Expression of mGluR5 in Pediatric Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma—A Comparative Analysis of Immunohistochemical and Clinical Findings Regarding the Association between Tumor and Paraneoplastic Neurological Disease
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tissue Samples
2.2. Immunohistochemistry with DAB for CD30 and mGluR5 on HL and NHL Tissue
2.3. Analysis of RNA-Sequencing Data of Lymphocytes
2.4. Immunofluorescence Co-Staining on Tumor Tissue of HL and NHL Patients
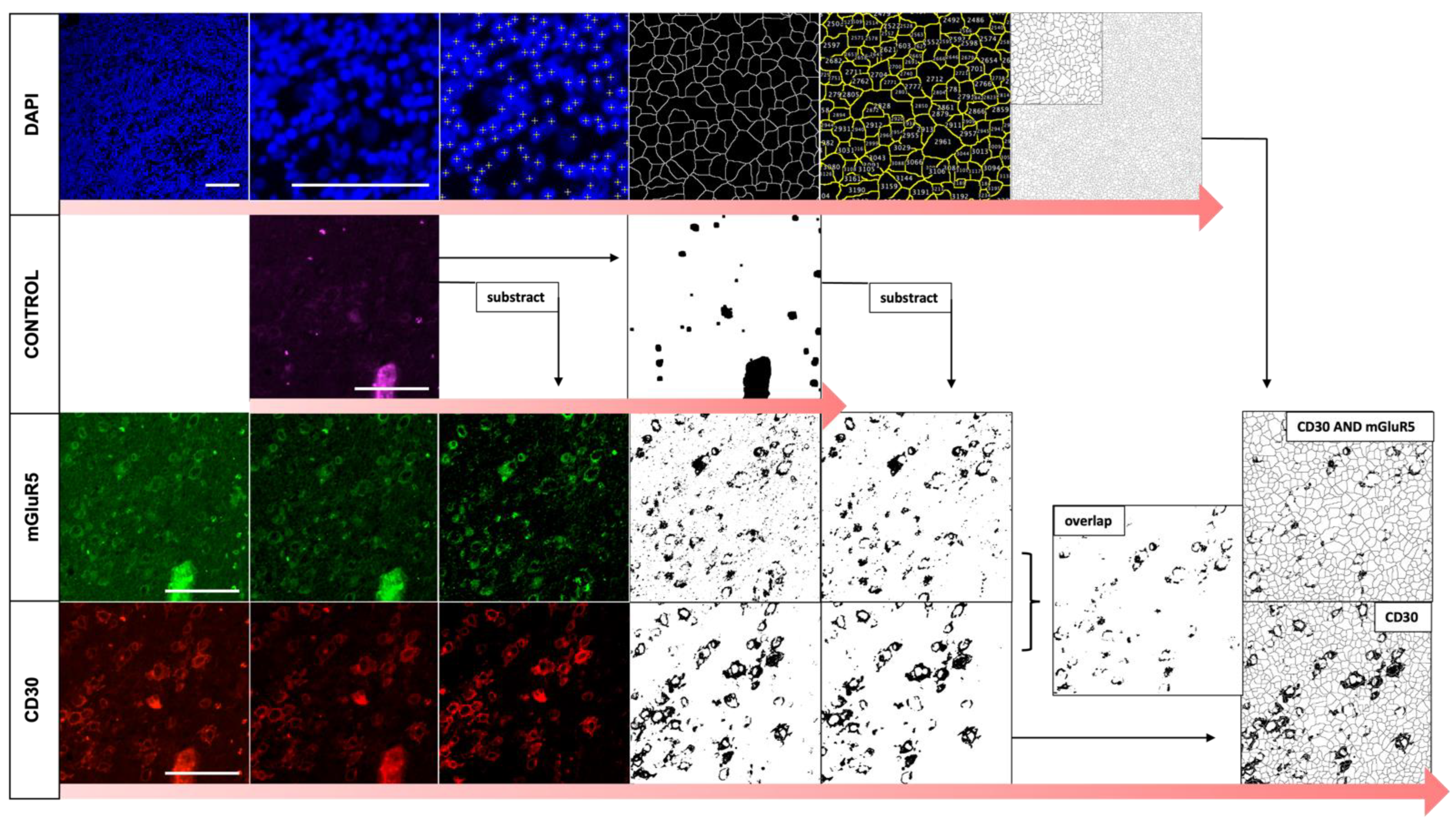
2.5. Automated Image Analysis of Immunofluorescence Co-Staining
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Description: Diagnosis and Course of Disease in Representative Groups of Children with HL and NHL
3.1.1. HL Patients with Neurologic Symptoms and Paraneoplastic Manifestations
3.1.2. Histopathological Spectrum of Entities and Association with EBV in Our Cohort
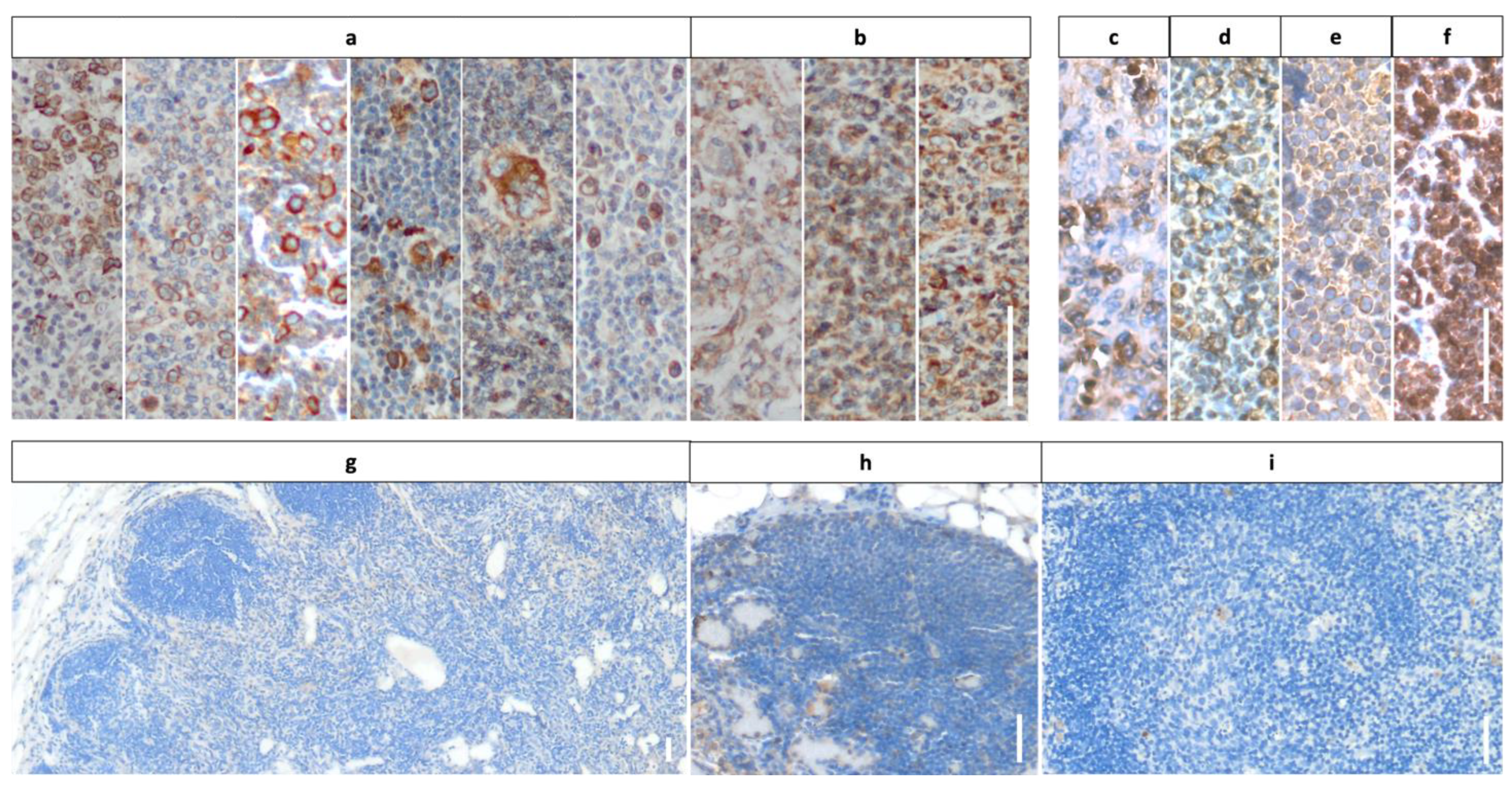
3.2. Staining Results Indicating Frequent Expression of mGluR5 in Pediatric Lymphoma Tissue
3.3. RNA-Sequencing: No Relevant Expression of GRM5 in Non-Malignant Lymphocytes
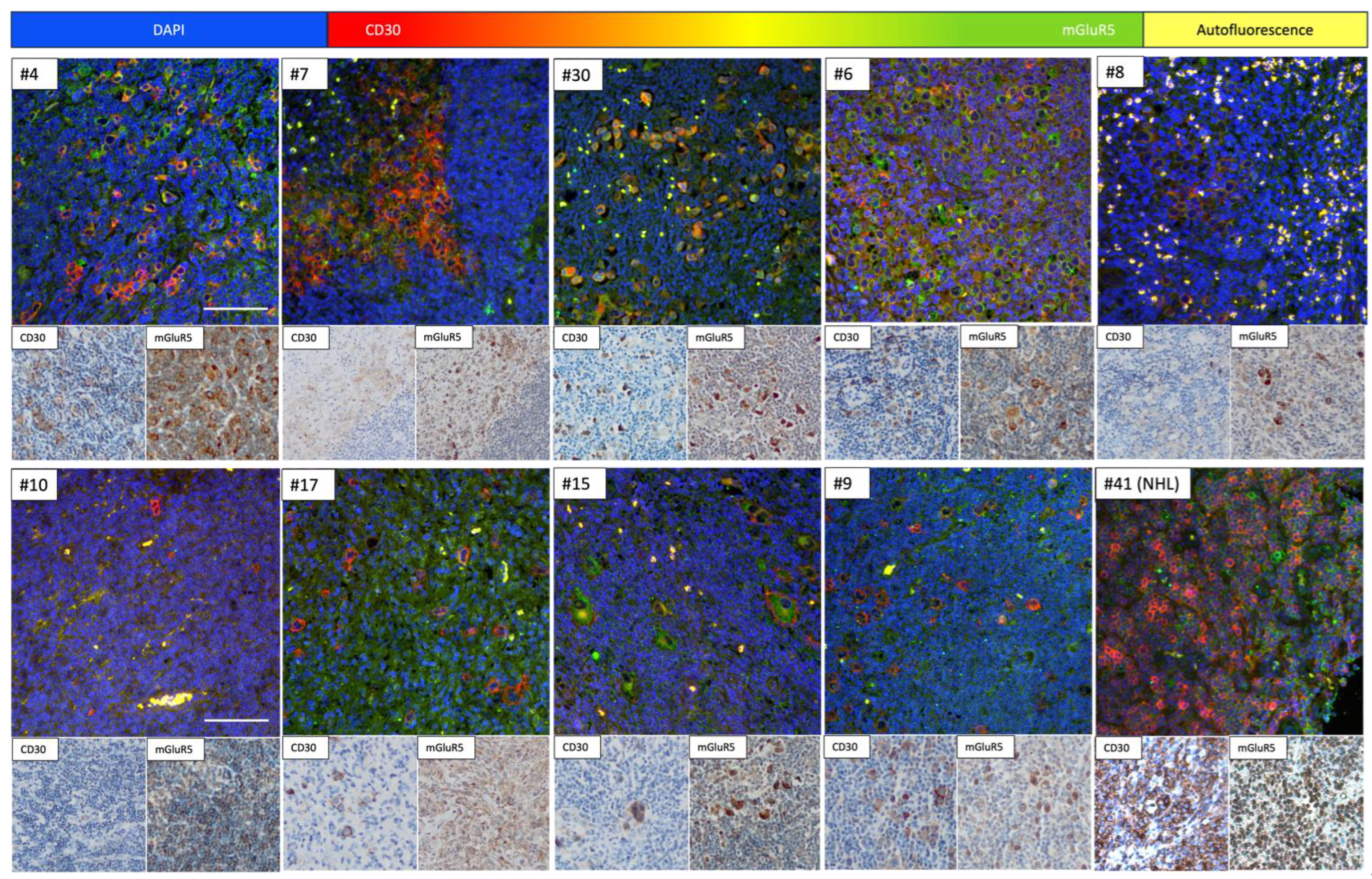
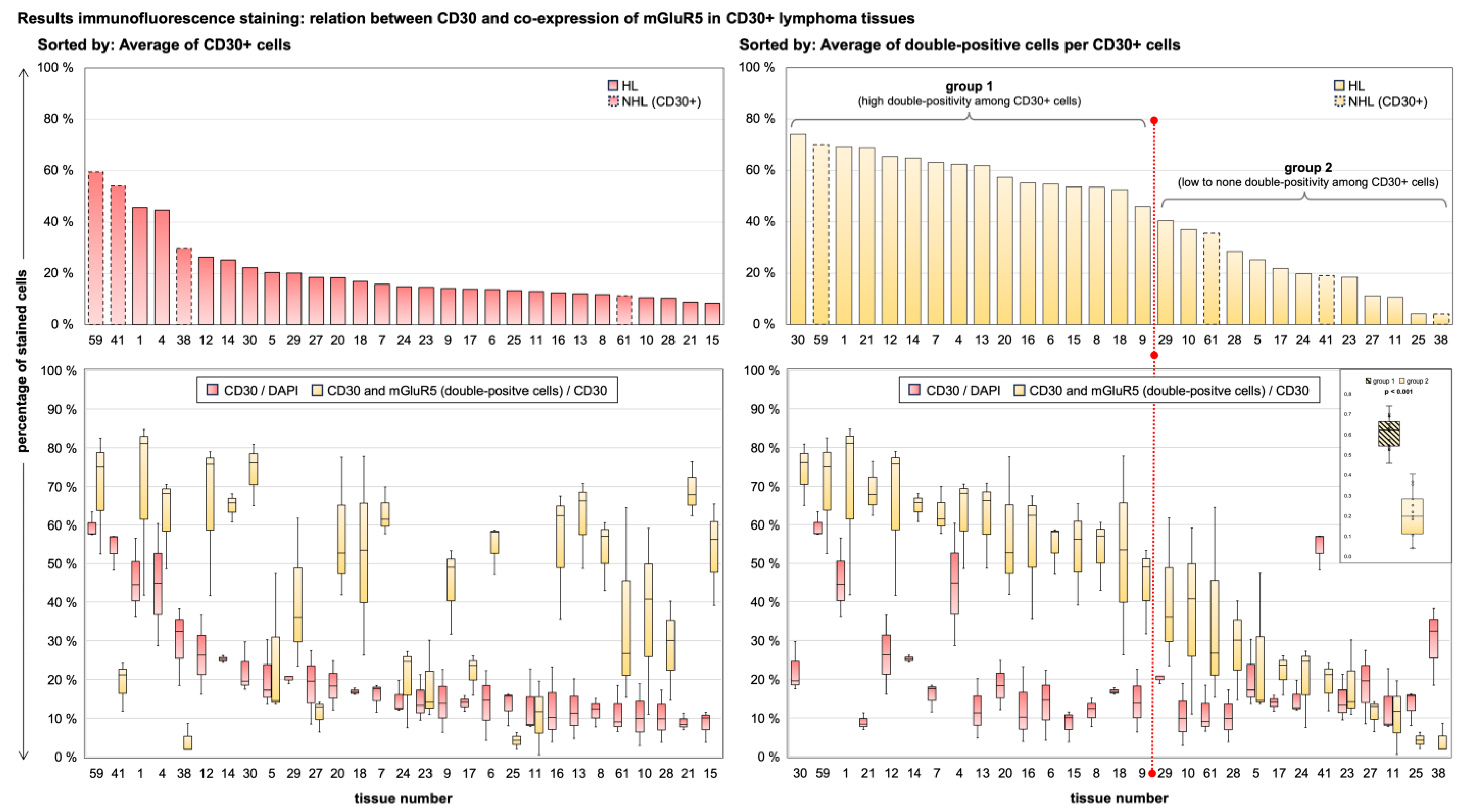
3.4. Immunofluorescence Co-Staining Analysis and Clinical Associations
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carr, I. The Ophelia syndrome: Memory loss in Hodgkin’s disease. Lancet 1982, 1, 844–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, E.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Titulaer, M.; Boulos, M.; Weaver, S.; Antoine, J.-C.; Liebers, E.; Kornblum, C.; Bien, C.; Honnorat, J.; et al. Antibodies to metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in the Ophelia syndrome. Neurology 2011, 77, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niswender, C.M.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: Physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 295–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levite, M. Glutamate receptor antibodies in neurological diseases: Anti-AMPA-GluR3 antibodies, anti-NMDA-NR1 antibodies, anti-NMDA-NR2A/B antibodies, anti-mGluR1 antibodies or anti-mGluR5 antibodies are present in subpopulations