Refining the Characterization and Outcome of Pathological Complete Responders after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Lessons from the Randomized Phase III VESPER (GETUG-AFU V05) Trial
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients and Treatments
2.2. Pathological Review
2.3. Statistical Methods
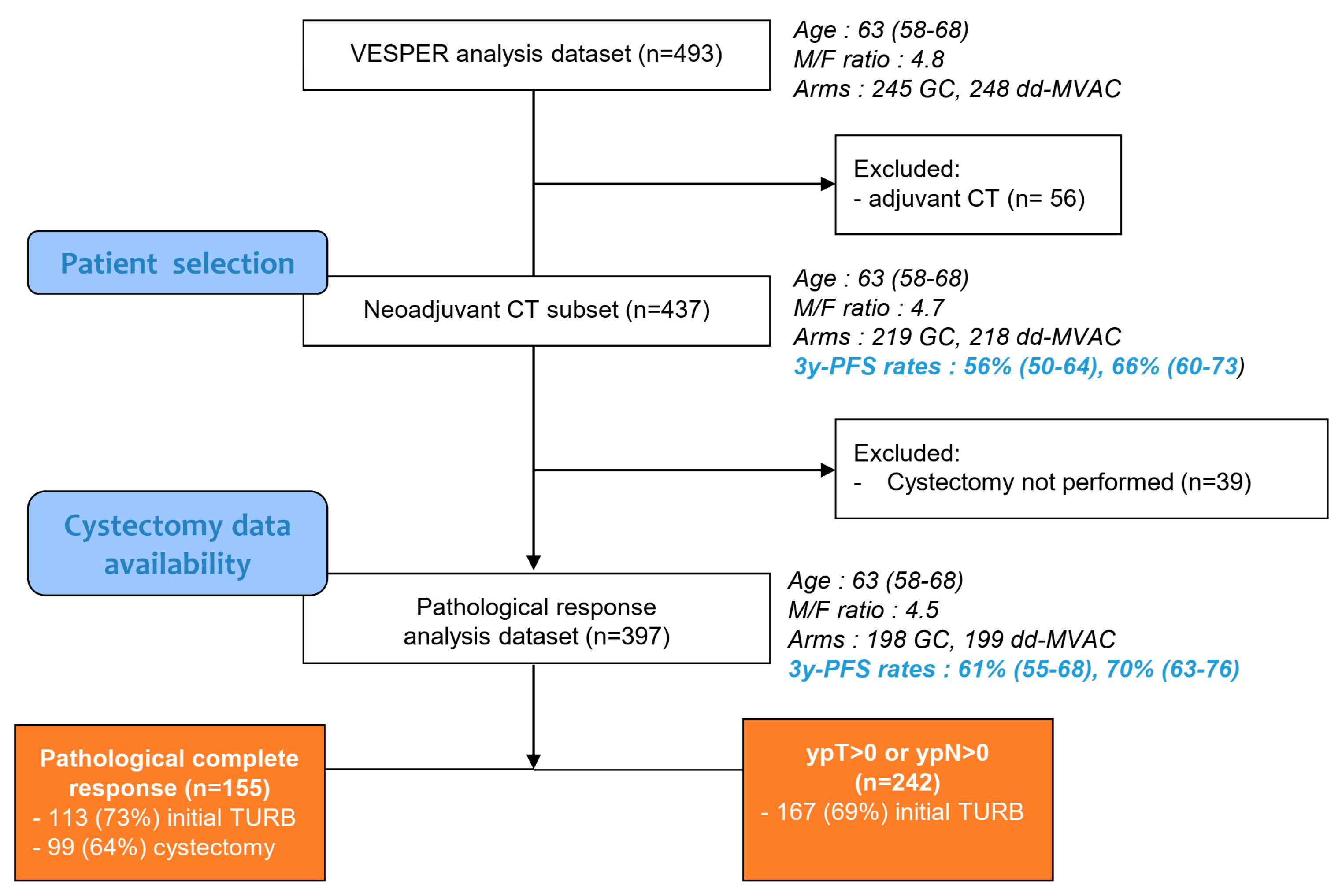
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient Characteristics
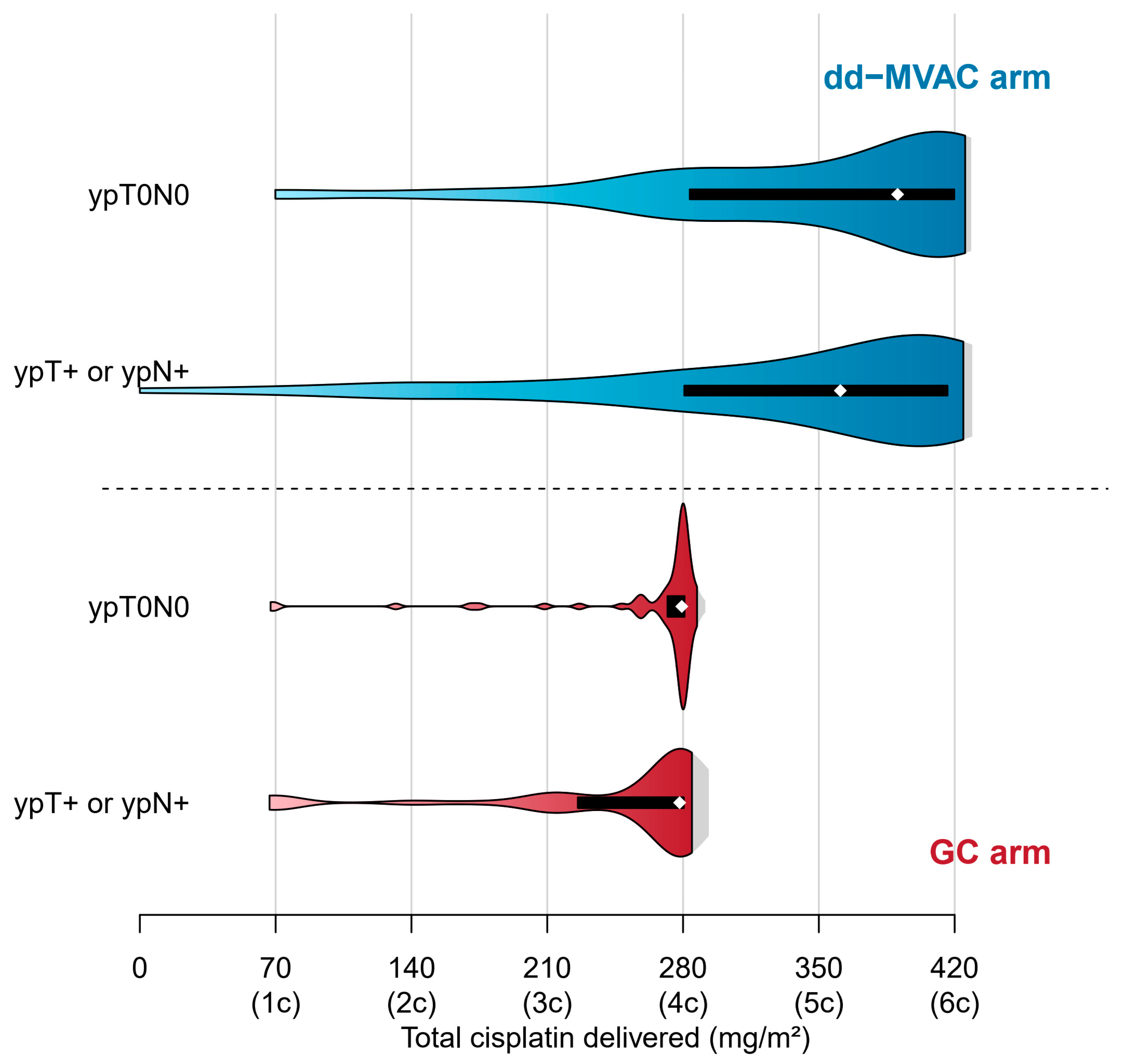
3.2. Treatment Delivery
3.3. Pathological Characterization of pCR
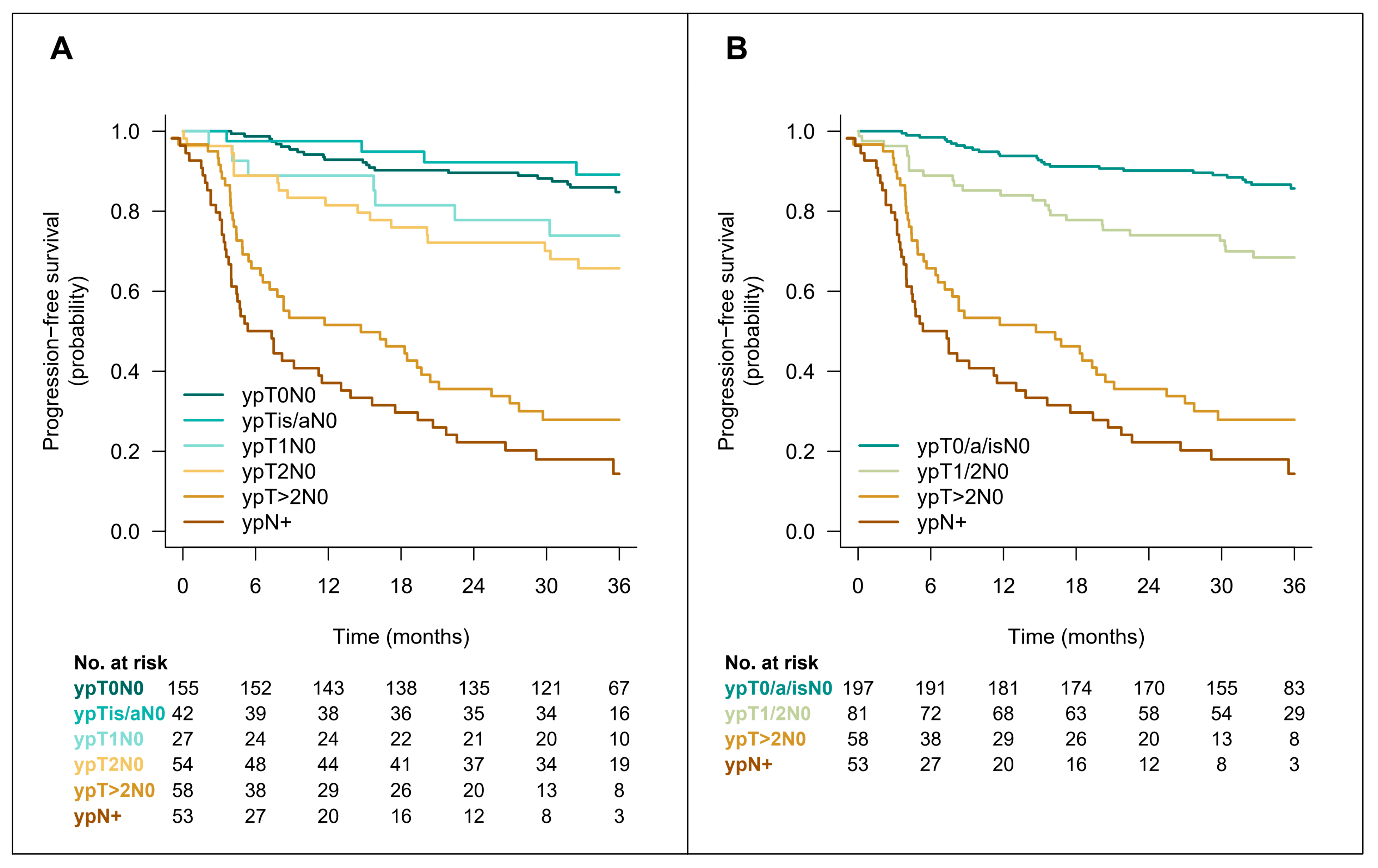
3.4. Patient Outcome
3.5. Variables Affecting Outcome of Patients with pCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flaig, T.W.; Spiess, P.E.; Abern, M.; Agarwal, N.; Bangs, R.; Boorjian, S.A.; Buyyounouski, M.K.; Chan, K.; Chang, S.; Friedlander, T.; et al. NCCN guidelines® insights: Bladder cancer, version 2.2022. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2022, 20, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.A.; Babjuk, M.; Bellmunt, J.; Bruins, H.M.; De Reijke, T.M.; De Santis, M.; Gillessen, S.; James, N.; Maclennan, S.; Palou, J.; et al. EAU-ESMO consensus statements on the management of advanced and variant bladder cancer—An international collaborative multistakeholder effort: Under the auspices of the EAU-ESMO Guidelines Committees. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, J.P.; Lieskovsky, G.; Cote, R.; Groshen, S.; Feng, A.C.; Boyd, S.; Skinner, E.; Bochner, B.; Thangathurai, D.; Mikhail, M.; et al. Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: Long-term results in 1054 patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariat, S.F.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Palapattu, G.S.; Lotan, Y.; Rogers, C.G.; Amiel, G.E.; Vazina, A.; Gupta, A.; Bastian, P.J.; Sagalowsky, A.I.; et al. Outcomes of radical cystectomy for transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: A contemporary series from the Bladder Cancer Research Consortium. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 2414–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, H.B.; Natale, R.B.; Tangen, C.M.; Speights, D.O.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Trump, D.L.; de Were White, R.W.; Sarosdy, M.F.; Wood, D.P.; Raghavan, D.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International collaboration of trialists. International phase III trial assessing neoadjuvant cisplatin, methotrexate, and vinblastine chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Long-term results of the BA06 30894 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2171–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Bladder Cancer Meta-analysis Collaboration. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: Update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. Eur. Urol. 2005, 48, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Joshi, M.; Meijer, R.P.; Glantz, M.; Holder, S.; Harvey, H.A.; Kaag, M.; Fransen van de Putte, E.E.; Horenblas, S.; Drabick, J.J. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and two-step meta-analysis. Oncologist 2016, 21, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.; Jacobus, S.; Bellmunt, J.; Qu, A.; Appleman, L.L.; Tretter, C.; Bubley, G.J.; Stack, E.C.; Signoretti, S.; Walsh, M.; et al. Neoadjuvant dose-dense methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin with pegfilgrastim support in muscle-invasive urothelial cancer: Pathologic, radiologic, and biomarker correlates. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimack, E.R.; Hoffman-Censits, J.H.; Viterbo, R.; Trabulsi, E.J.; Ross, E.A.; Greenberg, R.E.; Chen, D.Y.; Lallas, C.D.; Wong, Y.N.; Lin, J.; et al. Accelerated methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin is safe, effective, and efficient neoadjuvant treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Results of a multicenter phase II study with molecular correlates of response and toxicity. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, G.; Balar, A.V.; Milowsky, M.I.; Bochner, B.H.; Dalbagni, G.; Donat, S.M.; Herr, H.W.; Huang, W.C.; Taneja, S.S.; Woods, M.; et al. Multicenter prospective phase II trial of neoadjuvant dose-dense gemcitabine plus cisplatin in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galsky, M.D.; Pal, S.K.; Chowdhury, S.; Harshman, L.C.; Crabb, S.J.; Wong, Y.N.; Yu, E.Y.; Powles, T.; Moshier, E.L.; Ladoire, S.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of gemcitabine plus cisplatin versus methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, plus cisplatin as neoadjuvant therapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer 2015, 121, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyton, C.C.; Tang, D.; Reich, R.R.; Azizi, M.; Chipollini, J.; Pow-Sang, J.M.; Manley, B.; Spiess, P.E.; Poch, M.A.; Sexton, W.J.; et al. Downstaging and survival outcomes associated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimens among patients treated with cystectomy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, H.; Shah, J.B.; van Rhijn, B.W.; Daneshmand, S.