Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein/Parathyroid Hormone Receptor 1 Signaling in Cancer and Metastasis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The PTHrP and PTH1R Proteins
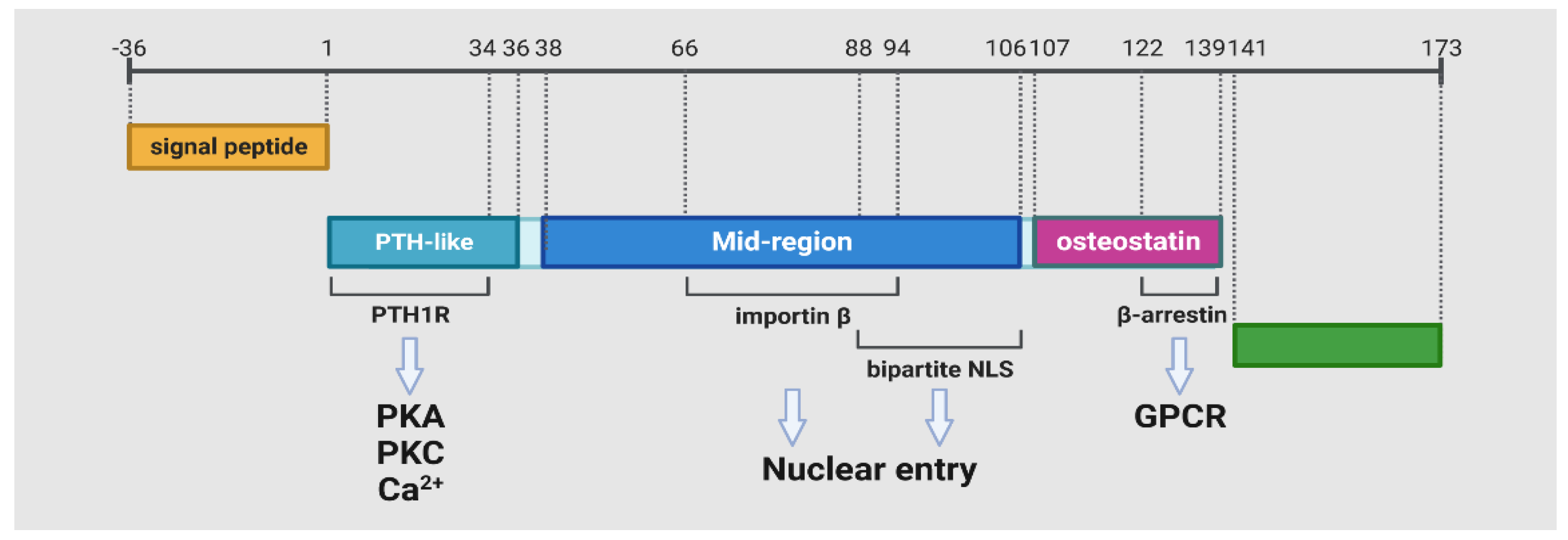
2.1. The Isoforms of PTHrP
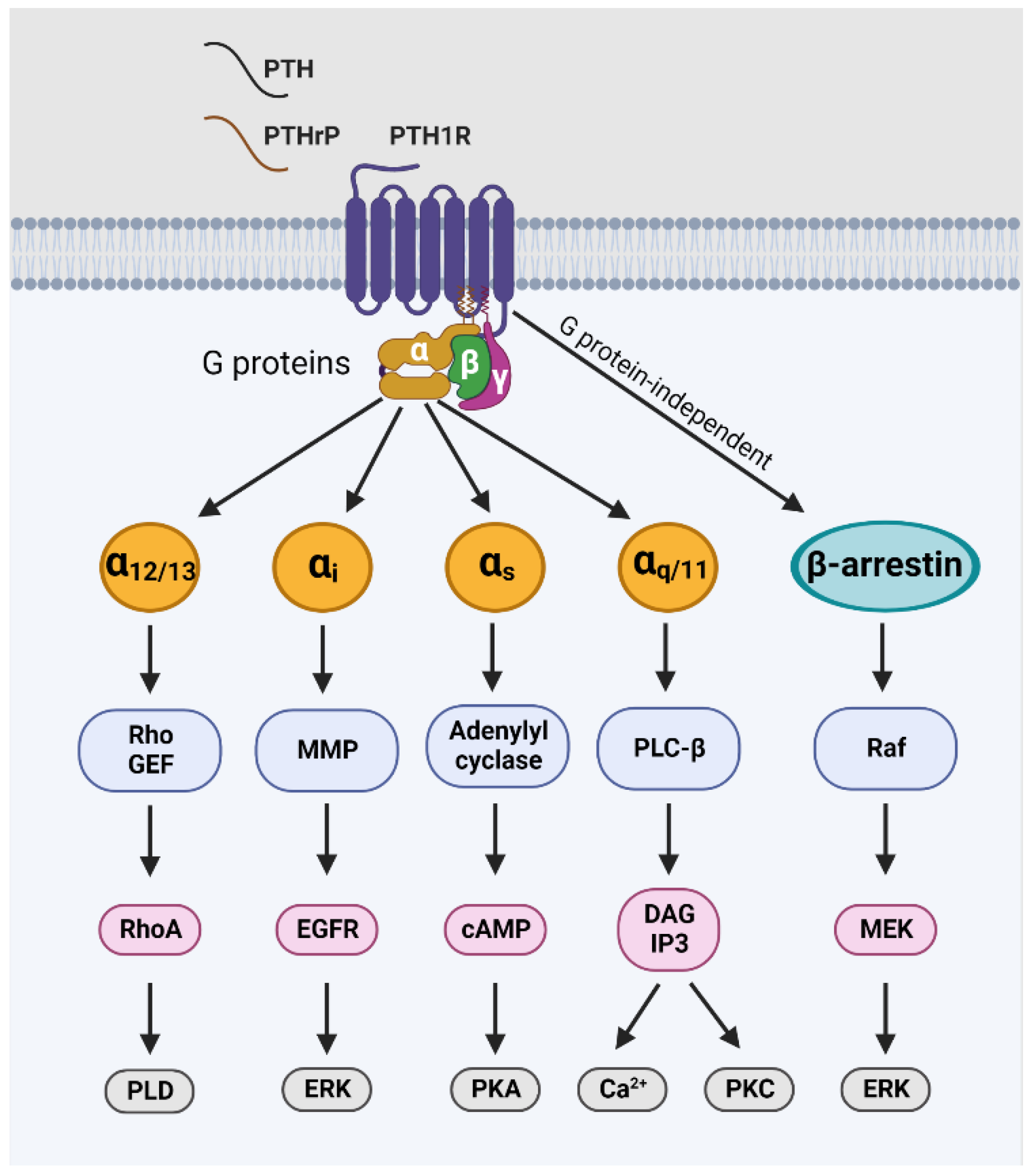
2.2. The Protein Isoform and Downstream Signaling of PTH1R
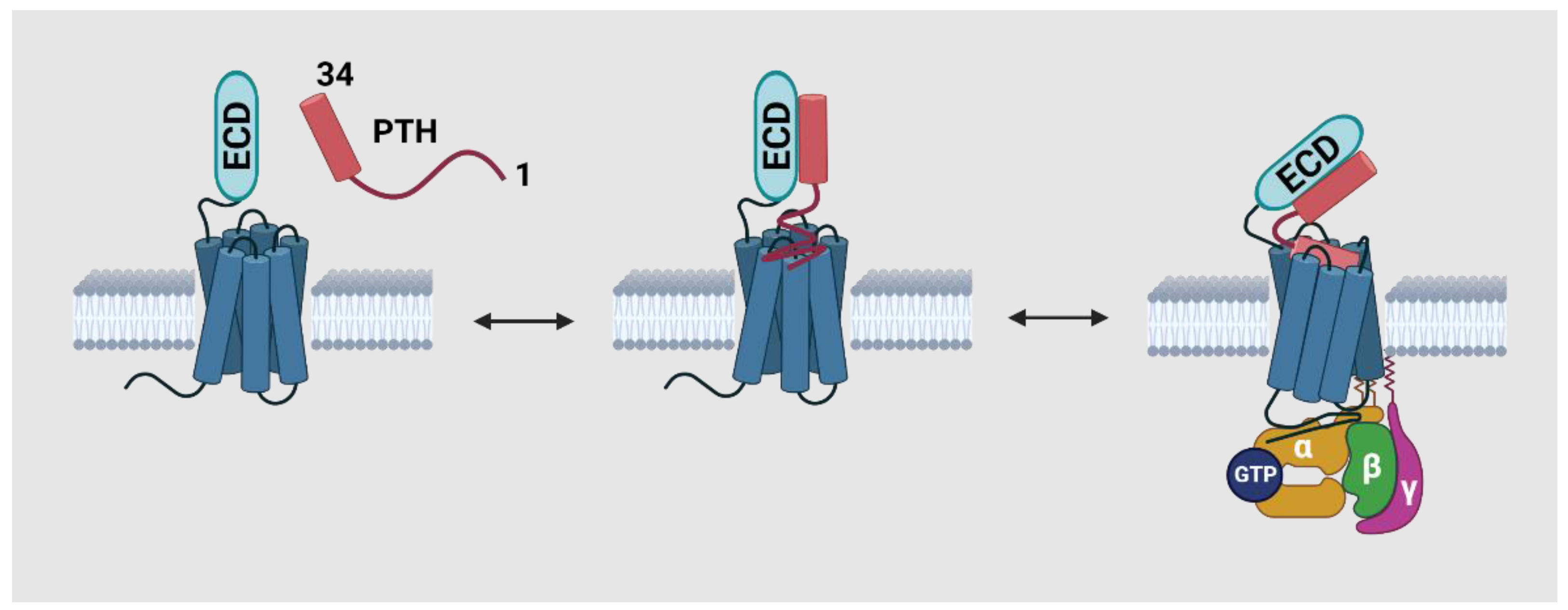
2.3. The Conformational Changes of PTH1R during Activation and Recycling
3. PTHrP/PTH1R Signaling in Tumor Progression and Metastasis
3.1. Diverse Mechanisms of Action Revealed from Preclinical Studies
3.2. Opposite Effects in Tumor-Associated Angiogenesis
3.3. Consensus Has Yet to Be Reached: The Elusive Readouts of Targeting PTHrP/PTH1R in Clinical Studies
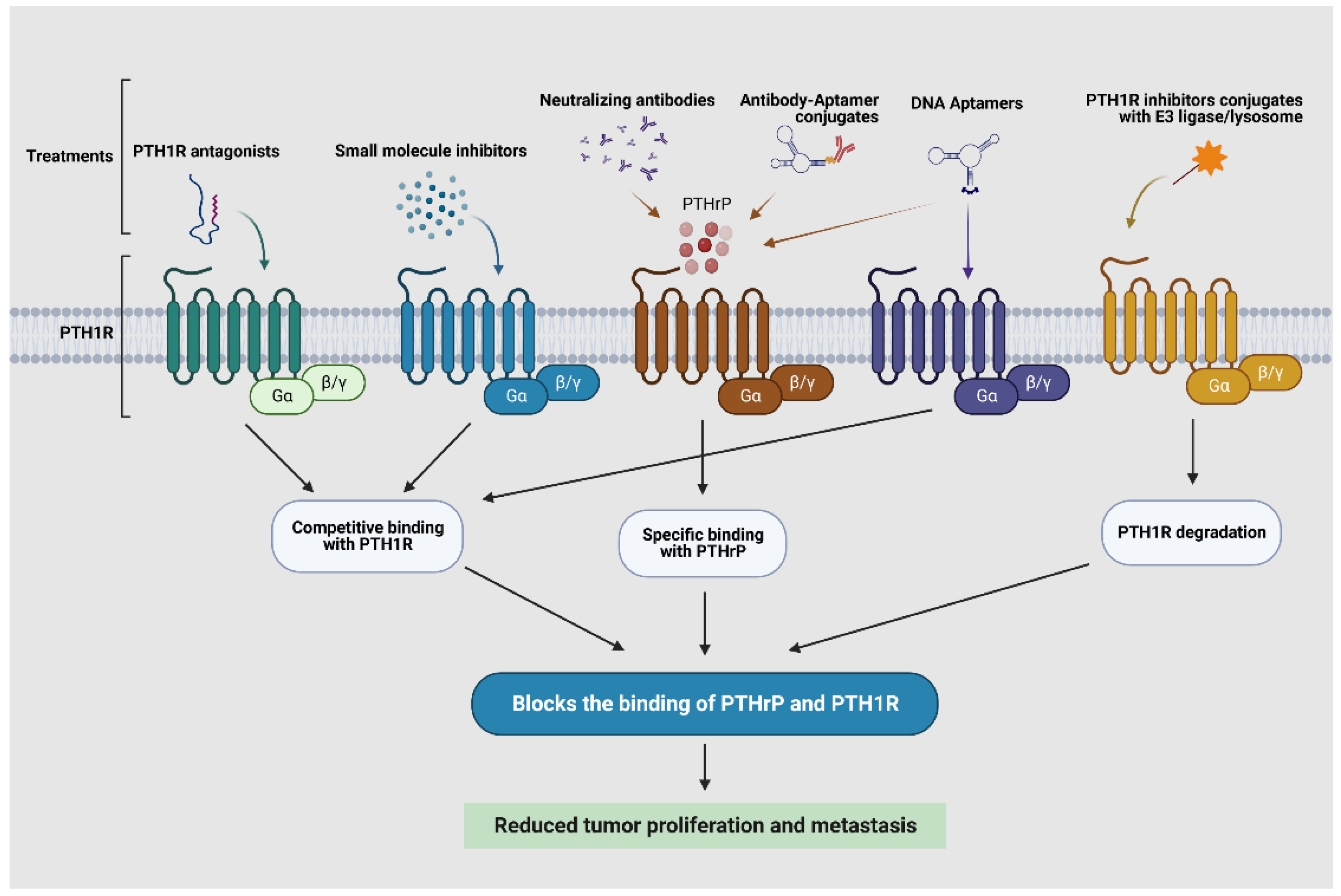
3.4. Potential Targeting PTHrP/PTH1R Indirectly in Tumor Progression and Metastasis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burtis, W.J. Parathyroid hormone-related protein: Structure, function, and measurement. Clin. Chem. 1992, 38, 2171–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, T.L.; Cormier, S.; Eichinger, A.; Endlich, K.; Fiaschi-Taesch, N.; Fischer, E.; Friedman, P.A.; Karaplis, A.C.; Massfelder, T.; Rossert, J.; et al. Parathyroid hormone-related protein and its receptors: Nuclear functions and roles in the renal and cardiovascular systems, the placental trophoblasts and the pancreatic islets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 1113–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, N.K.; Martinez, D. Physiological roles of parathyroid hormone-related protein. Acta Biomed. 2019, 90, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, M.; Wysolmerski, J. Parathyroid hormone-related protein specifies the mammary mesenchyme and regulates embryonic mammary development. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2013, 18, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysolmerski, J.J. Parathyroid hormone-related protein: An update. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 2947–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaplis, A.C.; Luz, A.; Glowacki, J.; Bronson, R.T.; Tybulewicz, V.L.; Kronenberg, H.M.; Mulligan, R.C. Lethal skeletal dysplasia from targeted disruption of the parathyroid hormone-related peptide gene. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amizuka, N.; Karaplis, A.C.; Henderson, J.E.; Warshawsky, H.; Lipman, M.L.; Matsuki, Y.; Ejiri, S.; Tanaka, M.; Izumi, N.; Ozawa, H.; et al. Haploinsufficiency of parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) results in abnormal postnatal bone development. Dev. Biol. 1996, 175, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, F.; Bauer, W.; Ropes, M.; Aub, J.C. Studies of calcium and phosphorus metabolism: IV. The effect of the parathyroid hormone. J. Clin. Investig. 1929, 7, 139–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzon, M.; Du, P. Enhanced growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells overexpressing parathyroid hormone-related peptide. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, M.A.; Carron, J.A.; Scott, M.; Fraser, W.D.; Gallagher, J.A. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related protein (PTHrP) receptor expression and mitogenic responses in human breast cancer cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 72, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.A.; Danks, J.A.; Slavin, J.L.; Byrnes, G.B.; Choong, P.F.M.; Spillane, J.B.; Hopper, J.L.; Martin, T.J. Parathyroid hormone-related protein localization in breast cancers predict improved prognosis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2250–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, M.; Danks, J.; Moseley, J.; Slavin, J.; Harris, T.; McKinlay, M.; Hopper, J.; Martin, T. Parathyroid hormone-related protein production by breast cancers, improved survival, and reduced bone metastases. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, H.; Tsunenari, T.; Onuma, E.; Sato, K.; Ogata, E.; Yamada-Okabe, H. Humanized monoclonal antibody against parathyroid hormone-related protein suppresses osteolytic bone metastasis of human breast cancer cells derived from MDA-MB-231. Anticancer. Res. 2005, 25, 3817–3823. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guise, T.A.; Yin, J.J.; Taylor, S.D.; Kumagai, Y.; Dallas, M.; Boyce, B.F.; Yoneda, T.; Mundy, G.R. Evidence for a causal role of parathyroid hormone-related protein in the pathogenesis of human breast cancer-mediated osteolysis. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, T.; Yano, S.; Hanibuchi, M.; Kanematsu, T.; Muguruma, H.; Sone, S. Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) is responsible for production of bone metastasis, but not visceral metastasis, by human small cell lung cancer SBC-5 cells in natural killer cell-depleted SCID mice. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Yamakawa, Y.; Shizume, K.; Satoh, T.; Nohtomi, K.; Demura, H.; Akatsu, T.; Nagata, N.; Kasahara, T.; Ohkawa, H. Passive immunization with anti-parathyroid hormone-related protein monoclonal antibody markedly prolongs survival time of hypercalcemic nude mice bearing transplanted human PTHrP-producing tumors. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1993, 8, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuma, E.; Sato, K.; Saito, H.; Tsunenari, T.; Ishii, K.; Esaki, K.; Yabuta, N.; Wakahara, Y.; Yamada-Okabe, H.; Ogata, E. Generation of a humanized monoclonal antibody against human parathyroid hormone-related protein and its efficacy against humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Karaplis, A.C.; Huang, D.C.; Siegel, P.M.; Camirand, A.; Yang, X.F.; Muller, W.J.; Kremer, R. PTHrP drives breast tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis in mice and is a potential therapy target. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4655–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, I.W.Y.; Cowan, R.W.; Turcotte, R.E.; Singh, G.; Ghert, M. PTHrP induces autocrine/paracrine proliferation of bone tumor cells through inhibition of apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, C.; Sadler, W.D.; Koh, A.J.; Jones, J.; Seo, J.W.; Soki, F.N.; Cho, S.W.; Daignault, S.D.; McCauley, L.K. Parathyroid hormone-related protein drives a CD11b+Gr1+ cell-mediated positive feedback loop to support prostate cancer growth. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6574–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitarresi, J.R.; Norgard, R.J.; Chiarella, A.M.; Suzuki, K.; Bakir, B.; Sahu, V.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Marchand, B.; Wengyn, M.D.; et al. PTHrP Drives Pancreatic Cancer Growth and Metastasis and Reveals a New Therapeutic Vulnerability. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1774–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talon, I.; Lindner, V.; Sourbier, C.; Schordan, E.; Rothhut, S.; Barthelmebs, M.; Lang, H.; Helwig, J.-J.; Massfelder, T. Antitumor effect of parathyroid hormone-related protein neutralizing antibody in human renal cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massfelder, T.; Lang, H.; Schordan, E.; Lindner, V.; Rothhut, S.; Welsch, S.; Simon-Assmann, P.; Barthelmebs, M.; Jacqmin, D.; Helwig, J.-J. Parathyroid hormone-related protein is an essential growth factor for human clear cell renal carcinoma and a target for the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estell, E.G.; Rosen, C.J. Emerging insights into the comparative effectiveness of anabolic therapies for osteoporosis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, N.; Shinoda, Y.; Wettschureck, N.; Offermanns, S.; Takeda, S.; Nakamura, K.; Segre, G.V.; Chung, U.; Kawaguchi, H. G alpha(q) signal in osteoblasts is inhibitory to the osteoanabolic action of parathyroid hormone. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 13733–13740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, M.J.; Tedesco, M.B.; Sereika, S.M.; Prebehala, L.; Gundberg, C.M.; Hollis, B.W.; Bisello, A.; Garcia-Ocaña, A.; Carneiro, R.M.; Stewart, A.F. A 7-day continuous infusion of PTH or PTHrP suppresses bone formation and uncouples bone turnover. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 2287–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, E.C.; Boudignon, B.M.; Chang, W.C.; Bencsik, M.; Peng, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Manalac, C.; Halloran, B.P.; Conklin, B.R.; Nissenson, R.A. Osteoblast expression of an engineered Gs-coupled receptor dramatically increases bone mass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, M.J.; Tedesco, M.B.; Sereika, S.M.; Syed, M.A.; Garcia-Ocaña, A.; Bisello, A.; Hollis, B.W.; Rosen, C.J.; Wysolmerski, J.J.; Dann, P.; et al. Continuous PTH and PTHrP infusion causes suppression of bone formation and discordant effects on 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005, 20, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Raggatt, L.J.; Partridge, N.C. Parathyroid hormone: A double-edged sword for bone metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 15, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogeorgos, G.; Krantz, E.; Trimpou, P.; Laine, C.M.; Landin-Wilhelmsen, K. Teriparatide treatment in severe osteoporosis—A controlled 10-year follow-up