Carboplatin and Etoposide for the Treatment of Metastatic Prostate Cancer with or without Neuroendocrine Features: A French Single-Center Experience
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Treatment and Follow-Up
2.3. Tolerance and Toxicity Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Treatments
3.2.1. Previous Treatments
3.2.2. Carboplatin/Etoposide Chemotherapy
3.2.3. PSA Response in Patients Treated for Primary Adenocarcinoma
3.2.4. Radiological Response
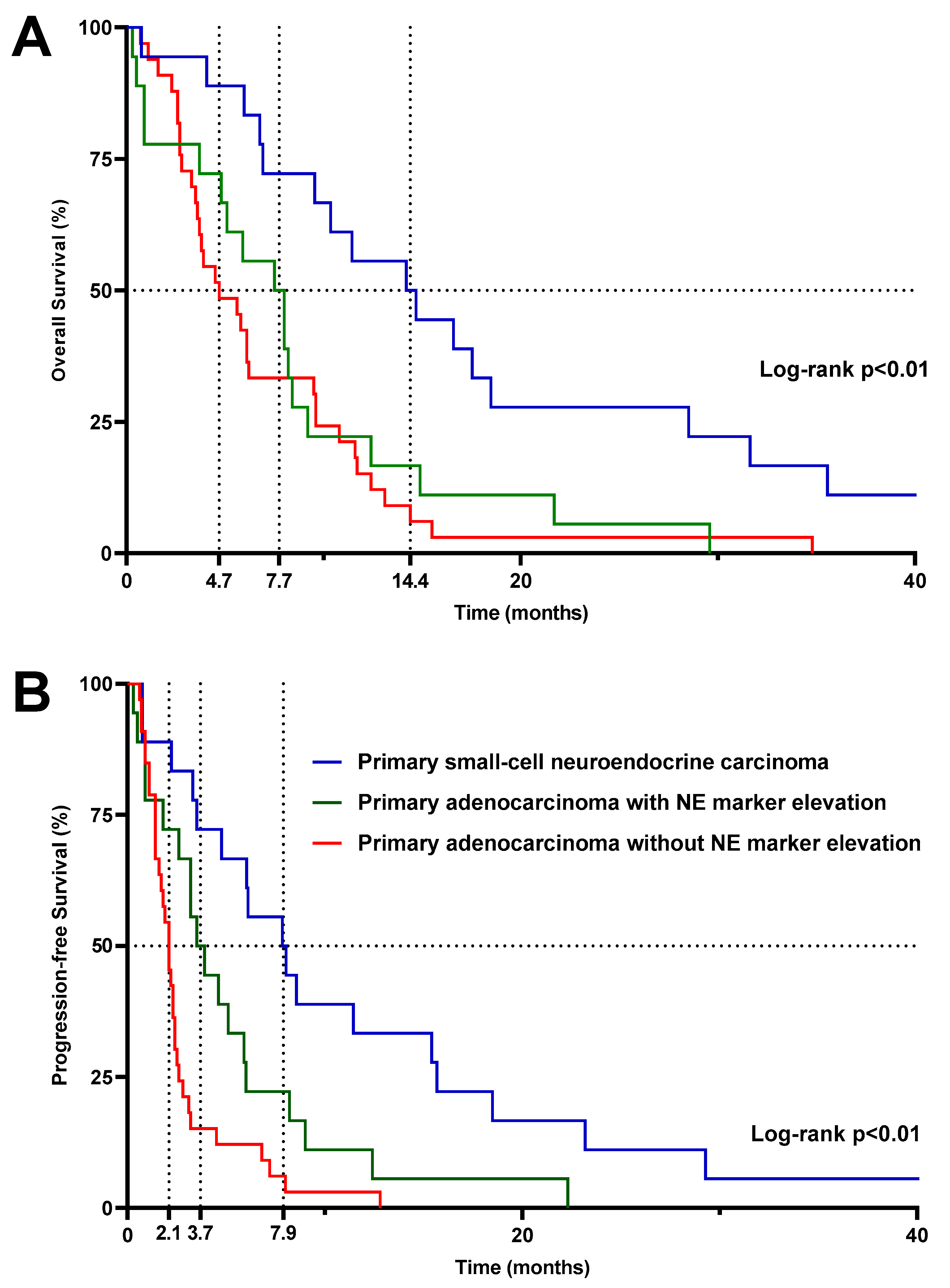
3.2.5. Survival
3.2.6. Tolerance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tannock, I.F.; de Witt, R.; Berry, W.R.; Horti, J.; Pluzanska, A.; Chi, K.N.; Oudard, S.; Théodore, C.; James, N.D.; Turesson, I.; et al. Docetaxel plus Prednisone or Mitoxantrone plus Prednisone for Advanced Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bono, J.S.; Oudard, S.; Ozguroglu, M.; Hansen, S.; Machiels, J.-P.; Kocak, I.; Gravis, G.; Bodrogi, I.; Mackenzie, M.J.; Shen, L.; et al. Prednisone plus Cabazitaxel or Mitoxantrone for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Progressing after Docetaxel Treatment: A Randomised Open-Label Trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Koo, K.C. Current Status and Future Perspectives of Androgen Receptor Inhibition Therapy for Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.; Nilsson, S.; Heinrich, D.; Helle, S.I.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; Fosså, S.D.; Chodacki, A.; Wiechno, P.; Logue, J.; Seke, M.; et al. Alpha Emitter Radium-223 and Survival in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, O.; de Bono, J.; Chi, K.N.; Fizazi, K.; Herrmann, K.; Rahbar, K.; Tagawa, S.T.; Nordquist, L.T.; Vaishampayan, N.; El-Haddad, G.; et al. Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Survival with Olaparib in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, S.; Ackermann, C.J.; Joerger, M.; Gillessen, S.; Omlin, A. Anti-Tumour Activity of Platinum Compounds in Advanced Prostate Cancer-a Systematic Literature Review. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culine, S.; El Demery, M.; Lamy, P.-J.; Iborra, F.; Avancès, C.; Pinguet, F. Docetaxel and Cisplatin in Patients with Metastatic Androgen Independent Prostate Cancer and Circulating Neuroendocrine Markers. J. Urol. 2007, 178, 844–848, discussion 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corn, P.G.; Heath, E.I.; Zurita, A.; Ramesh, N.; Xiao, L.; Sei, E.; Li-Ning-Tapia, E.; Tu, S.-M.; Subudhi, S.K.; Wang, J.; et al. Cabazitaxel plus Carboplatin for the Treatment of Men with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancers: A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 1–2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loriot, Y.; Massard, C.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Di Palma, M.; Escudier, B.; Bossi, A.; Fizazi, K. Combining Carboplatin and Etoposide in Docetaxel-Pretreated Patients with Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Prospective Study Evaluating Also Neuroendocrine Features. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fléchon, A.; Pouessel, D.; Ferlay, C.; Perol, D.; Beuzeboc, P.; Gravis, G.; Joly, F.; Oudard, S.; Deplanque, G.; Zanetta, S.; et al. Phase II Study of Carboplatin and Etoposide in Patients with Anaplastic Progressive Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC) with or without Neuroendocrine Differentiation: Results of the French Genito-Urinary Tumor Group (GETUG) P01 Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 2476–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran, H.; Tomlins, S.; Aparicio, A.; Arora, V.; Rickman, D.; Ayala, G.; Huang, J.; True, L.; Gleave, M.E.; Soule, H.; et al. Aggressive Variants of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2846–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.-C.; Veeramani, S.; Lin, M.-F. Neuroendocrine-like Prostate Cancer Cells: Neuroendocrine Transdifferentiation of Prostate Adenocarcinoma Cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caubet, M.; Dobi, E.; Pozet, A.; Almotlak, H.; Montcuquet, P.; Maurina, T.; Mouillet, G.; N’guyen, T.; Stein, U.; Thiery-Vuillemin, A.; et al. Carboplatin-Etoposide Combination Chemotherapy in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Retrospective Study. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillessen, S.; Attard, G.; Beer, T.M.; Beltran, H.; Bjartell, A.; Bossi, A.; Briganti, A.; Bristow, R.G.; Chi, K.N.; Clarke, N.; et al. Management of Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer: Report of the Advanced Prostate Cancer Consensus Conference 2019. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 508–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mick, R.; Crowley, J.J.; Carroll, R.J. Phase II Clinical Trial Design for Noncytotoxic Anticancer Agents for Which Time to Disease Progression Is the Primary Endpoint. Control. Clin. Trials 2000, 21, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannock, I.F.; Osoba, D.; Stockler, M.R.; Ernst, D.S.; Neville, A.J.; Moore, M.J.; Armitage, G.R.; Wilson, J.J.; Venner, P.M.; Coppin, C.M.; et al. Chemotherapy with Mitoxantrone plus Prednisone or Prednisone Alone for Symptomatic Hormone-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Canadian Randomized Trial with Palliative End Points. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, S.; Bossi, A.; Davis, I.D.; de Bono, J.; Fizazi, K.; James, N.D.; Mottet, N.; Shore, N.; Small, E.; Smith, M.; et al. Management of Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer-Metastatic and/or Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Report of the Advanced Prostate Cancer Consensus Conference (APCCC) 2022. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 185, 178–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrecque, M.P.; Alumkal, J.J.; Coleman, I.M.; Nelson, P.S.; Morrissey, C. The Heterogeneity of Prostate Cancers Lacking AR Activity Will Require Diverse Treatment Approaches. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, T51–T66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Benelli, M.; Karthaus, W.R.; Hoover, E.; Chen, C.-C.; Wongvipat, J.; Ku, S.-Y.; Gao, D.; Cao, Z.; et al. SOX2 Promotes Lineage Plasticity and Antiandrogen Resistance in TP53- and RB1-Deficient Prostate Cancer. Science 2017, 355, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.Y.; Rosario, S.; Wang, Y.; Mu, P.; Seshadri, M.; Goodrich, Z.W.; Goodrich, M.M.; Labbé, D.P.; Gomez, E.C.; Wang, J.; et al. Rb1 and Trp53 Cooperate to Suppress Prostate Cancer Lineage Plasticity, Metastasis, and Antiandrogen Resistance. Science 2017, 355, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papandreou, C.N.; Daliani, D.D.; Thall, P.F.; Tu, S.