of patients with either: Epilepsy, encephalitis, cerebellar ataxia, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and neuropsychiatric SLE, Sjogren’s syndrome, schizophrenia, mania or stroke. These autoimmune anti-glutamate receptor antibodies can bind neurons in few brain regions, activate glutamate receptors, decrease glutamate receptor’s expression, impair glutamate-induced signaling and function, activate blood brain barrier endothelial cells, kill neurons, damage the brain, induce behavioral/psychiatric/cognitive abnormalities and ataxia in animal models, and can be removed or silenced in some patients by immunotherapy. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 1029–1075. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Garcia, R.; Martínez-Hernández, E.; Joubert, B.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Pajarón-Boix, E.; Fernández, V.; Salais, L.; del Pozo, M.; Armangué, T.; Sabater, L.; et al. Paraneoplastic cerebellar ataxia and antibodies to metabotropic glutamate receptor 2. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillevis Smitt, P.; Kinoshita, A.; De Leeuw, B.; Moll, W.; Coesmans, M.; Jaarsma, D.; Henzen-Logmans, S.; Vecht, C.; De Zeeuw, C.; Sekiyama, N.; et al. Paraneoplastic cerebellar ataxia due to autoantibodies against a glutamate receptor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocke, K.S.; Staufner, C.; Luksch, H.; Geiger, K.D.; Stepulak, A.; Marzahn, J.; Schackert, G.; Temme, A.; Ikonomidou, C. Glutamate receptors in pediatric tumors of the central nervous system. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, S.; Knierim, E.; Bittigau, P.; Kreye, J.; Hauptmann, K.; Hundsdoerfer, P.; Morales-Gonzalez, S.; Schuelke, M.; Nikolaus, M. Hodgkin Lymphoma Cell Lines and Tissues Express mGluR5: A Potential Link to Ophelia Syndrome and Paraneoplastic Neurological Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.-A.; Han, I.-H.; Yoo, B.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, J.-Y.; Cha, I.-H.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.