Harnessing the Power of Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of the Evolving Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guidance
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
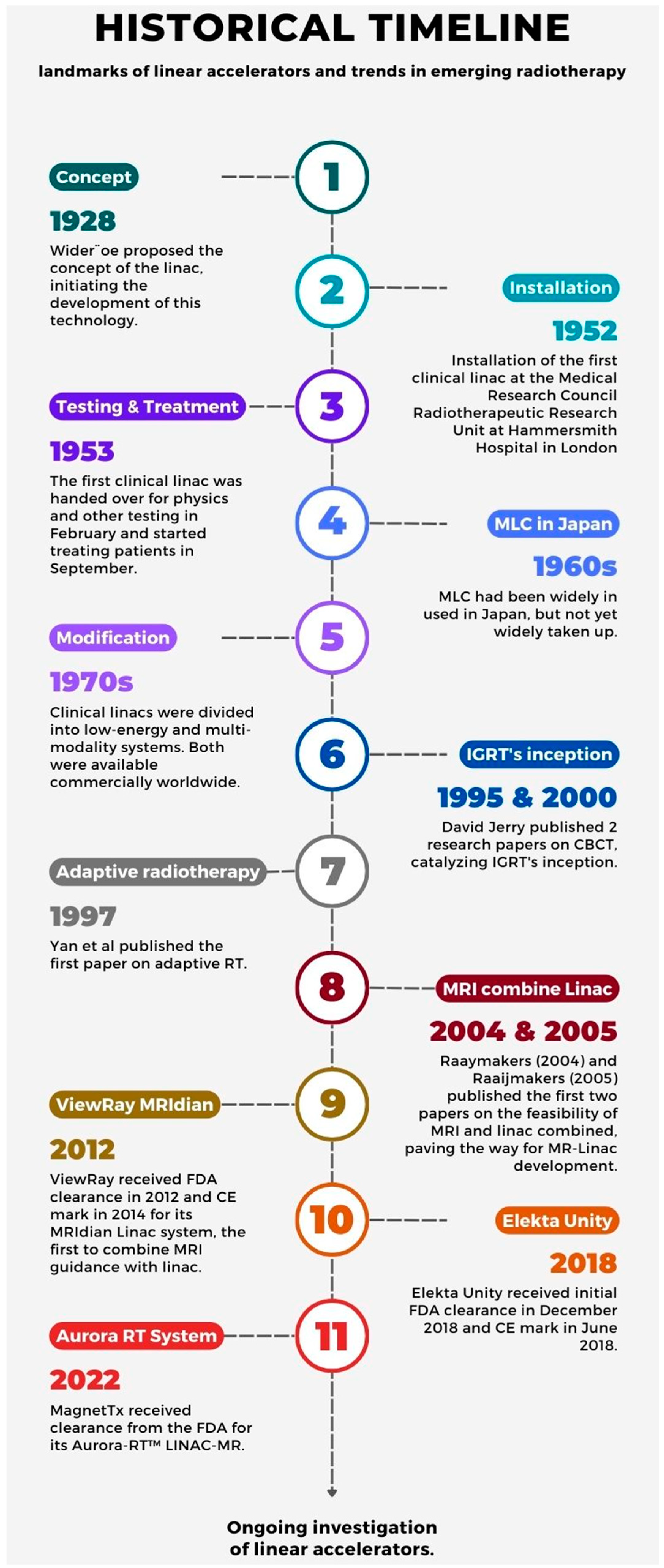
2. A Brief Overview of the Linear Accelerator’s Development
3. Advantages of MRgRT in Lung Cancer Treatment
3.1. Superior Soft Tissue Visualization
3.2. Daily Adaptive Capability
3.3. Real-Time Target Tracking
3.4. Early Assessment of Treatment Response
3.5. Combining Biological Targeting with Conventional ART
3.6. AI and Machine Learning
4. MRgRT Clinical Application
4.1. Central and Ultracentral Lung Tumor
4.2. Early-Stage Lung Cancer
4.3. Locally Advanced (LA)/Oligo-Progressive Lung Cancer
5. Challenges for MRgRT in Lung Cancer Treatment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.C.; Smith, L.M.; Woolf, D.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Lee, P. Exploring the Advantages and Challenges of MR-Guided Radiotherapy in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Who are the Optimal Candidates? Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 34, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammohan, N.; Randall, J.W.; Yadav, P. History of Technological Advancements towards MR-Linac: The Future of Image-Guided Radiotherapy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuong, M.D.; Clark, M.A.; Henke, L.E.; Kishan, A.U.; Portelance, L.; Parikh, P.J.; Bassetti, M.F.; Nagar, H.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Mehta, M.P.; et al. Patterns of utilization and clinical adoption of 0.35 Tesla MR-guided radiation therapy in the United States—Understanding the transition to adaptive, ultra-hypofractionated treatments. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 38, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotman, B.J.; Clark, M.A.; Özyar, E.; Kim, M.; Itami, J.; Tallet, A.; Debus, J.; Pfeffer, R.; Gentile, P.; Hama, Y.; et al. Clinical adoption patterns of 0.35 Tesla MR-guided radiation therapy in Europe and Asia. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaskou Badra, E.; Baumgartl, M.; Fabiano, S.; Jongen, A.; Guckenberger, M. Stereotactic radiotherapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: Current standards and ongoing research. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1930–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwaites, D.I.; Tuohy, J.B. Back to the future: The history and development of the clinical linear accelerator. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, R343–R362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffray, D.A.; Siewerdsen, J.H. Cone-beam computed tomography with a flat-panel imager: Initial performance characterization. Med. Phys. 2000, 27, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhao, D.; Beeraka, N.M.; Wang, X.; Lu, P.; Song, R.; Chen, K.; Liu, J. Novel Implications of Nanoparticle-Enhanced Radiotherapy and Brachytherapy: Z-Effect and Tumor Hypoxia. Metabolites 2022, 12, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaymakers, B.W.; Raaijmakers, A.J.; Kotte, A.N.; Jette, D.; Lagendijk, J.J. Integrating a MRI scanner with a 6 MV radiotherapy accelerator: Dose deposition in a transverse magnetic field. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, 4109–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaijmakers, A.J.; Raaymakers, B.W.; Lagendijk, J.J. Integrating a MRI scanner with a 6 MV radiotherapy accelerator: Dose increase at tissue-air interfaces in a lateral magnetic field due to returning electrons. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 1363–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladbury, C.; Amini, A.; Schwer, A.; Liu, A.; Williams, T.; Lee, P. Clinical Applications of Magnetic Resonance-Guided Radiotherapy: A Narrative Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keall, P.J.; Barton, M.; Crozier, S. The Australian magnetic resonance imaging-linac program. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 24, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bainbridge, H.; Salem, A.; Tijssen, R.H.N.; Dubec, M.; Wetscherek, A.; Van Es, C.; Belderbos, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; McDonald, F. Magnetic resonance imaging in precision radiation therapy for lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 689–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaj-Levra, N.; Borghetti, P.; Bruni, A.; Ciammella, P.; Cuccia, F.; Fozza, A.; Franceschini, D.; Scotti, V.; Vagge, S.; Alongi, F. Current radiotherapy techniques in NSCLC: Challenges and potential solutions. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2020, 20, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (Version 2. 2024). Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2024).
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Lung Cancer: Diagnosis and Management. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng122 (accessed on 17 February 2024).
