Neuronal Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors Suppress the Growth of Melanoma Brain Metastases by Inhibiting Glutamatergic Signalling
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Interrogation of GDC-TCGA Melanoma Datasets
2.2. Cells
2.3. Quantitative PCR
2.4. Cell Viability Assays
2.5. Immunofluorescence
2.6. Animals
2.7. Tumour Allografts
2.8. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Intracarotid Artery Injection
2.11. Brain Metastatic Burden Analysis
2.12. Tail Vein Injection
3. Results
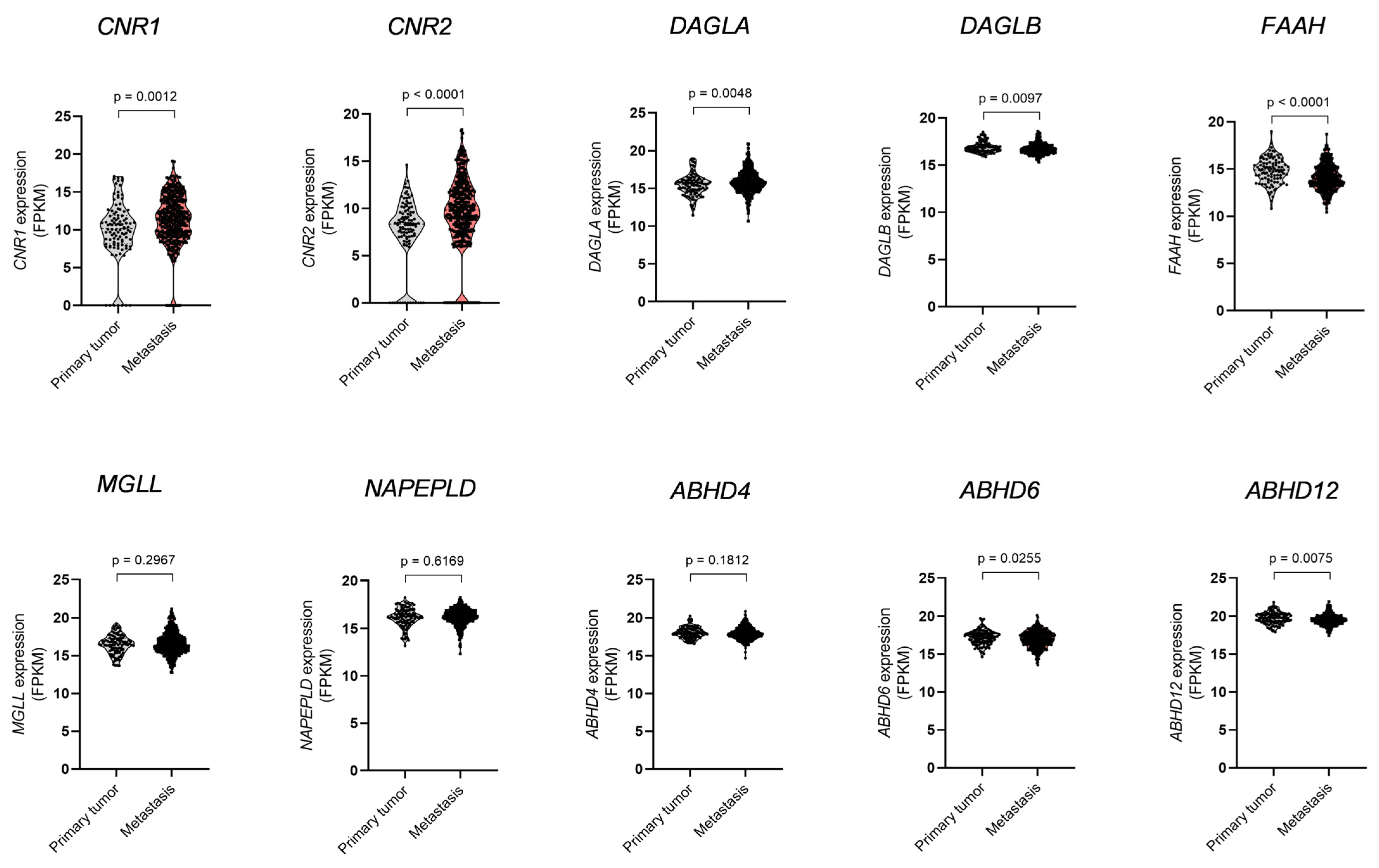
3.1. Dysregulation of ECS Elements and Glutamate Receptors in Melanoma Metastases
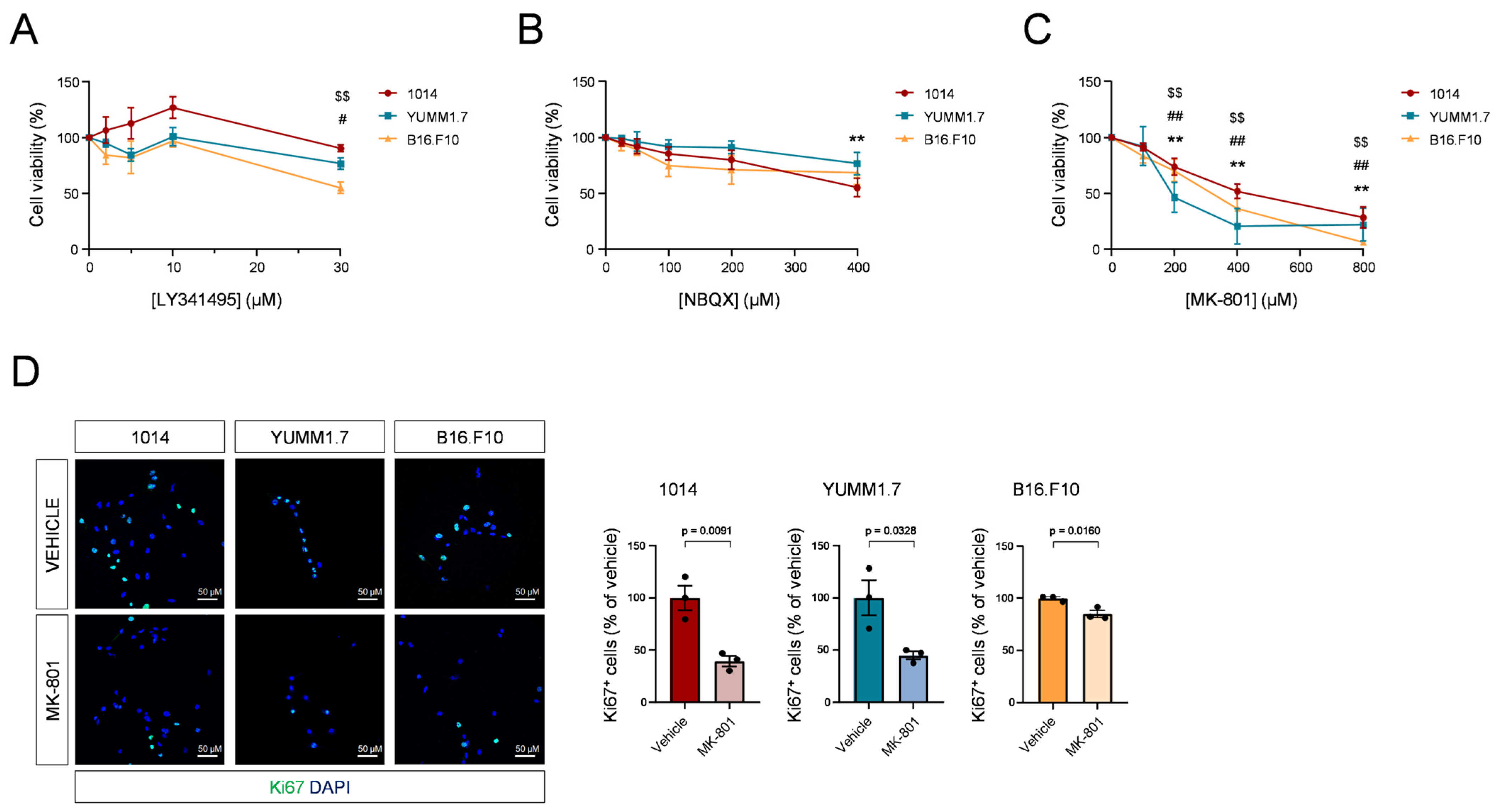
3.2. Blockade of NMDARs Inhibits Melanoma Cell Proliferation In Vitro
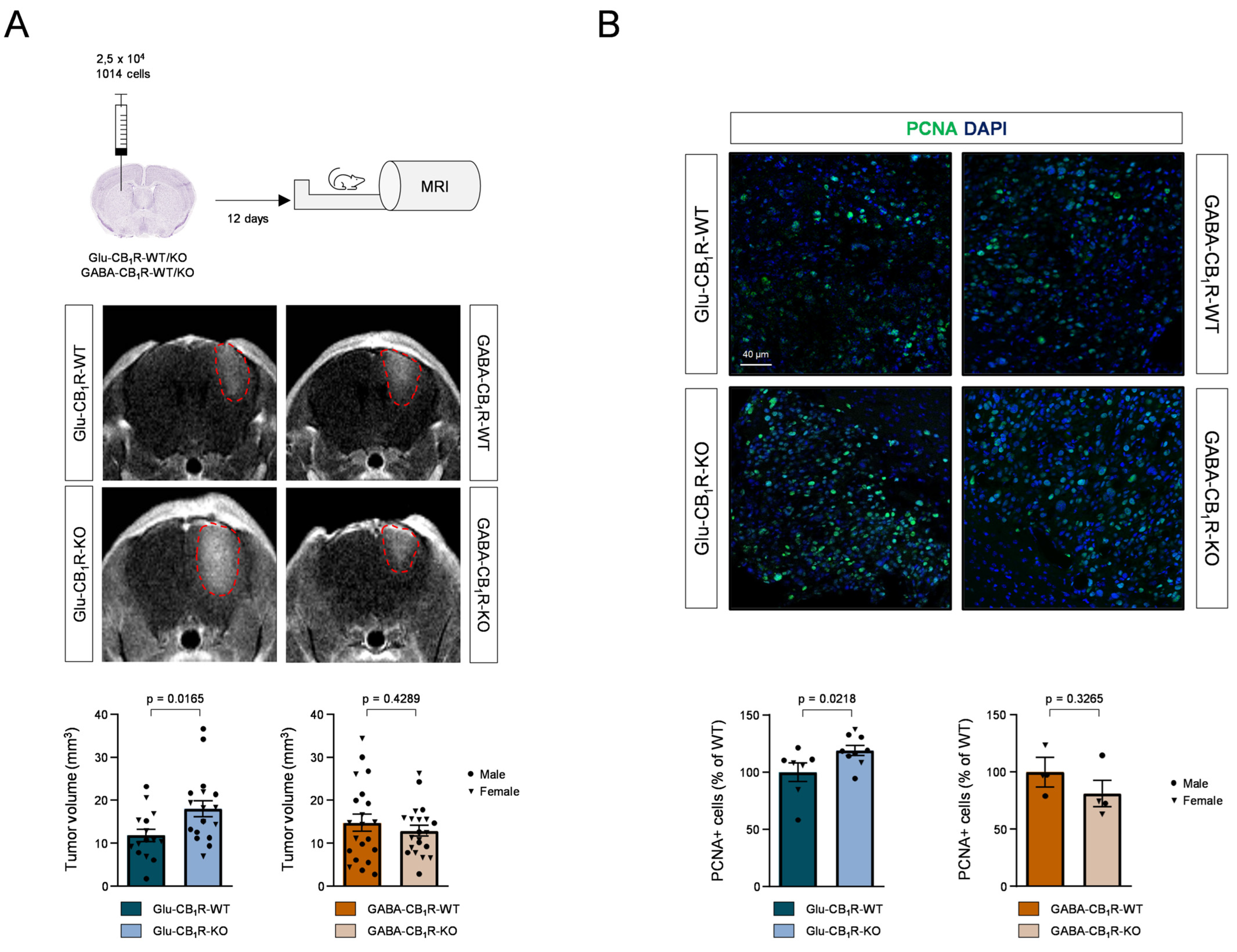
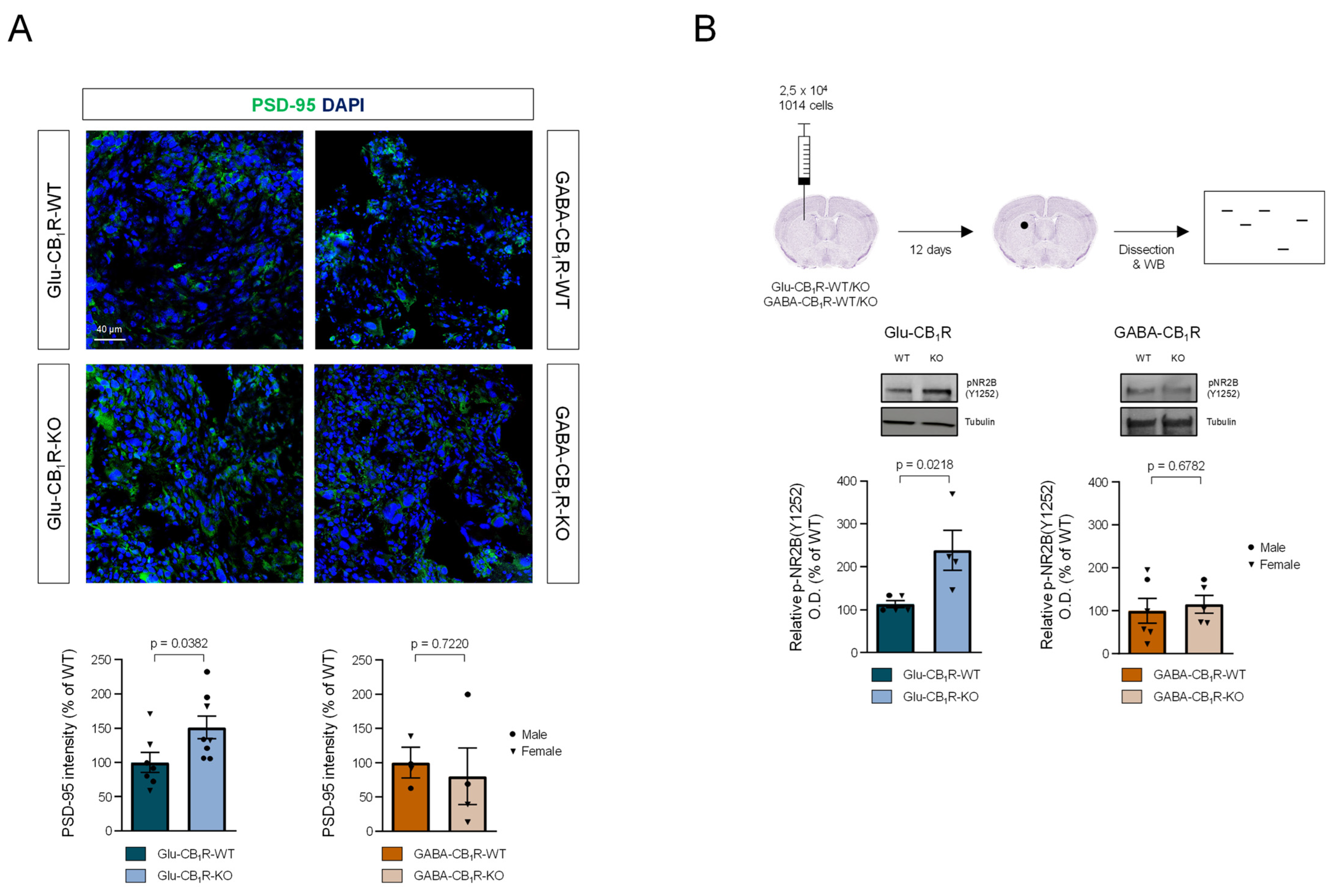
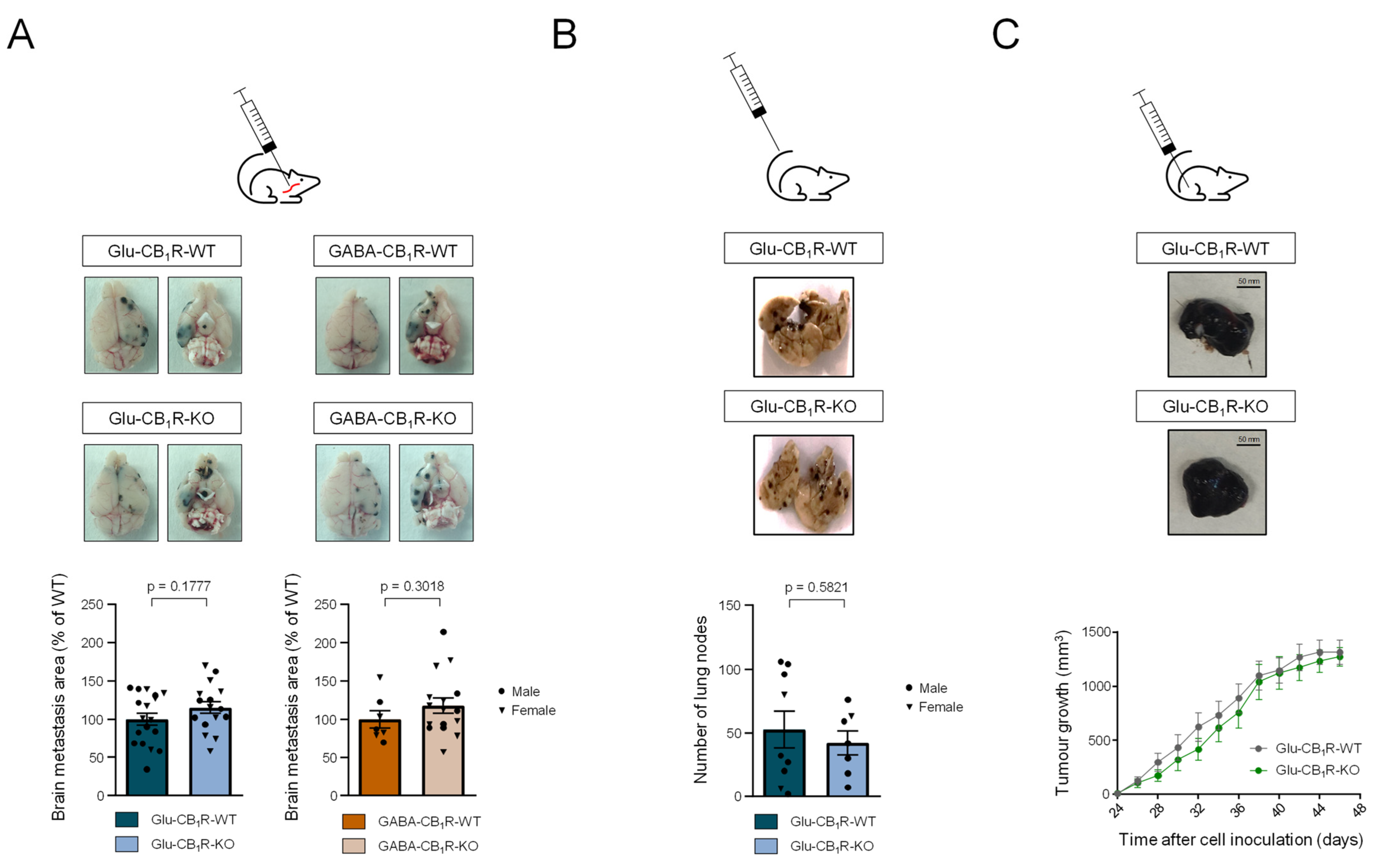
3.3. CB1Rs Located on Glutamatergic Neurons Control the Growth of MBMs In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schadendorf, D.; Fisher, D.E.; Garbe, C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Grob, J.J.; Halpern, A.; Herlyn, M.; Marchetti, M.A.; McArthur, G.; Ribas, A.; et al. Melanoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, A.; Bannister, P.; Rogers, I.; Sundin, J.; Al-Ayadhy, B.; James, P.W.; McNally, R.J.Q. Changing Epidemiology and Age-Specific Incidence of Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma in England: An Analysis of the National Cancer Registration Data by Age, Gender and Anatomical Site, 1981–2018. Lancet Reg. Health-Eur. 2021, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutzmer, R.; Vordermark, D.; Hassel, J.C.; Krex, D.; Wendl, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Sickmann, T.; Rieken, S.; Pukrop, T.; Höller, C.; et al. Melanoma Brain Metastases–Interdisciplinary Management Recommendations 2020. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 89, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, E.E.; Mueller, K.L.; Adams, D.J.; Anandasabapathy, N.; Aplin, A.E.; Bertolotto, C.; Bosenberg, M.; Ceol, C.J.; Burd, C.E.; Chi, P.; et al. Melanoma Models for the next Generation of Therapies. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 610–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smedby, K.E.; Brandt, L.; Bäcklund, M.L.; Blomqvist, P. Brain Metastases Admissions in Sweden between 1987 and 2006. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Sloan, A.E.; Davis, F.G.; Vigneau, F.D.; Lai, P.; Sawaya, R.E. Incidence Proportions of Brain Metastases in Patients Diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Atkinson, V.; Lo, S.; Sandhu, S.; Guminski, A.D.; Brown, M.P.; Wilmott, J.S.; Edwards, J.; Gonzalez, M.; Scolyer, R.A.; et al. Combination Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone in Melanoma Brain Metastases: A Multicentre Randomised Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bander, E.D.; Yuan, M.; Carnevale, J.A.; Reiner, A.S.; Panageas, K.S.; Postow, M.A.; Tabar, V.; Moss, N.S. Melanoma Brain Metastasis Presentation, Treatment, and Outcomes in the Age of Targeted and Immunotherapies. Cancer 2021, 127, 2062–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, L.; Bisogno, T.; Di Marzo, V. Cannabinoids and the Expanded Endocannabinoid System in Neurological Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, C.; Carracedo, A.; Barrado, L.; José Real, P.; Luis Fernández-Luna, J.; Velasco, G.; Malumbres, M.; Guzmán, M.; Blázquez, C.; Carracedo, A.; et al. Cannabinoid Receptors as Novel Targets for the Treatment of Melanoma. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, G.; Sánchez, C.; Guzmán, M. Endocannabinoids and Cancer. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 231, 449–472. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, J.L.; Hill, D.S.; McKee, C.S.; Hernandez-Tiedra, S.; Lorente, M.; Lopez-Valero, I.; Anagnostou, M.E.; Babatunde, F.; Corazzari, M.; Redfern, C.P.F.; et al. Exploiting Cannabinoid-Induced Cytotoxic Autophagy to Drive Melanoma Cell Death. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herkenham, M.; Lynn, A.B.; Little, M.D.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; De Costa, B.R.; Rice, K.C. Cannabinoid Receptor Localization in Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1932–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, G.A.; Raborn, E.S.; Griffin, L.; Dennis, J.; Marciano-Cabral, F. CB2 Receptors in the Brain: Role in Central Immune Function. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piomelli, D. The Molecular Logic of Endocannabinoid Signalling. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, M.; Borniger, J.C.; D’Silva, N.J.; Deneen, B.; Dirks, P.B.; Fattahi, F.; Frenette, P.S.; Garzia, L.; Gutmann, D.H.; Hanahan, D.; et al. Roadmap for the Emerging Field of Cancer Neuroscience. Cell 2020, 181, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleffman, K.; Levinson, G.; Rose, I.V.L.; Blumenberg, L.M.; Shadaloey, S.A.A.; Dhabaria, A.; Wong, E.; Galán-Echevarría, F.; Karz, A.; Argibay, D.; et al. Melanoma-Secreted Amyloid Beta Suppresses Neuroinflammation and Promotes Brain Metastasis. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 1314–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priego, N.; Zhu, L.; Monteiro, C.; Mulders, M.; Wasilewski, D.; Bindeman, W.; Doglio, L.; Martínez, L.; Martínez-Saez, E.; Cajal, S.R.Y.; et al. STAT3 Labels a Subpopulation of Reactive Astrocytes Required for Brain Metastasis. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Boire, A.; Jin, X.; Valiente, M.; Er, E.E.; Lopez-Soto, A.; Jacob, L.S.; Patwa, R.; Shah, H.; Xu, K.; et al. Carcinoma-Astrocyte Gap Junctions Promote Brain Metastasis by CGAMP Transfer. Nature 2016, 533, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Michael, I.P.; Zhang, P.; Saghafinia, S.; Knott, G.; Jiao, W.; McCabe, B.D.; Galván, J.A.; Robinson, H.P.C.; Zlobec, I.; et al. Synaptic Proximity Enables NMDAR Signalling to Promote Brain Metastasis. Nature 2019, 573, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, H.S.; Morishita, W.; Geraghty, A.C.; Silverbush, D.; Gillespie, S.M.; Arzt, M.; Tam, L.T.; Espenel, C.; Ponnuswami, A.; Ni, L.; et al. Electrical and Synaptic Integration of Glioma into Neural Circuits. Nature 2019, 573, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataramani, V.; Tanev, D.I.; Strahle, C.; Studier-Fischer, A.; Fankhauser, L.; Kessler, T.; Körber, C.; Kardorff, M.; Ratliff, M.; Xie, R.; et al. Glutamatergic Synaptic Input to Glioma Cells Drives Brain Tumour Progression. Nature 2019, 573, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataramani, V.; Yang, Y.; Schubert, M.C.; Reyhan, E.; Tetzlaff, S.K.; Wißmann, N.; Botz, M.; Soyka, S.J.; Beretta, C.A.; Pramatarov, R.L.; et al. Glioblastoma Hijacks Neuronal Mechanisms for Brain Invasion. Cell 2022, 185, 2899–2917.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and Interpreting Cancer Genomics Data via the Xena Platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, V.; Raymond, J.; Alberti, C.; Pouteaux, M.; Gallagher, S.J.; Nguyen, M.Q.; Aplin, A.E.; Delmas, V.; Larue, L. C57BL/6 Congenic Mouse NRASQ61K Melanoma Cell Lines Are Highly Sensitive to the Combination of Mek and Akt Inhibitors In Vitro and In Vivo. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2019, 32, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costas-Insua, C.; Moreno, E.; Maroto, I.B.; Ruiz-Calvo, A.; Bajo-Grañeras, R.; Martín-Gutiérrez, D.; Diez-Alarcia, R.; Teresa Vilaró, M.; Cortés, R.; García-Font, N.; et al. Identification of BiP as a CB1 Receptor-Interacting Protein That Fine-Tunes Cannabinoid Signaling in the Mouse Brain. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 7924–7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monory, K.; Massa, F.; Egertová, M.; Eder, M.; Blaudzun, H.; Westenbroek, R.; Kelsch, W.; Jacob, W.; Marsch, R.; Ekker, M.; et al. The Endocannabinoid System Controls Key Epileptogenic Circuits in the Hippocampus. Neuron 2006, 51, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monory, K.; Blaudzun, H.; Massa, F.; Kaiser, N.; Lemberger, T.; Schütz, G.; Wotjak, C.T.; Lutz, B.; Marsicano, G. Genetic Dissection of Behavioural and Autonomic Effects of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol in Mice. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhao, H.; Fang, X.; Li, H. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Is Upregulated in Melanoma. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2012, 8, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, Y.; Funakoshi, T.; Mori, M.; Emoto, K.; Masugi, Y.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Amagai, M.; Tanese, K. Expression of Monoacylglycerol Lipase as a Marker of Tumour Invasion and Progression in Malignant Melanoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 2038–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, P.M.; Cohen-Solal, K.; Sood, R.; Namkoong, J.; Martino, J.J.; Koganti, A.; Zhu, H.; Robbins, C.; Makalowska, I.; Shin, S.S.; et al. Melanoma Mouse Model Implicates Metabotropic Glutamate Signaling in Melanocytic Neoplasia. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namkoong, J.; Shin, S.S.; Hwa, J.L.; Marín, Y.E.; Wall, B.A.; Goydos, J.S.; Chen, S. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 and Glutamate Signaling in Human Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2298–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, S.A.; Chung, W.J.; Weaver, A.K.; Ogunrinu, T.; Sontheimer, H. Autocrine Glutamate Signaling Promotes Glioma Cell Invasion. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9463–9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hanahan, D. Hijacking the Neuronal NMDAR Signaling Circuit to Promote Tumor Growth and Invasion. Cell 2013, 153, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeth, K.; Wang, J.X.; Micevic, G.; Damsky, W.; Bosenberg, M.W. The YUMM Lines: A Series of Congenic Mouse Melanoma Cell Lines with Defined Genetic Alterations. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbani, R.; Akdemir, K.C.; Aksoy, B.A.; Albert, M.; Ally, A.; Amin, S.B.; Arachchi, H.; Arora, A.; Auman, J.T.; Ayala, B.; et al. Genomic Classification of Cutaneous Melanoma. Cell 2015, 161, 1681–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, V.O.; Bolshakov, S.V.; Walker, C.; Ananthaswamy, H.N. Genomic Alterations in Spontaneous and Carcinogen-Induced Murine Melanoma Cell Lines. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, A.E.; Ornstein, P.L.; Wright, R.A.; Johnson, B.G.; Mayne, N.G.; Burnett, J.P.; Belagaje, R.; Wu, S.; Schoepp, D.D. LY341495 Is a Nanomolar Potent and Selective Antagonist of Group II Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheardown, M.J.; Nielsen, E.; Hansen, A.J.; Jacobsen, P.; Honoré, T. 2,3-Dihydrox-6-Nitro-7-Sulfamoyl-Benzo(F)Quinoxaline: A Neuroprotectant for Cerebral Ischemnia. Science 1990, 247, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.H.F.; Kemp, J.A.; Priestley, T.; Knight, A.R.; Woodruff, G.N.; Iversen, L.L. The Anticonvulsant MK-801 Is a Potent N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Antagonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 7104–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Calvo, A.; Maroto, I.B.; Bajo-Grañeras, R.; Chiarlone, A.; Gaudioso, Á.; Ferrero, J.J.; Resel, E.; Sánchez-Prieto, J.; Rodríguez-Navarro, J.A.; Marsicano, G.; et al. Pathway-Specific Control of Striatal Neuron Vulnerability by Corticostriatal Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors. Cerebral Cortex 2018, 28, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prybylowski, K.; Chang, K.; Sans, N.; Kan, L.; Vicini, S.; Wenthold, R.J. The Synaptic Localization of NR2B-Containing NMDA Receptors Is Controlled by Interactions with PDZ Proteins and AP-2. Neuron 2005, 47, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, A.D.; Xiao, X.; Shaw, J.E.; Sudarsana Devi, S.P.; Katrancha, S.M.; Bennett, A.M.; Greer, C.A.; Howe, J.R.; Machida, K.; Koleske, A.J. Noonan Syndrome-Associated SHP2 Dephosphorylates GluN2B to Regulate NMDA Receptor Function. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 1523–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Kabraji, S.; Xie, S.; Pan, P.; Liu, Z.; Ni, J.; Zhao, J.J. Improving Orthotopic Mouse Models of Patient-Derived Breast Cancer Brain Metastases by a Modified Intracarotid Injection Method. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasinger, C.; Hofer, A.; Spadiut, O.; Hohenegger, M. Amino Acid Signature in Human Melanoma Cell Lines from Different Disease Stages. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, B.A.; Wangari-Talbot, J.; Shin, S.S.; Schiff, D.; Sierra, J.; Yu, L.J.; Khan, A.; Haffty, B.; Goydos, J.S.; Chen, S. Disruption of GRM1-Mediated Signalling Using Riluzole Results in DNA Damage in Melanoma Cells. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; He, C.D.; Liu, J.; Sun, C.; Lu, P.; Li, L.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shan, L.; et al. Blocking Glutamate-Mediated Signalling Inhibits Human Melanoma Growth and Migration. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdú, T.; Juhász, T.; Szűcs-Somogyi, C.; Rácz, K.; Zákány, R. NR1 and NR3B Composed Intranuclear N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Complexes in Human Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzeski, W.; Ikonomidou, C.; Turski, L. Glutamate Antagonists Limit Tumor Growth. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Lin, J.H.C.; Arcuino, G.; Gao, Q.; Yang, J.; Nedergaard, M. Glutamate Release Promotes Growth of Malignant Gliomas. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontheimer, H. Malignant Gliomas: Perverting Glutamate and Ion Homeostasis for Selective Advantage. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantakou, E.G.; Velentzas, A.D.; Anagnostopoulos, A.K.; Litou, Z.I.; Konstandi, O.A.; Giannopoulou, A.F.; Anastasiadou, E.; Voutsinas, G.E.; Tsangaris, G.T.; Stravopodis, D.J. Deep-Proteome Mapping of WM-266-4 Human Metastatic Melanoma Cells: From Oncogenic Addiction to Druggable Targets. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasdogan, A.; Faubert, B.; Ramesh, V.; Ubellacker, J.M.; Shen, B.; Solmonson, A.; Murphy, M.M.; Gu, Z.; Gu, W.; Martin, M.; et al. Metabolic Heterogeneity Confers Differences in Melanoma Metastatic Potential. Nature 2019, 577, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygaard, V.; Prasmickaite, L.; Vasiliauskaite, K.; Clancy, T.; Hovig, E. Melanoma Brain Colonization Involves the Emergence of a Brain-Adaptive Phenotype. Oncoscience 2014, 1, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermann, J.; Melms, J.C.; Amin, A.D.; Wang, Y.; Caprio, L.A.; Karz, A.; Tagore, S.; Barrera, I.; Ibarra-Arellano, M.A.; Andreatta, M.; et al. Dissecting the Treatment-Naive Ecosystem of Human Melanoma Brain Metastasis. Cell 2022, 185, 2591–2608.e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshmit, Y.; Perelroizen, R.; Yakovchuk, A.; Banyas, E.; Mayo, L.; David, S.; Benbenishty, A.; Blinder, P.; Shalom, M.; Ruban, A. Blood Glutamate Scavengers Increase Pro-Apoptotic Signaling and Reduce Metastatic Melanoma Growth In-Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudt, M.; Lasithiotakis, K.; Leiter, U.; Meier, F.; Eigentler, T.; Bamberg, M.; Tatagiba, M.; Brossart, P.; Garbe, C. Determinants of Survival in Patients with Brain Metastases from Cutaneous Melanoma. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Walia, V.; Lin, J.C.; Teer, J.K.; Prickett, T.D.; Gartner, J.; Davis, S.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Davies, M.A.; Gershenwald, J.E.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identifies GRIN2A as Frequently Mutated in Melanoma. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’mello, S.A.N.; Flanagan, J.U.; Green, T.N.; Leung, E.Y.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E.; Joseph, W.R.; McCrystal, M.R.; Isaacs, R.J.; Shaw, J.H.F.; Furneaux, C.E.; et al. Evidence That GRIN2A Mutations in Melanoma Correlate with Decreased Survival. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou, Q. NMDA Receptor Subunit Diversity: Impact on Receptor Properties, Synaptic Plasticity and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, P.V.; Cota, D.; Marsicano, G. The CB1 Receptor as the Cornerstone of Exostasis. Neuron 2017, 93, 1252–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galve-Roperh, I.; Sánchez, C.; Cortés, M.L.; del Pulgar, T.G.; Izquierdo, M.; Guzmán, M. Anti-Tumoral Action of Cannabinoids: Involvement of Sustained Ceramide Accumulation and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Activation. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, G.; Sánchez, C.; Guzmán, M. Towards the Use of Cannabinoids as Antitumour Agents. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| GRIA1 | ACCACTACATCCTCGCCAAC | TCACTTGTCCTCCACTGCTG |
| GRIA2 | ATTCTGCATGCTCCCACCTA | TTCTAAAACTTGCTTTTCAGGCTAT |
| GRIA3 | AGCCGTGTGATACGATGAAA | CAAGGTTTACAGGCGTTCCT |
| GRIA4 | CTGCCAACAGTTTTGCTGTG | AAATGGCAAACACCCCTCTA |
| GRIN1 | GCTTTTGCAGCCGTGAAC | GGGCTCTGCTCTACCACTCTT |
| GRIN2A | ATTCAACCAGAGGGGCGTA | TTCAAGACAGCTGCGTCATAG |
| GRIN2B | CTTCCTCCTTGCTTTCCACTT | GGTGAGAAAAGCCAACCTGA |
| GRIN2C | AGTTCGGGGGACAGACAAG | TCTCATGGCCAGAATTTCAA |
| GRIN2D | TGCGATACAACCAGCCAAG | AGATGAAGGCGTCCAGTTTC |
| GRM1 | GCCCAATGCAGAGCTCAC | GTCACTCCACTCGAGGTAACG |
| GRM2 | GATGTCTCCATCCAGGTGGC | AGCCTACCTTCTGGTAGCGA |
| GRM8 | CTGATATGGAGCTGCGGGT | CATGGGGGAAGGCTTTAGGG |
| DLG4 | GCCAATTCTCCCCCTGTGAT | CGTTCACCTGCAACTCATATCC |
| DLGAP1 | CAGCACACATCCAACTTGCC | CAACAGCAATCGCAGTCCG |