-M.; Wang, X.; Reyes, A.; Troncoso, P.; Logothetis, C.J. Results of a Phase II Study with Doxorubicin, Etoposide, and Cisplatin in Patients with Fully Characterized Small-Cell Carcinoma of the Prostate. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 3072–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, C.N.; Petrylak, D.P.; Sartor, O.; Witjes, J.A.; Demkow, T.; Ferrero, J.-M.; Eymard, J.-C.; Falcon, S.; Calabrò, F.; James, N.; et al. Multinational, Double-Blind, Phase III Study of Prednisone and Either Satraplatin or Placebo in Patients with Castrate-Refractory Prostate Cancer Progressing after Prior Chemotherapy: The SPARC Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5431–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Hoff, D.D. There Are No Bad Anticancer Agents, Only Bad Clinical Trial Designs--Twenty-First Richard and Hinda Rosenthal Foundation Award Lecture. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Massard, C.; Michiels, S.; Ferté, C.; Le Deley, M.-C.; Lacroix, L.; Hollebecque, A.; Verlingue, L.; Ileana, E.; Rosellini, S.; Ammari, S.; et al. High-Throughput Genomics and Clinical Outcome in Hard-to-Treat Advanced Cancers: Results of the MOSCATO 01 Trial. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiriou, Z.; Bianchini, D.; Chandler, R.; Rescigno, P.; Yuan, W.; Carreira, S.; Barrero, M.; Petremolo, A.; Miranda, S.; Riisnaes, R.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Three Metastatic Prostate Cancer Patients with Exceptional Responses to Carboplatin Indicating Different Types of DNA Repair Deficiency. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, J.; Carreira, S.; Sandhu, S.; Miranda, S.; Mossop, H.; Perez-Lopez, R.; Nava Rodrigues, D.; Robinson, D.; Omlin, A.; Tunariu, N.; et al. DNA-Repair Defects and Olaparib in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, J.; Boysen, G.; Barbieri, C.E.; Bryant, H.E.; Castro, E.; Nelson, P.S.; Olmos, D.; Pritchard, C.C.; Rubin, M.A.; de Bono, J.S. DNA Repair in Prostate Cancer: Biology and Clinical Implications. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abida, W.; Armenia, J.; Gopalan, A.; Brennan, R.; Walsh, M.; Barron, D.; Danila, D.; Rathkopf, D.; Morris, M.; Slovin, S.; et al. Prospective Genomic Profiling of Prostate Cancer Across Disease States Reveals Germline and Somatic Alterations That May Affect Clinical Decision Making. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 2017, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wu, Y.-M.; Schultz, N.; Lonigro, R.J.; Mosquera, J.-M.; Montgomery, B.; Taplin, M.