Development and Validation of an Explainable Radiomics Model to Predict High-Aggressive Prostate Cancer: A Multicenter Radiomics Study Based on Biparametric MRI
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. MRI Acquisition and Reference Standard
2.3. Tumor Segmentation and Feature Extraction
2.4. Model Development and Validation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Explanation of the Classification Model
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Best Model
3.3. Explanation of the Best Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dyba, T.; Randi, G.; Bettio, M.; Gavin, A.; Visser, O.; Bray, F. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 Countries and 25 Major Cancers in 2018. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 103, 356–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, N.; Conford, P.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E. EAU Guidelines. Edn. Presented at the EAU Annual Congress Amsterdam. In European Urology; EAU Guidelines Office: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 978-94-92671-07-3. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flach, R.N.; Willemse, P.-P.M.; Suelmann, B.B.M.; Deckers, I.A.G.; Jonges, T.N.; van Dooijeweert, C.; van Diest, P.J.; Meijer, R.P. Significant Inter- and Intralaboratory Variation in Gleason Grading of Prostate Cancer: A Nationwide Study of 35,258 Patients in The Netherlands. Cancers 2021, 13, 5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, S.; Shoag, J.E.; Gross, M.D.; Al Hussein Al Awamlh, B.; Robinson, B.; Khani, F.; Baltich Nelson, B.; Margolis, D.J.; Hu, J.C. Concordance Between Biopsy and Radical Prostatectomy Pathology in the Era of Targeted Biopsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.I.; Feng, Z.; Trock, B.J.; Pierorazio, P.M. Upgrading and Downgrading of Prostate Cancer from Biopsy to Radical Prostatectomy: Incidence and Predictive Factors Using the Modified Gleason Grading System and Factoring in Tertiary Grades. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The Bridge between Medical Imaging and Personalized Medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzo, S.; Bezzi, C.; Presotto, L.; Mapelli, P.; Bettinardi, V.; Savi, A.; Neri, I.; Preza, E.; Samanes Gajate, A.M.; De Cobelli, F.; et al. State of the Art of Radiomic Analysis in the Clinical Management of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 169, 