Navigating Brain Metastases: Unveiling the Potential of 3-Tesla Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
2.2. Surgical Procedure and Imaging Analysis
2.3. Postoperative Protocol
2.4. Institutional Review Board Statement
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics and Baseline Characteristics
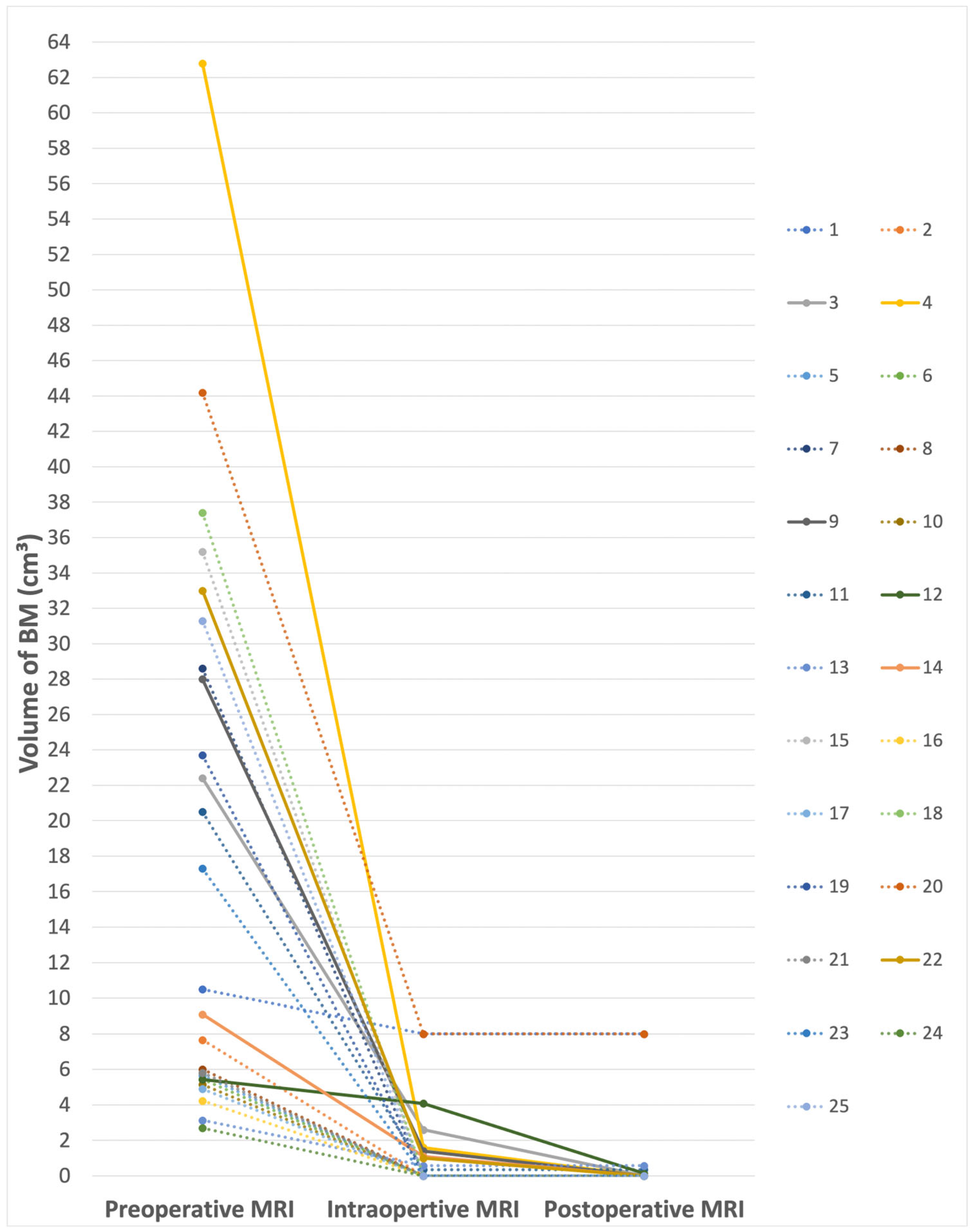
3.2. Impact of iMRI on Increasing Excess of Resection (EOR)
3.3. Postoperative Outcome and Follow-Up
3.4. Complications and Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Ille, S.; Schwendner, M.; Wiestler, B.; Meyer, B.; Krieg, S.M. The Impact of IoMRI on Glioblastoma Resection and Clinical Outcomes in a State-of-the-Art Neuro-Oncological Setup. Cancers 2023, 15, 3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, M.; Norman, S.; Sehgal, R.; Juthani, R. Updates on Surgical Management and Advances for Brain Tumors. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Saxena, S.; Khosla, A.A.; McDermott, M.W.; Kotecha, R.R.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Update on the Management of Brain Metastasis. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Kaiser, Y.; Wiestler, B.; Bernhardt, D.; Combs, S.E.; Delbridge, C.; Meyer, B.; Gempt, J.; Aftahy, A.K. Cytoreduction of Residual Tumor Burden Is Decisive for Prolonged Survival in Patients with Recurrent Brain Metastases—Retrospective Analysis of 219 Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Mesko, S.; Li, J.; Cagney, D.; Aizer, A.; Lin, N.U.; Nesbit, E.; Kruser, T.J.; Chan, J.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Survival in Patients with Brain Metastases: Summary Report on the Updated Diagnosis-Specific Graded Prognostic Assessment and Definition of the Eligibility Quotient. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3773–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apra, C.; Bemora, J.S.; Palfi, S. Achieving Gross Total Resection in Neurosurgery: A Review of Intraoperative Techniques and Their Influence on Surgical Goals. World Neurosurg. 2024, 185, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubben, P.L.; ter Meulen, K.J.; Schijns, O.E.; ter Laak-Poort, M.P.; van Overbeeke, J.J.; Santbrink, H. van Intraoperative MRI-Guided Resection of Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Systematic Review. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahanda, A.T.; Chicoine, M.R. Intraoperative MRI for Glioma Surgery: Present Overview and Future Directions. World Neurosurg. 2021, 149, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesrud, I.C.; Schulz, M.K.; Marcovic, L.; Kristensen, B.W.; Pedersen, C.B.; Kristiansen, C.; Poulsen, F.R. Early Postoperative MRI after Resection of Brain Metastases—Complete Tumour Resection Associated with Prolonged Survival. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, L.; Aftahy, A.K.; Anetsberger, A.; Thunstedt, D.; Wiestler, B.; Bernhardt, D.; Combs, S.E.; Meyer, B.; Meyer, H.S.; Gempt, J. Brain Metastases in the Elderly—Impact of Residual Tumor Volume on Overall Survival. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1149628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftahy, A.K.; Barz, M.; Lange, N.; Baumgart, L.; Thunstedt, C.; Eller, M.A.; Wiestler, B.; Bernhardt, D.; Combs, S.E.; Jost, P.J.; et al. The Impact of Postoperative Tumor Burden on Patients with Brain Metastases. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 869764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, M.; Mondragon-Soto, M.G.; Dieringer, L.; Altawalbeh, G.; Pöser, P.; Baumgart, L.; Wiestler, B.; Gempt, J.; Meyer, B.; Aftahy, A.K. Navigating Post-Operative Outcomes: A Comprehensive Reframing of an Original Graded Prognostic Assessment in Patients with Brain Metastases. Cancers 2024, 16, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.; Mondragon-Soto, M.G.; Altawalbeh, G.; Baumgart, L.; Gempt, J.; Bernhardt, D.; Combs, S.E.; Meyer, B.; Kaywan Aftahy, A.; Proescholdt, M.; et al. Enhancing Outcomes: Neurosurgical Resection in Brain Metastasis Patients with Poor Karnofsky Performance Score-a Comprehensive Survival Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1343500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Wright, C.H.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Brain Metastases: Epidemiology. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 149, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fox, B.D.; Cheung, V.J.; Patel, A.J.; Suki, D.; Rao, G. Epidemiology of Metastatic Brain Tumors. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichardo-Rojas, P.S.; Angulo-Lozano, J.C.; Alvarez-Castro, J.A.; Vázquez-Alva, D.; Osuna-Lau, R.A.; Choque-Ayala, L.C.; Tandon, N.; Esquenazi, Y. Intraoperative MRI-Guided Resection of Glioblastoma: A Meta-Analysis of 1847 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2024, 182, e807–e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, D.H.; Wein, W.; Lindseth, F.; Unsgård, G.; Reinertsen, I. Automatic Intraoperative Correction of Brain Shift for Accurate Neuronavigation. World Neurosurg. 2018, 120, e1071–e1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollon, T.; Stummer, W.; Orringer, D.; Suero Molina, E. Surgical Adjuncts to Increase the Extent of Resection. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 30, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulder, M.; Carmel, P.W. Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Impact on Brain Tumor Surgery. Cancer Control 2003, 10, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.H.; Sylvester, P.T.; Kulwin, C.; Shah, M.V.; Somasundaram, A.; Kamath, A.A.; Beaumont, T.L.; Rich, K.M.; Chicoine, M.R. Initial Experience Using Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging during a Trans-Sulcal Tubular Retractor Approach for the Resection of Deep-Seated Brain Tumors: A Case Series. Oper. Neurosurg. 2019, 16, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ius, T.; Sabatino, G.; Panciani, P.P.; Fontanella, M.M.; Rudà, R.; Castellano, A.; Barbagallo, G.M.V.; Belotti, F.; Boccaletti, R.; Catapano, G.; et al. Surgical Management of Glioma Grade 4: Technical Update from the Neuro-Oncology Section of the Italian Society of Neurosurgery (SINch®): A Systematic Review. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 162, 267–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caras, A.; Mugge, L.; Miller, W.K.; Mansour, T.R.; Schroeder, J.; Medhkour, A. Usefulness and Impact of Intraoperative Imaging for Glioma Resection on Patient Outcome and Extent of Resection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senft, C.; Bink, A.; Franz, K.; Vatter, H.; Gasser, T.; Seifert, V. Intraoperative MRI Guidance and Extent of Resection in Glioma Surgery: A Randomised, Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Farrukh Hameed, N.U.; Yuan, S.; Wu, S.; Gong, X.; Zhuang, D.; Lu, J.; Zhu, F.; Qiu, T.; et al. Effect of High-Field IMRI Guided Resection in Cerebral Glioma Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 199, 113528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-S.; Gong, X.; Song, Y.