study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brixen, K.T.; Christensen, P.M.; Ejersted, C.; Langdahl, B.L. Teriparatide (biosynthetic human parathyroid hormone 1-34): A new paradigm in the treatment of osteoporosis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 94, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orwoll, E.S.; Scheele, W.H.; Paul, S.; Adami, S.; Syversen, U.; Diez-Perez, A.; Kaufman, J.M.; Clancy, A.D.; Gaich, G.A. The effect of teriparatide human parathyroid hormone (1-34) therapy on bone density in men with osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, R.; Wang, O.; Satterwhite, J.; Mitlak, B. The skeletal response to teriparatide is largely independent of age, initial bone mineral density, and prevalent vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neer, R.M.; Arnaud, C.D.; Zanchetta, J.R.; Prince, R.; Gaich, G.A.; Reginster, J.Y.; Hodsman, A.B.; Eriksen, E.F.; Ish-Shalom, S.; Genant, H.K.; et al. Effect of parathyroid hormone (1-34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.-H.; Ma, S.; Sutkeviciute, I.; Shen, D.-D.; Zhou, X.E.; de Waal, P.W.; Li, C.-Y.; Kang, Y.; Clark, L.J.; Jean-Alphonse, F.G.; et al. Structure and dynamics of the active human parathyroid hormone receptor-1. Science 2019, 364, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkeviciute, I.; Clark, L.J.; White, A.D.; Gardella, T.J.; Vilardaga, J.-P. PTH/PTHrP Receptor Signaling, Allostery, and Structures. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkeviciute, I.; Lee, J.Y.; White, A.D.; Maria, C.S.; Peña, K.A.; Savransky, S.; Doruker, P.; Li, H.; Lei, S.; Kaynak, B.; et al. Precise druggability of the PTH type 1 receptor. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Noda, H.; Joyashiki, E.; Hoshino, M.; Watanabe, T.; Kinosaki, M.; Nishimura, Y.; Esaki, T.; Ogawa, K.; Miyake, T.; et al. Identification of an orally active small-molecule PTHR1 agonist for the treatment of hypoparathyroidism. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P.H.; Dean, T.; Bhayana, B.; Khatri, A.; Rajur, R.; Gardella, T.J. Actions of the small molecule ligands SW106 and AH-3960 on the type-1 parathyroid hormone receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, I.M.; Austin, C.; Buck, I.M.; Dunstone, D.J.; Gaffen, J.; Griffin, E.; Harper, E.A.; Hull, R.A.D.; Kalindjian, S.B.; Linney, I.D.; et al. Discovery and characterization of novel, potent, non-peptide parathyroid hormone-1 receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 4789–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P.H.; Liu, R.-Q.; Foster, W.R.; Tamasi, J.A.; Tebben, A.J.; Favata, M.; Staal, A.; Cvijic, M.E.; French, M.H.; Dell, V.; et al. Discovery of a small molecule antagonist of the parathyroid hormone receptor by using an N-terminal parathyroid hormone peptide probe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6846–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, K.; Insel, P.A. G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Targets for Approved Drugs: How Many Targets and How Many Drugs? Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, M.; Ferrandon, S.; Vilardaga, J.-P.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Potts, J.T.; Gardella, T.J. Prolonged signaling at the parathyroid hormone receptor by peptide ligands targeted to a specific receptor conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16525–16530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, T.; Linglart, A.; Mahon, M.J.; Bastepe, M.; Jüppner, H.; Potts, J.T.; Gardella, T.J. Mechanisms of ligand binding to the parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related protein receptor: Selectivity of a modified PTH(1-15) radioligand for GalphaS-coupled receptor conformations. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, N.; Dean, T.; Tsang, J.C.; Khatri, A.; Potts, J.T.; Gardella, T.J. Novel parathyroid hormone (PTH) antagonists that bind to the juxtamembrane portion of the PTH/PTH-related protein receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, N.; Guo, J.; Gardella, T.J. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)-(1-14) and -(1-11) analogs conformationally constrained by alpha-aminoisobutyric acid mediate full agonist responses via the juxtamembrane region of the PTH-1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 49003–49012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoare, S.R.; Usdin, T.B. Molecular mechanisms of ligand recognition by parathyroid hormone 1 (PTH1) and PTH2 receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2001, 7, 689–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kir, S.; Komaba, H.; Garcia, A.P.; Economopoulos, K.P.; Liu, W.; Lanske, B.; Hodin, R.A.; Spiegelman, B.M. PTH/PTHrP Receptor Mediates Cachexia in Models of Kidney Failure and Cancer. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, S.; Johnson, J.; Bettinson, L.A.; Kimura, T.; Zhu, H.; Albertelli, M.A.; Johnson, R.W.; Wu, J.Y. Prevention of breast cancer skeletal metastases with parathyroid hormone. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e90874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plawner, L.L.; Philbrick, W.M.; Burtis, W.J.; Broadus, A.E.; Stewart, A.F. Cell type-specific secretion of parathyroid hormone-related protein via the regulated versus the constitutive secretory pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 14078–14084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frieling, J.S.; Lynch, C.C. Proteolytic Regulation of Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein: Functional Implications for Skeletal Malignancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardella, T.J.; Vilardaga, J.-P. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCIII. The parathyroid hormone receptors—Family B G protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 310–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, D.A.; Thomas, R.J.; Gillespie, M.T. Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP): A nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein with distinct paracrine and intracrine roles. Vitam. Horm. 2003, 66, 345–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massfelder, T.; Dann, P.; Wu, T.L.; Vasavada, R.; Helwig, J.J.; Stewart, A.F. Opposing mitogenic and anti-mitogenic actions of parathyroid hormone-related protein in vascular smooth muscle cells: A critical role for nuclear targeting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13630–13635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.A.; Karaplis, A.C. The nucleus: A target site for parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) action. J. Cell. Biochem. 1998, 70, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.E.; Amizuka, N.; Warshawsky, H.; Biasotto, D.; Lanske, B.M.; Goltzman, D.; Karaplis, A.C. Nucleolar localization of parathyroid hormone-related peptide enhances survival of chondrocytes under conditions that promote apoptotic cell death. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 4064–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, M.M.; Davidson, D.; Corluka, A.; Petroulakis, E.; Guo, J.; Bringhurst, F.R.; Galipeau, J.; Henderson, J.E. Parathyroid hormone-related protein promotes quiescence and survival of serum-deprived chondrocytes by inhibiting rRNA synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 37934–37943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, J.; Callon, K.E.; Nicholson, G.C.; Reid, I.R. Parathyroid hormone-related protein-(107-139) inhibits bone resorption in vivo. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlan, L.A.; Martin, T.J.; Gillespie, M.T. The COOH-terminus of parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) interacts with beta-arrestin 1B. FEBS Lett. 2002, 527, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, K.; Schihada, H.; Kleinau, G.; Zabel, U.; Grushevskyi, E.O.; Scheerer, P.; Lohse, M.J.; Maiellaro, I. Functional modulation of PTH1R activation and signaling by RAMP2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2122037119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranelletti, F.O.; Monego, G. Parathyroid Hormone–Related Peptide Signaling in Cancer. In Cell Signaling & Molecular Targets in Cancer; Chatterjee, M., Kashfi, K., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 53–85. ISBN 978-1-4614-0729-4. [Google Scholar]
- Gardella, T.J.; Jüppner, H. Molecular properties of the PTH/PTHrP receptor. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 12, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesty-Palmer, D.; Chen, M.; Reiter, E.; Ahn, S.; Nelson, C.D.; Wang, S.; Eckhardt, A.E.; Cowan, C.L.; Spurney, R.F.; Luttrell, L.M.; et al. Distinct beta-arrestin- and G protein-dependent pathways for parathyroid hormone receptor-stimulated ERK1/2 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10856–10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesty-Palmer, D.; Flannery, P.; Yuan, L.; Corsino, L.; Spurney, R.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Luttrell, L.M. A beta-arrestin-biased agonist of the parathyroid hormone receptor (PTH1R) promotes bone formation independent of G protein activation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2009, 1, 1ra1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, Y.; Böttke, T.; Lam, J.H.; Ernicke, S.; Fortmann, A.; Tretbar, M.; Zarzycka, B.; Gurevich, V.V.; Katritch, V.; Coin, I. Structural details of a Class B GPCR-arrestin complex revealed by genetically encoded crosslinkers in living cells. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, M.; Merten, N.; Malfacini, D.; Inoue, A.; Preis, P.; Simon, K.; Rüttiger, N.; Ziegler, N.; Benkel, T.; Schmitt, N.K.; et al. Lack of beta-arrestin signaling in the absence of active G proteins. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergwitz, C.; Gardella, T.J.; Flannery, M.R.; Potts, J.T.; Kronenberg, H.M.; Goldring, S.R.; Jüppner, H. Full activation of chimeric receptors by hybrids between parathyroid hormone and calcitonin. Evidence for a common pattern of ligand-receptor interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 26469–26472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Palm, D.; Lohse, M.J.; Vilardaga, J.-P. Turn-on switch in parathyroid hormone receptor by a two-step parathyroid hormone binding mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16084–16089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Carter, P.H.; Gardella, T.J. Autoactivation of type-1 parathyroid hormone receptors containing a tethered ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 19456–19460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Yang, H.; Shaw, G.; Raizada, M.K. Angiotensin II-induced nuclear targeting of the angiotensin type 1 (AT1) receptor in brain neurons. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Peri, K.; Ribeiro-da-Silva, A.; Almazan, G.; Shichi, H.; Hou, X.; Varma, D.R.; Chemtob, S. Localization of functional prostaglandin E2 receptors EP3 and EP4 in the nuclear envelope. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 15719–15724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Lança, A.J.; Cheng, R.; Nguyen, T.; Ji, X.D.; Gobeil, F.; Chemtob, S.; George, S.R.; O’Dowd, B.F. Agonist-independent nuclear localization of the Apelin, angiotensin AT1, and bradykinin B2 receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 7901–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jong, Y.-J.I.; Kumar, V.; Kingston, A.E.; Romano, C.; O’Malley, K.L. Functional metabotropic glutamate receptors on nuclei from brain and primary cultured striatal neurons. Role of transporters in delivering ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30469–30480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosle, V.K.; Rivera, J.C.; Chemtob, S. New insights into mechanisms of nuclear translocation of G-protein coupled receptors. Small GTPases 2019, 10, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.H.; Fraher, L.J.; Hendy, G.N.; Chung, U.I.; Kisiel, M.; Natale, B.V.; Hodsman, A.B. Nuclear localization of the type 1 PTH/PTHrP receptor in rat tissues. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2000, 15, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, B.W.; Hodsman, A.B.; Fraher, L.J.; Watson, P.H. Type 1 parathyroid hormone receptor (PTH1R) nuclear trafficking: Regulation of PTH1R nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling by importin-alpha/beta and chromosomal region maintenance 1/exportin 1. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Nissenson, R.A. The cytoplasmic tail of the G-protein-coupled receptor for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related protein contains positive and negative signals for endocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, E.K.; Watson, P.H.; Hodsman, A.B.; Hendy, G.N.; Canaff, L.; Bringhurst, F.R.; Poschwatta, C.H.; Fraher, L.J. Expression of PTH1R constructs in LLC-PK1 cells: Protein nuclear targeting is mediated by the PTH1R NLS. Bone 2007, 41, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, B.W.; Hodsman, A.B.; Fraher, L.J.; Watson, P.H. Type 1 parathyroid hormone receptor (PTH1R) nuclear trafficking: Association of PTH1R with importin alpha1 and beta. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3326–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syme, C.A.; Friedman, P.A.; Bisello, A. Parathyroid hormone receptor trafficking contributes to the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases but is not required for regulation of cAMP signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11281–11288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brent, M.B.; Thomsen, J.S.; Brüel, A. The Efficacy of PTH and Abaloparatide to Counteract Immobilization-Induced Osteopenia Is in General Similar. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 588773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, T.; Vilardaga, J.