A Novel Preclinical Murine Model to Monitor Inflammatory Breast Cancer Tumor Growth and Lymphovascular Invasion
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Generation of Transgenic Mice with Red Fluorescent Lymphatic Vasculature
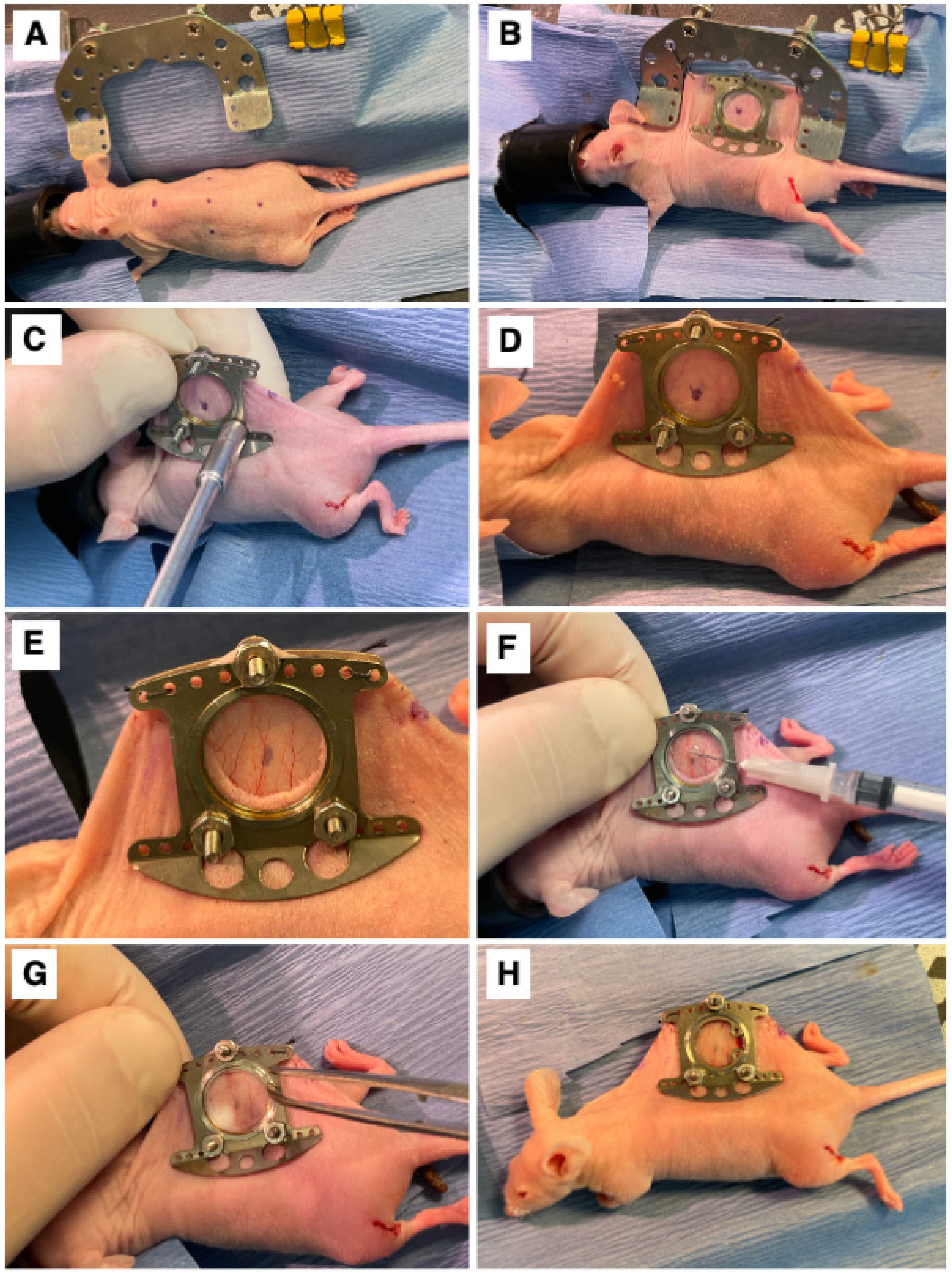
2.3. Dorsal Window Chamber Surgery and Tumor Cell Transplantation
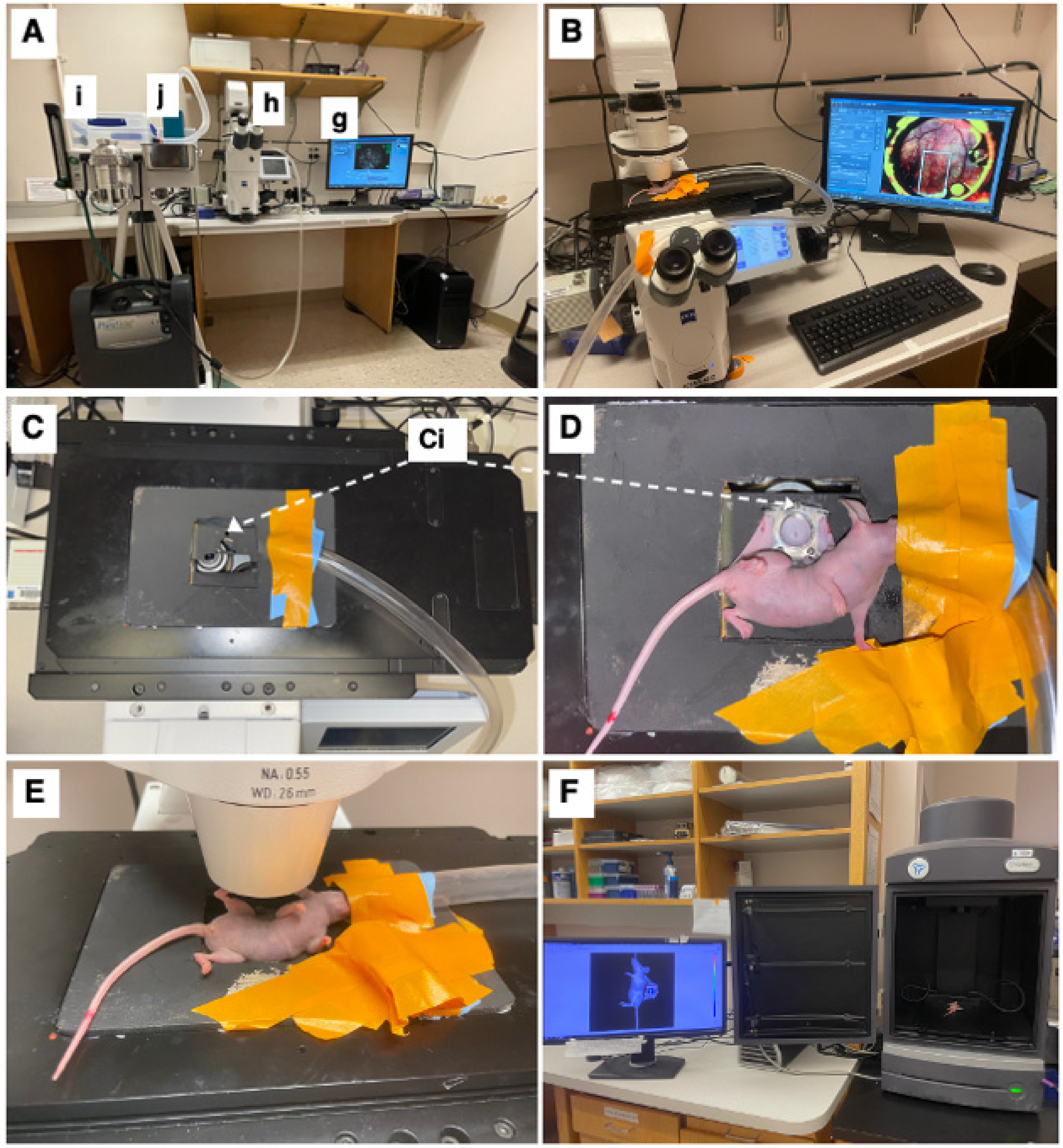
2.4. Intravital Imaging of Tumor Cell and Lymphatic Dynamics in the Mice Bearing Dorsal Window Chambers
2.5. Image Processing
2.6. Image Analysis
2.7. Quantifying Linear Lymph and Blood Vessel Density
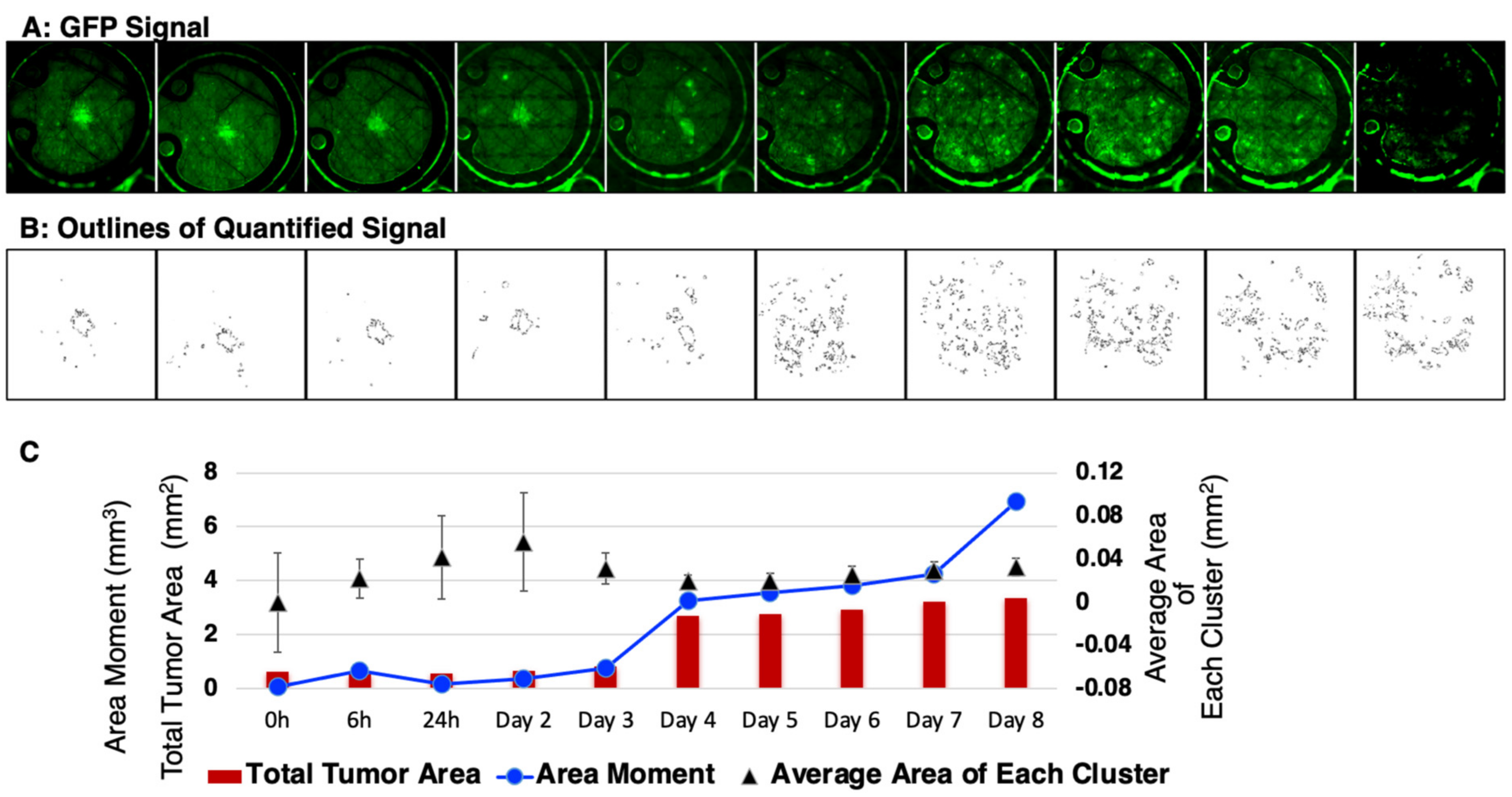
3. Results
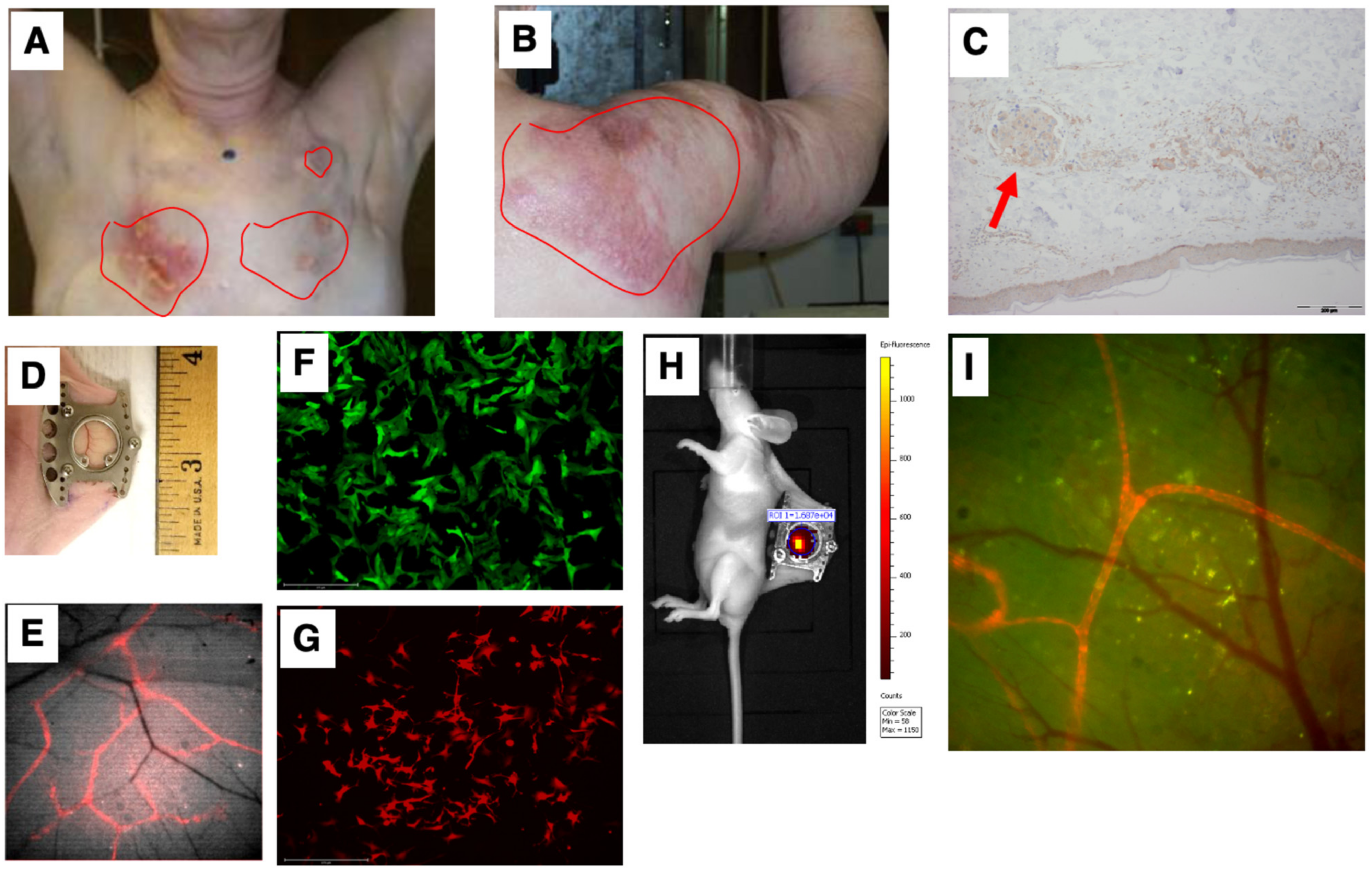
3.1. Murine Models to Simulate IBC Clinical Presentation
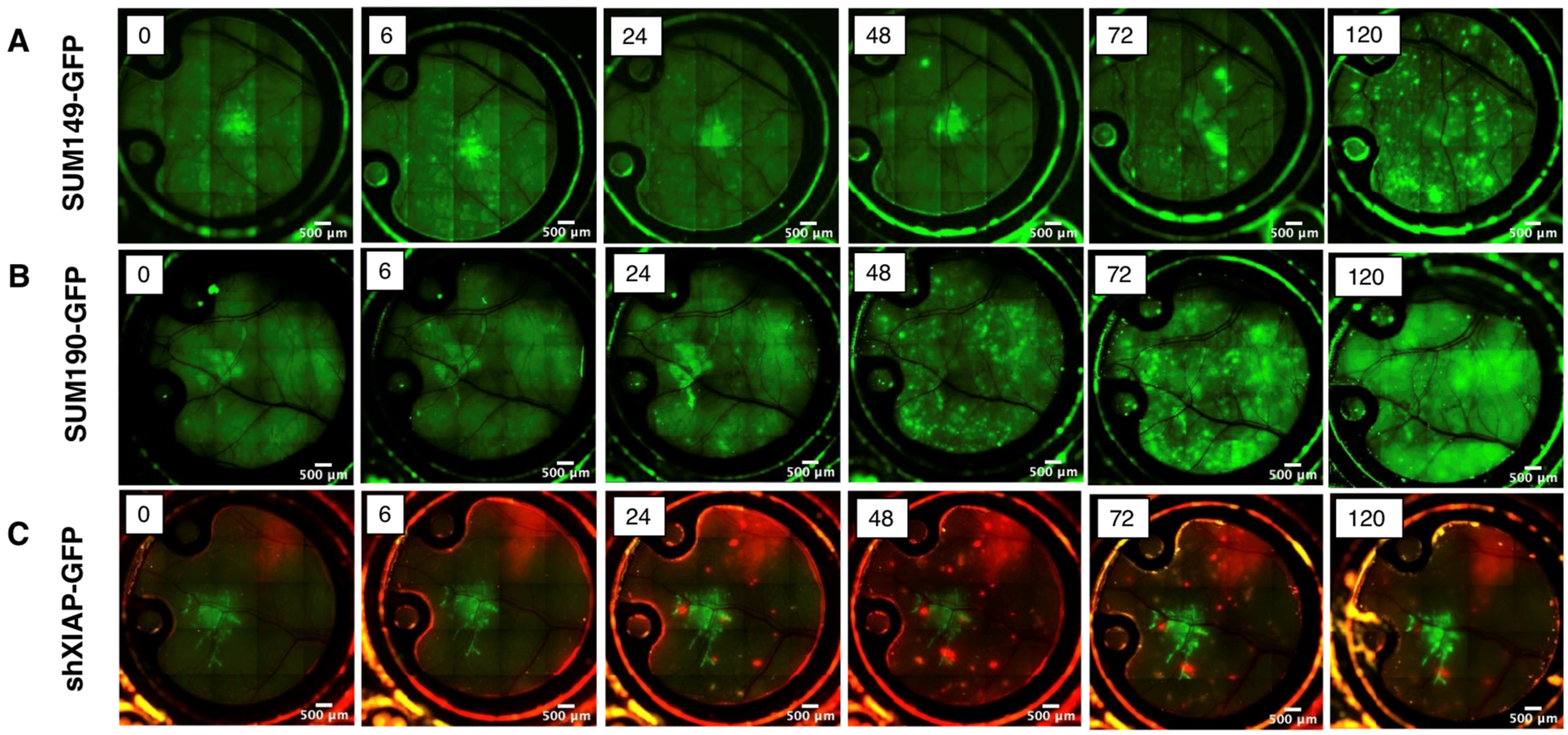
3.2. Multichannel Imaging of IBC Tumor Cells and Lymphatics Demonstrates Co-Localization
3.3. Quantitative Analysis of In Vivo Motility of IBC Tumor Cell Clusters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abraham, H.G.; Xia, Y.; Mukherjee, B.; Merajver, S.D. Incidence and survival of inflammatory breast cancer between 1973 and 2015 in the SEER database. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 185, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad, T.; Kogawa, T.; Liu, D.; Shen, Y.; Masuda, H.; El-Zein, R.; Woodward, W.; Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Alvarez, R.; Arun, B.; et al. Overall survival differences between patients with inflammatory and noninflammatory breast cancer presenting with distant metastasis at diagnosis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 152, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, S.; Ueno, N.T.; Valero, V.; Woodward, W.A.; Buchholz, T.A.