-W. Clinical significance of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Choi, K.Y.; Chang, K.; Pickel, J.M.; Badger, J.D.; Roche, K.W. Expression of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) induces melanoma in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15219–15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Ruiz, Y.; Gulzar, H.; Yelskaya, Z.; Taouit, L.A.; Houssou, M.; Jaikaran, T.; Schvarts, Y.; Kozlitina, K.; Basu-Roy, U.; et al. Osteosarcoma cell proliferation and survival requires mGluR5 receptor activity and is blocked by Riluzole. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, W.; Huang, H.; Dai, S.; Tan, X.; Chen, Q.; Huang, R.; Zou, H. mGluR5 promotes the progression of multiple myeloma in vitro via Ras-MAPK signaling pathway. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 31, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maudes, E.; Mannara, F.; García-Serra, A.; Radosevic, M.; Mellado, A.; Serafim, A.B.; Planagumà, J.; Sabater, L.; Dalmau, J.; Spatola, M. Human Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Antibodies Alter Receptor Levels and Behavior in Mice. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 92, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spatola, M.; Sabater, L.; Planagumà, J.; Martínez-Hernandez, E.; Armangué, T.; Prüss, H.; Iizuka, T.; Oblitas, R.L.C.; Antoine, J.-C.; Li, R.; et al. Encephalitis with mGluR5 antibodies: Symptoms and antibody effects. Neurology 2018, 90, e1964–e1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchwalow, I.; Atiakshin, D.; Samoilova, V.; Boecker, W.; Tiemann, M. Identification of autofluorescent cells in human angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 149, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weniger, M.A.; Kuppers, R. Molecular biology of Hodgkin lymphoma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flerlage, J.E.; Hiniker, S.M.; Armenian, S.; Benya, E.C.; Bobbey, A.J.; Chang, V.; Cooper, S.; Coulter, D.W.; Cuglievan, B.; Hoppe, B.S.; et al. Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma, Version 3. 2021. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 733–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Antoine, J.