Molecular Subtypes and the Role of TP53 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Richter Syndrome
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Current Molecular Classifications of DLBCL
2.1. Gene Expression Profiling and Cytogenetics
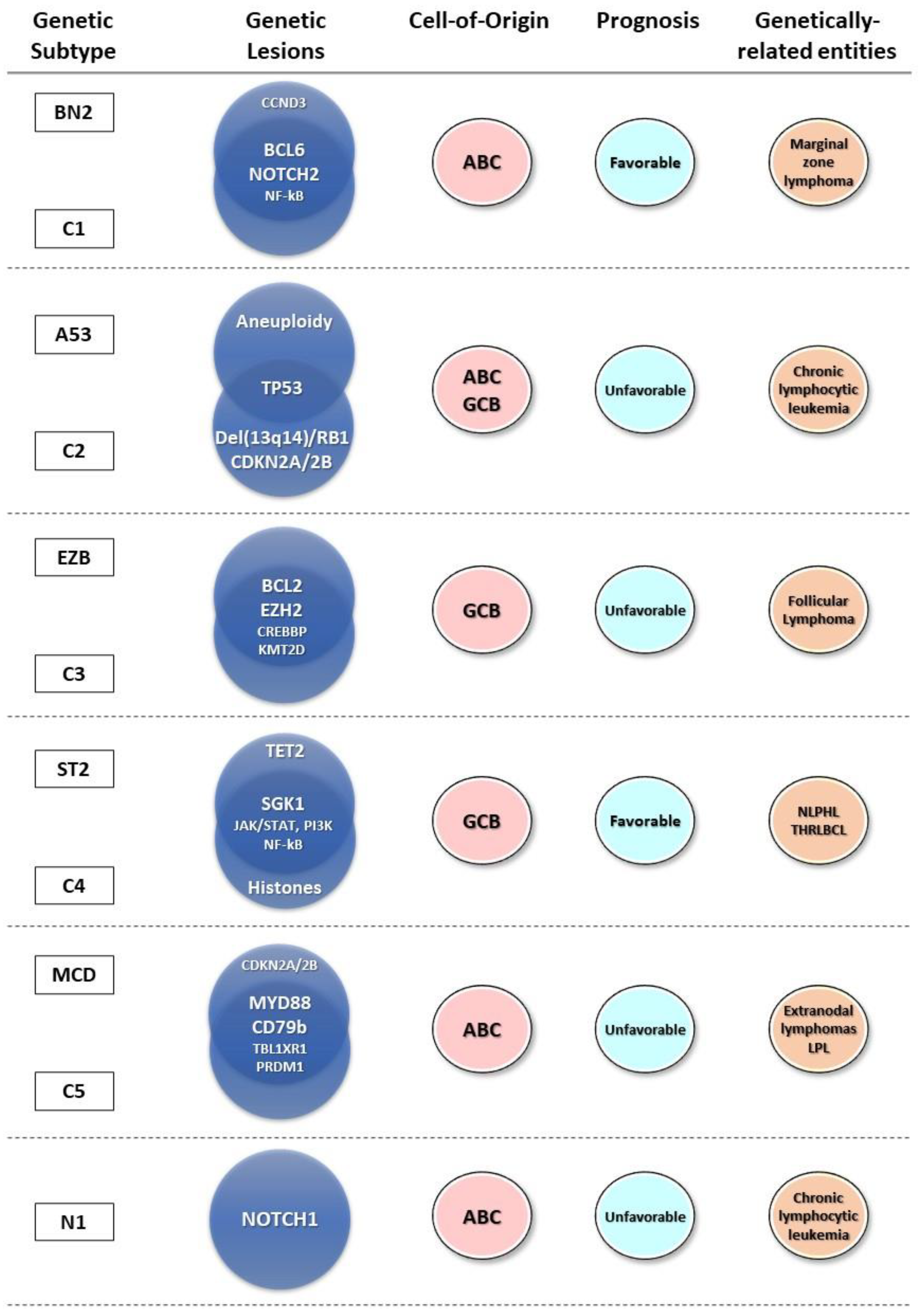
2.2. Genetic Profiling of DLBCL
2.3. Genetic Subtypes and Tumor Microenvironment
2.4. Genetic Subtypes and Prognosis
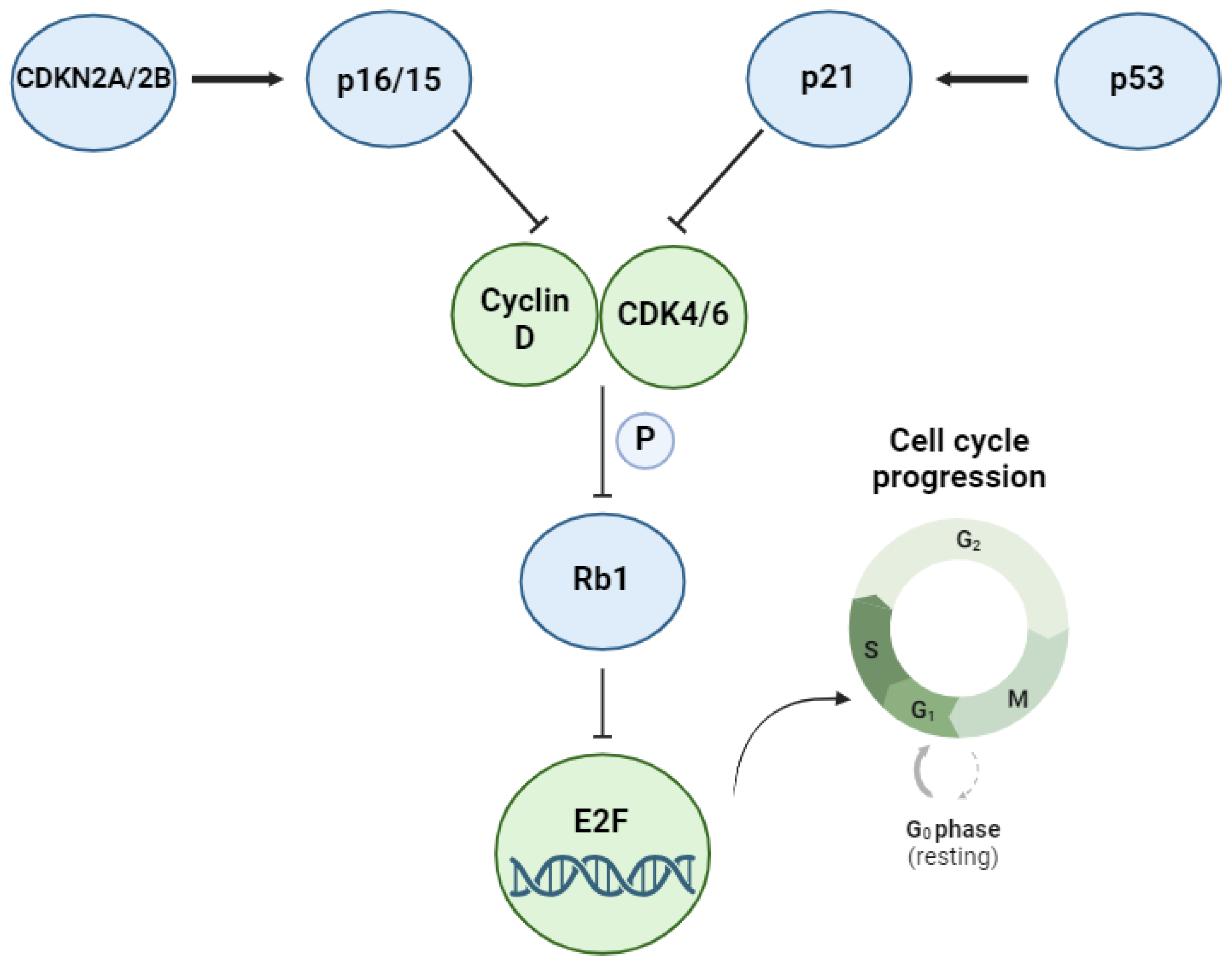
3. The TP53 Pathway and Its Alterations in DLBCL
4. Prognostic Significance of TP53 Alterations in DLBCL
5. TP53 Alterations in Richter Syndrome
5.1. The Interplay between TP53 Alterations, DLBCL and Richter Syndrome
5.2. Prognostic Significance of TP53 Alterations in Richter Syndrome
6. Treatment Options for TP53-Mutated DLBCL
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Crouch, S.; Lax, S.; Li, J.; Painter, D.; Howell, D.; Patmore, R.; Jack, A.; Roman, E. Lymphoma incidence, survival and prevalence 2004–2014: Sub-type analyses from the UK’s Haematological Malignancy Research Network. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehn, L.H.; Salles, G. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 842–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.J.; Ghesquières, H.; Jais, J.-P.; Witzig, T.E.; Haioun, C.; Thompson, C.A.; Delarue, R.; Micallef, I.N.; Peyrade, F.; Macon, W.R.; et al. Event-free survival at 24 months is a robust end point for disease-related outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coiffier, B.; Lepage, E.; Briere, J.; Herbrecht, R.; Tilly, H.; Bouabdallah, R.; Morel, P.; Van Den Neste, E.; Salles, G.; Gaulard, P.; et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfreundschuh, M.; Kuhnt, E.; Trümper, L.; Osterborg, A.; Trneny, M.; Shepherd, L.; Gill, D.S.; Walewski, J.; Pettengell, R.; Jaeger, U.; et al. CHOP-like chemotherapy with or without rituximab in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma: 6-year results of an open-label randomised study of the MabThera International Trial (MInT) Group. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coiffier, B.; Thieblemont, C.; Van Den Neste, E.; Lepeu, G.; Plantier, I.; Castaigne, S.; Lefort, S.; Marit, G.; Macro, M.; Sebban, C.; et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: A study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood 2010, 116, 2040–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisselbrecht, C.; Glass, B.; Mounier, N.; Singh Gill, D.; Linch, D.C.; Trneny, M.; Bosly, A.; Ketterer, N.; Shpilberg, O.; Hagberg, H.; et al. Salvage regimens with autologous transplantation for relapsed large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4184–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitz, F.; Connors, J.M.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Hoskins, P.; Moccia, A.; Savage, K.J.; Sehn, L.H.; Shenkier, T.; Villa, D.; Klasa, R. Outcome of patients with primary refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma after R-CHOP treatment. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 1839–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elstrom, R.L.; Martin, P.; Ostrow, K.; Barrientos, J.; Chadburn, A.; Furman, R.; Ruan, J.; Shore, T.; Schuster, M.; Cerchietti, L.; et al. Response to second-line therapy defines the potential for cure in patients with recurrent diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Implications for the development of novel therapeutic strategies. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2010, 10, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Dalla-Favera, R. Genetics of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Dalla-Favera, R. The genetic landscape of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Rocco, A.; De Angelis, F.; Ansuinelli, M.; Foà, R.; Martelli, M. Is now the time for molecular driven therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma? Expert. Rev. Hematol. 2017, 10, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roschewski, M.; Staudt, L.M.; Wilson, W.H. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma—Treatment approaches in the molecular era. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Phelan, J.D.; Staudt, L.M. B-cell receptor signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.d.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturutti, L.; Melnick, A.M. The dangers of déjà vu: Memory B cells as the cells of origin of ABC-DLBCLs. Blood 2020, 136, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, S.; Savage, K.J.; Kutok, J.L.; Feuerhake, F.; Kurtin, P.; Mihm, M.; Wu, B.; Pasqualucci, L.; Neuberg, D.; Aguiar, R.C.T.; et al. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood 2005, 105, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.H.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Yang, Y.; Pittaluga, S.; Wright, G.; Lih, C.-J.; Williams, P.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Gerecitano, J.; et al. Targeting B cell receptor signaling with ibrutinib in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lenz, G.; Tolar, P.; Young, R.M.; Romesser, P.B.; Kohlhammer, H.; Lamy, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010, 463, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, J.D.; Young, R.M.; Webster, D.E.; Roulland, S.; Wright, G.W.; Kasbekar, M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Ceribelli, M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; et al. A multiprotein supercomplex controlling oncogenic signalling in lymphoma. Nature 2018, 560, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havranek, O.; Xu, J.; Köhrer, S.; Wang, Z.; Becker, L.; Comer, J.M.; Henderson, J.; Ma, W.; Man Chun Ma, J.