A User-Friendly System for Mailed Dosimetric Audits of 192Ir or 60Co HDR Brachytherapy Sources
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
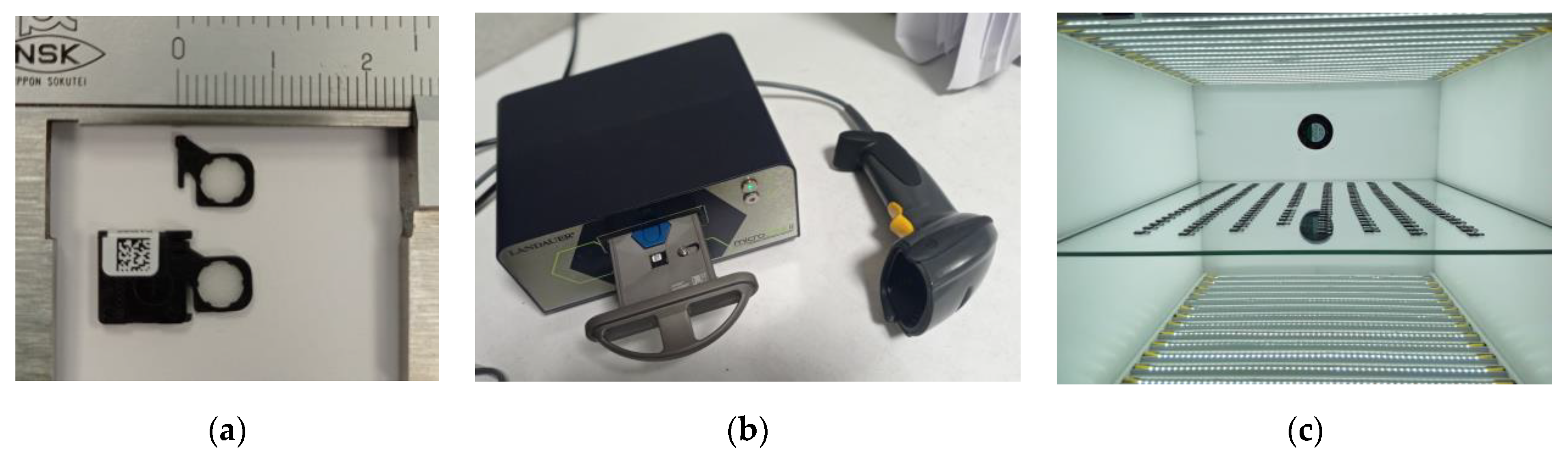
2.1. Dosimetry System
2.2. Phantom Design
2.3. Calibration of the System
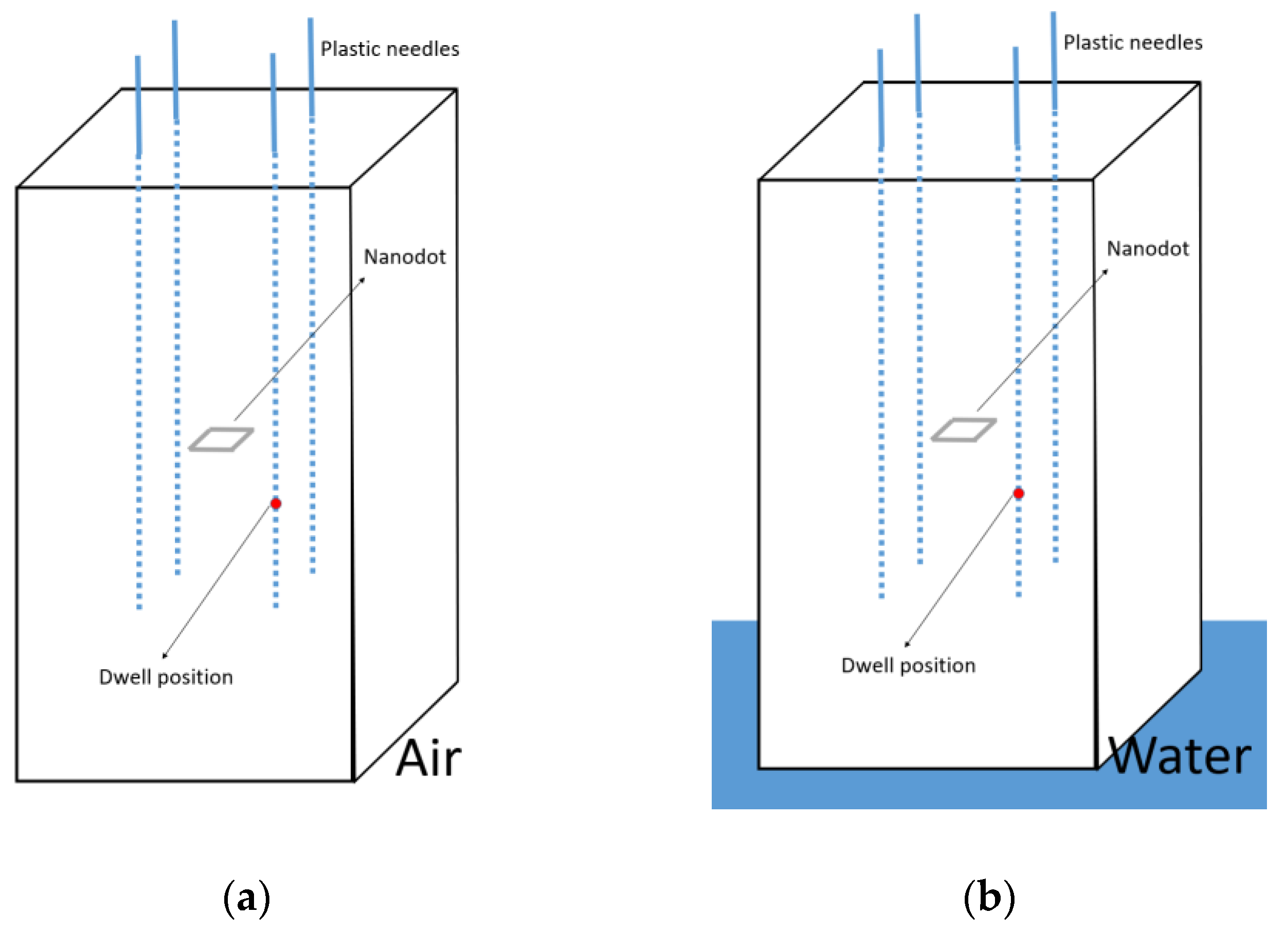
2.4. Characterization of the Scatter Conditions
