Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy as a Curative Treatment for De Novo Mucosal Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: A Feasible Alternative Option for Fragile Patients with Small Lesion: A Systematic Review †
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
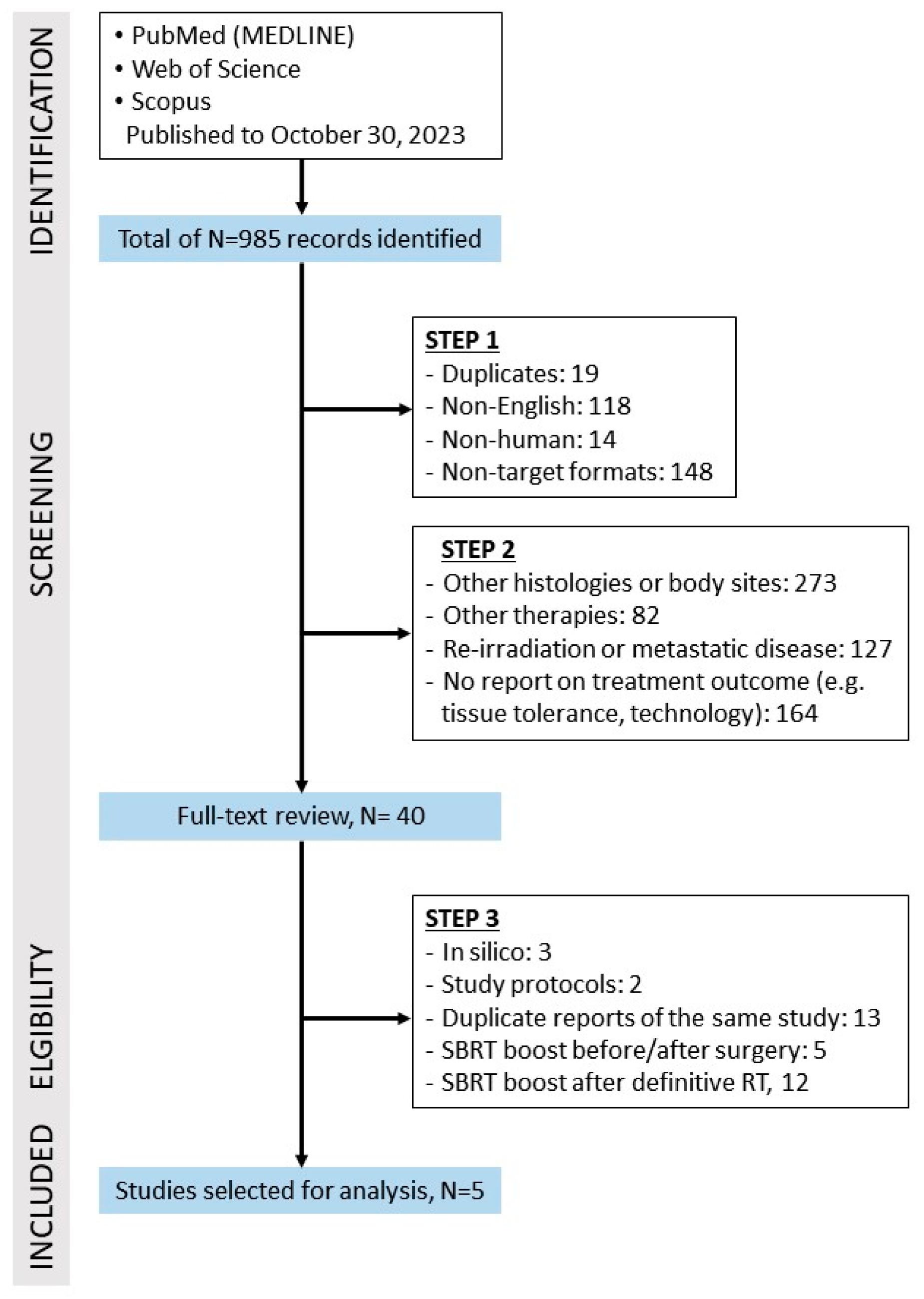
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Eligible Studies
3.2. Treatment Details
3.3. Toxicity
3.4. Tumor Control and Survival
3.5. Quality of Life
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karam, I.; Poon, I.; Lee, J.; Liu, S.; Higgins, K.; Enepekides, D.; Sahgal, A.; Lo, S.S. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for head and neck cancer: An addition to the armamentarium against head and neck cancer. Future Oncol. 2015, 11, 2937–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.W.; Glatstein, E.; Marks, L.B.; Emami, B.; Grimm, J.; Sperduto, P.W.; Kim, M.-S.; Hui, S.; Dusenbery, K.E.; Cho, L.C. Biological principles of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and stereotactic radiation surgery (SRS): Indirect cell death. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, C.; Morera, R.; Hernando, O.; Leroy, T.; Lartigau, S.E. Extracranial stereotactic body radiotherapy. Review of main SBRT features and indications in primary tumors. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2013, 18, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, S.H.; Yenice, K.M.; Followill, D.; Galvin, J.M.; Hinson, W.; Kavanagh, B.; Keall, P.; Lovelock, M.; Meeks, S.; Papiez, L.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy: The report of AAPM Task Group 101. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 4078–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viani, G.A.; Gouveia, A.G.; Yan, M.; Matsuura, F.K.; Moraes, F.Y. Stereotactic body radiotherapy versus surgery for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: An updated meta-analysis involving 29,511 patients included in comparative studies. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2022, 48, e20210390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.Q.; Su, T.S.; Wu, Q.Y.; Lin, Z.T.; Liang, S.X. Therapeutic outcome of stereotactic body radiotherapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma lesions—A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin. Oncol. (R Coll. Radiol.) 2023, 35, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishan, A.U.; Dang, A.; Katz, A.J.; Mantz, C.A.; Collins, S.P.; Aghdam, N.; Chu, F.-I.; Kaplan, I.D.; Appelbaum, L.; Fuller, D.B.; et al. Long-term outcomes of stereotactic body radiotherapy for low-risk and intermediate-risk prostate cancer. AMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e188006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrow, S.; Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P.; et al. Stereotactic radiation for the comprehensive treatment of oligometastases (SABR-COMET): Extended long-term outcomes. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiotto, M.; Fu, Y.X.; Weichselbaum, R.R. The intersection of radiotherapy and immunotherapy: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, EAAG1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, J.A.; Moiseenko, V.; Grimm, J.; Caudell, J.; Clump, D.A.; Yorke, E.; Xue, J.; Vinogradskiy, Y.; Moros, E.G.; Mavroidis, P.; et al. Head and neck tumor control probability: Radiation dose-volume effects in stereotactic body radiation therapy for locally recurrent previously-irradiated head and neck cancer: Report of the AAPM working group. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, I.; Yao, M.; E Heron, D.; Poon, I.; A Koyfman, S.; Yom, S.S.; Siddiqui, F.; Lartigau, E.; Cengiz, M.; Yamazaki, H.; et al. Survey of current practices from the International Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Consortium (ISBRTC) for head and neck cancers. Future Oncol. 2017, 13, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delerue, C.; Pasquier, D.; Bogart, E.; Mirabel, X.; Laffarguette, J.; Lals, S.; Barthoulot, M.; Lartigau, E.; Liem, X. Stereotactic reirradiation in the treatment of head and neck cancers: A retrospective study on the long-term experience of the Oscar Lambret Center. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 190, 110029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, B.I.; Soliman, H.; Moravan, V.; Myrehaug, S.; Tseng, C.-L.; Detsky, J.; Sahgal, A.; Warner, E.; Jerzak, K.J. Outcomes for oligometastatic head and neck cancer treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: Results from an international multi-institutional consortium. J. Neurooncol 2023, 164, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ 2015, 350, g7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. Br. Med. J. 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, J.F. 21 years of biologically effective dose. Br. J. Radiol. 2010, 83, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Sato, K.; Yamada, H.; Horie, A.; Nomura, T.; Iketani, S.; Kanai, I.; Suzuki, S.; Nakatani, Y.; Hamada, Y. Stereotactic radiosurgery in combination with chemotherapy as primary treatment for head and neck cancer. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, J.A.; Ferris, R.L.; Clump, D.A.; Heron, D.E. Stereotactic body radiotherapy as primary treatment for elderly patients with medically inoperable head and neck cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, D.J.; Timmerman, R.D.; Nedzi, L.; Ding, C.; Pham, N.-L.; Zhao, B.; Sumer, B.D. Phase 1 fractional dose-escalation study of equipotent stereotactic radiation therapy regimens for early-stage glottic larynx cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Assaf, H.; Erler, D.; Karam, I.; Lee, J.W.; Higgins, K.; Enepekides, D.; Zhang, L.; Eskander, A.; Poon, I. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for medically unfit patients with cancers to the head and neck. Head Neck 2020, 42, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogineni, E.; Rana, Z.; Vempati, P.; Karten, J.; Sharma, A.; Taylor, P.; Pereira, L.; Frank, D.; Paul, D.; Seetharamu, N.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy as primary treatment for elderly and medically inoperable patients with head and neck cancer. Head. Neck 2020, 42, 2880–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Simone, C.B. 2nd. Approaches to stereotactic body radiation therapy for large (≥5 centimeter) non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joiner, M.C.; van der Kogel, A.J. Basic Clinical Radiobiology, 5th ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, K.; Peters, L.J.; Weber, R.S.; Morrison, W.H.; Frankenthaler, R.A.; Garden, A.S.; Goepfert, H.; Ha, C.S.; Byers, R.M. Postoperative radiotherapy for cutaneous melanoma of the head and neck region. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 30, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozyigit, G.; Cengiz, M.; Hurmuz, P.; Yazici, G.; Gultekin, M.; Akyol, F.; Yildiz, F.; Gurkaynak, M.; Zorlu, F. Robotic stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with nasal cavity and paranasal sinus tumors. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 13, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Verduijn, G.M.; Petit, S.; Sewnaik, A.; Mast, H.; Koljenović, S.; Nuyttens, J.J.; Heemsbergen, W.D. Long-term outcomes following stereotactic body radiotherapy boost for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Cheon, J.S.; Song, J.H.; Son, S.H.; Jang, J.S.; Kang, Y.N.; Kang, J.H.; Jung, S.L.; Yoo, I.R.; et al. Long-term outcome and toxicity of hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy as a boost treatment for head and neck cancer: The importance of boost volume assessment. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olteanu, L.A.M.; Duprez, F.; De Neve, W.; Berwouts, D.; Vercauteren, T.; Bauters, W.; Deron, P.; Huvenne, W.; Bonte, K.; Goethals, I.; et al. Late mucosal ulcers in dose-escalated adaptive dose-painting treatments for head-and-neck cancer. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.-H.; Yu, T.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.M.; Chung, E.-J.; Kwon, S.K.; Kim, J.-H.; Wu, H.-G. Early closure of a phase 1 clinical trial for SABR in early-stage glottic cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.R.; Decker, R.H. SBRT for early stage laryngeal cancer: Progress, but not quite ready for prime time. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörr, W.; Hendry, J.H. Consequential late effects in normal tissues. Radiother. Oncol. 2001, 61, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduijn, G.M.; Petit, S.F.; Lauwers, I.; van Norden, Y.; Sijtsema, N.D.; Sewnaik, A.; Mast, H.; Capala, M.; Nout, R.; Baker, S.; et al. Post radiation mucosal ulcer risk after a hypofractionated stereotactic boost and conventional fractionated radiotherapy for oropharyngeal carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2023, 62, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsley, P.J.; Perera, L.; Veness, M.J.; Stevens, M.J.; Eade, T.N.; Back, M.; Brown, C.; Jayamanne, D.T. Outcomes for elderly patients 75 years and older treated with curative intent radiotherapy for mucosal squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Head Neck 2020, 42, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haehl, E.; Rühle, A.; David, H.; Kalckreuth, T.; Sprave, T.; Stoian, R.; Becker, C.; Knopf, A.; Grosu, A.-L.; Nicolay, N.H. Radiotherapy for geriatric head-and-neck cancer patients: What is the value of standard treatment in the elderly? Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macià, I.; Garau, M. Radiobiology of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2017, 22, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Carlson, D.J.; Brenner, D.J. The tumor radiobiology of SRS and SBRT: Are more than the 5 Rs involved? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 88, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgioia, L.; Becherini, C.; Bacigalupo, A.; Bonomo, P. Chemo-immunotherapy and radiation in locally advanced head and neck cancer: Where do we stand? Oral. Oncol. 2022, 127, 105773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, I.; Karam, I.; El-Sehemy, A.; Abu-Gheida, I.; Al-Ibraheem, A.; Al-Assaf, H. The evolving role of stereotactic body radiation therapy for head and neck cancer: Where do we stand? Cancers 2023, 15, 5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, I.J.; Yadav, P.; Andersen, A.D.; Chen, Z.J.; Huang, L.; Langer, M.P.; Lee, C.; Li, L.; Popple, R.A.; Rice, R.K.; et al. Dose prescription and reporting in stereotactic body radiotherapy: A multi-institutional study. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 182, 109571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, W.C.; Yoon, W.S.; Koom, W.S.; Rim, C.H. Reirradiation using stereotactic body radiotherapy in the management of recurrent or second primary head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Oral. Oncol. 2020, 107, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Population | Patients with treatment-naive mucosal cancer of the head and neck. |