-Y.; Zhuang, D.-X.; Yao, C.-J.; Qiu, T.-M.; Lu, J.-F.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Mao, Y.; et al. 3.0-T Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Resection in Cerebral Glioma Surgery. Neurosurgery 2014, 61, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joerger, A.K.; Laho, X.; Kehl, V.; Meyer, B.; Krieg, S.M.; Ille, S. The impact of intraoperative MRI on cranial surgical site infections-a single-center analysis. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aibar-Duran, J.A.; Salgado-López, L.; Anka-Tugbiyele, M.O.; Mirapeix, R.M.; Gallardo Alcañiz, A.; Patino Alvarado, J.D.; Rico Pereira, M.; Rodríguez Rodríguez, R.; Munoz-Hernandez, F.; de Quintana-Schmidt, C. Navigated Intraoperative Ultrasound in Neuro-Oncology: Volumetric Accuracy and Correlation with High-Field MRI. J. Neurosurg. 2024, 141, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.; Sylvester, P.T.; Yahanda, A.T.; Vellimana, A.K.; Dunn, G.P.; Evans, J.; Rich, K.M.; Dowling, J.L.; Leuthardt, E.C.; Dacey, R.G.; et al. Intraoperative MRI for newly diagnosed supratentorial glioblastoma: A multicenter-registry comparative study to conventional surgery. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 135, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Age at Operation | Sex | Duration of Operation (min) | Duration of iMRI (min) | Indication of iMRI * | Histology | Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 37 | Male | 450 | 60 | 2 | Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) | Sellar |
| 2 | 65 | Male | 170 | 40 | 1 | Urothelial carcinoma | Temporal |
| 3 | 58 | Female | 320 | 40 | 2 | Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Occipital |
| 4 | 65 | Male | 290 | 60 | 1 + 3 | Cancer of unknown primary (CUP) | Frontal |
| 5 | 73 | Male | 180 | 80 | 2 | Ovarian cancer | Parietal |
| 6 | 47 | Male | 136 | 40 | 2 | Seminoma | Precentral |
| 7 | 63 | Male | 280 | 45 | 1 | Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Central |
| 8 | 69 | Male | 116 | 70 | 2 | Colorectal cancer (CRC) | Parietal |
| 9 | 67 | Female | 220 | 75 | 3 | Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Parietal |
| 10 | 55 | Female | 110 | 40 | 1 | Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Parietal |
| 11 | 79 | Male | 180 | 80 | 1 | Melanoma | Parietal |
| 12 | 52 | Female | 240 | 65 | 2 | Breast cancer | Thalamic |
| 13 | 67 | Female | 180 | 60 | 2 | Colorectal cancer (CRC) | Postcentral |
| 14 | 55 | Male | 300 | 75 | 1 | Urothelial carcinoma | Frontal |
| 15 | 80 | Male | 210 | 60 | 3 | Melanoma | Frontal |
| 16 | 66 | Female | 180 | 80 | 1 | Esophageal cancer | Postcentral |
| 17 | 42 | Female | 240 | 40 | 1 | Breast cancer | Temporal |
| 18 | 73 | Female | 290 | 60 | 1 | Breast cancer | Occipital |
| 19 | 47 | Female | 230 | 105 | 2 | Cervical cancer | Postcentral |
| 20 | 60 | Female | 210 | 70 | 3 | Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) | Temporal |
| 21 | 71 | Female | 180 | 60 | 2 | Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Postcentral |
| 22 | 76 | Male | 260 | 90 | 1 | Prostate cancer | Temporal |
| 23 | 70 | Female | 190 | 40 | 1 | Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Occipital |
