Using Patient-Specific 3D Modeling and Simulations to Optimize Microwave Ablation Therapy for Liver Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
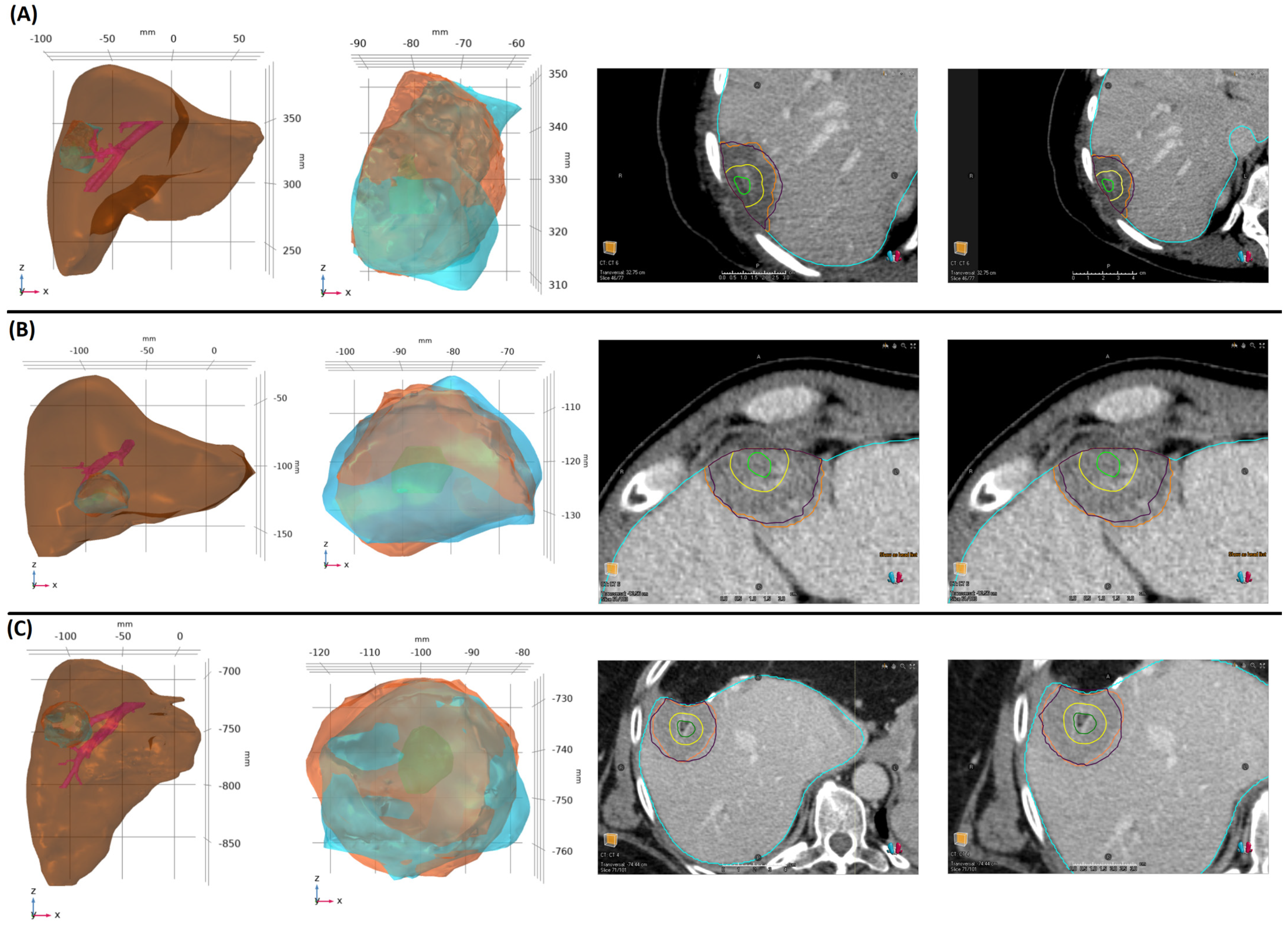
2.1. Patient Characteristics, Ablation Procedure, and Ablation Margins Assessment
2.2. Model Construction
2.3. Mathematical Model
2.4. Model Performance
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wells, S.A.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Lubner, M.G.; Ziemlewicz, T.J.; Brace, C.; Lee, F.T. Liver Ablation: Best Practice. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 53, 933–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radosevic, A.; Quesada, R.; Serlavos, C.; Sánchez, J.; Zugazaga, A.; Sierra, A.; Coll, S.; Busto, M.; Aguilar, G.; Flores, D.; et al. Microwave versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver malignancies: A randomized controlled phase 2 trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, T.J.; Martin, S.S.; Gruber-Rouh, T.; Booz, C.; Koch, V.; Nour-Eldin, N.-E.A.; Said, M.N.H. Comparison of Microwave and Radiofrequency Ablation for the Treatment of Small- and Medium-Sized Hepatocellular Carcinomas in a Prospective Randomized Trial. In RöFo-Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Röntgenstrahlen und der Bildgebenden Verfahren; Georg Thieme Verlag KG: Leipzig, Germany, 2024; Volume 196, pp. 482–490. [Google Scholar]
- Andreano, A.; Huang, Y.; Meloni, M.F.; Lee Jr, F.T.; Brace, C. Microwaves Create Larger Ablations than Radiofrequency When Controlled for Power in Ex Vivo Tissue. Med. Phys. 2010, 37 Pt 1, 2967–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Converse, M.C.; Mahvi, D.M.; Webster, J.G. Measurement and Analysis of Tissue Temperature During Microwave Liver Ablation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 54, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, M.; Prakash, P.; Faridi, P.; Radosevic, A.; Curto, S.; Burdio, F.; Berjano, E. How Large Is the Periablational Zone after Radiofrequency and Microwave Ablation? Computer-Based Comparative Study of Two Currently Used Clinical Devices. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violi, N.V.; Duran, R.; Guiu, B.; Cercueil, J.-P.; Aubé, C.; Digklia, A.; Pache, I.; Deltenre, P.; Knebel, J.-F.; Denys, A. Efficacy of microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: A randomised controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adwan, H.; Vogl, T.J.; Balaban, Ü.; Nour-Eldin, N.-E.A. Percutaneous Thermal Ablation Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): Microwave Ablation (MWA) versus Laser-Induced Thermotherapy (LITT). Diagnostics 2022, 12, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreozzi, A.; Brunese, L.; Iasiello, M.; Tucci, C.; Vanoli, G.P. Numerical analysis of the pulsating heat source effects in a tumor tissue. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 200, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreozzi, A.; Brunese, L.; Iasiello, M.; Tucci, C.; Vanoli, G.P. A novel local thermal non-equilibrium model for biological tissue applied to multiple-antennas configurations for thermal ablation. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2020, 79, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ning, Z.-Y.; Wang, P.; Zhuang, L.-P.; Xu, L.-T.; Zhu, Z.-F.; Sheng, J.; Shen, Y.-H.; Hua, Y.-Q.; Meng, Z.-Q. Combined ablation-chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for pancreatic cancer with liver metastasis: A propensity score matching study. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kei, S.K.; Rhim, H.; Choi, D.; Lee, W.J.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, Y.-S. Local Tumor Progression after Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Tumors: Analysis of Morphologic Pattern and Site of Recurrence. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laimer, G.; Schullian, P.; Jaschke, N.; Putzer, D.; Eberle, G.; Alzaga, A.; Odisio, B.; Bale, R. Minimal ablative margin (MAM) assessment with image fusion: An independent predictor for local tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma after stereotactic radiofrequency ablation. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2463–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Petre, E.N.; Gonen, M.; Do, K.G.; Brown, K.T.; Covey, A.M.; Brody, L.A.; Alago, W.; et al. Margin Size is an Independent Predictor of Local Tumor Progression after Ablation of Colon Cancer Liver Metastases. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shady, W.; Petre, E.N.; Gonen, M.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Brown, K.T.; Covey, A.M.; Alago, W.; Durack, J.C.; Maybody, M.; Brody, L.A.; et al. Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: Factors Affecting Outcomes—A 10-year Experience at a Single Center. Radiology 2016, 278, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandri, M.; Yamashita, S.; Gazzera, C.; Fonio, P.; Veltri, A.; Bustreo, S.; Sheth, R.A.; Yevich, S.M.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Odisio, B.C. Ablation of colorectal liver metastasis: Interaction of ablation margins and RAS mutation profiling on local tumour progression-free survival. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odisio, B.C.; Yamashita, S.; Huang, S.Y.; Harmoush, S.; Kopetz, S.E.; Ahrar, K.; Chun, Y.S.; Conrad, C.; Aloia, T.A.; Gupta, S.; et al. Local tumour progression after percutaneous ablation of colorectal liver metastases according to RAS mutation status. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-M.; Paolucci, I.; Brock, K.K.; Odisio, B.C. Image-Guided Ablation for Colorectal Liver Metastasis: Principles, Current Evidence, and the Path Forward. Cancers 2021, 13, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Wang, X.; Qu, J.; Lu, W.; Pang, Z.; Shao, T.; Xia, J.