Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor versus Beta-Blocker Use for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk among People with Hepatitis B or C Virus Infection and Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. National Health Insurance
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’souza, S.; Lau, K.C.; Coffin, C.S.; Patel, T.R. Molecular mechanisms of viral hepatitis induced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 5759–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagnelli, E.; Macera, M.; Russo, A.; Coppola, N.; Sagnelli, C. Epidemiological and etiological variations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Infection 2020, 48, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Wei, S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Yan, L. Type 2 diabetes mellitus increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in subjects with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldt, B.J.; Chen, W.; Heathcote, E.J.; Wedemeyer, H.; Reichen, J.; Hofmann, W.P.; de Knegt, R.J.; Zeuzem, S.; Manns, M.P.; Hansen, B.E.; et al. Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with hepatitis C cirrhosis and diabetes mellitus. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Li, F.; Xiang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhu, C.; Maroufy, V.; Wang, Q.; Tao, W.; Dang, Y.; Pham, H.A.; et al. Nonselective beta-blockers are associated with a lower risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among cirrhotic patients in the United States. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 54, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, I.; Pascual, S.; Zapater, P.; Carnicer, F.; Bellot, P.; María Palazón, J. The use of β-blockers is associated with a lower risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 1194–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Pocock, S.J.; Carson, P.; Januzzi, J.; Verma, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Brueckmann, M.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; DeMets, D.L.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Langkilde, A.M.; Martinez, F.A.; Bengtsson, O.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; et al. A trial to evaluate the effect of the sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (DAPA-HF). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Research Institutes. National Health Insurance Research Database. Available online: http://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/index.html (accessed on 14 April 2015).
- Parsons, L.S. Performing a 1:N Case-Control Match on Propensity Score. In Proceedings of the 29th SAS Users Group International Conference, Montréal, QC, Canada, 9–12 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.S.; Lin, C.L. Increased risk of suicide attempt among patients receiving blood transfusion: A propensity matched analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e28335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.S.; Lin, C.L. Association Between Cataract and Risk of Incident Atrial Fibrillation: A Nationwide Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, L.; Yuan, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X. SGLT2i: Beyond the glucose-lowering effect. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Adachi, H.; Katsuyama, H. Multi-Organ Protective Effects of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.K.; Strong, J. The Pleiotropic Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors: Beyond the Glycemic Benefit. Diabetes Ther. 2019, 10, 1771–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Seki, K.; Sato, S.; Saikawa, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Furukawa, M.; Kawaratani, H.; Kitade, M.; Moriya, K.; et al. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor canagliflozin attenuates liver cancer cell growth and angiogenic activity by inhibiting glucose uptake. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 1712–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.L.; Kao, Y.H.; Lin, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Lai, M.L. Validation of the national health insurance research database with ischemic stroke cases in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2011, 20, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.L.; Lee, C.H.; Chen, P.S.; Li, Y.H.; Lin, S.J.; Yang, Y.H. Validation of acute myocardial infarction cases in the national health insurance research database in Taiwan. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.L.; Chien, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Lin, S.J.; Yang, Y.H. Validity of in-hospital mortality data among patients with acute myocardial infarction or stroke in National Health Insurance Research Database in Taiwan. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 201, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | β-Blocker | SGLT2is | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%)/Mean ± SD | n (%)/Mean ± SD | ||
| All | 7023 | 7023 | |
| Sex | 0.8780 | ||
| Female | 2998 (42.69) | 3007 (42.82) | |
| Male | 4025 (57.31) | 4016 (57.18) | |
| Age group (year) | 0.9788 | ||
| <50 | 1189 (16.93) | 1195 (17.02) | |
| 50–59 | 2052 (29.22) | 2058 (29.30) | |
| 60+ | 3782 (53.85) | 3770 (53.68) | |
| Age (year) | 60.39 ± 11.03 | 60.21 ± 10.97 | 0.3326 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.3174 | ||
| No | 1969 (28.04) | 1916 (27.28) | |
| Yes | 5054 (71.96) | 5107 (72.72) | |
| Hypertension | 0.7610 | ||
| No | 1887 (26.87) | 1903 (27.10) | |
| Yes | 5136 (73.13) | 5120 (72.90) | |
| Obesity | 0.8422 | ||
| No | 6813 (97.01) | 6817 (97.07) | |
| Yes | 210 (2.99) | 206 (2.93) | |
| Coronary heart disease | 0.4661 | ||
| No | 5000 (71.19) | 5039 (71.75) | |
| Yes | 2023 (28.81) | 1984 (28.25) | |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 0.4357 | ||
| No | 6099 (86.84) | 6130 (87.28) | |
| Yes | 924 (13.16) | 893 (12.72) | |
| Chronic kidney disease | 0.7957 | ||
| No | 6170 (87.85) | 6180 (88.00) | |
| Yes | 853 (12.15) | 843 (12.00) | |
| Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis | 0.9575 | ||
| No | 2412 (34.34) | 2409 (34.30) | |
| Yes | 4611 (65.66) | 4614 (65.70) | |
| Alcohol-related disorders | 0.9186 | ||
| No | 6560 (93.41) | 6563 (93.45) | |
| Yes | 463 (6.59) | 460 (6.55) | |
| Medications | |||
| α-glucosidase inhibitors | 0.9277 | ||
| No | 4795 (68.28) | 4800 (68.35) | |
| Yes | 2228 (31.72) | 2223 (31.65) | |
| Biguanides | 0.1708 | ||
| No | 306 (4.36) | 340 (4.84) | |
| Yes | 6717 (95.64) | 6683 (95.16) | |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors | 0.9044 | ||
| No | 2868 (40.84) | 2875 (40.94) | |
