Diagnosis and Management of Adult Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
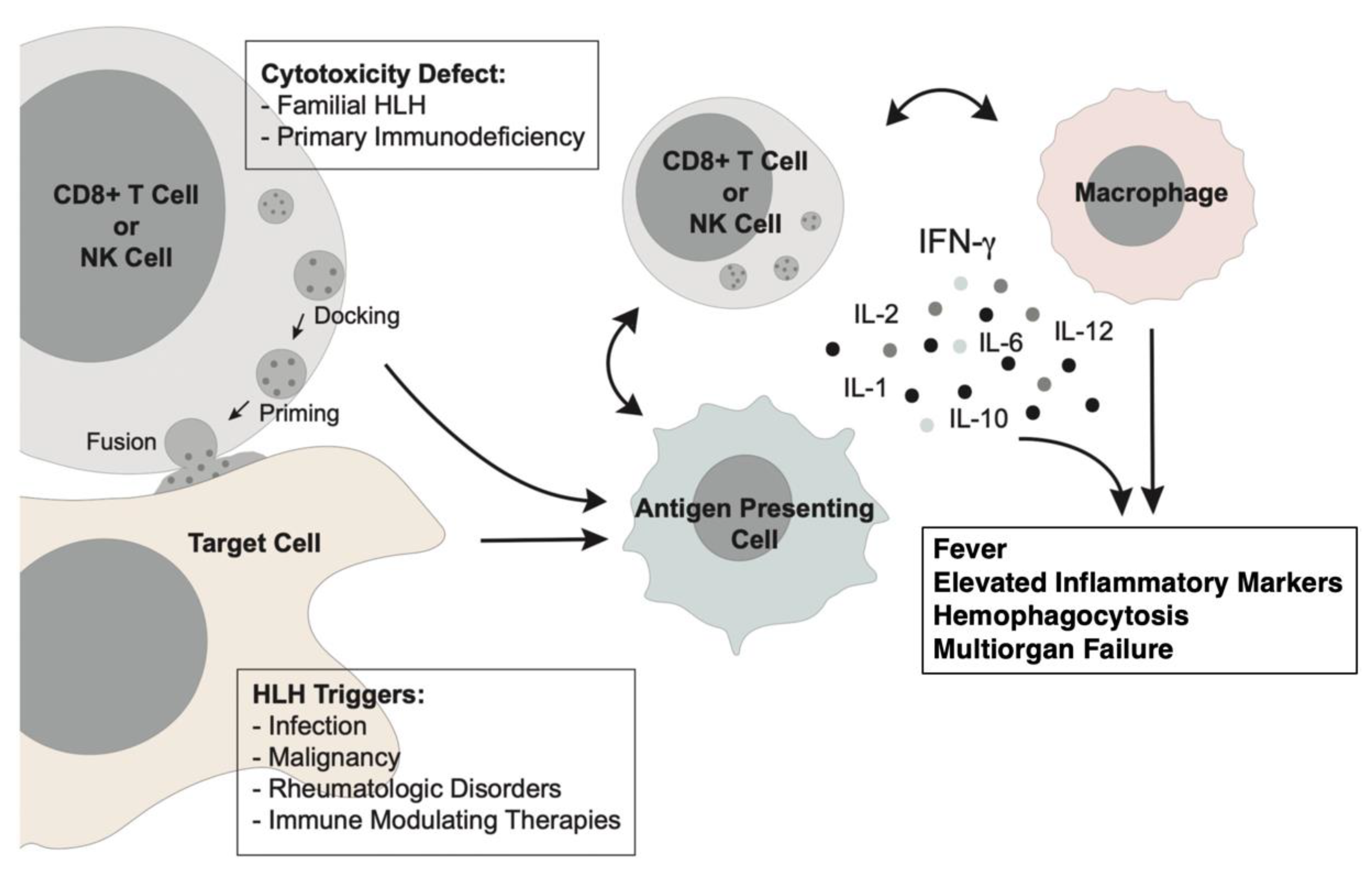
1. Introduction
2. Diagnosis of Malignancy-Associated HLH
2.1. HLH-2004 Diagnostic Guidelines
2.2. Alternatives to HLH-2004 Diagnostic Guidelines
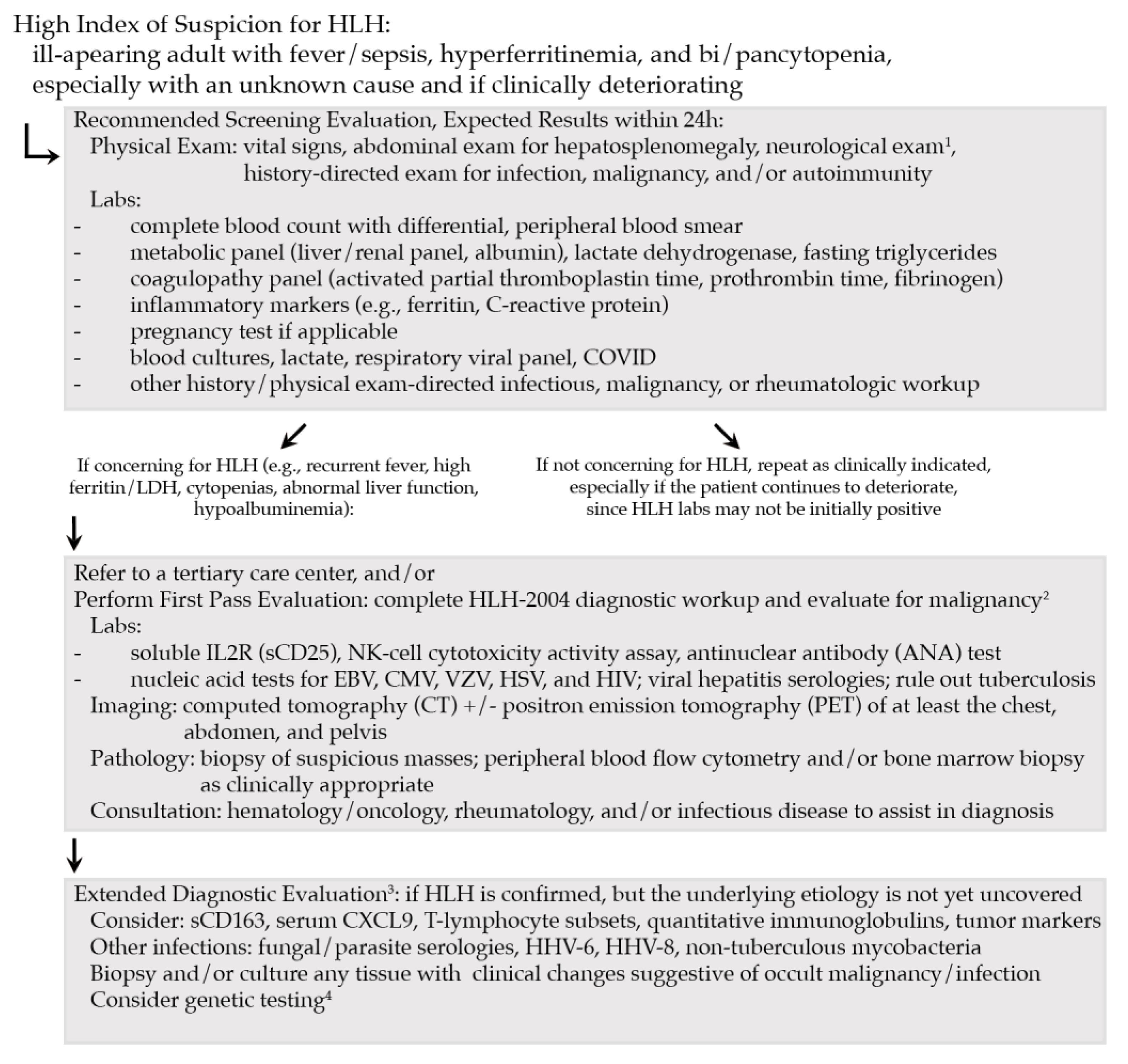
3. Initial Workup of Adult HLH
4. Treatment of mHLH
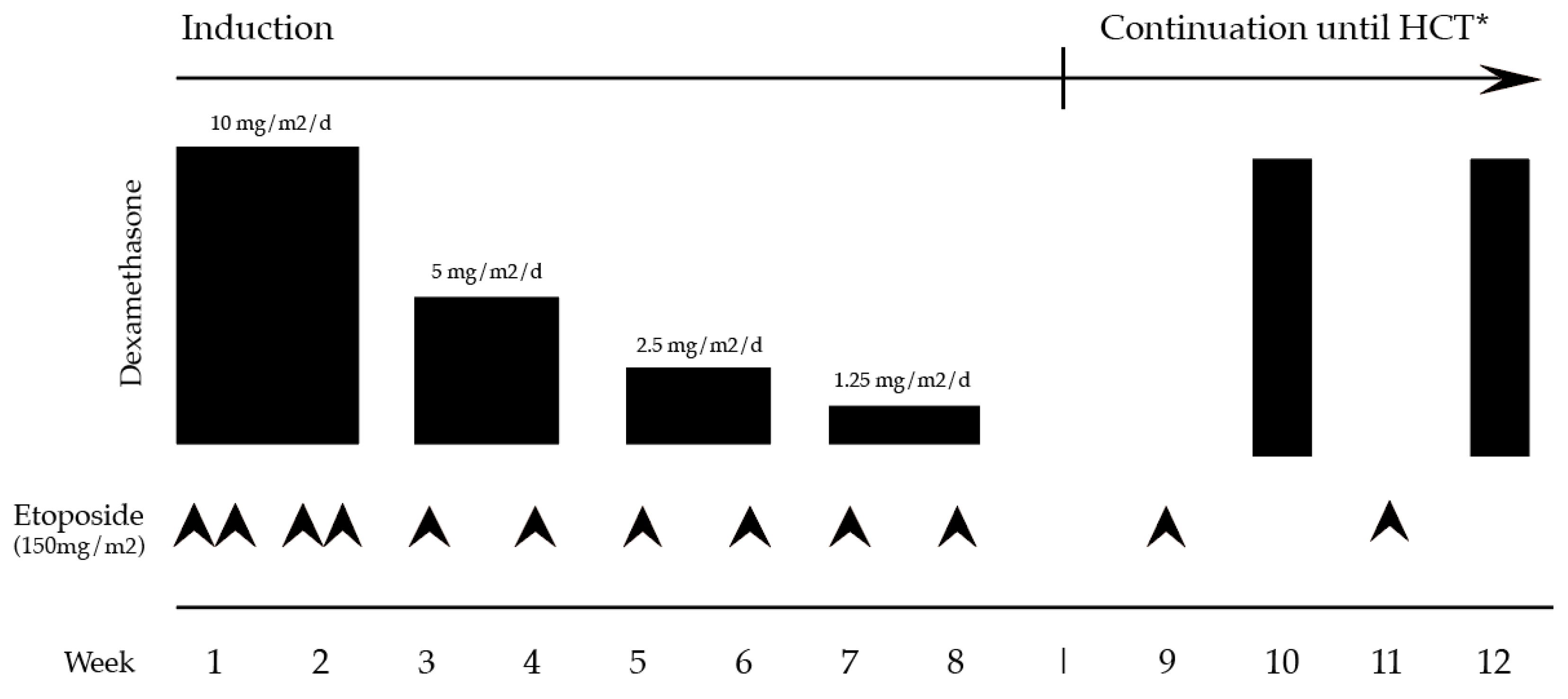
4.1. HLH-94 Protocol
4.2. Strategies to Treat mHLH
4.3. Role of Allogeneic Transplantation
4.4. Biologic Therapy
4.5. Ruxolitinib
4.6. Investigational Agents
5. Special Populations and Treatment-Related HLH
5.1. Lymphoma-Associated HLH (LAHS)
5.2. Leukemia, Myelodysplastic Syndromes, and Allogeneic Transplantation
5.3. Solid Cancers and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICI)
5.4. Bispecific T Cell Engagers, CAR T Therapy, and Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janka, G.E. Familial and Acquired Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2007, 166, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Berliner, N. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2018, 13, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, M.B.; Hildeman, D.; Kappler, J.; Marrack, P. An Animal Model of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH): CD8+ T Cells and Interferon Gamma Are Essential for The. Blood 2004, 104, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akashi, K.; Hayashi, S.; Gondo, H.; Mizuno, S.; Harada, M.; Tamura, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Shibuya, T.; Uike, N.; Okamura, T. Involvement of Interferon-Gamma and Macrophage Colony-Stimulating in Pathogenesis of Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in adults. Br. J. Haematol. 1994, 87, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrell, C.E.; Jordan, M.B. Perforin Deficiency Impairs a Critical Immunoregulatory Loop Murine CD8(+) T Cells and Dendritic Cells. Blood 2013, 121, 5184–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykens, J.E.; Terrell, C.E.; Zoller Erin, E.; Risma, K.; Jordan, M.B. Perforin Is a Critical Physiologic Regulator of T-Cell. Blood 2011, 118, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, S.E.; Dufourcq-Lagelouse, R.; le Deist, F.; Bhawan, S.; Certain, S.; Mathew, P.A.; Henter, J.I.; Bennett, M.; Fischer, A.; de Saint Basile, G.; et al. Perforin Gene Defects in Familial Hemophagocytic. Science (1979) 1999, 286, 1957–1959. [Google Scholar]
- Sumegi, J.; Barnes, M.G.; Nestheide, S.v.; Molleran-Lee, S.; Villanueva, J.; Zhang, K.; Risma, K.A.; Grom, A.A.; Filipovich, A.H. Gene Expression Profiling of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Children with Active Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2011, 117, e151–e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canna, S.W.; Marsh, R.A. Pediatric Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2020, 135, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janka, G.E.; Lehmberg, K. Hemophagocytic Syndromes—An Update. Blood Rev. 2014, 28, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvelli, J.; Piperoglou, C.; Farnarier, C.; Vely, F.; Mazodier, K.; Audonnet, S.; Nitschke, P.; Bole-Feysot, C.; Boucekine, M.; Cambon, A.; et al. Functional and Genetic Testing in Adults with HLH Reveals an Inflammatory Profile Rather than a Cytotoxicity Defect. Blood 2020, 136, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulert, G.S.; Cron, R.Q. The Genetics of Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Genes. Immun. 2020, 21, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jordan, M.B.; Marsh, R.A.; Johnson, J.A.; Kissell, D.; Meller, J.; Villanueva, J.; Risma, K.A.; Wei, Q.; Klein, P.S.; et al. Hypomorphic Mutations in PRF1, MUNC13-4, and STXBP2 Are Associated with Adult-Onset Familial HLH. Blood 2011, 118, 5794–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinn, I.K.; Eckstein, O.S.; Peckham-Gregory Erin, C.; Goldberg, B.R.; Forbes, L.R.; Nicholas Sarah, K.; Mace, E.M.; Vogel, T.P.; Abhyankar Harshal, A.; Diaz, M.I.; et al. Genetic and Mechanistic Diversity in Pediatric Hemophagocytic. Blood 2018, 132, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Q.; Tang, R.; Qi, J.; Li, L.; Ye, L.; Wang, J.; Ye, L. Genetic Features of Late Onset Primary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adolescence or Adulthood. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolino, J.; Berliner, N.; Degar, B. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis as an Etiology of Bone Marrow Failure. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brito-Zerón, P.; López-Guillermo, A.; Khamashta, M.A.; Bosch, X. Adult Haemophagocytic Syndrome. Lancet 2014, 383, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, E.; Ohga, S.; Imashuku, S.; Yasukawa, M.; Tsuda, H.; Miura, I.; Yamamoto, K.; Horiuchi, H.; Takada, K.; Ohshima, K.; et al. Nationwide Survey of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Japan. Int. J. Hematol. 2007, 86, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkefi, A.; ben Jamil, W.; Torjman, L.; Ladeb, S.; Ksouri, H.; Lakhal, A.; ben Hassen, A.; ben Abdeladhim, A.; Othman, T. ben Hemophagocytic Syndrome after Hematopoietic Stem Cell: A Prospective Observational Study. Int. J. Hematol. 2009, 89, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, H.; Castanares-Zapatero, D.; d’Abadie, P.; Bailly, S.; Yombi, J.C. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults: A Retrospective in a Belgian Teaching Hospital. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 8111–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, S.A.; Kapoor, P.; Letendre, L.; Kumar, S.; Wolanskyj, A.P. Prognostic Factors and Outcomes of Adults with Hemophagocytic. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamamyan, G.N.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Ning, J.; Jain, P.; Sasaki, K.; McClain, K.L.; Allen, C.E.; Pierce, S.A.; Cortes, J.E.; Ravandi, F.; et al. Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in adults: Relation to Hemophagocytosis, Characteristics, and outcomes. Cancer 2016, 122, 2857–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, A.M.; Comstock, P.; Campo, M.; Gorovets, D.; Mullally, A.; Bodio, K.; Arnason, J.; Berliner, N. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults: A Multicentre Case Series over 7 Years. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 172, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- la Rosée, P.; Horne, A.; Hines, M.; von Bahr Greenwood, T.; Machowicz, R.; Berliner, N.; Birndt, S.; Gil-Herrera, J.; Girschikofsky, M.; Jordan, M.B.; et al. Recommendations for the Management of Hemophagocytic in Adults. Blood 2019, 133, 2465–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmberg, K.; Nichols, K.E.; Henter, J.-I.; Girschikofsky, M.; Greenwood, T.; Jordan, M.; Kumar, A.; Minkov, M.; la Rosée, P.; Weitzman, S.; et al. Consensus Recommendations for the Diagnosis and Management of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Associated with Malignancies. Haematologica 2015, 100, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daver, N.; McClain, K.; Allen, C.E.; Parikh, S.A.; Otrock, Z.; Rojas-Hernandez, C.; Blechacz, B.; Wang, S.; Minkov, M.; Jordan, M.B.; et al. A Consensus Review on Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults. Cancer 2017, 123, 3229–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, M.R.; von Bahr Greenwood, T.; Beutel, G.; Beutel, K.; Hays, J.A.; Horne, A.; Janka, G.; Jordan, M.B.; van Laar, J.A.M.; Lachmann, G.; et al. Consensus-Based Guidelines for the Recognition, Diagnosis, and management of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Critically Children and Adults. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henter, J.-I.; Horne, A.; Aricó, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; McClain, K.; Webb, D.; Winiarski, J.; et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Guidelines for hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 48, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esumi, N.; Ikushima, S.; Todo, S.; Imashuku, S. Hyperferritinemia in Malignant Histiocytosis, Virus-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome and Familial Erythrophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Acta Paediatr. 1989, 78, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komp, D.M.; McNamara, J.; Buckley, P. Elevated Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor in Childhood Hemophagocytic Histiocytic Syndromes. Blood 1989, 73, 2128–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.B.; Allen, C.E.; Weitzman, S.; Filipovich, A.H.; McClain, K.L. How I Treat Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2011, 118, 4041–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.E.; McClain, K.L. Pathophysiology and Epidemiology of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Hematology 2015, 2015, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmberg, K.; Sprekels, B.; Nichols, K.E.; Woessmann, W.; Müller, I.; Suttorp, M.; Bernig, T.; Beutel, K.; Bode, S.F.N.; Kentouche, K.; et al. Malignancy-Associated Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Children and Adolescents. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 170, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiforow, S.; Berliner, N. The Unique Aspects of Presentation and Diagnosis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults. Hematology 2015, 2015, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmberg, K.; McClain, K.L.; Janka, G.E.; Allen, C.E. Determination of an Appropriate Cut-off Value for Ferritin in the Diagnosis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 2101–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.E.; Yu, X.; Kozinetz, C.A.; McClain, K.L. Highly Elevated Ferritin Levels and the Diagnosis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 50, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, C.; Tabata, R. Possible Prediction of Underlying Lymphoma by High SIL-2R/Ferritin Ratio in Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Ann. Hematol. 2012, 91, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schram, A.M.; Campigotto, F.; Mullally, A.; Fogerty, A.; Massarotti, E.; Neuberg, D.; Berliner, N. Marked Hyperferritinemia Does Not Predict for HLH in the Adult Population. Blood 2015, 125, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipovich, A.H. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and Related Disorders. Hematology 2009, 2009, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejblum, G.; Lambotte, O.; Galicier, L.; Coppo, P.; Marzac, C.; Aumont, C.; Fardet, L. A Web-Based Delphi Study for Eliciting Helpful Criteria in the Positive Diagnosis of Hemophagocytic Syndrome in Adult Patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardet, L.; Galicier, L.; Lambotte, O.; Marzac, C.; Aumont, C.; Chahwan, D.; Coppo, P.; Hejblum, G. Development and Validation of the HScore, a Score for the Diagnosis of Reactive Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debaugnies, F.; Mahadeb, B.; Ferster, A.; Meuleman, N.; Rozen, L.; Demulder, A.; Corazza, F. Performances of the H-Score for Diagnosis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adult and Pediatric Patients. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 145, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivière, S.; Galicier, L.; Coppo, P.; Marzac, C.; Aumont, C.; Lambotte, O.; Fardet, L. Reactive Hemophagocytic Syndrome in Adults: A Retrospective Analysis of 162 Patients. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, T.; Hirano, T.; Yamasaki, H.; Tsuji, M.; Tsuda, H. A High SIL-2R/Ferritin Ratio Is a Useful Marker for the Diagnosis of Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Ann. Hematol. 2014, 93, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhong, Y.; Shuang, Y.; Huang, H.; Huang, Y.; Yu, L.; Huang, X. High Concentration of MiR-133 Is a Useful Marker for the Diagnosis of Lymphoma- Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 20, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruoka, H.; Inoue, D.; Takiuchi, Y.; Nagano, S.; Arima, H.; Tabata, S.; Matsushita, A.; Ishikawa, T.; Oita, T.; Takahashi, T. IP-10/CXCL10 and MIG/CXCL9 as Novel Markers for the Diagnosis of Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Ann. Hematol. 2014, 93, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoref-Lorenz, A.; Murakami, J.; Hofstetter, L.; Iyer, S.; Alotaibi, A.S.; Mohamed, S.F.; Miller, P.G.; Guber, E.; Weinstein, S.; Yacobovich, J.; et al. An Improved Index for Diagnosis and Mortality Prediction in Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2022, 139, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machaczka, M.; Vaktnäs, J.; Klimkowska, M.; Hägglund, H. Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults: A Retrospective Population-Based Analysis from a Single Center. Leuk. Lymphoma 2011, 52, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Tummala, S.; Kebriaei, P.; Wierda, W.; Gutierrez, C.; Locke, F.L.; Komanduri, K.v.; Lin, Y.; Jain, N.; Daver, N.