103544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuocolo, R.; Cipullo, M.B.; Stanzione, A.; Romeo, V.; Green, R.; Cantoni, V.; Ponsiglione, A.; Ugga, L.; Imbriaco, M. Machine Learning for the Identification of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer on MRI: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6877–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleker, J.; Yakar, D.; van Noort, B.; Rouw, D.; de Jong, I.J.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Kwee, T.C.; Huisman, H. Single-center versus multi-center biparametric MRI radiomics approach for clinically significant peripheral zone prostate cancer. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, C.J.; Eggener, S.E.; Shindel, A.W.; Andriole, G.L. Variability in Outcomes for Patients with Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer (Gleason Score 7, International Society of Urological Pathology Gleason Group 2-3) and Implications for Risk Stratification: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. Focus 2017, 3, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.L.; Salinas, C.A.; Lin, D.W.; Kolb, S.; Koopmeiners, J.; Feng, Z.; Stanford, J.L. Prostate Cancer Specific Mortality and Gleason 7 Disease Differences in Prostate Cancer Outcomes between Cases with Gleason 4 + 3 and Gleason 3 + 4 Tumors in a Population Based Cohort. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 2702–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tollefson, M.K.; Leibovich, B.C.; Slezak, J.M.; Zincke, H.; Blute, M.L. Long-Term Prognostic Significance of Primary Gleason Pattern in Patients with Gleason Score 7 Prostate Cancer: Impact on Prostate Cancer Specific Survival. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertelli, E.; Mercatelli, L.; Marzi, C.; Pachetti, E.; Baccini, M.; Barucci, A.; Colantonio, S.; Gherardini, L.; Lattavo, L.; Pascali, M.A.; et al. Machine and Deep Learning Prediction Of Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness Using Multiparametric MRI. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 802964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatz, S.; Ackermann, J.; Mandel, P.; Kaltenbach, B.; Zhdanovich, Y.; Harter, P.N.; Döring, C.; Hammerstingl, R.; Bodelle, B.; Smith, K.; et al. Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms to Predict Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer of the Peripheral Zone with Multiparametric MRI Using Clinical Assessment Categories and Radiomic Features. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6757–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaddad, A.; Niazi, T.; Probst, S.; Bladou, F.; Anidjar, M.; Bahoric, B. Predicting Gleason Score of Prostate Cancer Patients Using Radiomic Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuocolo, R.; Stanzione, A.; Ponsiglione, A.; Romeo, V.; Verde, F.; Creta, M.; La Rocca, R.; Longo, N.; Pace, L.; Imbriaco, M. Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Detection on MRI: A Radiomic Shape Features Study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 116, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, V.; Mazzetti, S.; Defeudis, A.; Stranieri, G.; Calandri, M.; Bollito, E.; Bosco, M.; Porpiglia, F.; Manfredi, M.; De Pascale, A.; et al. A Fully Automatic Artificial Intelligence System Able to Detect and Characterize Prostate Cancer Using Multiparametric MRI: Multicenter and Multi-Scanner Validation. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 718155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, V.; Mazzetti, S.; Armando, E.; Carabalona, S.; Russo, F.; Giacobbe, A.; Muto, G.; Regge, D. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Prostate with Computer-Aided Detection: Experienced Observer Performance Study. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4200–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-Guided 3D Active Contour Segmentation of Anatomical Structures: Significantly Improved Efficiency and Reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, G.; Barra, D.; Defeudis, A.; Mazzetti, S.; Gatti, M.; Faletti, R.; Russo, F.; Regge, D.; Giannini, V. Virtual Biopsy in Prostate Cancer: Can Machine Learning Distinguish Low and High Aggressive Tumors on MRI? Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. Annu. Int. Conf. 2021, 2021, 3374–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-Based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Akoglu, H. User’s Guide to Correlation Coefficients. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; de Vet, H.C.W.; et al. STARD 2015: An Updated List of Essential Items for Reporting Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanzione, A.; Gambardella, M.; Cuocolo, R.; Ponsiglione, A.; Romeo, V.; Imbriaco, M. Prostate MRI Radiomics: A Systematic Review and Radiomic Quality Score Assessment. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 129, 109095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, A.; Meyer, H.J.; Wienke, A. Correlations between Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Gleason Score in Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaarslan, E.; Altan Kus, A.; Alis, D.; Karaarslan, U.C.; Saglican, Y.; Argun, O.B.; Kural, A.R. Performance of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values and Ratios for the Prediction of Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness across Different MRI Acquisition Settings. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 28, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrino, F.; Taghipour, M.; Hassanzadeh, E.; Ziaei, A.; Vangel, M.; Fedorov, A.; Tempany, C.M.; Fennessy, F.M. Predictive Role of PI-RADSv2 and ADC Parameters in Differentiating Gleason Pattern 3 + 4 and 4 + 3 Prostate Cancer. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, T.; Prabhu, V.; Li, J.; Babb, J.S.; Taneja, S.S.; Rosenkrantz, A.B. Assessment of Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Impact of Patient Race and Age. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibmer, A.; Hricak, H.; Gondo, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Veeraraghavan, H.; Fehr, D.; Zheng, J.; Goldman, D.; Moskowitz, C.; Fine, S.W.; et al. Haralick Texture Analysis of Prostate MRI: Utility for Differentiating Non-Cancerous Prostate from Prostate Cancer and Differentiating Prostate Cancers with Different Gleason Scores. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 2840–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


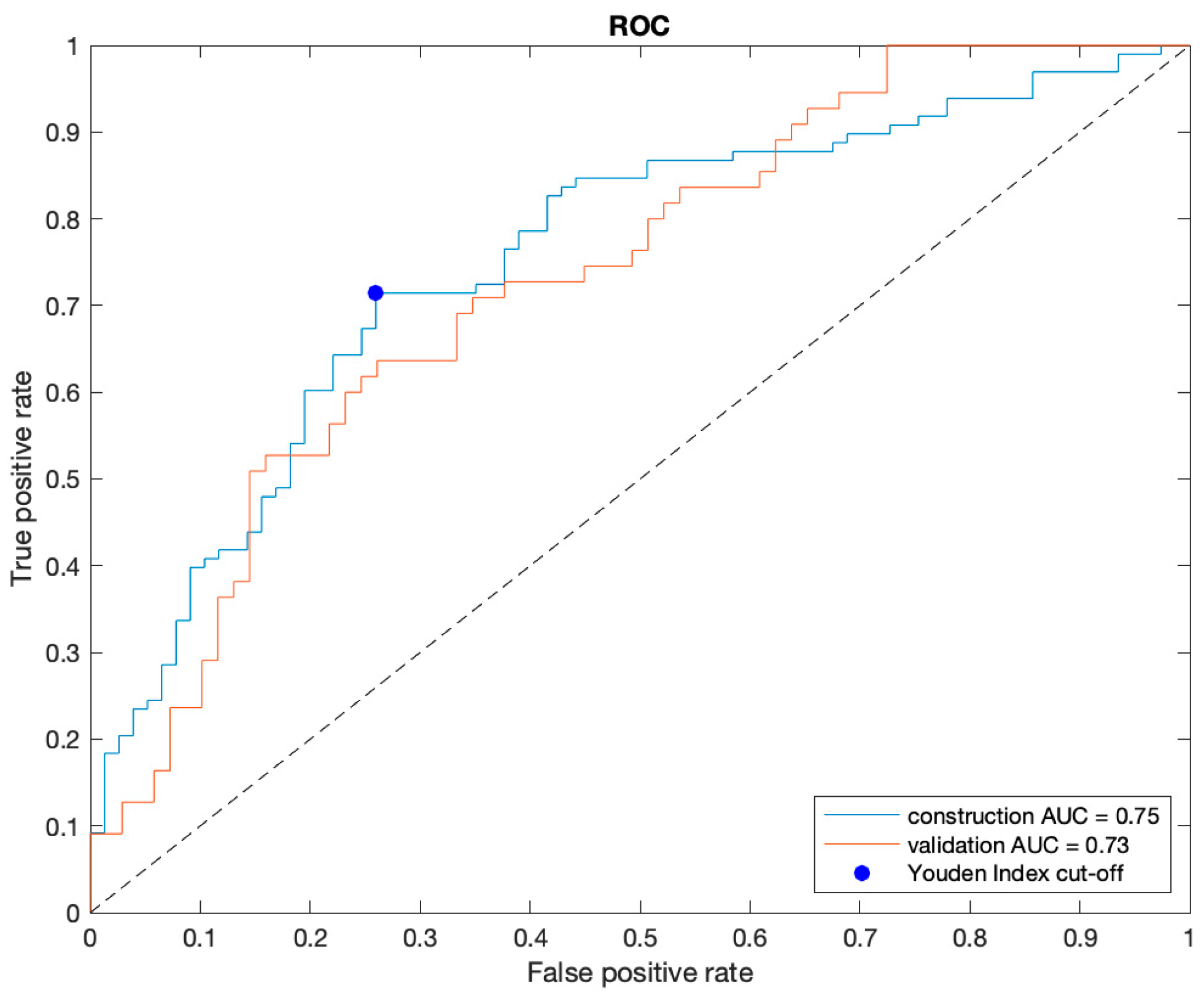
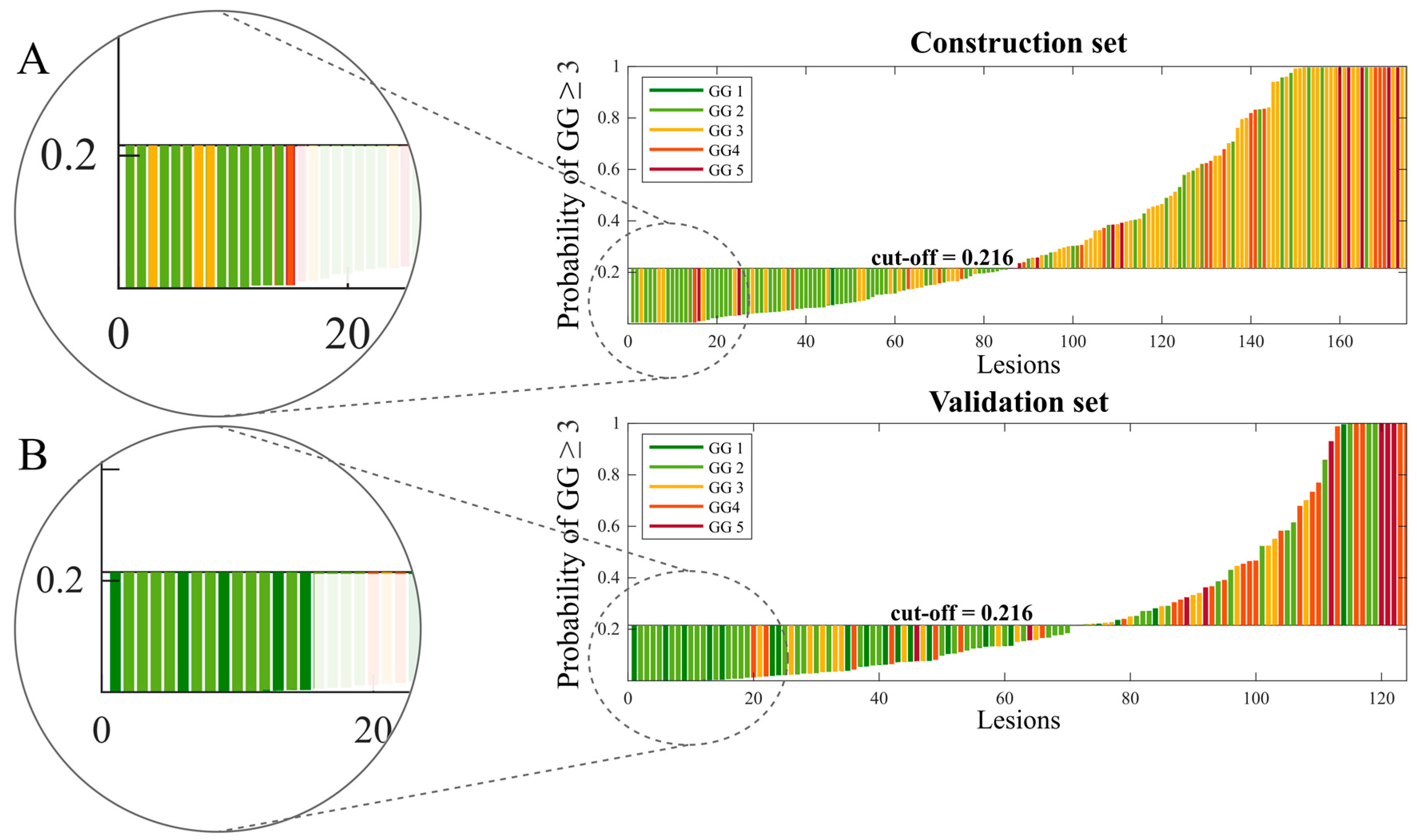

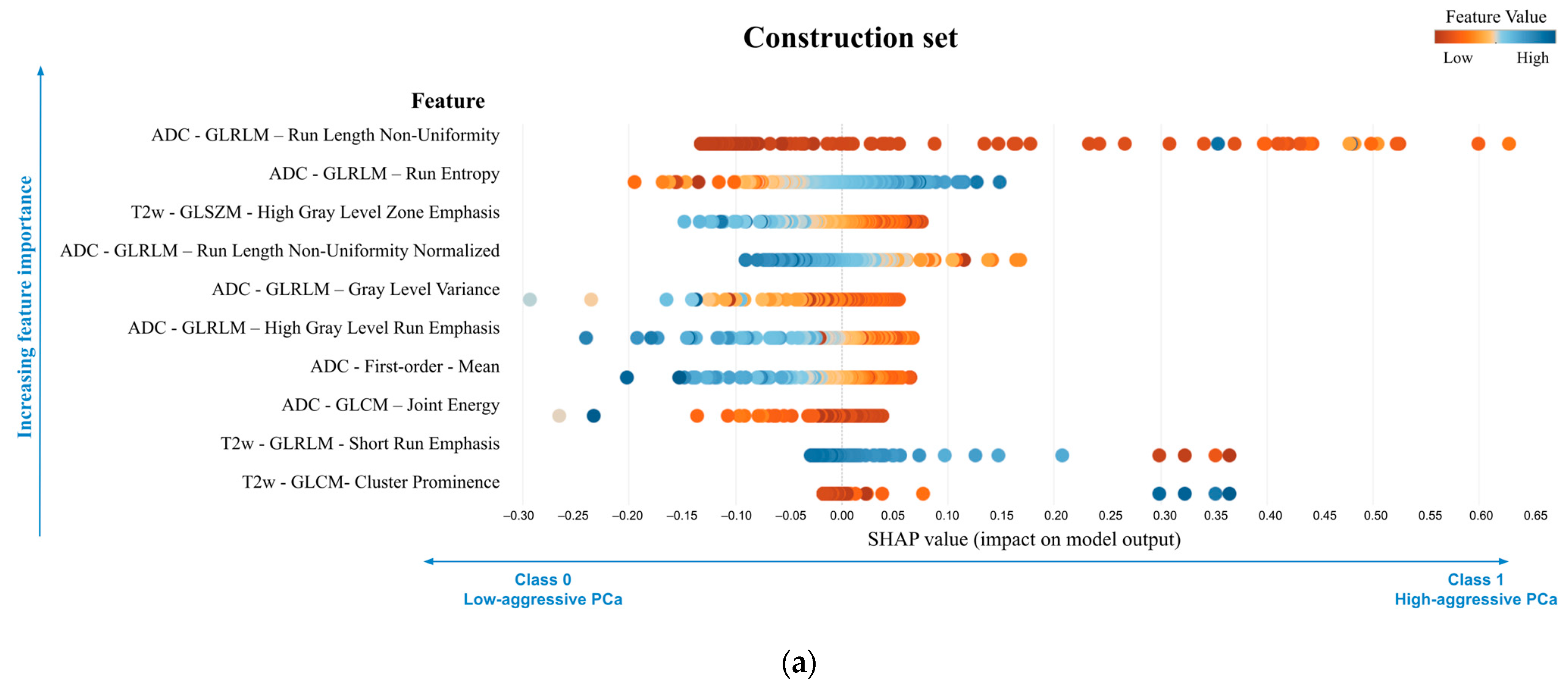


| Construction Set (Sample 1) vs. Validation Set (Sample 2) | Center C (Sample 1) vs. Center D (Sample 2) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (95%CI) | Balanced Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) (95%CI) | Specificity (%) (95%CI) | PPV (%) (95%CI) | NPV (%) (95%CI) | AUC (95%CI) | Balanced Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) (95%CI) | Specificity (%) (95%CI) | PPV (%) (95%CI) | NPV (%) (95%CI) | |
| Sample 1 | 0.75 (0.68–0.81) | 72.2 | 70.4 [69/98] (60.3–79.2) | 74.0 [57/77] (62.8–83.4) | 77.5 [69/89] (69.8–83.7) | 66.3 [57/86] (58.5–73.3) | 0.77 (0.67–0.86) | 69.4 | 55.2 [16/29] (35.7–73.5) | 83.7 [41/49] (70.3–92.7) | 66.7 [16/24] (49.5–80.3) | 75.9 [41/54] (67.4–82.8) |
