Genomic Landscape of Endometrial, Ovarian, and Cervical Cancers in Japan from the Database in the Center for Cancer Genomics and Advanced Therapeutics
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
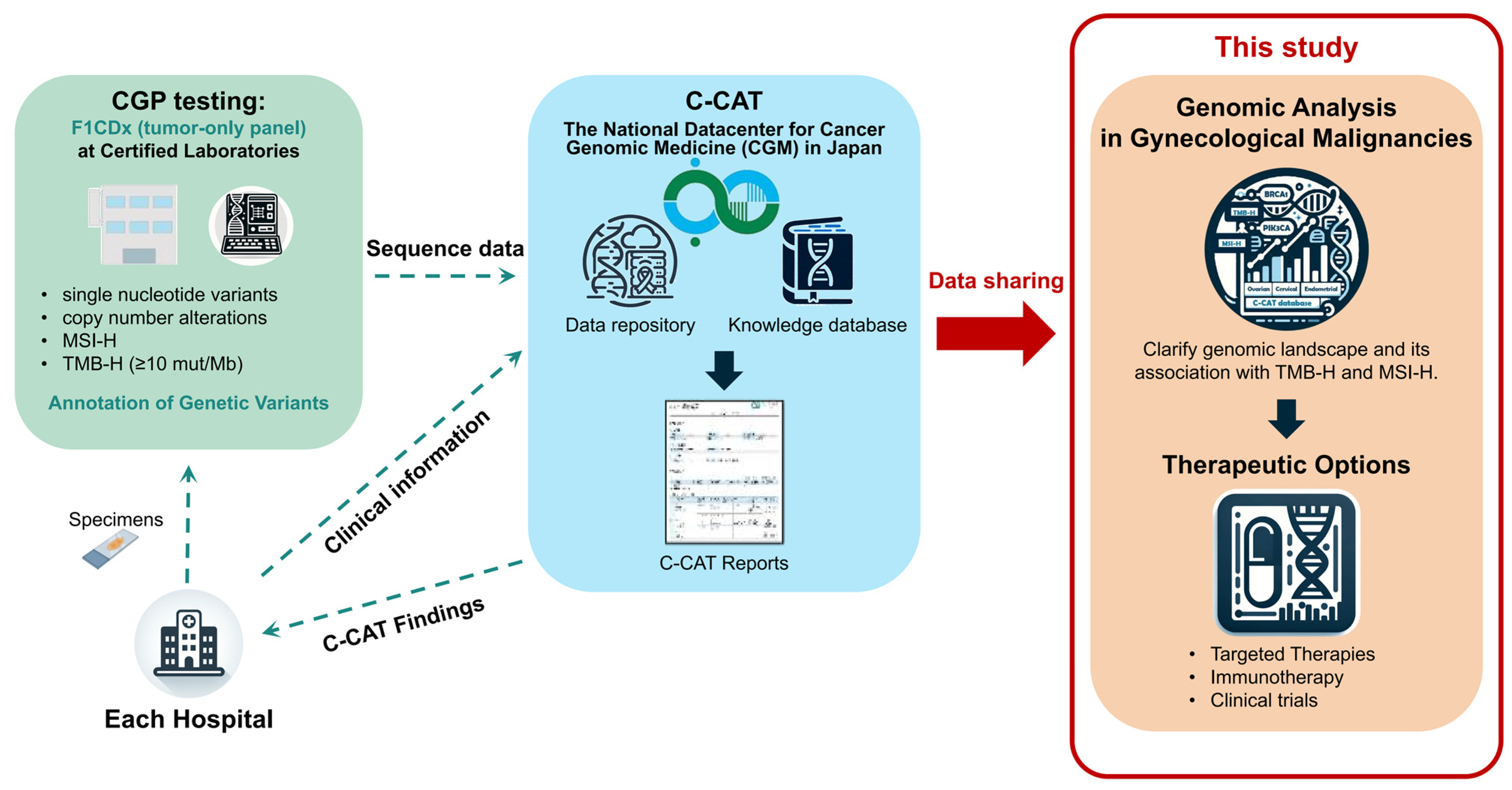
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples of FoundationOne® CDx (F1CDx) from the Center for Cancer Genomics and Advanced Therapeutics Database
2.2. F1CDx Testing
2.3. Statistical Analyses and Graphical Representations
3. Results
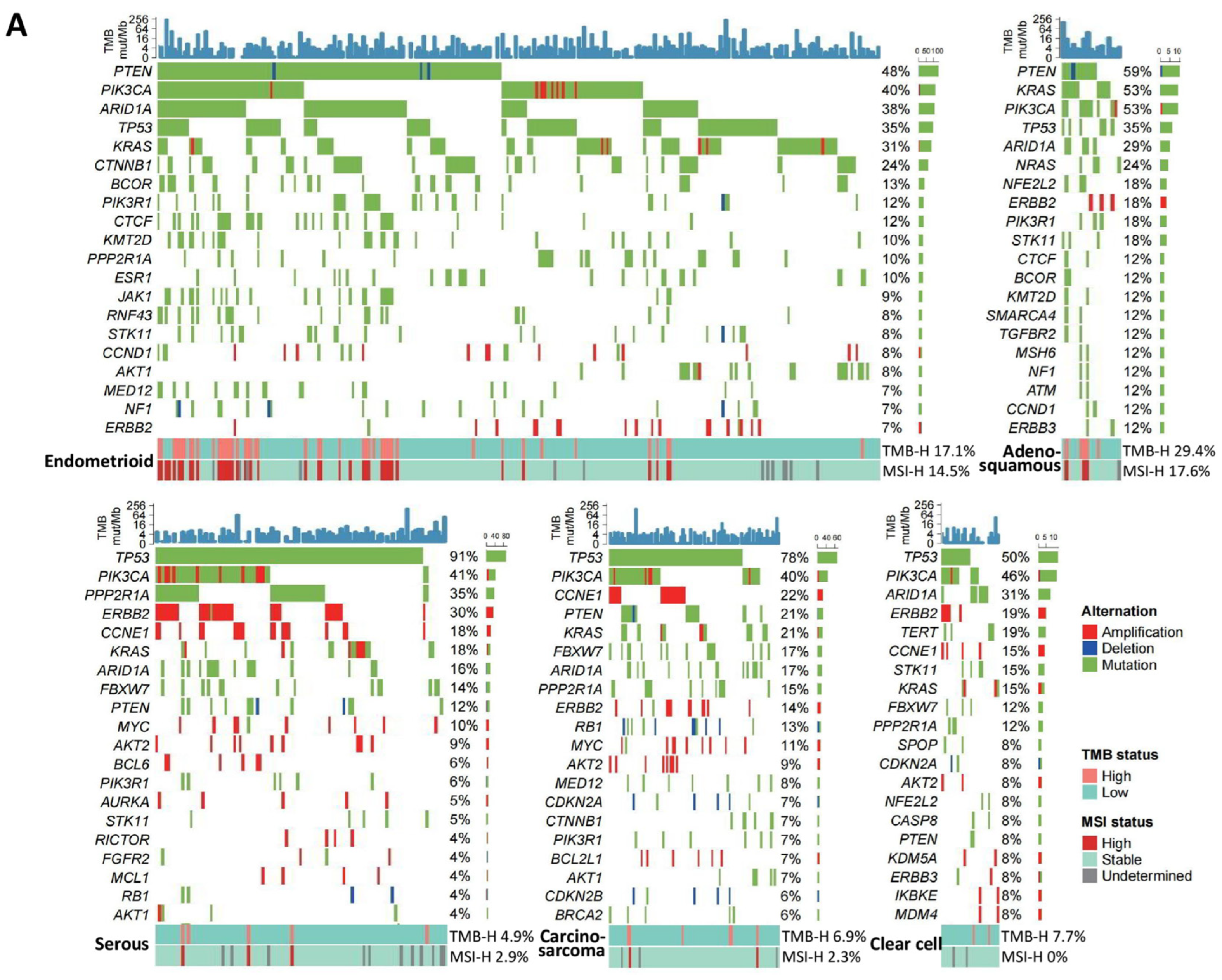
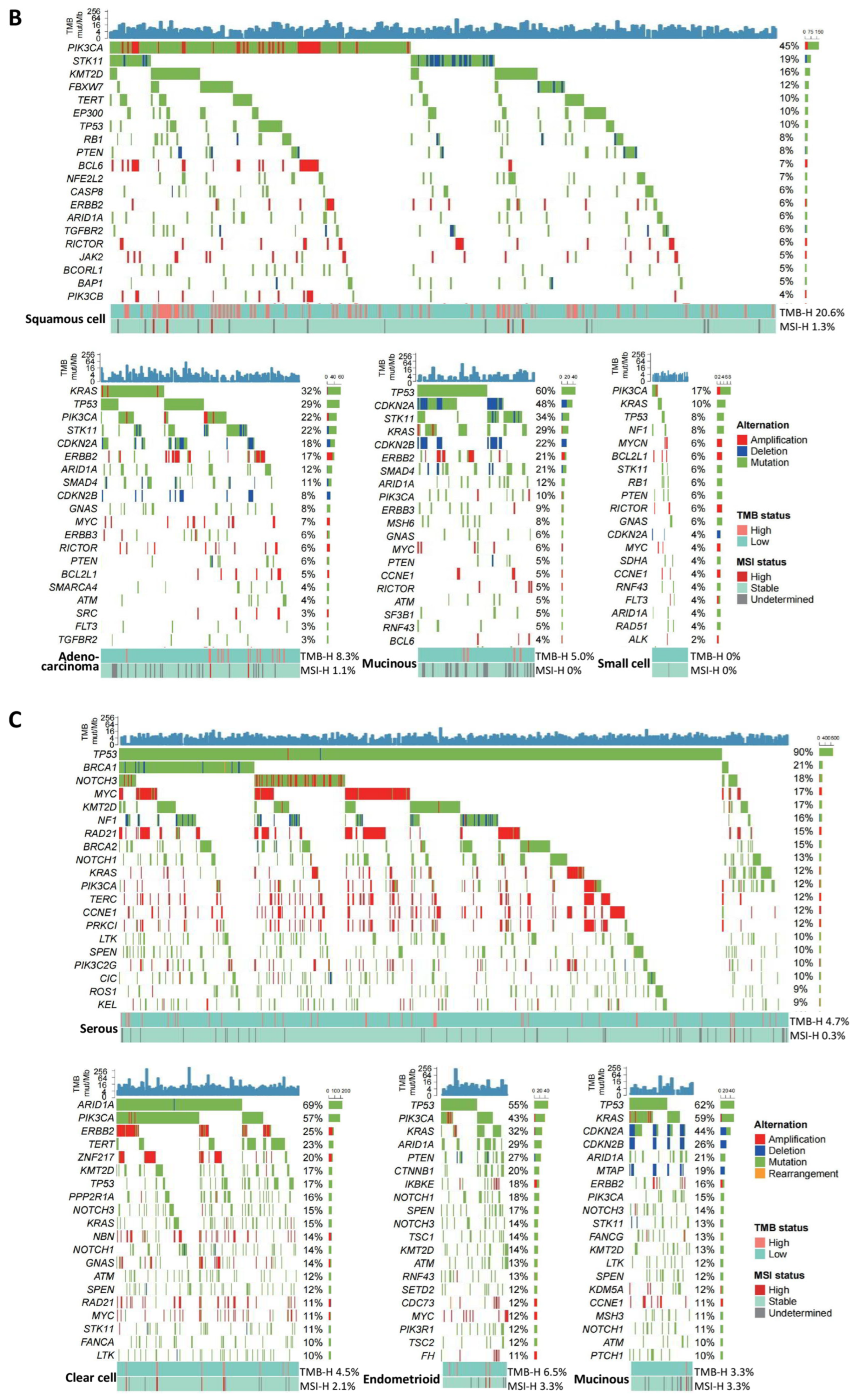
3.1. Genomic Alteration Profiles across Cancer Types
3.1.1. Endometrial Cancer
3.1.2. Cervical Cancer
3.1.3. Ovarian Cancer
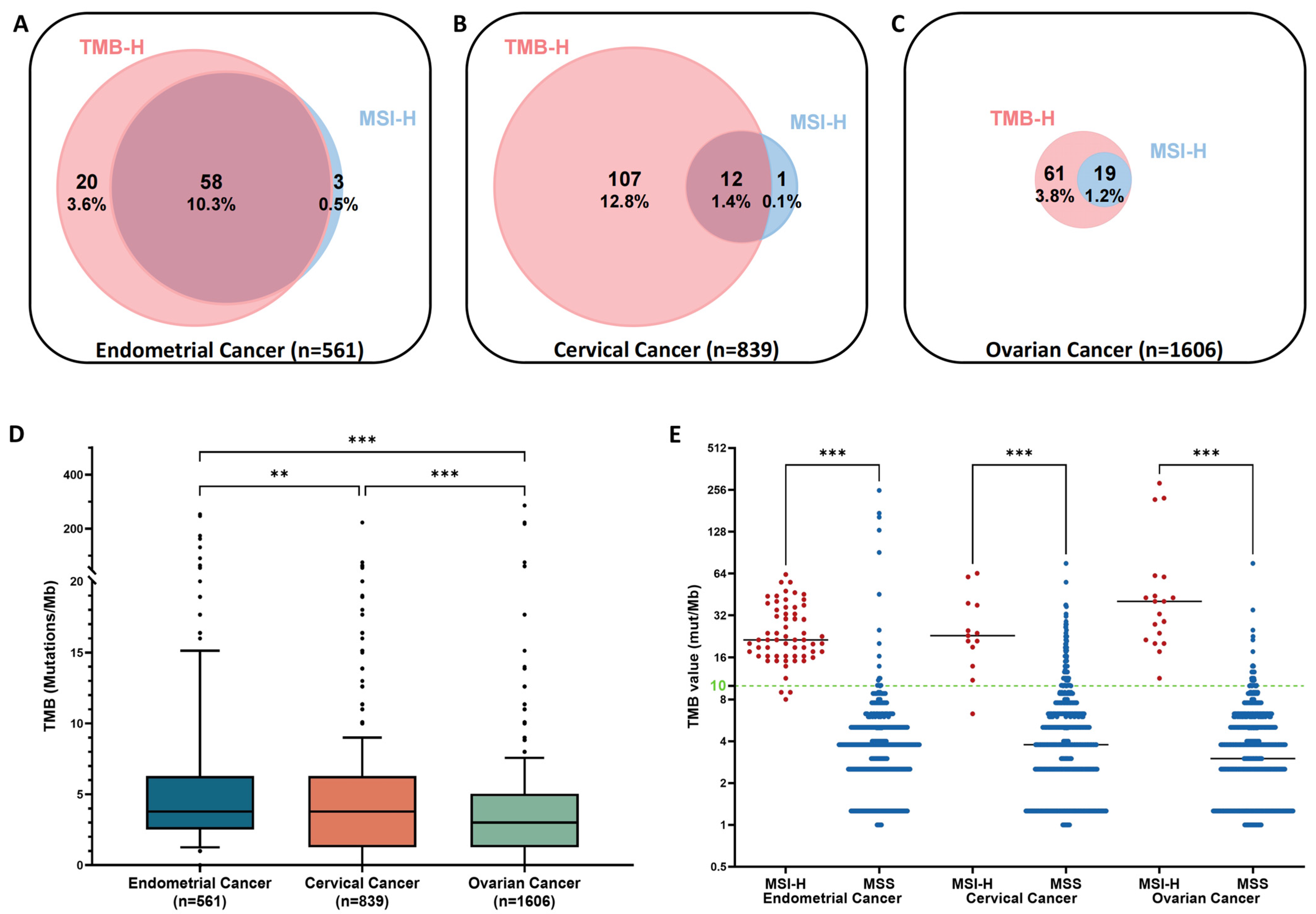
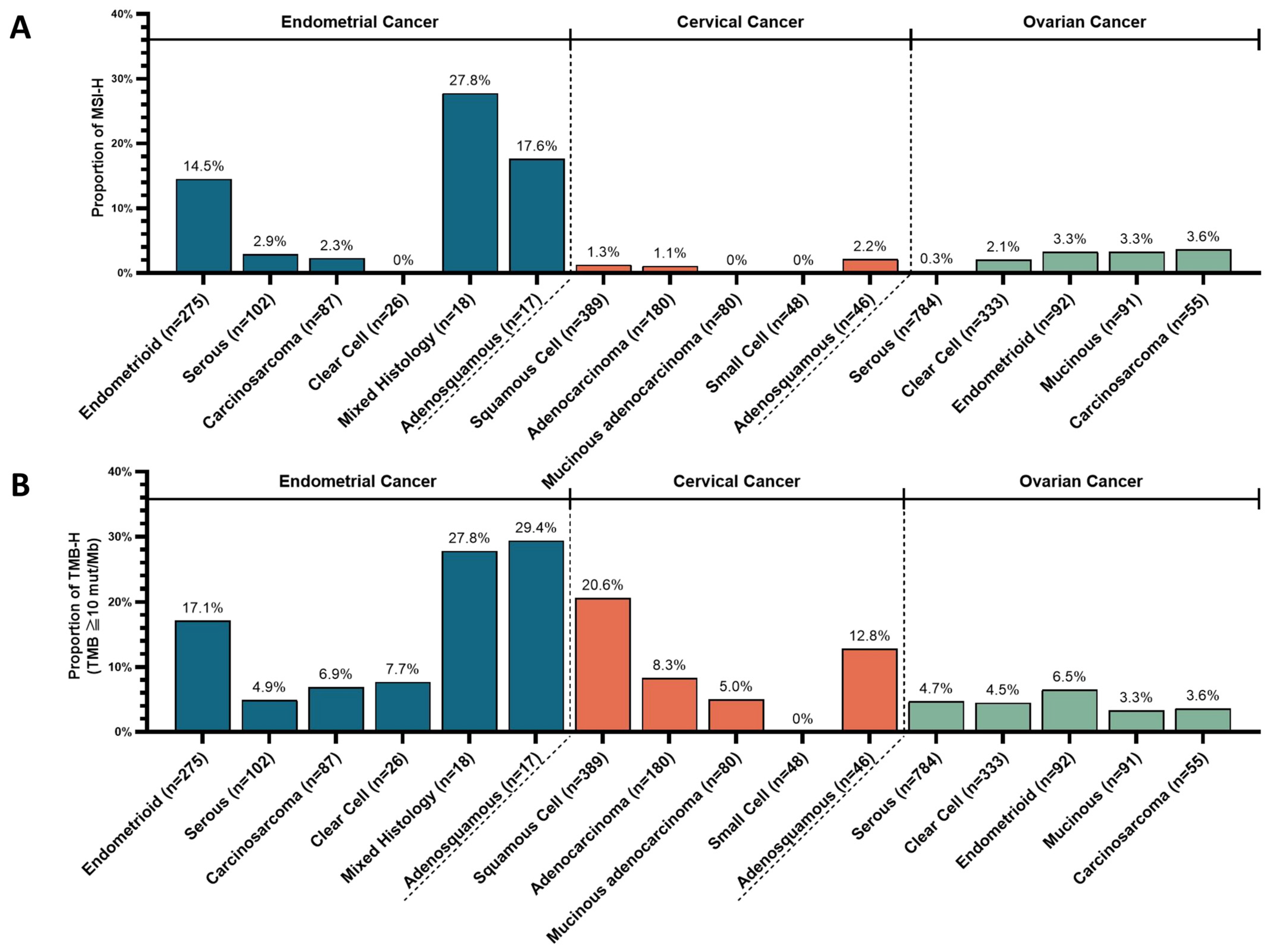
3.2. Prevalence of Microsatellite Instability-High (MSI-H) and Tumor Mutation Burden-High (TMB-H)
3.3. Mismatch Repair-Related Mutations in Tumors with MSI-H and TMB-H
3.4. Distribution of POLE Genomic Alterations in the Exonuclease Domain among TMB-H and Microsatellite Stable Subsets
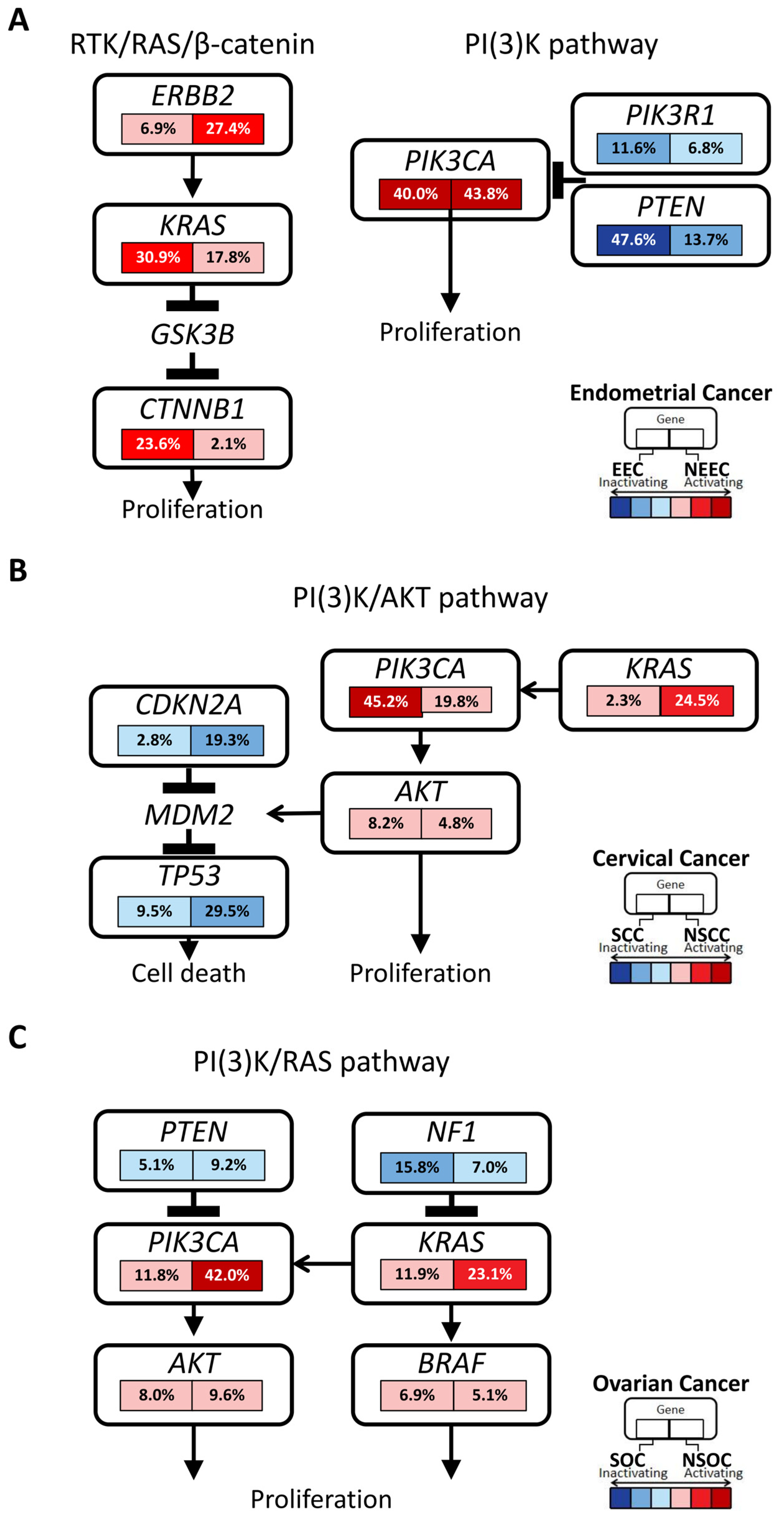
3.5. Correlation among Genomic Alterations, MSI, and TMB
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naito, Y.; Aburatani, H.; Amano, T.; Baba, E.; Furukawa, T.; Hayashida, T.; Hiyama, E.; Ikeda, S.; Kanai, M.; Kato, M.; et al. Clinical practice guidance for next-generation sequencing in cancer diagnosis and treatment (edition 2.1). Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 26, 233–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, Y.; Okazaki, S.; Takeda, M. Current status of next-generation sequencing-based cancer genome profiling tests in Japan and prospects for liquid biopsy. Life 2021, 11, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, T.; Kato, M.; Kohsaka, S.; Sudo, T.; Tamai, I.; Shiraishi, Y.; Okuma, Y.; Ogasawara, D.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshida, T.; et al. C-CAT: The National Datacenter for Cancer Genomic Medicine in Japan. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, D. The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature 2013, 497, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiden-Amissah, R.E.M.; Annibali, D.; Tuyaerts, S.; Amant, F. Endometrial cancer molecular characterization: The key to identifying high-risk patients and defining guidelines for clinical decision-making? Cancers 2021, 13, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Castillo, A.; Britton, H.; McConechy, M.K.; McAlpine, J.N.; Nout, R.; Kommoss, S.; Brucker, S.Y.; Carlson, J.W.; Epstein, E.; Rau, T.T.; et al. Interpretation of somatic POLE mutations in endometrial carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2020, 250, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rustum, N.; Yashar, C.; Arend, R.; Barber, E.; Bradley, K.; Brooks, R.; Campos, S.M.; Chino, J.; Chon, H.S.; Chu, C.; et