Prognostic Relevance and In Vitro Targeting of Concomitant PTEN and p16 Deficiency in Chordomas
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
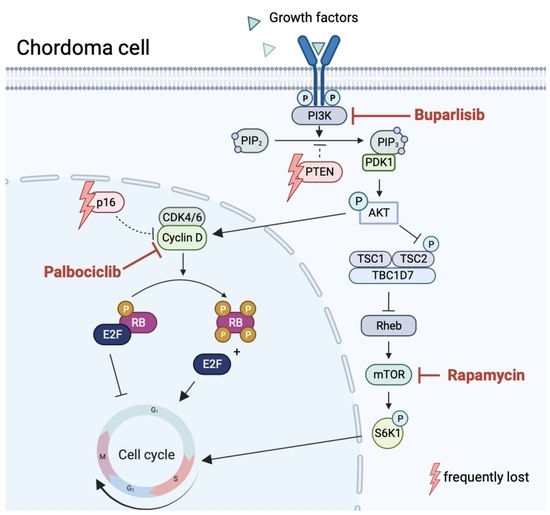
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Chordoma Tissue Bank and Survival Analysis
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Protein Isolation and Western Blot Analyses
2.5. MTS Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Isobologram Analysis of Drug Interactions
3. Results
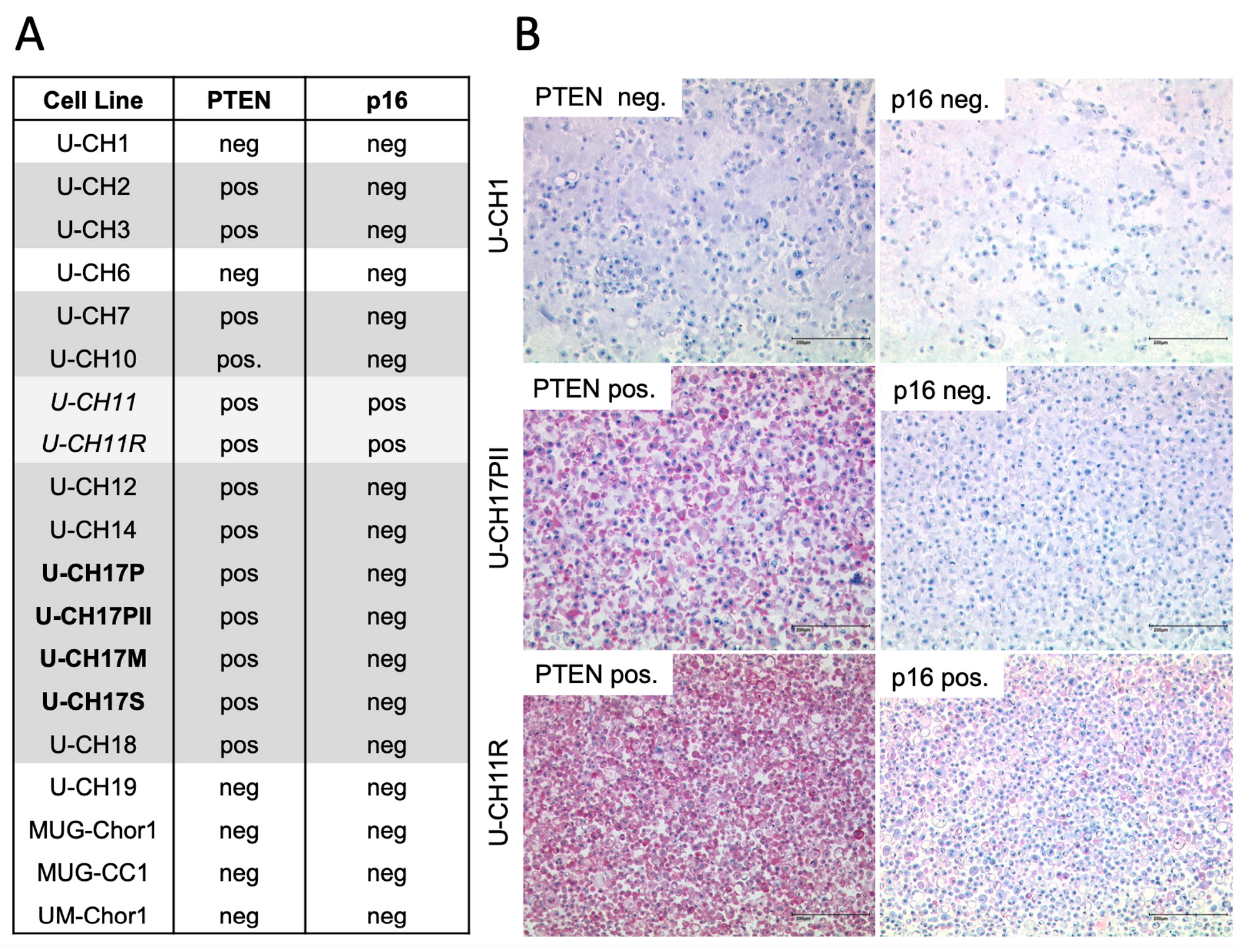
3.1. PTEN and p16 Deficiency in Chordoma Cell Lines
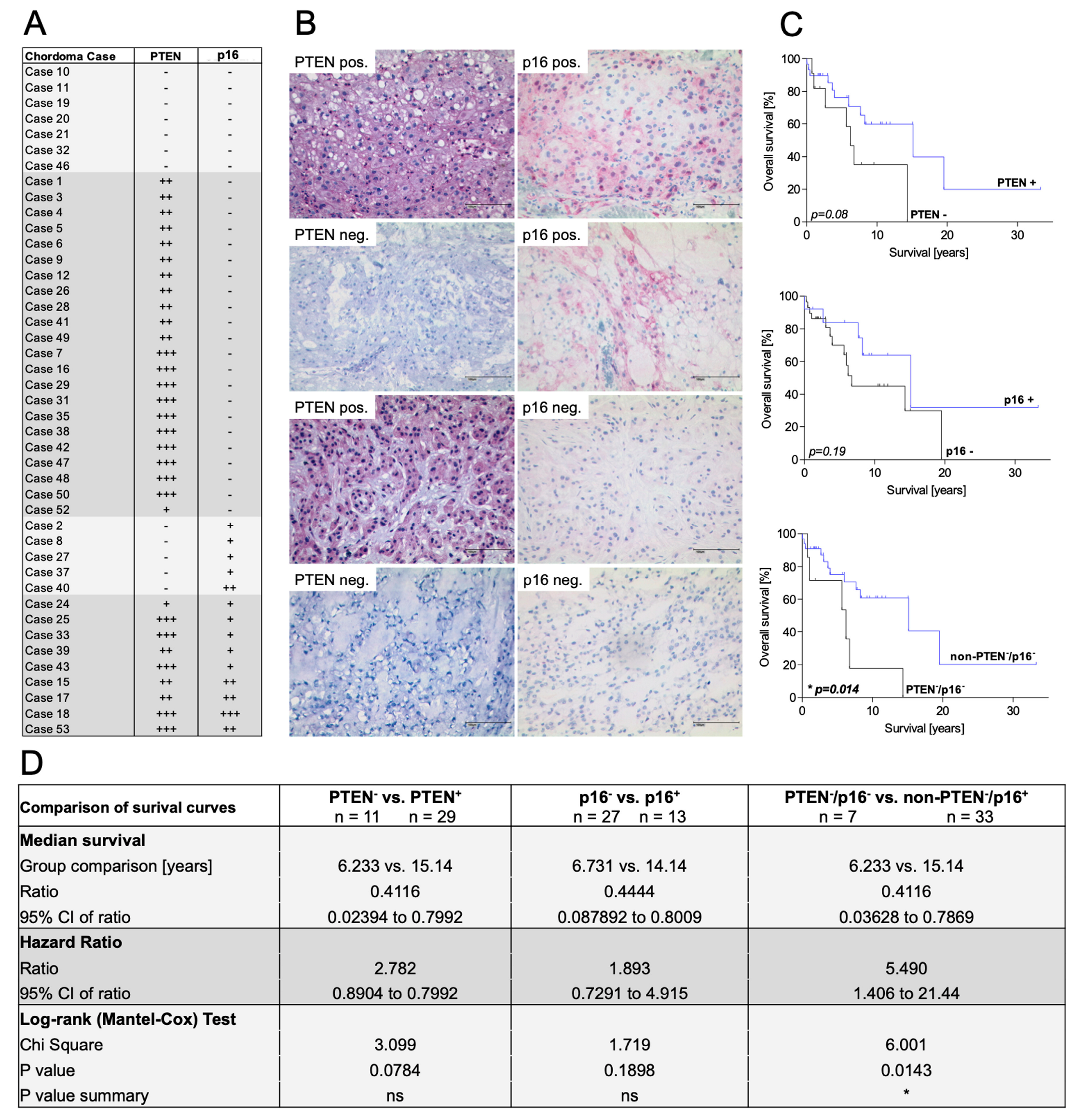
3.2. Concomitant Loss of Both PTEN and p16 Predicts a Shorter Overall Survival in Chordoma Patients
3.3. Combined Inhibition of the PTEN and p16 Signaling Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flanagan, A.M. Chordoma. In World Health Organization classification of tumours. In Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone; Fletcher, C.D.M., Bridge, J.A., Hogendoorn, P.C.W., Mertens, F., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2013; pp. 328–329. [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen, M.; Wang, Z.; Lasota, J.; Heery, C.; Schlom, J.; Palena, C. Nuclear Brachyury Expression Is Consistent in Chordoma, Common in Germ Cell Tumors and Small Cell Carcinomas, and Rare in Other Carcinomas and Sarcomas: An Immunohistochemical Study of 5229 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacchiotti, S.; Sommer, J. Building a global consensus approach to chordoma: A position paper from the medical and patient community. Lancet. Oncol. 2015, 16, e71–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Witzleben, A.; Goerttler, L.T.; Marienfeld, R.; Barth, H.; Lechel, A.; Mellert, K.; Böhm, M.; Kornmann, M.; Mayer-Steinacker, R.; von Baer, A.; et al. Preclinical Characterization of Novel Chordoma Cell Systems and Their Targeting by Pharmocological Inhibitors of the CDK4/6 Cell-Cycle Pathway. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3823–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallor, K.H.; Staaf, J.; Jonsson, G.; Heidenblad, M.; Vult von Steyern, F.; Bauer, H.C.; Ijszenga, M.; Hogendoorn, P.C.; Mandahl, N.; Szuhai, K.; et al. Frequent deletion of the CDKN2A locus in chordoma: Analysis of chromosomal imbalances using array comparative genomic hybridisation. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenonos, G.A.