| Intervention | Stereotactic body radiotherapy, defined as the delivery of potentially ablative radiation doses, typically in 1–5 fractions (hypofractionation), with high precision to a well-defined and small target volume. |
| Control | No control groups. |
| Outcome | Primary outcomes: toxicity and local control. Secondary outcomes: regional control, progression-free survival, overall survival, quality of life. |
| Study design | Prospective and retrospective studies with more than 3 patients included. |
| Author (Ref) | Study Type | Recruitment Period | N | Age, Median (Years) | Criteria/Reasons for Referral to SBRT | Tumor Site | Histology | T-Stage | N-Stage | TNM Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kawaguchi et al., 2012 [19] | R | 3/2006–9/2007 | 14 | 73 | to avoid surgery/hospitalization, to achieve good cosmetic/functional result | oral cavity = 11 maxillary sinus = 2 oropharynx = 1 | SCC | T2 = 5 T3 = 3 T4 = 6 | N0 = 13 N1 = 1 | n.r. |
| Vargo et al., 2014 [20] | R | 2002–2013 | 5/12 | 88 | medical inoperability, well-lateralized tumor | base of tongue = 2 oral cavity = 1 maxillary sinus = 1 larynx = 1 | SCC | T2 = 1 T4 = 4 | N0 = all | II = 1 IVA = 4 |
| Sher et al., 2019 [21] | P | 11/2013–3/2017 | 12/29 | 61 1 | PS 0-1 | glottis | SCC | Tis-T2 | N0 = all | n.r. |
| Al Assaf et al., 2020 [22] | R | 10/2011–10/2016 | 48/114 | 81 1 | comorbidities, poor PS | different sites, n.s. | SCC, 69.3% 1 | n.s. | n.s. | n.r. |
| Gogineni et al., 2020 [23] | R | 8/2011–6/2018 | 45/66 | 80 1 | advanced age, comorbidities, bulky disease | oral cavity, 23 larynx, 5 hypopharynx 4 | SCC, 67% 1 | n.r. | n.r. | n.r. |
| Author (Ref) | Pre-Intervention | At Intervention | Post-Intervention | Overall Judgement of Bias | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias Due to Confounding | Bias in Selection of Participants into the Study | Bias in Classification of Intervention | Bias Due to Deviation from Intended Intervention | Bias Due to Missing Data | Bias in Measurement of Outcomes | Bias in Selection of the Reported Results | ||
| Kawaguchi et al., 2012 [19] | serious | serious | serious | serious | moderate | moderate | moderate | serious |
| Vargo et al., 2014 [20] | serious | serious | serious | moderate | moderate | low | moderate | serious |
| Sher et al., 2019 [21] | moderate | moderate | low | low | low | low | low | moderate |
| Al Assaf et al., 2020 [22] | serious | serious | serious | serious | serious | moderate | moderate | serious |
| Gogineni et al., 2020 [23] | serious | serious | serious | serious | serious | serious | moderate | serious |
| Author (Ref) | Delivery Platform and Immobilization | PTV, cm3 | Margins | Elective Nodal RT | Dose Prescription | RT Schedule | BED10 | EQD210 | Image Guidance | Systemic Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kawaguchi et al., 2012 [19] | CyberKnife, and custom-made mountpiece, thermoplastic mask | n.r. | n.r. | No | 80–85% isodose line, covering periphery of GTV | 35–42 Gy/5 fx | 59.5–77.28 Gy | 49.58–64.4 Gy | daily, 2 orthogonal kV x-ray sources | yes, all (S-1, 5-FU) |
| Vargo et al., 2014 [20] | CyberKnife Triology TrueBeam and thermoplastic mask | 41 | PTV = GTV; since 2012: PTV = GTV + 2–5 mm | No | n.r. | 44 Gy/5 fx 3 fx/wk | 82.72 Gy | 68.93 Gy | daily X-Sight skull tracking or CBCT or ExacTrac | yes, 2 pts (CMb) |
| Sher et al., 2019 [21] | CyberKnife and five-point thermoplastic mask | 5.3 1 | CTV = IGTV + 2 mm 2 PTV = CTV + 3 mm | No | 57–90% isodose line (median, 86%) 1 | 42.5 Gy/5 fx; 2 fx/wk | 78.63 Gy | 65.52 Gy | n.r. | no |