-E.; Pritchard, C.C.; Attard, G.; et al. Integrative Clinical Genomics of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantz, M.M.; Spisák, S.; Jia, L.; Cronin, A.M.; Csabai, I.; Ledet, E.; Sartor, A.O.; Rainville, I.; O’Connor, E.P.; Herbert, Z.T.; et al. The Association between Germline BRCA2 Variants and Sensitivity to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy among Men with Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Cancer 2017, 123, 3532–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.H.; Pritchard, C.C.; Boyd, T.; Nelson, P.S.; Montgomery, B. Biallelic Inactivation of BRCA2 in Platinum-Sensitive Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, N.W.; Armstrong, A.J.; Thiery-Vuillemin, A.; Oya, M.; Shore, N.; Loredo, E.; Procopio, G.; de Menezes, J.; Girotto, G.; Arslan, C.; et al. Abiraterone and Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2200043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; Piulats, J.M.; Reaume, M.N.; Ostler, P.; McDermott, R.; Gingerich, J.R.; Pintus, E.; Sridhar, S.S.; Bambury, R.M.; Emmenegger, U.; et al. Rucaparib or Physician’s Choice in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.; Azad, A.A.; Carles, J.; Fay, A.P.; Matsubara, N.; Heinrich, D.; Szczylik, C.; De Giorgi, U.; Young Joung, J.; Fong, P.C.C.; et al. Talazoparib plus Enzalutamide in Men with First-Line Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (TALAPRO-2): A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.; Omlin, A.; Higano, C.; Sweeney, C.; Martinez Chanza, N.; Mehra, N.; Kuppen, M.C.P.; Beltran, H.; Conteduca, V.; Vargas Pivato de Almeida, D.; et al. Activity of Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer with and Without DNA Repair Gene Aberrations. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2021692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Overall Population | Primary Small-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma | Primary Adenocarcinoma | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Elevation of NE Markers | Elevation of NE Markers | p-Value | |||
| N | 69 | 18 | 33 | 18 | |
| Mean age, years (SD) | 69.4 (9.3) | 67.2 (9.0) | 71.6 (9.5) | 67.4 (8.8) | 0.12 |
| ECOG status (%) | 0.65 | ||||
| 0–1 | 38 (55.1) | 14 (77.8) | 14 (42.4) | 10 (55.6) | |
| >1 | 31 (44.9) | 4 (22.2) | 19 (57.6) | 8 (44.4) | |
| Gleason score (%) | 0.60 | ||||
| 6 or 7 | 26 (37.7) | 5 (27.8) | 13 (39.4) | 8 (44.4) | |
| 8, 9 or 10 | 31 (44.9) | 7 (38.9) | 17 (51.5) | 7 (38.9) | |
| Unknown | 12 (17.4) | 6 (33.3) | 3 (9.1) | 3 (16.7) | |
| Median PSA at start of carboplatin/etoposide ng/mL (Q1–Q3) | 103.0 (7.5–422.0) | 4.4 (0.8–12.9) | 232.0 (103.0–681.0) | 58.0 (6.2–267.0) | 0.03 |
| Median NSE at start of carboplatin/etoposide ng/mL (Q1–Q3) | 23.4 (10.2–46.6) | 50.3 (15.4–331.0) | 9.25 (8.6–10.3) | 26 (12.2–37.6) | 0.03 |
| Median chromogranin A at beginning of carboplatin/etoposide ng/mL (Q1–Q3) | 161.5 (124.5–1204.3) | 232.0 (127.0–612.8) | 161.5 (126.5–1639.5) | ||
| Metastatic sites (%) | 0.72 | ||||
| Bones | 60 (87.0) | 12 (66.7) | 31 (93.9) | 17 (94.4) | |
| Lymph nodes | 43 (62.3) | 10 (55.6) | 23 (69.7) | 10 (55.6) | |
| Liver | 24 (34.8) | 9 (50.0) | 9 (27.3) | 6 (33.3) | |
| Lung | 20 (29.0) | 5 (27.8) | 8 (24.2) | 7 (38.9) | |
| Brain | 4 (5.8) | 1 (5.6) | 2 (6.1) | 1 (5.6) | |
| Other visceral | 12 (17.4) | 2 (11.1) | 8 (24.2) | 2 (11.1) | |
| None | 4 (5.8) | 1 (5.6) | 1 (3.0) | 2 (11.1) | |
| Median number of metastatic sites (Q1–Q3) | 2 (2–3) | 2 (1.25–2.75) | 2 (2–3) | 2 (2–3) | 1 |
| Median prior treatment lines (Q1–Q3) | 3 (1–4) | 0 (0–0) | 4 (4–5) | 3 (1–4) | 0.01 |
| Previous NHA (%) | <0.01 | ||||
| 0 | 27 (39.1) | 17 (94.4) | 2 (6.1) | 8 (44.4) | |
