The Health Impacts of Better Access to Axicabtagene Ciloleucel: The Case of Spain
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
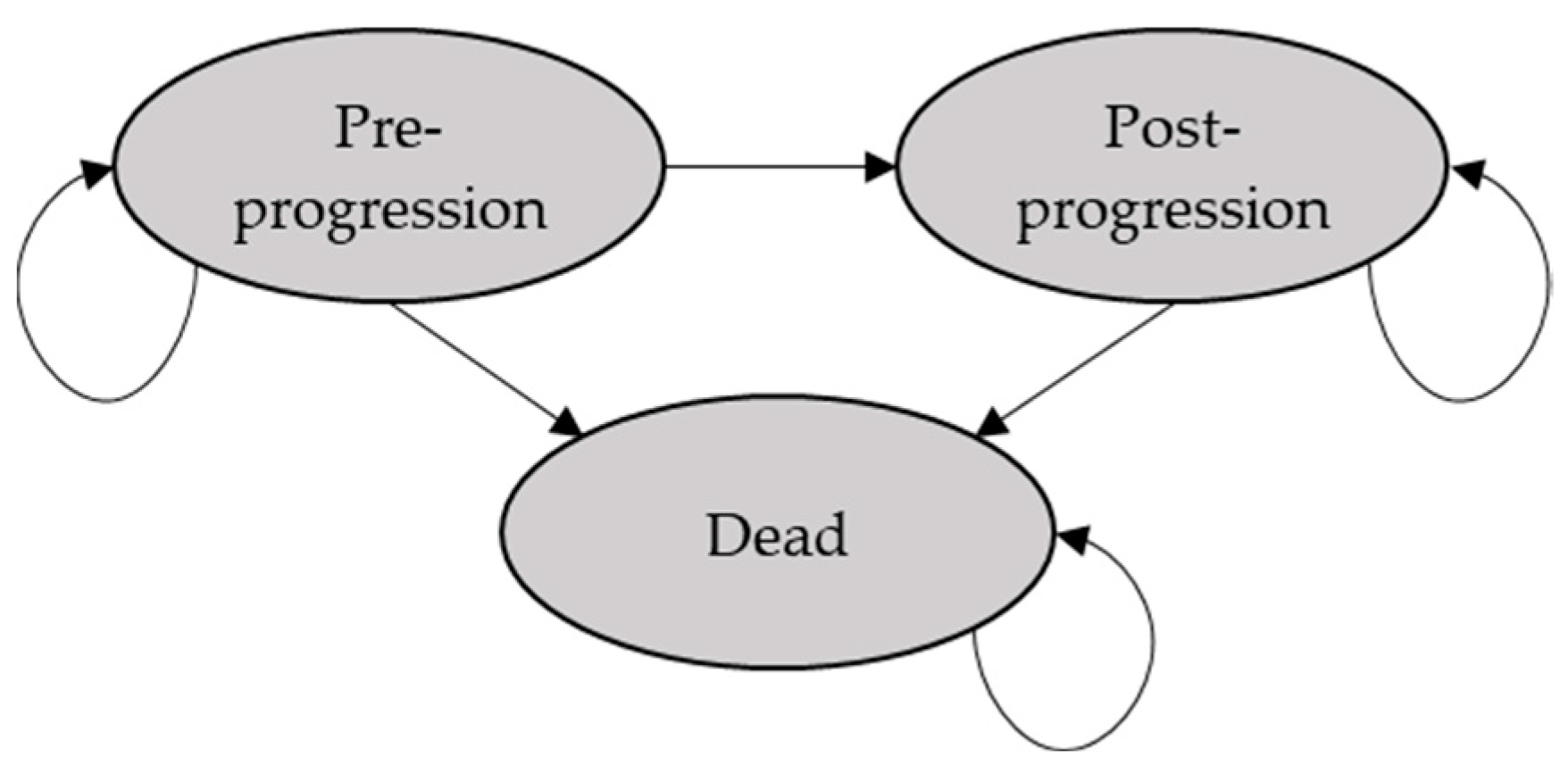
2.1. Modelling Approach
2.2. Population
2.3. Comparator
2.4. Clinical Data
2.5. Utilities
3. Results
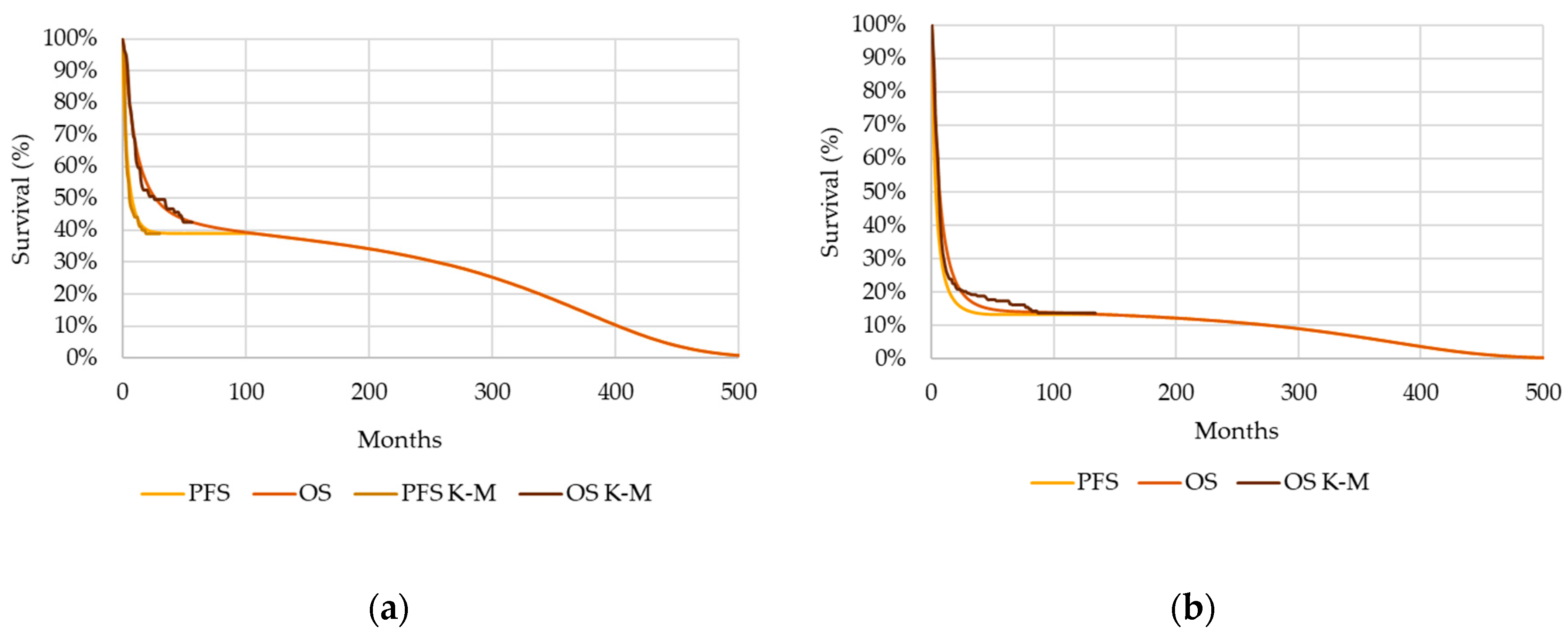
3.1. Base Case
3.2. Alternative Scenario
3.3. Comparison between the Base Case and Alternative Scenario
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morton, L.M.; Slager, S.L.; Cerhan, J.R.; Wang, S.S.; Vajdic, C.M.; Skibola, C.F.; Bracci, P.M.; de Sanjosé, S.; Smedby, K.E.; Chiu, B.C.; et al. Etiologic heterogeneity among non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes: The InterLymph Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Subtypes Project. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2014, 2014, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Cancer Observatory. Cancer Today. Estimated Number of New Cases in 2020. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/ (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Tilly, H.; da Silva, M.G.; Vitolo, U.; Jack, A.; Meignan, M.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Walewski, J.; André, M.; Johnson, P.W.; Pfreundschuh, M.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, v116-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, M.; Oeser, A.; Besiroglu, B.; Caro-Valenzuela, J.; El Aziz, M.A.; Monsef, I.; Borchmann, P.; Estcourt, L.J.; Skoetz, N.; Goldkuhle, M. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for people with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 9, CD013365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bastos-Oreiro, M.; Muntanola, A.; Panizo, C.; Gonzalez-Barca, E.; de Villambrosia, S.G.; Cordoba, R.; López, J.L.B.; Gonzalez-Sierra, P.; Terol, M.J.; Gutierrez, A.; et al. RELINF: Prospective epidemiological registry of lymphoid neoplasms in Spain. A project from the GELTAMO group. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedberg, J.W. Relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2011, 2011, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, M.; Neelapu, S.S.; Farooq, U.; Van Den Neste, E.; Kuruvilla, J.; Westin, J.; Link, B.K.; Hay, A.; Cerhan, J.R.; Zhu, L.; et al. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood 2017, 130, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounier, N.; El Gnaoui, T.; Tilly, H.; Canioni, D.; Sebban, C.; Casasnovas, R.O.; Delarue, R.; Sonet, A.; Beaussart, P.; Petrella, T.; et al. Rituximab plus gemcitabine and oxaliplatin in patients with refractory/relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who are not candidates for high-dose therapy. A phase II Lymphoma Study Association trial. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1726–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmachi, K.; Niitsu, N.; Uchida, T.; Kim, S.J.; Ando, K.; Takahashi, N.; Takahashi, N.; Uike, N.; Eom, H.S.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Multicenter phase II study of bendamustine plus rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2103–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czuczman, M.S.; Trněný, M.; Davies, A.; Rule, S.; Linton, K.M.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Slack, G.W.; Brousset, P.; Eberhard, D.A.; et al. A Phase 2/3 Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Efficacy and Safety of Lenalidomide Versus Investigator’s Choice in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4127–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, E.C.; Margolis, D.; Landsburg, D.J. Real World Outcomes in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Receiving Palliative Intent Therapies. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. JULIET Investigators. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Product Information: Yescarta®. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/yescarta (accessed on 9 May 2022).
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Reagan, P.M.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; et al. Comparison of 2-year outcomes with CAR T cells (ZUMA-1) vs salvage chemotherapy in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4149–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Jacobson, C.A.; Ghobadi, A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Five-year follow-up of ZUMA-1 supports the curative potential of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2023, 141, 2307–2315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sierra, J.; Briones, J.; Calleja, M.A.; Camacho, C.; Casado, M.A.; Presa, M.; Díez, J.L.; Solano, C.; Moraleda, J.M.; Caballero, D. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for the Management of Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Primary Mediastinal Large B-cell Lymphoma: An Economic Evaluation for Spain. Abstract Book: 25th Congress of the European Hematology Association Virtual Edition. HemaSphere 2020, 4, 1–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos-Oreiro, M.; de Las Heras, A.; Presa, M.; Casado, M.A.; Pardo, C.; Martín-Escudero, V.; Sureda, A. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel vs. Tisagenlecleucel for the Management of Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in Spain. Cancers 2022, 14, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo-Torres, L.; García-Lorenzo, B.; Serrano-Aguilar, P. Estimating a cost-effectiveness threshold for the Spanish NHS. Health Econ. 2018, 27, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacristán, J.A.; Oliva, J.; Campillo-Artero, C.; Puig-Junoy, J.; Pinto-Prades, J.L.; Dilla, T.; Rubio-Terrés, C.; Ortún, V. ¿Qué es una intervención sanitaria eficiente en España en 2020? [What is an efficient health intervention in Spain in 2020?]. Gac Sanit 2020, 34, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Sanidad, Consumo y Bienestar Social [Ministry of Health]. Plan to Tackle Advanced Therapies in the National Health System: CAR (Chimeric Antigen Receptor) Medicines. Available online: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/profesionales/farmacia/Terapias_Avanzadas.htm (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Lin, J.K.; Muffly, L.S.; Spinner, M.A.; Barnes, J.I.; Owens, D.K.; Goldhaber-Fiebert, J.D. Cost effectiveness of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in multiply relapsed or refractory adult large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2105–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.A.; Sullivan, S.D.; Lin, V.W.; Bansal, A.; Purdum, A.G.; Navale, L.; Cheng, P.; Ramsey, S.D. Cost-effectiveness of axicabtagene ciloleucel for adult patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma in the United States. J. Med. Econ. 2018, 21, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittington, M.D.; McQueen, R.B.; Ollendorf, D.A.; Kumar, V.M.; Chapman, R.H.; Tice, J.A.; Pearson, S.D.; Campbell, J.D. Long-term survival and cost-effectiveness associated with axicabtagene ciloleucel vs chemotherapy for treatment of B-Cell lymphoma. JAMA Netw. Open. 2019, 2, e190035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for Treating Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma after 2 or More Systemic Therapies. Technology Appraisal Guidance [TA559]. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta559 (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- INE. Tablas de Mortalidad por año, Sexo, edad y Funciones. Available online: https://www.ine.es/jaxiT3/Tabla.htm?t=27153 (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Sonnenberg, F.A.; Beck, J.R. Markov models in medical decision making: A practical guide. Med. Decis. Mak. 1993, 13, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group for Innovation, Assessment, Standardization and Research in the Selection of Drugs of the Spanish Society of Hospital Pharmacy (SEFH). Informe GENESIS-SEFH: Axicabtagén Ciloleucel en Linfoma Difuso de Células B Grandes Refractario o en Recaída. Available online: https://gruposdetrabajo.sefh.es/genesis/genesis/Enlaces/InformesHosp_abc.htm?ml=1#A (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Jacobson, C.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; Deol, A.; et al. Long-Term (≥4 Year and ≥5 Year) Overall Survival (OS) By 12- and 24-Month Event-Free Survival (EFS): An Updated Analysis of ZUMA-1, the Pivotal Study of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) in Patients (Pts) with Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma (LBCL). Blood 2021, 138, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Assessment Report of Yescarta®. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/assessment-report/yescarta-epar-public-assessment-report_en.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2024).
- Food & Drug Administration. Cellular & Gene Therapy Products: Yescarta®. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/cellular-gene-therapy-products/yescarta (accessed on 8 March 2024).
- Faria, R.; Alava, M.H.; Manca, A.; Wailoo, A.J. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 17: The Use of Observational Data to Inform Estimates of Treatment Effectiveness in Technology Appraisal: Methods for Comparative Individual Patient Data. Available online: http://www.nicedsu.org.uk/TSD17%20-%20DSU%20Observational%20data%20FINAL.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Lin, V.; Jiang, Y.; Chuang, L. Health utilities for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma: Ad hoc analysis from an axicabtagene ciloleucel safety management study. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, Lisbon, Portugal, 20 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Staton, A.D.; Ayer, T.; Goldstein, D.A.; Koff, J.L.; Flowers, C.R. Exploring the potential cost-effectiveness of precision medicine treatment strategies for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, V.W.; Blaylock, B.; Epstein, J.; Purdum, A. Systematic literature review of health-related quality of life among aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma survivors. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2018, 34, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Social Services and Equality. Annual Report of the National Health System of Spain, 2011/2012. Available online: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/estadEstudios/estadisticas/encuestaNacional/encuesta2011.htm (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Canales Albendea, M.Á.; Canonico, P.L.; Cartron, G.; Deiters, B.; Jommi, C.; Marks, R.; Rioufol, C.; Sancho Cia, J.M.; Santoro, A.; Wagner-Drouet, E.M. Comparative analysis of CAR T-cell therapy access for DLBCL patients: Associated challenges and solutions in the four largest EU countries. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1128295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, M.; Duarte, A.; Melton, H.; Walker, S.; Wright, K.; Eastwood, A.; Palmer, S. Axicabtagene ciloleucel for Treating Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma, Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma and Follicular Lymphoma: A Single Technology Appraisal; CRD and CHE, University of York, Technology Assessment Group: York, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
| Health Outcomes | Axi-Cel | Chemotherapy | Incremental |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total LYG per patient | 2168 | 827 | 1341 |
| LYGs in preprogression | 2052 | 768 | 1284 |
| LYGs in postprogression | 116 | 59 | 58 |
| Total QALYs per patient | 1690 | 638 | 1053 |
| QALYs in preprogression | 1645 * | 615 | 1030 |
| QALYs in postprogression | 45 | 23 | 22 |
| Patients in preprogression state, n (%) | |||
| Patients in preprogression at 6 months | 102 (55%) | 65 (35%) | 37 (56%) ** |
| Patients in preprogression at 1 year | 82 (44%) | 42 (22%) | 41 (98%) ** |
| Patients in preprogression at 2 years | 74 (40%) | 29 (15%) | 45 (157%) ** |
| Patients in preprogression at 5 years | 73 (39%) | 25 (13%) | 48 (195%) ** |
| Patients in preprogression at 10 years | 72 (38%) | 25 (13%) | 47 (190%) ** |
| Patients alive, n (%) | |||
| Patients alive at 6 months | 149 (80%) | 95 (51%) | 53 (56%) ** |
| Patients alive at 1 year | 121 (65%) | 61 (33%) | 60 (98%) ** |
| Patients alive at 2 years | 97 (52%) | 38 (20%) | 59 (157%) ** |
| Patients alive at 5 years | 79 (42%) | 27 (14%) | 52 (194%) ** |
| Patients alive at 10 years | 72 (38%) | 25 (14%) | 46 (184%) ** |
| Health Outcomes | Axi-Cel | Chemotherapy | Incremental |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total LYG per patient | 5681 | 2166 | 3515 |
| LYGs in preprogression | 5377 | 2013 | 3363 |
| LYGs in postprogression | 304 | 153 | 151 |
| Total QALYs per patient | 4430 | 1671 | 2759 |
| QALYs in preprogression | 4311 * | 1611 | 2700 |
| QALYs in postprogression | 119 | 60 | 59 |
