The Role of cMET in Gastric Cancer—A Review of the Literature
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
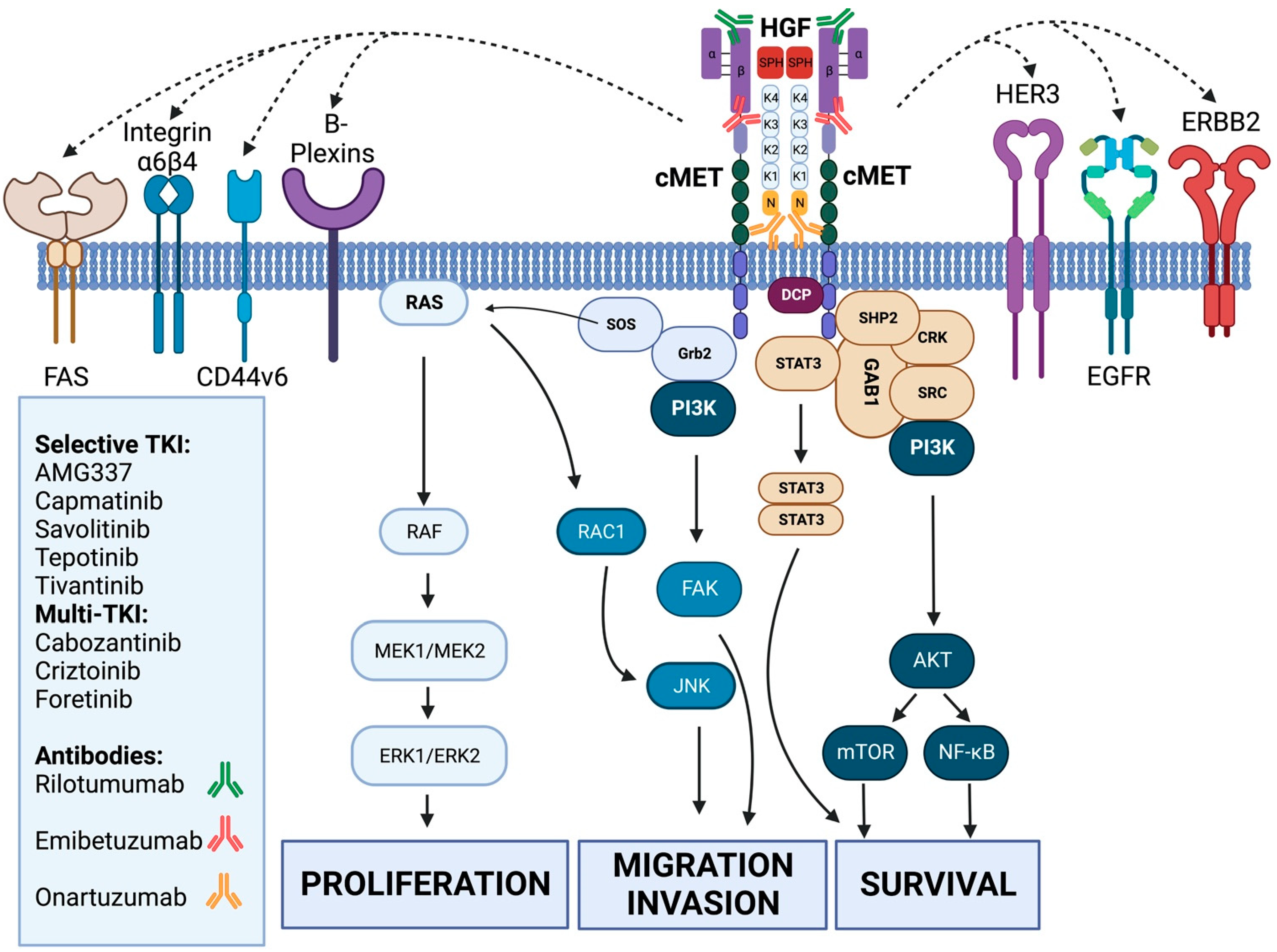
3.1. General Background and Preclinical Data on cMET in Gastric Cancer
3.1.1. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
3.1.2. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)/Comprehensive Genomic Profiling (CGP)
3.2. Clinical Exposure of cMET-Driven Therapies in Gastric Cancer
3.2.1. Monoclonal Antibodies
3.2.2. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, Y.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Feyereislova, A.; Chung, H.C.; Shen, L.; Sawaki, A.; Lordick, F.; Ohtsu, A.; Omuro, Y.; Satoh, T.; et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, K.; Van Cutsem, E.; Narita, Y.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Baba, E.; Li, J.; Ryu, M.H.; Zamaniah, W.I.W.; Yong, W.P.; Yeh, K.H.; et al. Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic gastric cancer: A JSMO-ESMO initiative endorsed by CSCO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Shitara, K.; Moehler, M.; Garrido, M.; Salman, P.; Shen, L.; Wyrwicz, L.; Yamaguchi, K.; Skoczylas, T.; Campos Bragagnoli, A.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Kawazoe, A.; Yañez, P.; Li, N.; Lonardi, S.; Kolesnik, O.; Barajas, O.; Bai, Y.; Shen, L.; Tang, Y.; et al. The KEYNOTE-811 trial of dual PD-1 and HER2 blockade in HER2-positive gastric cancer. Nature 2021, 600, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Jin, R.U. Molecular pathogenesis, targeted therapies, and future perspectives for gastric cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 86 Pt 3, 566–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Su, X.; Li, Z.; Deng, L.; Liu, X.; Feng, X.; Peng, J. HGF/c-MET pathway in cancer: From molecular characterization to clinical evidence. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4625–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandino, L.; Longati, P.; Medico, E.; Prat, M.; Comoglio, P.M. Phosphorylation of ser 985 negatively regulates the hepatocyte growth factor receptor kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1815–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoyama, K.; Funakoshi, H.; Ohya-Shimada, W.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsuyama, S.; Nakamura, T. Disease-dependent reciprocal phosphorylation of serine and tyrosine residues of c-Met/HGF receptor contributes disease retardation of a transgenic mouse model of ALS. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 65, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Sakai, K.; Yamashita, A.; Nakamura, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Matsumoto, K. Met/HGF receptor activation is regulated by juxtamembrane Ser985 phosphorylation in hepatocytes. Cytokine 2013, 62, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschard, P.; Fournier, T.M.; Lamorte, L.; Naujokas, M.A.; Band, H.; Langdon, W.Y.; Park, M. Mutation of the c-Cbl TKB domain binding site on the Met receptor tyrosine kinase converts it into a transforming protein. Mol. Cell. 2001, 8, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Shiraha, H.; Fujikawa, T.; Takaoka, N.; Ueda, N.; Nakanishi, Y.; Koike, K.; Takaki, A.; Shiratori, Y. Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin is a potential autologous growth factor for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 6409–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusolino, L.; Bertotti, A.; Comoglio, P.M. A signaling adapter function for alpha6beta4 integrin in the control of HGF-dependent invasive growth. Cell 2001, 107, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrotto, P.; Corso, S.; Gamberini, S.; Comoglio, P.M.; Giordano, S. Interplay between scatter factor receptors and B plexins controls invasive growth. Oncogene 2004, 23, 5131–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; DeFrances, M.C.; Dai, Y.; Pediaditakis, P.; Johnson, C.; Bell, A.