients. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Zheng, C. Association between sarcopenia and clinical outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: An updated meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigman, G.; Ryan, A.S. Implications of Race and Ethnicity in Sarcopenia US National Prevalence of Sarcopenia by Muscle Mass, Strength, and Function Indices. Gerontol. Geriatr. Res. 2021, 4, 126. [Google Scholar]
- March, C.; Omari, J.; Thormann, M.; Pech, M.; Wienke, A.; Surov, A. Prevalence and role of low skeletal muscle mass (LSMM) in hepatocellular carcinoma. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 49, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M. Sarcopenia from mechanism to diagnosis and treatment in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, M.I.; Waitzberg, D.L. The impact of malnutrition on morbidity, mortality, length of hospital stay and costs evaluated through a multivariate model analysis. Clin Nutr. 2003, 22, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Author Year | Country | Setting | Patients, n (M/F) | Age, Years | Method Estimated Muscle Mass | Cut-Off Value for Pre-Treatment LSMM | LSMM (%) Yes/No | Study Period (Year) | OS Adjustment Factors | OS HR (95% CI) | RoB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. TACE | |||||||||||
| Kobayashi 2018 [17] | Japan | multi-center | 102 (70/32) | 68.3 # | SMI | M: 42 cm2/m2 F: 38 cm2/m2 | 30.4% (31/71) | 11 | univariate | 1.41 (0.86–2.29) | high |
| Fujita 2019 [15] | Japan | single center | 179 (130/49) | 72 # | PMI | M: <6.0 cm2/m2 F: <3.4 cm2/m2 | 44% (80/99) | 8.3 | univariate | 1.28 (0.83–1.99) | high |
| Lim 2021 [19] | Korea | single center | 266 (187/79) | 69.9 * | SMI | M: 49.6 cm2/m2 F: 43.1 cm2/m2 | 29.69% (79/187) | 4.1 | age, MELD score, size of tumor, albumin, platelet, BCLC, and objective tumor response | 1.52 (0.66–1.11) | moderate |
| Zhang 2022 [22] | China | single center | 228 (175/53) | 55.6–63 * | SMI, PMI | (PMI) M: 42.28 mm2/m2 F: 37.42 mm2/m2 | 39% (89/139) | 3.3 | AFP, Child–Pugh class, maximum tumor diameter, metastasis, and BCLC stage | 1.96 (1.39–2.78) | moderate |
| Yang 2022 [21] | China | single center | 62 (49/13) | 59.4 * | SMI | M: 42 cm2/m2 F: 38 cm2/m2 | 35.4% (22/40) | 6.0 | AFP | NR | moderate |
| Chien 2022 [13] | Taiwan | single center | 260 (192/68) | 64 # | PMI | M: <6.36 cm2/m2 F: <3.92 cm2/m2 | 50% (130/130) | 16.7 | maximal tumor diameter ≥ 5 cm, multiple tumors, AFP ≥ 200 ng/mL, albumin < 3.5 g/dL, and VP3/4 | 1.36 (1.00–1.85) | moderate |
| Roth 2022 [20] | France | multi-center | 225 (200/25) | 65 # | SMI | M: <50 cm2/m2 F: <39 cm2/m2 | 57.8% (130/95) | 5.0 | ascites, size of the largest nodule, AFP, Child–Pugh B | 1.68 (1.04–2.72) | moderate |
| Li 2023 [23] | China | single center | 235 (173/62) | 54 # | SMI | M: <52.4 cm2/m2 F: <38.5 cm2/m2 | 60% (141/94) | 5 | age, gender, BMI, smoking history, CNLC staging, CTP, MELD, AST, ALT, hemoglobin, A/G, visceral apodosis | 5.74 (3.61–9.11) | moderate |
| Bannangkoon 2023 [24] | Thailand | single center | 611 (445/166) | 61 # | SMI | M: <36.2 cm2/m2 F: <29.6 cm2/m2 | 32.2% (197/414) | 11 | age, chronic lung disease, and chronic kidney disease | 1.26 (1.04–1.52) | high |
| B. TAE | |||||||||||
| Lanza 2020 [18] | Italy | single center | 142 (110/32) | 75 # | SMI | M: <55 cm2/m2 F: <39 cm2/m2 | 85% (121/21) | 8.3 | performance status, previous treatments, and multifocal disease | 2.22 (1.01–4.86) | moderate |
| Faron 2020 [14] | Germany | single center | 58 (45/13) | 68 * | FFMA | M: 3582 mm2 F: 2301 mm2 | 50% (29/29) | 4.1 | ECOG-PS, and estimated liver tumor burden | 2.68 (1.26–5.70) | moderate |
| C. TARE | |||||||||||
| Guichet 2021 [16] | USA | single center | 82 (65/17) | 65 * | FFMA | M: 31.97 cm2 F: 28.95 cm2 | 30.5% (25/57) | 5.0 | BCLC stage | 1.94 (1.01–3.74) | moderate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-C.; Kuo, M.-H.; Hsu, C.-S.; Kao, I.-T.; Wu, C.-Y.; Tseng, C.-W.; Shao, S.-C. Impact of Low Muscle Mass on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Liver-Directed Therapies: Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020319
Chen Y-C, Kuo M-H, Hsu C-S, Kao I-T, Wu C-Y, Tseng C-W, Shao S-C. Impact of Low Muscle Mass on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Liver-Directed Therapies: Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020319
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yen-Chun, Meng-Hsuan Kuo, Ching-Sheng Hsu, I-Ting Kao, Chen-Yi Wu, Chih-Wei Tseng, and Shih-Chieh Shao. 2024. "Impact of Low Muscle Mass on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Liver-Directed Therapies: Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 2: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020319
APA StyleChen, Y.-C., Kuo, M.-H., Hsu, C.-S., Kao, I.-T., Wu, C.-Y., Tseng, C.-W., & Shao, S.-C. (2024). Impact of Low Muscle Mass on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Liver-Directed Therapies: Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(2), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020319






