ERK3 Increases Snail Protein Stability by Inhibiting FBXO11-Mediated Snail Ubiquitination
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Plasmid Construction and Transfection
2.3. Antibodies and Reagents
2.4. Point Mutagenesis
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Immunoprecipitation
2.7. Total RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
2.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.9. Cycloheximide Chase Assay
2.10. Ubiquitination Assay
2.11. In Vitro Kinase Assay
2.12. GST Pull-Down Assay
2.13. Pancreatic Cancer Tissue Specimens
2.14. Immunohistochemistry
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
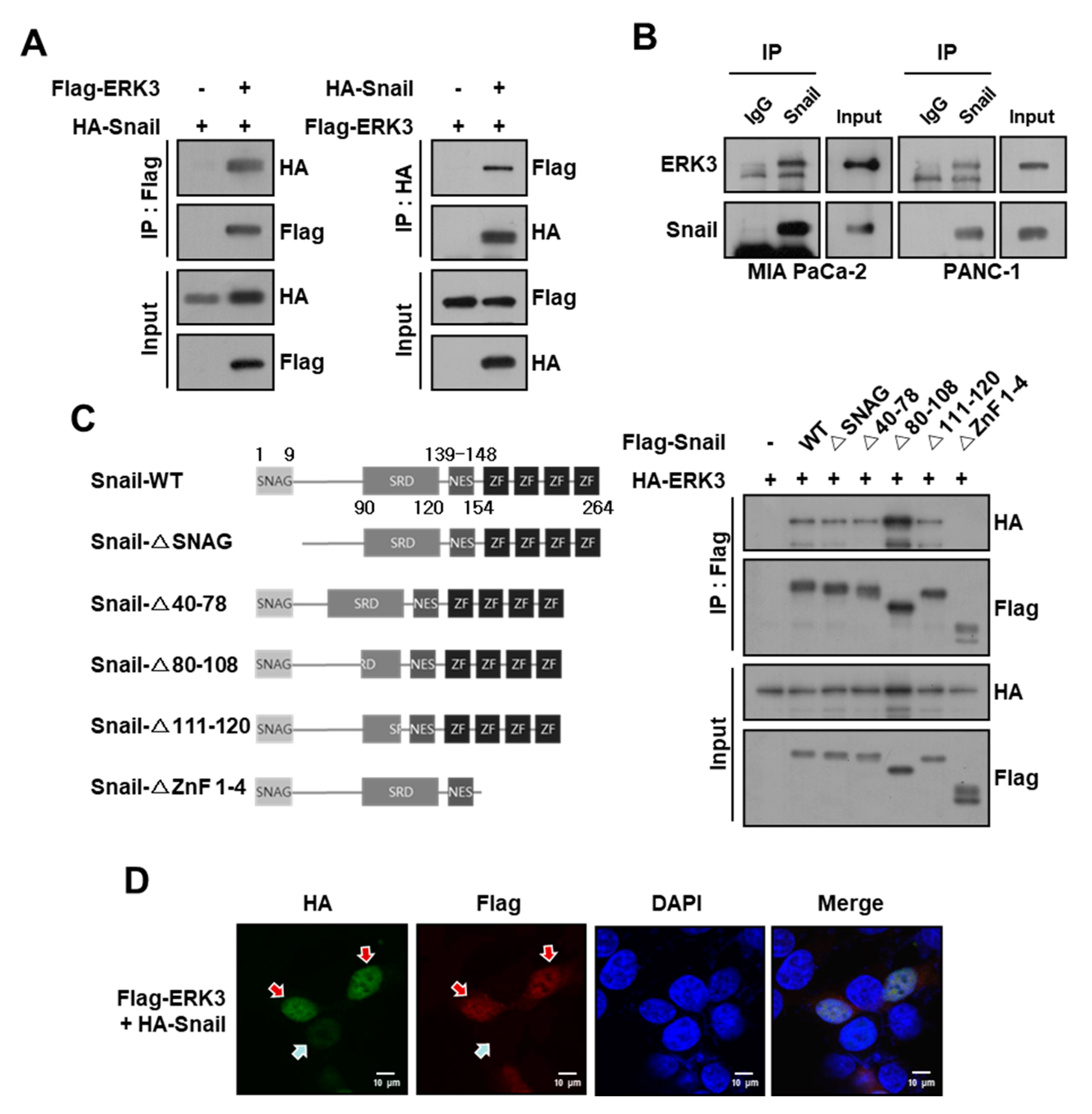
3.1. ERK3 Interacts with Snail in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
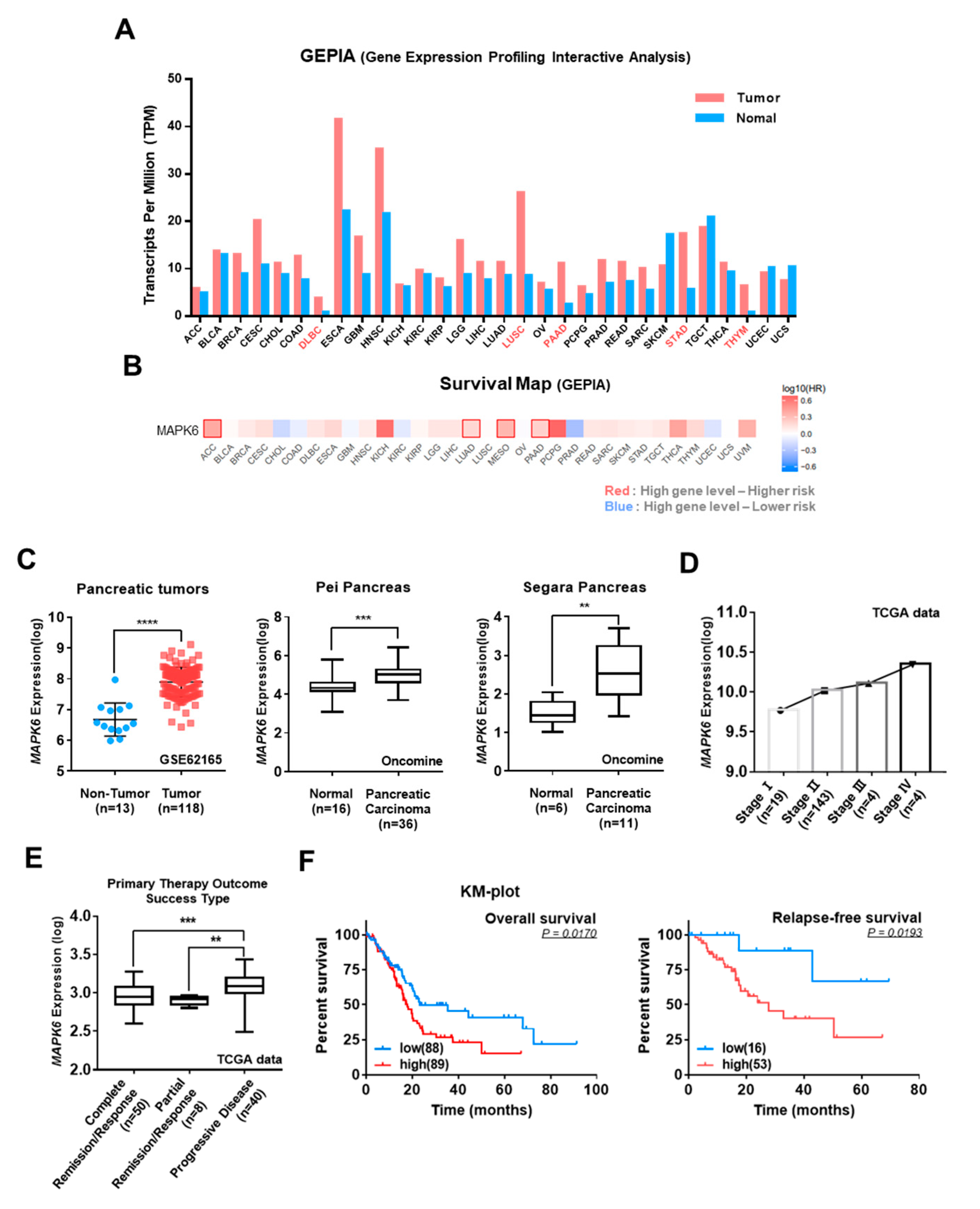
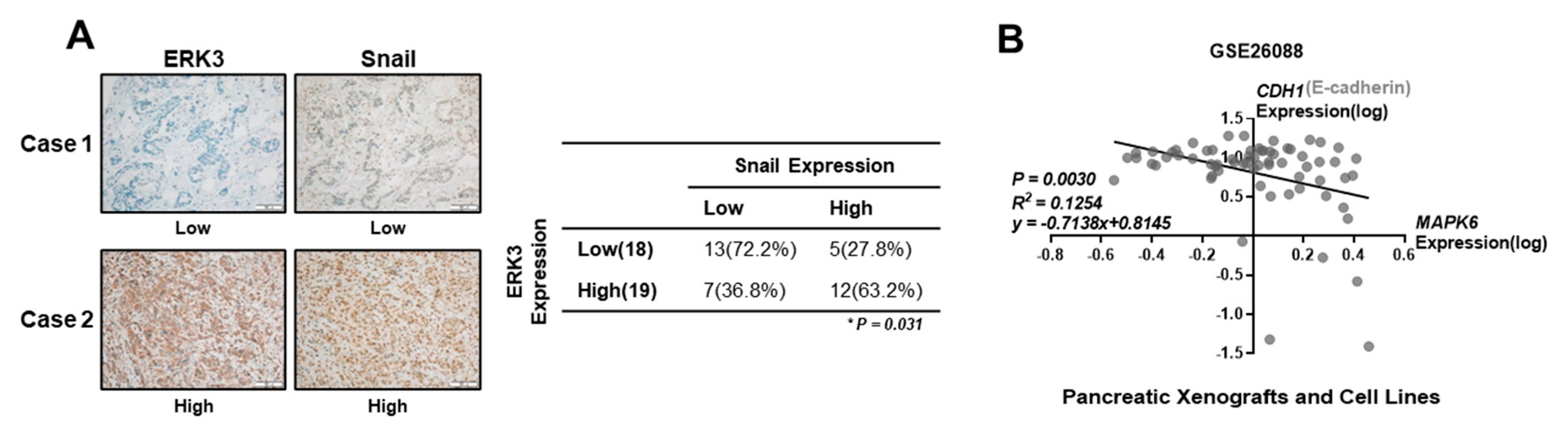
3.2. Correlation of ERK3 Expression Levels with Clinical-Pathological Features of Pancreatic Cancer
3.3. Correlation of ERK3 and Snail Protein Levels in Pancreatic Cancer Patients and Cell Lines
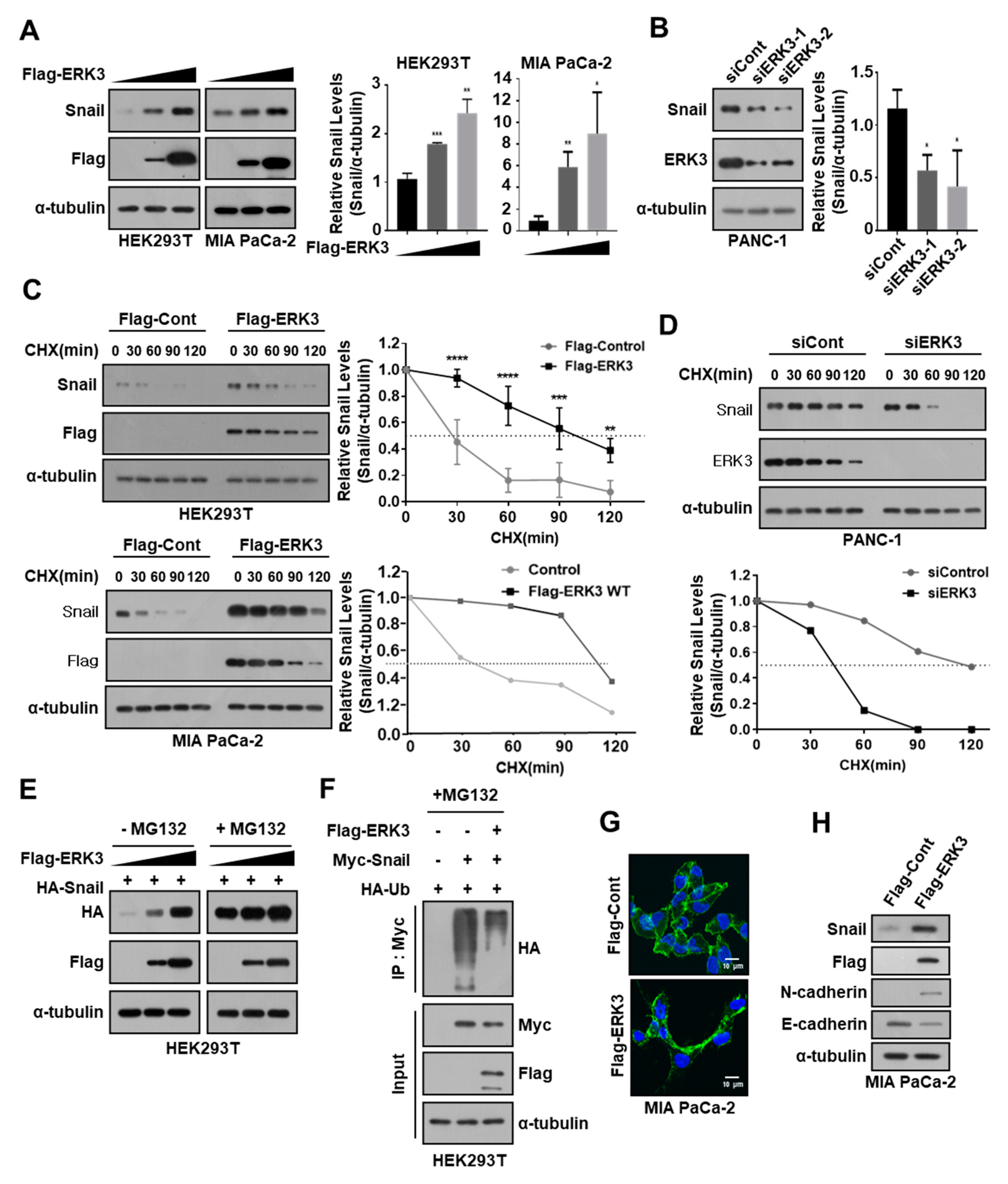
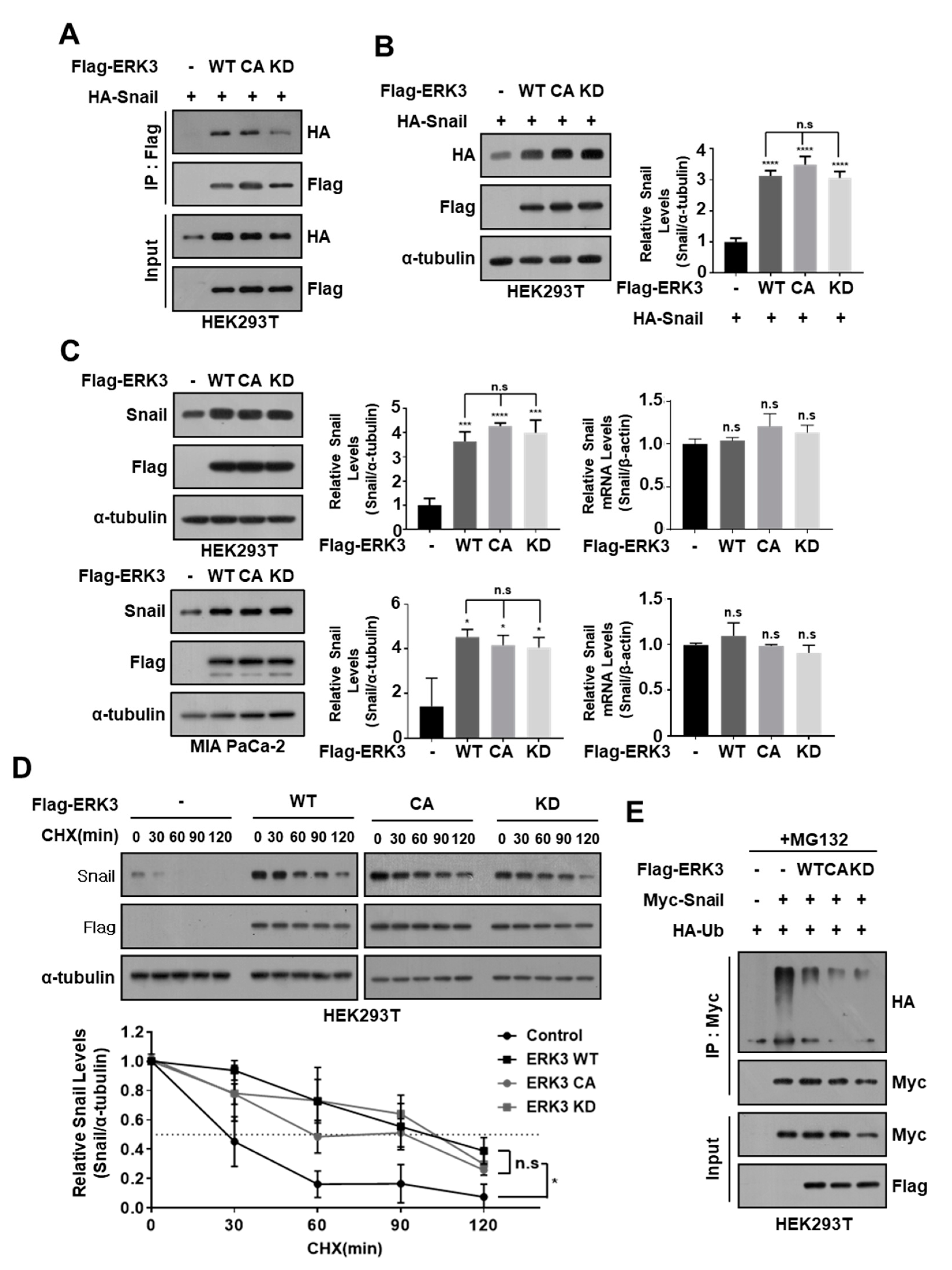
3.4. ERK3 Increases Snail Protein Stability by Suppressing Ubiquitination-Dependent Snail Degradation in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
3.5. ERK3 Kinase Activity Is Not Essential for Increasing the Stability of Snail Protein
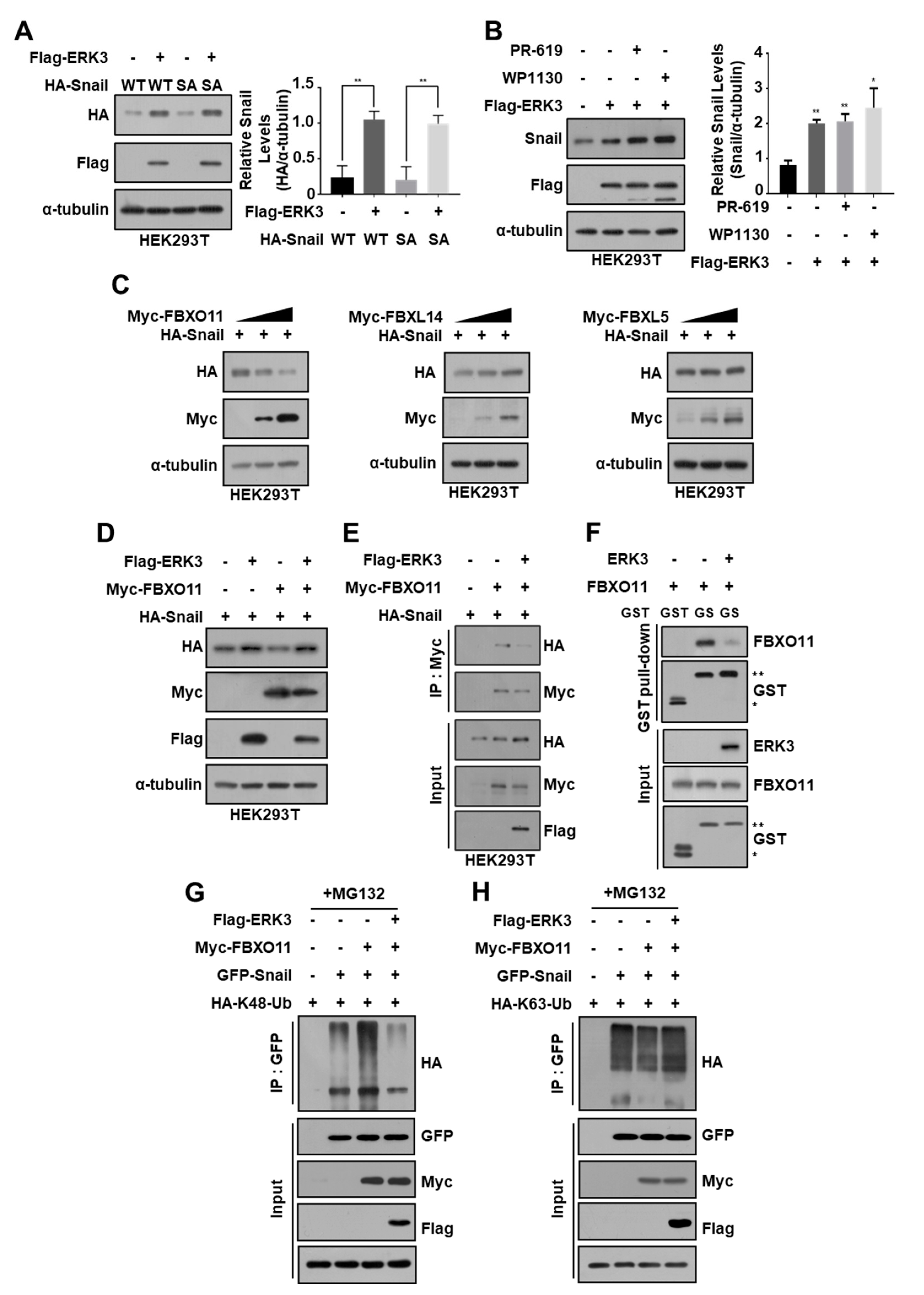
3.6. ERK3 Increases Snail Expression Levels by Inhibiting FBXO11 Binding to Snail
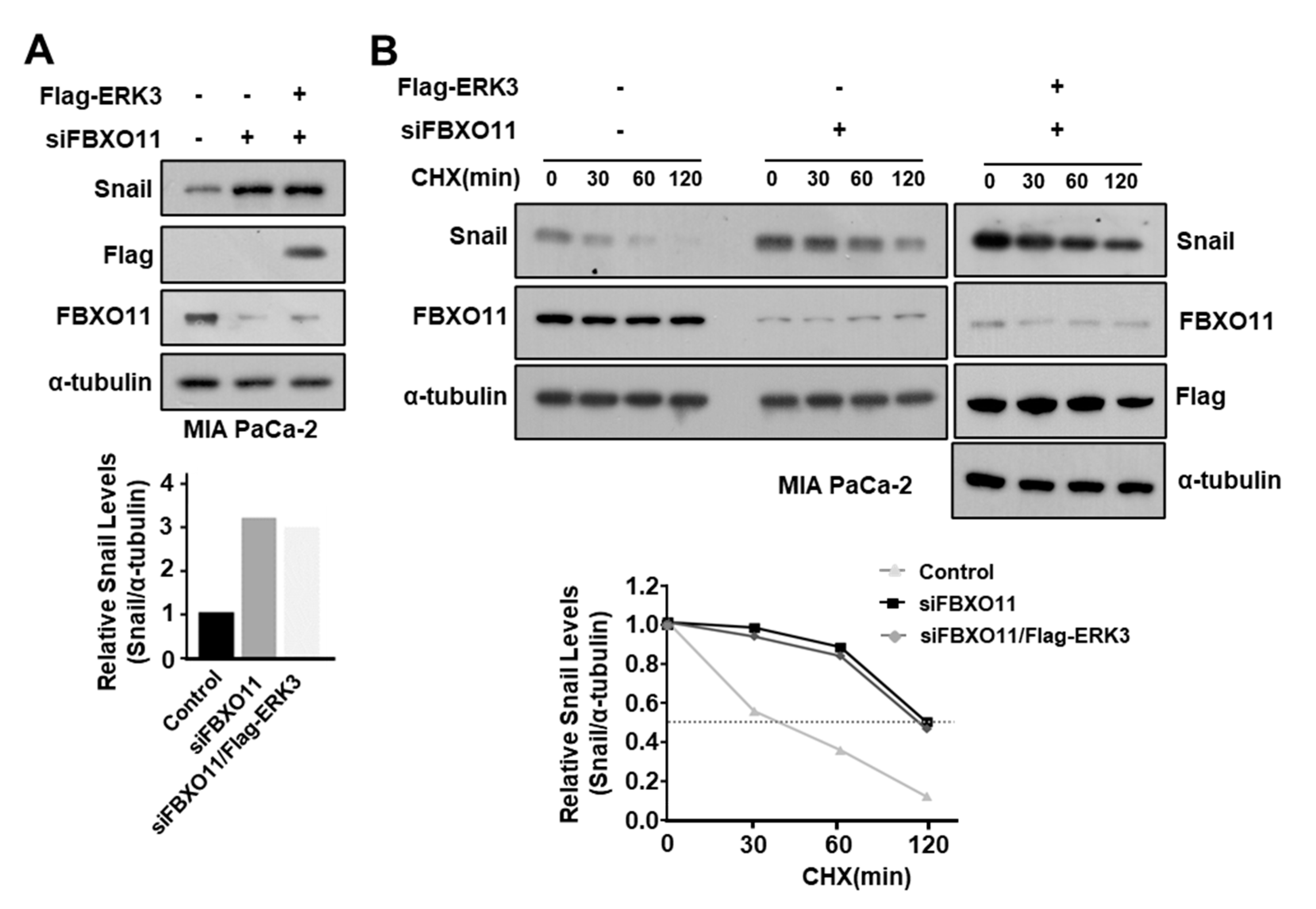
3.7. FBXO11 Plays an Important Role in ERK3-Induced Increase in Snail Protein Stability in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