| Yes | 4155 (59.16) | 4148 (59.06) | |
| Meglitinides | 0.8475 | ||
| No | 5662 (80.62) | 5671 (80.75) | |
| Yes | 1361 (19.38) | 1352 (19.25) | |
| Sulphonylureas | 0.8910 | ||
| No | 1729 (24.62) | 1736 (24.72) | |
| Yes | 5294 (75.38) | 5287 (75.28) | |
| Thiazolidinediones | 0.2659 | ||
| No | 4997 (71.15) | 4937 (70.30) | |
| Yes | 2026 (28.85) | 2086 (29.70) | |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists | 0.3450 | ||
| No | 6949 (98.95) | 6960 (99.10) | |
| Yes | 74 (1.05) | 63 (0.90) | |
| Insulins | 0.3482 | ||
| No | 2975 (42.36) | 3030 (43.14) | |
| Yes | 4048 (57.64) | 3993 (56.86) | |
| Follow-up period (year) | 2.05 ± 1.00 | 2.20 ± 0.83 | <0.0001 |
| Variable | IR # | HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta Blockers | SGLT2is | Crude | Adjusted $ | |
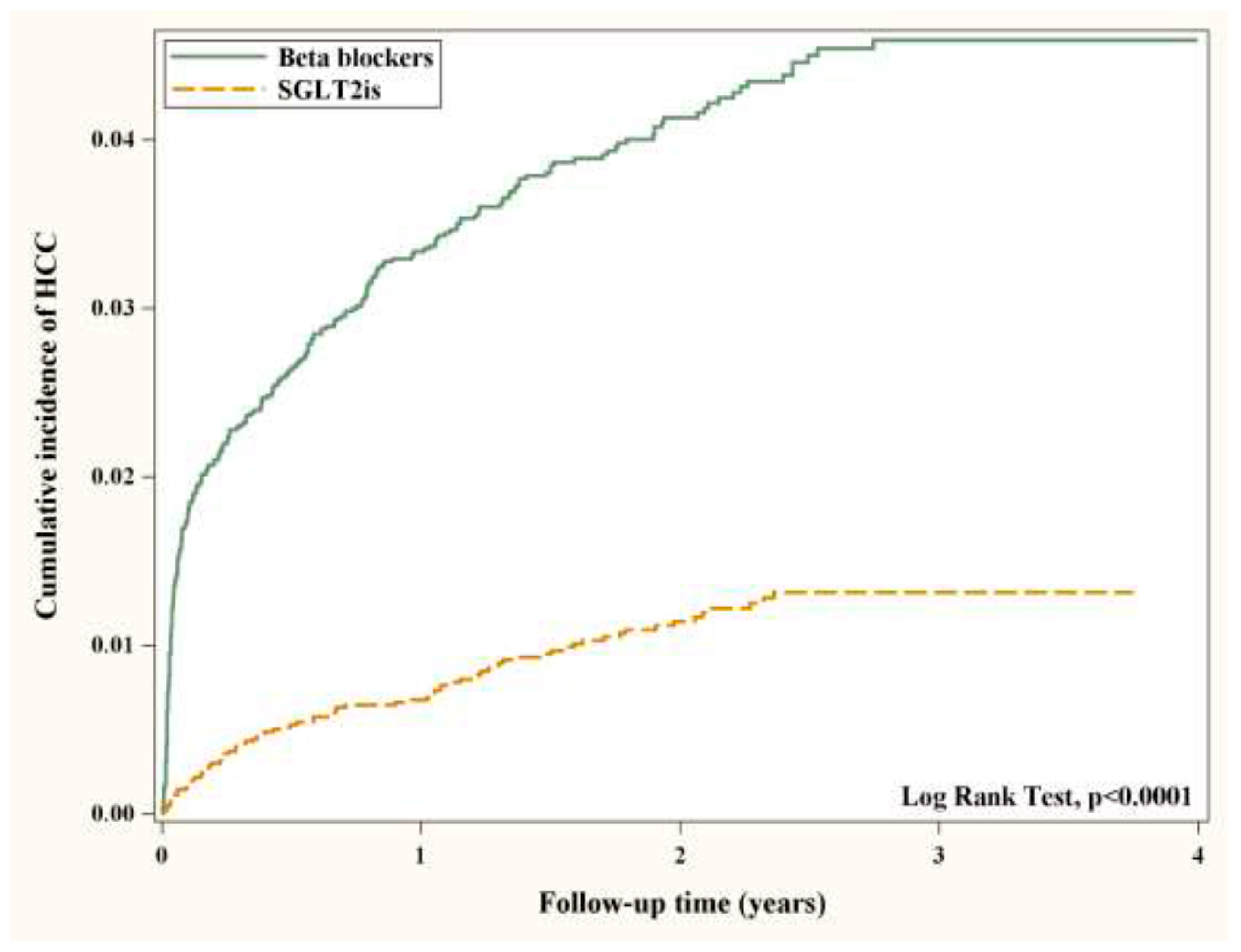
| All | 19.59 | 5.11 | 0.27 (0.21, 0.34) *** | 0.27 (0.21, 0.34) *** |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 10.71 | 4.48 | 0.43 (0.28, 0.66) *** | 0.42 (0.27, 0.64) *** |
| Male | 26.43 | 5.60 | 0.22 (0.16, 0.29) *** | 0.22 (0.16, 0.29) *** |
| Age group (year) | ||||
| <50 | 7.26 | 0.73 | 0.10 (0.02, 0.44) ** | 0.10 (0.02, 0.45) ** |
| 50–59 | 18.61 | 4.08 | 0.22 (0.13, 0.37) *** | 0.22 (0.13, 0.37) *** |
| 60+ | 24.52 | 7.21 | 0.30 (0.22, 0.40) *** | 0.29 (0.22, 0.40) *** |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Hyperlipidemia | ||||
| No | 29.93 | 7.91 | 0.27 (0.19, 0.40) *** | 0.28 (0.19, 0.41) *** |
| Yes | 15.87 | 4.08 | 0.26 (0.19, 0.36) *** | 0.25 (0.18, 0.35) *** |
| Hypertension | ||||
| No | 19.25 | 3.81 | 0.20 (0.12, 0.35) *** | 0.20 (0.11, 0.34) *** |
| Yes | 19.72 | 5.60 | 0.29 (0.22, 0.38) *** | 0.29 (0.22, 0.38) *** |
| Obesity | ||||
| No | 19.84 | 5.14 | 0.26 (0.20, 0.34) *** | 0.26 (0.20, 0.34) *** |
| Yes | 11.62 | 4.30 | 0.39 (0.08, 2.01) | 0.28 (0.03, 2.44) |
| Coronary heart disease | ||||
| No | 20.88 | 4.93 | 0.24 (0.18, 0.33) *** | 0.25 (0.18, 0.33) *** |
| Yes | 16.46 | 5.61 | 0.34 (0.21, 0.54) *** | 0.30 (0.19, 0.48) *** |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | ||||
| No | 20.12 | 5.24 | 0.27 (0.20, 0.35) *** | 0.27 (0.21, 0.35) *** |
| Yes | 15.95 | 4.20 | 0.27 (0.12, 0.59) ** | 0.25 (0.12, 0.56) *** |
| Chronic kidney disease | ||||
| No | 19.72 | 4.74 | 0.24 (0.19, 0.32) *** | 0.24 (0.19, 0.32) *** |
| Yes | 18.55 | 8.09 | 0.45 (0.24, 0.85) * | 0.42 (0.22, 0.81) ** |
| Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis | ||||
| No | 10.07 | 3.76 | 0.38 (0.23, 0.64) *** | 0.34 (0.20, 0.57) *** |
| Yes | 24.77 | 5.83 | 0.24 (0.18, 0.32) *** | 0.24 (0.18, 0.32) *** |
| Alcohol-related disorders | ||||
| No | 19.10 | 5.04 | 0.27 (0.21, 0.35) *** | 0.27 (0.21, 0.35) *** |
| Yes | 27.70 | 6.19 | 0.24 (0.10, 0.58) ** | 0.22 (0.09, 0.56) ** |
| Medications | ||||
| α-glucosidase inhibitors | ||||
| No | 19.59 | 4.26 | 0.22 (0.16, 0.30) *** | 0.22 (0.16, 0.31) *** |
| Yes | 19.59 | 6.85 | 0.36 (0.25, 0.54) *** | 0.35 (0.24, 0.52) *** |
| Biguanides | ||||
| No | 13.11 | 3.04 | 0.22 (0.05, 1.04) | 0.15 (0.03, 0.87) * |
| Yes | 19.88 | 5.21 | 0.27 (0.21, 0.34) *** | 0.27 (0.21, 0.34) *** |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors | ||||
| No | 16.47 | 3.15 | 0.19 (0.11, 0.30) *** | 0.19 (0.11, 0.30) *** |
| Yes | 21.83 | 6.37 | 0.30 (0.23, 0.41) *** | 0.30 (0.23, 0.41) *** |
| Meglitinides | ||||