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Spiess, P.E.; Black, P.C.; Kassouf, W. Neoadjuvant dose dense MVAC versus gemcitabine and cisplatin in patients with cT3-4aN0M0 bladder cancer treated with radical cystectomy. J. Urol. 2018, 199, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, C.; Harter, V.; Allory, Y.; Radvanyi, F.; Culine, S. Design of a randomized controlled phase III study of dose dense methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin and cisplatin (dd-MVAC) or gemcitabine and cisplatin (GC) as peri-operative chemotherapy for patients with locally advanced transitional cell cancer of the bladder. The French GETUG/AFU V05 VESPER trial. Contemp. Clin. Trials. 2020, 17, 100536. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, C.; Gravis, G.; Fléchon, A.; Chevreau, C.; Mahammedi, H.; Laguerre, B.; Guillot, A.; Joly, F.; Soulié, M.; Allory, Y.; et al. Dose-dense methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin or gemcitabine and cisplatin as perioperative chemotherapy for patients with nonmetastatic muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Results of the GETUG-AFU V05 VESPER trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2013–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, H.; Humphrey, P.A.; Ulbright, T.M.; Reuter, V. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, B.S.; Winer, E.P.; Mamon, H.J. Perils of the pathologic complete response. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3959–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Pantel, K.; Kang, Y. Tumor metastasis: Moving new biological insights into the clinic. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassouf, W.; Spiess, P.E.; Brown, G.A.; Munsell, M.F.; Barton Grossman, H.; Siefker-radtke, A.; Dinney, C.P.N.; Kamat, A.M. P0 stage at radical cystectomy for bladder cancer is associated with improved outcome independent of traditional clinical risk factors. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonpavde, G.; Goldman, B.H.; Speights, V.O.; Lerner, S.P.; Wood, D.P.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Trump, D.P.; Natale, R.B.; Grossman, H.B.; Crawford, E.D. Quality of pathologic response and surgery correlate with survival for patients with completely resected bladder cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer 2009, 115, 4104–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, R.; Sherif, A.; Rintala, E.; Wahlqvist, R.; Ullen, A.; Nilsson, S.; Malmström, P.U. Pathologic downstaging is a surrogate