-C.G.; Desestret, V.; Dubey, D.; Giometto, B.; Irani, S.R.; Joubert, B.; Leypoldt, F.; et al. Updated Diagnostic Criteria for Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau, J.; Geis, C.; Graus, F. Autoantibodies to Synaptic Receptors and Neuronal Cell Surface Proteins in Autoimmune Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 839–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsili, L.; Marcucci, S.; LaPorta, J.; Chirra, M.; Espay, A.J.; Colosimo, C. Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes of the Central Nervous System: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, S.; Uy, C.; Honnorat, J.; Irani, S.R. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes: A practical approach to diagnosis and management. Pract. Neurol. 2022, 22, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Arino, H.; Dalmau, J. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes in Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood 2014, 123, 3230–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punnett, A.; Tsang, R.W.; Hodgson, D.C. Hodgkin lymphoma across the age spectrum: Epidemiology, therapy, and late effects. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 20, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connors, J.M.; Cozen, W.; Steidl, C.; Carbone, A.; Hoppe, R.T.; Flechtner, H.H.; Bartlett, N.L. Hodgkin lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koda, S.; Hu, J.; Ju, X.; Sun, G.; Shao, S.; Tang, R.-X.; Zheng, K.-Y.; Yan, J. The role of glutamate receptors in the regulation of the tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1123841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, R.; Ciruela, F.; Casadó, V.; Mallol, J.; Gallart, T.; Lluis, C.; Franco, R. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors mediate a dual role of glutamate in T cell activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33352–33358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prickett, T.D.; Samuels, Y. Molecular pathways: Dysregulated glutamatergic signaling pathways in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4240–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard, S.S.; Koochekpour, S. Glutamate signaling in benign and malignant disorders: Current status, future perspectives, and therapeutic implications. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.J.; Wall, B.A.; Wangari-Talbot, J.; Chen, S. Metabotropic glutamate receptors in cancer. Neuropharmacology 2017, 115, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, G.; Han, G.; Chen, G.; Hou, C.; Wang, T.; Shen, B.; et al. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 is involved in B-cell-related tumor apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Hsueh, Y.; Chen, L.; Cheng, W.; Yu, C.; Chen, W.; Lu, T.; Lan, K.; Lee, C.; Huang, S.; et al. Clinical significance of glutamate metabotropic receptors in renal cell carcinoma risk and survival. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 6104–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.X.; Gu, L.; Yang, H.M.; Xi, S.S.; Xia, N.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H. Downregulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 inhibits hepatoma development in a neurotoxin rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 288, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiaansen, A.E.M.; Timmermans, A.M.; Smid, M.; van Deurzen, C.H.M.; Hulsenboom, E.S.P.; der Smissen, W.J.C.P.-V.; Foekens, R.; Trapman-Jansen, A.M.A.C.; Smitt, P.A.E.S.; Luider, T.M.; et al. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in ER-negative and triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetaille, B.; Bertucci, F.; Finetti, P.; Esterni, B.; Stamatoullas, A.; Picquenot, J.M.; Copin, M.C.; Morschhauser, F.; Casasnovas, O.; Petrella, T.; et al. Molecular profiling of classical Hodgkin lymphoma tissues uncovers variations in the tumor microenvironment and correlations with EBV infection and outcome. Blood 2009, 113, 2765–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, M.L.; Mauz-Korholz, C. Epidemiology, outcome, targeted agents and immunotherapy in adolescent and young adult non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 1142–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigenwald, C.; Galimard, J.