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Periprocedural risk factors for incomplete radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases from colorectal cancer: A single-center retrospective analysis. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izaaryene, J.; Drai, M.; Deniel, C.; Bridge, P.; Rico, G.; Daidj, N.; Gilabert, M.; Ewald, J.; Turrini, O.; Piana, G. Computed tomography-guided microwave ablation of perivascular liver metastases from colorectal cancer: A study of the ablation zone, feasibility, and safety. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Singh, T.; Soni, S. Pre-operative Assessment of Ablation Margins for Variable Blood Perfusion Metrics in a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based Complex Breast Tumour Anatomy: Simulation Paradigms in Thermal Therapies. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 198, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotirchos, V.S.; Petrovic, L.M.; Gönen, M.; Klimstra, D.S.; Do, R.K.G.; Petre, E.N.; Garcia, A.R.; Barlas, A.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Brown, K.T.; et al. Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: Biopsy of the Ablation Zone and Margins Can Be Used to Predict Oncologic Outcome. Radiology 2016, 280, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-M.; Paolucci, I.; O’connor, C.S.; Anderson, B.M.; Rigaud, B.; Fellman, B.M.; Jones, K.A.; Brock, K.K.; Odisio, B.C. Ablative Margins of Colorectal Liver Metastases Using Deformable CT Image Registration and Autosegmentation. Radiology 2023, 307, e221373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selmi, M.; Bajahzar, A.; Belmabrouk, H. Effects of target temperature on thermal damage during temperature-controlled MWA of liver tumor. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 31, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Moser, M.A.J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B. A review of antenna designs for percutaneous microwave ablation. Phys. Medica 2021, 84, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahi, H.; Prakash, P. Antenna Designs for Microwave Tissue Ablation. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 495–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Saija, C.; Choo, J.; Ou, Z.; Birsoan, M.; Germanos, S.; Rothwell, J.; Vakili, B.; Kotadia, I.; Xu, Z.; et al. Cardiac Radiofrequency Ablation Simulation Using a 3D-Printed Bi-Atrial Thermochromic Model. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valinoti, M.; Fabbri, C.; Turco, D.; Mantovan, R.; Pasini, A.; Corsi, C. 3D patient-specific models for left atrium characterization to support ablation in atrial fibrillation patients. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 45, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.-S.; Yun, Y.H.; Hong, S.-B.; Pak, H.