al. Uterine Neoplasms, Version 1.2023, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2023, 21, 181–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic and molecular characterization of cervical cancer. Nature 2017, 543, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature 2011, 474, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Baba, T.; Tokunaga, H.; Nishino, K.; Sekine, M.; Takamatsu, S.; Matsumura, N.; Yoshida, H.; Kajiyama, H.; Shimada, M.; et al. Homologous recombination inquiry through ovarian malignancy investigations: JGOG3025 Study. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2515–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, K.C.; Shah, S.P.; Al-Agha, O.M.; Zhao, Y.; Tse, K.; Zeng, T.; Senz, J.; McConechy, M.K.; Anglesio, M.S.; Kalloger, S.E.; et al. ARID1A mutations in endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryland, G.L.; Hunter, S.M.; Doyle, M.A.; Caramia, F.; Li, J.; Rowley, S.M.; Christie, M.; Allan, P.E.; Stephens, A.N.; Bowtell, D.D.; et al. Mutational landscape of mucinous ovarian carcinoma and its neoplastic precursors. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Business Wire. Merck’s KEYTRUDA® (Pembrolizumab) Receives Five New Approvals in Japan, Including in Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), as Adjuvant Therapy for Melanoma, and in Advanced Microsatellite Instability-High (MSI-H) Tumors; Business Wire: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Merck. FDA Approves KEYTRUDA® (Pembrolizumab) plus LENVIMA® (Lenvatinib) Combination for First-Line Treatment of Adult Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC). Available online: https://www.merck.com/news/fda-approves-keytruda-pembrolizumab-plus-lenvima-lenvatinib-combination-for-first-line-treatment-of-adult-patients-with-advanced-renal-cell-carcinoma-rcc/ (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Tewari, K.S.; Monk, B.J.; Vergote, I.; Miller, A.; de Melo, A.C.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Lisyanskaya, A.; Samouëlian, V.; Lorusso, D.; et al. Survival with cemiplimab in recurrent cervical cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makker, V.; Colombo, N.; Casado Herráez, A.; Santin, A.D.; Colomba, E.; Miller, D.S.; Fujiwara, K.; Pignata, S.; Baron-Hay, S.; Ray-Coquard, I.; et al. Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab for advanced endometrial cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskander, R.N.; Sill, M.W.; Beffa, L.; Moore, R.G.; Hope, J.M.; Musa, F.B.; Mannel, R.; Shahin, M.S.; Cantuaria, G.H.; Girda, E.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced endometrial cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.R.; Chase, D.M.; Slomovitz, B.M.; dePont Christensen, R.; Novák, Z.; Black, D.; Gilbert, L.; Sharma, S.; Valabrega, G.; Landrum, L.M.; et al. Dostarlimab for primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2145–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, N.; Dubot, C.; Lorusso, D.; Caceres, M.V.; Hasegawa, K.