| 1 | 13 (18.9) | 1 (5.6) | 8 (24.2) | 4 (22.3) | |
| 2 | 29 (42.0) | 0 (0) | 23 (69.7) | 6 (33.3) | |
| Previous chemotherapies (%) | <0.01 | ||||
| 0 | 17 (24.6) | 15 (83.3) | 0 (0) | 2 (11.1) | |
| 1 | 10 (14.5) | 3 (16.7) | 2 (6.1) | 5 (27.8) | |
| 2 | 25 (36.2) | 0 (0) | 20 (60.6) | 5 (27.8) | |
| 3 | 10 (14.5) | 0 (0) | 6 (18.2) | 4 (22.3) | |
| 4 | 3 (4.4) | 0 (0) | 2 (6.1) | 1 (5.5) | |
| 5 or more | 4 (5.8) | 0 (0) | 3 (9.0) | 1 (5.5) | |
| Patients previously treated by taxanes (%) | 0.34 | ||||
| Docetaxel | 49 (71.0) | 2 (11.1) | 33 (100) | 16 (88.9) | |
| Cabazitaxel | 38 (55.1) | 0 (0) | 30 (90.9) | 8 (44.4) | |
| Rechallenge docetaxel | 11 (15.9) | 0 (0) | 6 (18.2) | 5 (27.8) | |
| Rechallenge cabazitaxel | 3 (4.4) | 0 (0) | 2 (6.1) | 1 (5.6) | |
| Overall Population | Primary Small-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma | Primary Adenocarcinoma with or without Elevated NE Markers | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 69 | 18 | 51 |
| All-type toxicities (%) | |||
| Grade 3–4 | 43 (62.3) | 12 (66.7%) | 31 (60.8%) |
| Grade 4 | 6 (8.7) | 2 (11.1%) | 4 (7.8%) |
| Treatment-related death | 3 (4.3) | 1 (5.6%) | 2 (3.9%) |
| Grade 3–4 toxicity (%) | |||
| Anemia | 26 (37.7) | 8 (44.4%) | 18 (35.3%) |
| Neutropenia | 17 (24.6) | 7 (38.9%) | 10 (19.6%) |
| Thrombopenia | 9 (13.0) | 5 (27.8%) | 4 (7.8%) |
| Nausea and vomiting | 7 (10.1) | 3 (16.7%) | 4 (7.8%) |
| Creatinine elevation | 2 (2.9) | 1 (5.6%) | 1 (2.0%) |
| Asthenia | 23 (33.3) | 2 (11.1%) | 21 (41.2%) |
| Febrile neutropenia (%) | 6 (8.7) | 3 (16.7%) | 3 (5.88%) |
| Treatment interruption because of toxicity (%) | 4 (5.8) | 1 (5.6%) | 3 (5.88%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baude, J.; Niogret, J.; Jacob, P.; Bardet, F.; Desmoulins, I.; Zanetta, S.; Kaderbhai, C.; Galland, L.; Mayeur, D.; Delattre, B.; et al. Carboplatin and Etoposide for the Treatment of Metastatic Prostate Cancer with or without Neuroendocrine Features: A French Single-Center Experience. Cancers 2024, 16, 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020280
Baude J, Niogret J, Jacob P, Bardet F, Desmoulins I, Zanetta S, Kaderbhai C, Galland L, Mayeur D, Delattre B, et al. Carboplatin and Etoposide for the Treatment of Metastatic Prostate Cancer with or without Neuroendocrine Features: A French Single-Center Experience. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020280
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaude, Jérémy, Julie Niogret, Pierre Jacob, Florian Bardet, Isabelle Desmoulins, Sylvie Zanetta, Courèche Kaderbhai, Loïck Galland, Didier Mayeur, Benjamin Delattre, and et al. 2024. "Carboplatin and Etoposide for the Treatment of Metastatic Prostate Cancer with or without Neuroendocrine Features: A French Single-Center Experience" Cancers 16, no. 2: 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020280
APA StyleBaude, J., Niogret, J., Jacob, P., Bardet, F., Desmoulins, I., Zanetta, S., Kaderbhai, C., Galland, L., Mayeur, D., Delattre, B., Cormier, L., & Ladoire, S. (2024). Carboplatin and Etoposide for the Treatment of Metastatic Prostate Cancer with or without Neuroendocrine Features: A French Single-Center Experience. Cancers, 16(2), 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020280






