Kinin Receptors and Kinin-Related Gene Expression in Astrocytic Brain Tumors
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Extraction of Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) from Tissue Specimens
2.3. Oligonucleotide Microarray Analysis
2.4. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.5. Immunolocalization of Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors in Astrocytic Brain Tumors
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gene Expression Profile of Kinin-Related Genes Based on Oligonucleotide Microarray
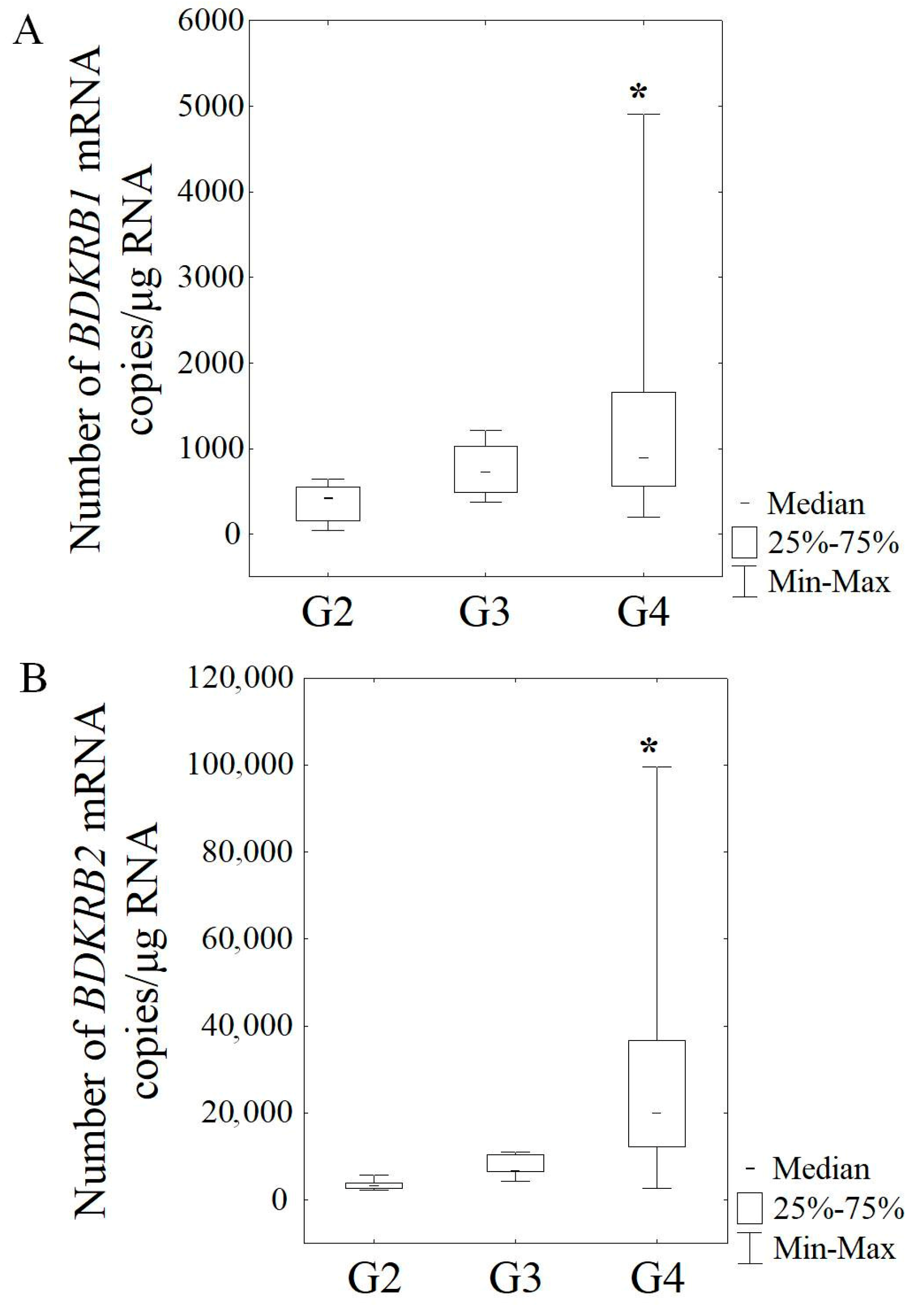
3.2. Expression of mRNA in Gliomas of Various Malignancy Stages Based on RT-qPCR
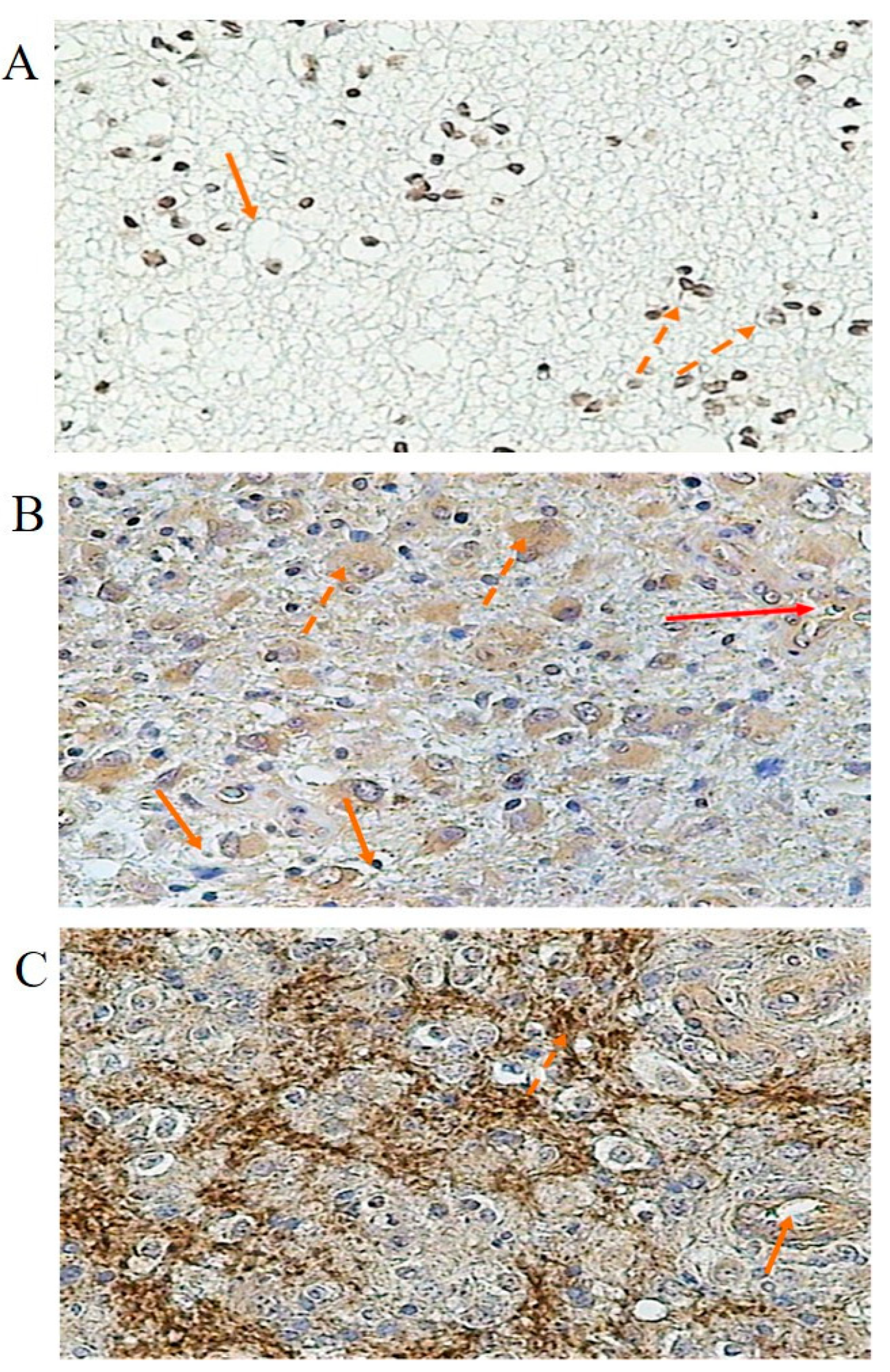
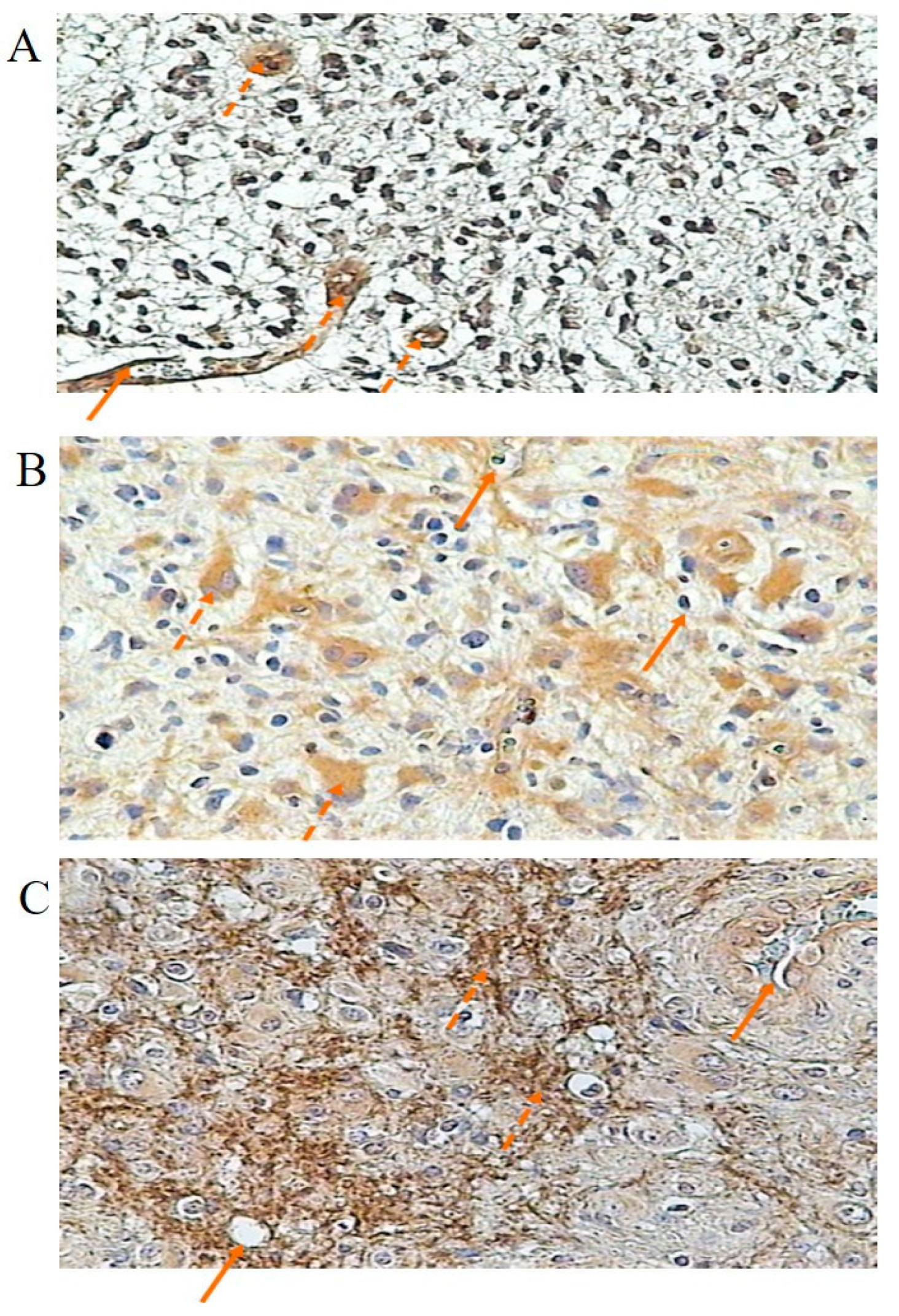
3.3. Immunochemical Localization and Concentration of Kinin Receptor Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bryant, J.W.; Shariat-Madar, Z. Human plasma kallikrein-kinin system: Physiological and biochemical parameters. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 7, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, K.; Kaplan, A.P. Formation of bradykinin: A major contributor to the innate inflammatory response. Adv. Immunol. 2005, 86, 159–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.; Rousseau, J.; Kwon, D.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.S. A Systematic Review of Molecular Imaging Agents Targeting Bradykinin B1 and B2 Receptors. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.M.; Leal, P.C.; Yunes, R.A.; Calixto, J.B. Non-peptide antagonists for kinin B1 receptors: New insights into their therapeutic potential for the management of inflammation and pain. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, F.; Bachelard, H.; Bouthillier, J.; Fortin, J.P.; Morissette, G.; Bawolak, M.T.; Charest-Morin, X.; Gera, L. Bradykinin receptors: Agonists, antagonists, expression, signaling, and adaptation to sustained stimulation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 24, 106305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, P.L.N.; Sirois, P.; Tannock, I.F.; Chammas, R. The role of kinin receptors in cancer and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, C.D.; Ehrenfeld, P.; Bhoola, K.D. Kinin receptors as targets for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Therap. Targets 