marker for efficacy and increased survival following neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical cystectomy for muscle-invasive urothelial bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Coinu, A.; Cabiddu, M.; Ghilardi, M.; Vavassori, I.; Barni, S. Correlation of pathologic complete response with survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in bladder cancer treated with cystectomy: A meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, A.; Jia, R.; Ferket, B.S.; Waingankar, N.; Plimack, E.R.; Crabb, S.J.; Harshman, L.C.; Yu, E.Y.; Powles, T.; Rosenberg, J.E.; et al. Tumor downstaging as an intermediate endpoint to assess the activity of neoadjuvant systemic therapy in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer 2019, 125, 3155–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, C.; Gravis, G.; Fléchon, A.; Soulié, M.; Guy, L.; Laguerre, B.; Mottet, N.; Joly, F.; Allory, H.; Harter, V.; et al. Randomized phase III of dose dense methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin and cisplatin (dd-MVAC) or gemcitabine and cisplatin (GC) as peri-operative chemotherapy for patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). Analysis of the GETUG/AFU V05 VESPER trial secondary end-points: Chemotherapy toxicity and pathological responses. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Black, A.J.; Zargar, H.; Zargar-Shoshtari, K.; Fairey, A.S.; Mertens, L.S.; Dinney, C.P.; Mir, M.C.; Krabbe, L.M.; Cookson, M.S.; Jacobsen, N.E.; et al. The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical cystectomy. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3.e17–3.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culine, S.; Harter, V.; Gravis, G.; Fléchon, A.; Chevreau, C.; Mahammedi, H.; Laguerre, B.; Guillot, A.; Joly, F.; Abadie-Lacourtoisie, S.; et al. Chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Impact of cisplatin delivery on renal function and local control rate in the randomized phase III VESPER (GETUG-AFU V05) trial. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2021, 19, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veskimäe, E.; Linares Espinos, E.; Maxim Brunis, H.; Yuan, Y.; Sylvester, R.; Kamat, A.M.; Shariat, S.F.; Alfred Witjes, J.; Compérat, E.M. What is the prognostic and clinical importance of urothelial and nonurothelial histological variants of bladder cancer in predicting oncological outcomes in patients with muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer? A European Association of Urology muscle invasive and metastatic bladder cancer guidelines panel systematic review. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 2, 625–642. [Google Scholar]
