SKF-96365 Expels Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Treated CML Stem and Progenitor Cells from the HS27A Stromal Cell Niche in a RhoA-Dependent Mechanism
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
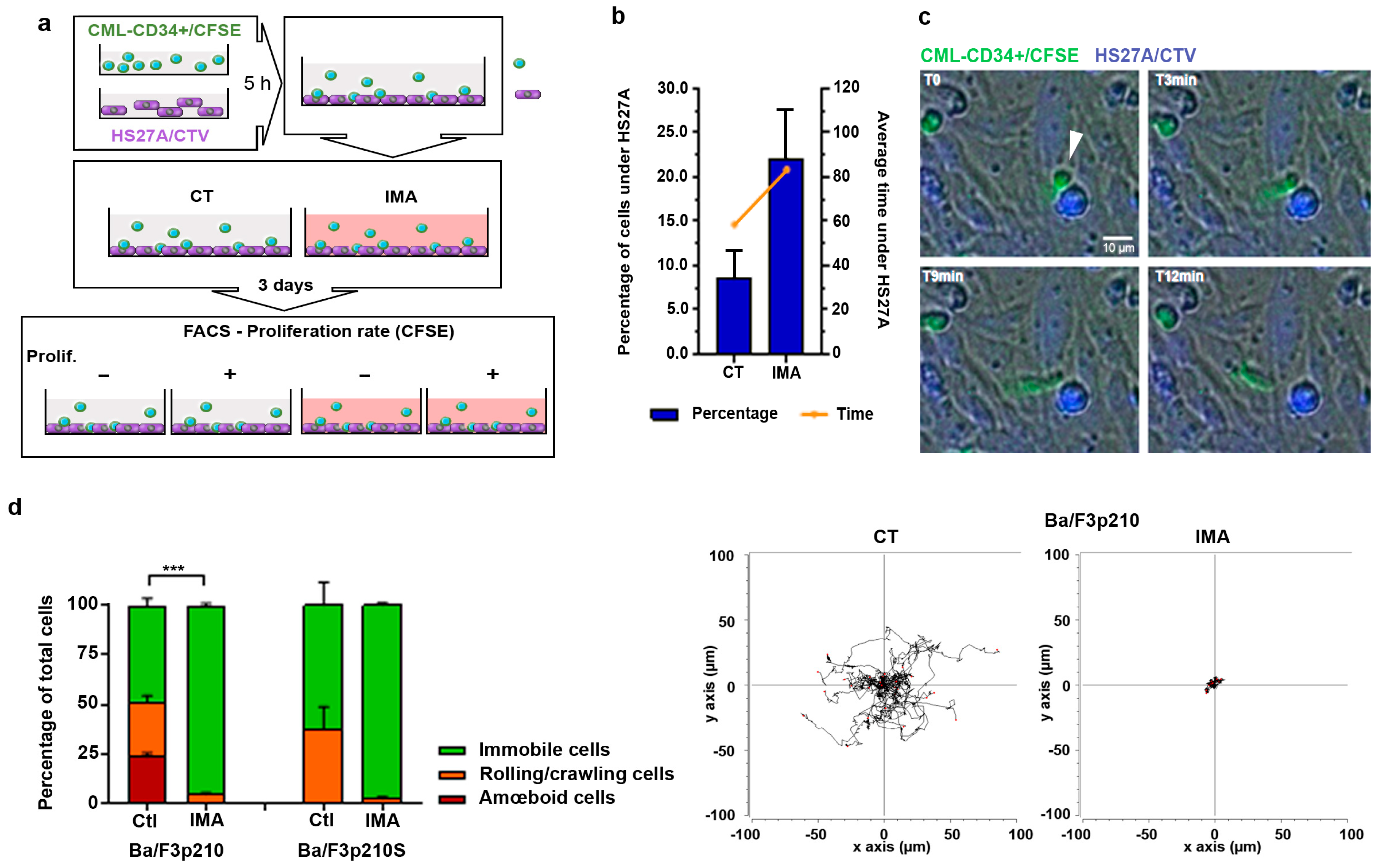
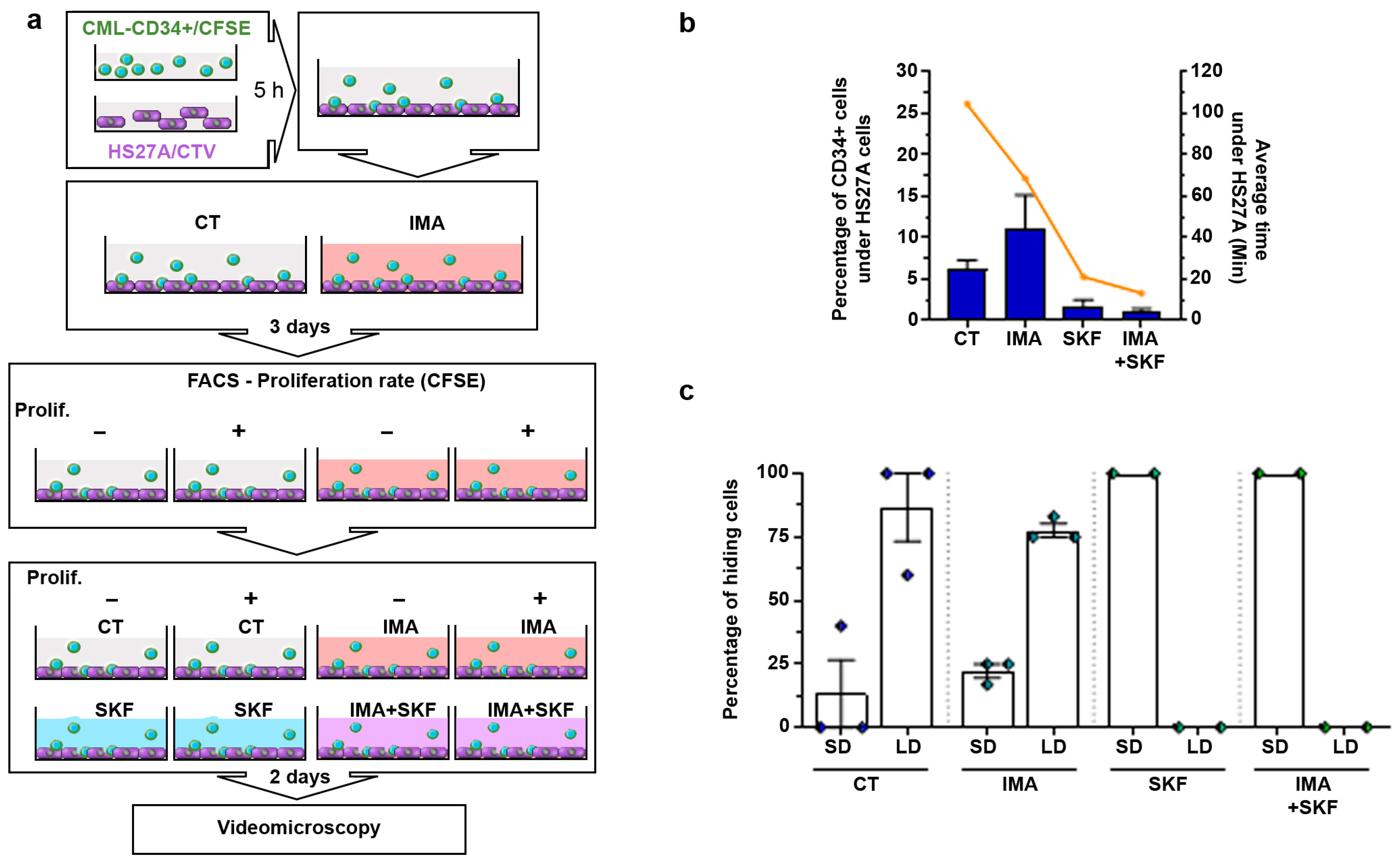
3.1. CD34+ Cells from CML Patients Hide under Stromal HS27A Cells under Imatinib Treatment
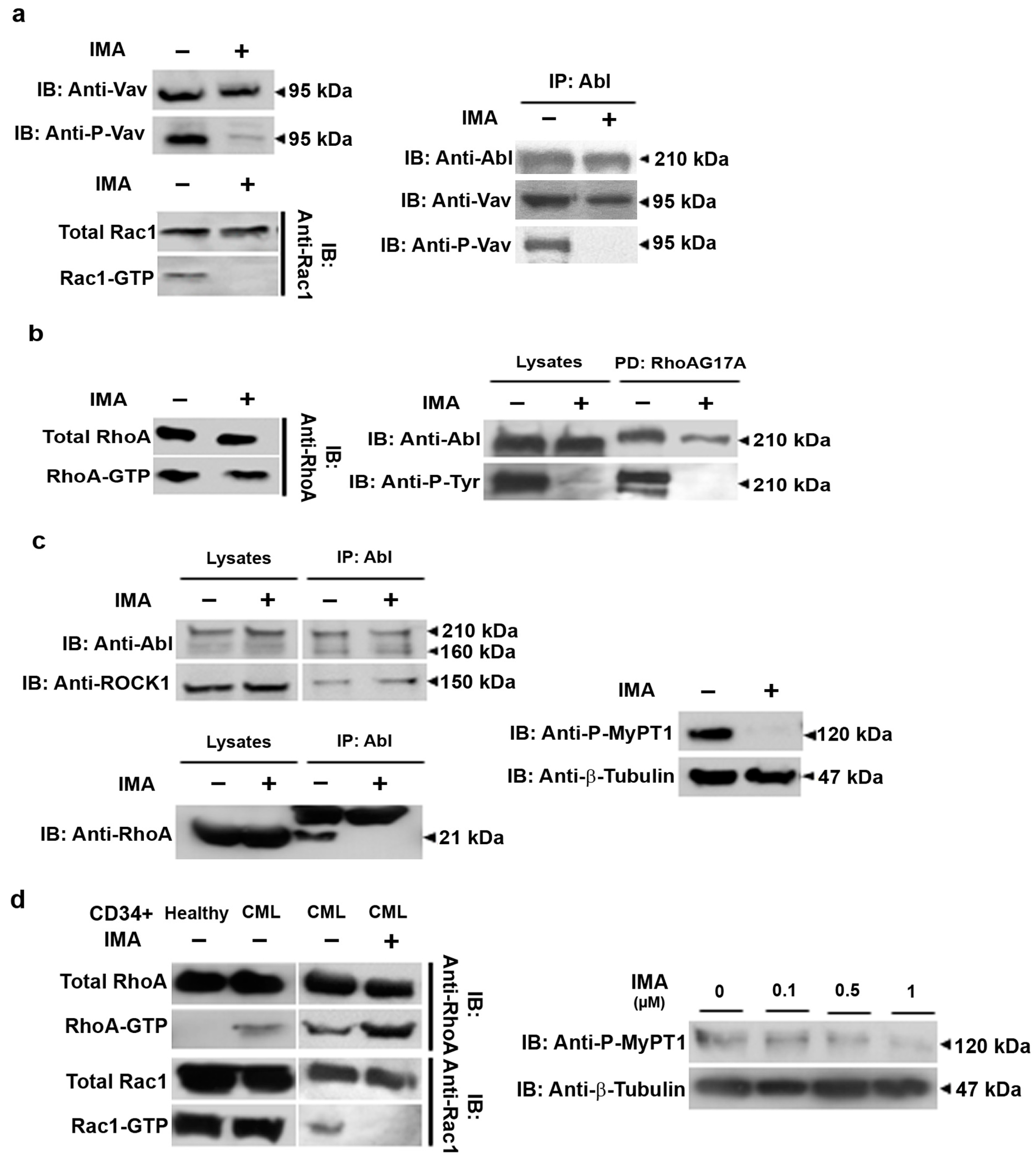
3.2. RhoA Activation Persists in Imatinib Conditions in Ba/F3p210 and CML Patients’ CD34+ Cells
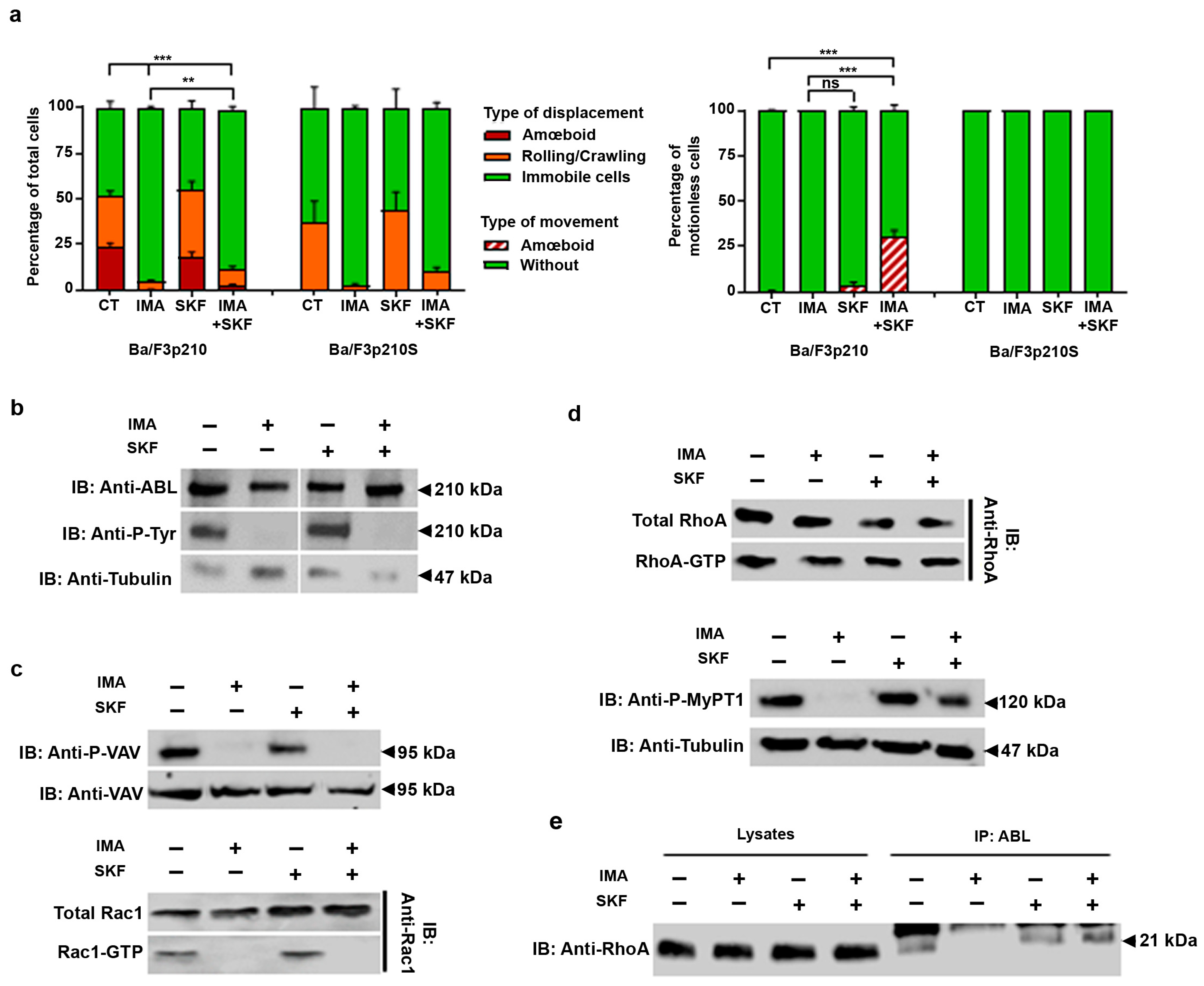
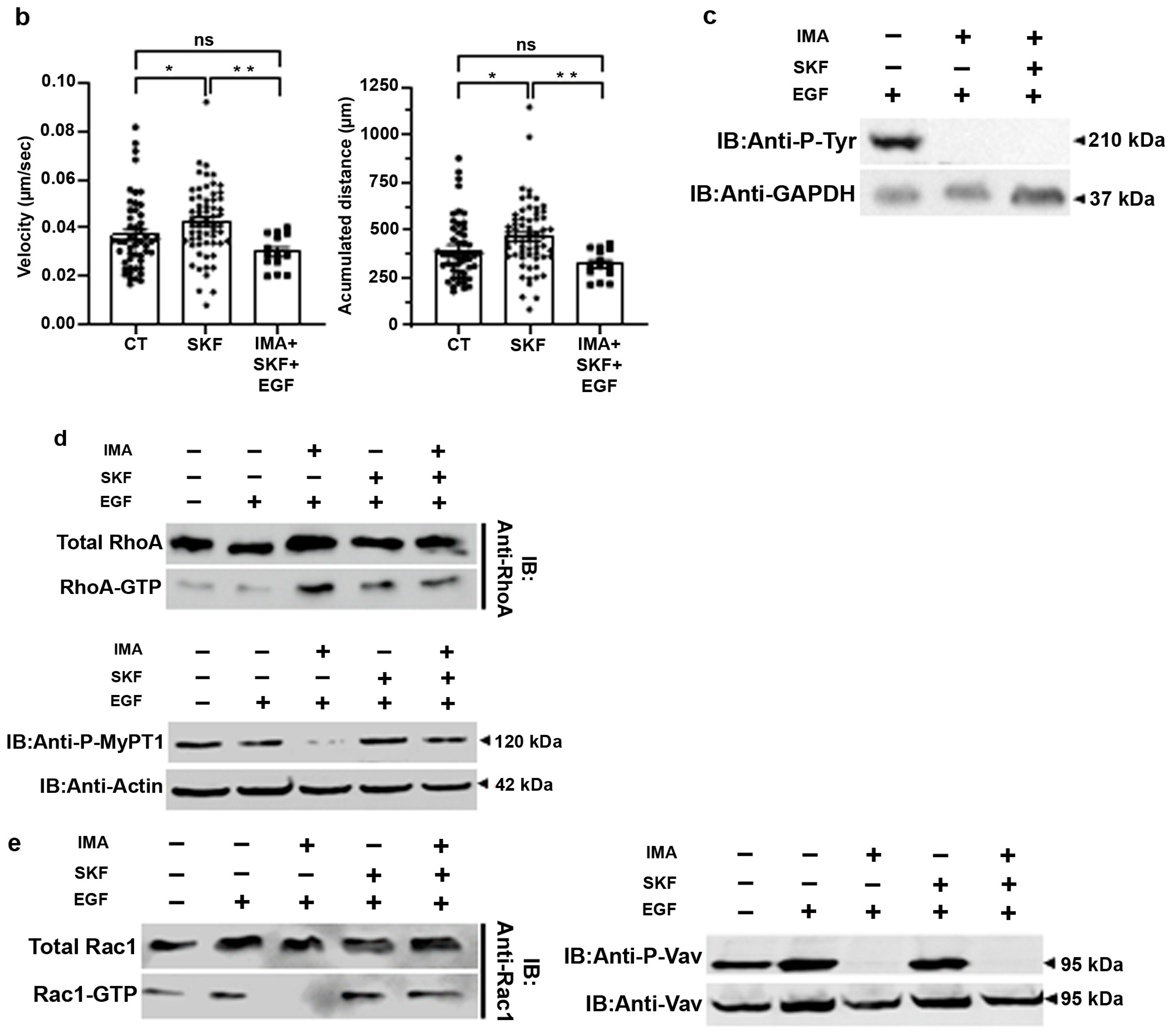
3.3. SKF-96365 Restores ROCK Signaling, Lost under Imatinib Treatment
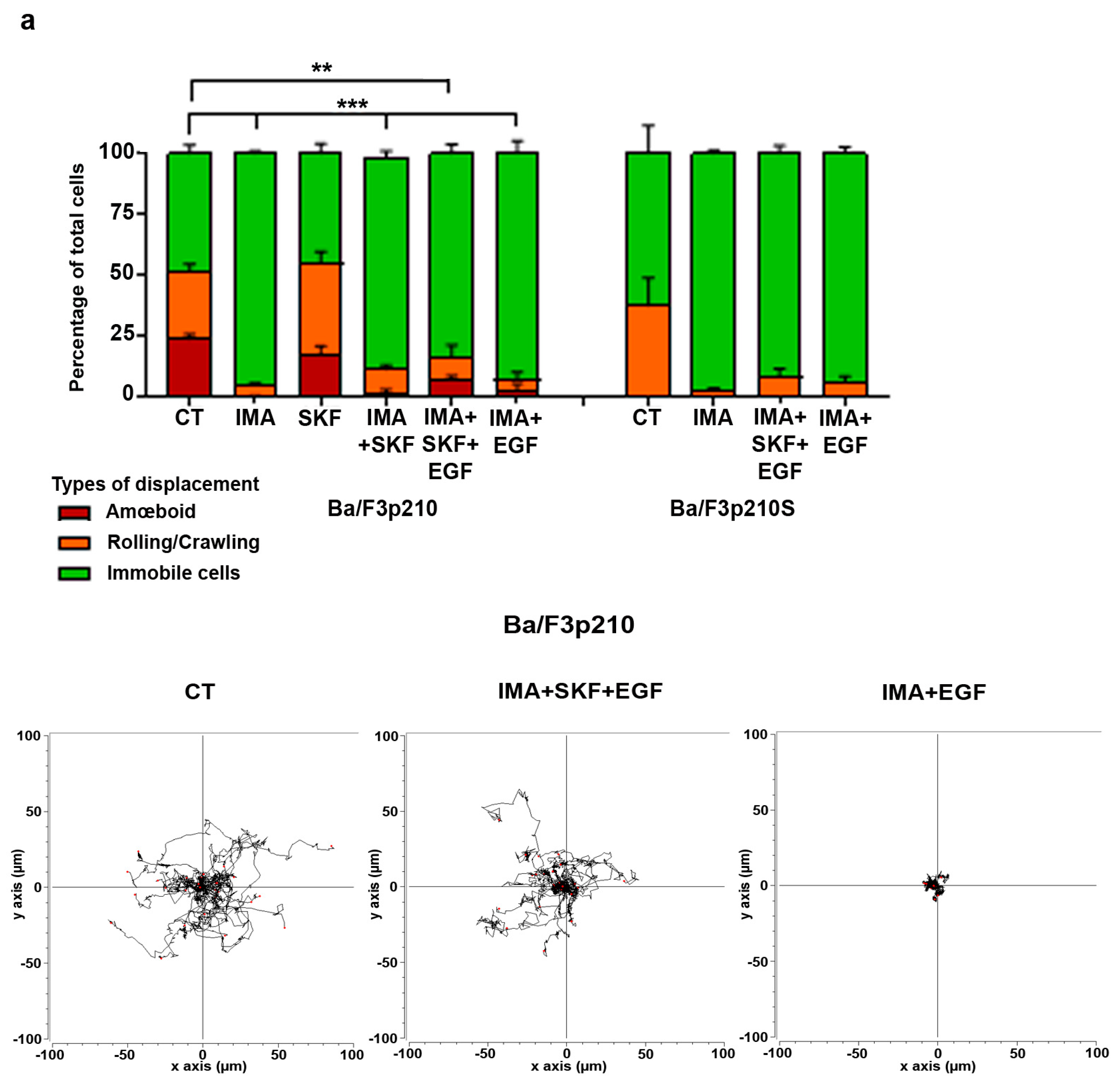
3.4. EGF in Conjunction with SKF-96365 Restores Ba/F3p210 Cell Motility Inhibited by Imatinib
3.5. SKF-96365 Expels Low-Proliferating CD34+ Cells from the HS27A Niche
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osman, A.E.G.; Deininger, M.W. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Modern therapies, current challenges and future directions. Blood Rev. 2021, 49, 100825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, F.X.; Réa, D.; Guilhot, J.; Guilhot, F.; Huguet, F.; Nicolini, F.; Legros, L.; Charbonnier, A.; Guerci, A.; Varet, B. Discontinuation of imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia who have maintained complete molecular remission for at least 2 years: The prospective, multicentre Stop