-P.; Potts, J.T.; Gardella, T.J. Altered selectivity of parathyroid hormone (PTH) and PTH-related protein (PTHrP) for distinct conformations of the PTH/PTHrP receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinstein, T.N.; Wehbi, V.L.; Ardura, J.A.; Wheeler, D.S.; Ferrandon, S.; Gardella, T.J.; Vilardaga, J.-P. Retromer terminates the generation of cAMP by internalized PTH receptors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidon, A.; Al-Bataineh, M.M.; Jean-Alphonse, F.G.; Stevenson, H.P.; Watanabe, T.; Louet, C.; Khatri, A.; Calero, G.; Pastor-Soler, N.M.; Gardella, T.J.; et al. Endosomal GPCR signaling turned off by negative feedback actions of PKA and v-ATPase. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.G.; Croucher, P.I. The dormant cancer cell life cycle. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deftos, L.J.; Barken, I.; Burton, D.W.; Hoffman, R.M.; Geller, J. Direct evidence that PTHrP expression promotes prostate cancer progression in bone. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Hoang, B.H.; Kubo, T.; Kawano, H.; Chou, A.; Sowers, R.; Huvos, A.G.; Meyers, P.A.; Healey, J.H.; Gorlick, R. Over-expression of parathyroid hormone Type 1 receptor confers an aggressive phenotype in osteosarcoma. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, N.; Gulespie, M.T.; Traianedes, K.; Zhou, H.; Ho, P.W.; Hards, D.K.; Allan, E.H.; Martin, T.J.; Moseley, J.M. Expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein in cells of osteoblast lineage. J. Cell. Physiol. 1996, 166, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodan, S.B.; Wesolowski, G.; Ianacone, J.; Thiede, M.A.; Rodan, G.A. Production of parathyroid hormone-like peptide in a human osteosarcoma cell line: Stimulation by phorbol esters and epidermal growth factor. J. Endocrinol. 1989, 122, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.W.M.; Goradia, A.; Russell, M.R.; Chalk, A.M.; Milley, K.M.; Baker, E.K.; Danks, J.A.; Slavin, J.L.; Walia, M.; Crimeen-Irwin, B.; et al. Knockdown of PTHR1 in osteosarcoma cells decreases invasion and growth and increases tumor differentiation in vivo. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2922–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsaers, A.J.; Ng, A.J.M.; Baker, E.K.; Russell, M.R.; Chalk, A.M.; Wall, M.; Liddicoat, B.J.J.; Ho, P.W.M.; Slavin, J.L.; Goradia, A.; et al. Modeling distinct osteosarcoma subtypes in vivo using Cre:lox and lineage-restricted transgenic shRNA. Bone 2013, 55, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, C.R.; Qudsi, R.; Sankaran, V.G.; Perry, J.A.; Gostissa, M.; Roth, S.I.; Rodda, S.J.; Snay, E.; Dunning, P.; Fahey, F.H.; et al. Conditional mouse osteosarcoma, dependent on p53 loss and potentiated by loss of Rb, mimics the human disease. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1662–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, M.K.; Taylor, S.; Ho, P.W.M.; Martin, T.J.; Walkley, C.R. Tolerance to sustained activation of the cAMP/Creb pathway activity in osteoblastic cells is enabled by loss of p53. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, M.K.; Ho, P.M.; Taylor, S.; Ng, A.J.; Gupte, A.; Chalk, A.M.; Zannettino, A.C.; Martin, T.J.; Walkley, C.R. Activation of PTHrP-cAMP-CREB1 signaling following p53 loss is essential for osteosarcoma initiation and maintenance. eLife 2016, 5, e13446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beristain, A.G.; Molyneux, S.D.; Joshi, P.A.; Pomroy, N.C.; Di Grappa, M.A.; Chang, M.C.; Kirschner, L.S.; Privé, G.G.; Pujana, M.A.; Khokha, R. PKA signaling drives mammary tumorigenesis through Src. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1160–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Cao, J.; Meng, X.; Liu, R.; Vander Ark, A.; Woodford, E.; Zhang, R.; Stiver, I.; Zhang, X.; Madaj, Z.B.; et al. Enzalutamide-induced and PTH1R-mediated TGFBR2 degradation in osteoblasts confers resistance in prostate cancer bone metastases. Cancer Lett. 2022, 525, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakre, M.M.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, H.; Burton, D.W.; Terkeltaub, R.; Deftos, L.J.; Varner, J.A. Parathyroid hormone-related peptide is a naturally occurring, protein kinase A-dependent angiogenesis inhibitor. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, N.; Carriere, P.; Martín, M.J.; Gigola, G.; Gentili, C. PTHrP treatment of colon cancer cells promotes tumor associated-angiogenesis by the effect of VEGF. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 483, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isowa, S.; Shimo, T.; Ibaragi, S.; Kurio, N.; Okui, T.; Matsubara, K.; Hassan, N.M.M.; Kishimoto, K.; Sasaki, A. PTHrP regulates angiogenesis and bone resorption via VEGF expression. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 2755–2767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akino, K.; Ohtsuru, A.; Kanda, K.; Yasuda, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Akino, Y.; Naito, S.; Kurokawa, M.; Iwahori, N.; Yamashita, S. Parathyroid hormone-related peptide is a potent tumor angiogenic factor. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4313–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoussaini, M.; Fletcher, O.; Michailidou, K.; Turnbull, C.; Schmidt, M.K.; Dicks, E.; Dennis, J.; Wang, Q.; Humphreys, M.K.; Luccarini, C.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies three new breast cancer susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Utama, F.E.; Sato, T.; Peck, A.R.; Langenheim, J.F.; Udhane, S.S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Girondo, M.A.; Kovatich, A.J.; et al. Loss of Nuclear Localized Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein in Primary Breast Cancer Predicts Poor Clinical Outcome and Correlates with Suppressed Stat5 Signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6355–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryden, A.A.G.; Hoyland, J.A.; Freemont, A.J.; Clarke, N.W.; George, N.J.R. Parathyroid hormone related peptide and receptor expression in paired primary prostate cancer and bone metastases. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monego, G.; Lauriola, L.; Ramella, S.; D’Angelillo, R.M.; Lanza, P.; Granone, P.; Ranelletti, F.O. Parathyroid hormone-related peptide and parathyroid hormone-related peptide receptor type 1 expression in human lung adenocarcinoma. Chest 2010, 137, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, A.R.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Liu, C.; Klimowicz, A.C.; Stringer, G.A.; Pequignot, E.; Freydin, B.; Yang, N.; Ertel, A.; Tran, T.H.; et al. Low levels of Stat5a protein in breast cancer are associated with tumor progression and unfavorable clinical outcomes. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, A.R.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Liu, C.; Stringer, G.A.; Klimowicz, A.C.; Pequignot, E.; Freydin, B.; Tran, T.H.; Yang, N.; Rosenberg, A.L.; et al. Abstract 2277: Loss of nuclear localized and tyrosine phosphorylated Stat5: A predictor of poor clinical outcome and increased risk of antiestrogen therapy failure in breast cancer. In Clinical Research, 2011/04/15; American Association for Cancer Research: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Assaker, G.; Camirand, A.; Abdulkarim, B.; Omeroglu, A.; Deschenes, J.; Joseph, K.; Noman, A.S.M.; Ramana Kumar, A.V.; Kremer, R.; Sabri, S. PTHrP, A Biomarker for CNS Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Selection for Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Node-Negative Disease. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020, 4, pkz063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgrain, P.R.; Deftos, L.J.; Arenberg, D.; Tipps, A.; Quintana, R.; Carskadon, S.; Hastings, R.H. Prognostic implications of parathyroid hormone-related protein in males and females with non—Small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2011, 12, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamura, M.; Wu, W.; Muramoto, M.; Ohori, M.; Egawa, S.; Uchida, T.; Baba, S. Parathyroid hormone-related protein is an independent prognostic factor for renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 1999, 86, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowder, M.E.; Johnson, R.W. Bone as a Preferential Site for Metastasis. JBMR Plus 2019, 3, e10126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, L.A.; Fournier, P.G.J.; Chirgwin, J.M.; Guise, T.A. Molecular biology of bone metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2609–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Harada, M.; Kameda, Y.; Nagano, A.; Inaba, M.; Asaga, T. Significance of the parathyroid hormone-related protein expression in breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer 2000, 7, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southby, J.; Danks, J.A.; Hayman, J.A.; Moseley, J.M.; Martin, T.J. Immunohistochemical localization of parathyroid hormone-related protein in the lesions of breast disease. Pathology 1990, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.W.; Merkel, A.R.; Page, J.M.; Ruppender, N.S.; Guelcher, S.A.; Sterling, J.A. Wnt signaling induces gene expression of factors associated with bone destruction in lung and breast cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2014, 31, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.W.; Nguyen, M.P.; Padalecki, S.S.; Grubbs, B.G.; Merkel, A.R.; Oyajobi, B.O.; Matrisian, L.M.; Mundy, G.R.; Sterling, J.A. TGF-beta promotion of Gli2-induced expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein, an important osteolytic factor in bone metastasis, is independent of canonical Hedgehog signaling. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, J.A.; Oyajobi, B.O.; Grubbs, B.; Padalecki, S.S.; Munoz, S.A.; Gupta, A.; Story, B.; Zhao, M.; Mundy, G.R. The hedgehog signaling molecule Gli2 induces parathyroid hormone-related peptide expression and osteolysis in metastatic human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7548–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekulic, A.; Migden, M.R.; Oro, A.E.; Dirix, L.; Lewis, K.D.; Hainsworth, J.D.; Solomon, J.A.; Yoo, S.; Arron, S.T.; Friedlander, P.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of vismodegib in advanced basal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Kim, J.; Spaunhurst, K.; Montoya, J.; Khodosh, R.; Chandra, K.; Fu, T.; Gilliam, A.; Molgo, M.; Beachy, P.A.; et al. Open-label, exploratory phase II trial of oral itraconazole for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorch, G.; Gilmore, J.L.; Koltz, P.F.; Gonterman, R.M.; Laughner, R.; Lewis, D.A.; Konger, R.L.; Nadella, K.S.; Toribio, R.E.; Rosol, T.J.; et al. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor signalling reduces hypercalcaemia induced by human lung squamous-cell carcinoma in athymic mice. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furugaki, K.; Moriya, Y.; Iwai, T.; Yorozu, K.; Yanagisawa, M.; Kondoh, K.; Fujimoto-Ohuchi, K.; Mori, K. Erlotinib inhibits osteolytic bone invasion of human non-small-cell lung cancer cell line NCI-H292. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.W.; Finger, E.C.; Olcina, M.M.; Vilalta, M.; Aguilera, T.; Miao, Y.; Merkel, A.R.; Johnson, J.R.; Sterling, J.A.; Wu, J.Y.; et al. Induction of LIFR confers a dormancy phenotype in breast cancer cells disseminated to the bone marrow. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Andrade, C.D.C.; Yoon, S.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Greenlee, W.J.; Weber, P.C.; Viswanathan, U.; Kulp, J.; Brooks, D.J.; Demay, M.B.; et al. Structure-based design of selective, orally available salt-inducible kinase inhibitors that stimulate bone formation in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2214396119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-H.; Yuan, Q.; Dai, A.; Chen, C.-W.; He, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, M.-W.; Yang, D.; et al. Molecular recognition of two endogenous hormones by the human parathyroid hormone receptor-1. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Kawakami, K.; Kusakizako, T.; Miyauchi, H.; Tomita, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Shihoya, W.; Yamashita, K.; Nishizawa, T.; Kato, H.E.; et al. Endogenous ligand recognition and structural transition of a human PTH receptor. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 3468–3483.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Gao, X.; Pan, D.; Hua, Y.; He, J.; Liu, Z.; Dang, Y. Advances in the stability challenges of bioactive peptides and improvement strategies. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffilli, C.; Roth, S.; Rodrigo, M.; Boyd, H.; Zelcer, N.; Moreau, K. Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras (PROTACs): A Perspective on Integral Membrane Protein Degradation. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2022, 5, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, B.; He, Q.; Zhu, C.; Cao, J. The Role of Membrane-Associated E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 928794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Su, S.; Li, X. Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein/Parathyroid Hormone Receptor 1 Signaling in Cancer and Metastasis. Cancers 2023, 15, 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071982
Zhao Y, Su S, Li X. Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein/Parathyroid Hormone Receptor 1 Signaling in Cancer and Metastasis. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071982
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yawei, Shang Su, and Xiaohong Li. 2023. "Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein/Parathyroid Hormone Receptor 1 Signaling in Cancer and Metastasis" Cancers 15, no. 7: 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071982
APA StyleZhao, Y., Su, S., & Li, X. (2023). Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein/Parathyroid Hormone Receptor 1 Signaling in Cancer and Metastasis. Cancers, 15(7), 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071982