-N.; Shim, E.B. A Patient-Specific Model of Virtual Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1522–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Loya, R.R.; Jutte, P.C.; Kwee, T.C.; van Ooijen, P.M.A. Computer 3D modeling of radiofrequency ablation of atypical cartilaginous tumours in long bones using finite element methods and real patient anatomy. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2022, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breschi, L.; Santos, E.; Camacho, J.C.; Solomon, S.B.; Ridouani, F. Preclinical assessment of a mathematical model for ablation zone prediction in thyroid laser ablation. Lasers Med. Sci. 2024, 39, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-M.; Paolucci, I.; Anderson, B.M.; O’connor, C.S.; Rigaud, B.; Briones-Dimayuga, M.; Jones, K.A.; Brock, K.K.; Fellman, B.M.; Odisio, B.C. Study Protocol COVER-ALL: Clinical Impact of a Volumetric Image Method for Confirming Tumour Coverage with Ablation on Patients with Malignant Liver Lesions. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 45, 1860–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.M.; Lin, Y.; Lin, E.Y.; Cazoulat, G.; Gupta, S.; Jones, A.K.; Odisio, B.C.; Brock, K.K. A novel use of biomechanical model-based deformable image registration (DIR) for assessing colorectal liver metastases ablation outcomes. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 6226–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Brace, C.L. Expanded modeling of temperature-dependent dielectric properties for microwave thermal ablation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 5249–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopresto, V.; Pinto, R.; Cavagnaro, M. Experimental characterisation of the thermal lesion induced by microwave ablation. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennes, H.H. Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm. J. Appl. Physiol. 1948, 1, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keangin, P.; Rattanadecho, P.; Wessapan, T. An analysis of heat transfer in liver tissue during microwave ablation using single and double slot antenna. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, B.; Xu, B. Theoretical evaluation of high frequency microwave ablation applied in cancer therapy. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 107, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvano, J.W.; Cochran, J.R.; Diller, K.R. Thermal conductivity and diffusivity of biomaterials measured with self-heated thermistors. Int. J. Thermophys. 1985, 6, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci, C.; Trujillo, M.; Berjano, E.; Iasiello, M.; Andreozzi, A.; Vanoli, G.P. Mathematical modeling of microwave liver ablation with a variable-porosity medium approach. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 214, 106569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Moser, M.A.; Zhang, E.M.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W. Numerical analysis of the relationship between the area of target tissue necrosis and the size of target tissue in liver tumours with pulsed radiofrequency ablation. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, M.; Thompson, L.; Cain, C.; Dewey, W. Time-temperature analysis of cell killing of BHK cells heated at temperatures in the range of 43.5 °C to 57.0 °C. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1990, 19, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, F.C., Jr. Studies of Thermal Injury; the Predictability and the Significance of Thermally Induced Rate Processes Leading to Irreversible Epidermal Injury. Arch. Pathol. 1947, 43, 489–502. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: II. Measurements in the frequency range 10 Hz to 20 GHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2251–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, W.C. Arrhenius relationships from the molecule and cell to the clinic. Int. J. Hyperth. 1994, 10, 457–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.A. Relationship between Arrhenius models of thermal damage and the CEM 43 thermal dose. In Energy-Based Treatment of Tissue and Assessment V; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7181, pp. 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, P.; Diederich, C.J. Considerations for theoretical modelling of thermal ablation with catheter-based ultrasonic sources: Implications for treatment planning, monitoring and control. Int. J. Hyperth. 2012, 28, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yu, M.-A.; Qiu, L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Zhao, Z.-L.; Wu, J.; Peng, L.-L.; Wang, Z.-L.; Xiao, R.-X. Theoretical Evaluation of Microwave Ablation Applied on Muscle, Fat and Bone: A Numerical Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanadecho, P.; Keangin, P. Numerical study of heat transfer and blood flow in two-layered porous liver tissue during microwave ablation process using single and double slot antenna. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 58, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stättner, S.; Jones, R.; Yip, V.; Buchanan, K.; Poston, G.; Malik, H.; Fenwick, S. Microwave ablation with or without resection for colorectal liver metastases. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2013, 39, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparchez, Z.; Mocan, T.; Radu, P.; Mocan, L.P.; Sparchez, M.; Leucuta, D.C.; Al Hajjar, N. Prognostic Factors after Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Impact of Incomplete Ablation on Recurrence and Overall Survival Rates. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2018, 27, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Ni, J.; Zuo, M.; Zhang, T.; Ma, R.; An, C.; Huang, J. Four types of tumor progression after microwave ablation of single hepatocellular carcinoma of ≤5 cm: Incidence, risk factors and clinical significance. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Ma, R.; Zhu, L. Quantitative evaluation of effects of coupled temperature elevation, thermal damage, and enlarged porosity on nanoparticle migration in tumors during magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 126, 105393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmilović-Radjenović, M.; Radjenović, D.; Radjenović, B. Finite element analysis of the effect of microwave ablation on the liver, lung, kidney, and bone malignant tissues. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 2022, 136, 28001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keangin, P.; Rattanadecho, P. A numerical investigation of microwave ablation on porous liver tissue. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 1687814017734133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, J.; Tan, W.; Abraham, J. Numerical Simulation of Microwave Ablation in the Human Liver. Processes 2022, 10, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenović, B.; Sabo, M.; Šoltes, L.; Prnova, M.; Čičak, P.; Radmilović-Radjenović, M. On Efficacy of Microwave Ablation in the Thermal Treatment of an Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffrè, M.; Zuliani, E.; Visintin, A.; Tarchi, P.; Martingano, P.; Pizzolato, R.; Bonazza, D.; Masutti, F.; Moretti, R.; Crocè, L.S. Predictors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Early Recurrence in Patients Treated with Surgical Resection or Ablation Treatment: A Single-Center Experience. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggi, G.; Montagna, B.; Di Cesare, P.; Riva, G.; Bernardo, G.; Mazzucco, M.; Riccardi, A. Microwave ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma using a new percutaneous device: Preliminary results. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Shi, J.; Ren, C.; Du, Z.; Shu, G.; Wang, Y. Survival analysis following microwave ablation or surgical resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma conforming to the Milan criteria. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 4066–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Dong, B.; Yu, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Feng, L.; Xiao, Q. Prognostic Factors for Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Percutaneous Microwave Ablation. Radiology 2005, 235, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radmilović-Radjenović, M.; Bošković, N.; Sabo, M.; Radjenović, B. An Analysis of Microwave Ablation Parameters for Treatment of Liver Tumors from the 3D-IRCADb-01 Database. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, M.H.H.; Soltani, M.; Kashkooli, F.M.; Raahemifar, K. Use of microwave ablation for thermal treatment of solid tumors with different shapes and sizes-A computational approach. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, G.; Ptaszek, L.M.; Zilberman, I.; Douglas, V.; Heist, E.K.; Beeckler, C.; Altmann, A.; Ruskin, J.N.; Govari, A.; Mansour, M. Safety and efficacy of delivering high-power short-duration radiofrequency ablation lesions utilizing a novel temperature sensing technology. EP Eur. 2018, 20, f444–f450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines-Peralta, A.U.; Pirani, N.; Clegg, P.; Cronin, N.; Ryan, T.P.; Liu, Z.; Goldberg, S.N. Microwave Ablation: Results with a 2.45-GHz Applicator in ex Vivo Bovine and in Vivo Porcine Liver. Radiology 2006, 239, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winokur, R.S.; Du, J.Y.; Pua, B.B.; Talenfeld, A.D.; Sista, A.K.; Schiffman, M.A.; Trost, D.W.; Madoff, D.C. Characterization of in Vivo Ablation Zones Following Percutaneous Microwave Ablation of the Liver with Two Commercially Available Devices: Are Manufacturer Published Reference Values Useful? J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1939–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlorogiannis, D.-D.; Sotirchos, V.S.; Georgiades, C.; Filippiadis, D.; Arellano, R.S.; Gonen, M.; Makris, G.C.; Garg, T.; Sofocleous, C.T. The Importance of Optimal Thermal Ablation Margins in Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 21 Studies. Cancers 2023, 15, 5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M. Modified Pennes bioheat equation with heterogeneous blood perfusion: A newer perspective. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 218, 124698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, A.; Iasiello, M.; Tucci, C. An Overview of Mathematical Models and Modulated-Heating Protocols for Thermal Ablation. Adv. Heat Transf. 2020, 52, 489–541. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, W. The Energy Conservation Equation for Living Tissue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1974, BME-21, 494–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, H.G. Heat Transfer in Perfused Biological Tissue—I: General Theory. Bull. Math. Biol. 1974, 36, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.M.; Holmes, K.R. MICROVASCULAR CONTRIBUTIONS IN TISSUE HEAT TRANSFER. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1980, 335, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, A.; Kuwahara, F. A General Bioheat Transfer Model Based on the Theory of Porous Media. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transf. 2008, 51, 3190–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
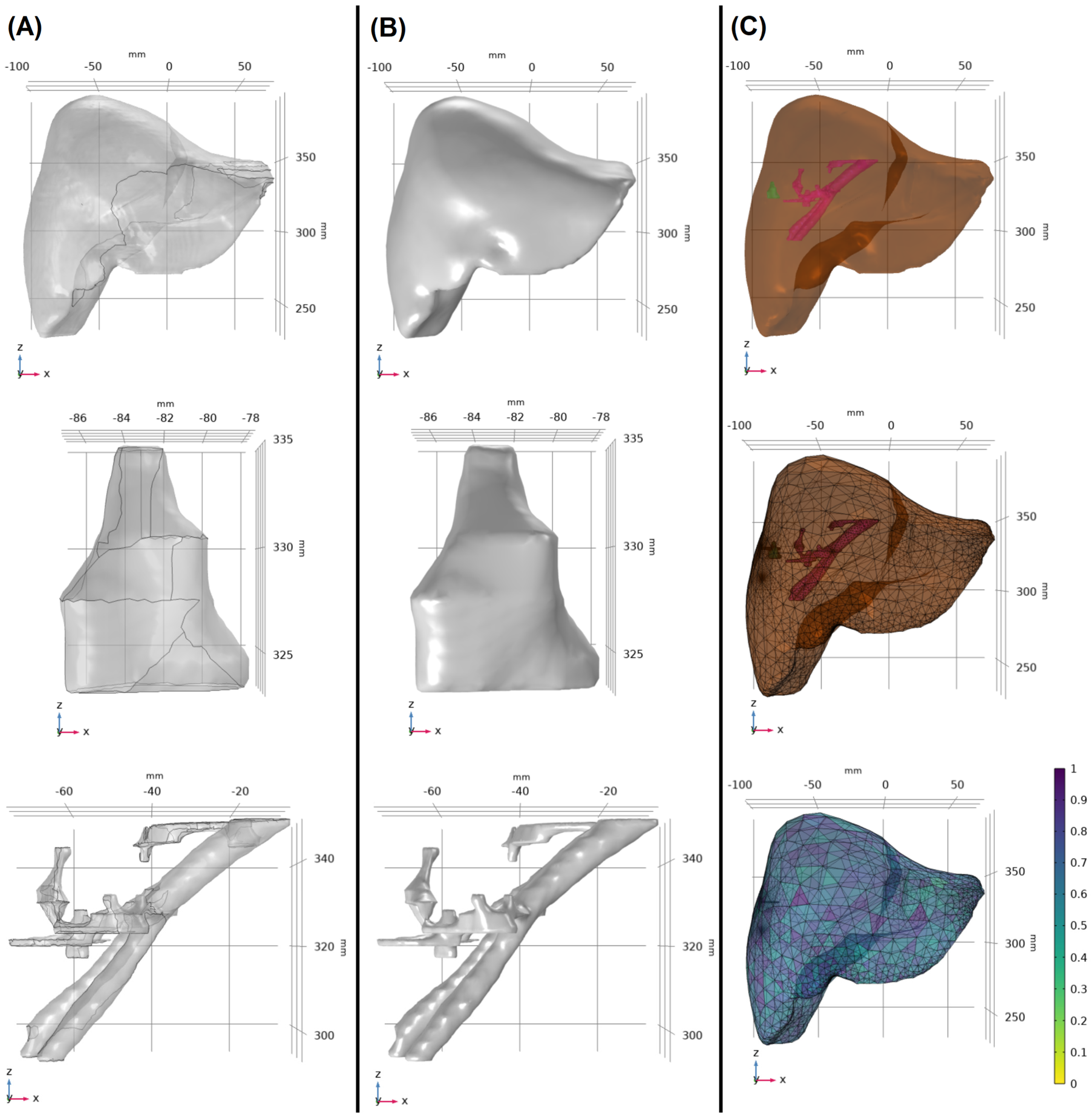
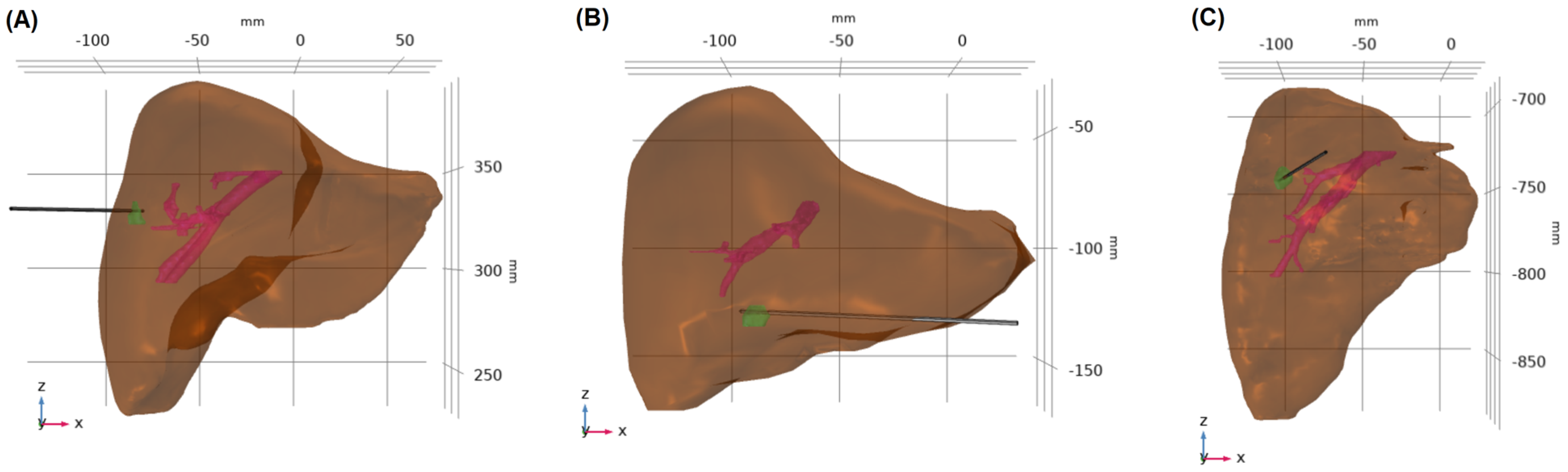
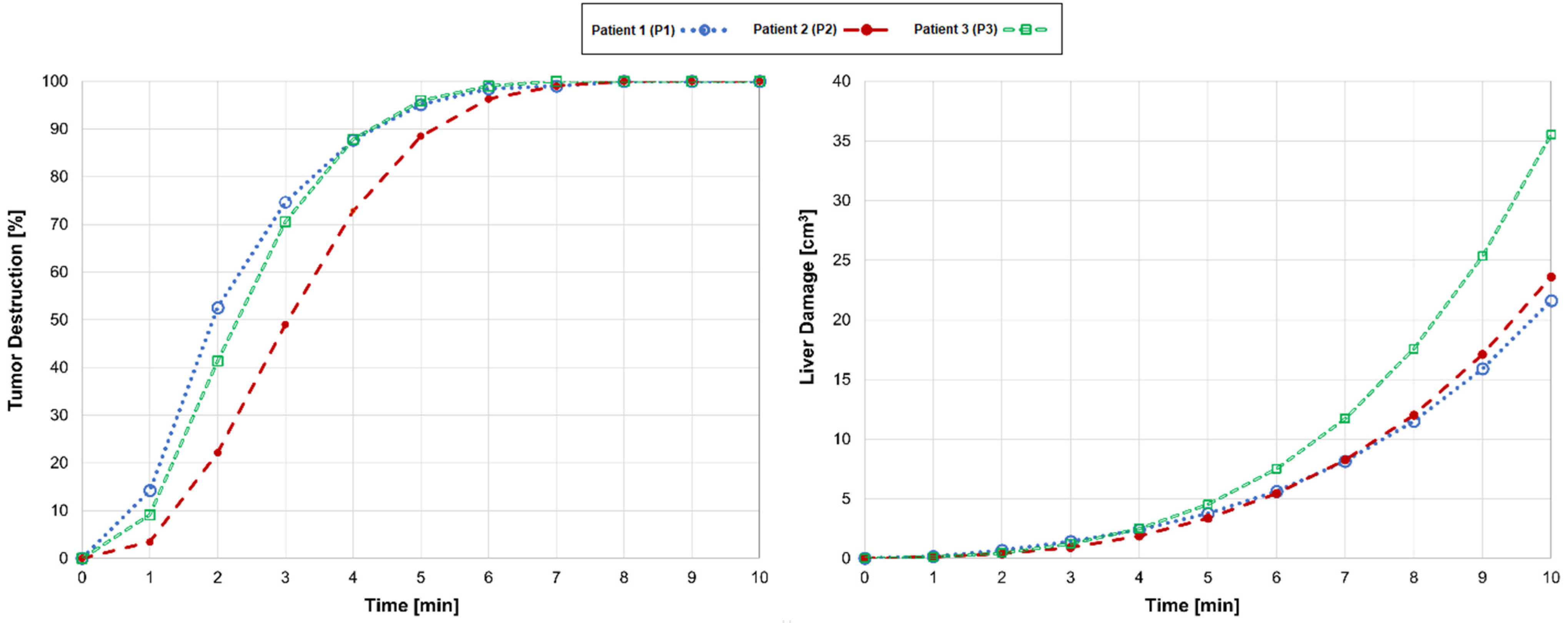
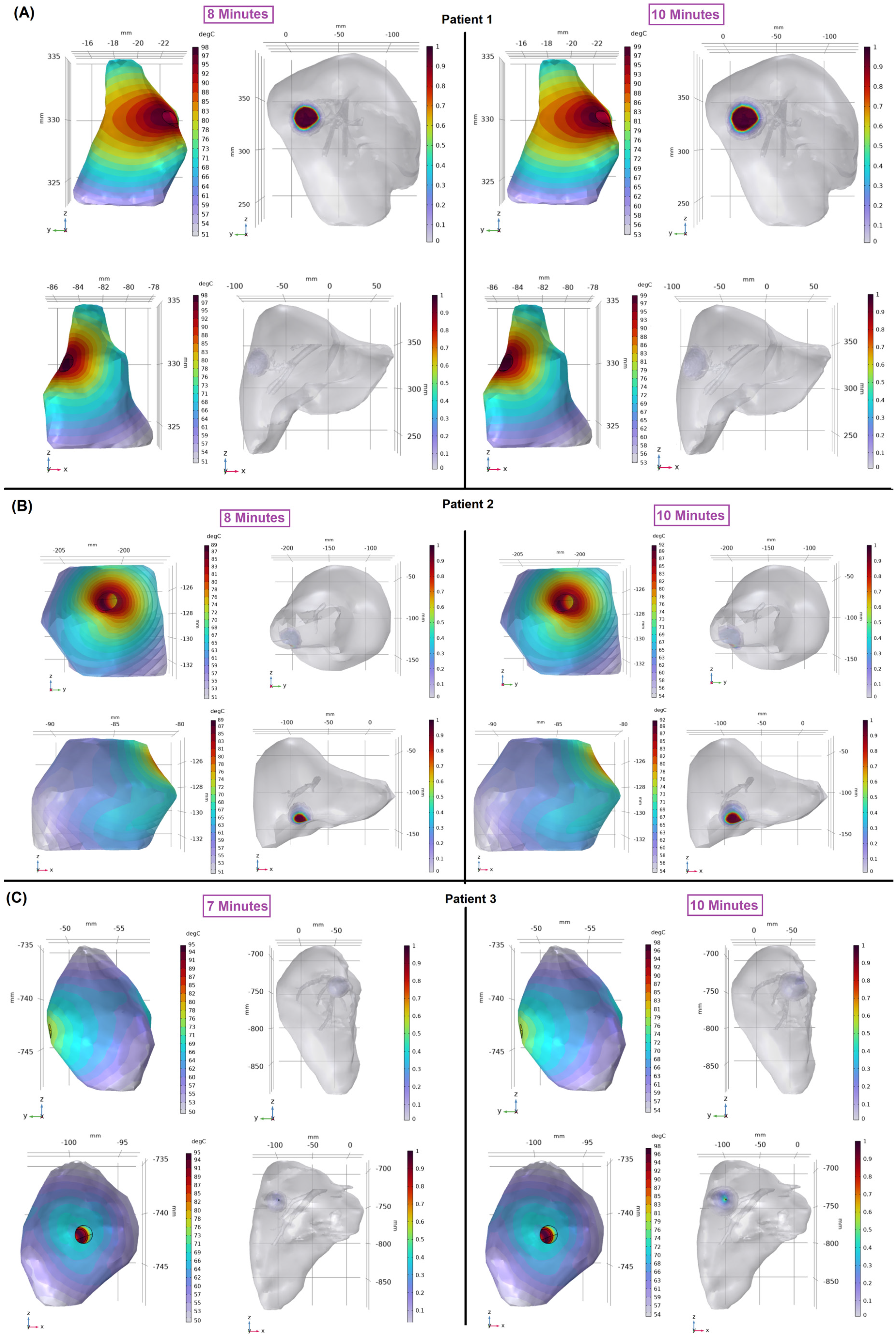
| Age | Sex | Tumor Histology | Specify Histology | Tumor Location | Tumor Size [cm3] | Liver Size [cm3] | Blood Vessels Size [cm3] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 41 | Female | Non-colorectal | Breast cancer liver metastasis | Right lobe (Segment 5–8) | 0.43 | 1288 | 7.3 |
| P2 | 51 | Male | Colorectal | - | Left medial (Segment 4) | 0.62 | 5547 | 2.1 |