2012, 16, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, K.; Roy, P.K.; Kola, P.; Mukherjee, B.; Mandal, M. An overview of kinin mediated events in cancer progression and therapeutic applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, N.F.; Senecal, J.; da Silva, V.D.; Roxo, M.R.; Ferreira, N.P.; de Morais, R.L.T.; Bosco Pesquero, J.; Campos, J.M.M.; Couture, R.; Morrone, F.B. Primary role for kinin B1 and B2 receptors in glioma proliferation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7869–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusco, I.; Becker, G.; Palma, T.V.; Pillat, M.M.; Scussel, R.; Steiner, B.T.; Sampaio, T.B.; Ardisson-Araújo, D.M.P.; de Andrade, C.M.; Oliveira, M.S.; et al. Kinin B1 and B2 receptors mediate cancer pain associated with both the tumor and oncology therapy using aromatase inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchel, J.; Witek, L.; Kimsa, M.; Strzalka-Mrozik, B.; Kimsa, M.; Olejek, A.; Mazurek, U. Expression patterns of kinin-dependent genes in endometrial cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2012, 22, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Lora, I. Kinin-mediated inflammation in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadnicka, I.; Strzałka-Mrozik, B.; Solarz, K.; Stadnicki, A. Znaczenie układu kalikreina-kininy w chorobach ośrodkowego układu nerwowego. Wiad. Lek. 2018, 71, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Nokkari, A.; Abou-El-Hassan, H.; Mechref, Y.; Mondello, S.; Kindy, M.S.; Jaffa, A.A.; Kobeissy, F. Implication of the Kallikrein-Kinin system in neurological disorders: Quest for potential biomarkers and mechanisms. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 165–167, 26–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.P.; Lee, Y.W.; Chen, J.T.; Lin, Y.W.; Chen, R.M. The bradykinin-BDKRB1 axis regulates aquaporin 4 gene expression and consequential migration and invasion of malignant glioblastoma cells via a Ca2+-MEK1-ERK1/2-NF-κB mechanism. Cancers 2020, 12, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, J.D.