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Zarnegar, R. A mechanism of cell survival: Sequestration of Fas by the HGF receptor. Met. Mol. Cell. 2002, 9, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.; Stolz, D.B.; Esplen, J.E.; Dorko, K.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Strom, S.C. Cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and c-Met signal pathways in transformed cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 8806–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, N.; Salgia, R. Synergism of EGFR and c-Met pathways, cross-talk and inhibition, in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Carcinog. 2008, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachleitner-Hofmann, T.; Sun, M.Y.; Chen, C.T.; Tang, L.; Song, L.; Zeng, Z.; Shah, M.; Christensen, J.G.; Rosen, N.; Solit, D.B.; et al. HER kinase activation confers resistance to MET tyrosine kinase inhibition in MET oncogene-addicted gastric cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 3499–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, H.; Naujokas, M.A.; Zuo, D.; Sangwan, V.; Frigault, M.M.; Petkiewicz, S.; Dankort, D.L.; Muller, W.J.; Park, M. HGF converts ErbB2/Neu epithelial morphogenesis to cell invasion. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2005, 16, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, S.; Lazzari, L.; Arnesano, A.; Li Chiavi, G.; Gentile, A.; Comoglio, P.M. Ron kinase transphosphorylation sustains MET oncogene addiction. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Rao, B.; Lou, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, A.; Cui, G.; Ren, Z.; Yu, Z. The function of the HGFc-Met axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.S.; Park, M.; Blair, D.G.; Tainsky, M.A.; Huebner, K.; Croce, C.M.; Vande Woude, G.F. Molecular cloning of a new transforming gene from a chemically transformed human cell line. Nature 1984, 311, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuniyasu, H.; Yasui, W.; Kitadai, Y.; Yokozaki, H.; Ito, H.; Tahara, E. Frequent amplification of the c-met gene in scirrhous type stomach cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 189, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, M.; Yonemura, Y.; Harada, S.; Liu, X.; Terada, I.; Yamamoto, H. Participation of c-met in the progression of human gastric cancers: Anti-c-met oligonucleotides inhibit proliferation or invasiveness of gastric cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 1996, 3, 393–404. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, T.; Chung, Y.S.; Yashiro, M.; Nishimura, S.; Hasuma, T.; Otani, S.; Sowa, M. Transforming growth factor-beta and hepatocyte growth factor produced by gastric fibroblasts stimulate the invasiveness of scirrhous gastric cancer cells. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1997, 88, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toiyama, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Saigusa, S.; Matushita, K.; Fujikawa, H.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, K.; Mohri, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Goel, A.; et al. Co-expression of hepatocyte growth factor and c-Met predicts peritoneal dissemination established by autocrine hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling in gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2012, 130, 2912–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 513, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ge, S.; Shen, L. Prognostic significance of MET amplification and expression in gastric cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, C.A.