| Gene | 1014 | YUMM 1.7 | B16.F10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRIN1 | 33.29 ± 1.30 | 31.84 ± 0.02 | 27.62 ± 0.62 |
| GRIN2A | 33.45 ± 1.28 | 27.78 ± 0.94 | N.D. |
| GRIN2B | 30.01 ± 1.53 | 28.15 ± 1.41 | 27.55 ± 1.87 |
| GRIN2C | 30.20 ± 1.11 | 28.77 ± 2.31 | 29.18 ± 1.12 |
| GRIN2D | 32.88 ± 1.48 | 26.84 ± 1.30 | 31.00 ± 0.08 |
| GRIA1 | 34.59 ± 2.41 | 31.72 ± 1.10 | 35.40 ± 3.44 |
| GRIA2 | 30.79 ± 1.87 | 28.66 ± 1.10 | 30.17 ± 2.09 |
| GRIA3 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| GRIA4 | 24.62 ± 2.57 | 33.81 ± 1.23 | 26.86 ± 0.80 |
| GRM1 | 29.15 ± 1.60 | 32.41 ± 2.02 | 30.08 ± 0.58 |
| GRM2 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| GRM8 | 37.72 ± 1.88 | 33.55 ± 2.46 | 31.31 ± 1.41 |
| DLG4 | 23.57 ± 2.88 | 20.98 ± 3.38 | 25.25 ± 0.31 |
| DLGAP1 | 34.65 ± 2.12 | 29.81 ± 8.80 | 36.86 ± 2.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costas-Insua, C.; Seijo-Vila, M.; Blázquez, C.; Blasco-Benito, S.; Rodríguez-Baena, F.J.; Marsicano, G.; Pérez-Gómez, E.; Sánchez, C.; Sánchez-Laorden, B.; Guzmán, M. Neuronal Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors Suppress the Growth of Melanoma Brain Metastases by Inhibiting Glutamatergic Signalling. Cancers 2023, 15, 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092439
Costas-Insua C, Seijo-Vila M, Blázquez C, Blasco-Benito S, Rodríguez-Baena FJ, Marsicano G, Pérez-Gómez E, Sánchez C, Sánchez-Laorden B, Guzmán M. Neuronal Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors Suppress the Growth of Melanoma Brain Metastases by Inhibiting Glutamatergic Signalling. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092439
Chicago/Turabian StyleCostas-Insua, Carlos, Marta Seijo-Vila, Cristina Blázquez, Sandra Blasco-Benito, Francisco Javier Rodríguez-Baena, Giovanni Marsicano, Eduardo Pérez-Gómez, Cristina Sánchez, Berta Sánchez-Laorden, and Manuel Guzmán. 2023. "Neuronal Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors Suppress the Growth of Melanoma Brain Metastases by Inhibiting Glutamatergic Signalling" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092439
APA StyleCostas-Insua, C., Seijo-Vila, M., Blázquez, C., Blasco-Benito, S., Rodríguez-Baena, F. J., Marsicano, G., Pérez-Gómez, E., Sánchez, C., Sánchez-Laorden, B., & Guzmán, M. (2023). Neuronal Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors Suppress the Growth of Melanoma Brain Metastases by Inhibiting Glutamatergic Signalling. Cancers, 15(9), 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092439