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.L.; Wu, C.Y.; Yang, C.M. Bradykinin induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and cell migration through a PKC-delta-dependent ERK/elk-1 pathway in astrocytes. Glia 2008, 56, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifuku, M.; Farber, K.; Okuno, Y.; Yamakawa, Y.; Miyamoto, T.; Nolte, C.; Merrino, V.F.; Kita, S.; Iwamoto, T.; Komuro, I.; et al. Bradykinin-induced microglial migration mediated by B1- bradykinin receptors depends on Ca2+ influx via reverse-mode activity of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 13065–13073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montana, V.; Sontheimer, H. Bradykinin promotes the chemotactic invasion of primary brain tumors. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 4858–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.Y.; Leung, Y.M.; Huang, S.M.; Wong, K.L. Bradykinin-induced cell migration and COX-2 production mediated by the bradykinin B1 receptor in glioma cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 110, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, N.F.; Erig, T.C.; Zanin, R.F.; Pereira, T.C.; Bogo, M.R.; Campos, M.M.; Fernanda Bueno Morrone, F.B. Mechanisms involved in kinin-induced glioma cell proliferation: The role of ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 120, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillat, M.M.; Oliveira, M.N.; Motaln, H.; Breznik, B.; Glaser, T.; Lah, T.T.; Ulrich, H. Glioblastoma-mesenchymal stem cell communication modulates expression patterns of kinin receptors: Possible involvement of bradykinin in information flow. Cytom. A 2016, 89, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.N.; Breznik, B.; Pillat, M.M.; Pereira, R.L.; Ulrich, H.; Lah, T.T. Kinins in Glioblastoma Microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron. 2019, 12, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naido, S.; Raido, D.M. Tissue kallikrein and kinin receptor expression in an angiogenic co-culture neuroblastoma model. Metab. Brain Dis. 2006, 21, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raido, D.M.; Sawant, S.; Mahabeer, R.; Bhoola, K.D. Kinin receptors are expressed in human astrocytic tumor cells. Immunopharmacology 1999, 43, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fu, W.; Jiang, N.; An, P.; Wang, P.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y. Study of correlation between expression of bradykinin B2 receptor and pathological grade in human gliomas. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 19, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska, N.; Strzalka-Mrozik, B.; Madej, M.; Pająk, K.; Kruszniewska-Rajs, C.; Kaspera, W.; Gola, J.M. Differences in the Expression Patterns of TGFβ Isoforms and Associated Genes in Astrocytic Brain Tumors. Cancers 2022, 14, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzalka-Mrozik, B.; Stanik-Walentek, A.; Kapral, M.; Kowalczyk, M.; Adamska, J.; Gola, J.; Mazurek, U. Differential expression of transforming growth factor-beta isoforms in bullous keratopathy corneas. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. Genetic alterations and signaling pathways in the evolution of gliomas. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 2235–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szopa, W.; Burley, W.T.; Kramer-Marek, G.; Kaspera, W. Diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers in glioblastoma: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8013575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. The definition of primary and secondary glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Familiari, P.; Lapolla, P.; Picotti, V.; Palmieri, M.; Pesce, A.; Carosi, G.; Relucenti, M.; Nottola, S.; Gianno, F.; Minasi, S.; et al. Role of 1p/19q Codeletion in Diffuse Low-grade Glioma Tumour Prognosis. Anticancer Res. 2023, 43, 2659–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, W.; Weller, M.; van den Bent, M.; Sanson, M.; Weiler, M.; von Deimling, A.; Plass, C.; Hegi, M.; Platten, M.; Reifenberger, G. MGMT testing-the challenges for biomarker-based glioma treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.K.; Huang, B.R.; Charoensaensuk, V.; Yang, L.Y.; Tsai, C.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Lu, D.Y.; Yeh, W.L.; Lin, C. Bradykinin B1 Receptor Affects Tumor-Associated Macrophage Activity and Glioblastoma Progression. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongali, B.; Campos, M.M.; Bregola, G.; Rodi, D.; Regoli, D.; Thibault, G.; Simonato, M.; Couture, R. Autoradiographic analysis of rat brain kinin B1 and B2 receptors: Normal distribution and alterations induced by epilepsy. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 461, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachvarov, D.R.; Houle, S.; Bachvarova, M.; Bouthillier, J.; Adam, A.; Marceau, F. Bradykinin B2 receptor endocytosis, recycling, and down-regulation assessed using green fluorescent protein conjugates. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sabourin, T.; Bastien, L.; Bachvarov, D.R.; Marceau, F. Agonist-induced translocation of the kinin B1 receptor to caveolae-related rafts. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, R.C. Kinin receptors: Key regulators of autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, C.; Graness, A.; Ludwig, B.; Adomeit, A.; Boehmer, A.; Boehmer, F.D.; Nürnberg, B.; Wetzker, R. Dual bradykinin B2 receptor signalling in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells: Activation of protein kinase C is counteracted by a GS-mediated stimulation of the cyclic AMP pathway. Biochem. J. 1996, 313, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Hu, B.; Vuori, K.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Furnari, F.B.; Cavenee, W.K.; Cheng, S.Y. EGFRvIII stimulates glioma growth and invasion through PKA-dependent serine phosphorylation of Dock180. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2504–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K.; Kozawa, O.; Iida, H. cAMP/PKA enhances interleukin-1β-induced interleukin-6 synthesis through STAT3 in glial cells. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.L.; Yen, M.H.; Jou, M.J.; Yang, C.M. Intracellular signalings underlying bradykinin-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in rat brain astrocyte-1. Cell. Signal. 2004, 16, 1163–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Elia, M.G.; Muscella, A.; Romano, S.; Storelli, C.; Marsigliante, S. Bradykinin stimulates cell proliferation through an extracellular-regulated kinase 1 and 2-dependent mechanism in breast cancer cells in primary culture. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 186, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.W.; Weiss, W.A. Inhibition of PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling in glioblastoma by mTORC1/2 inhibitors. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 821, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Etemad, S.; Rezaei, S.; Ziaolhagh, S.; Rajabi, R.; Rahmanian, P.; Abdi, S.; Koohpar, Z.K.; Rafiei, R.; Raei, B.; et al. Progress in targeting PTEN/PI3K/Akt axis in glioblastoma therapy: Revisiting molecular interactions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.C.; Ashley, D.M.; López, G.Y.; Malinzak, M.; Friedman, H.S.; Khasraw, M. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Bhaskara, V.K.; Babu, P.P. Implications of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in glioma. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.L.; Wu, C.Y.; Hwang, T.L.; Yen, M.H.; Parker, P.; Yang, C.M. BK-induced cytosolic phospholipase A2 expression via sequential PKC-delta, p42/p44 MAPK, and NF-kappaB activation in rat brain astrocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 206, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko, N.F.; Weil, R.J. The molecular biology of WHO grade II gliomas. Neurosurg. Focus 2013, 34, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryall, S.; Tabori, U.; Hawkins, C. Pediatric low-grade glioma in the era of molecular diagnostics. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venneti, S.; Huse, J.T. The evolving molecular genetics of low-grade glioma. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2015, 22, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larysz, D.; Kula, D.; Kowal, M.; Rudnik, A.; Jarząb, M.; Blamek, S.; Bierzyńska-Macyszyn, G.; Kowalska, M.; Bażowski, P.; Jarząb, B. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression in high grade gliomas. Folia Neuropathol. 2011, 49, 28–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Meng, X.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ali, S.; Li, S.; Xiong, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; et al. Identification of the Prognostic Signatures of Glioma With Different PTEN Status. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 633357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.L.; Colman, H. Glioma biology and molecular markers. In Current Understanding and Treatment of Gliomas; Cancer Treatment and Research Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 63, pp. 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Bovenzi, V.; Savard, M.; Dubuc, C.; Fortier, A.; Neugebauer, W.; Tremblay, L.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Tsanaclis, A.M.; Lepage, M.; et al. Induction of selective blood-tumor barrier permeability and macromolecular transport by a biostable kinin B1 receptor agonist in a glioma rat model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Savard, M.; Neugebauer, W.; Fortin, D.; Lepage, M.; Goebeil, F. Dual kinin B1 and B2 receptor activation provides enhanced blood–brain barrier permeability and anticancer drug delivery into brain tumors. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikpa, D.; Whittingstall, L.; Savard, M.; Lebel, R.; Côté, J.; McManus, S.; Chemtob, S.; Fortin, D.; Lepage, M.; Gobeil, F. Pharmacological Modulation of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability by Kinin Analogs in Normal and Pathologic Conditions. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
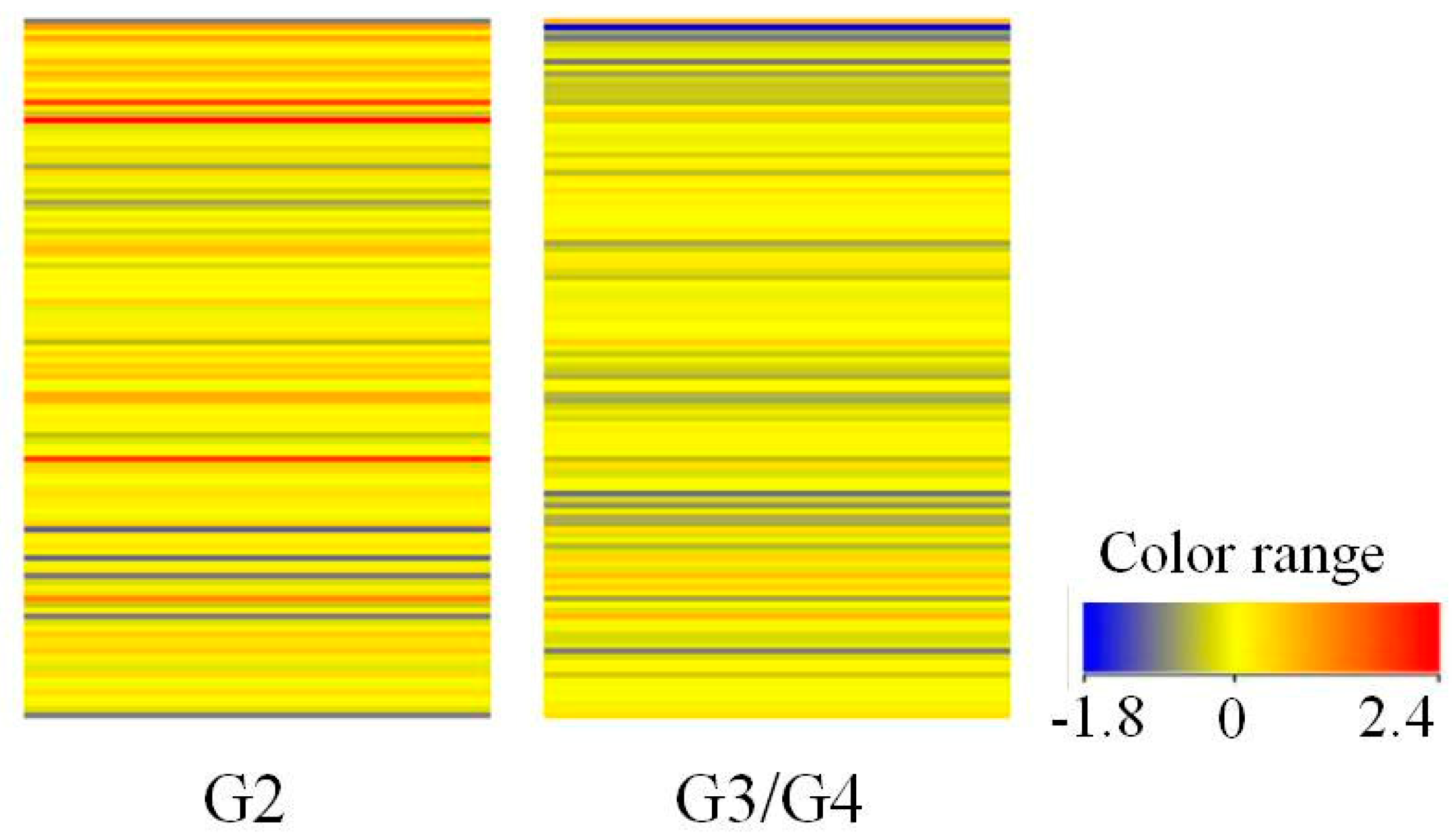

| Gene | Oligonucleotide Sequence | Amplimer Length (bp) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAP2K2 | Forward: 5′ CTGGACTATATTGTGAACGAG 3′ Reverse:5′ CTTGATGAAGGTGTGGTTTG 3′ | 147 | 85.0 |
| SHC1 | Forward: 5′ GAGGAGAAAGCCCTGTAG 3′ Reverse: 5′ AGACGGTGAGAGTGATTG 3′ | 89 | 82.0 |
| EGFR | Forward: 5′ GGAAAAGAAAGTTTGCCAAG 3′ Reverse: 5′ ATGAGGACATAACCAGCC 3′ | 195 | 81.4 |
| PRKACA | Forward: 5′ CCAAAGTGTGTGGCAAAG 3′ Reverse: 5′ TCAGACTGGTCTATGTTAGC 3′ | 109 | 82.0 |
| PRKAR1A | Forward: 5′ TTTAGAGTCTCTGGACAAGTG 3′ Reverse: 5′ TAATGAAGAACTCATCCCCTG 3′ | 119 | 82.2 |
| BDKRB1 | Forward: 5′ CCTTCATTTTCTGCCTGAG 3′ Reverse: 5′ GGAGAATCGTTTAAGCCTG 3′ | 105 | 84.2 |
| BDKRB2 | Forward: 5′ ACTTAGAAAAGCAAAGGGTG 3′ Reverse: 5′ CAATACTGATTCTGCTCCAC 3′ | 126 | 79.4 |
| ACTB | Forward: 5′TCACCCACACTGTGCCCATCTACGA 3′ Reverse: 5′CAGCGGAACCGCTCATTGCCAATGG 3′ | 295 | 88.4 |
| Total p | p < 0.05 | p < 0.02 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.005 | p < 0.001 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G3/4 vs. G2 | |||||||
| Number of probes | 22,283 | 6378 | 3991 | 2760 | 1856 | 670 | |
 | FC > 1.0 | 120 | 23 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| FC > 1.1 | 93 | 23 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |
| FC > 1.5 | 34 | 18 | 11 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |
| FC > 2.0 | 16 | 12 * | 9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| FC > 3.0 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Probe Number | Gene Symbol | Name of Gene | FC | p * | Alteration of Expression G3/G4 vs. G2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200603_at | PRKAR1A | Protein Kinase CAMP-dependent Type I Regulatory Subunit Alpha | 2.45 | 0.005 | ↑ |