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Mukherjee, D.; Chang, Y.F.; Panayidou, K.; Snyderman, C.H.; Wang, E.W.; Seethala, R.R.; Gardner, P.A. Prospective validation of a molecular prognostication panel for clival chordoma. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 130, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbinski, C.; Oakley, G.J.; Cieply, K.; Mantha, G.S.; Nikiforova, M.N.; Dacic, S.; Seethala, R.R. The prognostic value of Ki-67, p53, epidermal growth factor receptor, 1p36, 9p21, 10q23, and 17p13 in skull base chordomas. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2010, 134, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Sun, J.; Yong, L.; Liang, C.; Liu, T.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, X. Deficiency of PTEN and CDKN2A Tumor-Suppressor Genes in Conventional and Chondroid Chordomas: Molecular Characteristics and Clinical Relevance. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2020, 13, 4649–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpey, P.S.; Behjati, S.; Young, M.D.; Martincorena, I.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Farndon, S.J.; Guzzo, C.; Hardy, C.; Latimer, C.; Butler, A.P.; et al. The driver landscape of sporadic chordoma. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presneau, N.; Shalaby, A.; Idowu, B.; Gikas, P.; Cannon, S.R.; Gout, I.; Diss, T.; Tirabosco, R.; Flanagan, A.M. Potential therapeutic targets for chordoma: PI3K/AKT/TSC1/TSC2/mTOR pathway. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, E.; MacConaill, L.E.; Cote, G.M.; Le, L.P.; Shen, J.K.; Nielsen, G.P.; Iafrate, A.J.; Garraway, L.A.; Hornicek, F.J.; Duan, Z. Genotyping cancer-associated genes in chordoma identifies mutations in oncogenes and areas of chromosomal loss involving CDKN2A, PTEN, and SMARCB1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.R.; Chen, M.; Pandolfi, P.P. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor: New modes and prospects. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 19, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michmerhuizen, N.L.; Owen, J.H.; Heft Neal, M.E.; Mann, J.E.; Leonard, E.; Wang, J.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, H.; McHugh, J.B.; Brenner, J.C.; et al. Rationale for the advancement of PI3K pathway inhibitors for personalized chordoma therapy. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 147, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Ma, J.; Wang, K.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z. PTEN is recognized as a prognostic-related biomarker and inhibits proliferation and invasiveness of skull base chordoma cells. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 1011845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzyme. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Zhang, Y.; Kassam, A.B.; Park, M.J.; Gardner, P.; Prevedello, D.; Henry, S.; Horbinski, C.; Beumer, J.H.; Tawbi, H.; et al. Combined PDGFR and HDAC Inhibition Overcomes PTEN Disruption in Chordoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Mo, J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, G.; Wu, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, K.; Yang, H. Expression of PTEN and mTOR in sacral chordoma and association with poor prognosis. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottone, L.; Eden, N.; Usher, I.; Lombard, P.; Ye, H.; Ligammari, L.; Lindsay, D.; Brandner, S.; Pizem, J.; Pillay, N.; et al. Frequent alterations in p16/CDKN2A identified by immunohistochemistry and FISH in chordoma. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2020, 6, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Shi, J.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Hua, X.; Zhu, B.; Koka, H.; Wu, H.H.; Song, L.; et al. Whole genome sequencing of skull-base chordoma reveals genomic alterations associated with recurrence and chordoma-specific survival. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, J.; Itani, D.M.; Homlar, K.C.; Keedy, V.L.; Halpern, J.L.; Holt, G.E.; Schwartz, H.S.; Coffin, C.M.; Kelley, M.J.; Cates, J.M. Methylthioadenosine phosphorylase and activated insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor/insulin receptor: Potential therapeutic targets in chordoma. J. Pathol. 2010, 220, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, M.-V.; Heilig, C.E.; Hamacher, R.W.; Bauer, S.; Mayer-Steinacker, R.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Horak, P.; Lanz, L.-M.; Muskatewitz, T.; Susse, H.; et al. CDK4/6 inhibition in locally advanced/metastatic chordoma (NCT PMO-1601). Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, V.M.; Bhola, N.E.; Bauer, J.A.; Formisano, L.; Lee, K.M.; Hutchinson, K.E.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Moore, P.D.; Estrada, M.V.; Sanchez, V.; et al. Kinome-Wide RNA Interference Screen Reveals a Role for PDK1 in Acquired Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition in ER-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2488–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asby, D.J.; Killick-Cole, C.L.; Boulter, L.J.; Singleton, W.G.; Asby, C.A.; Wyatt, M.J.; Barua, N.U.; Bienemann, A.S.; Gill, S.S. Combined use of CDK4/6 and mTOR inhibitors induce synergistic growth arrest of diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma cells via mutual downregulation of mTORC1 activity. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 3483–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshiro, H.; Tome, Y.; Miyake, K.; Higuchi, T.; Sugisawa, N.; Kanaya, F.; Nishida, K.; Hoffman, R.M. Combination of CDK4/6 and mTOR Inhibitors Suppressed Doxorubicin-resistant Osteosarcoma in a Patient-derived Orthotopic Xenograft Mouse Model: A Translatable Strategy for Recalcitrant Disease. Anticancer. Res. 2021, 41, 3287–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.; Di Cristofano, F.; Ranieri, M.; De Martino, D.; Di Cristofano, A. PI3K/mTOR inhibition potentiates and extends palbociclib activity in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonelli, M.A.; Digiacomo, G.; Fumarola, C.; Alfieri, R.; Quaini, F.; Falco, A.; Madeddu, D.; La Monica, S.; Cretella, D.; Ravelli, A.; et al. Combined Inhibition of CDK4/6 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathways Induces a Synergistic Anti-Tumor Effect in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cells. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cretella, D.; Ravelli, A.; Fumarola, C.; La Monica, S.; Digiacomo, G.; Cavazzoni, A.; Alfieri, R.; Biondi, A.; Generali, D.; Bonelli, M.; et al. The anti-tumor efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibition is enhanced by the combination with PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors through impairment of glucose metabolism in TNBC cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, P.; Geng, Y.; Wang, B.; Gan, W.; Guo, J.; Wu, F.; Chin, Y.R.; Berrios, C.; et al. Inhibition of Rb Phosphorylation Leads to mTORC2-Mediated Activation of Akt. Mol. Cell. 2016, 62, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmez, I.; Brenneman, B.; Xiao, A.; Serbulea, V.; Benamar, M.; Zhang, Y.; Manigat, L.; Abbas, T.; Lee, J.; Nakano, I.; et al. Combined CDK4/6 and mTOR Inhibition Is Synergistic against Glioblastoma via Multiple Mechanisms. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2017, 23, 6958–6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborini, E.; Virdis, E.; Negri, T.; Orsenigo, M.; Brich, S.; Conca, E.; Gronchi, A.; Stacchiotti, S.; Manenti, G.; Casali, P.G.; et al. Analysis of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and downstream pathways in chordomas. Neuro. Oncol. 2010, 12, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Non-PTEN−/p16− (n = 36) | PTEN−/p16− (n = 7) | p-Value | PTEN+ (n = 31) | PTEN− (n = 12) | p-Value | CDKN2A+ (n = 14) | CDKN2A− (n = 29) | p-Value | Statistical Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Chi-squared test | |||||||||
