Smoking-Mediated miR-301a/IRF1 Axis Controlling Immunotherapy Response in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Revealed by Bioinformatic Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. UALCAN Database Analysis
2.2. MirDB Database Analysis
2.3. LinkedOmics Database Analysis
2.4. TargetScan Database Analysis
2.5. Metascape and Cancerhallmarks Databases Analysis
2.6. TFlink Database Analysis
2.7. TIMER Database Analysis
2.8. KMplot Database Analysis
2.9. Patients and Tissue Collection
2.10. Total RNA Extraction and the Real-Time PCR
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
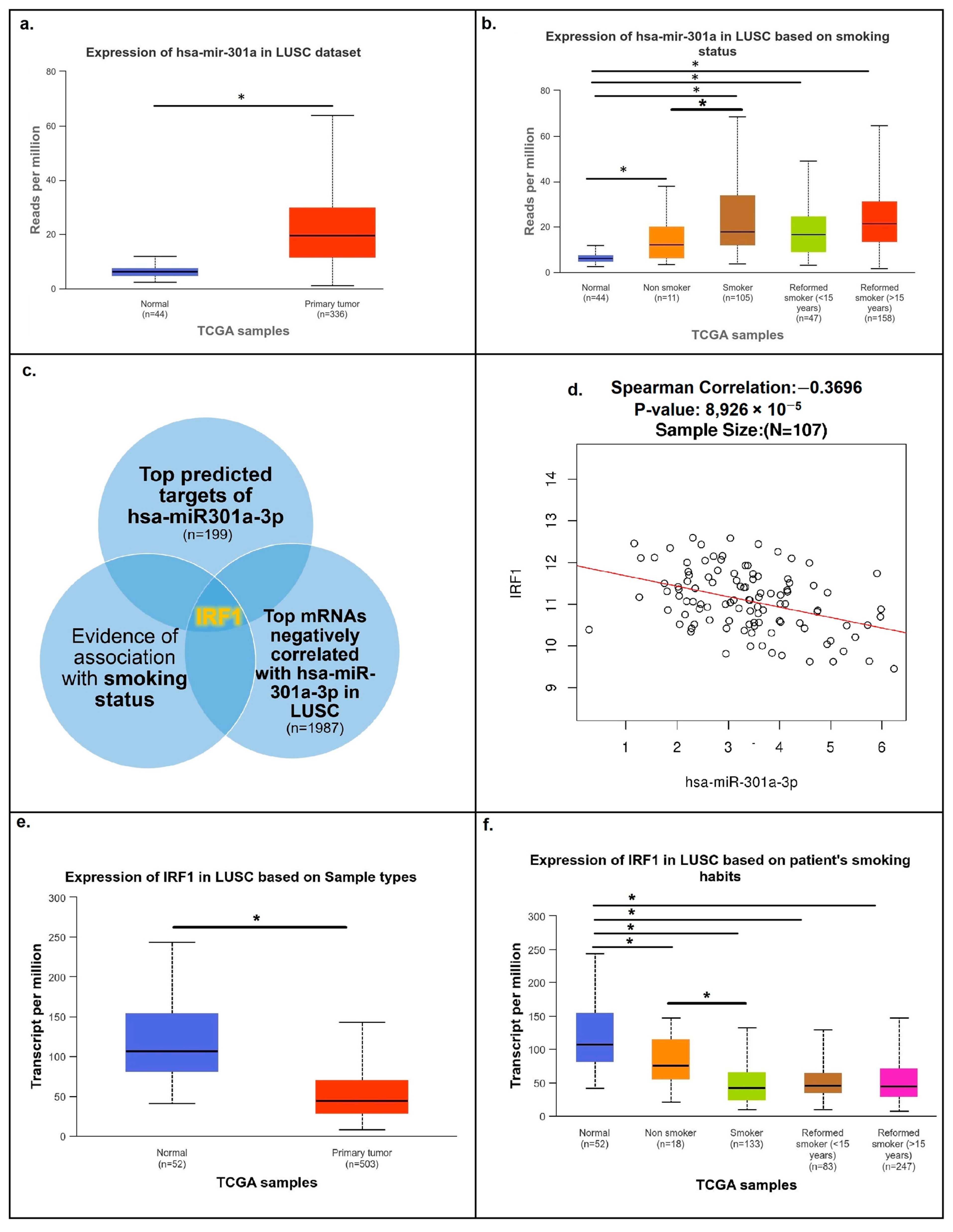
3.1. The Main Smoking-Related Target of miR301a Is IRF1
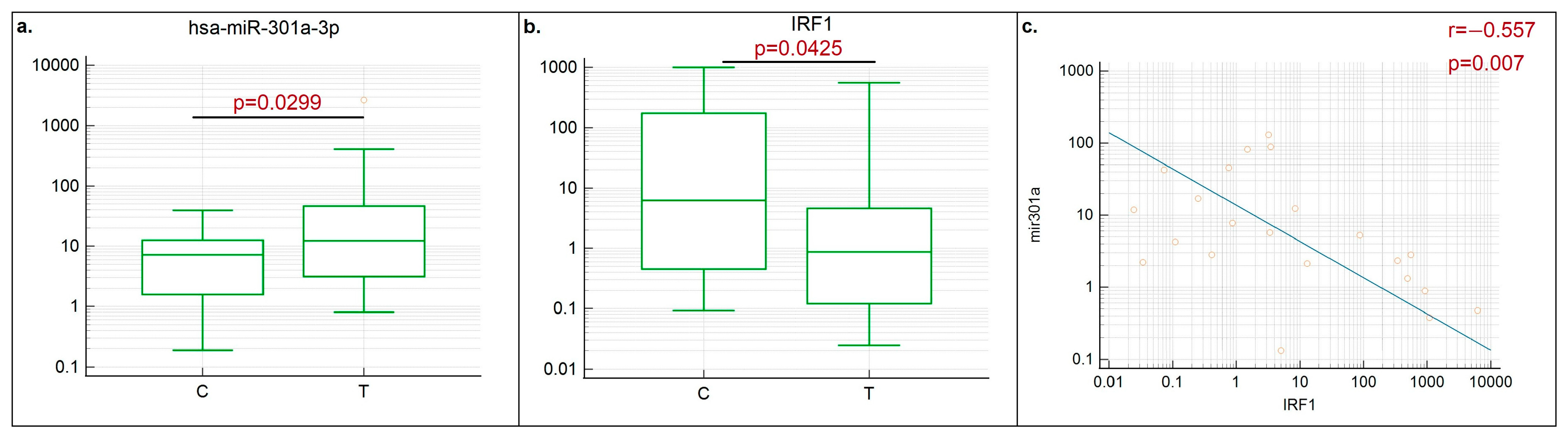
3.2. Negative Correlation between miR301a and IRF1 Was Demonstrated in LUSC Clinical Samples
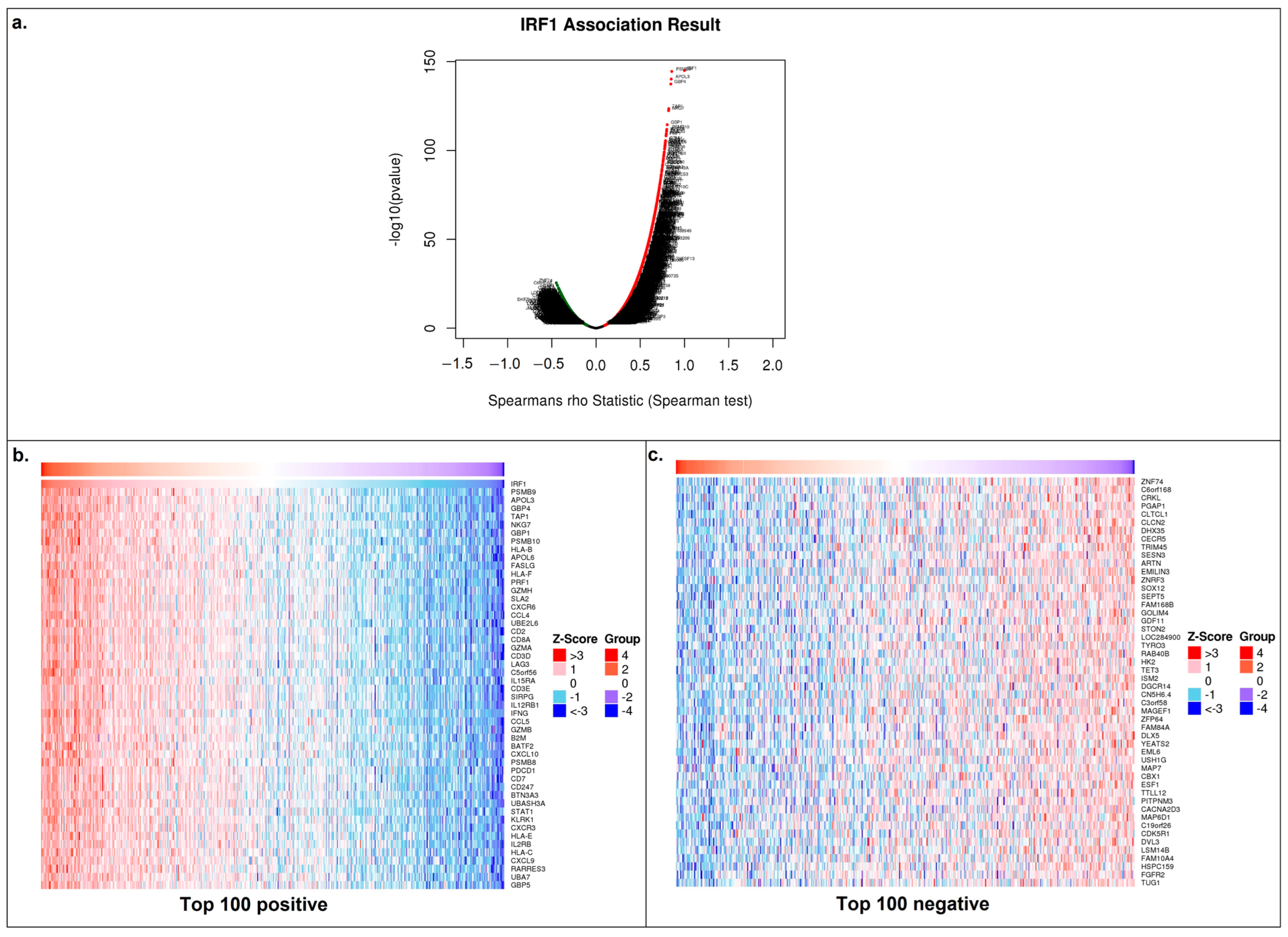
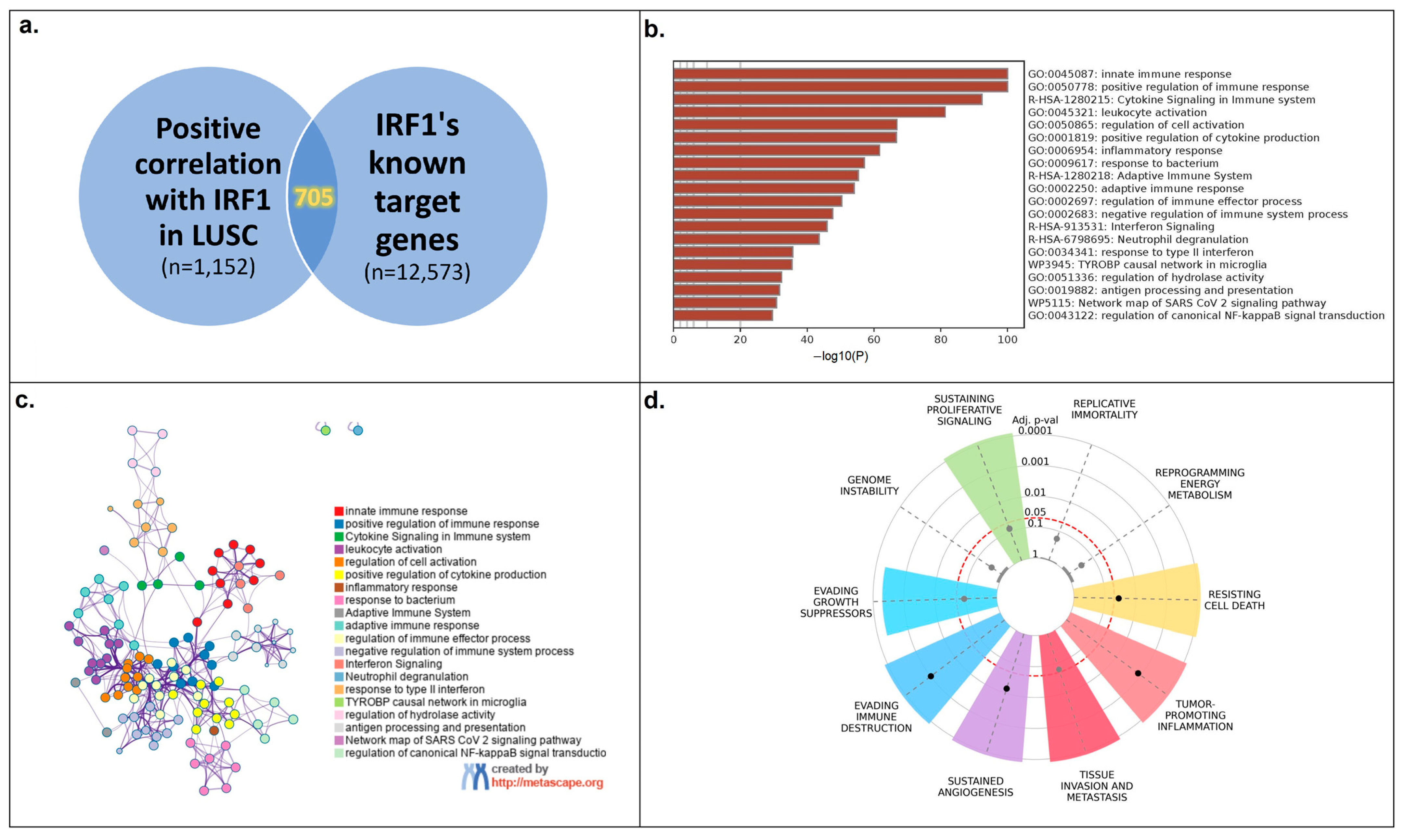
3.3. IRF1′s Function in LUSC
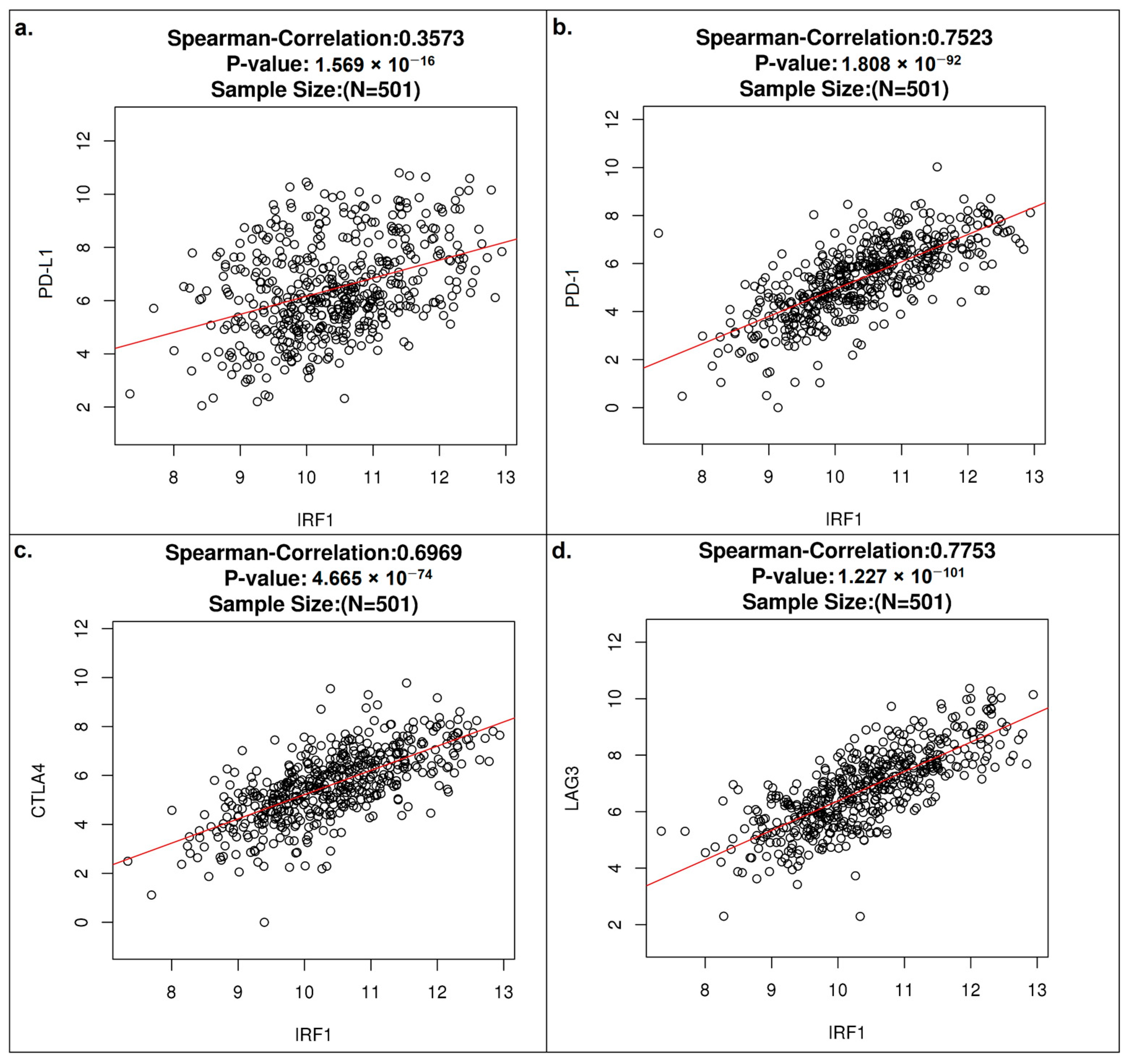
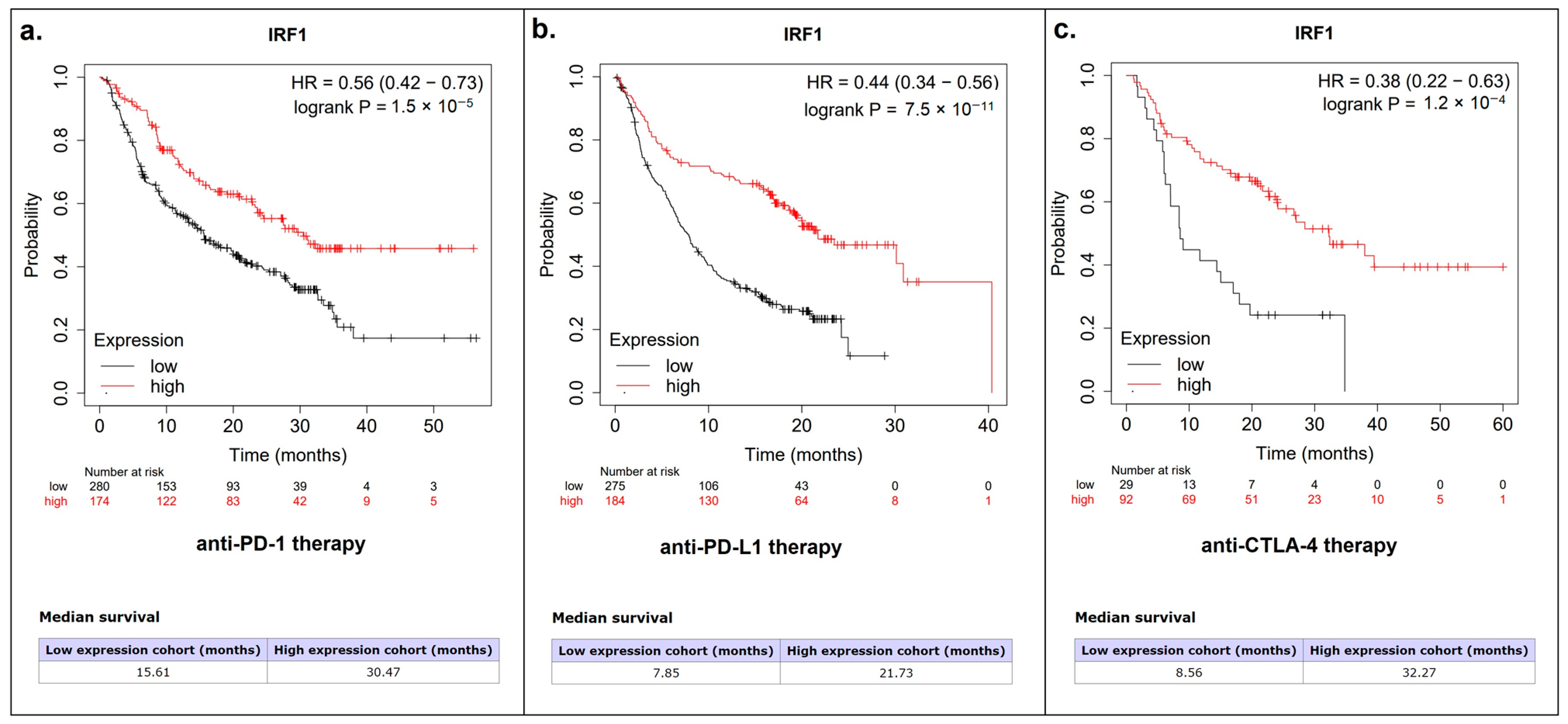
3.4. IRF1 Controls the Antitumor Immune Response in LUSC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiter, A.; Veluswamy, R.R.; Wisnivesky, J.P. The global burden of lung cancer: Current status and future trends. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliri, A.W.; Tommasi, S.; Besaratinia, A. Relationships among smoking, oxidative stress, inflammation, macromolecular damage, and cancer. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2021, 787, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesch, B.; Kendzia, B.; Gustavsson, P.; Jockel, K.H.; Johnen, G.; Pohlabeln, H.; Olsson, A.; Ahrens, W.; Gross, I.M.; Bruske, I.; et al. Cigarette smoking and lung cancer—Relative risk estimates for the major histological types from a pooled analysis of case-control studies. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.Y.; Huang, J.Y.; Chen, H.C.; Lin, C.H.; Lin, S.H.; Hung, W.H.; Cheng, Y.F. The comparison between adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma in lung cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caini, S.; Del Riccio, M.; Vettori, V.; Scotti, V.; Martinoli, C.; Raimondi, S.; Cammarata, G.; Palli, D.; Banini, M.; Masala, G.; et al. Quitting Smoking At or Around Diagnosis Improves the Overall Survival of Lung Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, P.H.; Landi, M.T. DNA Methylation in Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Associations with Histological Subtypes, Molecular Alterations, and Major Epidemiological Factors. Cancers 2022, 14, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Fu, J.H.; Zhang, W.; Guo, M. Lung carcinoma signaling pathways activated by smoking. Chin. J. Cancer 2011, 30, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Hu, S.; Li, C.; Ma, H.; Wang, Q.; Meng, G.; Guo, T.; Zhang, J. Cigarette Smoke Induced Lung Barrier Dysfunction, EMT, and Tissue Remodeling: A Possible Link between COPD and Lung Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2025636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrichard, A.; Kuo, F.; Chowell, D.; Lee, K.W.; Riaz, N.; Wong, R.J.; Chan, T.A.; Morris, L.G.T. Tobacco Smoking-Associated Alterations in the Immune Microenvironment of Squamous Cell Carcinomas. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugg, S.T.; Scott, A.; Parekh, D.; Naidu, B.; Thickett, D.R. Cigarette smoke exposure and alveolar macrophages: Mechanisms for lung disease. Thorax 2022, 77, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutic, M.; Vukic, A.; Baranasic, J.; Forsti, A.; Dzubur, F.; Samarzija, M.; Jakopovic, M.; Brcic, L.; Knezevic, J. Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prognostic Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Management. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, J.M.; Nguyen, T.; Shivdasani, P.; Sacher, A.G.; Cheng, M.L.; Alden, R.S.; Janne, P.A.; Kuo, F.C.; Oxnard, G.R.; Sholl, L.M. Next-generation sequencing informs diagnosis and identifies unexpected therapeutic targets in lung squamous cell carcinomas. Lung Cancer 2020, 140, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Raese, R.; Luo, D.; Cao, S.; Wan, Y.W.; Qian, Y.; Guo, N.L. MicroRNA, mRNA, and Proteomics Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Improving Lung Cancer Treatment Outcomes. Cancers 2023, 15, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Li, S.; Liu, T.; He, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhou, H. MicroRNAs: Emerging oncogenic and tumor-suppressive regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021, 502, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Salazar, E.G.; Gayosso-Gomez, L.V.; Baez-Saldana, R.; Falfan-Valencia, R.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Higuera-Iglesias, A.L.; Vazquez-Manriquez, M.E.; Ortiz-Quintero, B. Cigarette Smoking Alters the Expression of Circulating microRNAs and Its Potential Diagnostic Value in Female Lung Cancer Patients. Biology 2021, 10, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirra, D.; Esposito, R.; Spaziano, G.; Sportiello, L.; Panico, F.; Squillante, A.; Falciani, M.; Cerqua, I.; Gallelli, L.; Cione, E.; et al. MicroRNA Monitoring in Human Alveolar Macrophages from Patients with Smoking-Related Lung Diseases: A Preliminary Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pustylnyak, V.O.; Alekseenok, E.Y.; Perevalova, A.M.; Kozlov, V.V.; Gulyaeva, L.F. Tumor suppressor PTEN regulation by tobacco smoke in lung squamous-cell carcinoma based on bioinformatics analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yan, F.; Deng, Q.; Li, F.; Lu, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Conklin, D.J.; McCracken, J.; Srivastava, S.; et al. Modulation of tumorigenesis by the pro-inflammatory microRNA miR-301a in mouse models of lung cancer and colorectal cancer. Cell Discov. 