- Kozower, B.D.; Larner, J.M.; Detterbeck, F.C.; Jones, D.R. Special treatment issues in non-small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. CHEST 2013, 143, e369S–e399S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.M.; Ritter, T.; Quint, D.J.; Senan, S.; Gaspar, L.E.; Komaki, R.U.; Hurkmans, C.W.; Timmerman, R.; Bezjak, A.; Bradley, J.D.; et al. Consideration of dose limits for organs at risk of thoracic radiotherapy: Atlas for lung, proximal bronchial tree, esophagus, spinal cord, ribs, and brachial plexus. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 1442–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, J.D.; Paulus, R.; Komaki, R.; Masters, G.; Blumenschein, G.; Schild, S.; Bogart, J.; Hu, C.; Forster, K.; Magliocco, A.; et al. Standard-dose versus high-dose conformal radiotherapy with concurrent and consolidation carboplatin plus paclitaxel with or without cetuximab for patients with stage IIIA or IIIB non-small-cell lung cancer (RTOG 0617): A randomised, two-by-two factorial phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Pol, L.H.G.; Hackett, S.L.; Hoesein, F.; Snoeren, L.M.W.; Pomp, J.; Raaymakers, B.W.; Verhoeff, J.J.C.; Fast, M.F. On the feasibility of cardiac substructure sparing in magnetic resonance imaging guided stereotactic lung radiotherapy. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuter, R.; Prestwich, R.; Bird, D.; Scarsbrook, A.; Sykes, J.; Wilson, D.; Speight, R. The use of deformable image registration to integrate diagnostic MRI into the radiotherapy planning pathway for head and neck cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 122, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasch, C.; Barillot, I.; Remeijer, P.; Touw, A.; van Herk, M.; Lebesque, J.V. Definition of the prostate in CT and MRI: A multi-observer study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 43, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, H.; Shirato, H.; Nishioka, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kagei, K.; Onimaru, R.; Watanabe, Y.; Miyasaka, K. Magnetic resonance imaging system for three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and its impact on gross tumor volume delineation of central nervous system tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 50, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, L.; McDaid, L.; Hales, R.B.; Rodgers, J.; Dubec, M.; Huddart, R.A.; Choudhury, A.; Eccles, C.L. To see or not to see: Evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging sequences for use in MR Linac-based radiotherapy treatment. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2022, 53, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, K.; Saraiya, S.; Hugo, G.D.; Mukhopadhyay, N.; Jan, N.; Schuster, J.; Schutzer, M.; Fahrner, L.; Groves, R.; Olsen, K.M.; et al. Variabilities of Magnetic Resonance Imaging-, Computed Tomography-, and Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography-Based Tumor and Lymph Node Delineations for Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy Planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, A.; Budgell, G.; MacKay, R.; Falk, S.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Dubec, M.; van Herk, M.; McWilliam, A. The Future of Image-guided Radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. (R Coll. Radiol.) 2017, 29, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eccles, C.L.; Adair Smith, G.; Bower, L.; Hafeez, S.; Herbert, T.; Hunt, A.; McNair, H.A.; Ofuya, M.; Oelfke, U.; Nill, S.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging sequence evaluation of an MR Linac system; early clinical experience. Tech. Innov. Patient Support. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 12, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleckenstein, J.; Jelden, M.; Kremp, S.; Jagoda, P.; Stroeder, J.; Khreish, F.; Ezziddin, S.; Buecker, A.; Rübe, C.; Schneider, G.K. The Impact of Diffusion-Weighted MRI on the Definition of Gross Tumor Volume in Radiotherapy of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, C.W.; An, H.J.; Kang, H.C.; Kim, H.J.; Wu, H.G. Variability of Gross Tumor Volume Delineation for Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy of the Lung With Tri-(60)Co Magnetic Resonance Image-Guided Radiotherapy System (ViewRay): A Comparative Study With Magnetic Resonance- and Computed Tomography-Based Target Delineation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818787383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Xie, K.; Wu, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, J.; Lin, T.; Sui, J.; Ni, X. Generating synthetic CT from low-dose cone-beam CT by using generative adversarial networks for adaptive radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenkowicz, J.; Votta, C.; Nardini, M.; Quaranta, F.; Catucci, F.; Boldrini, L.; Vagni, M.; Menna, S.; Placidi, L.; Romano, A.; et al. A deep learning approach to generate synthetic CT in low field MR-guided radiotherapy for lung cases. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 176, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, J.N.; Bainbridge, H.E.; Nill, S.; Collins, D.J.; Kachelrieß, M.; Leach, M.O.; McDonald, F.; Oelfke, U.; Wetscherek, A. Synthetic 4D-CT of the thorax for treatment plan adaptation on MR-guided radiotherapy systems. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, K.K. Adaptive Radiotherapy: Moving Into the Future. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 29, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Vicini, F.; Wong, J.; Martinez, A. Adaptive radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 1997, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramella, S.; Fiore, M.; Silipigni, S.; Zappa, M.C.; Jaus, M.; Alberti, A.M.; Matteucci, P.; Molfese, E.; Cornacchione, P.; Greco, C.; et al. Local Control and Toxicity of Adaptive Radiotherapy Using Weekly CT Imaging: Results from the LARTIA Trial in Stage III NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, J.; Cao, M.; Kishan, A.; Agazaryan, N.; Thomas, D.H.; Shaverdian, N.; Yang, Y.; Ray, S.; Low, D.A.; Raldow, A.; et al. Online Adaptive Radiation Therapy: Implementation of a New Process of Care. Cureus 2017, 9, e1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Schaal, D.; Curry, H.; Clark, R.; Magliari, A.; Kupelian, P.; Khuntia, D.; Beriwal, S. Review of cone beam computed tomography based online adaptive radiotherapy: Current trend and future direction. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, P.; Tree, A.C.; Chuong, M.D.; Raldow, A.C.; Kishan, A.U.; Fuller, C.D.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Hall, W.A.; Chie, E.K.; et al. Adaptive Radiation Therapy Physician Guidelines: Recommendations From an Expert Users’ Panel. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 12, e355–e362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.J.; Kwak, Y.K.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.J. Application of real-time MRI-guided linear accelerator in stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: One step forward to precise targeting. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 3215–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.; Gregucci, F.; Pennell, R.T.; Nagar, H.; Golden, E.B.; Knisely, J.P.S.; Sanfilippo, N.J.; Formenti, S.C. MRI-LINAC: A transformative technology in radiation oncology. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1117874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.H.; Santhanam, A.; Kishan, A.U.; Cao, M.; Lamb, J.; Min, Y.; O’Connell, D.; Yang, Y.; Agazaryan, N.; Lee, P.; et al. Initial clinical observations of intra- and interfractional motion variation in MR-guided lung SBRT. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.; Banfill, K.; Aznar, M.C.; Whitehurst, P.; Faivre Finn, C. The evolving role of radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menten, M.J.; Fast, M.F.; Nill, S.; Kamerling, C.P.; McDonald, F.; Oelfke, U. Lung stereotactic body radiotherapy with an MR-linac—Quantifying the impact of the magnetic field and real-time tumor tracking. Radiother. Oncol. 2016, 119, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Glitzner, M.; Woodhead, P.L.; Borman, P.T.S.; Lagendijk, J.J.W.; Raaymakers, B.W. Technical note: MLC-tracking performance on the Elekta unity MRI-linac. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 15NT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, E.; Rabe, M.; Xiong, Y.; Nierer, L.; Cusumano, D.; Placidi, L.; Boldrini, L.; Corradini, S.; Niyazi, M.; Belka, C.; et al. Offline and online LSTM networks for respiratory motion prediction in MR-guided radiotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 095006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaza, E.; Dunlop, A.; Panek, R.; Collins, D.J.; Orton, M.; Symonds-Tayler, R.; McQuaid, D.; Scurr, E.; Hansen, V.; Leach, M.O. Lung volume reproducibility under ABC control and self-sustained breath-holding. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2017, 18, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, J.; McNair, H.A.; Panakis, N.; Symonds-Tayler, R.; Evans, P.M.; Brada, M. The use of the Active Breathing Coordinator throughout radical non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaza, E.; Symonds-Tayler, R.; Collins, D.J.; McDonald, F.; McNair, H.A.; Scurr, E.; Koh, D.-M.; Leach, M.O. First MRI application of an active breathing coordinator. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 1681–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Houdt, P.J.; Yang, Y.; van der Heide, U.A. Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Biological Image-Guided Adaptive Radiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 615643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Iizuka, Y.; Mitsuyoshi, T.; Umeoka, S.; Nakamoto, Y.; Mizowaki, T.; Togashi, K.; Hiraoka, M. Assessment of treatment response after lung stereotactic body radiotherapy using diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography: A pilot study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 92, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Wu, N.; Ouyang, H.; Huang, Y. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of lung cancer at 3.0 T: A preliminary study on monitoring diffusion changes during chemoradiation therapy. Clin. Imaging 2012, 36, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, E.; Ford, J.C.; Olsen, K.M.; Karki, K.; Saraiya, S.; Groves, R.; Hugo, G.D. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) change on repeated diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging during radiochemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: A pilot study. Lung Cancer 2016, 96, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabuuchi, H.; Hatakenaka, M.; Takayama, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Sunami, S.; Kamitani, T.; Jinnouchi, M.; Sakai, S.; Nakanishi, Y.; Honda, H. Non-small cell lung cancer: Detection of early response to chemotherapy by using contrast-enhanced dynamic and diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 2011, 261, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampath, S.; Rahmanuddin, S.; Sahoo, P.; Frankel, P.; Boswell, S.; Wong, J.; Rotter, A.; Rockne, R.; Wong, J.; Park, J.M. Change in Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Is Associated With Local Failure After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Prospective Clinical Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.S.; Cui, Y.; Tang, L.; Qi, L.P.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Cao, K.; Zhang, X.P. Early evaluation of cancer response by a new functional biomarker: Apparent diffusion coefficient. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, W23–W29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, S.; Fujisawa, Y.; Yui, M.; Kishida, Y.; Koyama, H.; Ohyu, S.; Sugihara, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ohno, Y. Dynamic Contrast-enhanced Area-detector CT vs Dynamic Contrast-enhanced Perfusion MRI vs FDG-PET/CT: Comparison of Utility for Quantitative Therapeutic Outcome Prediction for NSCLC Patients Undergoing Chemoradiotherapy. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2020, 19, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Wang, L.; Hui, Z.; Liu, L.; Ye, F.; Song, Y.; Tang, Y.; Men, Y.; Lambrou, T.; Su, Z.; et al. DCE-MRI Perfusion and Permeability Parameters as predictors of tumor response to CCRT in Patients with locally advanced NSCLC. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabian, H.; Desmond, K.L.; Chavez, S.; Bailey, C.; Rola, R.; Sahgal, A.; Czarnota, G.J.; Soliman, H.; Martel, A.L.; Stanisz, G.J. Water Exchange Rate Constant as a Biomarker of Treatment Efficacy in Patients With Brain Metastases Undergoing Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmond, K.L.; Mehrabian, H.; Chavez, S.; Sahgal, A.; Soliman, H.; Rola, R.; Stanisz, G.J. Chemical exchange saturation transfer for predicting response to stereotactic radiosurgery in human brain metastasis. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutsche, R.; Lohmann, P.; Hoevels, M.; Ruess, D.; Galldiks, N.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Treuer, H.; Ruge, M.; Kocher, M. Radiomics outperforms semantic features for prediction of response to stereotactic radiosurgery in brain metastases. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 166, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, A.; Little, R.A.; Latif, A.; Featherstone, A.K.; Babur, M.; Peset, I.; Cheung, S.; Watson, Y.; Tessyman, V.; Mistry, H.; et al. Oxygen-Enhanced MRI Is Feasible, Repeatable, and Detects Radiotherapy-induced Change in Hypoxia in Xenograft Models and in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3818–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.W.; Yang, E.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, O.J.; Park, M.A.-O.; Yi, C.A. Predicting Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Survival after Curative Surgery via Deep Learning of Diffusion MRI. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, N.A.; Yuh, W.T.; Magnotta, V.A.; Ehrhardt, J.C.; Wheeler, J.A.; Sorosky, J.I.; Davis, C.S.; Wen, B.-C.; Martin, D.D.; Pelsang, R.E.; et al. Tumor perfusion studies using fast magnetic resonance imaging technique in advanced cervical cancer: A new noninvasive predictive assay. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1996, 36, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, A.H.; Hoff, B.A.; Srinivasan, A.; Galbán, C.J.; Mukherji, S.K. Feasibility analysis of the parametric response map as an early predictor of treatment efficacy in head and neck cancer. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Ye, Z.; Pang, P.; Shao, G. Quantitative Multiparametric MRI May Augment the Response to Radiotherapy in Mid-Treatment Assessment of Patients with Esophageal Carcinoma. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2019, 42, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaar, R.; Rabe, M.; Gaass, T.; Schneider, M.J.; Benlala, I.; Eze, C.; Corradini, S.; Belka, C.; Landry, G.; Kurz, C.; et al. Ventilation and perfusion MRI at a 0.35 T MR-Linac: Feasibility and reproducibility study. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, A.; Mehrabian, H.; Conklin, J.; Symons, S.P.; Maralani, P.J.; Stanisz, G.J.; Sahgal, A.; Soliman, H.; Heyn, C.C. Temporal evolution of perfusion parameters in brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery: Comparison of intravoxel incoherent motion and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 135, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siva, S.; Thomas, R.; Callahan, J.; Hardcastle, N.; Pham, D.; Kron, T.; Hicks, R.J.; MacManus, M.P.; Ball, D.L.; Hofman, M.S. High-resolution pulmonary ventilation and perfusion PET/CT allows for functionally adapted intensity modulated radiotherapy in lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 115, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahasittiwat, P.; Yuan, S.; Xie, C.; Ritter, T.; Cao, Y.; Haken, R.K.T.; Kong, F.-M.S. Metabolic Tumor Volume on PET Reduced More than Gross Tumor Volume on CT during Radiotherapy in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with 3DCRT or SBRT. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 2, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, C.; Humm, J.; Larson, S.; Amols, H.; Fuks, Z.; Leibel, S.; Koutcher, J.A. Towards multidimensional radiotherapy (MD-CRT): Biological imaging and biological conformality. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 47, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, C.T.; Langton, D.; Thompson, B.R.; Thien, F. Functional lung imaging using novel and emerging MRI techniques. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1060940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, R.H.; Tahir, B.A.; Wild, J.M.; Lee, C.E.; Hatton, M.Q. Functional Image-guided Radiotherapy Planning for Normal Lung Avoidance. Clin. Oncol. (R Coll. Radiol.) 2016, 28, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Kabus, S.; Bal, M.; Keall, P.J.; Moran, A.; Wright, C.; Benedict, S.H.; Holland, D.; Mahaffey, N.; Qi, L.; et al. Four-Dimensional Computed Tomography Ventilation Image-Guided Lung Functional Avoidance Radiation Therapy: A Single-Arm Prospective Pilot Clinical Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 115, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, E.A.-O.; Myziuk, N.A.-O.; Quinn, T.J.; Lozano, D.; Peterson, A.B.; Quach, D.A.-O.; Siddiqui, Z.A.-O.; Guerrero, T.A.-O. Synthetic pulmonary perfusion images from 4DCT for functional avoidance using deep learning. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 175005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, R. Redefining Radiology: A Review of Artificial Intelligence Integration in Medical Imaging. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.-M.; Papanikolaou, N.; Bick, U.; Illing, R.; Kahn, C.E.; Kalpathi-Cramer, J.; Matos, C.; Martí-Bonmatí, L.; Miles, A.; Mun, S.K.; et al. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in cancer imaging. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikici, E.; Bigelow, M.; Prevedello, L.M.; White, R.D.; Erdal, B.S. Integrating AI into radiology workflow: Levels of research, production, and feedback maturity. J. Med. Imaging 2020, 7, 016502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, B.; Agarwal, S.; Coombs, L.; Wald, C.; Dreyer, K. 2020 ACR Data Science Institute Artificial Intelligence Survey. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2021, 18, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaton, L.; Bandula, S.; Gaze, M.N.; Sharma, R.A. How rapid advances in imaging are defining the future of precision radiation oncology. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.F.; Marschner, S.; Kawula, M.; Rabe, M.; Corradini, S.; Belka, C.; Riboldi, M.; Landry, G.; Kurz, C. Deep learning based automatic segmentation of organs-at-risk for 0.35 T MRgRT of lung tumors. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, K.; Grozman, V.; Karlsson, K.; Lindberg, S.; Lax, I.; Wersäll, P.; Persson, G.F.; Josipovic, M.; Khalil, A.A.; Moeller, D.S.; et al. The HILUS-Trial-a Prospective Nordic Multicenter Phase 2 Study of Ultracentral Lung Tumors Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, C.B., 2nd; Bogart, J.A.; Cabrera, A.R.; Daly, M.E.; DeNunzio, N.J.; Detterbeck, F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Gatschet, N.; Gore, E.; Jabbour, S.K.; et al. Radiation Therapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer: An ASTRO Clinical Practice Guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 10, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligtenberg, H.; Hackett, S.L.; Merckel, L.G.; Snoeren, L.; Kontaxis, C.; Zachiu, C.; Bol, G.H.; Verhoeff, J.J.C.; Fast, M.F. Towards mid-position based Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy using online magnetic resonance imaging guidance for central lung tumours. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 23, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, M.; Palacios, M.A.; van Sörnsen de Koste, J.R.; Eze, C.; Hillbrand, M.; Belka, C.; Landry, G.; Senan, S.; Kurz, C. Comparison of MR-guided radiotherapy accumulated doses for central lung tumors with non-adaptive and online adaptive proton therapy. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 2625–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnery, S.; Katsigiannopulos, E.; Hoegen, P.; Weykamp, F.; Sandrini, E.; Held, T.; Deng, M.; Eichkorn, T.; Buchele, C.; Rippke, C.; et al. To fly or not to fly: Stereotactic MR-guided adaptive radiotherapy effectively treats ultracentral lung tumors with favorable long-term outcomes. Lung Cancer 2023, 179, 107175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, M.L.; Sim, A.J.; Bryant, J.M.; Bhandari, M.; Wuthrick, E.J.; Perez, B.A.; Dilling, T.J.; Redler, G.; Andreozzi, J.; Nardella, L.; et al. Magnetic Resonance-Guided Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy/Hypofractionated Radiation therapy for Metastatic and Primary Central and Ultracentral Lung Lesions. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2023, 4, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finazzi, T.; Haasbeek, C.J.A.; Spoelstra, F.O.B.; Palacios, M.A.; Admiraal, M.A.; Bruynzeel, A.M.E.; Slotman, B.J.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Senan, S. Clinical Outcomes of Stereotactic MR-Guided Adaptive Radiation Therapy for High-Risk Lung Tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnery, S.; Ristau, J.; Weykamp, F.; Hoegen, P.; Sprengel, S.D.; Paul, K.M.; Buchele, C.; Klüter, S.; Rippke, C.; Renkamp, C.K.; et al. Magnetic resonance guided adaptive stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung tumors in ultracentral location: The MAGELLAN trial (ARO 2021-3). Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, M.E.; Perks, J.R.; Chen, A.M. Patterns-of-care for thoracic stereotactic body radiotherapy among practicing radiation oncologists in the United States. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Gomez-Suescun, J.A.; Stephans, K.L.; Bogart, J.A.; Hermann, G.M.; Tian, L.; Groman, A.; Videtic, G.M. One Versus Three Fractions of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Peripheral Stage I to II Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Randomized, Multi-Institution, Phase 2 Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videtic, G.M.; Paulus, R.; Singh, A.K.; Chang, J.Y.; Parker, W.; Olivier, K.R.; Timmerman, R.D.; Komaki, R.R.; Urbanic, J.J.; Stephans, K.L.; et al. Long-term Follow-Up on NRG Oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927): A Randomized Phase 2 Study Comparing 2 Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Schedules for Medically Inoperable Patients With Stage I Peripheral Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 103, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.S.W.; Ning, M.S.; Lee, P.; McMahon, R.A.; Siva, S.; Chuong, M.D. Single-Fraction Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: A Paradigm During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic and Beyond? Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 5, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finazzi, T.; van Sörnsen de Koste, J.R.; Palacios, M.A.; Spoelstra, F.O.B.; Slotman, B.J.; Haasbeek, C.J.A.; Senan, S. Delivery of magnetic resonance-guided single-fraction stereotactic lung radiotherapy. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 14, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, D.; Sanford, L.; Dhanireddy, B.; Molloy, J.; Randall, M.; McGarry, R.C. Flattening filter free VMAT for a stereotactic, single-dose of 30 Gy to lung lesion in a 15-min treatment slot. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2020, 21, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuong, M.D.; Kotecha, R.; Mehta, M.P.; Adamson, S.; Romaguera, T.; Hall, M.D.; Alvarez, D.; Gutierrez, A.N.; Mishra, V.; De Zarraga, F.; et al. Case report of visual biofeedback-driven, magnetic resonance-guided single-fraction SABR in breath hold for early stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Med. Dosim. 2021, 46, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choun, H.J.; Kim, J.I.; Choi, C.H.; Jung, S.; Jin, H.; Wu, H.G.; Chie, E.K.; Park, J.M. Performance evaluation of a visual guidance patient-controlled respiratory gating system for respiratory-gated magnetic-resonance image-guided radiation therapy. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2022, 45, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.S.; Higgins, K.A.; McGarry, R.C. Emerging Therapies for Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K. Magnetic resonance imaging for N staging in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorac. Cancer 2015, 6, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-M.; Xu, J.-R.; Gu, H.