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy—Assessment and Management of Toxicities. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henter, J.-I.; Elinder, G.; Söder, O.; Öst, Å. Incidence in Sweden and Clinical Features of Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Acta Paediatr. 1991, 80, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, M.; Janka, G.; Fischer, A.; Henter, J.I.; Blanche, S.; Elinder, G.; Martinetti, M.; Rusca, M.P. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Report of 122 Children from the International Registry. FHL Study Group of the Histiocyte Society. Leukemia 1996, 10, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henter, J.-I.; Samuelsson-Horne, A.; Aricò, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Elinder, G.; Filipovich, A.H.; Gadner, H.; Imashuku, S.; Komp, D.; Ladisch, S.; et al. Treatment of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis with HLH-94 and Bone Marrow Transplantation. Blood 2002, 100, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henter, J.I.; Aricò, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Elinder, G.; Favara, B.E.; Filipovich, A.H.; Gadner, H.; Imashuku, S.; Janka-Schaub, G.; Komp, D.; et al. HLH-94: A Treatment Protocol for Hemophagocytic. HLH Study Group of the Histiocyte Society. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 1997, 28, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottestam, H.; Horne, A.; Aricò, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Gadner, H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; Webb, D.; Janka, G.; et al. Chemoimmunotherapy for Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: Long-Term Results of the HLH-94 Treatment Protocol. Blood 2011, 118, 4577–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.S.; Terrell, C.E.; Millen Scott, H.; Katz, J.D.; Hildeman, D.A.; Jordan, M.B. Etoposide Selectively Ablates Activated T Cells to Control the immunoregulatory Disorder Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsten, E.; Horne, A.; Aricó, M.; Astigarraga, I.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Ishii, E.; Janka, G.; Ladisch, S.; Lehmberg, K.; et al. Confirmed Efficacy of Etoposide and Dexamethasone in HLH: Long-Term Results of the Cooperative HLH-2004 Study. Blood 2017, 130, 2728–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehl, S.; Astigarraga, I.; von Bahr Greenwood, T.; Hines, M.; Horne, A.; Ishii, E.; Janka, G.; Jordan, M.B.; la Rosée, P.; Lehmberg, K.; et al. Recommendations for the Use of Etoposide-Based Therapy and Bone Transplantation for the Treatment of HLH: Consensus by the HLH Steering Committee of the Histiocyte. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1508–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.H.; Grossbard, M.L.; Pittaluga, S.; Cole, D.; Pearson, D.; Drbohlav, N.; Steinberg, S.M.; Little, R.F.; Janik, J.; Gutierrez, M.; et al. Dose-Adjusted EPOCH Chemotherapy for Untreated Large B-Cell Lymphomas: A Pharmacodynamic Approach with High Efficacy. Blood 2002, 99, 2685–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Kwong, Y.-L.; Kim, W.S.; Maeda, Y.; Hashimoto, C.; Suh, C.; Izutsu, K.; Ishida, F.; Isobe, Y.; Sueoka, E.; et al. Phase II Study of SMILE Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Stage IV, Relapsed, or Refractory Extranodal Natural Killer (NK)/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: The NK-Cell Tumor Study Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4410–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellapandian, D.; Das, R.; Zelley, K.; Wiener, S.J.; Zhao, H.; Teachey, D.T.; Nichols, K.E. Treatment of Epstein Barr Virus-Induced Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis with Rituximab-Containing Chemo-Immunotherapeutic Regimens. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.; Cron, R.Q.; Hartwell, J.; Manson, J.J.; Tattersall, R.S. Silencing the Cytokine Storm: The Use of Intravenous Anakinra in Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis or Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e358–e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlfarth, P.; Agis, H.; Gualdoni, G.A.; Weber, J.; Staudinger, T.; Schellongowski, P.; Robak, O. Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist Anakinra, Intravenous Immunoglobulin, and Corticosteroids in the Management of Critically Ill Adult Patients With Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. J. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 34, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naymagon, L. Anakinra for the Treatment of Adult Secondary HLH: A Retrospective Experience. Int. J. Hematol. 2022, 116, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posas-Mendoza, T.F.; McLeod, C.; Davis, W.; Zakem, J.; Quinet, R. Etiologies and Management of Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: Is It Time for an Updated Protocol and Targeted Treatments? Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2927–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Aleem, S.; Saleh, H.; Petts, J.; Ballas, Z.K. A Personalized Diagnostic and Treatment Approach for Macrophage Activation Syndrome and Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baverez, C.; Grall, M.; Gerfaud-Valentin, M.; de Gail, S.; Belot, A.; Perpoint, T.; Weber, E.; Reynaud, Q.; Sève, P.; Jamilloux, Y. Anakinra for the Treatment of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: 21 Cases. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, R.C.; Dinarello, C.A.; Ferry, J.A.; Cin, P.D. A 36-Year-Old Woman with Recurrent High-Grade Fevers, Hypotension, and Hypertriglyceridemia. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2010, 62, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammut, L.; Murryam, S.; Vincent, N.; Davidson, B.; Edwards, C.J. EP18 Use of Anakinra for Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults. Rheumatology 2020, 59, keaa109.017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M.; Park, J.K.; Lee, E.B.; Park, J.W.; Hong, J. Limited Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Adult Patients with Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noveihed, A.; Liang, S.; Glotfelty, J.; Lawrence, I. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Rare Disease Unveiling the Diagnosis of EBV-Related Large B Cell Lymphoma in a Patient with HIV. Discover. Oncol. 