Overexpression of YEATS2 Remodels the Extracellular Matrix to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via the PI3K/AKT Pathway
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Western Blotting
2.4. Cell Transfection Assay
2.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.6. Wound Healing Assay
2.7. Transwell Migration and Invasion Assays
2.8. Immunofluorescence
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
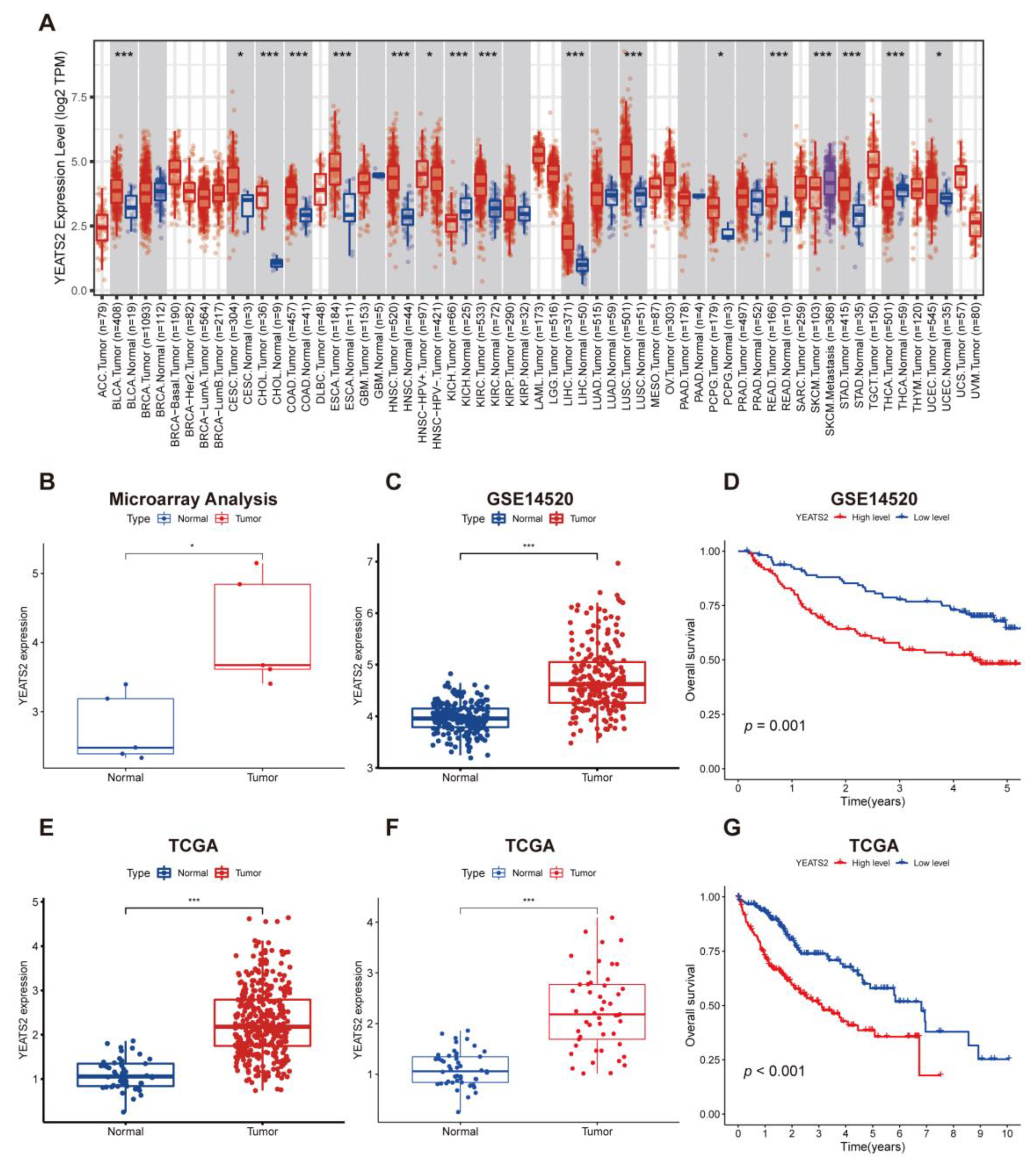
3.1. Expression and Prognosis Analysis of YEATS2 in Liver Cancer
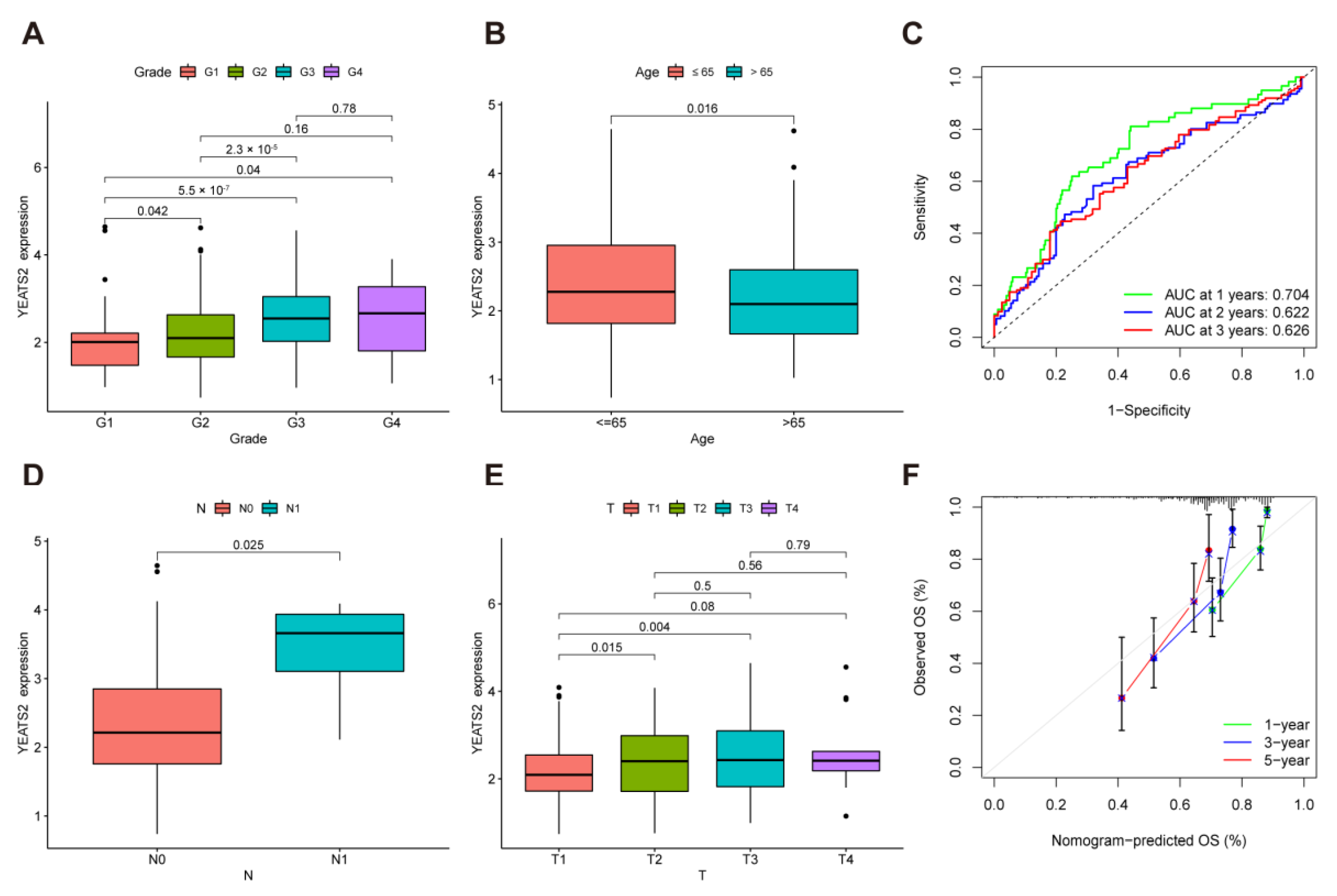
3.2. Correlation between YEATS2 Expression and Clinical Features in Liver Cancer
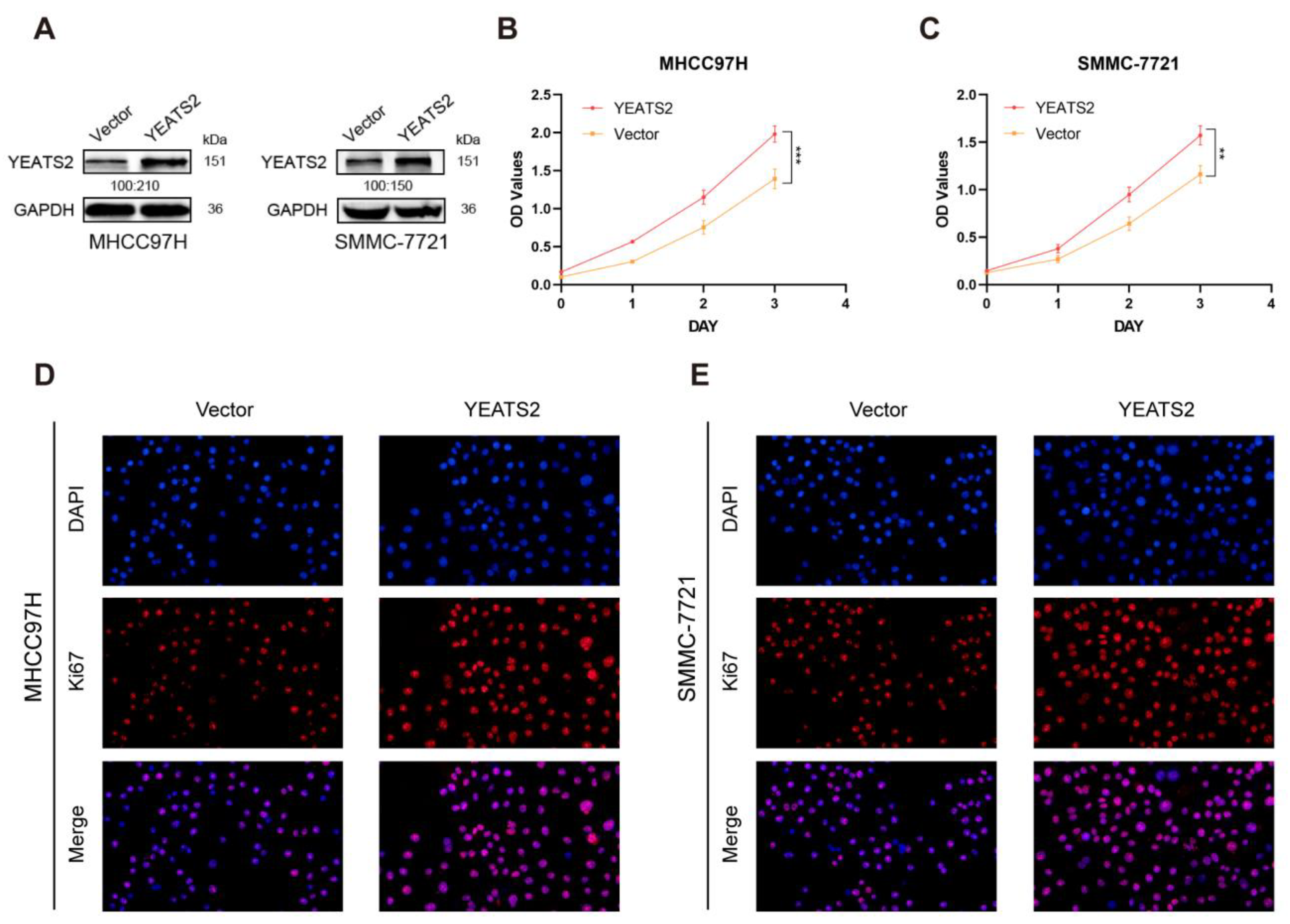
3.3. Overexpression of YEATS2 Promotes HCC Cell Proliferation
3.4. Effects of YEATS2 on Migration, Invasion, and Cycle of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
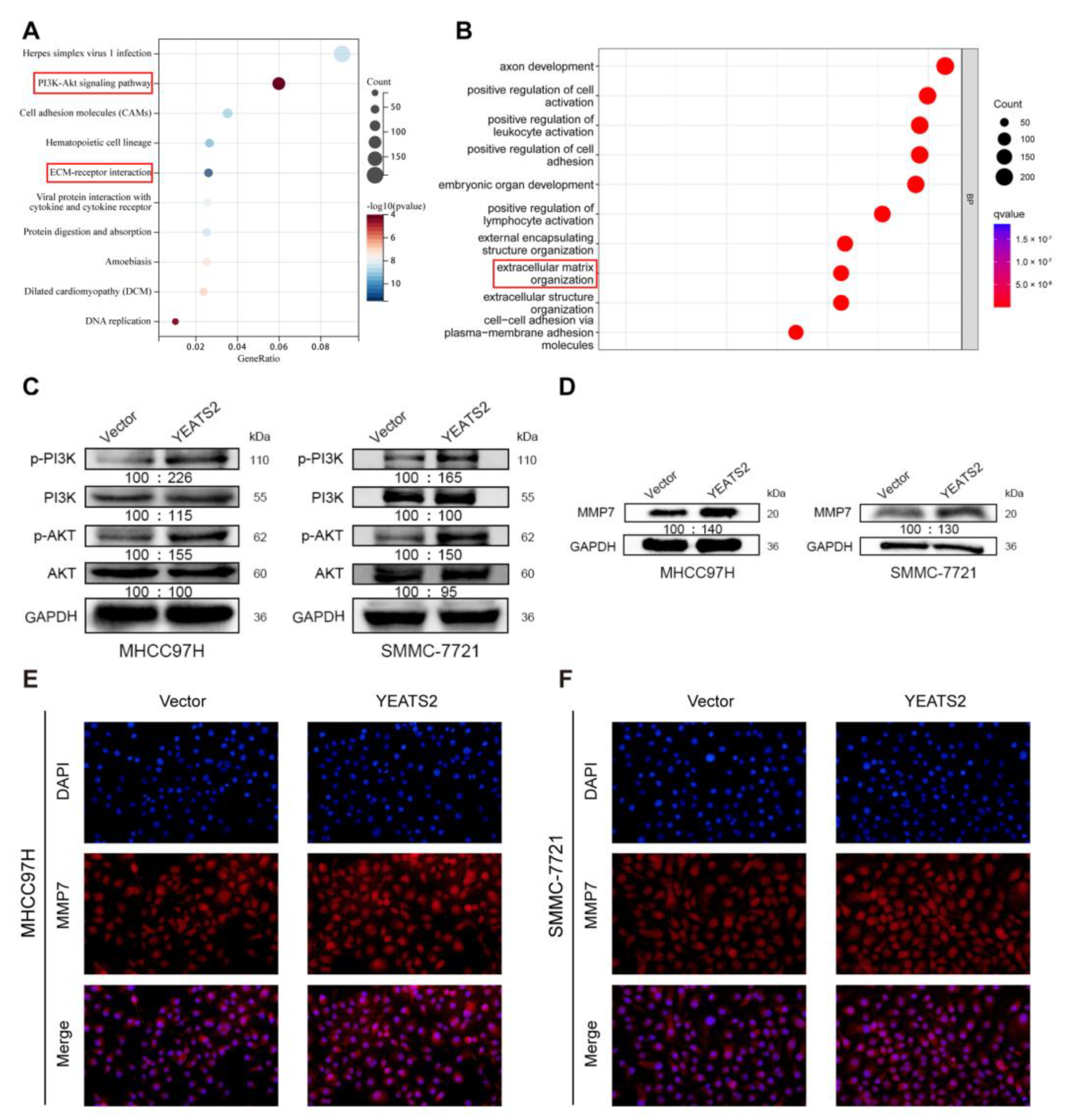
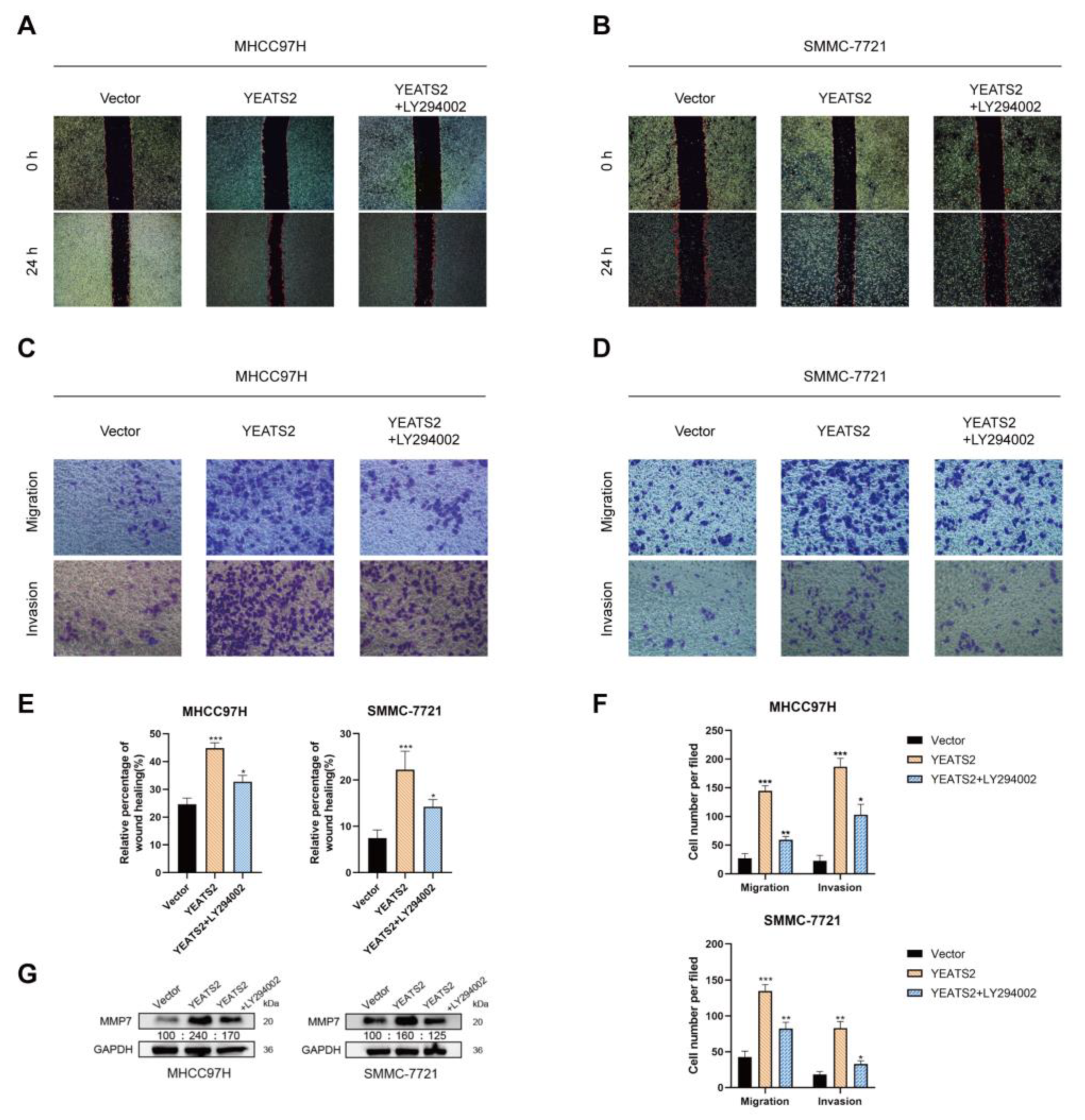
3.5. YEATS2 Activates PI3K/AKT Pathway and Mediates MMP7 to Remodel Extracellular Matrix
3.6. YEATS2 Regulates the Expression of MMP7 through the PI3K/Akt Pathway to Remodel the Extracellular Matrix
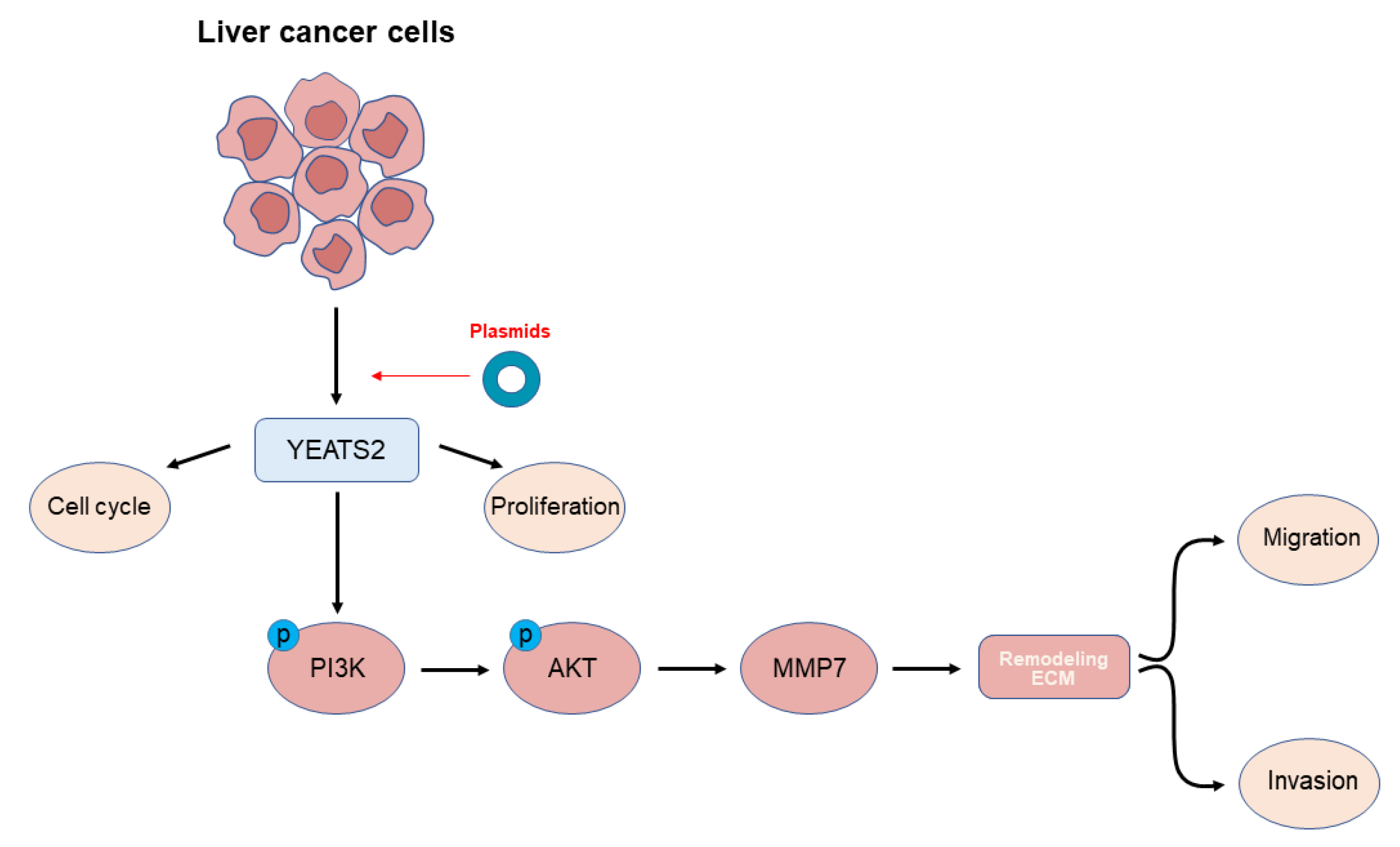