-Y.; Hua, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Haacke, E.M.; Hu, J. Preoperative mediastinal and hilar nodal staging with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: Which is better? J. Surg. Res. 2012, 178, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubec, M.; Brown, S.; Chuter, R.; Hales, R.; Whiteside, L.; Rodgers, J.; Parker, J.; Eccles, C.L.; van Herk, M.; Faivre-Finn, C.; et al. MRI and CBCT for lymph node identification and registration in patients with NSCLC undergoing radical radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 159, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bainbridge, H.E.; Menten, M.J.; Fast, M.F.; Nill, S.; Oelfke, U.; McDonald, F. Treating locally advanced lung cancer with a 1.5T MR-Linac—Effects of the magnetic field and irradiation geometry on conventionally fractionated and isotoxic dose-escalated radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 125, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eze, C.; Lombardo, E.; Nierer, L.; Xiong, Y.; Niyazi, M.; Belka, C.; Manapov, F.; Corradini, S. MR-guided radiotherapy in node-positive non-small cell lung cancer and severely limited pulmonary reserve: A report proposing a new clinical pathway for the management of high-risk patients. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, A.; Mittauer, K.E.; Chuong, M.D.; Hall, M.D.; Kutuk, T.; Bassiri, N.; McCulloch, J.; Alvarez, D.; Herrera, R.; Gutierrez, A.N.; et al. Accelerated hypofractionated magnetic resonance-guided adaptive radiotherapy for oligoprogressive non-small cell lung cancer. Med. Dosim. 2023, 48, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oborn, B.M.; Metcalfe, P.E.; Butson, M.J.; Rosenfeld, A.B. Monte Carlo characterization of skin doses in 6 MV transverse field MRI-linac systems: Effect of field size, surface orientation, magnetic field strength, and exit bolus. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 5208–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Yang, B.; Lam, W.W.; Geng, H.; Cheung, K.Y.; Yu, S.K. Magnetic field induced dose effects in radiation therapy using MR-linacs. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 3623–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, I.J.; Yadav, P.; Mittal, B.B. Emergence of MR-Linac in Radiation Oncology: Successes and Challenges of Riding on the MRgRT Bandwagon. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Mou, X.; Beeraka, N.M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, J.; Dai, J.; Fan, R. Machine Log File and Calibration Errors-based Patient-specific Quality Assurance (QA) for Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT). Curr. Pharm. Des. 2023, 29, 2738–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgić, J.; Gregov, M.; Mrčela, I.; Budanec, M.; Krengli, M.; Fröbe, A.; Franco, P. Mri-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer: A new paradigm. Acta Clin. Croat. 2022, 61, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Yuan, J.; Cheung, K.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Poon, D.M.C.; Yu, S.K. Magnetic Resonance-Guided Radiation Therapy of Patients With Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device on a 1.5 T Magnetic Resonance-Linac. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 12, e56–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keesman, R.; van der Bijl, E.; Janssen, T.M.; Vijlbrief, T.; Pos, F.J.; van der Heide, U.A. Clinical workflow for treating patients with a metallic hip prosthesis using magnetic resonance imaging-guided radiotherapy. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunenberg, E.J.L.; Kusters, J.M.A.M.; Van Kollenburg, P.G.M.; Braam, P.M. SP-0469: The development of a one-stop-shop palliative radiotherapy treatment using MR and CBCT. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 111, S183–S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, M.A.; Verheijen, S.; Schneiders, F.L.; Bohoudi, O.; Slotman, B.J.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Senan, S. Same-day consultation, simulation and lung Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy delivery on a Magnetic Resonance-linac. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 24, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnery, S.; de Colle, C.; Eze, C.; Corradini, S.; Thieke, C.; Sedlaczek, O.; Schlemmer, H.P.; Dinkel, J.; Seith, F.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; et al. Pulmonary magnetic resonance-guided online adaptive radiotherapy of locally advanced: The PUMA trial. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study, Publication Year | MRI Technique | qMRI Metric | Lung Cancer Type | Number of Patients | Follow-up Time Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shintani, T., et al., 2017 [51] | DWI | ADC, SUVmax | NSCLC | 14 | Pre, 3, 6, 9, 12 months |
| Chang, Q., et al., 2012 [52] | DWI | ADC | advanced lung carcinoma | 14 | at regular intervals until the date of death |
| Weiss, E., et al., 2016 [53] | DWI | ADC | Adenocarcinoma (4) SCC (6) | 10 | Pre, 3, 6 weeks |
| Yabuuchi, H., et al., 2011 [54] | DWI | ADC | NSCLC | 28 | Before and after the first course of chemotherapy |
| Sampath, S., et al., 2019 [55] | DWI | ADC | NSCLC | 13 | Pre, 1 month |
| Sun, Y. S., et al., 2011 [56] | DWI | ADC | Lung cancer | 21 | Pre, 1, 3, 6 weeks |
| Seki, S., et al., 2020 [57] | DCE-MRI | Pulmonary arterial perfusion Systemic arterial perfusion Total perfusion | Adenocarcinoma (35) SCC (7) LCLC (1) | 43 | Pre, every 6 months post-treatment |
| Tao, X., et al., 2016 [58] | DCE-MRI | BF, BV, MTT, Ktrans, Kep, Ve, Vp | NSCLC | 36 | Pre, 1 month |