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tonic B-cell receptor signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2017, 130, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremov, D.G.; Turkalj, S.; Laurenti, L. Mechanisms of B Cell Receptor Activation and Responses to B Cell Receptor Inhibitors in B Cell Malignancies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.M.; Wu, T.; Schmitz, R.; Dawood, M.; Xiao, W.; Phelan, J.D.; Xu, W.; Menard, L.; Meffre, E.; Chan, W.-C.C.; et al. Survival of human lymphoma cells requires B-cell receptor engagement by self-antigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13447–13454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eken, J.A.; Koning, M.T.; Kupcova, K.; Sepúlveda Yáñez, J.H.; de Groen, R.A.L.; Quinten, E.; Janssen, J.; van Bergen, C.A.M.; Vermaat, J.S.P.; Cleven, A.; et al. Antigen-independent, autonomous B cell receptor signaling drives activated B cell DLBCL. J. Exp. Med. 2024, 221, e20230941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiodin, G.; Allen, J.D.; Bryant, D.J.; Rock, P.; Martino, E.A.; Valle-Argos, B.; Duriez, P.J.; Watanabe, Y.; Henderson, I.; Blachly, J.S.; et al. Insertion of atypical glycans into the tumor antigen-binding site identifies DLBCLs with distinct origin and behavior. Blood 2021, 138, 1570–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasi, B.K.; Martines, C.; Xerxa, E.; Porro, F.; Kalkan, H.; Fazio, R.; Turkalj, S.; Bojnik, E.; Pyrzynska, B.; Stachura, J.; et al. Inhibition of SYK or BTK augments venetoclax sensitivity in SHP1-negative/BCL-2-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2416–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiger, A.M.; Ziepert, M.; Horn, H.; Scott, D.W.; Barth, T.F.E.; Bernd, H.-W.; Feller, A.C.; Klapper, W.; Szczepanowski, M.; Hummel, M.; et al. Clinical Impact of the Cell-of-Origin Classification and the MYC/BCL2 Dual Expresser Status in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated within Prospective Clinical Trials of the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, P.N.; Fu, K.; Greiner, T.C.; Smith, L.M.; Delabie, J.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Ott, G.; Rosenwald, A.; Braziel, R.M.; Campo, E.; et al. Immunohistochemical Methods for Predicting Cell of Origin and Survival in Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with Rituximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H. Diagnosis of “double hit” diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between DLBCL and Burkitt lymphoma: When and how, FISH versus IHC. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2014, 2014, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karube, K.; Campo, E. MYC alterations in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenwald, A.; Bens, S.; Advani, R.; Barrans, S.; Copie-Bergman, C.; Elsensohn, M.-H.; Natkunam, Y.; Calaminici, M.; Sander, B.; Baia, M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of MYC Rearrangement and Translocation Partner in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Study by the Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3359–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrich, A.M.; Gandhi, M.; Jovanovic, B.; Castillo, J.J.; Rajguru, S.; Yang, D.T.; Shah, K.A.; Whyman, J.D.; Lansigan, F.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.J.; et al. Impact of induction regimen and stem cell transplantation on outcomes in double-hit lymphoma: A multicenter retrospective analysis. Blood 2014, 124, 2354–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laude, M.-C.; Lebras, L.; Sesques, P.; Ghesquieres, H.; Favre, S.; Bouabdallah, K.; Croizier, C.; Guieze, R.; Drieu La Rochelle, L.; Gyan, E.; et al. First-line treatment of double-hit and triple-hit lymphomas: Survival and tolerance data from a retrospective multicenter French study. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, Q.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z. High-intensity chemotherapy improved the prognosis of patients with high-grade B-cell lymphoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1047115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.M.; Young, K.H.; Visco, C.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Orazi, A.; Go, R.S.; Nielsen, O.; Gadeberg, O.V.; Mourits-Andersen, T.; Frederiksen, M.; et al. Immunohistochemical double-hit score is a strong predictor of outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3460–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Tzankov, A.; Green, T.; Wu, L.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Liu, W.; Visco, C.; Li, Y.; Miranda, R.N.; et al. MYC/BCL2 protein coexpression contributes to the inferior survival of activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and demonstrates high-risk gene expression signatures: A report from The International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program. Blood 2013, 121, 4021–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriranta, L.; Pasanen, A.; Alkodsi, A.; Haukka, J.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.-L.; Leppä, S. Molecular background delineates outcome of double protein expressor diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 3742–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennishi, D.; Jiang, A.; Boyle, M.; Collinge, B.; Grande, B.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rushton, C.; Tang, J.; Thomas, N.; Slack, G.W.; et al. Double-Hit Gene Expression Signature Defines a Distinct Subgroup of Germinal Center B-Cell-Like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Painter, D.; Barrans, S.; Lacy, S.; Smith, A.; Crouch, S.; Westhead, D.; Sha, C.; Patmore, R.; Tooze, R.; Burton, C.; et al. Cell-of-origin in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Findings from the UK’s population-based Haematological Malignancy Research Network. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, C.; Barrans, S.; Cucco, F.; Bentley, M.A.; Care, M.A.; Cummin, T.; Kennedy, H.; Thompson, J.S.; Uddin, R.; Worrillow, L.; et al. Molecular High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma: Defining a Poor-Risk Group That Requires Different Approaches to Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.W.; Emre, N.C.T.; Kohlhammer, H.; Dave, S.S.; Davis, R.E.; Carty, S.; Lam, L.T.; Shaffer, A.L.; Xiao, W.