| 24 | 80 | Female | 147 | 40 | 1 | Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Frontal |
| 25 | 74 | Male | 188 | 67 | 3 | Renal-cell cancer (RCC) | Frontal |
| No. | Preoperative Tumor Volume (cm3) | Intraoperative Residual Volume (cm3) | Postoperative Residual Volume (cm3) | Further Resection after iMRI | EOR without iMRI (%) | EOR with iMRI (%) | KPS at Admission | KPS at Discharge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.5 | 8 | 8 | No | 23.81 | 23.81 | 70 | 90 |
| 2 | 7.66 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 90 | 90 |
| 3 | 22.4 | 2.6 | 0 | Yes | 88.39 | 100 | 60 | 60 |
| 4 | 62.8 | 1.59 | 0 | Yes | 97.47 | 100 | 90 | 90 |
| 5 | 5.66 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 90 | 90 |
| 6 | 5.44 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 90 | 80 |
| 7 | 28.6 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 40 | 0 |
| 8 | 6.01 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 9 | 28 | 1.4 | 0 | Yes | 95 | 100 | 90 | 90 |
| 10 | 5.15 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 11 | 20.5 | 0.35 | 0.35 | No | 98.29 | 98.29 | 90 | 90 |
| 12 | 5.43 | 4.08 | 0.13 | Yes | 24.86 | 97.61 | 70 | 50 |
| 13 | 3.13 | 0.57 | 0.57 | No | 81.79 | 81.79 | 80 | 90 |
| 14 | 9.1 | 1.1 | 0 | Yes | 87.91 | 100 | 90 | 90 |
| 15 | 35.2 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 70 | 80 |
| 16 | 4.23 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 90 | 50 |
| 17 | 4.9 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 90 | 90 |
| 18 | 37.4 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 80 | 80 |
| 19 | 23.7 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 70 | 80 |
| 20 | 44.2 | 8 | 8 | No | 81.9 | 81.9 | 90 | 90 |
| 21 | 5.82 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 90 | 90 |
| 22 | 33 | 1 | 0 | Yes | 96.97 | 100 | 80 | 80 |
| 23 | 17.3 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 90 | 90 |
| 24 | 2.7 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 90 | 60 |
| 25 | 31.3 | 0 | 0 | No | 100 | 100 | 60 | 80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altawalbeh, G.; Goldberg, M.; Mondragón-Soto, M.G.; Negwer, C.; Wagner, A.; Gempt, J.; Meyer, B.; Aftahy, A.K. Navigating Brain Metastases: Unveiling the Potential of 3-Tesla Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cancers 2024, 16, 2774. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162774
Altawalbeh G, Goldberg M, Mondragón-Soto MG, Negwer C, Wagner A, Gempt J, Meyer B, Aftahy AK. Navigating Brain Metastases: Unveiling the Potential of 3-Tesla Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2774. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162774
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltawalbeh, Ghaith, Maria Goldberg, Michel Gustavo Mondragón-Soto, Chiara Negwer, Arthur Wagner, Jens Gempt, Bernhard Meyer, and Amir Kaywan Aftahy. 2024. "Navigating Brain Metastases: Unveiling the Potential of 3-Tesla Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2774. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162774
APA StyleAltawalbeh, G., Goldberg, M., Mondragón-Soto, M. G., Negwer, C., Wagner, A., Gempt, J., Meyer, B., & Aftahy, A. K. (2024). Navigating Brain Metastases: Unveiling the Potential of 3-Tesla Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cancers, 16(16), 2774. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162774