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Tewari, K.S.; Salman, P.; Hoyos Usta, E.; Yañez, E.; et al. Pembrolizumab for persistent, recurrent, or metastatic cervical cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, I.; Karakasis, K.; Suku, S.; Oza, A.M. Chasing immune checkpoint inhibitors in ovarian cancer: Novel combinations and biomarker discovery. Cancers 2023, 15, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milbury, C.A.; Creeden, J.; Yip, W.K.; Smith, D.L.; Pattani, V.; Maxwell, K.; Sawchyn, B.; Gjoerup, O.; Meng, W.; Skoletsky, J.; et al. Clinical and analytical validation of FoundationOne®CDx, a comprehensive genomic profiling assay for solid tumors. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, C.; Repetto, M.; Anand, S.; Porta, C.; Subbiah, V.; Curigliano, G. The emerging role of PI3K inhibitors for solid tumour treatment and beyond. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 2150–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitler, B.G.; Aird, K.M.; Garipov, A.; Li, H.; Amatangelo, M.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Schultz, D.C.; Liu, Q.; Shih, I.e.M.; Conejo-Garcia, J.R.; et al. Synthetic lethality by targeting EZH2 methyltransferase activity in ARID1A-mutated cancers. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogiwara, H.; Takahashi, K.; Sasaki, M.; Kuroda, T.; Yoshida, H.; Watanabe, R.; Maruyama, A.; Makinoshima, H.; Chiwaki, F.; Sasaki, H.; et al. Targeting the vulnerability of glutathione metabolism in ARID1A-deficient cancers. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 177–190.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathod, L.S.; Dabhade, P.S.; Mokale, S.N. Recent progress in targeting KRAS mutant cancers with covalent G12C-specific inhibitors. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escher, T.E.; Satchell, K.J.F. RAS degraders: The new frontier for RAS-driven cancers. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 1904–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Hori, Y.; Inoue, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Iso, K.; Kamiyama, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kimura, T.; Uesugi, M.; Ito, J.; et al. E7386, a selective inhibitor of the interaction between β-catenin and CBP, exerts antitumor activity in tumor models with activated canonical Wnt signaling. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Mori, M.; Hirashima, Y.; Takehara, K.; Ariyoshi, K.; Kato, T.; Yagishita, S.; Hamada, A.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-expressing advanced or recurrent uterine carcinosarcoma (NCCH1615): The STATICE trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2789–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeta, S.; Shimada, M.; Suzuki, S.; Kajiyama, H.; Oda, K.; Takehara, K.; Mandai, M.; Aoki, D.; Enomoto, T.; Okamoto, A. An attempt to develop a new treatment strategy for rare refractory gynecological malignancies: The Japanese Gynecologic Oncology Group. JMA J. 2023, 6, 527–531. [Google Scholar]
