Risk Factors of Distant Recurrence and Dissemination of IDH Wild-Type Glioblastoma: A Single-Center Study and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
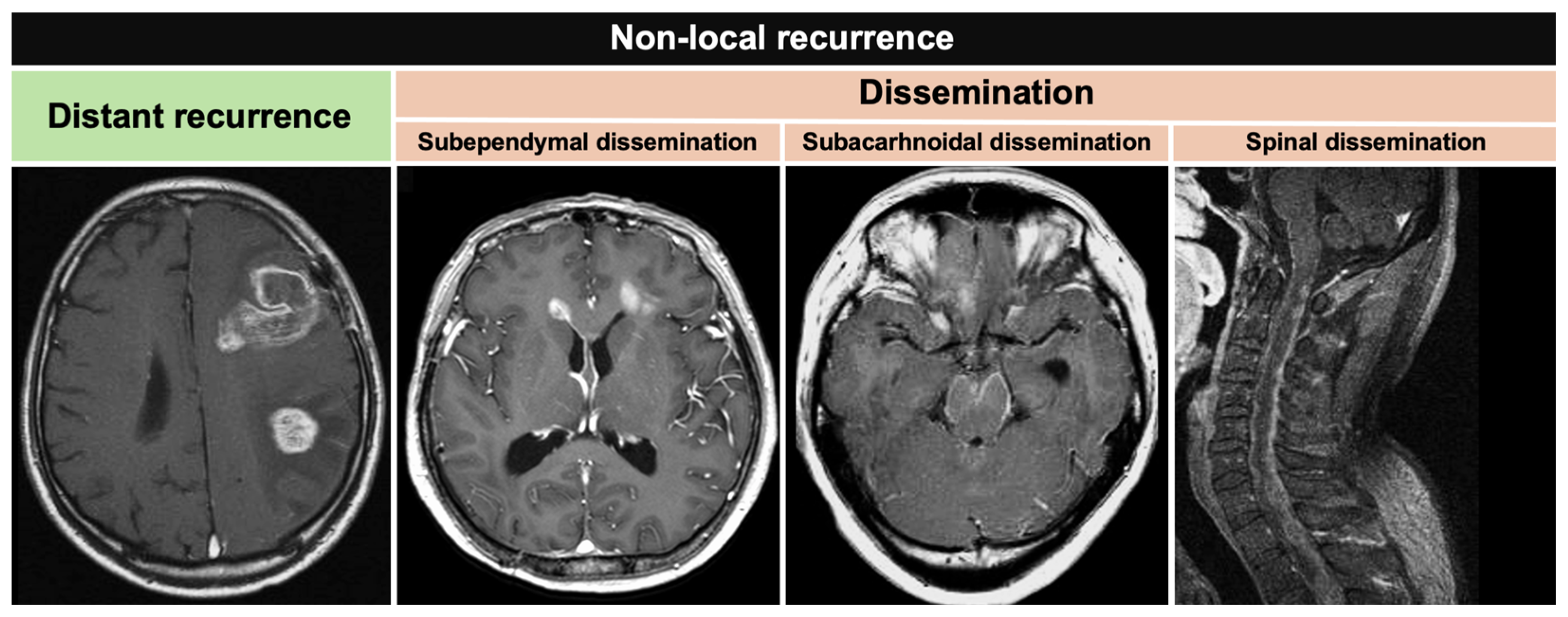
2.2. Recurrence Definition
2.3. Molecular Analysis
2.4. Systematic Review of the Literature
2.5. Statistical Analysis
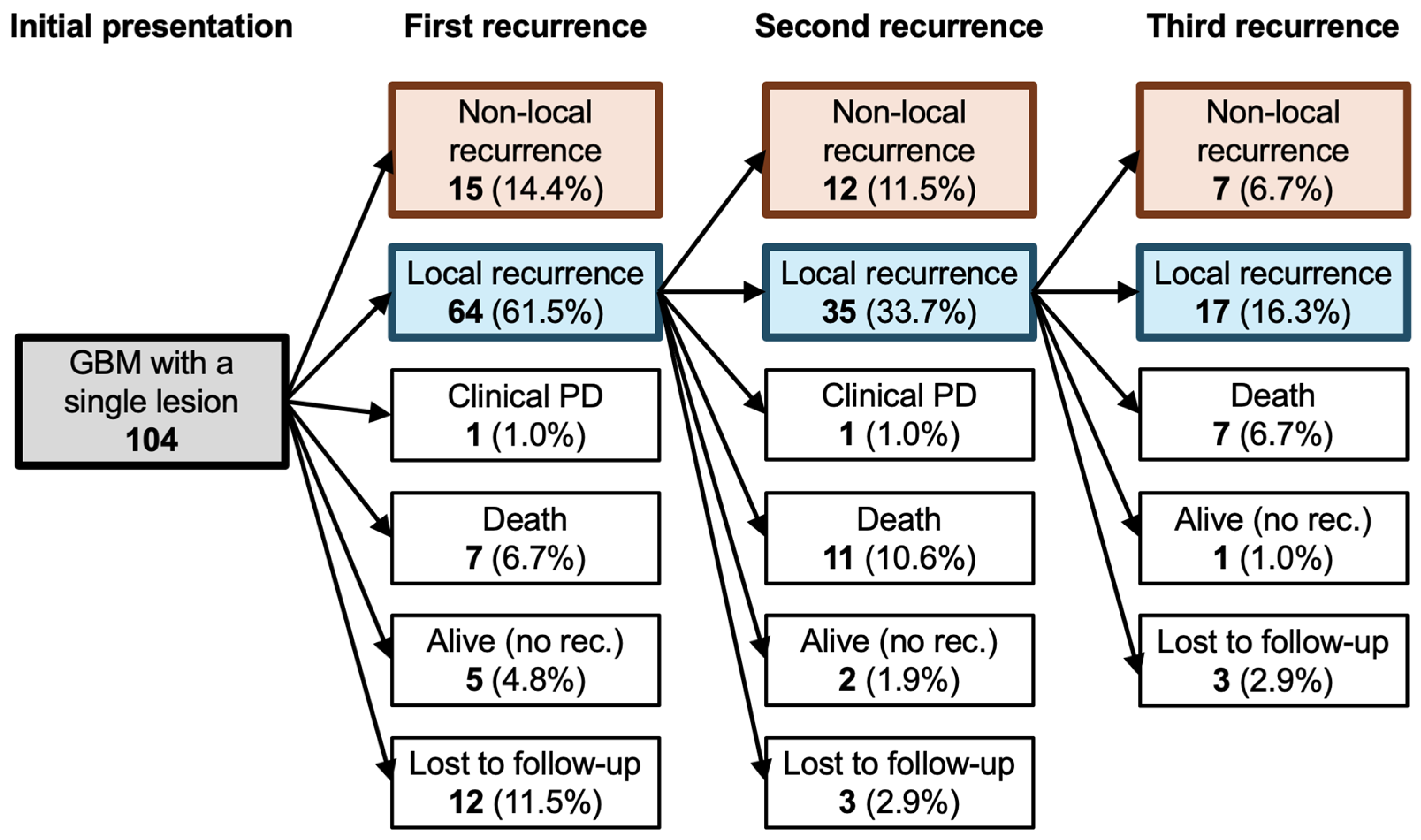
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Risk Factors of Non-Local Recurrence
3.3. Patterns of Non-Local Recurrence According to Tumor Location
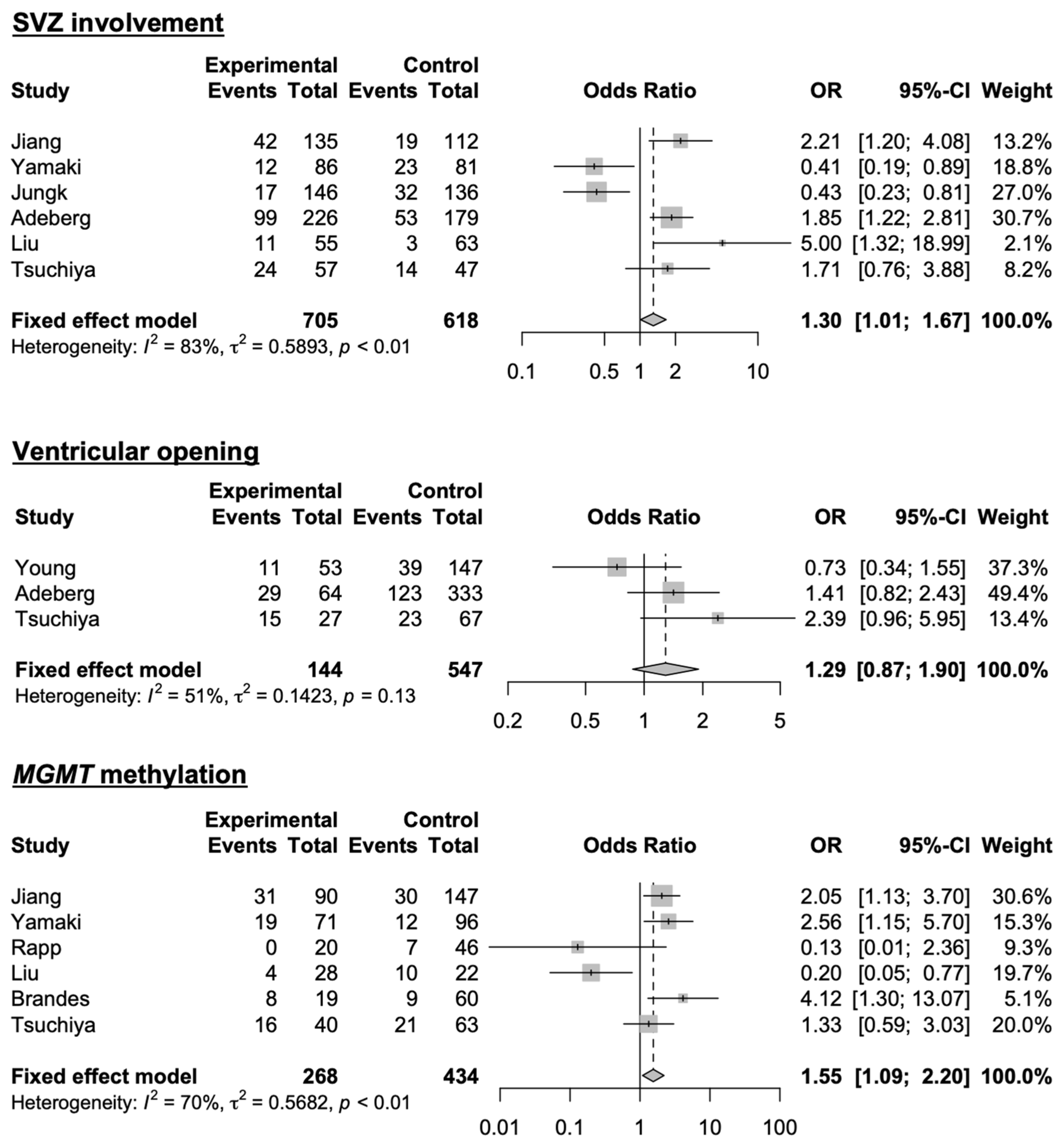
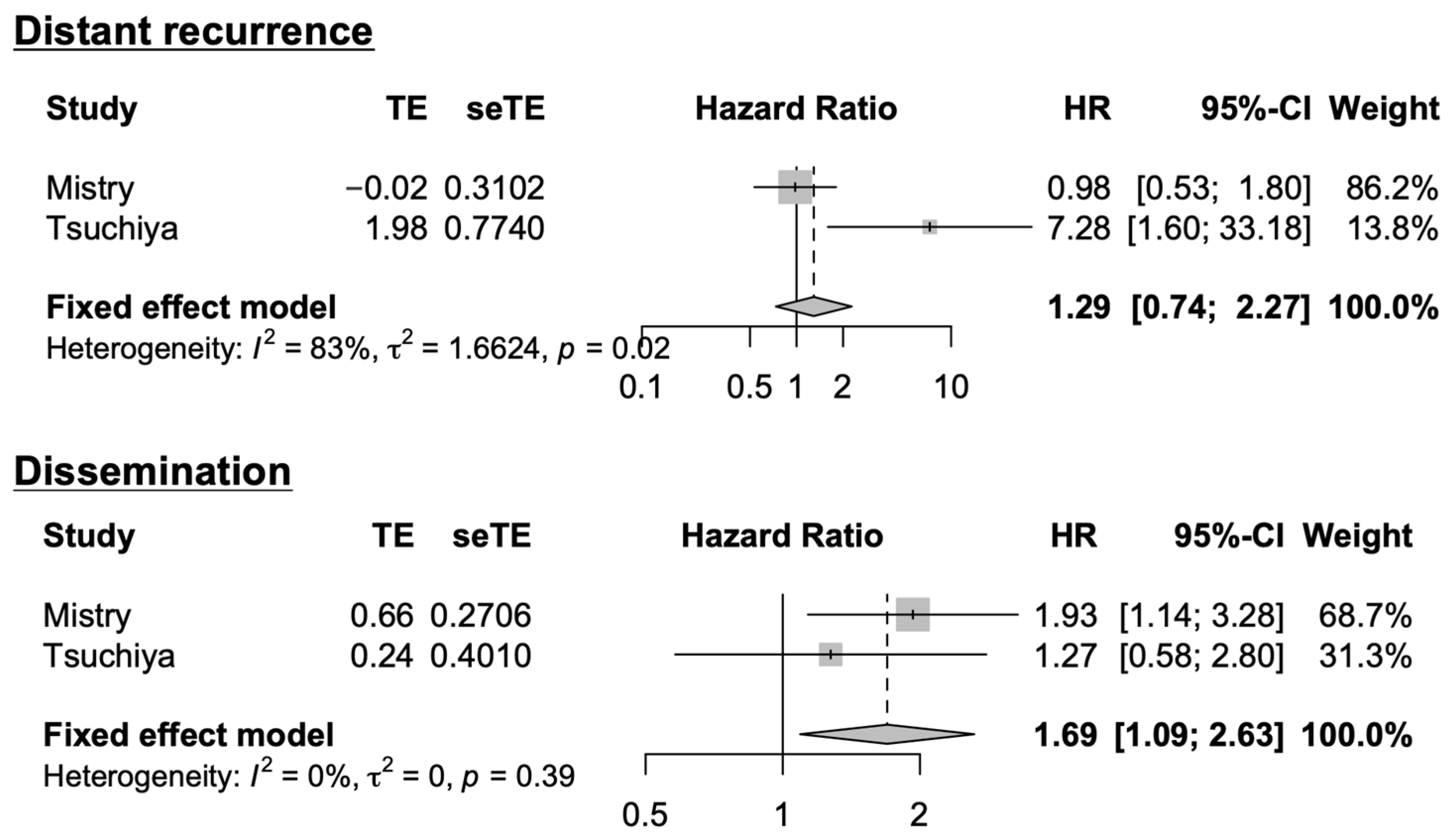
3.4. Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, L.E.; Fisher, B.J.; Macdonald, D.R.; LeBer, D.V.; Halperin, E.C.; Schold, S.C., Jr.; Cairncross, J.G. Supratentorial malignant glioma: Patterns of recurrence and implications for external beam local treatment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1992, 24, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneed, P.K.; Gutin, P.H.; Larson, D.A.; Malec, M.K.; Phillips, T.L.; Prados, M.D.; Scharfen, C.O.; Weaver, K.A.; Wara, W.M. Patterns of recurrence of glioblastoma multiforme after external irradiation followed by implant boost. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 29, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallner, K.E.; Galicich, J.H.; Krol, G.; Arbit, E.; Malkin, M.G. Patterns of failure following treatment for glioblastoma multiforme and anaplastic astrocytoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1989, 16, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, A.A.; Tosoni, A.; Franceschi, E.; Sotti, G.; Frezza, G.; Amistà, P.; Morandi, L.; Spagnolli, F.; Ermani, M. Recurrence pattern after temozolomide concomitant with and adjuvant to radiotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma: Correlation with MGMT promoter methylation status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, M.T.; Okunieff, P.; Donatello, R.S.; Mohile, N.A.; Sul, J.; Walter, K.A.; Korones, D.N. Patterns and timing of recurrence after temozolomide-based chemoradiation for glioblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 78, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogura, K.; Mizowaki, T.; Arakawa, Y.; Ogura, M.; Sakanaka, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Hiraoka, M. Initial and cumulative recurrence patterns of glioblastoma after temozolomide-based chemoradiotherapy and salvage treatment: A retrospective cohort study in a single institution. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birzu, C.; Tran, S.; Bielle, F.; Touat, M.; Mokhtari, K.; Younan, N.; Psimaras, D.