| Sample 2 | 0.73 (0.65–0.81) | 67.9 | 61.8 [34/55] (47.7–74.6) | 73.9 [51/69] (61.9–83.7) | 65.4 [34/52] (54.7–74.7) | 70.8 [51/72] (62.8–77.7) | 0.63 (0.56–0.77) | 59.6 | 69.2 [18/26] (48.2–85.7) | 50.0 [10/20] (27.2–72.8) | 64.3 [18/28] (52.0–74.9) | 55.6 [10/18] (37.7–72.1) |
| p-value | 0.731 | 0.423 | 0.278 | 0.989 | 0.120 | 0.546 | 0.143 | 0.274 | 0.290 | 0.004 | 0.857 | 0.103 |
| |Diff| (95% CI) | 0.02 (−0.1–0.1) | 4.3 (−6.0–14.9) | 8.6 (−6.5–24.1) | 0.1 (−13.9–14.3) | 12.1 (−2.9–27.6) | 4.5 (−10.0–18.5) | 0.15 (−0.1–0.3) | 9.8 (−7.3–26.9) | 14.0 (−11.3–36.7) | 33.7 (9.95–55.2) | 2.4 (−22.6–26.4) | 20.3 (−3.4–44.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicoletti, G.; Mazzetti, S.; Maimone, G.; Cignini, V.; Cuocolo, R.; Faletti, R.; Gatti, M.; Imbriaco, M.; Longo, N.; Ponsiglione, A.; et al. Development and Validation of an Explainable Radiomics Model to Predict High-Aggressive Prostate Cancer: A Multicenter Radiomics Study Based on Biparametric MRI. Cancers 2024, 16, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010203
Nicoletti G, Mazzetti S, Maimone G, Cignini V, Cuocolo R, Faletti R, Gatti M, Imbriaco M, Longo N, Ponsiglione A, et al. Development and Validation of an Explainable Radiomics Model to Predict High-Aggressive Prostate Cancer: A Multicenter Radiomics Study Based on Biparametric MRI. Cancers. 2024; 16(1):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010203
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicoletti, Giulia, Simone Mazzetti, Giovanni Maimone, Valentina Cignini, Renato Cuocolo, Riccardo Faletti, Marco Gatti, Massimo Imbriaco, Nicola Longo, Andrea Ponsiglione, and et al. 2024. "Development and Validation of an Explainable Radiomics Model to Predict High-Aggressive Prostate Cancer: A Multicenter Radiomics Study Based on Biparametric MRI" Cancers 16, no. 1: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010203
APA StyleNicoletti, G., Mazzetti, S., Maimone, G., Cignini, V., Cuocolo, R., Faletti, R., Gatti, M., Imbriaco, M., Longo, N., Ponsiglione, A., Russo, F., Serafini, A., Stanzione, A., Regge, D., & Giannini, V. (2024). Development and Validation of an Explainable Radiomics Model to Predict High-Aggressive Prostate Cancer: A Multicenter Radiomics Study Based on Biparametric MRI. Cancers, 16(1), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010203