- Oda, K.; Aoki, D.; Tsuda, H.; Nishihara, H.; Aoyama, H.; Inomata, H.; Shimada, M.; Enomoto, T. Japanese nationwide observational multicenter study of tumor BRCA1/2 variant testing in advanced ovarian cancer. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kage, H.; Oda, K.; Muto, M.; Tsuchihara, K.; Okita, N.; Okuma, Y.; Kikuchi, J.; Shirota, H.; Hayashi, H.; Kokuryo, T.; et al. Human resources for administrative work to carry out a comprehensive genomic profiling test in Japan. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 3041–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhouk, A.; McConechy, M.K.; Leung, S.; Yang, W.; Lum, A.; Senz, J.; Boyd, N.; Pike, J.; Anglesio, M.; Kwon, J.S.; et al. Confirmation of ProMisE: A simple, genomics-based clinical classifier for endometrial cancer. Cancer 2017, 123, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Xiong, N.; Campos, S.M.; Wright, A.A.; Krasner, C.; Schumer, S.; Horowitz, N.; Veneris, J.; Tayob, N.; Morrissey, S.; et al. Phase II study of the WEE1 inhibitor adavosertib in recurrent uterine serous carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Oza, A.M.; Colombo, N.; Oaknin, A. ADAGIO: A phase IIb international study of the Wee1 inhibitor adavosertib in women with recurrent or persistent uterine serous carcinoma. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolnicu, S. Cervical cancer: What’s new in classification, morphology, molecular findings and prognosis of glandular precursor and invasive lesions. Diagn. Histopathol. 2021, 27, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Kundu, R. Human papillomavirus E6 and E7: The cervical cancer hallmarks and targets for therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, S.; Mikami, Y.; Tokunaga, H.; Yaegashi, N.; Satoh, T.; Saito, M.; Okamoto, A.; Kasamatsu, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Shiozawa, T.; et al. Analysis of gastric-type mucinous carcinoma of the uterine cervix—An aggressive tumor with a poor prognosis: A multi-institutional study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 153, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, H.; Oda, K.; Yoshihara, K.; Ito, Y.M.; Matsumura, N.; Shimada, M.; Watari, H.; Enomoto, T. Phase II study of niraparib in recurrent or persistent rare fraction of gynecologic malignancies with homologous recombination deficiency (JGOG2052). J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 33, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, G.; Oki, E.; Taniguchi, H.; Nakatani, K.; Aoki, D.; Kuwata, T.; Yoshino, T. The real-world data on microsatellite instability status in various unresectable or metastatic solid tumors. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, S.; Naito, Y.; Akagi, K.; Hayashi, N.; Hirasawa, A.; Hishiki, T.; Igarashi, A.; Ikeda, M.; Kadowaki, S.; Kajiyama, H.; et al. Japanese Society of Medical Oncology/Japan Society of Clinical Oncology/Japanese Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology-led clinical recommendations on the diagnosis and use of immunotherapy in patients with high tumor mutational burden tumors. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 28, 941–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zuo, F.; Wang, H.; Jing, J.; He, X. The current landscape of predictive and prognostic biomarkers for immune checkpoint blockade in ovarian cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1045957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cancer Type | Genomic Alteration | Frequency | Histological Type | Potential Targeted Therapies | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endometrial | TP53 | 54.4% | Serous (91%); Carcinosarcoma (78%); Clear cell (50%), etc. | - | - |
| PIK3CA | 41.2% | Adenosquamous (53%); Clear cell (46%); Serous (41%), etc. | p110alpha selective inhibitor (alpelisib) | [22] | |
| PTEN | 34.6% | Adenosquamous (59%); Endometrioid (48%); Carcinosarcoma (21%), etc. | - | - | |
| ARID1A | 30.7% | Endometrioid (38%); Clear cell (31%); Adenosquamous (29%), etc. | EZH2 inhibitor; Enzyme for antioxidant glutathione synthesis | [23,24] | |
| KRAS | 26.0% | Adenosquamous (53%); Endometrioid (31%); Carcinosarcoma (21%), etc. | KRAS-G12C inhibitors (sotorasib); KRAS-G12D degrader (ASP3082) | [25,26] | |
| CTNNB1 | 15.0% | Endometrioid (24%), etc. | CBP/β-catenin inhibitor (E7386) | [27] | |
| ERBB2 | 14.0% | Serous (30%); Clear cell (19%); Adenosquamous (18%), etc. | Trastuzumab deruxtecan | [28] | |
| TMB-H | 13.9% | Adenosquamous (29%); Endometrioid (17%); Clear cell (8%), etc. | Pembrolizumab; Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab (regardless of MSI status); Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy; Dostarlimab | [13,14,16,17,18] | |
| MSI-H | 10.9% | Adenosquamous (18%); Endometrioid (15%), etc. | |||
| Cervical | PIK3CA | 32.2% | Squamous cell (45%); Adenocarcinoma (22%); Small cell (17%), etc. | p110alpha selective inhibitor (alpelisib) | [22] |
| STK11 | 20.3% | Mucinous (34%); Adenocarcinoma (22%); Squamous cell (19%), etc. | - | - | |
| TP53 | 19.8% | Mucinous (60%); Adenocarcinoma (29%); Squamous cell (10%), etc. | - | - | |
| KRAS | 13.9% | Adenocarcinoma (32%); Mucinous (29%); Small cell (10%), etc. | KRAS-G12C inhibitors (sotorasib); KRAS-G12D degrader (ASP3082) | [25,26] | |
| CDKN2A | 11.4% | Mucinous (48%); Adenocarcinoma (18%) Small cell (4%), etc. | - | - | |
| TMB-H | 14.2% | Squamous cell (21%); Adenocarcinoma (8%), etc. | Pembrolizumab | [13,14] | |