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arise by distinct genetic pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13520–13525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, S.E.; Barrans, S.L.; Beer, P.A.; Painter, D.; Smith, A.G.; Roman, E.; Cooke, S.L.; Ruiz, C.; Glover, P.; Van Hoppe, S.J.L.; et al. Targeted sequencing in DLBCL, molecular subtypes, and outcomes: A Haematological Malignancy Research Network report. Blood 2020, 135, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.H.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Hodkinson, B.; Balasubramanian, S.; Fan, Y.; Vermeulen, J.; Shreeve, M.; Staudt, L.M. Effect of ibrutinib with R-CHOP chemotherapy in genetic subtypes of DLBCL. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1643–1653.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, H.F.P.; Lacy, S.; Barrans, S.; Beer, P.A.; Painter, D.; Smith, A.; Roman, E.; Burton, C.; Crouch, S.; Tooze, R.; et al. Application of the LymphGen classification tool to 928 clinically and genetically-characterised cases of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.-X.; Li, J.; Cai, H.; Zhang, W.; Duan, M.-H.; Zhou, D.-B. Patients with primary breast and primary female genital tract diffuse large B cell lymphoma have a high frequency of MYD88 and CD79B mutations. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1867–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Stewart, C.; Tan, Y.; Abo, R.P.; Zhang, L.; Dunford, A.J.; Meredith, D.M.; Thorner, A.R.; Jordanova, E.S.; et al. Targetable genetic features of primary testicular and primary central nervous system lymphomas. Blood 2016, 127, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, R.D.; Arthur, S.E.; Hodson, D.J. Molecular profiling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Why so many types of subtypes? Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 814–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.J.; Gustine, J.; Meid, K.; Dubeau, T.; Hunter, Z.R.; Treon, S.P. Histological transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 1032–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-C.; Tian, S.; Fu, D.; Wang, L.; Cheng, S.; Yi, H.-M.; Jiang, X.-F.; Song, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; et al. Genetic subtype-guided immunochemotherapy in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: The randomized GUIDANCE-01 trial. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1705–1716.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, M.-C.; He, Y.; Li, C.; Fang, H.; Xu, P.-P.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Q.; et al. Human endogenous retroviruses as epigenetic therapeutic targets in TP53-mutated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-C.; Fang, Y.; Xu, P.-P.; Dong, L.; Shen, R.; Huang, Y.-H.; Fu, D.; Yan, Z.-X.; Cheng, S.; Jiang, X.-F.; et al. Clinical efficacy and tumour microenvironment influence of decitabine plus R-CHOP in patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma: Phase 1/2 and biomarker study. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Lv, X.; Cao, X.; Wan, T. Low-dose decitabine enhances the effect of PD-1 blockade in colorectal cancer with microsatellite stability by re-modulating the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Hong, F.; Scott, D.W.; Macon, W.R.; King, R.L.; Habermann, T.M.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Casulo, C.; Wade, J.L.; Nagargoje, G.G.; et al. Addition of Lenalidomide to R-CHOP Improves Outcomes in Newly Diagnosed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in a Randomized Phase II US Intergroup Study ECOG-ACRIN E1412. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Chiappella, A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Scott, D.W.; Zhang, Q.; Jurczak, W.; Özcan, M.; Hong, X.; Zhu, J.; Jin, J.; et al. ROBUST: A Phase III Study of Lenalidomide Plus R-CHOP Versus Placebo Plus R-CHOP in Previously Untreated Patients with ABC-Type Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martines, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Vujovikj, M.; Gobessi, S.; Vaisitti, T.; Deaglio, S.; Laurenti, L.; Dimovski, A.J.; Efremov, D.G. Macrophage- and BCR-derived but not TLR-derived signals support the growth of CLL and Richter syndrome murine models in vivo. Blood 2022, 140, 2335–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerchietti, L. Genetic mechanisms underlying tumor microenvironment composition and function in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2024, 143, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlov, N.; Bagaev, A.; Revuelta, M.V.; Phillip, J.M.; Cacciapuoti, M.T.; Antysheva, Z.; Svekolkin, V.; Tikhonova, E.; Miheecheva, N.; Kuzkina, N.; et al. Clinical and Biological Subtypes of B-cell Lymphoma Revealed by Microenvironmental Signatures. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1468–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, D.; Silwal-Pandit, L.; Dannenfelser, R.; Langerød, A.; Vollan, H.K.M.; Vaske, C.; Siegel, J.U.; Troyanskaya, O.; Chin, S.-F.; Caldas, C.; et al. Lymphocyte Invasion in IC10/Basal-Like Breast Tumors Is Associated with Wild-Type TP53. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiem, A.; Hesbacher, S.; Kneitz, H.; di Primio, T.; Heppt, M.V.; Hermanns, H.M.; Goebeler, M.; Meierjohann, S.; Houben, R.; Schrama, D. IFN-gamma-induced PD-L1 expression in melanoma depends on p53 expression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taura, M.; Eguma, A.; Suico, M.A.; Shuto, T.; Koga, T.; Komatsu, K.; Komune, T.; Sato, T.; Saya, H.; Li, J.-D.; et al. p53 Regulates Toll-Like Receptor 3 Expression and Function in Human Epithelial Cell Lines. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 6557–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Saha, S.; Bettke, J.; Nagar, R.; Parrales, A.; Iwakuma, T.; van der Velden, A.W.M.; Martinez, L.A. Mutant p53 suppresses innate immune signaling to promote tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 494–508.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, D.; Shatz, M.; Azzam, K.; Garantziotis, S.; Fessler, M.B.; Resnick, M.A. The Toll-Like Receptor Gene Family Is Integrated into Human DNA Damage and p53 Networks. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Kihira, S.; Liu, C.L.; Nair, R.V.; Salari, R.; Gentles, A.J.; Irish, J.; Stehr, H.; Vicente-Dueñas, C.; Romero-Camarero, I.; et al. Mutations in early follicular lymphoma progenitors are associated with suppressed antigen presentation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1116–E1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashwah, H.; Schmid, C.A.; Kasser, S.; Bertram, K.; Stelling, A.; Manz, M.G.; Müller, A. Inactivation of CREBBP expands the germinal center B cell compartment, down-regulates MHCII expression and promotes DLBCL growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9701–9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangolini, M.; Maiques-Diaz, A.; Charalampopoulou, S.; Gerhard-Hartmann, E.; Bloehdorn, J.; Moore, A.; Giachetti, G.; Lu, J.; Roamio Franklin, V.N.; Chilamakuri, C.S.R.; et al. Viral transduction of primary human lymphoma B cells reveals mechanisms of NOTCH-mediated immune escape. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonato, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Bomben, R.; Canarutto, G.; Felician, G.; Martines, C.; Zucchetto, A.; Pozzo, F.; Vujovikj, M.; Polesel, J.; et al. NFKBIE mutations are selected by the tumor microenvironment and contribute to immune escape in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia, 2024; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucco, F.; Barrans, S.; Sha, C.; Clipson, A.; Crouch, S.; Dobson, R.; Chen, Z.; Thompson, J.S.; Care, M.A.; Cummin, T.; et al. Distinct genetic changes reveal evolutionary history and heterogeneous molecular grade of DLBCL with MYC/BCL2 double-hit. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, L.; Fernández-Miranda, I.; Pérez-Callejo, D.; Quero, C.; Rodríguez, M.; Martín-Acosta, P.; Gómez, S.; González-Rincón, J.; Santos, A.; Tarin, C.; et al. Proposal and validation of a method to classify genetic subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.; Fu, D.; Dong, L.; Zhang, M.-C.; Shi, Q.; Shi, Z.-Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, L.; Xu, P.-P.; Zhao, W.-L. Simplified algorithm for genetic subtyping in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, V.-S.; Vela, V.; Dirnhofer, S.; Dobbie, M.; Stenner, F.; Knoblich, J.; Tzankov, A.; Menter, T. Molecular Characterization and Genetic Subclassification Comparison of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Real-Life Experience with 74 Cases. Pathobiology, 2023; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Medeiros, L.J.; Li, Y.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Andreeff, M.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Greiner, T.C.; McDonnell, T.J.; Young, K.H. Dysfunction of the TP53 tumor suppressor gene in lymphoid malignancies. Blood 2012, 119, 3668–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.-J.J.; Horsman, D.E.; Gascoyne, R.D. The significance of TP53 in lymphoid malignancies: Mutation prevalence, regulation, prognostic impact and potential as a therapeutic target. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 146, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peller, S.; Rotter, V. TP53 in hematological cancer: Low incidence of mutations with significant clinical relevance. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskelund, C.W.; Dahl, C.; Hansen, J.W.; Westman, M.; Kolstad, A.; Pedersen, L.B.; Montano-Almendras, C.P.; Husby, S.; Freiburghaus, C.; Ek, S.; et al. TP53 mutations identify younger mantle cell lymphoma patients who do not benefit from intensive chemoimmunotherapy. Blood 2017, 130, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Cerri, M.; Deambrogi, C.; Sozzi, E.; Cresta, S.; Rasi, S.; De Paoli, L.; Spina, V.; Gattei, V.; Capello, D.; et al. The prognostic value of TP53 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is independent of Del17p13: Implications for overall survival and chemorefractoriness. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenz, T.; Eichhorst, B.; Busch, R.; Denzel, T.; Häbe, S.; Winkler, D.; Bühler, A.; Edelmann, J.; Bergmann, M.; Hopfinger, G.; et al. TP53 mutation and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4473–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilda, M.; Bruch, J.; Harder, L.; Rawer, D.; Reiter, A.; Borkhardt, A.; Woessmann, W. Inactivation of the ARF-MDM-2-p53 pathway in sporadic Burkitt’s lymphoma in children. Leukemia 2004, 18, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkozy, C.; Hung, S.S.; Chavez, E.A.; Duns, G.; Takata, K.; Chong, L.C.; Aoki, T.; Jiang, A.; Miyata-Takata, T.; Telenius, A.; et al. Mutational landscape of gray zone lymphoma. Blood 2021, 137, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.-H.; Chang, W.-T.; Jou, S.-T.; Lin, T.-K.; Chang, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Lin, K.-H.; Lu, M.-Y.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, K.-H.; et al. TP53 alterations in relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Coco, F.; Gaidano, G.; Louie, D.C.; Offit, K.; Chaganti, R.S.; Dalla-Favera, R. p53 mutations are associated with histologic transformation of follicular lymphoma. Blood 1993, 82, 2289–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Lee, H.; Cho, J.; Yoon, S.E.; Kim, S.J.; Park, W.