| Patients in preprogression state, n (%) | |||
| Patients in preprogression at 6 months | 268 (55%) | 172 (35%) | 96 (56%) ** |
| Patients in preprogression at 1 year | 216 (44%) | 109 (22%) | 107 (98%) ** |
| Patients in preprogression at 2 years | 194 (40%) | 76 (15%) | 118 (157%) ** |
| Patients in preprogression at 5 years | 191 (39%) | 65 (13%) | 126 (195%) ** |
| Patients in preprogression at 10 years | 188 (38%) | 65 (13%) | 123 (190%) ** |
| Patients alive, n (%) | |||
| Patients alive at 6 months | 390 (80%) | 250 (51%) | 140 (56%) ** |
| Patients alive at 1 year | 317 (65%) | 160 (33%) | 157 (98%) ** |
| Patients alive at 2 years | 253 (52%) | 99 (20%) | 155 (157%) ** |
| Patients alive at 5 years | 207 (42%) | 70 (14%) | 137 (194%) ** |
| Patients alive at 10 years | 188 (38%) | 66 (14%) | 122 (184%) ** |
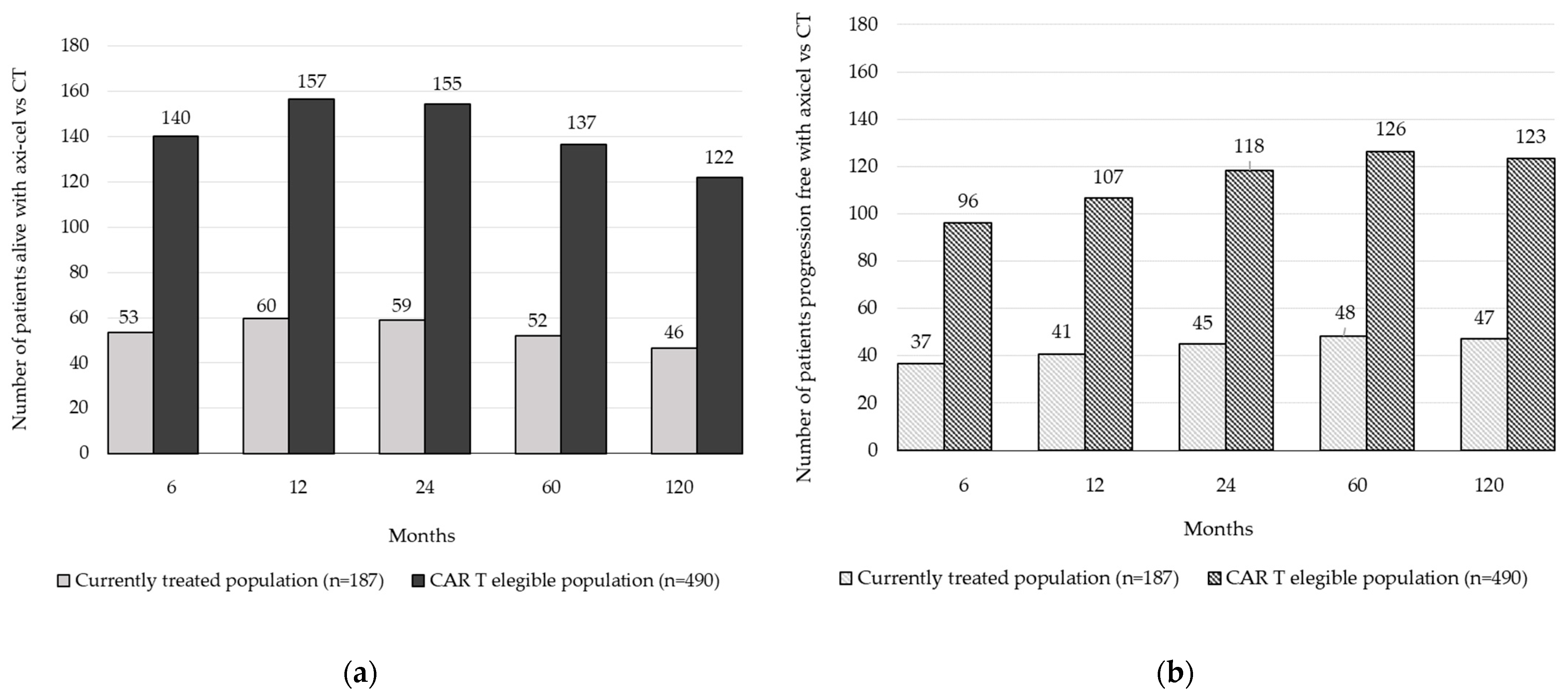
| Health Outcomes | CAR T-Eligible Population * (n = 490) | Currently Treated Population * (n = 187) | Incremental (CAR T-Eligible Population vs. Currently Treated Population, n = 303) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total LYG per patient | 3515 | 1341 | 2173 |
| LYGs in preprogression | 3363 | 1284 | 2080 |
| LYGs in postprogression | 151 | 58 | 93 |
| Total QALYs per patient | 2759 | 1053 | 1706 |
| QALYs in preprogression | 2700 | 1030 | 1669 |
| QALYs in postprogression | 59 | 22 | 36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Córdoba, R.; López-Corral, L.; Presa, M.; Martín-Escudero, V.; Vadgama, S.; Casado, M.Á.; Pardo, C. The Health Impacts of Better Access to Axicabtagene Ciloleucel: The Case of Spain. Cancers 2024, 16, 2712. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152712
Córdoba R, López-Corral L, Presa M, Martín-Escudero V, Vadgama S, Casado MÁ, Pardo C. The Health Impacts of Better Access to Axicabtagene Ciloleucel: The Case of Spain. Cancers. 2024; 16(15):2712. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152712
Chicago/Turabian StyleCórdoba, Raúl, Lucía López-Corral, María Presa, Victoria Martín-Escudero, Sachin Vadgama, Miguel Ángel Casado, and Carlos Pardo. 2024. "The Health Impacts of Better Access to Axicabtagene Ciloleucel: The Case of Spain" Cancers 16, no. 15: 2712. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152712
APA StyleCórdoba, R., López-Corral, L., Presa, M., Martín-Escudero, V., Vadgama, S., Casado, M. Á., & Pardo, C. (2024). The Health Impacts of Better Access to Axicabtagene Ciloleucel: The Case of Spain. Cancers, 16(15), 2712. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152712