| MSI-H | 1.5% | Adenocarcinoma (2%), etc. | |||
| Ovarian | TP53 | 65.6% | Serous (90%); Mucinous (62%); Endometrioid (55%), etc. | - | - |
| BRCA1/ BRCA2 | 25.4% | Serous (33%); Endometrioid (18%); Mucinous and Clear cell (13%), etc. | PARP inhibitors | - | |
| ARID1A | 25.3% | Clear cell (69%); Endometrioid (29%); Mucinous (21%), etc. | EZH2 inhibitor; Enzyme for antioxidant glutathione synthesis | [23,24] | |
| PIK3CA | 25.3% | Clear cell (57%); Endometrioid (43%); Mucinous (15%), etc. | p110alpha selective inhibitors (CYH33; alpelisib) | [22,29] | |
| KRAS | 16.9% | Mucinous (59%); Endometrioid (32%); Clear cell (15%), etc. | KRAS-G12C inhibitors (sotorasib); KRAS-G12D degrader (ASP3082) | [25,26] | |
| TMB-H | 5.0% | - | Pembrolizumab | [13,14] | |
| MSI-H | 1.2% | - |
| Endometrial Cancer (n = 561) | |||||||
| Histology | Gene | Variants | Clinical Significance | MSI Status | TMB Status | TMB Value (mut/Mb) | |
| Exonuclease Domain (n = 8; 1.4%) | MSI-H 12.5% | TMB-H 100% | Median 146.89 | ||||
| 1 | Endometrioid | POLE | P286R | Likely pathogenic | Stable | high | 253.4 |
| 2 | Endometrioid | POLE | P286R | Likely pathogenic | Undetermined | high | 247.1 |
| 3 | Adenosquamous | POLE | V411L | Likely pathogenic | Stable | high | 174.0 |
| 4 | Carcinosarcoma | POLE | P286R | Likely pathogenic | Stable | high | 162.7 |
| 5 | Endometrioid | POLE | P286R | Likely pathogenic | Stable | high | 131.1 |
| 6 | Endometrioid | POLE | P286R | Likely pathogenic | Stable | high | 90.8 |
| 7 | Endometrioid | POLE | V411L | Likely pathogenic | Stable | high | 25.2 |
| 8 | Adenosquamous | POLE | W243 * | Pathogenic | High | high | 18.9 |
| Non-Exonuclease Domain (n = 3; 0.5%) | MSI-H 100% | TMB-H 100% | Median 30.26 | ||||
| 1 | Endometrioid | POLE | K1170fs*49 | High | high | 20.2 | |
| 2 | Endometrioid | POLE | P172fs*3 | High | high | 36.6 | |
| 3 | Endometrioid | POLE | S2173fs*130 | High | high | 30.3 | |
| Cervical Cancer (n = 839) | |||||||
| Histology | Gene | Variants | Clinical Significance | MSI Status | TMB Status | TMB Value (mut/Mb) | |
| Exonuclease Domain (n = 1; 0.1%) | MSI-H 100% | TMB-H 100% | Median 23.0 | ||||
| 1 | Squamous Cell | POLE | L283fs*5 | Pathogenic | high | high | 23.0 |
| Non-Exonuclease Domain (n = 6; 0.7%) | MSI-H 0% | TMB-H 66.7% | Median 11.81 | ||||
| 1 | Squamous Cell | POLE | E179 * | stable | high | 22.7 | |
| 2 | Squamous Cell | POLE | E586 * | stable | high | 17.7 | |
| 3 | Squamous Cell | POLE | Q670 * | stable | high | 12.6 | |
| 4 | Squamous Cell | POLE | E1085K | stable | high | 11.0 | |
| 5 | Adenocarcinoma | POLE | E18K | stable | low | 7.6 | |
| 6 | Adenocarcinoma | POLE | R1077fs*43 | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| Ovarian Cancer (n = 1606) | |||||||
| Histology | Gene | Variants | Clinical Significance | MSI Status | TMB Status | TMB Value (mut/Mb) | |