2015, 1, 15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Karthikeyan, S.K.; Korla, P.K.; Patel, H.; Shovon, A.R.; Athar, M.; Netto, G.J.; Qin, Z.S.; Kumar, S.; Manne, U.; et al. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 2022, 25, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasaikar, S.V.; Straub, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. LinkedOmics: Analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D956–D963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeary, S.E.; Lin, K.S.; Shi, C.Y.; Pham, T.M.; Bisaria, N.; Kelley, G.M.; Bartel, D.P. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science 2019, 366, eaav1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liska, O.; Bohar, B.; Hidas, A.; Korcsmaros, T.; Papp, B.; Fazekas, D.; Ari, E. TFLink: An integrated gateway to access transcription factor-target gene interactions for multiple species. Database 2022, 2022, baac083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Fan, J.; Wang, B.; Traugh, N.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER: A Web Server for Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e108–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorffy, B. Integrated analysis of public datasets for the discovery and validation of survival-associated genes in solid tumors. Innovation 2024, 5, 100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinina, T.S.; Kononchuk, V.V.; Yakovleva, A.K.; Alekseenok, E.Y.; Sidorov, S.V.; Gulyaeva, L.F. Association between Lymph Node Status and Expression Levels of Androgen Receptor, miR-185, miR-205, and miR-21 in Breast Cancer Subtypes. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2020, 2020, 3259393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G. Tobacco, air pollution, environmental carcinogenesis, and thoughts on conquering strategies of lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2019, 16, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigan, S.S.; Murphy, S.E.; Stram, D.O.; Hecht, S.S.; Marchand, L.L.; Stepanov, I.; Park, S.L. Association of Urinary Biomarkers of Smoking-Related Toxicants with Lung Cancer Incidence in Smokers: The Multiethnic Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2023, 32, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderLaan, P.A.; Rangachari, D.; Majid, A.; Parikh, M.S.; Gangadharan, S.P.; Kent, M.S.; McDonald, D.C.; Huberman, M.S.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Costa, D.B. Tumor biomarker testing in non-small-cell lung cancer: A decade of change. Lung Cancer 2018, 116, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Shimada, K.; Nakai, T.; Ohbayashi, C. MicroRNAs in Smoking-Related Carcinogenesis: Biomarkers, Functions, and Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momi, N.; Kaur, S.; Rachagani, S.; Ganti, A.K.; Batra, S.K. Smoking and microRNA dysregulation: A cancerous combination. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasimi Shad, A.; Fanoodi, A.; Maharati, A.; Akhlaghipour, I.; Moghbeli, M. Molecular mechanisms of microRNA-301a during tumor progression and metastasis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 247, 154538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, G.; Feng, S. MicroRNA-301a modulates doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma cells by targeting AMP-activated protein kinase alpha 1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 459, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Taheri, M. Emerging roles of miRNAs in the development of pancreatic cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.K.; Zang, Q.L.; Li, G.X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.Z. Increased expression of microRNA-301a in nonsmall-cell lung cancer and its clinical significance. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitsky, D.; Tamura, T.; Yanai, H.; Taniguchi, T. Regulation of immunity and oncogenesis by the IRF transcription factor family. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2010, 59, 489–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, K.; Du, Q.; Cui, X.; Wan, P.; Kaltenmeier, C.; Luo, J.; Yan, B.; Yan, Y.; Geller, D.A. MicroRNA-301a (miR-301a) is induced in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and down- regulates the expression of interferon regulatory factor-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 524, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, L.; Damiani, I.; Castiglioni, S.; Carleo, A.; De Salvo, R.; Rossi, C.; Corsini, A.; Bellosta, S. Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switch Induced by Traditional Cigarette Smoke Condensate: A Holistic Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Du, Q.; Yazdani, H.; Dong, K.; Guo, Y.; Geller, D.A. Interferon regulatory factor 1(IRF-1) activates anti-tumor immunity via CXCL10/CXCR3 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Cancer Lett. 2021, 506, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Hou, W.; Scharping, N.E.; Vendetti, F.P.; Srivastava, R.; Roy, C.N.; Menk, A.V.; Wang, Y.; Chauvin, J.M.; Karukonda, P.; et al. IRF1 Inhibits Antitumor Immunity through the Upregulation of PD-L1 in the Tumor Cell. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Diaz, A.; Shin, D.S.; Moreno, B.H.; Saco, J.; Escuin-Ordinas, H.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Sun, L.; Hugo, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Interferon Receptor Signaling Pathways Regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, M.; Ramaiya, N.H.; Hatabu, H.; Hodi, F.S. Monitoring immune-checkpoint blockade: Response evaluation and biomarker development. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tray, N.; Weber, J.S.; Adams, S. Predictive Biomarkers for Checkpoint Immunotherapy: Current Status and Challenges for Clinical Application. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandini, S.; Massi, D.; Mandala, M. PD-L1 expression in cancer patients receiving anti PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 100, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Zhao, B. Efficacy of PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors and PD-L1 expression status in cancer: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2018, 362, k3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroshow, D.B.; Bhalla, S.; Beasley, M.B.; Sholl, L.M.; Kerr, K.M.; Gnjatic, S.; Wistuba, I.I.; Rimm, D.L.; Tsao, M.S.; Hirsch, F.R. PD-L1 as a biomarker of response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungabeesoon, J.; Gort-Freitas, N.A.; Kiss, M.; Bolli, E.; Messemaker, M.; Siwicki, M.; Hicham, M.; Bill, R.; Koch, P.; Cianciaruso, C.; et al. A neutrophil response linked to tumor control in immunotherapy. Cell 2023, 186, 1448–1464.e1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithy, J.W.; Moore, L.M.; Pelekanou, V.; Rehman, J.; Gaule, P.; Wong, P.F.; Neumeister, V.M.; Sznol, M.; Kluger, H.M.; Rimm, D.L. Nuclear IRF-1 expression as a mechanism to assess “Capability” to express PD-L1 and response to PD-1 therapy in metastatic melanoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschen, A.; Melero, I.; Ribas, A. Central Role of the Antigen-Presentation and Interferon-γ Pathways in Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2022, 6, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbasi, A.; Ribas, A. Tumour-intrinsic resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Number of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| ≤65 | 28 (50) |
| >65 | 28 (50) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 55 (98) |
| Female | 1 (2) |
| Smoking history | |
| Current smokers | 56 (100) |
| Pack-years | |
| ≤40 | 32 (57) |
| >40 | 24 (43) |