Imatinib (STIM) trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomel, J.C.; Bonnet, M.L.; Sorel, N.; Bertrand, A.; Meunier, M.C.; Fichelson, S.; Melkus, M.; Bennaceur-Griscelli, A.; Guilhot, F.; Turhan, A.G. Leukemic stem cell persistence in chronic myeloid leukemia patients with sustained undetectable molecular residual disease. Blood 2011, 118, 3657–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charaf, L.; Mahon, F.X.; Lamrissi-Garcia, I.; Moranvillier, I.; Beliveau, F.; Cardinaud, B.; Dabernat, S.; de Verneuil, H.; Moreau-Gaudry, F.; Bedel, A. Effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on stemness in normal and chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia 2017, 31, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Lorenzana, D.; Avilés-Vazquez, S.; Sandoval Esquivel, M.A.; Alvarado-Moreno, A.; Ortiz-Navarrete, V.; Torres-Martínez, H.; Ayala-Sánchez, M.; Mayani, H.; Chavez-Gonzalez, A. CDKIs p18INK4c and p57Kip2 are involved in quiescence of CML leukemic stem cells after treatment with TKI. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, A.; Jamieson, C.H.; Fereshteh, M.; Abrahamsson, A.; Blum, J.; Kwon, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Chute, J.P.; Rizzieri, D.; et al. Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem cells in myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2009, 458, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljedai, A.; Buckle, A.M.; Hiwarkar, P.; Syed, F. Potential role of Notch signalling in CD34+ chronic myeloid leukaemia cells: Cross-talk between Notch and BCR-ABL. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naka, K.; Hoshii, T.; Hirao, A. Novel therapeutic approach to eradicate tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistant chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 1577–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanpierre, S.; Arizkane, K.; Thongjuea, S.; Grockowiak, E.; Geistlich, K.; Barral, L.; Voeltzel, T.; Guillemin, A.; Gonin-Giraud, S.; Gandrillon, O.; et al. The quiescent fraction of chronic myeloid leukemic stem cells depends on BMPR1B, Stat3 and BMP4-niche signals to persist in patients in remission. Haematologica 2021, 106, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, P.; Dawson, A.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Kuntz, E.M.; Mitchell, R.; Olivares, O.; Ianniciello, A.; Scott, M.T.; Dunn, K.; Nicastri, M.C.; et al. Targeting quiescent leukemic stem cells using second generation autophagy inhibitors. Leukemia 2019, 33, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.K.; Cancelas, J.A.; Zheng, Y.; Williams, D.A. Rac GTPases as key regulators of p210-BCR-ABL-dependent leukemogenesis. Leukemia 2008, 22, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soverini, S.; De Santis, S.; Monaldi, C.; Bruno, S.; Mancini, M. Targeting Leukemic Stem Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Is It Worth the Effort? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochelle, T.; Daubon, T.; Van Troys, M.; Harnois, T.; Waterschoot, D.; Ampe, C.; Roy, L.; Bourmeyster, N.; Constantin, B. p210(bcr-abl) induces amoeboid motility by recruiting ADF/destrin through RhoA/ROCK1. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, C.; Montes, R.; Menendez, P. The ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 negatively affects the expansion/survival of both fresh and cryopreserved cord blood-derived CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells: Y-27632 negatively affects the expansion/survival of CD34+HSPCs. Stem. Cell Rev. Rep. 2010, 6, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Yeih, D.F.; Liang, S.M.; Chien, C.Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Ko, B.S.; Jan, Y.J.; Kuo, C.C.; Sung, L.Y.; Shyue, S.K.; et al. Rho-associated kinase inhibitors promote the cardiac differentiation of embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 201, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanas, H.; Harnois, T.; Magaud, C.; Cousin, L.; Constantin, B.; Bourmeyster, N.; Déliot, N. Deregulation of calcium homeostasis in Bcr-Abl-dependent chronic myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubon, T.; Chasseriau, J.; Ali, A.E.; Rivet, J.; Kitzis, A.; Constantin, B.; Bourmeyster, N. Differential motility of p190bcr-abl and p210 bcr-abl -expressing cells: Respective roles of Vav and Bcr-Abl GEFs. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2673–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Harnois, T.; Constantin, B.; Rioux, A.; Grenioux, E.; Kitzis, A.; Bourmeyster, N. Differential interaction and activation of Rho family GTPases by p210bcr-abl and p190bcr-abl. Oncogene 2003, 22, 6445–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tinevez, J.Y.; Perry, N.; Schindelin, J.; Hoopes, G.M.; Reynolds, G.D.; Laplantine, E.; Bednarek, S.Y.; Shorte, S.L.; Eliceiri, K.W. TrackMate: An open and extensible platform for single-particle tracking. Methods 2017, 115, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassermann, F.; Jahn, T.; Miething, C.; Seipel, P.; Bai, R.Y.; Coutinho, S.; Peschel, C.; Duyster, J.; Tybulewicz, V.L. Association of Bcr-Abl with the Proto-oncogene Vav Is Implicated in Activation of the Rac-1 Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 12437–12445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mata, R.; Burridge, K. Catching a GEF by its tail. Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unwin, R.D.; Sternberg, D.W.; Lu, Y.; Pierce, A.; Gilliland, D.G.; Whetton, A.D. Global Effects of BCR/ABL and TEL/PDGFRβ Expression on the Proteome and Phosphoproteome Identification of the Rho Pathway as a Target of BCR/ABL. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 6316–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geay, J.F.; Buet, D.; Zhang, Y.; Foudi, A.; Jarrier, P.; Berthebaud, M.; Turhan, A.G.; Vainchenker, W.; Louache, F. p210BCR-ABL inhibits SDF-1 chemotactic response via alteration of CXCR4 signaling and down-regulation of CXCR4 expression. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2676–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, D.A.; Srivastava, T.; Dwarakanath, D.; Pierre, P.; Nygaard, S.; Derkach, V.A.; Soderling, T.R. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of CaM-kinase kinase via transient receptor potential canonical channels induces the translation and synaptic incorporation of GluA1-containing calcium-permeable AMPA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 8127–8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.; Sui, X.; Yao, J.; Xie, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, H.; Han, W. SKF-96365 activates cytoprotective autophagy to delay apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells through inhibition of the calcium/CaMKIIγ/AKT-mediated pathway. Cancer Lett. 2016, 372, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottosin, I.; Delgado-Enciso, I.; Bonales-Alatorre, E.; Nieto-Pescador, M.G.; Moreno-Galindo, E.G.; Dobrovinskaya, O. Mechanosensitive Ca2+-permeable channels in human leukemic cells: Pharmacological and molecular evidence for TRPV2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2015, 1848 Pt 1, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, J.A.; Kerschbaum, H.H.; Cahalan, M.D. Distinct properties