-Y.; Kim, W.S.; Ko, Y.H. Mutational Profile and Clonal Evolution of Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 628807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vousden, K.H.; Prives, C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of p53. Cell 2009, 137, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.L.; Levine, A.J. The p53 pathway: Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2899–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidarenko, O.; Xu, Y. Transcription activity is required for p53-dependent tumor suppression. Oncogene 2009, 28, 4397–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, G.; Moll, U.M. Mitochondrially targeted wild-type p53 suppresses growth of mutant p53 lymphomas in vivo. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6133–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voropaeva, E.N.; Pospelova, T.I.; Voevoda, M.I.; Maksimov, V.N.; Orlov, Y.L.; Seregina, O.B. Clinical aspects of TP53 gene inactivation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.H.; Leroy, K.; Møller, M.B.; Colleoni, G.W.B.; Sánchez-Beato, M.; Kerbauy, F.R.; Haioun, C.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Young, A.H.; Gaulard, P.; et al. Structural profiles of TP53 gene mutations predict clinical outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: An international collaborative study. Blood 2008, 112, 3088–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porpaczy, E.; Wohlfarth, P.; Königsbrügge, O.; Rabitsch, W.; Skrabs, C.; Staber, P.; Worel, N.; Müllauer, L.; Simonitsch-Klupp, I.; Kornauth, C.; et al. Influence of TP53 Mutation on Survival of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in the CAR T-Cell Era. Cancers 2021, 13, 5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.H.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Dave, B.J.; Smith, L.; Sanger, W.; Iqbal, J.; Campo, E.; Delabie, J.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Ott, G.; et al. Mutations in the DNA-binding codons of TP53, which are associated with decreased expression of TRAILreceptor-2, predict for poor survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2007, 110, 4396–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanel, W.; Marchenko, N.; Xu, S.; Yu, S.X.; Weng, W.; Moll, U. Two hot spot mutant p53 mouse models display differential gain of function in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Wu, L.; Visco, C.; Tai, Y.C.; Tzankov, A.; Liu, W.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Dybkær, K.; Chiu, A.; Orazi, A.; et al. Mutational profile and prognostic significance of TP53 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP: Report from an International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Blood 2012, 120, 3986–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobashi, A.; Togashi, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Yokoyama, M.; Tsuyama, N.; Baba, S.; Mori, S.; Hatake, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Noda, T.; et al. TP53 and OSBPL10 alterations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Prognostic markers identified via exome analysis of cases with extreme prognosis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19555–19568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenz, T.; Kreuz, M.; Fuge, M.; Klapper, W.; Horn, H.; Staiger, A.M.; Winter, D.; Helfrich, H.; Huellein, J.; Hansmann, M.-L.; et al. TP53 mutation and survival in aggressive B cell lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, P.; Yang, J.; Yang, S.; He, X.; Zhou, S.; Gui, L.; Lin, J.; Du, X.; et al. Characteristics and Management of TP53-Mutated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11515–11522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.-G.; Zhang, J.-J.; Li, N.; Cao, L.; Zhang, S.-Y. [Clinical Significance of P53, C-MYC and BCL-6 Abnormality in Patients with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2016, 24, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Gui, L.; He, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, S.; et al. Prognostic value of BCL2 and TP53 genetic alterations for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 19, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappella, A.; Diop, F.; Agostinelli, C.; Novo, M.; Nassi, L.; Evangelista, A.; Ciccone, G.; Di Rocco, A.; Martelli, M.; Melle, F.; et al. Prognostic impact of TP53 mutation in newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated in the FIL-DLCL04 trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, H.; Liu, B.; Shi, J.; Meng, F.; Liu, P.; Yang, J.; Yang, S.; He, X.; et al. Molecular profiling of Chinese R-CHOP treated DLBCL patients: Identifying a high-risk subgroup. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodero, A.; Guidetti, A.; Marino, F.; Tucci, A.; Barretta, F.; Re, A.; Balzarotti, M.; Carniti, C.; Monfrini, C.; Chiappella, A.; et al. Dose-adjusted EPOCH and rituximab for the treatment of double expressor and double-hit diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Impact of TP53 mutations on clinical outcome. Haematologica 2022, 107, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hong, X.; Song, Y.Q.; Hodkinson, B.; Balasubramanian, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Ibrutinib and rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone in patients with previously untreated non-germinal centre B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A Chinese subgroup analysis of the phase III PHOENIX trial. eJHaem 2022, 3, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Zi, J.; Liu, S.; Ge, Q.; Ge, Z. Mutational profiling of circulating tumor DNA and clinical characteristics in lymphoma: Based on next generation sequencing. Mol. Carcinog. 2023, 62, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, K.; Haioun, C.; Lepage, E.; Le Métayer, N.; Berger, F.; Labouyrie, E.; Meignin, V.; Petit, B.; Bastard, C.; Salles, G.; et al. p53 gene mutations are associated with poor survival in low and low-intermediate risk diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainuddin, N.; Berglund, M.; Wanders, A.; Ren, Z.