- Lobo, N.; Shariat, S.F.; Guo, C.C.; Fernandez, M.I.; Kassouf, W.; Choudhury, A.; Gao, J.; Williams, S.B.; Galsky, M.M.; Taylor, J.A., III; et al. What is the significance of variant histology in urothelial carcinoma? Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, A.L.; Cheng, L.; Montironi, R.; Blanca, A.; Leva, M.; Rouprêt, M.; Fonseca, J.; Vidal, A.; Menedez, C.L.; Pallares, J.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and outcome of nested carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Virchows Arch. 2014, 465, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyerer, V.; Weisser, R.; Moskalev, E.A.; Haller, F.; Stoehr, R.; Eckstein, M.; Zinnall, U.; Gaisa, N.T.; Compérat, E.; Perren, A.; et al. Distinct genetic alterations and luminal molecular subtype in nested variant of urothelial carcinoma. Histopathology 2019, 75, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Kimura, S.; Foerster, B.; Abufaraj, M.; D’Andrea, D.; Gust, K.M.; Shariat, S.F. A systematic review and meta-analysis of lymphovascular invasion in patients treated with radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colomer Gallardo, A.; Candela, L.; Buisan Rueda, O.; Freixa Sala, R.; Canavera, E.; Moschini, M.; Macek, P.; Bennamoun, M.; Mombet, A.; Cathelineau, X.; et al. The Cancer of the Bladder Risk Assessment (COBRA) score accurately predicts cancer-specific survival after radical cystectomy: External validation and lymphovascular assessment value to improve its performance. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2022, 20, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soave, A.; John, L.M.; Dahlem, R.; Minner, S.; Engel, O.; Schmidt, S.; Kluth, L.A.; Fisch, M.; Rink, M. The impact of tumor diameter and tumor necrosis on oncological outcomes in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder treated with radical cystectomy. Urology 2015, 86, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | ypT0N0 (N = 155) | ypT > 0 or ypN > 0 (N = 242) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, No (%) | |||
| <60 | 47 (30) | 83 (34) | 0.6 |
| 60–69 | 78 (50) | 120 (50) | |
| ≥70 | 30 (20) | 39 (16) | |
| Median (95% range) | 64 (58–68) | 63 (58–68) | 0.2 |
| Sex, No (%) | |||
| Male | 126 (81) | 199 (82) | >0.9 |
| Female | 29 (19) | 43 (18) | |
| Body mass index, kg/m2, No (%) | |||
| <18.5 | 4 (2.6) | 8 (3.3) | 0.046 |