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Sharma, I.; Sankpal, U.T.; Ghabach, B.; Narra, K.; Neerukonda, L.; Basha, R. Targeted Molecular Therapeutic Options for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2020, 25, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L.; Faiola, F.; Xu, M.; Pan, S.; Martinez, E. Human ATAC Is a GCN5/PCAF-containing acetylase complex with a novel NC2-like histone fold module that interacts with the TATA-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33808–33815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orpinell, M.; Fournier, M.; Riss, A.; Nagy, Z.; Krebs, A.R.; Frontini, M.; Tora, L. The ATAC acetyl transferase complex controls mitotic progression by targeting non-histone substrates. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2381–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, N.; Garcia, K.; Rajendran, D.; Lin, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.; Mitchell, K.A.; Borcherding, N.; Fullenkamp, C.; Chimenti, M.S.; Gingras, A.C.; et al. TAZ-CAMTA1 and YAP-TFE3 alter the TAZ/YAP transcriptome by recruiting the ATAC histone acetyltransferase complex. eLife 2021, 10, e62857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Guan, H.; Zhao, S.; Mi, W.; Wen, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Allis, C.D.; Shi, X.; Li, H. YEATS2 is a selective histone crotonylation reader. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Guan, H.; Lyu, J.; Zhao, D.; Xi, Y.; Jiang, S.; Andrews, F.H.; Wang, X.; Gagea, M.; Wen, H.; et al. YEATS2 links histone acetylation to tumorigenesis of non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Lei, S.; He, Z.; Chen, T.; Jiang, J. YEATS2 is a target of HIF1α and promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Zheng, F.; Lan, T.; Chen, H.F.; Xu, C.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Weng, Y.Y.; Xu, L.F.; Zhang, F. YEATS2 regulates the activation of TAK1/NF-κB pathway and is critical for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell survival. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, T.; Li, J.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Cui, Z. YEATS domain-containing 2 (YEATS2), targeted by microRNA miR-378a-5p, regulates growth and metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7286–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.T.; Xu, X.M.; Hu, Y.; Deng, J.J.; Ge, W.; Han, N.N.; Zhang, M.X. Long noncoding RNAs in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7208–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Parajuli, K.R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, K.; Mo, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, A.R.; et