-P.; Amini, R.-M.; Lindell, M.; Kanduri, M.; Roos, G.; Rosenquist, R.; Enblad, G. TP53 mutations predict for poor survival in de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of germinal center subtype. Leuk. Res. 2009, 33, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, A.; Kinoshita, T.; Watanabe, T.; Kato, H.; Nagai, H.; Tsushita, K.; Saito, H.; Hotta, T. Mutations of the p53 Gene as a Prognostic Factor in Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, C.; Arthur, S.; Alcaide, M.; Cheung, M.; Jiang, A.; Coyle, K.M.; Cleary, K.L.S.; Thomas, N.; Hilton, L.K.; Michaud, N.; et al. Genetic and evolutionary patterns of treatment resistance in relapsed B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2886–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, M.; Yi, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Ling, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; et al. Mutations or copy number losses of CD58 and TP53 genes in diffuse large B cell lymphoma are independent unfavorable prognostic factors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83294–83307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsburg, D.J.; Morrissette, J.J.; Nasta, S.D.; Barta, S.K.; Schuster, S.J.; Svoboda, J.; Chong, E.A.; Bagg, A. TP53 mutations predict for poor outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed aggressive B-cell lymphomas in the current era. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 7243–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albitar, M.; Zhang, H.; Goy, A.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Bhagat, G.; Visco, C.; Tzankov, A.; Fang, X.; Zhu, F.; Dybkaer, K.; et al. Determining clinical course of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using targeted transcriptome and machine learning algorithms. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.Y.; Perry, A.M.; Herrera, A.F.; Chen, L.; Skrabek, P.; Nasr, M.R.; Ottesen, R.A.; Nikowitz, J.; Bedell, V.; Murata-Collins, J.; et al. Double-hit signature with TP53 abnormalities predicts poor survival in patients with germinal center type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Shi, P.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Li, Z. A nomogram for predicting the rapid progression of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma established by combining baseline PET/CT total metabolic tumor volume, lesion diffusion, and TP53 mutations. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 16734–16743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Robrecht, S.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Cramer, P.; V Tresckow, J.; Lange, E.; Kiehl, M.; Dreyling, M.; Ritgen, M.; et al. Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)-a pooled analysis of German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG) front line treatment trials. Leukemia 2021, 35, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.A.; Bazinet, A.; Wierda, W.G.; Tam, C.S.; O’Brien, S.M.; Saha, S.; Peterson, C.B.; Plunkett, W.; Keating, M.J. Sustained remissions in CLL after frontline FCR treatment with very-long-term follow-up. Blood 2023, 142, 1784–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.A.; Siddiqi, T. Treatment of Richter’s syndrome. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2022, 2022, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Gaidano, G. Biology and treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood 2018, 131, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Deambrogi, C.; Rasi, S.; Laurenti, L.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Arcaini, L.; Lucioni, M.; Rocque, G.B.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; et al. The genetics of Richter syndrome reveals disease heterogeneity and predicts survival after transformation. Blood 2011, 117, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, G.; Khiabanian, H.; Holmes, A.B.; Wang, J.; Messina, M.; Mullighan, C.G.; Pasqualucci, L.; Rabadan, R.; Dalla-Favera, R. Genetic lesions associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia transformation to Richter syndrome. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2273–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chigrinova, E.; Rinaldi, A.; Kwee, I.; Rossi, D.; Rancoita, P.M.V.; Strefford, J.C.; Oscier, D.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Papadaki, T.; Berger, F.; et al. Two main genetic pathways lead to the transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to Richter syndrome. Blood 2013, 122, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klintman, J.; Appleby, N.; Stamatopoulos, B.; Ridout, K.; Eyre, T.A.; Robbe, P.; Pascua, L.L.; Knight, S.J.L.; Dreau, H.; Cabes, M.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic correlates of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2021, 137, 2800–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeu, F.; Royo, R.; Massoni-Badosa, R.; Playa-Albinyana, H.; Garcia-Torre, B.; Duran-Ferrer, M.; Dawson, K.J.; Kulis, M.; Diaz-Navarro, A.; Villamor, N.; et al. Detection of early seeding of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, E.M.; Leshchiner, I.; Guièze, R.; Johnson, C.; Tausch, E.; Parikh, S.A.; Lemvigh, C.; Broséus, J.; Hergalant, S.; Messer, C.; et al. Evolutionary history of transformation from chronic lymphocytic leukemia to Richter syndrome. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeksma, A.C.; Baliakas, P.; Moysiadis, T.; Puiggros, A.; Plevova, K.; Van der Kevie-Kersemaekers, A.-M.; Posthuma, H.; Rodriguez-Vicente, A.E.; Tran, A.N.; Barbany, G.; et al. Genomic arrays identify high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia with genomic complexity: A multi-center study. Haematologica 2021, 106, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teierle, S.M.; Huang, Y.; Kittai, A.S.; Bhat, S.A.; Grever, M.; Rogers, K.A.; Zhao, W.; Jones, D.; Byrd, J.C.; Avenarius, M.R.