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Bardelli, A.; Rolfo, C.; Tabernero, J.; Khawaja, H.A.; Lawler, M.; Johnston, P.G.; Van Schaeybroeck, S. MErCuRIC consortium. Targeting c-MET in gastrointestinal tumours: Rationale, opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 562–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.C.; Maulik, G.; Christensen, J.; Salgia, R. c-Met: Structure, functions and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Pennell, N.A.; Davies, K.D. Exon 14 Skipping Mutations in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Overview of Biology, Clinical Outcomes, and Testing Considerations. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, H.N.; Liu, P. Targeting MET in cancer therapy. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2017, 3, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenuti, S.; Comoglio, P.M. The MET receptor tyrosine kinase in invasion and metastasis. J. Cell Physiol. 2007, 213, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hack, S.P.; Bruey, J.M.; Koeppen, H. HGF/MET-directed therapeutics in gastroesophageal cancer: A review of clinical and biomarker development. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2866–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Luo, J.; Chang, J.; Rekhtman, N.; Arcila, M.; Drilon, A. MET-dependent solid tumours—Molecular diagnosis and targeted therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Tang, L.H.; Coit, D.G.; Kelsen, D.P.; Francone, T.D.; Weiser, M.R.; Jhanwar, S.C.; Shah, M.A. MET expression and amplification in patients with localized gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2011, 20, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Ervin, T.J.; Ramlau, R.A.; Daniel, D.B.; Goldschmidt, J.H.; Blumenschein, G.R.; Krzakowski, M.J.; Robinet, G.; Godbert, B.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Randomized phase II trial of Onartuzumab in combination with erlotinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4105–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuzzo, F.; Marchetti, A.; Skokan, M.; Rossi, E.; Gajapathy, S.; Felicioni, L.; Del Grammastro, M.; Sciarrotta, M.G.; Buttitta, F.; Incarbone, M.; et al. Increased MET gene copy number negatively affects survival of surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignard, X.; Ruppert, A.M.; Antoine, M.; Vasseur, J.; Girard, N.; Mazières, J.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Fallet, V.; Rabbe, N.; Thivolet-Bejui, F.; et al. c-MET Overexpression as a Poor Predictor of MET Amplifications or Exon 14 Mutations in Lung Sarcomatoid Carcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, N.; Hong, L.; Zhang, J.; Heymach, J.; Hong, D.; Le, X. Beyond epidermal growth factor receptor: MET amplification as a general resistance driver to targeted therapy in oncogene-driven non-small-cell lung cancer. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubendorf, L.; Dafni, U.; Schöbel, M.; Finn, S.P.; Tischler, V.; Sejda, A.; Marchetti, A.; Thunnissen, E.; Verbeken, E.K.; Warth, A.; et al. Prevalence and clinical association of MET gene overexpression and amplification in patients with NSCLC: Results from the European Thoracic Oncology Platform (ETOP) Lungscape project. Lung Cancer 2017, 111, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catenacci, D.V.T.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Davidenko, I.; Murad, A.M.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Ilson, D.H.; Tjulandin, S.; Gotovkin, E.; Karaszewska, B.