| No | 19.66 | 4.73 | 0.24 (0.18, 0.33) *** | 0.24 (0.18, 0.32) *** |
| Yes | 19.28 | 6.72 | 0.36 (0.21, 0.60) *** | 0.36 (0.21, 0.60) *** |
| Sulphonylureas | ||||
| No | 8.44 | 1.97 | 0.23 (0.10, 0.52) *** | 0.19 (0.08, 0.44) *** |
| Yes | 23.25 | 6.06 | 0.27 (0.21, 0.35) *** | 0.27 (0.21, 0.35) *** |
| Thiazolidinediones | ||||
| No | 18.46 | 4.69 | 0.26 (0.19, 0.35) *** | 0.25 (0.19, 0.35) *** |
| Yes | 22.43 | 6.05 | 0.28 (0.19, 0.43) *** | 0.28 (0.19, 0.43) *** |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists | ||||
| No | 19.65 | 5.16 | 0.27 (0.21, 0.34) *** | 0.27 (0.21, 0.34) *** |
| Yes | 13.89 | 0.00 | NA | NA |
| Insulins | ||||
| No | 15.52 | 3.00 | 0.19 (0.12, 0.31) *** | 0.20 (0.12, 0.32) *** |
| Yes | 22.90 | 6.72 | 0.30 (0.23, 0.41) *** | 0.30 (0.23, 0.41) *** |
| Variable | Event | Person-Years | IR # | HR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 361 | Crude | Adjusted $ | |||
| SGLT2is | |||||
| No (β-blockers) | 282 | 14,393 | 19.59 | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| 1–532 days | 73 | 6623 | 11.02 | 0.52 (0.40, 0.67) *** | 0.53 (0.41, 0.68) *** |
| >532 days | 6 | 8823 | 0.68 | 0.04 (0.02, 0.09) *** | 0.04 (0.02, 0.08) *** |
| β-blockers | |||||
| No (SGLT2is) | 79 | 15,446 | 5.11 | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| 1–35 days | 154 | 6966 | 22.11 | 4.20 (3.20, 5.51) *** | 4.20 (3.20, 5.51) *** |
| >35 days | 128 | 7427 | 17.24 | 3.34 (2.52, 4.42) *** | 3.36 (2.54, 4.45) *** |
| HBV/HCV | SGLT2is | Event | Person-Years | IR # | Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR $ (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBV | No (β-blockers) | 147 | 9464 | 15.53 | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| HBV | Yes | 45 | 11,502 | 3.91 | 0.26 (0.18, 0.36) *** | 0.25 (0.18, 0.35) *** |
| HCV | No (β-blockers) | 128 | 5506 | 23.25 | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| HCV | Yes | 33 | 4470 | 7.38 | 0.32 (0.22, 0.47) *** | 0.32 (0.22, 0.46) *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, W.-S.; Lin, C.-L. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor versus Beta-Blocker Use for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk among People with Hepatitis B or C Virus Infection and Diabetes Mellitus. Cancers 2023, 15, 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072104
Hu W-S, Lin C-L. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor versus Beta-Blocker Use for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk among People with Hepatitis B or C Virus Infection and Diabetes Mellitus. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072104
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Wei-Syun, and Cheng-Li Lin. 2023. "Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor versus Beta-Blocker Use for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk among People with Hepatitis B or C Virus Infection and Diabetes Mellitus" Cancers 15, no. 7: 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072104
APA StyleHu, W.-S., & Lin, C.-L. (2023). Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor versus Beta-Blocker Use for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk among People with Hepatitis B or C Virus Infection and Diabetes Mellitus. Cancers, 15(7), 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072104