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Sanson, M.; Delattre, J.Y.; et al. Leptomeningeal Spread in Glioblastoma: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges. Oncologist 2020, 25, e1763–e1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, J.J.; Yust-Katz, S.; Cachia, D.; Wu, J.; Liu, D.; de Groot, J.F.; Yung, A.W.; Gilbert, M.R. Leptomeningeal dissemination in glioblastoma; an inspection of risk factors, treatment, and outcomes at a single institution. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 120, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumm, M.R.; Dixit, K.S.; Grimm, S.; Kumthekar, P.; Lukas, R.V.; Raizer, J.J.; Stupp, R.; Chheda, M.G.; Kam, K.L.; McCord, M.; et al. Extensive brainstem infiltration, not mass effect, is a common feature of end-stage cerebral glioblastomas. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, H. Observation of the delineation of the target volume of radiotherapy in adult-type diffuse gliomas after temozolomide-based chemoradiotherapy: Analysis of recurrence patterns and predictive factors. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.S.; Gogos, A.J.; Pereira, M.P.; Morshed, R.A.; Li, J.; Barkovich, M.J.; Hervey-Jumper, S.L.; Berger, M.S. Effects of ventricular entry on patient outcome during glioblastoma resection. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 135, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yu, K.; Li, M.; Cui, Y.; Ren, X.; Yang, C.; Zhao, X.; Lin, S. Classification of Progression Patterns in Glioblastoma: Analysis of Predictive Factors and Clinical Implications. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 590648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaki, T.; Shibahra, I.; Matsuda, K.I.; Kanemura, Y.; Konta, T.; Kanamori, M.; Yamakawa, M.; Tominaga, T.; Sonoda, Y. Relationships between recurrence patterns and subventricular zone involvement or CD133 expression in glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 146, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, A.M.; Kelly, P.D.; Gallant, J.N.; Mummareddy, N.; Mobley, B.C.; Thompson, R.C.; Chambless, L.B. Comparative Analysis of Subventricular Zone Glioblastoma Contact and Ventricular Entry During Resection in Predicting Dissemination, Hydrocephalus, and Survival. Neurosurgery 2019, 85, E924–E932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungk, C.; Warta, R.; Mock, A.; Friauf, S.; Hug, B.; Capper, D.; Abdollahi, A.; Debus, J.; Bendszus, M.; von Deimling, A.; et al. Location-Dependent Patient Outcome and Recurrence Patterns in IDH1-Wildtype Glioblastoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, M.; Baernreuther, J.; Turowski, B.; Steiger, H.J.; Sabel, M.; Kamp, M.A. Recurrence Pattern Analysis of Primary Glioblastoma. World Neurosurg. 2017, 103, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.T.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Kam, M.K.; Cheung, T.C.; Ng, S.C.; Poon, W.S. Pattern of recurrence and factors associated with cerebrospinal fluid dissemination of glioblastoma in Chinese patients. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2016, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeberg, S.; Diehl, C.; Jung, C.S.; Rieken, S.; Combs, S.E.; Unterberg, A.; Debus, J. Is a modification of the radiotherapeutic target volume necessary after resection of glioblastomas with opening of the ventricles? J. Neurooncol. 2016, 127, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeberg, S.; König, L.; Bostel, T.; Harrabi, S.; Welzel, T.; Debus, J.; Combs, S.E. Glioblastoma recurrence patterns after radiation therapy with regard to the subventricular zone. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Lee, Y.; Miller, R.; Castillo, M. Glioblastoma multiforme: Relationship to subventricular zone and recurrence. Neuroradiol. J. 2013, 26, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, G.; Amelio, D.; Amichetti, M.; Salvati, M.; Muni, R.; Bozzao, A.; Lanzetta, G.; Scarpino, S.; Arcella, A.; Enrici, R.M. Patterns of failure and comparison of different target volume delineations in patients with glioblastoma treated with conformal radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 97, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, W.; Stupp, R.; Beule, A.C.; Bromberg, J.; Wick, A.; Ernemann, U.; Platten, M.; Marosi, C.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.; et al. A novel tool to analyze MRI recurrence patterns in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2008, 10, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, H.; Narita, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Yoshida, A.; Takami, H.; Miyakita, Y.; Ohno, M.; Shibui, S.; Ichimura, K. Development of a robust and sensitive pyrosequencing assay for the detection of IDH1/2 mutations in gliomas. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2015, 32, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, H.; Narita, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Tateishi, K.; Matsushita, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Miyakita, Y.; Ohno, M.; Collins, V.P.; Kawahara, N.; et al. Upregulating mutations in the TERT promoter commonly occur in adult malignant gliomas and are strongly associated with total 1p19q loss. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, M.; Miyakita, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Igaki, H.; Matsushita, Y.; Ichimura, K.; Narita, Y. Survival benefits of hypofractionated radiotherapy combined with temozolomide or temozolomide plus bevacizumab in elderly patients with glioblastoma aged ≥ 75 years. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Yoon, S.J.; Kim, K.H.; Jung, I.H.; Lim, S.H.; Kim, W.; Yoon, H.I.; Kim, S.H.; Sung, K.S.; Roh, T.H.; et al. Patterns of recurrence according to the extent of resection in patients with IDH-wild-type glioblastoma: A retrospective study. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 137, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.M.; Speers, C.; Li, P.; Schipper, M.; Junck, L.; Leung, D.; Orringer, D.; Heth, J.; Umemura, Y.; Spratt, D.E.; et al. Dose-intensified chemoradiation is associated with altered patterns of failure and favorable survival in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 143, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.; Liermann, J.; Verma, V.; Bernhardt, D.; Bougatf, N.; Paul, A.; Rieken, S.; Debus, J.; Adeberg, S. Survival and recurrence patterns of multifocal glioblastoma after radiation therapy. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 4229–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaub, C.; Kebir, S.; Junold, N.; Hattingen, E.; Schäfer, N.; Steinbach, J.P.; Weyerbrock, A.; Hau, P.; Goldbrunner, R.; Niessen, M.; et al. Tumor growth patterns of MGMT-non-methylated glioblastoma in the randomized GLARIUS trial. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bette, S.; Barz, M.; Huber, T.; Straube, C.; Schmidt-Graf, F.; Combs, S.E.; Delbridge, C.; Gerhardt, J.; Zimmer, C.; Meyer, B.; et al. Retrospective Analysis of Radiological Recurrence Patterns in Glioblastoma, Their Prognostic Value And Association to Postoperative Infarct Volume. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiepold, A.L.; Luger, S.; Wagner, M.; Filmann, N.; Ronellenfitsch, M.W.; Harter, P.N.; Braczynski, A.K.; Dützmann, S.; Hattingen, E.; Steinbach, J.P.; et al. Perioperative cerebral ischemia promote infiltrative recurrence in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14537–14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, O.; Safaee, M.; Sun, M.Z.; Butowski, N.A.; McDermott, M.W.; Berger, M.S.; Aghi, M.K.; Parsa, A.T. Disseminated progression of glioblastoma after treatment with bevacizumab. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, H.; Kuroda, J.I.; Uetani, H.; Matsuyama, T.; Kaku, Y.; Shinojima, N.; Hirai, T.; Mukasa, A. Postoperative disappearance of leptomeningeal enhancement around the brainstem in glioblastoma. Neuroradiology 2024, 66, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onda, K.; Tanaka, R.; Takahashi, H.; Takeda, N.; Ikuta, F. Cerebral glioblastoma with cerebrospinal fluid dissemination: A clinicopathological study of 14 cases examined by complete autopsy. Neurosurgery 1989, 25, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, M.; Morishita, Y.; Shimoda, Y.; Yamamori, E.; Sato, S.; Osada, Y.; Osawa, S.I.; Shibahara, I.; Saito, R.; Sonoda, Y.; et al. Distant recurrence in the cerebellar dentate nucleus through the dentato-rubro-thalamo-cortical pathway in supratentorial glioma cases. Acta Neurochir. 