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Cristofanilli, M. Differences in survival among women with stage III inflammatory and noninflammatory locally advanced breast cancer appear early: A large population-based study. Cancer 2011, 117, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, F.M.; Bondy, M.; Yang, W.; Yamauchi, H.; Wiggins, S.; Kamrudin, S.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Le-Petross, H.; Bidaut, L.; Player, A.N.; et al. Inflammatory breast cancer: The disease, the biology, the treatment. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 351–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagsi, R.; Mason, G.; Overmoyer, B.A.; Woodward, W.A.; Badve, S.; Schneider, R.J.; Lang, J.E.; Alpaugh, M.; Williams, K.P.; Vaught, D.; et al. Inflammatory breast cancer defined: Proposed common diagnostic criteria to guide treatment and research. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 192, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matro, J.M.; Li, T.; Cristofanilli, M.; Hughes, M.E.; Ottesen, R.A.; Weeks, J.C.; Wong, Y.N. Inflammatory breast cancer management in the national comprehensive cancer network: The disease, recurrence pattern, and outcome. Clin. Breast Cancer 2015, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dano, D.; Lardy-Cleaud, A.; Monneur, A.; Quenel-Tueux, N.; Levy, C.; Mouret-Reynier, M.A.; Coudert, B.; Mailliez, A.; Ferrero, J.M.; Guiu, S.; et al. Metastatic inflammatory breast cancer: Survival outcomes and prognostic factors in the national, multicentric, and real-life French cohort (ESME). ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, W.A.; Cristofanilli, M.; Merajver, S.D.; Van Laere, S.; Pusztai, L.; Bertucci, F.; Berditchevski, F.; Polyak, K.; Overmoyer, B.; Devi, G.R.; et al. Scientific Summary from the Morgan Welch MD Anderson Cancer Center Inflammatory BreastCancer (IBC) Program 10th Anniversary Conference. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 3607–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, G.R.; Hough, H.; Barrett, N.; Cristofanilli, M.; Overmoyer, B.; Spector, N.; Ueno, N.T.; Woodward, W.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Vincent, B.; et al. Perspectives on Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC) Research, Clinical Management and Community Engagement from the Duke IBC Consortium. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chainitikun, S.; Saleem, S.; Lim, B.; Valero, V.; Ueno, N.T. Update on systemic treatment for newly diagnosed inflammatory breast cancer. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayanju, O.M.; Ren, Y.; Greenup, R.A.; Plichta, J.K.; Rosenberger, L.H.; Force, J.; Suneja, G.; Devi, G.R.; King, T.A.; Nakhlis, F.; et al. Extent of axillary surgery in inflammatory breast cancer: A survival analysis of 3500 patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 180, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/about/types-of-breast-cancer/inflammatory-breast-cancer.html (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Denu, R.A.; Hampton, J.M.; Currey, A.; Anderson, R.T.; Cress, R.D.; Fleming, S.T.; Lipscomb, J.; Wu, X.C.; Wilson, J.F.; Trentham-Dietz, A. Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities Are More Pronounced in Inflammatory Breast Cancer Than Other Breast Cancers. J. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017, 2017, 7574946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedjou, C.G.; Sims, J.N.; Miele, L.; Noubissi, F.; Lowe, L.; Fonseca, D.D.; Alo, R.A.; Payton, M.; Tchounwou, P.B. Health and Racial Disparity in Breast Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1152, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Abo, M.; Gearhart-Serna, L.; Van Laere, S.; Freedman, J.A.; Patierno, S.R.; Hwang, E.-S.S.