| Exonuclease Domain (n = 4; 0.2%) | MSI-H 50% | TMB-H 75% | Median 146.89 | ||||
| 1 | Endometrioid | POLE | V411L | Likely pathogenic | high | high | 223.2 |
| 2 | Clear cell | POLE | T278K | Pathogenic | high | high | 218.1 |
| 3 | Unknown | POLE | P286R | Likely pathogenic | stable | high | 75.7 |
| 4 | Serous | POLE | L432V | stable | low | 5.0 | |
| Non-Exonuclease Domain (n = 64; 4.0%) | MSI-H 9.4% | TMB-H 17.2% | Median 3.78 | ||||
| 1 | Clear cell | POLE | H1356R; N1369S | high | high | 286.0 | |
| 2 | Unknown | POLE | c.4551 + 2_4551 + 3 delTG | high | high | 61.8 | |
| 3 | Clear cell | POLE | W1251 * | high | high | 60.5 | |
| 4 | Carcinosarcoma | POLE | T41M | high | high | 42.9 | |
| 5 | Mucinous | POLE | L1983fs*76 | high | high | 29.0 | |
| 6 | Carcinosarcoma | POLE | V1368M; V1929fs*70 | high | high | 17.7 | |
| 7 | Others | POLE | D934Y | stable | high | 22.7 | |
| 8 | Endometrioid | POLE | R847L | stable | high | 11.0 | |
| 9 | Clear cell | POLE | R2131C | stable | high | 10.1 | |
| 10 | Serous | POLE | T880L | stable | high | 10.1 | |
| 11 | Serous | POLE | N1521S | stable | high | 10.1 | |
| 12 | Serous | POLE | G2046R | stable | low | 9.0 | |
| 13 | Serous | POLE | R1059H | stable | low | 8.0 | |
| 14 | Serous | POLE | F695L | stable | low | 8.0 | |
| 15 | Serous | POLE | A1854S | stable | low | 7.6 | |
| 16 | Serous | POLE | L53V | stable | low | 7.6 | |
| 17 | Serous | POLE | amplification | stable | low | 6.3 | |
| 18 | Clear cell | POLE | A2192V | stable | low | 6.3 | |
| 19 | Unknown | POLE | A1778T | stable | low | 6.3 | |
| 20 | Serous | POLE | I238F | stable | low | 6.0 | |
| 21 | Serous | POLE | L1245V | stable | low | 6.0 | |
| 22 | Serous | POLE | E2155Q | stable | low | 6.0 | |
| 23 | Serous | POLE | I622M | stable | low | 5.0 | |
| 24 | Unknown | POLE | T737A | stable | low | 5.0 | |
| 25 | Serous | POLE | K1877E | stable | low | 5.0 | |
| 26 | Clear cell | POLE | Q394 * | stable | low | 5.0 | |
| 27 | Clear cell | POLE | R1382C | stable | low | 4.0 | |
| 28 | Endometrioid | POLE | R1284Q | stable | low | 3.8 | |
| 29 | Serous | POLE | L32P | stable | low | 3.8 | |
| 30 | Serous | POLE | D934G | stable | low | 3.8 | |
| 31 | Unknown | POLE | S1598C | stable | low | 3.8 | |
| 32 | Endometrioid | POLE | Q394fs*18 | stable | low | 3.8 | |
| 33 | Serous | POLE | R1324H | stable | low | 3.8 | |
| 34 | Endometrioid | POLE | V1736I | stable | low | 3.8 | |
| 35 | Clear cell | POLE | T1196M | stable | low | 3.0 | |
| 36 | Clear cell | POLE | V1512I | stable | low | 2.5 | |
| 37 | Serous | POLE | amplification | stable | low | 2.5 | |
| 38 | Clear cell | POLE | R847Q | stable | low | 2.5 | |
| 39 | Unknown | POLE | E1554K | stable | low | 2.5 | |
| 40 | Serous | POLE | A1140T | stable | low | 2.5 | |
| 41 | Serous | POLE | D1516G | stable | low | 2.5 | |
| 42 | Clear cell | POLE | S171F | stable | low | 2.5 | |
| 43 | Granulosa cell | POLE | A788V | stable | low | 2.5 | |