2024, 166, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, R.J.; Rich, J.N. Making a tumour’s bed: Glioblastoma stem cells and the vascular niche. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capilla-Gonzalez, V.; Lavell, E.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Guerrero-Cazares, H. Regulation of subventricular zone-derived cells migration in the adult brain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 853, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Seiz, M.; Nölte, I.; Pechlivanis, I.; Freyschlag, C.F.; Schmieder, K.; Vajkoczy, P.; Tuettenberg, J. Far-distant metastases along the CSF pathway of glioblastoma multiforme during continuous low-dose chemotherapy with temozolomide and celecoxib. Neurosurg. Rev. 2010, 33, 375–381; discussion 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestler, U.; Lutz, K.; Pichlmeier, U.; Stummer, W.; Franz, K.; Reulen, H.J.; Bink, A. Anatomic features of glioblastoma and their potential impact on survival. Acta Neurochir. 2015, 157, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawauchi, D.; Ohno, M.; Honda-Kitahara, M.; Miyakita, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Yanagisawa, S.; Tamura, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Ichimura, K.; Narita, Y. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of Glioblastoma patients with infratentorial recurrence. BMC Neurol. 2023, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallaert, G.; Pinson, H.; Van den Broecke, C.; Sweldens, C.; Van Roost, D.; Kalala, J.P.; Boterberg, T. Survival impact of incidental subventricular zone irradiation in IDH-wildtype glioblastoma. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hira, V.V.V.; Molenaar, R.J.; Breznik, B.; Lah, T.; Aronica, E.; Van Noorden, C.J.F. Immunohistochemical Detection of Neural Stem Cells and Glioblastoma Stem Cells in the Subventricular Zone of Glioblastoma Patients. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2021, 69, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffart, N.; Lombard, A.; Lallemand, F.; Kroonen, J.; Nassen, J.; Di Valentin, E.; Berendsen, S.; Dedobbeleer, M.; Willems, E.; Robe, P.; et al. CXCL12 mediates glioblastoma resistance to radiotherapy in the subventricular zone. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Dong, L.; Pan, Z.; Yang, G. Targeting the neural stem cells in subventricular zone for the treatment of glioblastoma: An update from preclinical evidence to clinical interventions. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeberg, S.; Knoll, M.; Koelsche, C.; Bernhardt, D.; Schrimpf, D.; Sahm, F.; König, L.; Harrabi, S.B.; Hörner-Rieber, J.; Verma, V.; et al. DNA-methylome-assisted classification of patients with poor prognostic subventricular zone associated IDH-wildtype glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 144, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ren, X.; Li, M.; Jiang, H.; Li, M.; Wan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhou, D. Subventricular zone-associated classification in isocitrate dehydrogenase-wildtype glioblastomas: Improved prognostic value through integration of FLAIR with contrast-enhanced imaging. J. Neurosurg. 2024, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofano, F.; Bianconi, A.; De Marco, R.; Consoli, E.; Zeppa, P.; Bruno, F.; Pellerino, A.; Panico, F.; Salvati, L.F.; Rizzo, F.; et al. The Impact of Lateral Ventricular Opening in the Resection of Newly Diagnosed High-Grade Gliomas: A Single Center Experience. Cancers 2024, 16, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaar, R.J.; Verbaan, D.; Lamba, S.; Zanon, C.; Jeuken, J.W.; Boots-Sprenger, S.H.; Wesseling, P.; Hulsebos, T.J.; Troost, D.; van Tilborg, A.A.; et al. The combination of IDH1 mutations and MGMT methylation status predicts survival in glioblastoma better than either IDH1 or MGMT alone. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristics (N = 104) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age, years, median, (IQR) | 61.5 | (50–72) |
| Male, (%) | 66 | (63.5) |
| KPS on admission, median, (IQR) | 80 | (70–90) |
| MGMT promoter methylation, (%) | 40 | (38.5) |
| TERT promoter mutation | ||
| C228T mutation | 52 | (50.0) |
| C250T mutation | 17 | (16.3) |
| wildtype | 35 | (33.7) |
| Tumor location, (%) | ||
| Frontal lobe | 37 | (35.6) |
| Parietal lobe | 31 | (29.8) |
| Temporal lobe | 18 | (17.3) |
| Multilobular | 7 | (6.7) |
| Infratentorial | 4 | (3.8) |
| Others | 7 | (6.7) |
| Laterality, (%) | ||
| Left | 54 | (51.9) |
| Right | 46 | (44.2) |
| Midline | 4 | (3.8) |
| Maximum tumor size, mm, median, (IQR) | 39.5 | (28.2–54.0) |
| SVZ involvement, (%) | 57 | (54.8) |
| Initial treatment, (%) | ||
| RT + TMZ | 45 | (43.3) |
| RT + TMZ + BEV | 20 | (19.2) |
| RT + TMZ + Gliadel wafer | 6 | (5.8) |
| Others | 13 | (12.5) |
| Ventricular opening, (%) | 30 | (28.8) |
| Extent of resection, (%) | ||
| GTR | 37 | (35.6) |
| STR | 21 | (20.2) |
| PR | 29 | (27.9) |
| Biopsy | 17 | (16.3) |
| Postoperative ischemia, (%) | 24 | (23.1) |
| OS, months, median (95% CI) | 32.1 | (26.3–37.4) |
| PFS, months, median (95% CI) | 9.6 | (8.0–12.8) |
| Non-local recurrence free survival, median (95% CI) | 41.6 | (28.9–61.3) |
| Type of non-local recurrence, (%) | ||
| Distant recurrence | 13 | (12.5) |
| Dissemination | 25 | (24.0) |
| Follow-up period, months, median (IQR) | 24.8 | (13.6–39.9) |
| Factor | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (≥65 years) | 1.527 (0.795–2.934) | 0.204 | NE | |
| Male | 1.339 (0.671–2.673) | 0.408 | NE | |
| KPS on admission (≥80) | 1.930 (0.995–3.744) | 0.052 | 0.713 (0.298–1.705) | 0.447 |