2.5. Study of the Spectra Reaching the nanoDot for Different 192Ir Source Models
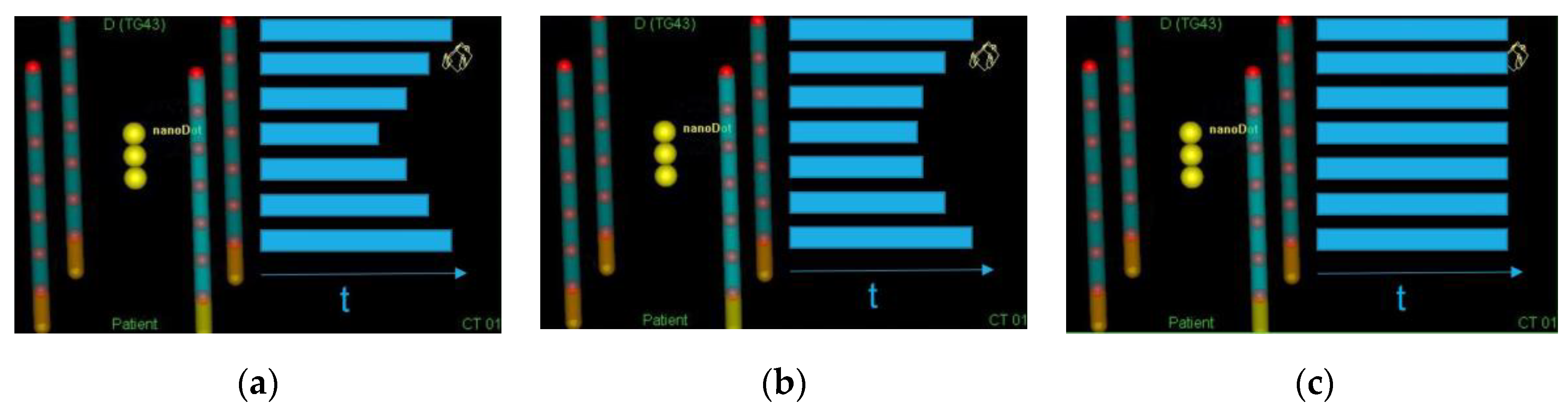
2.6. Dwell Times
2.7. Stability of the Reader
2.8. Final Dose Evaluation
3. Results
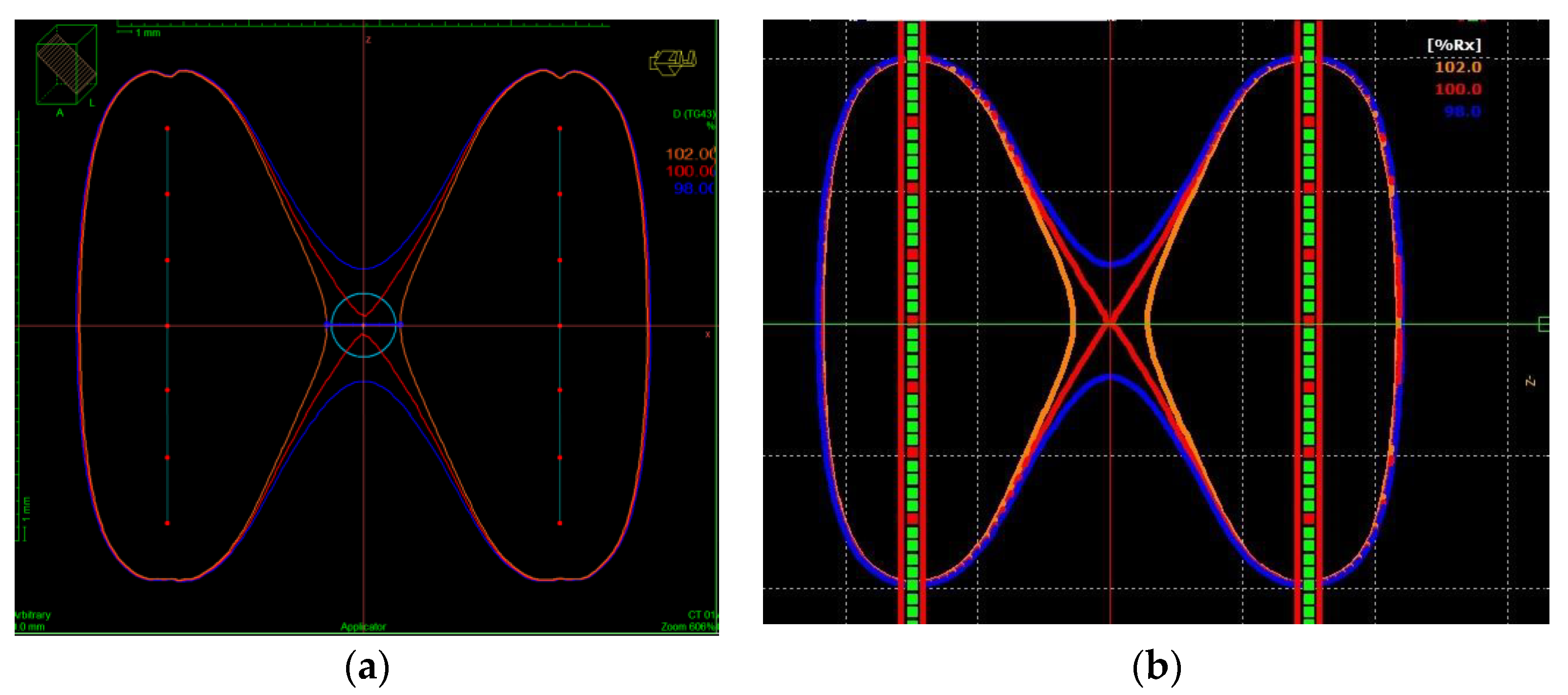
3.1. Dose Distribution
3.2. Calibration Coefficients
3.3. Characterization of the Scatter Conditions
3.4. Study of the Spectra Reaching the nanoDot for Different 192Ir Source Models
3.5. Estimated Uncertainty in the Dose Measurement
- Uncertainty in the dosimeter reading (L): The estimated uncertainty in the dosimeter reading is 0.5 % (k = 1), considering the uncertainty due to fading, depletion factor, and characterization of the ISF.