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Williams, K.P.; Devi, G.R. Adaptive Stress Response Genes Associated with Breast Cancer Subtypes and Survival Outcomes Reveal Race-Related Differences. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balema, W.; Liu, D.; Shen, Y.; El-Zein, R.; Debeb, B.G.; Kai, M.; Overmoyer, B.; Miller, K.D.; Le-Petross, H.T.; Ueno, N.T.; et al. Inflammatory breast cancer appearance at presentation is associated with overall survival. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 6261–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, P.B.; Van Laere, S.J.; Dirix, L.Y. Inflammatory breast carcinoma as a model of accelerated self-metastatic expansion by intravascular growth. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 1028–1029; author reply 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, P.B.; van Golen, K.L.; Dirix, L.Y. Angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, growth pattern, and tumor emboli in inflammatory breast cancer: A review of the current knowledge. Cancer 2010, 116, 2748–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, W.A. Inflammatory breast cancer: Unique biological and therapeutic considerations. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e568–e576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, J.; Sauer, S.J.; Tarpley, M.; Vermeulen, P.; Rypens, C.; Van Laere, S.; Williams, K.P.; Devi, G.R.; Dewhirst, M.W. Inflammatory breast cancer tumor emboli express high levels of anti-apoptotic proteins: Use of a quantitative high content and high-throughput 3D IBC spheroid assay to identify targeting strategies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25848–25863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaugh, M.L.; Tomlinson, J.S.; Shao, Z.-M.; Barsky, S.H. A Novel Human Xenograft Model of Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5079–5084. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.K.; Brown, M.C.; Geradts, J.; Bao, X.; Robinson, T.J.; Jolly, M.K.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Palmer, G.M.; Gromeier, M.; Levine, H.; et al. XIAP regulation by MNK links MAPK and NFκB signaling to determine an aggressive breast cancer phenotype. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1726–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacerda, L.; Debeb, B.G.; Smith, D.; Larson, R.; Solley, T.; Xu, W.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Gong, Y.; Levy, L.B.; Buchholz, T.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells mediate the clinical phenotype of inflammatory breast cancer in a preclinical model. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betof, A.S.; Lascola, C.D.; Weitzel, D.; Landon, C.; Scarbrough, P.M.; Devi, G.R.; Palmer, G.; Jones, L.W.; Dewhirst, M.W. Modulation of murine breast tumor vascularity, hypoxia and chemotherapeutic response by exercise. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, K.M.; Ding, X.; Baras, A.; Wei, J.; Morse, M.A.; Clay, T.; Lyerly, H.K.; Devi, G.R. Trastuzumab signaling in ErbB2-overexpressing inflammatory breast cancer correlates with X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein expression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.K.; Sauer, S.J.; Nath, S.; Robinson, T.J.; Morse, M.A.; Devi, G.R. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein mediates tumor cell resistance to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truman, L.A.; Bentley, K.L.; Smith, E.C.; Massaro, S.A.; Gonzalez, D.G.; Haberman, A.M.; Hill, M.; Jones, D.; Min, W.; Krause, D.S.; et al. ProxTom lymphatic vessel reporter mice reveal Prox1 expression in the adrenal medulla, megakaryocytes, and platelets. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, G.M.; Fontanella, A.N.; Shan, S.; Hanna, G.; Zhang, G.; Fraser, C.L.; Dewhirst, M.W. In vivo optical molecular imaging and analysis in mice using dorsal window chamber models applied to hypoxia, vasculature and fluorescent reporters. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, G.M.; Fontanella, A.N.; Shan, S.; Dewhirst, M.W. High-resolution in vivo imaging of fluorescent proteins using window chamber models. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 872, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Devi, G.R. Three-dimensional culture systems in cancer research: Focus on tumor spheroid model. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 163, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, F.; Gearhart-Serna, L.; Boareto, M.; Ribeiro, M.; Ben-Jacob, E.; Devi, G.R.; Levine, H.; Onuchic, J.N.; Jolly, M.K. Toward understanding cancer stem cell heterogeneity in the tumor microenvironment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, F.M.; Ogasawara, M.A.; Ye, Z.; Chu, K.; Pickei, R.; Debeb, B.G.; Woodward, W.A.; Hittelman, W.N.; Cristofanilli, M.; Barsky, S.H. Imaging and analysis of 3D tumor spheroids enriched for a cancer stem cell phenotype. J. Biomol. Screen 2010, 15, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, A.R.; Trenton, N.J.; Debeb, B.G.; Larson, R.; Ruffell, B.; Chu, K.; Hittelman, W.; Diehl, M.; Reuben, J.M.; Ueno, N.T.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages interact through IL-6 to promote inflammatory breast cancer in pre-clinical models. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 82482–82492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurth, R.; Tarn, K.; Jernigan, D.; Fernandez, S.V.; Cristofanilli, M.; Fatatis, A.; Meucci, O. A Preclinical Model of Inflammatory Breast Cancer to Study the Involvement of CXCR4 and ACKR3 in the Metastatic Process. Transl. Oncol. 