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients with CLL and CDKN2A/B deletion by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 7239–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broséus, J.; Hergalant, S.; Vogt, J.; Tausch, E.; Kreuz, M.; Mottok, A.; Schneider, C.; Dartigeas, C.; Roos-Weil, D.; Quinquenel, A.; et al. Molecular characterization of Richter syndrome identifies de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphomas with poor prognosis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierens, A.M.; Holte, H.; Warsame, A.; Ikonomou, I.M.; Wang, J.; Chan, W.C.; Delabie, J. Low levels of monoclonal small B cells in the bone marrow of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of activated B-cell type but not of germinal center B-cell type. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecka, A.; Tierens, A.; Østlie, I.; Schmitz, R.; Trøen, G.; Spetalen, S.; Staudt, L.M.; Smeland, E.; Holte, H.; Delabie, J. Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with clonally-related monoclonal B lymphocytosis indicates a common precursor cell. Haematologica 2015, 100, e415–e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Martines, C.; Porro, F.; Fortunati, I.; Bonato, A.; Dimishkovska, M.; Piazza, S.; Yadav, B.S.; Innocenti, I.; Fazio, R.; et al. B-cell receptor signaling and genetic lesions in TP53 and CDKN2A/CDKN2B cooperate in Richter transformation. Blood 2021, 138, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerbeins, P.; Busch, R.; Anheier, N.; Dürig, J.; Bergmann, M.; Goebeler, M.-E.; Hurtz, H.-J.; Stauch, M.B.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Döhner, H.; et al. Poor efficacy and tolerability of R-CHOP in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter transformation. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, E239–E243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.-M.; O’Brien, S.; Khouri, I.; Giles, F.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Champlin, R.; Wen, S.; Do, K.-A.; Smith, S.C.; Lerner, S.; et al. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with Richter’s syndrome treated with chemotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy with or without stem-cell transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, E.M.; ten Hacken, E.; Wu, C.J. Richter syndrome: Novel insights into the biology of transformation. Blood 2023, 142, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herling, C.D.; Abedpour, N.; Weiss, J.; Schmitt, A.; Jachimowicz, R.D.; Merkel, O.; Cartolano, M.; Oberbeck, S.; Mayer, P.; Berg, V.; et al. Clonal dynamics towards the development of venetoclax resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardin, F.; Jais, J.-P.; Molina, T.-J.; Parmentier, F.; Picquenot, J.-M.; Ruminy, P.; Tilly, H.; Bastard, C.; Salles, G.-A.; Feugier, P.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas with CDKN2A deletion have a distinct gene expression signature and a poor prognosis under R-CHOP treatment: A GELA study. Blood 2010, 116, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilly, H.; Morschhauser, F.; Sehn, L.H.; Friedberg, J.W.; Trněný, M.; Sharman, J.P.; Herbaux, C.; Burke, J.M.; Matasar, M.; Rai, S.; et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin in Previously Untreated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russler-Germain, D.A.; Cliff, E.R.S.; Bartlett, N.L. Cell-of-origin effect of polatuzumab vedotin in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: No ordinary subgroup analysis. Blood 2023, 142, 2216–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.J.; Barrans, S.; Stanton, L.; Caddy, J.; Wilding, S.; Saunders, G.; Mamot, C.; Novak, U.; McMillan, A.; Fields, P.; et al. Differential Efficacy from the Addition of Bortezomib to R-CHOP in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma According to the Molecular Subgroup in the REMoDL-B Study with a 5-Year Follow-Up. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2718–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westin, J.; Davis, R.E.; Feng, L.; Hagemeister, F.; Steiner, R.; Lee, H.J.; Fayad, L.; Nastoupil, L.; Ahmed, S.; Rodriguez, A.; et al. Smart Start: Rituximab, Lenalidomide, and Ibrutinib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burack, W.R.; Li, H.; Adlowitz, D.; Spence, J.M.; Rimsza, L.M.; Shadman, M.; Spier, C.M.; Kaminski, M.S.; Leonard, J.P.; Leblanc, M.L.; et al. Subclonal TP53 mutations are frequent and predict resistance to radioimmunotherapy in follicular lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 5082–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, C.; Canzonieri, V.; Spina, M.; Michieli, M.; Ermacora, A.; Maestro, R.; Piccinin, S.; Bomben, R.; Dal Bo, M.; Trovo, M.; et al. Low-dose radiotherapy in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoops, L.; Haas, R.; de Kemp, S.; Majoor, D.; Broeks, A.; Eldering, E.; de Boer, J.P.; Verheij, M.; van Ostrom, C.; de Vries, A.; et al. In vivo p53 response and immune reaction underlie highly effective low-dose radiotherapy in follicular lymphoma. Blood 2007, 110, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassin, O.; Oren, M. Drugging p53 in cancer: One protein, many targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluzeau, T.; Sebert, M.; Rahmé, R.; Cuzzubbo, S.; Lehmann-Che, J.; Madelaine, I.; Peterlin, P.; Bève, B.; Attalah, H.; Chermat, F.; et al. Eprenetapopt Plus Azacitidine in TP53-Mutated Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Phase II Study by the Groupe Francophone des Myélodysplasies (GFM). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Goldberg, A.D.; Winer, E.S.; Altman, J.K.; Fathi, A.T.; Odenike, O.; Roboz, G.J.; Sweet, K.; Miller, C.; Wennborg, A.; et al. Eprenetapopt combined with venetoclax and azacitidine in TP53-mutated acute myeloid leukaemia: A phase 1, dose-finding and expansion study. Lancet Haematol. 