- Uncertainty in the reader stability (C): An uncertainty of 1.3% (k = 1) was estimated for the stability of the reader. This uncertainty was reduced from 5% (see Section 2.7) to 1.3% using the control dosimeters described above.
- Uncertainty in the RAKR: This was taken from the calibration certificate of the source, being 1.7% (k = 1) for both 60Co and 192Ir sources.
- Uncertainty in the dwell position: The phantom is designed to insert 6F needles, which have 2 mm of external diameter. Considering the dwell thickness, a dwell shift in the direction of the catheter below 1 mm (according to the tolerance established in the quality protocols) and the dose homogeneity in the area where the nanoDot is placed leads to an estimated uncertainty of 0.7% (k = 1).
- Uncertainty in the irradiation time: Considering that there are 7 active positions per catheter and a time resolution of 0.1 s/position, the estimated uncertainty is 0.1% (k = 1).
- Uncertainty in the OSLD response due to differences in the spectra of the VS2000 192Ir source: Our results show a mean photon energy reaching the nano-Dot for the Varisource VS2000 model of 240.6 keV to be compared with the 234.6 keV found for the MicroSelectron V2 source. If these data are contrasted with the energy dependence reported by Cruz et al. [26], considering the angular incidences of our irradiation set-up, the variation in the nanoDot response due to this energy variation would be between 0.1% and 0.3%. Therefore, a conservative uncertainty of 0.3% (k = 1) is considered.
| Components | Uncertainty (%) (k = 1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 192Ir (V2, Flexisource and BEBIG) | 192Ir (VS2000) | 60Co | |
| OSLD reading (L) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Reader stability (C) | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| RAKR | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| Dwell position | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0. 7 |
| Irradiation time | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Calibration coefficient (F) | 1.9 | 1.9 | 2.0 |
| OSLD response | 0.3 | ||
| Overall uncertainty | 3.0 | 3.1 | 3.0 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirisits, C.; Rivard, M.J.; Baltas, D.; Ballester, F.; De Brabandere, M.; van der Laarse, R.; Niatsetski, Y.; Papagiannis, P.; Hellebust, T.P.; Perez-Calatayud, J.; et al. Review of Clinical Brachytherapy Uncertainties: Analysis Guidelines of GEC-ESTRO and the AAPM. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 110, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanderup, K.; Beddar, S.; Andersen, C.E.; Kertzscher, G.; Cygler, J.E. In Vivo Dosimetry in Brachytherapy. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 070902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidmead, M.; Venselaar, J.; Burger, J.; Pérez-Calatayud, J. A Practical Guide to Quality Control of Brachytherapy Equipment; ESTRO Booklet; ESTRO: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, A.L.; Bradley, D.A.; Nisbet, A. Dosimetric audit in brachytherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20140105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivard, M.J.; Coursey, B.M.; DeWerd, L.A.; Hanson, W.F.; Saiful Huq, M.; Ibbott, G.S.; Mitch, M.G.; Nath, R.; Williamson, J.F. Update of AAPM Task Group No. 43 Report: A revised AAPM protocol for brachytherapy dose calculations. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 633–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson Tedgren, A.; Grindborg, J.-E. Audit on Source Strength Determination for HDR and PDR 192Ir Brachytherapy in Sweden. Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 86, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreros, A.; Pérez-Calatayud, J.; Ballester Pallarés, F.; Melo, J.; Fernández-Varea, J.M. Diseño de un maniquí para la calibración de un sistema de dosimetría in vivo en braquiterapia. In Proceedings of the 6º Congreso Conjunto SEFM SEPR, Burgos, Spain, 11–14 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Roué, A.; Venselaar, J.L.M.; Ferreira, I.H.; Bridier, A.; Van Dam, J. Development of a TLD Mailed System for Remote Dosimetry Audit for 192Ir HDR and PDR Sources. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 83, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, K.E.; Alvarez, P.; Kry, S.F.; Howell, R.M.; Lawyer, A.; Followill, D. Development and Implementation of a Remote Audit Tool for High Dose Rate (HDR) Ir-192 Brachytherapy Using Optically Stimulated Luminescence Dosimetry. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 112102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roué, A.; Ferreira, I.H.; Van Dam, J.; Svensson, H.; Venselaar, J.L.M. The EQUAL-ESTRO Audit on Geometric Reconstruction Techniques in Brachytherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2006, 78, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi Medical Research. 3D Matrix Phantom (Baltas Phantom). [about 1 p.] Cited 21 January 2014. Available online: http://www.pi-medical.gr/products/tools/matrix-phantom (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Palmer, A.L.; Diez, P.; Gandon, L.; Wynn-Jones, A.; Bownes, P.; Lee, C.; Aird, E.; Bidmead, M.; Lowe, G.; Bradley, D.; et al. A Multicentre “end to End” Dosimetry Audit for Cervix HDR Brachytherapy Treatment. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 114, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.L.; Lee, C.; Ratcliffe, A.J.; Bradley, D.; Nisbet, A. Design and Implementation of a Film Dosimetry Audit Tool for Comparison of Planned and Delivered Dose Distributions in High Dose Rate (HDR) Brachytherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 6623–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, D.J.; Earner, B.; Faulkner, P.; Dancer, N. A National Dosimetry Audit of Intraoperative Radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2013, 86, 20130447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, A.; Mzenda, B.; Kearton, J.; Wills, R. Analysis of Regional Radiotherapy Dosimetry Audit Data and Recommendations for Future Audits. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, F.; Pérez-Calatayud, J.; Carmona, V.; Lliso, F.; Torres, I. Determinación de la exactitud en la reconstrucción espacial de implantes en braquiterapia. Rev. Física Médica 2002, 3, 95–96. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, A.J.; King, D.M.; Browne, J.E. A Review of the Recommendations Governing Quality Assurance of Ultrasound Systems Used for Guidance in Prostate Brachytherapy. Phys. Med. 2017, 44, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisciandaro, J.; Zoberi, J.E.; Cohen, G.; Kim, Y.; Johnson, P.; Paulson, E.; Song, W.; Hwang, K.-P.; Erickson, B.; Beriwal, S.; et al. AAPM Task Group Report 303 Endorsed by the ABS: MRI Implementation in HDR Brachytherapy-Considerations from Simulation to Treatment. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, e983–e1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgani, M.J.T.; Khorshidsavar, H.; Bagheri, A.; Danyaei, A.; Abdalvand, N. The Design of an Audit Test for (60)Co Brachytherapy Treatment Planning System. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2022, 12, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagenberg, T.; Fonseca, G.P.; Voncken, R.; van Beveren, C.; van Limbergen, E.; Lutgens, L.; Vanneste, B.G.L.; Berbee, M.; Reniers, B.; Verhaegen, F. Treatment Verification in High Dose Rate Brachytherapy Using a Realistic 3D Printed Head Phantom and an Imaging Panel. Brachytherapy 2023, 22, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujades-Claumarchirant, M.C.; Candela-Juan, C.; Oliver-Cañamás, L.; Soriano-Cruz, Á.; Rovira-Escutia, J.J.; Ballester-Pallarés, F. Estudio Piloto De Una auditoría Postal dosimétrica Para Radioterapia En Condiciones De Referencia. Rev. Fis. Med. 2022, 23, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Calatayud, J.; Ballester, F.; Das, R.K.; Dewerd, L.A.; Ibbott, G.S.; Meigooni, A.S.; Ouhib, Z.; Rivard, M.J.; Sloboda, R.S.; Williamson, J.F. Dose Calculation for Photon-Emitting Brachytherapy Sources with Average Energy Higher than 50 KeV: Report of the AAPM and ESTRO. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 2904–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granero, D.; Perez-Calatayud, J.; Pujades-Claumarchirant, M.C.; Ballester, F.; Melhus, C.S.; Rivard, M.J. Equivalent Phantom Sizes and Shapes for Brachytherapy Dosimetric Studies of 192Ir and 137Cs. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 4872–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Dunn, L.; Lye, J.E.; Kenny, J.W.; Alves, A.D.C.; Cole, A.; Asena, A.; Kron, T.; Williams, I.M. Angular Dependence of the Response of the NanoDot OSLD System for Measurements at Depth in Clinical Megavoltage Beams. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 061712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, W.W.; Cross, C.L. Biostatistics: A Foundation for Analysis in the Health Sciences, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, V.L.E.; Okazaki, T.; Hayashi, H. Energy and Angular Dependence of the Small-Type OSL Dosimeter in Nuclear Medicine Regions Using Monte Carlo Simulation. Prog. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.; Holloway, L.; Baldock, C. A Dosimetric Evaluation of Water Equivalent Phantoms for Kilovoltage X-Ray Beams. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, N331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.P.; Seong, Y.M.; Kim, T.Y.; Choi, Y.; Kim, T.H.; Choi, H.J.; Min, C.H.; Benmakhlouf, H.; Chun, K.J.; Chung, H.-T. Development of a PMMA Phantom as a Practical Alternative for Quality Control of Gamma Knife® Dosimetry. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, A.; Kakakhel, M.B.; Shahid, S.A.; Younas, L.; Zareen, S. Soft Tissue and Water Substitutes for Megavoltage Photon Beams: An EGSnrc-Based Evaluation. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2016, 17, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meli, J.A.; Meigooni, A.S.; Nath, R. On the Choice of Phantom Material for the Dosimetry of 192Ir Sources. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1988, 14, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Source to NanoDot Distance (cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source Model | 2.12 | 1.80 | 1.58 | 1.50 |
| V2 | 300.1 ± 0.9 | 300.0 ± 0.9 | 287.2 ± 0.9 | 234.6 ± 0.7 |
| Flexisource | 299.4 ± 0.9 | 299.2 ± 0.9 | 286.4 ± 0.9 | 233.9 ± 0.7 |
| VS2000 | 296.9 ± 0.9 | 296.4 ± 0.9 | 283.1 ± 0.9 | 240.6 ± 0.7 |
| BEBIG | 299.3 ± 0.9 | 299.4 ± 0.9 | 286.3 ± 0.9 | 233.9 ± 0.7 |
| Source to NanoDot Distance (cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source Model | 2.12 | 1.80 | 1.58 | 1.50 |
| Flexisource/V2 | −0.3 ± 0.4% | −0.3 ± 0.4% | −0.3 ± 0.4% | −0.3 ± 0.4% |
| VS2000/V2 | −1.1 ± 0.4% | −1.2 ± 0.4% | −1.4 ± 0.4% | 2.6 ± 0.4% |
| BEBIG/V2 | −0.3 ± 0.4% | −0.2 ± 0.4% | −0.3 ± 0.4% | −0.3 ± 0.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliver-Cañamás, L.; Vijande, J.; Candela-Juan, C.; Gimeno-Olmos, J.; Pujades-Claumarchirant, M.C.; Rovira-Escutia, J.J.; Ballester, F.; Perez-Calatayud, J. A User-Friendly System for Mailed Dosimetric Audits of 192Ir or 60Co HDR Brachytherapy Sources. Cancers 2023, 15, 2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092484
Oliver-Cañamás L, Vijande J, Candela-Juan C, Gimeno-Olmos J, Pujades-Claumarchirant MC, Rovira-Escutia JJ, Ballester F, Perez-Calatayud J. A User-Friendly System for Mailed Dosimetric Audits of 192Ir or 60Co HDR Brachytherapy Sources. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092484
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliver-Cañamás, Laura, Javier Vijande, Cristian Candela-Juan, Jose Gimeno-Olmos, Mª Carmen Pujades-Claumarchirant, Juan J. Rovira-Escutia, Facundo Ballester, and Jose Perez-Calatayud. 2023. "A User-Friendly System for Mailed Dosimetric Audits of 192Ir or 60Co HDR Brachytherapy Sources" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092484
APA StyleOliver-Cañamás, L., Vijande, J., Candela-Juan, C., Gimeno-Olmos, J., Pujades-Claumarchirant, M. C., Rovira-Escutia, J. J., Ballester, F., & Perez-Calatayud, J. (2023). A User-Friendly System for Mailed Dosimetric Audits of 192Ir or 60Co HDR Brachytherapy Sources. Cancers, 15(9), 2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092484