2015, 8, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agollah, G.D.; Wu, G.; Sevick-Muraca, E.M.; Kwon, S. In vivo lymphatic imaging of a human inflammatory breast cancer model. J. Cancer 2014, 5, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, J.S.; Alpaugh, M.L.; Barsky, S.H. An intact overexpressed E-cadherin/alpha,beta-catenin axis characterizes the lymphovascular emboli of inflammatory breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5231–5241. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, S.; Sorg, B.; Dewhirst, M.W. A novel rodent mammary window of orthotopic breast cancer for intravital microscopy. Microvasc. Res. 2003, 65, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frees, A.E.; Rajaram, N.; McCachren, S.S., III; Fontanella, A.N.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Ramanujam, N. Delivery-Corrected Imaging of Fluorescently-Labeled Glucose Reveals Distinct Metabolic Phenotypes in Murine Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaugh, M.L.; Tomlinson, J.S.; Kasraeian, S.; Barsky, S.H. Cooperative role of E-cadherin and sialyl-Lewis X/A-deficient MUC1 in the passive dissemination of tumor emboli in inflammatory breast carcinoma. Oncogene 2002, 21, 3631–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopp, A.H.; Lacerda, L.; Gupta, A.; Debeb, B.G.; Solley, T.; Li, L.; Spaeth, E.; Xu, W.; Zhang, X.; Lewis, M.T.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote mammosphere formation and decrease E-cadherin in normal and malignant breast cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, G.R.; Finetti, P.; Morse, M.A.; Lee, S.; de Nonneville, A.; Van Laere, S.; Troy, J.; Geradts, J.; McCall, S.; Bertucci, F. Expression of X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (XIAP) in Breast Cancer Is Associated with Shorter Survival and Resistance to Chemotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duckett, C.S.; Nava, V.E.; Gedrich, R.W.; Clem, R.J.; Van Dongen, J.L.; Gilfillan, M.C.; Shiels, H.; Hardwick, J.M.; Thompson, C.B. A conserved family of cellular genes related to the baculovirus iap gene and encoding apoptosis inhibitors. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2685–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rickard, A.G.; Sannareddy, D.S.; Bennion, A.; Patel, P.; Sauer, S.J.; Rouse, D.C.; Bouchal, S.; Liu, H.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Palmer, G.M.; et al. A Novel Preclinical Murine Model to Monitor Inflammatory Breast Cancer Tumor Growth and Lymphovascular Invasion. Cancers 2023, 15, 2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082261
Rickard AG, Sannareddy DS, Bennion A, Patel P, Sauer SJ, Rouse DC, Bouchal S, Liu H, Dewhirst MW, Palmer GM, et al. A Novel Preclinical Murine Model to Monitor Inflammatory Breast Cancer Tumor Growth and Lymphovascular Invasion. Cancers. 2023; 15(8):2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082261
Chicago/Turabian StyleRickard, Ashlyn G., Dorababu S. Sannareddy, Alexandra Bennion, Pranalee Patel, Scott J. Sauer, Douglas C. Rouse, Samantha Bouchal, Harrison Liu, Mark W. Dewhirst, Gregory M. Palmer, and et al. 2023. "A Novel Preclinical Murine Model to Monitor Inflammatory Breast Cancer Tumor Growth and Lymphovascular Invasion" Cancers 15, no. 8: 2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082261
APA StyleRickard, A. G., Sannareddy, D. S., Bennion, A., Patel, P., Sauer, S. J., Rouse, D. C., Bouchal, S., Liu, H., Dewhirst, M. W., Palmer, G. M., & Devi, G. R. (2023). A Novel Preclinical Murine Model to Monitor Inflammatory Breast Cancer Tumor Growth and Lymphovascular Invasion. Cancers, 15(8), 2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082261