| Male (n) | 23 | 5 | 0.65 | 20 | 8 | 0.89 | 10 | 18 | 0.55 | |
| Female (n) | 13 | 2 | 11 | 4 | 4 | 11 | ||||
| Age (Years; mean ± SD) | 61.64 ± 18.14 | 57.86 ± 17.81 | 0.61 | 64.29 ± 16.38 | 52.58 ± 17.08 | * 0.049 | 57.36 ± 19.15 | 62.79 ± 16.18 | 0.35 | Student’s t-test |
| Ki-67 | Chi-squared test | |||||||||
| <10% | 30 | 3 | * 0.04 | 27 | 7 | * 0.038 | 12 | 22 | 0.46 | |
| ≥10% | 6 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 7 | ||||
| Maximal Diameter (cm ± SD) | 7.13 ± 8.86 | 10 ± 3.71 | 0.42 | 6.01 ± 8.96 | 11.19 ± 4.5 | 0.072 | 10.97 ± 12.5 | 5.76 ± 4.45 | 0.058 | Student’s t-test |
| Recurrence | Chi-squared test | |||||||||
| Presence (n) | 18 | 5 | 0.26 | 14 | 9 | 0.078 | 9 | 14 | 0.21 | |
| Absence (n) | 18 | 2 | 17 | 3 | 4 | 15 | ||||
| Metastasis | Chi-squared test | |||||||||
| Presence (n) | 6 | 5 | ** 0.0026 | 3 | 8 | *** 0.00012 | 4 | 7 | 0.75 | |
| Absence (n) | 30 | 2 | 28 | 4 | 10 | 22 | ||||
| Location | Fisher’s exact test | |||||||||
| Clivus (n) | 6 | 0 | 0.47 | 6 | 0 | 0.21 | 3 | 3 | 0.25 | |
| Mobile spine (n) | 10 | 1 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 7 | ||||
| Os sacrum (n) | 19 | 6 | 15 | 10 | 6 | 19 | ||||
| Other (n) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seeling, C.; Mosca, E.; Mantel, E.; Möller, P.; Barth, T.F.E.; Mellert, K. Prognostic Relevance and In Vitro Targeting of Concomitant PTEN and p16 Deficiency in Chordomas. Cancers 2023, 15, 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071977
Seeling C, Mosca E, Mantel E, Möller P, Barth TFE, Mellert K. Prognostic Relevance and In Vitro Targeting of Concomitant PTEN and p16 Deficiency in Chordomas. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071977
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeeling, Carolin, Elena Mosca, Eva Mantel, Peter Möller, Thomas F. E. Barth, and Kevin Mellert. 2023. "Prognostic Relevance and In Vitro Targeting of Concomitant PTEN and p16 Deficiency in Chordomas" Cancers 15, no. 7: 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071977
APA StyleSeeling, C., Mosca, E., Mantel, E., Möller, P., Barth, T. F. E., & Mellert, K. (2023). Prognostic Relevance and In Vitro Targeting of Concomitant PTEN and p16 Deficiency in Chordomas. Cancers, 15(7), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071977