| MGMT promoter methylation | 0.613 (0.310–1.210) | 0.159 | 0.520 (0.233–1.162) | 0.111 |
| TERT promoter mutation | 0.774 (0.400–1.498) | 0.447 | NE | |
| Frontal location | 0.649 (0.331–1.273) | 0.209 | NE | |
| Parietal location | 1.005 (0.470–2.148) | 0.990 | NE | |
| Temporal location | 1.043 (0.513–2.123) | 0.907 | NE | |
| Maximum tumor size (≥40 mm) | 0.789 (0.415–1.498) | 0.468 | NE | |
| SVZ involvement | 2.088 (1.076–4.048) | 0.029 * | 1.403 (0.576–3.422) | 0.456 |
| Ventricular opening | 2.539 (1.278–5.043) | 0.008 * | 1.960 (0.822–4.672) | 0.129 |
| Extent of resection (GTR/STR) | 1.010 (0.514–1.984) | 0.977 | NE | |
| Postoperative ischemia | 1.824 (0.905–3.676) | 0.093 | 1.118 (0.491–2.546) | 0.791 |
| Distant Recurrence | Subependymal Dissemination | Subarachnoidal Dissemination | Spinal Dissemination | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior horn | 5 (33.3%) | 2 (13.3%) | 2 (13.3%) | 1 (6.7%) |
| Body | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Trigone | 2 (7.6%) | 9 (35.6%) | 0 | 0 |
| Inferior horn | 2 (40.0%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Others | 1 (20.0%) | 0 | 1 (20.0%) | 0 |
| Author, Year | Sample Size | Incidence of Non-Local Recurrence | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liu, 2023 [11] | 66 | 15.2% | SVZ involvement is an independent risk factor for non-local recurrence. |
| Yoo, 2021 [29] | 358 | 29.5% | The patterns of recurrence are associated with the extent of resection; supratotal resection, gross-total resection, and subtotal resection. |
| Young, 2021 [12] | 200 | 25.0% | There is no increase in leptomeningeal spread or distant parenchymal recurrence in patients with ventricular opening. |
| Jiang, 2020 [13] | 247 | 24.7% | Being male, SVZ involvement, and MGMT promoter methylation are risk factors for non-local progression. |
| Yamaki, 2020 [14] | 167 | 21.0% | Distant recurrence is the most frequent in the SVZ-negative and cortex-positive groups, and high CD133 expression is associated with distant recurrence. |
| Mistry, 2019 [15] | 232 | ≥33.6% | SVZ contact is associated with leptomeningeal dissemination, and ventricular opening is not associated with non-local recurrence. |
| Kim, 2019 [30] | 82 | 23.5% | Distant recurrence is associated with a longer time to progression. |
| Jungk, 2019 [16] | 285 | 26.2% | Distant recurrence is more frequent in cortex-positive GBM. |
| Syed, 2018 [31] | 265 | 34.7% | Local vs. distant brain recurrences occur similarly in both unifocal and multifocal GBM. |
| Schaub, 2018 [32] | 142 | 15.5% | BEV/irinotecan (IRI) is not associated with increased rates of multifocal, distant, or highly invasive tumors at the time of recurrence. |
| Bette, 2018 [33] | 129 | 44.2% | Postoperative infarct volume is associated with multifocal and diffuse recurrence patterns and impaired survival. |