2022, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.A.; Vaughn, G.; Kim, M.-O.; Li, D.; Jodele, S.; Joshi, S.; Mehta, P.A.; Davies, S.M.; Jordan, M.B.; Bleesing, J.J.; et al. Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Significantly Improves Survival of Patients with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Blood 2010, 116, 5824–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, E.-J.; Ko, S.-H.; Seol, M.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kang, Y.-A.; Jeon, M.; Lee, K.-H. Fludarabine/Melphalan 100 Mg/M2 Conditioning Therapy Followed by Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Adult Patients with Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooptu, M.; Kim, H.T.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Fisher, D.C.; LaCasce, A.S.; Ho, V.T.; Cutler, C.S.; Koreth, J.; Soiffer, R.J.; Antin, J.H.; et al. Favorable Outcomes Following Allogeneic Transplantation in Adults with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Blood Adv. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.A.; Jordan, M.B.; Talano, J.-A.; Nichols, K.E.; Kumar, A.; Naqvi, A.; Vaiselbuh, S.R.; Histiocyte Society Salvage Therapy Working Group. Salvage Therapy for Refractory Hemophagocytic: A Review of the Published Experience. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.A.; Allen, C.E.; McClain, K.L.; Weinstein, J.L.; Kanter, J.; Skiles, J.; Lee, N.D.; Khan, S.P.; Lawrence, J.; Mo Jun, Q.; et al. Salvage Therapy of Refractory Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with Alemtuzumab. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Hu, L.; Cen, X.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Shen, J.; Wei, N.; Wang, Z. Multicenter Study of Combination DEP Regimen as a Salvage Therapy for Adult Refractory Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2015, 126, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Jordan, M.B.; Allen, C.; Cesaro, S.; Rizzari, C.; Rao, A.; Degar, B.; Garrington, T.P.; Sevilla, J.; Putti, M.-C.; et al. Emapalumab in Children with Primary Hemophagocytic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.T.; Epstein-Peterson, Z.D.; Ganesan, N.; Chang, T.; Galasso, N.; Stuver, R.; Khan, N.; Salles, G.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Vardhana, S.; et al. Emapalumab for Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: The Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Experience. Blood 2022, 140, 3704–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Saint Basile, G.; Ménasché, G.; Fischer, A. Molecular Mechanisms of Biogenesis and Exocytosis of Cytotoxic. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xu, X.; Song, H.; Yang, S.; Shi, S.; Wei, J.; Pan, B.; Zhao, F.; Liao, C.; Luo, C. Early Diagnostic and Prognostic Significance of a Specific/Th2 Cytokine Pattern in Children with Haemophagocytic. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 143, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-L.; Xu, X.-J.; Tang, Y.-M.; Song, H.; Xu, W.-Q.; Zhao, F.-Y.; Shen, D.-Y. Associations between Inflammatory Cytokines and Organ Damage in pediatric Patients with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Cytokine 2016, 85, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.K.; Verbist, K.C.; Albeituni, S.; Scull, B.P.; Bassett, R.C.; Stroh, A.N.; Tillman, H.; Allen, C.E.; Hermiston, M.L.; Nichols, K.E. JAK/STAT Pathway Inhibition Sensitizes CD8 T Cells to dexamethasone-Induced Apoptosis in Hyperinflammation. Blood 2020, 136, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, C.; Nichols, K.E.; Albeituni, S. Use of the JAK Inhibitor Ruxolitinib in the Treatment of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 614704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonstra, P.S.; Ahmed, A.; Merrill, S.A.; Wilcox, R.A. Ruxolitinib in Adult Patients with Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.; Alduaij, W.; Biggs, C.M.; Belga, S.; Luecke, K.; Merkeley, H.; Chen, L.Y.C. Ruxolitinib as Adjunctive Therapy for Secondary Hemophagocytic: A Case Series. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, G.; Suffiotti, M.; Segot, A.; Noto, A.; Pantaleo, G.; Spertini, O.; Obeid, M. Response-Adjusted Regimen Combining Ruxolitinib, Etoposide and Dexamethasone (AdRED) in Adult Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Single-Center Pilot Trial. Haematologica 2023, 108, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trantham, T.; Auten, J.; Muluneh, B.; van Deventer, H. Ruxolitinib for the Treatment of Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Cautionary Tale. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 26, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindiapina, P.; Saadey, R.; Yasin, A.; Mao, C.; Wandke, A.; Ahmed, E.H.; Baiocchi, E.; Vaddi, K.; Scherle, P.; Brown, F.; et al. PRMT5 Inhibition Reduces Autoinflammation in a Murine Model of Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2022, 140, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gu, J.; Liang, X.; Mao, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, W. Low Dose Ruxolitinib plus HLH-94 Protocol: A Potential choice for Secondary HLH. Semin. Hematol. 2020, 57, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, M.; Zhu, Q.; Qiu, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Ruxolitinib Combined with Doxorubicin, Etoposide, and Dexamethasone for the Treatment of the Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 3063–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Wu, X.; Li, F.; Yang, H.; Liu, L.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Mai, H.; Li, H.; et al. Ruxolitinib-Combined Doxorubicin-Etoposide-Methylprednisolone Regimen as a Salvage Therapy for Refractory/Relapsed Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 2 Trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Ma, H.-H.; Wang, D.; Cui, L.; Li, W.-J.; Wei, A.; Wang, C.-J.; Wang, T.-Y.; Li, Z.-G.; et al. A Study of Ruxolitinib Response-Based Stratified Treatment for pediatric Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2022, 139, 3493–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeo, K.M.