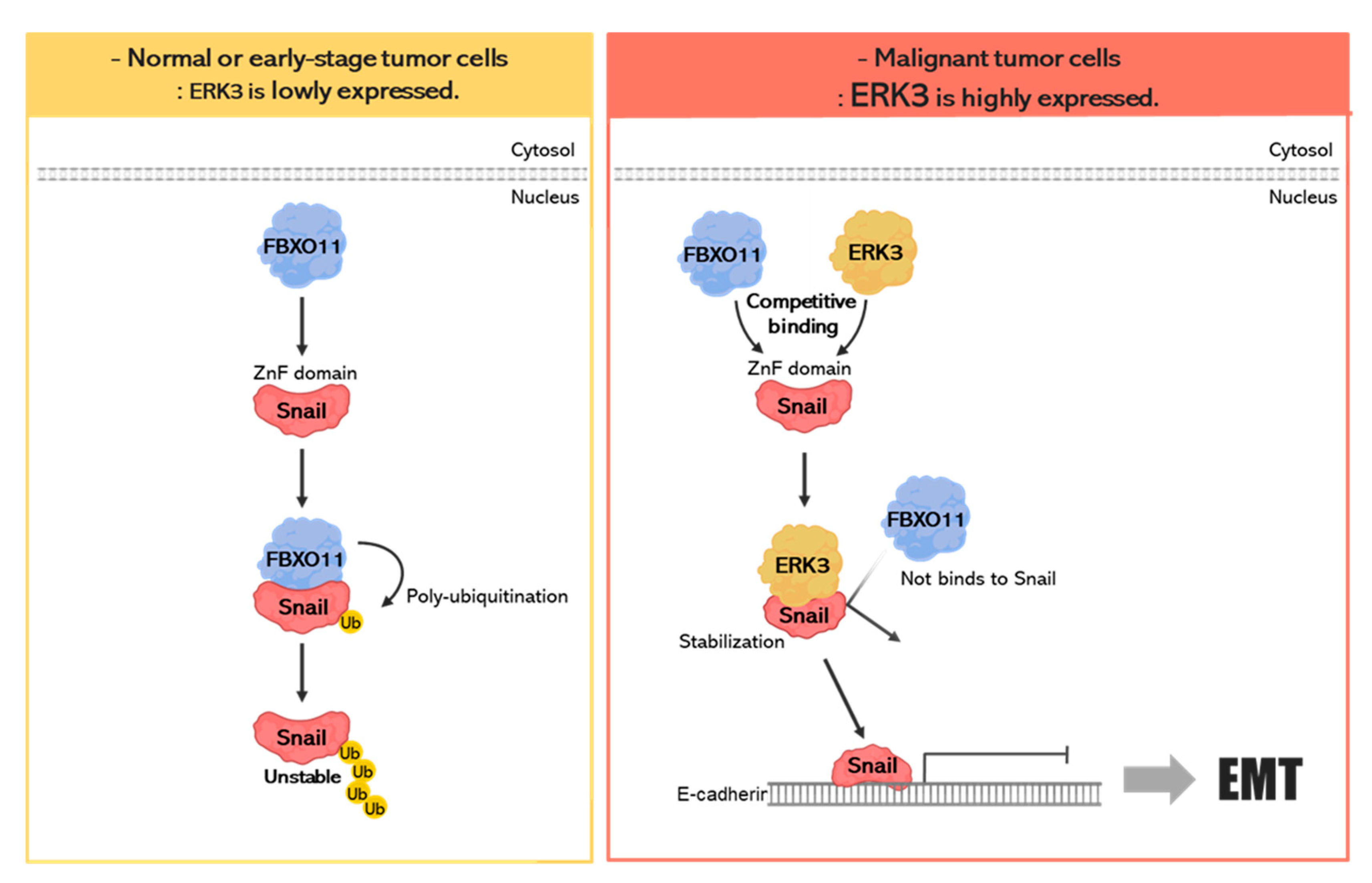
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wan, L.; Pantel, K.; Kang, Y. Tumor metastasis: Moving new biological insights into the clinic. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikenouchi, J.; Matsuda, M.; Furuse, M.; Tsukia, S. Regulation of tight junctions during the epithelium-mesenchyme transition: Direct repression of the gene expression of claudins/occludin by Snail. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, M.A.; Huang, R.Y.; Jackson, R.A.; Thiery, J.P. EMT: 2016. Cell 2016, 166, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaffer, C.L.; San Juan, B.P.; Lim, E.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, cell plasticity and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, A.; Perez-Moreno, M.A.; Rodrigo, I.; Locascio, A.; Blanco, M.J.; del Barrio, M.G.; Portillo, F.; Nieto, M.A. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, E.; Sancho, E.; Franci, C.; Dominguez, D.; Monfar, M.; Baulida, J.; Garcia De Herreros, A. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotegut, S.; von Schweinitz, D.; Christofori, G.; Lehembre, F. Hepatocyte growth factor induces cell scattering through MAPK/Egr-1-mediated upregulation of Snail. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3534–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Wang, Q.; He, X.L.; Chu, Y.K.; Lu, J.G.; Ma, Q.J. Role of nuclear factor kappa B and reactive oxygen species in the tumor necrosis factor-a-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of MCF-7 cells. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2007, 40, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, M.; Seidler, B.; Haller, F.; Adamski, J.; Schmid, R.M.; Saur, D.; Schneider, G. IKK(α) controls canonical TGF(ß)-SMAD signaling to regulate genes expressing SNAIL and SLUG during EMT in panc1 cells. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 4231–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.P.; Deng, J.; Xia, W.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.M.; Gunduz, M.; Hung, M.C. Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yook, J.I.; Li, X.Y.; Ota, I.; Fearon, E.R.; Weiss, S.J. Wnt dependent regulation of the E-cadherin repressor Snail. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11740–11748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yook, J.I.; Li, X.Y.; Ota, I.; Hu, C.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, N.H.; Cha, S.Y.; Ryu, J.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.; et al. A Wnt-Axin2-GSK3beta cascade regulates Snail1 activity in breast cancer cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Rayala, S.; Nguyen, D.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Chen, S.; Kumar, R. Pak1 phosphorylation of snail, a master regulator of epithelial-to-mesenchyme transition, modulates snail’s subcellular localization and functions. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3179–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Rodriguez-Aznar, E.; Yabuta, N.; Owen, R.J.; Mingot, J.M.; Nojima, H.; Nieto, M.A.; Longmore, G.D. Lats2 kinase potentiates Snail1 activity by promoting nuclear retention upon phosphorylation. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Guo, X.; Qian, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Brinkman, K.L.; Serrano-Gonzalez, M.; Jope, R.S.; Zhou, B.; Engler, D.A.; et al. Activation of the ATM-Snail pathway promotes breast cancer metastasis. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 4, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyun, B.J.; Seo, H.R.; Lee, H.J.; Jin, Y.B.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.S.; Nam, H.W.; Yook, J.I.; Lee, Y.S. Mutual regulation between DNA-PKcs and snail1 leads to increased genomic instability and aggressive tumor characteristics. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Corsa, C.A.; Ponik, S.M.; Prior, J.L.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Keely, P.J.; Longmore, G.D. The collagen receptor discoidin domain receptor 2 stabilizes SNAIL1 to facilitate breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.J.; Park, S.M.; Park, S.H.; Kim, I.K.; Han, H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Hong, K.S.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.; et al. p38 stabilizes Snail by suppressing DYRK2-mediated phosphorylation that is required for GSK3β-βTrCP-induced Snail degradation. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4135–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Shenoy, A.K.; Doernberg, S.; Chen, H.; Luo, H.; Shen, H.; Lin, T.; Tarrash, M.; Cai, Q.; Hu, X.; et al. FBXO11 promotes ubiquitination of the Snail family of transcription factors in cancer progression and epidermal development. Cancer Lett. 2015, 362, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Foulds, C.E.; Qin, J.; Liu, J.; Ding, C.; Lonard, D.M.; Solis, L.M.; Wistuba, I.I.; Qin, J.; Tsai, S.Y.; et al. ERK3 signals through SRC-3 coactivator to promote human lung cancer cell invasion. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahdi, R.; Babteen, N.; Thillai, K.; Holt, M.; Johansen, B.; Wetting, H.L.; Seternes, O.M.; Wells, C.M. A novel role for atypical MAPK kinase ERK3 in regulating breast cancer cell morphology and migration. Cell Adh. Migr. 2015, 9, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seternes, O.M.; Mikalsen, T.; Johansen, B.; Michaelsen, E.; Armstrong, C.G.; Morrice, N.A.; Turgeon, B.; Meloche, S.; Moens, U.; Keyse, S.M. Activation of MK5/PRAK by the atypical MAP kinase ERK3 defines a novel signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4780–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, R.; Ding, F.; Li, Y.; Cao, X.; Liu, Z. SPSB3 targets SNAIL for degradation in GSK-3β phosphorylation-dependent manner and regulates metastasis. Oncogene 2018, 37, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, M.; Jing, P.; Xiong, J.; Han, Z.; Kong, J.; Li, M.; Lai, X.; Chang, N.; et al. FBW7 loss promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer through the stabilization of Snail protein. Cancer Lett. 2018, 419, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinas-Castells, R.; Alex, F.; Estefania, R.L.; Kun, Z.; Longmore, G.D.; Garcia de Herreros, A.; Diaz, V.M. Nuclear ubiquitylation by FBXL5 modulates Snail1 DNA binding and stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 1079–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.Y.; Wang, T.; Su, S.; Shen, L.T.; Zhu, G.X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, K.W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.H.; et al. BRD4 promotes gastric cancer progression and metastasis through acetylation-dependent stabilization of Snail. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4869–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, H.; Sekimoto, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Douchi, T.; Nagata, Y.; Ozawa, M.; Yoneda, Y. Zinc finger domain of Snail functions as a nuclear localization signal for importin beta-mediated nuclear import pathway. Genes Cells 2005, 10, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yu, J.; Deng, M.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, K.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Ren, T.; et al. CDK4/6-dependent activation of DUB3 regulates cancer metastasis through SNAIL1. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, J.; Singh, P.; Chi, Y.I.; Wang, C.; Dong, C.; et al. Dub3 inhibition suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by promoting Snail1 degradation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Ding, F.; Cao, X.; Lin, D.; Liu, Z. OTUB1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through modulating Snail stability. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3356–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonego, M.; Pellarin, I.; Costa, A.; Vinciguerra, G.L.R.; Coan, M.; Kraut, A.; D’Andrea, S.; Dall’Acqua, A.; Castillo-Tong, D.C.; Califano, D.; et al. USP1 links platinum resistance to cancer cell dissemination by regulating Snail stability. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Chen, Z.; Wu, X.; Cai, X.; Feng, S.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, N. Ubiquitin-specific protease 3 promotes glioblastoma cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via stabilizing Snail. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y. Upregulation of USP11 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by deubiquitinating Snail in ovarian cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Zheng, C.; Huang, L.; Lin, C.; Wang, J. USP18 directly regulates Snail1 protein through ubiquitination pathway in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, R.; Liu, Z. USP26 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through stabilizing Snail. Cancer Lett. 2019, 448, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Hou, Z.; Jia, H.; Liu, S. USP37 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Migration by Stabilizing Snail Protein via Deubiquitination. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambies, G.; Miceli, M.; Martinez-Guillamon, C.; Olivera-Salguero, R.; Pena, R.; Frias, C.P.; Calderon, I.; Atanassov, B.S.; Dent, S.Y.R.; Arribas, J.; et al. TGFβ-activated USP27X deubiquitinase regulates cell migration and chemoresistance via stabilization of Snail1. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, F.F.; Drabasch, Y.; Gao, R.; Snaar-Jagalska, B.E.; Mickanin, C.; Huang, H.; Sheppard, K.A.; Porter, J.A.; Lu, C.X.; et al. USP4 is regulated by AKT phosphorylation and directly deubiquitylates TGF-β type I receptor. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.; Song, H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.T. Vaccinia-related kinase 2 controls the stability of the eukaryotic chaperonin TRiC/CCT by inhibiting the deubiquitinating enzyme USP25. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, C.; Chu, H.; Pan, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; et al. The deubiquitinase USP21 maintains the stemness of mouse embryonic stem cells via stabilization of Nanog. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-H.; Ryu, K.-J.; Hong, K.-S.; Kim, H.; Han, H.; Kim, M.; Kim, T.; Ok, D.W.; Yang, J.W.; Hwangbo, C.; et al. ERK3 Increases Snail Protein Stability by Inhibiting FBXO11-Mediated Snail Ubiquitination. Cancers 2024, 16, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010105
Kim S-H, Ryu K-J, Hong K-S, Kim H, Han H, Kim M, Kim T, Ok DW, Yang JW, Hwangbo C, et al. ERK3 Increases Snail Protein Stability by Inhibiting FBXO11-Mediated Snail Ubiquitination. Cancers. 2024; 16(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010105
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seon-Hee, Ki-Jun Ryu, Keun-Seok Hong, Hyemin Kim, Hyeontak Han, Minju Kim, Taeyoung Kim, Dong Woo Ok, Jung Wook Yang, Cheol Hwangbo, and et al. 2024. "ERK3 Increases Snail Protein Stability by Inhibiting FBXO11-Mediated Snail Ubiquitination" Cancers 16, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010105
APA StyleKim, S.-H., Ryu, K.-J., Hong, K.-S., Kim, H., Han, H., Kim, M., Kim, T., Ok, D. W., Yang, J. W., Hwangbo, C., Kim, K. D., & Yoo, J. (2024). ERK3 Increases Snail Protein Stability by Inhibiting FBXO11-Mediated Snail Ubiquitination. Cancers, 16(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010105