| Rapp, 2017 [17] | 97 | 20.6% | There is no correlation between MGMT methylation status and the recurrence pattern. |
| Chan, 2016 [18] | 36 | 38.9% | Ventricular opening and MGMT methylation are associated with the development of CSF dissemination. |
| Adeberg, 2016 [19] | 311 | ≥18.0% | Distant, contralateral recurrence is not influenced by ventricle opening. |
| Thiepold, 2015 [34] | 245 | 27.2% | Perioperative cerebral ischemia is associated with distant or diffuse recurrence. |
| Adeberg, 2014 [20] | 607 | 26.9% | SVZ involvement is associated with decreased survival and a higher risk of multifocal or distant progression. |
| Kimura, 2013 [21] | 49 | 55.1% | SVZ involvement does not predict the pattern of tumor recurrence and/or extension. |
| Bloch, 2013 [35] | 71 | 16.9% | The risk of dissemination does not increase due to the use of BEV. |
| Minniti, 2010 [22] | 105 | 13.3% | MGMT methylation is associated with non-local recurrence. |
| Brandes, 2009 [5] | 95 | 21.5% | MGMT methylation is associated with non-local recurrence. |
| Wick, 2008 [23] | 63 | 20.0% | MGMT methylation is not associated with non-local recurrence. |
| Present study | 104 | 36.5% | SVZ is associated with distant recurrence, and GBM in contact with the trigone of the lateral ventricle is associated with subependymal dissemination. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsuchiya, T.; Kawauchi, D.; Ohno, M.; Miyakita, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Yanagisawa, S.; Osawa, S.; Fujita, S.; Omura, T.; Narita, Y. Risk Factors of Distant Recurrence and Dissemination of IDH Wild-Type Glioblastoma: A Single-Center Study and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162873
Tsuchiya T, Kawauchi D, Ohno M, Miyakita Y, Takahashi M, Yanagisawa S, Osawa S, Fujita S, Omura T, Narita Y. Risk Factors of Distant Recurrence and Dissemination of IDH Wild-Type Glioblastoma: A Single-Center Study and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162873
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsuchiya, Takahiro, Daisuke Kawauchi, Makoto Ohno, Yasuji Miyakita, Masamichi Takahashi, Shunsuke Yanagisawa, Sho Osawa, Shohei Fujita, Takaki Omura, and Yoshitaka Narita. 2024. "Risk Factors of Distant Recurrence and Dissemination of IDH Wild-Type Glioblastoma: A Single-Center Study and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162873
APA StyleTsuchiya, T., Kawauchi, D., Ohno, M., Miyakita, Y., Takahashi, M., Yanagisawa, S., Osawa, S., Fujita, S., Omura, T., & Narita, Y. (2024). Risk Factors of Distant Recurrence and Dissemination of IDH Wild-Type Glioblastoma: A Single-Center Study and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(16), 2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162873