| P3 | 64 | Female | Non-colorectal | Cholangiocarcinoma | Right lobe (Segment 5–8) | 0.88 | 1310 | 8.9 |
| Liver | Tumor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative permittivity () | 0.076 | 82.271 | 48.391 | 5.223 | 0.052 | 54.8 |
| Electrical conductivity () | 0.069 | 85.375 | 2.173 | 6.583 | 0.059 | 2 |
| Tissue | Electrical Conductivity (S/m) | Relative Permittivity | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Specific Heat (J/kg·K) | Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | Equation (3) | Equation (2) | Equation (9) | 3540 | 1079 |
| Tumor | Equation (3) | Equation (2) | Equation (9) | 3960 | 1040 |
| Blood vessels | 2.54 | 58.3 | 0.5 | 3600 | 1060 |
| Tissue | Activation Energy [J/mol] | Frequency Factor [1/s] |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | 2.58 × 105 | 7.39 × 1039 |
| Tumor | 2.81 × 105 | 3.25 × 104 |
| Ablation Time (min) | Dice Score | Sensitivity | Specificity | Mean DTA (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Model | Vendor Prediction | 3D Model | Vendor Prediction | 3D Model | Vendor Prediction | 3D Model | Vendor Prediction | ||
| P1 | 10 | 0.73 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.88 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
| 9.5 | 0.77 | - | 0.72 | - | 0.85 | - | 2.3 | - | |
| P2 | 10 | 0.86 | 0.54 | 0.79 | 0.38 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 1.2 | 4.3 |
| 9.5 | 0.83 | - | 0.72 | - | 0.98 | - | 1.2 | - | |
| P3 | 10 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.85 | 0.58 | 0.74 | 0.91 | 2.5 | 3.7 |
| 9.5 | 0.8 | - | 0.79 | - | 0.82 | - | 2.5 | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heshmat, A.; O’Connor, C.S.; Albuquerque Marques Silva, J.; Paolucci, I.; Jones, A.K.; Odisio, B.C.; Brock, K.K. Using Patient-Specific 3D Modeling and Simulations to Optimize Microwave Ablation Therapy for Liver Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112095
Heshmat A, O’Connor CS, Albuquerque Marques Silva J, Paolucci I, Jones AK, Odisio BC, Brock KK. Using Patient-Specific 3D Modeling and Simulations to Optimize Microwave Ablation Therapy for Liver Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(11):2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112095
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeshmat, Amirreza, Caleb S. O’Connor, Jessica Albuquerque Marques Silva, Iwan Paolucci, Aaron Kyle Jones, Bruno C. Odisio, and Kristy K. Brock. 2024. "Using Patient-Specific 3D Modeling and Simulations to Optimize Microwave Ablation Therapy for Liver Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 11: 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112095
APA StyleHeshmat, A., O’Connor, C. S., Albuquerque Marques Silva, J., Paolucci, I., Jones, A. K., Odisio, B. C., & Brock, K. K. (2024). Using Patient-Specific 3D Modeling and Simulations to Optimize Microwave Ablation Therapy for Liver Cancer. Cancers, 16(11), 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112095