| Mehrabian, H., et al., 2017 [59] | DCE-MRI | kIE, kep, M0,I, M0,E, M0,V | Primary lung cancer | 9 | Pre, 1 week, 1 month |
| Desmond, K. L., et al., 2017 [60] | CEST | APTw, AREX, Lorentzian peak properties | Brain metastases from primary lung cancer | 25 | Pre, 1 week, 1 month |
| Gutsche, R., et al., 2022 [61] | Radiomics | Local textural features | Brain metastases from NSCLC | 80 | Pre, 180 days post-treatment |
| Salem, A., et al., 2019 [62] | OE-MRI | perfused Oxy-R | NSCLC | 23 | Pre, post-treatment |
| NCT Number (Registration Year) | Study Type | Tumor Type | RT Regimen | Combined Therapy | Trial Design (Arms) | Primary Outcome | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03048760 (2017) | Prospective | Stage I-III NSCLC or SCLC | N/A | Nil | MRI scan | Measure differences between target and OAR volumes contoured on PET, CT, and MRI images | To evaluate the feasibility of MRI for the delineation of OAR and target volumes in lung cancer patients |
| NCT05237453 (2022) | Prospective | Locally advanced NSCLC | MR-guided ART | Nil | Experimental: MR-guided ART | Clinical feasibility | To demonstrate the feasibility of MR-guided online ART for locally advanced NSCLC |
| NCT03916419 (2019) | Phase 2 | Inoperable stage IIB, IIIA, and select IIIB and IIIC NSCLC | 60 Gy/15 Fr | Paclitaxel + Carboplatin + Durvalumab | Chemoradiation + Durvalumab | Safety lead-in only: number of participants with dose-limiting toxicities Phase II only: local control rate; regional control rate | To test the feasibility and outcomes of MR-guided hypofractionated ART with concurrent chemotherapy and consolidation Durvalumab for inoperable stage IIB, IIIA, and select IIIB and IIIC NSCLC |
| NCT04925583 (2021) | Phase 1 | Ultracentral-located lung tumor | SBRT | Nil | Level 0: 10 Fr × 5.0 Gy Level 1: 10 Fr × 5.5 Gy Level 2: 10 Fr × 6.0 Gy Level 3: 10 Fr × 6.5 Gy | Dose-limiting toxicity | To identify the maximum tolerated dose of MR-guided SBRT of ultracentral lung tumors |
| NCT05354596 (2022) | Phase II | Ultracentrally located lung tumors | SBRT | Nil | MR-Linacs with daily MR-guided plan adaptation | Toxicity: cumulative CTCAE grade ≥ 4 SABR-related toxicity (6, 12, 24, 60 months) | To evaluate the feasibility and safety of daily adaptive MR-Linac-based SBRT in ultracentrally located lung tumors (primary, oligo-metastatic, or oligo-progressive) |
| NCT05903430 (2023) | Prospective cohort | Centrally located lung cancer | SABR | Nil | Not mentioned | >85% success in delivery and completion of SABR to patients recruited on protocol | To determine if the investigators are able to deliver highly focused, intense radiation to tumors in the abdominal region or chest cavity whilst limiting the dose to OAR using a high-field-strength MR-Linac |
| NCT04789486 (2021) | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Centrally located lung tumors | SMART | AGuIX | Phase 1: AGUIX + SMART Phase 2: AGUIX + SMART; SMART only | Phase 1: MTD Phase 2: compare local control at 12 months of MTD | To help determine the safety and efficacy of gadolinium-based nanoparticle, AGuIX, used in conjunction with SMART in the treatment of pancreatic cancer and lung tumors |
| NCT04075305 (2019) | Prospective cohort | Cancer patients receiving treatment and/or imaging on an MR-Linac machine | Not mentioned | Nil | Not mentioned | PFS; survival; DFS (3, 6, 24 months) Patient-reported health-related quality of life and tumor-specific quality of life; acute toxicity in CTCAE (3, 6, 12, 24 months) Clinical tumor response; pathological tumor response (2 years) | To facilitate the evidence-based introduction of MR-Linac into clinical practice |
| NCT04946019 (2021) | Phase 2 | Brain metastases from NSCLC | 30 Gy/5 Fr | Nil | Experimental: MR-Linac-guided adaptive FSRT | 1-year intracranial PFS | To determine the efficacy and safety of MR-Linac-guided adaptive FSRT in patients with brain metastases in NSCLC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, S.H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-H. Harnessing the Power of Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of the Evolving Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guidance. Cancers 2024, 16, 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152710
Cheng SH, Lee S-Y, Lee H-H. Harnessing the Power of Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of the Evolving Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guidance. Cancers. 2024; 16(15):2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152710
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Sarah Hsin, Shao-Yun Lee, and Hsin-Hua Lee. 2024. "Harnessing the Power of Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of the Evolving Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guidance" Cancers 16, no. 15: 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152710
APA StyleCheng, S. H., Lee, S.-Y., & Lee, H.-H. (2024). Harnessing the Power of Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of the Evolving Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guidance. Cancers, 16(15), 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152710