-E.; Quero, L.; Cabannes-Hamy, A.; Thieblemont, C.; Boissel, N.; Brice, P. Hodgkin lymphoma in adolescent and young adults: Insights from an adult tertiary single-center cohort of 349 patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 80073–80082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Maura, F.; Ziccheddu, B.; Xiang, J.Z.; Bhinder, B.; Rosiene, J.; Abascal, F.; Maclachlan, K.H.; Eng, K.W.; Uppal, M.; He, F.; et al. Molecular Evolution of Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma Revealed Through Whole-Genome Sequencing of Hodgkiand Reed Sternberg Cells. Blood Cancer Discov. 2023, 4, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massini, G.; Siemer, D.; Hohaus, S. EBV in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 1, e2009013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vockerodt, M.; Yap, L.; Shannon-Lowe, C.; Curley, H.; Wei, W.; Vrzalikova, K.; Murray, P.G. The Epstein-Barr virus and the pathogenesis of lymphoma. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienand, K.; Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Wu, D.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Wood, T.R.; Cader, F.Z.; Ducar, M.D.; et al. Genomic analyses of flow-sorted Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells reveal complementary mechanisms of immune evasion. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 4065–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weniger, M.A.; Kuppers, R. NF-kappaB deregulation in Hodgkin lymphoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 39, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepulak, A.; Luksch, H.; Gebhardt, C.; Uckermann, O.; Marzahn, J.; Sifringer, M.; Rzeski, W.; Staufner, C.; Brocke, K.S.; Turski, L.; et al. Expression of glutamate receptor subunits in human cancers. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 132, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.A. In Sickness and in Health: The Immunological Roles of the Lymphatic System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciopinto, P.; Dell’olio, G.; De Robertis, R.; Specchia, G.; Musto, P.; Albano, F. The Role of Autoimmune Diseases in the Prognosis of Lymphoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristinsson, S.Y.; Landgren, O.; Sjöberg, J.; Turesson, I.; Björkholm, M.; Goldin, L.R. Autoimmunity and risk for Hodgkin’s lymphoma by subtype. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1468–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El Fakih, R.; Bajuaifer, Y.S.; Shah, A.Y.; Sulaiman, R.; Almohamady, R.; Elgohary, G.; Alothaimeen, H.S.; Aljurf, M. Paraneoplastic syndromes associated with classic Hodgkin lymphoma, a systematic literature review. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briani, C.; Vitaliani, R.; Grisold, W.; Honnorat, J.; Graus, F.; Antoine, J.; Bertolini, G.; Giometto, B.; Euronetwork, F.T.P. Spectrum of paraneoplastic disease associated with lymphoma. Neurology 2011, 76, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotton, W.J.; Karim, A.; Jacob, S. Glutamate Receptor Antibodies in Autoimmune Central Nervous System Disease: Basic Mechanisms, Clinical Features, and Antibody Detection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1941, 225–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, E. CNS syndromes associated with antibodies against metabotropic receptors. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Gigli, G.L.; Segatti, S.; Corazza, E.; Marini, A.; Bernardini, A.; Valent, F.; Fabris, M.; Curcio, F.; Brigo, F.; et al. Epidemiology of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes: A population-based study. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HL | NHL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 29 | n = 28 | |||
| Sex | ||||
| female | 17/29 | (59%) | 3/28 | (11%) |
| male | 12/29 | (41%) | 25/28 | (89%) |
| Age * | ||||
| mean, [range] | 14.1 | [5.5–17.5] | 10.5 | [3.0–17.8] |
| Staging ** | ||||
| I | 0/29 | (0%) | 2/28 | (7%) |
| II | 17/29 | (59%) | 8/28 | (29%) |
| III | 4/29 | (14%) | 9/28 | (32%) |
| IV | 8/29 | (27%) | 9/28 | (32%) |
| B-symptoms | 11/29 | (38%) | 5/28 | (18%) |
| Onset of symptoms *** | ||||
| mean, [range] | 4.7 | [1–27] | 1.9 | [0.25–9] |
| Event free survival status | ||||
| 0—no event | 25/29 | (86%) | 23/28 | (82%) |
| 1—event (relapse) | 4/29 | (14%) | 3/28 | (11%) |
| no data | 0/29 | (0%) | 2/28 | (7%) |
| Overall survival status | ||||
| 0—alive | 28/29 | (97%) | 26/28 | (92%) |
| 1—succumbed to disease | 1/29 | (3%) | 1/28 | (4%) |
| 2—died of other causes | 0/29 | (0%) | 1/28 | (4%) |
| Special symptoms | ||||
| neurological-psychiatric | 4/29 | (14%) | 6/28 | (21%) |