al. Interleukin-17 promotes prostate cancer via MMP7-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2017, 36, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Liang, Q.; Xu, K.; Cui, D.; Jiang, L.; Yin, P.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, J. MiR-139 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.A.; Vainer, B.; Bartels, A.; Brünner, N.; Sørensen, J.B. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1) by colorectal cancer cells and adjacent stroma cells--associations with histopathology and patients outcome. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.L.; Wang, J.Z.; Xia, X.P.; Pan, C.W.; Shao, X.X.; Xia, S.L.; Yang, S.X.; Zheng, B. Rab11-FIP2 promotes colorectal cancer migration and invasion by regulating PI3K/AKT/MMP7 signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufu, T.; Di, X.; Yilin, Z.; Gege, L.; Xi, C.; Ling, W. Celastrol inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and migration through suppression of MMP3 and MMP7 by the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2018, 29, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwanwan, D.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, S.; Saikam, V.; Singh, R. Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment approaches. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.J.; von Felden, J.; Garcia-Lezana, T.; Sarcognato, S.; Villanueva, A. Tumour evolution in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartke, J.; Johnson, M.; Ghabril, M. The diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2017, 34, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Cai, J.; Ke, A.; Fan, J. The progress of immune checkpoint therapy in primary liver cancer. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta. Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, S.; Craig, A.J.; Ma, L.; Heinrich, B.; Greten, T.F.; Wang, X.W. Understanding tumour cell heterogeneity and its implication for immunotherapy in liver cancer using single-cell analysis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 700–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, T.; Pandey, V.; Banjare, N.; Gupta, P.N.; Soni, V. Drug resistance in cancer: Mechanisms and tackling strategies. Pharmacol. Rep. PR 2020, 72, 1125–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez Martín, O.; Schlosser, A.; Furtwängler, R.; Wegert, J.; Gessler, M. MYCN and MAX alterations in Wilms tumor and identification of novel N-MYC interaction partners as biomarker candidates. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, S.; Wen, W.; Zhang, J. Multi-Omics Analysis of the Effects of Smoking on Human Tumors. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 704910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacchini, J.; Heidari, N.; Mediani, L.; Capitani, S.; Shahjahani, M.; Ahmadzadeh, A.; Saki, N. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR network for treatment of leukemia. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2015, 72, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, S.; Amjadi-Moheb, F.; Tabaripour, R.; Ashrafi, G.H.; Akhavan-Niaki, H. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in gastric cancer: Epigenetics and beyond. Life Sci. 2020, 262, 118513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhai, G.; Shao, H.; Yu, X.; Guo, J. FAM107A Inactivation Associated with Promoter Methylation Affects Prostate Cancer Progression through the FAK/PI3K/AKT Pathway. Cancers 2022, 14, 3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miricescu, D.; Totan, A.; Stanescu-Spinu, I.I.; Badoiu, S.C.; Stefani, C.; Greabu, M. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: From Molecular Landscape to Clinical Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresno Vara, J.A.; Casado, E.; de Castro, J.; Cejas, P.; Belda-Iniesta, C.; González-Barón, M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2004, 30, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, M.; Fujishita, T. Oncogenic Roles of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Axis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 407, 153–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickup, M.W.; Mouw, J.K.; Weaver, V.M. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnans, C.; Chou, J.; Werb, Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 786–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niland, S.; Riscanevo, A.X.; Eble, J.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases Shape the Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Cao, N.; Gao, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, S.; Tang, X. ASIC1α up-regulates MMP-2/9 expression to enhance mobility and proliferation of liver cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibody | Specificity | WB | IF | Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YEATS2 | Rabbit | 1:1000 | - | Proteintech |
| PI3K | Rabbit | 1:1000 | - | Affinity |
| p-PI3K | Rabbit | 1:1000 | - | Bioss |
| AKT | Rabbit | 1:1000 | - | ABclonal |
| p-AKT | Rabbit | 1:1000 | - | ABclonal |
| Ki67 | Rabbit | - | 1:200 | Abcam |
| MMP7 | Rabbit | 1:1000 | 1:200 | Abcam |
| GAPDH | Mouse | 1:1000 | - | Proteintech |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W.; Xu, X. Overexpression of YEATS2 Remodels the Extracellular Matrix to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Cancers 2023, 15, 1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061850
Liu X, Hu Y, Li C, Chen J, Liu X, Shen Y, Xu Y, Chen W, Xu X. Overexpression of YEATS2 Remodels the Extracellular Matrix to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061850
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xin, Yi Hu, Cairong Li, Jiayu Chen, Xiaohong Liu, Yang Shen, Yangtao Xu, Wenliang Chen, and Ximing Xu. 2023. "Overexpression of YEATS2 Remodels the Extracellular Matrix to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via the PI3K/AKT Pathway" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061850
APA StyleLiu, X., Hu, Y., Li, C., Chen, J., Liu, X., Shen, Y., Xu, Y., Chen, W., & Xu, X. (2023). Overexpression of YEATS2 Remodels the Extracellular Matrix to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Cancers, 15(6), 1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061850