of CRAC and MIC channels in RBL cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 2002, 120, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubanov, V.; Schäfer, S.; Ferioli, S.; Gudermann, T. Natural and Synthetic Modulators of the TRPM7 Channel. Cells 2014, 3, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.L.; Ambudkar, I.S. The dynamic complexity of the TRPC1 channelosome. Channels 2011, 5, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, D.; Ahmmed, G.U.; Paria, B.C.; Holinstat, M.; Voyno-Yasenetskaya, T.; Tiruppathi, C.; Minshall, R.D.; Malik, A.B. RhoA Interaction with Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor and Transient Receptor Potential Channel-1 Regulates Ca2+ Entry: Role in signaling increased endothelial permeability. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 33492–33500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Chen, D.; Yu, S.P. The TRPC channel blocker SKF 96365 inhibits glioblastoma cell growth by enhancing reverse mode of the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger and increasing intracellular Ca(2+). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrié, E.; Déliot, N.; Benzidane, Y.; Harnois, T.; Cousin, L.; Bois, P.; Oliver, L.; Arnault, P.; Vallette, F.; Constantin, B.; et al. Store-Operated Calcium Channels Control Proliferation and Self-Renewal of Cancer Stem Cells from Glioblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ye, J. The Effects of Calcium Channel Blocker Combined with Oxaliplatin on Apoptosis of Bladder Cancer Cells. J. Oncol. 2023, 3, 1118. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dubourg, A.; Harnois, T.; Cousin, L.; Constantin, B.; Bourmeyster, N. SKF-96365 Expels Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Treated CML Stem and Progenitor Cells from the HS27A Stromal Cell Niche in a RhoA-Dependent Mechanism. Cancers 2024, 16, 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162791
Dubourg A, Harnois T, Cousin L, Constantin B, Bourmeyster N. SKF-96365 Expels Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Treated CML Stem and Progenitor Cells from the HS27A Stromal Cell Niche in a RhoA-Dependent Mechanism. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162791
Chicago/Turabian StyleDubourg, Audrey, Thomas Harnois, Laetitia Cousin, Bruno Constantin, and Nicolas Bourmeyster. 2024. "SKF-96365 Expels Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Treated CML Stem and Progenitor Cells from the HS27A Stromal Cell Niche in a RhoA-Dependent Mechanism" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162791
APA StyleDubourg, A., Harnois, T., Cousin, L., Constantin, B., & Bourmeyster, N. (2024). SKF-96365 Expels Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Treated CML Stem and Progenitor Cells from the HS27A Stromal Cell Niche in a RhoA-Dependent Mechanism. Cancers, 16(16), 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162791