| Family history of cancer | |
| Yes (lung cancer) | 8 (14.3) |
| Yes (other cancer types) | 12 (21.4) |
| No | 36 (64.3) |
| Comorbidities | |
| COPD | 26 (46.4) |
| CVD without COPD | 22 (39.3) |
| None | 8 (14.3) |
| Lymph node metastasis | |
| No | 34 (60.7) |
| Yes | 22 (39.3) |
| Pathologic stage (AJCC staging) | |
| I | 22 (39) |
| II | 24 (43) |
| III | 10 (18) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perevalova, A.M.; Kononchuk, V.V.; Kalinina, T.S.; Kozlov, V.V.; Gulyaeva, L.F.; Pustylnyak, V.O. Smoking-Mediated miR-301a/IRF1 Axis Controlling Immunotherapy Response in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Revealed by Bioinformatic Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 2208. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122208
Perevalova AM, Kononchuk VV, Kalinina TS, Kozlov VV, Gulyaeva LF, Pustylnyak VO. Smoking-Mediated miR-301a/IRF1 Axis Controlling Immunotherapy Response in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Revealed by Bioinformatic Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(12):2208. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122208
Chicago/Turabian StylePerevalova, Alina M., Vladislav V. Kononchuk, Tatiana S. Kalinina, Vadim V. Kozlov, Lyudmila F. Gulyaeva, and Vladimir O. Pustylnyak. 2024. "Smoking-Mediated miR-301a/IRF1 Axis Controlling Immunotherapy Response in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Revealed by Bioinformatic Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 12: 2208. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122208
APA StylePerevalova, A. M., Kononchuk, V. V., Kalinina, T. S., Kozlov, V. V., Gulyaeva, L. F., & Pustylnyak, V. O. (2024). Smoking-Mediated miR-301a/IRF1 Axis Controlling Immunotherapy Response in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Revealed by Bioinformatic Analysis. Cancers, 16(12), 2208. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122208