2023, 10, e272–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Tamari, R.; DeZern, A.E.; Byrne, M.T.; Gooptu, M.; Chen, Y.-B.; Deeg, H.J.; Sallman, D.; Gallacher, P.; Wennborg, A.; et al. Eprenetapopt Plus Azacitidine after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for TP53-Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3985–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutz, A.; Lund, S.; Guidinger, J.; Weber, K.; Forberg, A.; Hartert, K.T. The DLBCL Axis of Low TNFRSF10B Expression, TP53 Loss, and a Cold Immune Microenvironment May be Addressed by the Synergistic Combination of Eprenetapopt and Idasnutlin. Blood 2022, 140, 6401–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wu, J.-L.; Liang, Y.; Tang, Y.-G.; Song, H.-X.; Wu, L.-L.; Xing, Y.-F.; Yan, N.; Li, Y.-T.; Wang, Z.-Y.; et al. Arsenic Trioxide Rescues Structural p53 Mutations through a Cryptic Allosteric Site. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 225–239.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Call, T.G.; Ding, W.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Leis, J.F.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Bowen, D.; Conte, M.; Schwager, S.M.; et al. The efficacy of ibrutinib in the treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood 2015, 125, 1676–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A.; Schuh, A.; Wierda, W.G.; Brown, J.R.; Ghia, P.; Pagel, J.M.; Furman, R.R.; Cheung, J.; Hamdy, A.; Izumi, R.; et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ACE-CL-001): Analysis of the Richter transformation cohort of an open-label, single-arm, phase 1–2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e912–e921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, C.; Munoz, J.; Cull, G.; Opat, S.; Allewelt, H.; Zhang, X.; Stern, J.C.; Hilger, J.; By, K.; Cohen, A.; et al. Zanubrutinib, Alone and in Combination with Tislelizumab, for the Treatment of Richter Transformation of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierda, W.G.; Lewis, D.J.; Ghia, P.; Shah, N.N.; Coombs, C.C.; Cheah, C.Y.; Lamanna, N.; Rhodes, J.M.; Hoffmann, M.; Ma, S.; et al. Efficacy of Pirtobrutinib, a Highly Selective, Non-Covalent (Reversible) BTK Inhibitor in Richter Transformation: Results from the Phase 1/2 BRUIN Study. Blood 2022, 140, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Rogers, K.A.; Tyekucheva, S.; Wang, Z.; Pazienza, S.; Renner, S.K.; Montegaard, J.; Ihuoma, U.; Lehmberg, T.Z.; Parry, E.M.; et al. Venetoclax plus dose-adjusted R-EPOCH for Richter syndrome. Blood 2022, 139, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davids, M.S.; Rogers, K.A.; Jain, N.; Tyekucheva, S.; Ren, Y.; Carey, C.; Montegaard, J.; Hajdenberg, M.; Ryan, C.E.; Merryman, R.; et al. Initial results of a multicenter phase 2 study of venetoclax in combination with R-CHOP (VR-CHOP) for patients with Richter Syndrome. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouval, R.; Alarcon Tomas, A.; Fein, J.A.; Flynn, J.R.; Markovits, E.; Mayer, S.; Olaide Afuye, A.; Alperovich, A.; Anagnostou, T.; Besser, M.J.; et al. Impact of TP53 Genomic Alterations in Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with CD19-Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, A.A.; Topper, M.J.; Dellomo, A.J.; Stojanovic, L.; McLaughlin, L.J.; Creed, T.M.; Eberly, C.L.; Kingsbury, T.J.; Baer, M.R.; Kessler, M.D.; et al. Activating STING1-dependent immune signaling in TP53 mutant and wild-type acute myeloid leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2123227119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number of Patients | Prevalence of TP53 Alterations | Complete Response Rate (TP53mut vs. TP53wt) a | Survival (TP53mut vs. TP53wt) a | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | 9% | 36% vs. 80% | 5-year OS 34% vs. 83% 5-year FFS 24% vs. 72% | [104] |
| 196 | 14.8% | Poor in TP53mut | Poor in TP53mut | [113] |
| 74 | 16.2% | 58% vs. 82% | 5-year OS 42% vs. 69% | [93] |
| 506 | 21.9% | 60% vs. 80% | 5-year OS 48% vs. 66% 5-year PFS 46% vs. 64% | [98] |
| 69 | 23% | N/A | 2-year OS 62% vs. 88% 2-year PFS 58% vs. 80% | [106] |
| 265 | 23.8% | 62% vs. 80% | 3-year OS 50% vs. 76% 3-year PFS 42% vs. 68% | [100] |
| 170 | 24.1% | N/A | Median OS: 12.55 months vs. not reached | [95] |
| 81 | 29% | 50% vs. 87% b | Poor OS, TTP in TP53mut | [105] |
| 191 | 30.9% | N/A | 5-year OS 53% vs. 66% 5-year PFS 30% vs. 36% | [103] |
| 117 | 36% | 55% vs. 77% | 2-year OS 70% vs. 99% 2-year PFS 57% vs. 77% | [114] |
| 477 | 21.4% | 57% vs. 69% c | 5-year OS 19% vs. 45% | [94] |
| 102 | 22% | 27% vs. 76% | 5-year OS 16% vs. 64% | [111] |
| 69 | 23% | 69% vs. 83% d | 6-year OS 44% vs. 79% | [109] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negara, I.; Tomuleasa, C.; Buruiana, S.; Efremov, D.G. Molecular Subtypes and the Role of TP53 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Richter Syndrome. Cancers 2024, 16, 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122170
Negara I, Tomuleasa C, Buruiana S, Efremov DG. Molecular Subtypes and the Role of TP53 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Richter Syndrome. Cancers. 2024; 16(12):2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122170
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegara, Ivan, Ciprian Tomuleasa, Sanda Buruiana, and Dimitar G. Efremov. 2024. "Molecular Subtypes and the Role of TP53 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Richter Syndrome" Cancers 16, no. 12: 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122170
APA StyleNegara, I., Tomuleasa, C., Buruiana, S., & Efremov, D. G. (2024). Molecular Subtypes and the Role of TP53 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Richter Syndrome. Cancers, 16(12), 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122170