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Rilotumumab plus epirubicin, cisplatin, and capecitabine as first-line therapy in advanced MET-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (RILOMET-1): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1467–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iveson, T.; Donehower, R.C.; Davidenko, I.; Tjulandin, S.; Deptala, A.; Harrison, M.; Nirni, S.; Lakshmaiah, K.; Thomas, A.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Rilotumumab in combination with epirubicin, cisplatin, and capecitabine as first-line treatment for gastric or oesophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma: An open-label, dose de-escalation phase 1b study and a double-blind, randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malka, D.; François, E.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Castan, F.; Bouché, O.; Bennouna, J.; Ghiringhelli, F.; de la Fouchardière, C.; Borg, C.; Samalin, E.; et al. FOLFOX alone or combined with rilotumumab or panitumumab as first-line treatment for patients with advanced gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma (PRODIGE 17-ACCORD 20-MEGA): A randomised, open-label, three-arm phase II trial. Eur. J Cancer. 2019, 115, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.; Bang, Y.J.; Lordick, F.; Alsina, M.; Chen, M.; Hack, S.P.; Bruey, J.M.; Smith, D.; McCaffery, I.; Shames, D.S.; et al. Effect of Fluorouracil, Leucovorin, and Oxaliplatin with or Without Onartuzumab in HER2-Negative, MET-Positive Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma: The METGastric Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, D.; Chung, H.C.; Oh, D.Y.; Park, S.H.; Kadowaki, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Tsuji, A.; Komatsu, Y.; Kang, Y.K.; Uenaka, K.; et al. A non-randomized, open-label, single-arm, Phase 2 study of emibetuzumab in Asian patients with MET diagnostic positive, advanced gastric cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Karaszewska, B.; Kang, Y.K.; Chung, H.C.; Shankaran, V.; Siena, S.; Go, N.F.; Yang, H.; Schupp, M.; Cunningham, D. A Multicenter Phase II Study of AMG 337 in Patients with. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, T.; Cozic, N.; de la Fouchardière, C.; Meriaux, E.; Plaza, J.; Mineur, L.; Guimbaud, R.; Samalin, E.; Mary, F.; Lecomte, T.; et al. The Activity of Crizotinib in Chemo-Refractory MET-Amplified Esophageal and Gastric Adenocarcinomas: Results from the AcSé-Crizotinib Program. Target. Oncol. 2021, 16, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, Y.J.; Su, W.C.; Schuler, M.; Nam, D.H.; Lim, W.T.; Bauer, T.M.; Azaro, A.; Poon, R.T.P.; Hong, D.; Lin, C.C.; et al. Phase 1 study of capmatinib in MET-positive solid tumor patients: Dose escalation and expansion of selected cohorts. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Catenacci, D.V.; Hochster, H.S.; Ford, J.; Kunz, P.; Lee, F.C.; Kallender, H.; Cecchi, F.; Rabe, D.C.; et al. Phase II study evaluating 2 dosing schedules of oral foretinib (GSK1363089), cMET/VEGFR2 inhibitor, in patients with metastatic gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.K.; Muro, K.; Ryu, M.H.; Yasui, H.; Nishina, T.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Akinaga, S.; Boku, N. A phase II trial of a selective c-Met inhibitor tivantinib (ARQ 197) monotherapy as a second- or third-line therapy in the patients with metastatic gastric cancer. Investig. New Drugs. 2014, 32, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, S.; Patel, M.; Kurkjian, C.; Hemphill, B.; Flores, M.; Thompson, D.; Bendell, J. A Phase II Study of the c-Met Inhibitor Tivantinib in Combination with FOLFOX for the Treatment of Patients with Previously Untreated Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Distal Esophagus, Gastroesophageal Junction, or Stomach. Cancer Investig. 2017, 35, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.T.