| CNS involvement | 0/4 | (0%) | 6/6 | (100%) |
| paraneoplastic | 3/29 | (10%) | 0/28 | (0%) |
| Neurological diagnostics | ||||
| EEG | 21/29 | (72%) | 19/28 | (68%) |
| cMRI | 8/29 | (27%) | 11/28 | (39%) |
| CSF | 5/29 | (17%) | 28/28 | (100%) |
| antineuronal antibody screening | 2/29 | (6%) | 0/28 | (0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viezens, I.; Knierim, E.; Deubzer, H.E.; Hauptmann, K.; Fassbender, J.; Morales-Gonzalez, S.; Kaindl, A.M.; Schuelke, M.; Nikolaus, M. Expression of mGluR5 in Pediatric Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma—A Comparative Analysis of Immunohistochemical and Clinical Findings Regarding the Association between Tumor and Paraneoplastic Neurological Disease. Cancers 2024, 16, 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16132452
Viezens I, Knierim E, Deubzer HE, Hauptmann K, Fassbender J, Morales-Gonzalez S, Kaindl AM, Schuelke M, Nikolaus M. Expression of mGluR5 in Pediatric Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma—A Comparative Analysis of Immunohistochemical and Clinical Findings Regarding the Association between Tumor and Paraneoplastic Neurological Disease. Cancers. 2024; 16(13):2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16132452
Chicago/Turabian StyleViezens, Ingeborg, Ellen Knierim, Hedwig E. Deubzer, Kathrin Hauptmann, Jessica Fassbender, Susanne Morales-Gonzalez, Angela M. Kaindl, Markus Schuelke, and Marc Nikolaus. 2024. "Expression of mGluR5 in Pediatric Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma—A Comparative Analysis of Immunohistochemical and Clinical Findings Regarding the Association between Tumor and Paraneoplastic Neurological Disease" Cancers 16, no. 13: 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16132452
APA StyleViezens, I., Knierim, E., Deubzer, H. E., Hauptmann, K., Fassbender, J., Morales-Gonzalez, S., Kaindl, A. M., Schuelke, M., & Nikolaus, M. (2024). Expression of mGluR5 in Pediatric Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma—A Comparative Analysis of Immunohistochemical and Clinical Findings Regarding the Association between Tumor and Paraneoplastic Neurological Disease. Cancers, 16(13), 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16132452