| 213093_at | PRKCA | Protein Kinase C Alpha | 2.25 | 0.002 | ↑ |
| 212688_at | PIK3CB | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase Catalytic Subunit Beta | 2.11 | 0.001 | ↑ |
| 211607_x_at | EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor | 5.46 | 0.008 | ↓ |
| 201469_s_at | SHC1 | SHC Adaptor Protein 1 | 4.90 | 0.000 | ↓ |
| 200604_s_at | PRKAR1A | Protein Kinase CAMP-dependent Type I Regulatory Subunit Alpha | 4.54 | 0.001 | ↓ |
| 213490_s_at | MAP2K2 | Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase 2 | 3.25 | <0.001 | ↓ |
| 200744_s_at | GNB1 | G-protein Subunit Beta 1 | 3.05 | 0.001 | ↓ |
| 200852_x_at | GNB2 | G-protein Subunit Beta 2 | 2.53 | 0.001 | ↓ |
| 208351_s_at | MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase 1 | 2.30 | 0.001 | ↓ |
| 201040_at | GNAI2 | G-protein Subunit Alpha I2 | 2.27 | 0.002 | ↓ |
| 214853_s_at | SHC1 | SHC Adaptor Protein 1 | 2.25 | 0.005 | ↓ |
| Grade of Malignancy | Number of Samples | BR1 | BR2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| G2 | 12 | 77.72 ± 7.36 | 70.05 ± 11.38 |
| G3 | 5 | 105.10 ± 13.17 a | 116.79 ± 12.36 a |
| G4 | 26 | 145.55 ± 15.13 b,c | 148.12 ± 19.12 b,c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stadnicka, I.; Strzałka-Mrozik, B.; Kimsa-Dudek, M.; Kaspera, W.; Plewka, A.; Szopa, W.; Stadnicki, A. Kinin Receptors and Kinin-Related Gene Expression in Astrocytic Brain Tumors. Cancers 2024, 16, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020241
Stadnicka I, Strzałka-Mrozik B, Kimsa-Dudek M, Kaspera W, Plewka A, Szopa W, Stadnicki A. Kinin Receptors and Kinin-Related Gene Expression in Astrocytic Brain Tumors. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020241
Chicago/Turabian StyleStadnicka, Izabela, Barbara Strzałka-Mrozik, Magdalena Kimsa-Dudek, Wojciech Kaspera, Andrzej Plewka, Wojciech Szopa, and Antoni Stadnicki. 2024. "Kinin Receptors and Kinin-Related Gene Expression in Astrocytic Brain Tumors" Cancers 16, no. 2: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020241
APA StyleStadnicka, I., Strzałka-Mrozik, B., Kimsa-Dudek, M., Kaspera, W., Plewka, A., Szopa, W., & Stadnicki, A. (2024). Kinin Receptors and Kinin-Related Gene Expression in Astrocytic Brain Tumors. Cancers, 16(2), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020241