| 44 | Clear cell | POLE | G702R | stable | low | 2.5 | |
| 45 | Serous | POLE | C2187Y | stable | low | 2.5 | |
| 46 | Serous | POLE | R1077fs*43 | undetermined | low | 2.5 | |
| 47 | Endometrioid | POLE | F1435L | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| 48 | Serous | POLE | T1666R | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| 49 | Serous | POLE | T1196M | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| 50 | Serous | POLE | R1284Q | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| 51 | Serous | POLE | I218M | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| 52 | Serous | POLE | R1485C | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| 53 | Clear cell | POLE | T1313M | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| 54 | Unknown | POLE | G541R | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| 55 | Serous | POLE | T41M | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| 56 | Unknown | POLE | R1284W | stable | low | 1.3 | |
| 57 | Serous | POLE | L3V | stable | low | 1.0 | |
| 58 | Mucinous | POLE | E1964D | stable | low | 0.0 | |
| 59 | Clear cell | POLE | R1382C | stable | low | 0.0 | |
| 60 | Mucinous | POLE | T1196M | stable | low | 0.0 | |
| 61 | Clear cell | POLE | D1700V | stable | low | 0.0 | |
| 62 | Serous | POLE | R1382C | stable | low | 0.0 | |
| 63 | Clear cell | POLE | A1778T | stable | low | 0.0 | |
| 64 | Clear cell | POLE | A1260T | undetermined | low | 0.0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, Q.; Kage, H.; Ogawa, M.; Matsunaga, A.; Nishijima, A.; Sone, K.; Kawana, K.; Oda, K. Genomic Landscape of Endometrial, Ovarian, and Cervical Cancers in Japan from the Database in the Center for Cancer Genomics and Advanced Therapeutics. Cancers 2024, 16, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010136
Xi Q, Kage H, Ogawa M, Matsunaga A, Nishijima A, Sone K, Kawana K, Oda K. Genomic Landscape of Endometrial, Ovarian, and Cervical Cancers in Japan from the Database in the Center for Cancer Genomics and Advanced Therapeutics. Cancers. 2024; 16(1):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010136
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Qian, Hidenori Kage, Miho Ogawa, Asami Matsunaga, Akira Nishijima, Kenbun Sone, Kei Kawana, and Katsutoshi Oda. 2024. "Genomic Landscape of Endometrial, Ovarian, and Cervical Cancers in Japan from the Database in the Center for Cancer Genomics and Advanced Therapeutics" Cancers 16, no. 1: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010136
APA StyleXi, Q., Kage, H., Ogawa, M., Matsunaga, A., Nishijima, A., Sone, K., Kawana, K., & Oda, K. (2024). Genomic Landscape of Endometrial, Ovarian, and Cervical Cancers in Japan from the Database in the Center for Cancer Genomics and Advanced Therapeutics. Cancers, 16(1), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010136