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.; Kozarewa, I.; Mortimer, P.G.S.; Odegaard, J.I.; Harrington, E.A.; Lee, J.; Lee, T.; et al. Tumor Genomic Profiling Guides Patients with Metastatic Gastric Cancer to Targeted Treatment: The VIKTORY Umbrella Trial. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1388–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Hanna, D.L.; Llovet, J.; Kelley, R.K. Cabozantinib: An evolving therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 98, 102221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, P.K.; Felip, E.; Veillon, R.; Sakai, H.; Cortot, A.B.; Garassino, M.C.; Mazieres, J.; Viteri, S.; Senellart, H.; Van Meerbeeck, J.; et al. Tepotinib in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitara, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Tsushima, T.; Naito, T.; Matsubara, N.; Watanabe, M.; Sarholz, B.; Johne, A.; Doi, T. Phase I trial of the MET inhibitor tepotinib in Japanese patients with solid tumors. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 50, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Sawada, H.; Yamada, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Tatsumi, M.; Yamashita, J.; Matsuda, M.; Sakaguchi, T.; Hirao, T.; Nakano, H. The prognostic significance of amplification and overexpression of c-met and c-erb B-2 in human gastric carcinomas. Cancer 1999, 85, 1894–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.E.; Kim, M.A.; Lee, H.S.; Jung, E.J.; Yang, H.K.; Lee, B.L.; Bang, Y.J.; Kim, W.H. MET in gastric carcinomas: Comparison between protein expression and gene copy number and impact on clinical outcome. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, J.P.; Vande Woude, G.F.; Boerner, S.A.; LoRusso, P.M. Novel therapeutic inhibitors of the c-Met signaling pathway in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type | Target | Name | Mechanism of Action | Trial (Ref.) | Phase | N° of Patients Included | Inclusion Diagnostic Marker | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monoclonal antibody | HGF | mFolfox + Rilotumumab | Blocks HGF | Rilomet I [19] | III | 608 | IHC ≥ 1 ≤ | No benefit of mAb |
| mFolfox + Rilotumumab or EGFRi | MEGA [21] | III | 162 | IHC 2+ or 3+ | No benefit of mAb | |||
| MET | Onartuzumab + mFolfox | Blocks MET | METGastric [22] | III | 562 | none | No benefit of mAb | |
| HGF and MET | Emibetuzumab | Blocks HGF binding and internalization of MET | NA [23] | II | 15 | IHC 2+ or 3+ | No patients with PR | |
| Tyrosine kinase inhibitor | Crizotinib | Multi TKI | AcSé Crizotinib Program [25] | II | 9 | IHC 2+ or 3+ | ORR 33% | |
| Foretinib | NA [27] | II | 74 | None | No PR, 15 patiënts SD | |||
| Capmatinib | Selective MET TKI | NA [26] | II | 9 | IHC 2+ or 3+ or Hscore > 150 MET/CEN7 ≥ 2 or MET GCN ≥ 5 | 2 patients with SD | ||
| Tivantinib | NA [28] | II | 30 | None | No ORR, 36 DCR | |||
| Savolitinib | Viktory Umbrella Trial [30] | II | 20 | Amplification ≥ 10 on NGS | ORR 50% | |||
| AMG337 | NA [24] | II | 55 | MET/CEN7 ≥ 2 | ORR 19% | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Herpe, F.; Van Cutsem, E. The Role of cMET in Gastric Cancer—A Review of the Literature. Cancers 2023, 15, 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071976
Van Herpe F, Van Cutsem E. The Role of cMET in Gastric Cancer—A Review of the Literature. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071976
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Herpe, Filip, and Eric Van Cutsem. 2023. "The Role of cMET in Gastric Cancer—A Review of the Literature" Cancers 15, no. 7: 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071976
APA StyleVan Herpe, F., & Van Cutsem, E. (2023). The Role of cMET in Gastric Cancer—A Review of the Literature. Cancers, 15(7), 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071976