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Beitinjaneh, A.; Chaganti, S.; Choquet, S.; Dierickx, D.; Dinavahi, R.; Gamelin, L.; Ghobadi, A.; Guzman-Becerra, N.; et al. New and Updated Results from a Multicenter, Open-Label, Global Phase 3 Study of Tabelecleucel (Tab-Cel) for Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease (EBV+ PTLD) Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell (HCT) or Solid Organ Transplant (SOT) after Failure of Rituximab or Rituximab and Chemotherapy (ALLELE). Blood 2022, 140, 10374–10376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, T.; Takenaka, K.; Kohno, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Daitoku, S.; Yoshimoto, G.; Kikushige, Y.; Kishimoto, J.; Abe, Y.; Harada, N.; et al. Engulfment of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Caused by Down-Regulation of CD47 Is Critical in the Pathogenesis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2012, 120, 4058–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazaki, C.; Inaba, T.; Nakagawa, M. B-Cell Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Leuk. Lymphoma 2000, 38, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imashuku, S.; Hibi, S.; Fujiwara, F.; Ikushima, S.; Todo, S. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis, Interferon-Gamma-Naemia and Epstein-Barr Virus Involvement. Br. J. Haematol. 1994, 88, 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodley Scott, R.; Robb-Smith, A.H.T. Histiocytic Medullary Reticulosis. Lancet 1939, 234, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Pileri, S.; de Solas, I.; Martelli, M.; Mason, D.; Delsol, G.; Gatter, K.; Fagioli, M. Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Associated with Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Blood 1990, 75, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Hu, K.; Xu, F.; Zhou, D.; He, J.; Shi, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, M.; et al. Clinical Analysis and Prognostic Significance of Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytosis in Peripheral T Cell Lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2013, 92, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, P.; Zhang, R.; Yang, G.; Ji, D.; Huang, X.; Xu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Rao, J.; Huang, R.; et al. Identification of Clinical Features of Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome (LAHS): An Analysis of 69 Patients with Hemophagocytic Syndrome from a Single-Center in Central Region of China. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.-R.; Lee, H.R.; Park, B.-B.; Hwang, I.G.; Park, S.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, K.; Lim, H.Y.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome: Clinical Features and Treatment Outcome. Ann. Hematol. 2007, 86, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jiang, M.; Wu, W.; Zhou, H.; Zou, L. Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome: A Retrospective Study from a Single Center. Hematology 2022, 27, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Pei, R.; Lai, W.; Wang, Z. Multivariate Analysis of Prognosis for Patients with Natural Killer/T Cell Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Hematology 2018, 23, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Ma, W.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Clinical Features and Treatment of Natural Killer/T Cell Lymphoma Associated with Hemophagocytic Syndrome: Comparison with Other T Cell Lymphoma Associated with Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 2048–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimazaki, C.; Inaba, T.; Okano, A.; Hatsuse, M.; Takahashi, R.; Hirai, H.; Sudo, Y.; Ashihara, E.; Adachi, Y.; Murakami, S.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of B-Cell Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome (B-LAHS): Comparison of CD5+ with CD5- B-LAHS. Intern. Med. 2001, 40, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, T.; Nakamura, S.; Kawauchi, K.; Matsuzaki, H.; Sakai, C.; Inaba, T.; Nasu, K.; Tashiro, K.; Suchi, T.; Saito, H. An Asian Variant of Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Clinical, Pathological and Cytogenetic Approaches to Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Associated with Haemophagocytic Syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 111, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, T.; Nakamura, S.; Tashiro, K.; Suchi, T.; Hiraga, J.; Hayasaki, N.; Kimura, M.; Murakami, M.; Mizoguchi, Y.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Malignant Histiocytosis-like B-Cell Lymphoma, a Distinct Pathologic Variant of Intravascular Lymphomatosis: A Report of Five Cases and Review of the Literature. Br. J. Haematol. 1997, 99, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, T.; Nakamura, S. An Asian Variant of Intravascular Lymphomatosis: An Updated Review of Malignant Histiocytosis-Like B-Cell Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 1999, 33, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigenwald, C.; Fardet, L.; Coppo, P.; Meignin, V.; Lazure, T.; Fabiani, B.; Kohn, M.; Oksenhendler, E.; Boutboul, D.; Uzzan, M.; et al. A Comprehensive Analysis of Lymphoma-Associated Haemophagocytic Syndrome in a Large French Multicentre Cohort Detects Some Clues to Improve Prognosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 183, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Z. Requirement for Containing Etoposide in the Initial Treatment of Lymphoma Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2021, 22, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Jin, Z.; He, L.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Hua, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Clinical Features and Prognostic Risk Prediction of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yin, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Patients with Lymphoma-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Cell Transplant. 2021, 30, 096368972110570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köppler, H.; Pflüger, K.H.; Eschenbach, I.; Pfab, R.; Lennert, K.; Wellens, W.; Schmidt, M.; Gassel, W.D.; Kolb, T.; Hässler, R. CHOP-VP16 Chemotherapy and Involved Field Irradiation for High Grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas: A Phase II Multicentre Study. Br. J. Cancer 1989, 60, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, C.; Snedecor, S.J.; Landsburg, D.J.; Svoboda, J.; Chong, E.A.; Schuster, S.J.; Nasta, S.D.; Feldman, T.; Rago, A.; Walsh, K.M.; et al. Front-Line, Dose-Escalated Immunochemotherapy Is Associated with a Significant Progression-Free Survival Advantage in Patients with Double-Hit Lymphomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 170, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, A.O.; Strøm, C.; Pedersen, M.; d’Amore, F.; Pedersen, L.M.; Bukh, A.; Pedersen, B.B.; Moeller, M.B.; Mortensen, L.S.; Gadeberg, O.V.; et al. R-CHOEP-14 Improves Overall Survival in Young High-Risk Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Compared with R-CHOP-14. A Population-Based Investigation from the Danish Lymphoma Group. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Kogawa, K.; Morimoto, A.; Ishida, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Ohga, S.; Kudo, K.; Ohta, S.; Wakiguchi, H.; Tabuchi, K.; et al. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Children: A Nationwide Survey in Japan. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 59, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, R.; Tanaka, J.; Hashino, S.; Ota, S.; Torimoto, Y.; Kakinoki, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Kurosawa, M.; Hatakeyama, N.; Haseyama, Y.; et al. Etoposide-Containing Conditioning Regimen Reduces the Occurrence of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis after SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014, 49, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Choi, I.; Hara, K.; Matsushima, T.; Nishimura, J.; Inaba, S.; Nawata, H.; Muta, K. Hemophagocytic Syndrome: A Rare Complication of Allogeneic Nonmyeloablative Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002, 29, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, R.D.; Tattersall, R.S.; Schoemans, H.; Greco, R.; Badoglio, M.; Labopin, M.; Alexander, T.; Kirgizov, K.; Rovira, M.; Saif, M.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Secondary HLH/MAS Following HSCT and CAR-T Cell Therapy in Adults; A Review of the Literature and a Survey of Practice Within EBMT Centres on Behalf of the Autoimmune Diseases Working Party (ADWP) and Transplant Complications Working Party (TCWP). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, N.; Coiteux, V.; Srour, M.; Magro, L.; Chauvet, P.; Terriou, L.; Varlet, P.; Ballot, C.; Yakoub-Agha, I.; Beauvais, D. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation from Mismatched Unrelated Donors Associated with Low CD34 and CD3 Cell Counts in the Graft. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022, 57, 658–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, S.; Masuoka, K.; Uchida, N.; Ishiwata, K.; Araoka, H.; Tsuji, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Kato, D.; Matsuhashi, Y.; Kusumi, E.; et al. High Incidence of Haemophagocytic Syndrome Following Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation for Adults. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 147, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadfar, N.; Burns, L.J.; Mupfudze, T.; Shaw, B.E.; Bollard, C.M.; Devine, S.M.; Horowitz, M.M.; Jones, R.J.; Murthy, H.S.; Wingard, J.R.; et al. Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Practice Predictions for the Year 2023. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 183.e1–183.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auletta, J.; Kou, J.; Chen, M.; Shaw, B. Current Use and Outcome of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: CIBMTR US Summary Slides. 2021. Available online: https://cibmtr.org/CIBMTR/Resources/Summary-Slides-Reports (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- Shaw, B.E.; Jimenez-Jimenez, A.M.; Burns, L.J.; Logan, B.R.; Khimani, F.; Shaffer, B.C.; Shah, N.N.; Mussetter, A.; Tang, X.-Y.; McCarty, J.M.; et al. Three-Year Outcomes in Recipients of Mismatched Unrelated Bone Marrow Donor Transplants Using Post-Transplantation Cyclophosphamide: Follow-Up from a National Marrow Donor Program-Sponsored Prospective Clinical Trial. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, P.; Raj, K.; Pagliuca, A. High Fever Occurring 4 to 5 Days Post-Transplant of Haploidentical Bone Marrow or Peripheral Blood Stem Cells after Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Associated with the Use of Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide as Prophylaxis for Graft-versus-Host Disease. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abboud, R.; Keller, J.; Slade, M.; DiPersio, J.F.; Westervelt, P.; Rettig, M.P.; Meier, S.; Fehniger, T.A.; Abboud, C.N.; Uy, G.L.; et al. Severe Cytokine-Release Syndrome after T Cell–Replete Peripheral Blood Haploidentical Donor Transplantation Is Associated with Poor Survival and Anti–IL-6 Therapy Is Safe and Well Tolerated. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, X.-J.; Liu, K.-Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.-H.; Wang, F.-R.; Han, W.; Wang, J.-Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Infusion-Related Febrile Reaction after Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation in Children Is Associated with Higher Rates of Engraftment Syndrome and Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease. Pediatr. Transplant. 2015, 19, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, R.D.; Carter, S.; Kaur, H.; Francis, S.; Tattersall, R.S.; Snowden, J.A. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) Following Allogeneic Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)—Time to Reappraise with Modern Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies? Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020, 55, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, R.; von Bubnoff, N.; Butler, J.; Mohty, M.; Niederwieser, D.; Or, R.; Szer, J.; Wagner, E.M.; Zuckerman, T.; Mahuzier, B.; et al. Ruxolitinib for Glucocorticoid-Refractory Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, R.; Polverelli, N.; Ram, R.; Hashmi, S.K.; Chakraverty, R.; Middeke, J.M.; Musso, M.; Giebel, S.; Uzay, A.; Langmuir, P.; et al. Ruxolitinib for Glucocorticoid-Refractory Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xiong, L.; Tang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, F. A Systematic Review of Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis That Needs More Attentions. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59977–59985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, G.N.; Woda, B.A.; Newburger, P.E. Advances in Understanding the Pathogenesis of HLH. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabler, S.; Becquart, C.; Dumezy, F.; Terriou, L.; Mortier, L. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Patients with Metastatic Malignant Melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2017, 27, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaat, M.; Jang, S. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis with Immunotherapy: Brief Review and Case Report. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; He, W.; Sun, W.; Wu, C.; Ren, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Huang, M.; Ji, N. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Two Patients Following Treatment with Pembrolizumab: Two Case Reports and a Literature Review. Transl. Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 2960–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malissen, N.; Lacotte, J.; Du-Thanh, A.; Gaudy-Marqueste, C.; Guillot, B.; Grob, J.-J. Macrophage Activation Syndrome: A New Complication of Checkpoint Inhibitors. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 77, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marar, R.; Prathivadhi-Bhayankaram, S.; Krishnan, M. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a Patient With Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Hematol. 2022, 11, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, M.; Anai, S.; Mishima, S.; Inoue, K. Coincidence of Immunotherapy-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome and Rapid Tumor Regression. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honjo, O.; Kubo, T.; Sugaya, F.; Nishizaka, T.; Kato, K.; Hirohashi, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Torigoe, T. Severe Cytokine Release Syndrome Resulting in Purpura Fulminans despite Successful Response to Nivolumab Therapy in a Patient with Pleomorphic Carcinoma of the Lung: A Case Report. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, S.; Kayatani, H.; Fujiwara, K.; Ozeki, T.; Takada, K.; Iwamoto, Y.; Minami, D.; Sato, K.; Shibayama, T. Pembrolizumab-Induced Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia and Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Intern. Med. 2019, 58, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, D.; Shrestha, R.; Ramlal, R.; Hatton, J.; Saeed, H. Pembrolizumab Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laderian, B.; Koehn, K.; Holman, C.; Lyckholm, L.; Furqan, M. Association of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and Programmed Death 1 Checkpoint Inhibitors. Journal. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e77–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Snyder, G.D.; Nikiforow, S.; Tolaney, S.M.; Freedman, R.A.; Losman, J.-A. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Complicating Pembrolizumab Treatment for Metastatic Breast Cancer in a Patient with the PRF1A91V Gene Polymorphism. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 56, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thummalapalli, R.; Heumann, T.; Stein, J.; Khan, S.; Priemer, D.S.; Duffield, A.S.; Laterra, J.; Couzi, R.; Lim, M.; Holdhoff, M. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to PD-1 and IDO Inhibition in a Patient with Refractory Glioblastoma. Case Rep. Oncol. 2020, 13, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, B.C.; Latifyan, S.; Perreau, M.; Fenwick, C.; Alberio, L.; Waeber, G.; Spertini, F.; de Leval, L.; Michielin, O.; Obeid, M. Cytokine-Directed Therapy with Tocilizumab for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1775–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupré, A.; Michot, J.; Schoeffler, A.; Frumholtz, L.; Baroudjian, B.; Delyon, J.; Lebbe, C.; Lambotte, O. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Descriptive Case Study and Literature Review. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, M.H.; Rojas-Hernandez, C.; Yee, C. Hematologic Complications of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Blood 2022, 139, 3594–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, N.R.; Lockhart, J.R.; Garcia-Perdomo, H.A.; Oo, T.H.; Rojas-Hernandez, C.M. Management and Outcomes of Hematological Immune-Related Adverse Events: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Immunother. 2022, 45, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noseda, R.; Bertoli, R.; Müller, L.; Ceschi, A. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Analysis of WHO Global Database of Individual Case Safety Reports. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Schadendorf, D.; Lipson, E.J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Matamala, L.; Castillo Gutiérrez, E.; Rutkowski, P.; Gogas, H.J.; Lao, C.D.; de Menezes, J.J.; et al. Relatlimab and Nivolumab versus Nivolumab in Untreated Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, Z.; Courtney, A.; Hiong, A. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis as a Complication of Combination Anti-PD-1 and Anti-CTLA-4 Checkpoint Inhibitor Immunotherapy for Metastatic Melanoma, and the Outcome of Rechallenge with Single-Agent Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e251052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, M.J.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Bachy, E.; Corradini, P.; Iacoboni, G.; Khan, C.; Wróbel, T.; Offner, F.; Trněný, M.; et al. Glofitamab for Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2220–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieblemont, C.; Phillips, T.; Ghesquieres, H.; Cheah, C.Y.; Clausen, M.R.; Cunningham, D.; Do, Y.R.; Feldman, T.; Gasiorowski, R.; Jurczak, W.; et al. Epcoritamab, a Novel, Subcutaneous CD3xCD20 Bispecific T-Cell–Engaging Antibody, in Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Dose Expansion in a Phase I/II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, A.; Minnema, M.C.; Berdeja, J.G.; Oriol, A.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; Askari, E.; Mateos, M.-V.; Costa, L.J.; Caers, J.; et al. Talquetamab, a T-Cell–Redirecting GPRC5D Bispecific Antibody for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2232–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teachey, D.T.; Rheingold, S.R.; Maude, S.L.; Zugmaier, G.; Barrett, D.M.; Seif, A.E.; Nichols, K.E.; Suppa, E.K.; Kalos, M.; Berg, R.A.; et al. Cytokine Release Syndrome after Blinatumomab Treatment Related to Abnormal Macrophage Activation and Ameliorated with Cytokine-Directed Therapy. Blood 2013, 121, 5154–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maude, S.L.; Barrett, D.; Teachey, D.T.; Grupp, S.A. Managing Cytokine Release Syndrome Associated With Novel T Cell-Engaging Therapies. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotch, C.; Barrett, D.; Teachey, D.T. Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell-Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Santomasso, B.D.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Turtle, C.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.v.; Park, J.H.; Mead, E.; Pavletic, S.; et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, M.R.; Keenan, C.; Maron Alfaro, G.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Sharma, A.; Hurley, C.; Nichols, K.E.; Gottschalk, S.; Triplett, B.M.; et al. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis-like Toxicity (CarHLH) after CD19-specific CAR T-cell Therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 194, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Schischlik, F.; Shao, L.; Steinberg, S.M.; Yates, B.; Wang, H.-W.; Wang, Y.; Inglefield, J.; Dulau-Florea, A.; Ceppi, F.; et al. Characterization of HLH-like Manifestations as a CRS Variant in Patients Receiving CD22 CAR T Cells. Blood 2021, 138, 2469–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, T.J.; Lazarevic, A.; Ziggas, J.E.; Fuchs, E.; Kim, K.; Byrnes, H.; Luznik, L.; Bolaños-Meade, J.; Ali, S.A.; Shah, N.N.; et al. Hyperinflammatory Syndrome Resembling Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Following Axicabtagene Ciloleucel and Brexucabtagene Autoleucel. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 199, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.N.; Highfill, S.L.; Shalabi, H.; Yates, B.; Jin, J.; Wolters, P.L.; Ombrello, A.; Steinberg, S.M.; Martin, S.; Delbrook, C.; et al. CD4/CD8 T-Cell Selection Affects Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Potency and Toxicity: Updated Results From a Phase I Anti-CD22 CAR T-Cell Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1938–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, V.E.; Wong, C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Kambhampati, S.; Wolf, J.; Martin, T.G.; Shah, N.; Wong, S.W. Macrophage Activation Syndrome-like (MAS-L) Manifestations Following BCMA-Directed CAR T Cells in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 5344–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNerney, K.O.; Lim, S.S.; Ishikawa, K.; Dreyzin, A.; Vatsayan, A.; Chen, J.J.; Baggott, C.; Prabhu, S.; Pacenta, H.; Phillips, C.L.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (CarHLH) Predicts Poor Survival with Real-World Use of Tisagenlecleucel for B-ALL. SSRN Electron. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, S.; Harris, A.; Treisman, D.; Cupac, J.N.; Li, N.; Yan, D.; Munker, R. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to CAR-T Cells: Update from the FDA and Vizient Databases. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Furqan, F.; Strati, P.; Westin, J.; Fayad, L.; Hagemeister, F.B.; Lee, H.J.; Iyer, S.P.; Nair, R.; Nastoupil, L.J.; et al. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in Patients with Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with Standard of Care (SOC) Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Huang, H. Clinical Features of Hemophagocytic Syndrome Following BCMA CAR-T Cell Therapy in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2022, 51, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Specific Causes |
|---|---|
| Infection | |
| Viral | Human Herpesviridae (e.g., EBV, HSV, CMV, VZV), HIV, viral hepatitis, influenza, parvovirus B19, dengue |
| Bacterial | Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Staphylococcus aureus, Rickettsia, Mycoplasma |
| Parasitic | Leishmania, Plasmodium, Toxoplasma |
| Fungal | Histoplasma, Candida, Cryptococcus, Aspergillus |
| Malignancy | |
| Hematologic | T/NK-cell lymphomas, aggressive B-cell lymphomas, leukemia, Hodgkin lymphoma, Castleman disease |
| Solid | Metastatic carcinomas, sarcomas |
| Autoimmune | Systemic lupus erythematosus, adult-onset Still’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis, inflammatory bowel disease |
| Treatment-Related | |
| Transplantation | Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation, solid organ transplantation |
| T Cell Therapy | CAR T cell therapy, bispecific T cell engagers |
| Other Therapy | Immune checkpoint inhibitors, chemotherapy-induced, drug-induced hypersensitivity, surgery, vaccination, hemodialysis |
| Other | Pregnancy, trauma, idiopathic, unknown, multifactorial |
| Either: |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Reference | N | Mean Age (Range) | HLH Type | New or R/R HLH | Target Rux Dose (BID) | Rux Duration | HLH Therapy | Response | OS * (f/u if Known) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boonstra 2021 [84] | 1 | 70 | R/R Hodgkin; EBV viremia | New | 15 mg | 1.5 m | Rux | PR | 100% |
| Hansen 2021 [85] | 1 | 33 | SPTL | R/R | 15 mg | 11 m | Dex/Etop −> Cy, Doxo, Vin, Pred −>Rux, Etop, IVIG +Alem | CR | 100% (1 y) |
| Stalder 2023 [86] | 6 | 52 y (34–72 y) | AML | New | 10 mg | 31–122 d | Dex, Etop, Rux, induction chemo | CR (83%), PR (17%) | 33% (120 d) |
| Trantham 2020 [87] | 2 | 66 y, 24 y | Suspected Hodgkin DLBCL | R/R | 10 mg 15 mg | ~6 m ~25 d | Dex/Etop −> Benda/Brentux −> Rux −> Alem/Anakinra R-EPOCH x3 −> R-CHOP x3 −> Rux, HD MTX, AraC, IT −> R-GCD −> R-ICE −> Alem/Dex | CR (100%) | 0% (1 y, 14.5 m) |
| J Wang 2021 [88] | 3 | 27 y, 28 y, 66 y | B cell lymphoma | R/R | 10 mg | NR | HLH94 −> Rux, Doxo (lipo), Etop, Methylpred −> chemo −> HCT | NR | NR |
| H Wang 2020 [89] | 2 | 24 y, 45 y | EBV+ NK cell leukemia Relapsed PTL | New | 5 mg | ~5 w | Dex/Etop, PLEX, Rux, Gem/Ox/Peg −> Pred Dex/Etop/Rux −> Gem/Ox/Peg | ?CR (100%) | 0% (~2 m?) |
| Zhou 2020 [90] | 36 | 44.7 y (31–58 y) | Lymphoma | New | 0.3 mg/kg daily | 14 d | Dex/Etop/Rux/Doxo −> chemo | CR (28%), PR (56%) | 39% (5 m) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.C.; Logan, A.C. Diagnosis and Management of Adult Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Cancers 2023, 15, 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061839
Lee JC, Logan AC. Diagnosis and Management of Adult Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061839
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jerry C., and Aaron C. Logan. 2023. "Diagnosis and Management of Adult Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061839
APA StyleLee, J. C., & Logan, A. C. (2023). Diagnosis and Management of Adult Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Cancers, 15(6), 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061839