| Al Assaf et al., 2020 [22] | Elekta Synergy (IMRT, VMAT) and five-point thermoplastic mask | GTV, 33.2 1 | PTV = GTV + 3–5 mm | 12/114 pts: immediately adjacent nodal basins; PTV = CTV + 3–5 mm PTV D95% = 25 Gy | GTV D95 | 40–50 Gy/5 fx (89.8% of pts) 1; 1–2 fx/wk | 72–100 Gy | 60–83.33 Gy | daily, kV CBCT, | no |
| Gogineni et al., 2020 [23] | Gantry-based linear accelerator (VMAT) and standard thermoplastic mask | 32 1 | PTVprimary = GTV + 2 mm PTVnodal = CTV + 2 mm | NF primary: lateral retropharyngeal nodes; N+ pts: ipsilateral nodal regions II-IV; CTV = 30 Gy | PTV D95% = 98–100% | 35 Gy/5 fx (50% of pts) 1 40 Gy/5 fx (50% of ts); 1 2 fx/wk | 59.5–72 Gy | 49.58–60 Gy | daily, CBCT or kV | yes, 48% 1 |
| Author (Ref) | FUP, Median (mos) | LC | RC | Survival | Acute Toxicity G ≥ 3 | Late Toxicity G ≥ 3 | QoL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kawaguchi et al. 2012 [19] | 36 | 71.4% at 3 yrs 3 | 11/14 (78.6%) | OS 78.6% at 3 yrs | none | Osteoradionecrosis,1 (7.1%), 4 | n.r. |
| Vargo et al., 2014 [20] | 20 | 80% | 100% | 40%: DWOD 3 NED 2 | G3 dysphagia,1 (8.3%) 1 | G3 late mucositis, 1 (8.3%) 1 | UW-QoL-R: improved/stable QoL compared to baseline in 71% of pts (N = 7) 1 |
| Sher et al., 2019 [21] | 25.7 | 100% | 100% | 100% | none | G3 soft tissue and arytenoid necrosis, 1 (8.3%) | MDADI: no decline after treatment VHI: rapid improvement at FUP |
| Al Assaf et al., 2020 [22] | mean, 10.5 | 78.9% at 2 yrs | LRC outside PTV 89% at 1 yr | PFS 23.7 mos OS 40% at 2 yrs 2 | G3, 52.1% 1:
| G4 osteonecrosis, skin ulceration, 2 (4.2%) | n.r. |
| Gogineni et al., 2020 [23] | 15 | 73% at 1 yr 1 (13 pts with 24 mos FUP = 69%) | 73% at 1 yr 1 | OS 64% at 1 yr 1 | G3, 2 (3%) 1:
| none | n.r. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strojan, P.; Kokalj, M.; Plavc, G.; Ng, S.P.; Nuyts, S.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Eisbruch, A.; de Bree, R.; Chow, J.C.H.; Mäkitie, A.A.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy as a Curative Treatment for De Novo Mucosal Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: A Feasible Alternative Option for Fragile Patients with Small Lesion: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 2096. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112096
Strojan P, Kokalj M, Plavc G, Ng SP, Nuyts S, Chiesa-Estomba CM, Eisbruch A, de Bree R, Chow JCH, Mäkitie AA, et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy as a Curative Treatment for De Novo Mucosal Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: A Feasible Alternative Option for Fragile Patients with Small Lesion: A Systematic Review. Cancers. 2024; 16(11):2096. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112096
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrojan, Primož, Marko Kokalj, Gaber Plavc, Sweet Ping Ng, Sandra Nuyts, Carlos M. Chiesa-Estomba, Avraham Eisbruch, Remco de Bree, James C. H. Chow, Antti A. Mäkitie, and et al. 2024. "Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy as a Curative Treatment for De Novo Mucosal Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: A Feasible Alternative Option for Fragile Patients with Small Lesion: A Systematic Review" Cancers 16, no. 11: 2096. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112096
APA StyleStrojan, P., Kokalj, M., Plavc, G., Ng, S. P., Nuyts, S., Chiesa-Estomba, C. M., Eisbruch, A., de Bree, R., Chow, J. C. H., Mäkitie, A. A., Lopez, F., Saba, N. F., & Ferlito, A. (2024). Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy as a Curative Treatment for De Novo Mucosal Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: A Feasible Alternative Option for Fragile Patients with Small Lesion: A Systematic Review. Cancers, 16(11), 2096. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112096