| 18.5–<25 | 41 (26) | 96 (40) | |
| 25–<30 | 74 (48) | 90 (37) | |
| ≥30 | 36 (23) | 48 (20) | |
| Median (95% range) | 26.8 (24.4–29.6) | 25.8 (22.9–29.3) | 0.088 |
| Body surface area (m2) | |||
| Median (95% range) | 1.9 (1.8–2.1) | 1.9 (1.8–2.1) | 0.2 |
| Medical history, No (%) | |||
| Tobacco | 121 (82) | 202 (86) | 0.4 |
| Hypertension | 62 (42) | 98 (42) | >0.9 |
| Coronary artery disease | 7 (4.5) | 5 (2.1) | 0.3 |
| Diabetes | 7 (4.5) | 8 (3.3) | 0.4 |
| Performance status, No (%) | |||
| 0 | 113 (73) | 168 (69) | 0.8 |
| 1 | 41 (26) | 72 (30) | |
| Unknown | 1 (0.6) | 2 (0.8) | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | |||
| Median (95% range) | 14.2 (13.2–15) | 14.1 (13.2–15.1) | 0.4 |
| Alkaline phosphatases (UI/L) | |||
| Median (95% range) | 70.5 (59–82.8) | 71.5 (60.2–88) | 0.2 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/L) | |||
| Median (95% range) | 9 (8–10) | 9 (8–11) | 0.7 |
| Creatinine clearance (mL/min), No (%) | |||
| 50–59 | 9 (5.8) | 27 (11) | 0.19 |
| 60–89 | 68 (44) | 106 (44) | |
| ≥90 | 78 (50) | 109 (45) | |
| Median (95% range) | 90 (73–107) | 87 (71–102) | 0.17 |
| Initial clinical stage | |||
| T2a | 102 (66) | 152(63) | >0.9 |
| T2b | 41 (26) | 73 (30) | |
| T3a | 4 (2.6) | 6 (2.5) | |
| T3b | 4 (2.6) | 4 (1.7) | |
| T4a | 4 (2.6) | 7 (2.9) | |
| Histology at baseline, No (%) | |||
| Central review | 113 (73) | 167 (69) | |
| Pure urothelial carcinoma | 50 (44) | 64 (38) | 0.4 |
| Urothelial carcinoma with divergence or subtypes > 10% | 63 (56) | 103 (62) | |
| Squamous | 22 (19) | 38 (23) | 0.6 |
| Glandular | 5 (4.4) | 12 (7.2) | 0.5 |
| Micropapillary | 16 (14) | 17 (10) | 0.4 |
| Nested | 6 (5.3) | 23 (14) | 0.038 |
| Sarcomatoid | 9 (8.0) | 8 (4.8) | 0.4 |
| Concomitant carcinoma in situ | 49 (43) | 82 (49) | 0.4 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | 36 (32) | 75 (45) | 0.039 |
| Perineural invasion | 7 (6.2) | 16 (9.6) | 0.4 |
| Necrosis > 10% | 13 (12) | 34 (20) | 0.075 |
| pT0pN0 | pT > 0 or p > N0 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC | dd-MVAC | GC | dd-MVAC | ||
| (N = 71) | (N = 84) | (N = 127) | (N = 115) | ||
| Number of cycles of chemotherapy Median (range) | 4 (1–4) | 6 (1–6) | 4 (1–4) | 6 (0–6) | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.4 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 11 | 4 | |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | |
| 3 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 7 | |
| 4 | 65 (92%) | 12 (14%) | 16 (14%) | ||
| 5 | 8 (9.5%) | 13 (11%) | |||
| 6 | 57 (68%) | 69 (60%) | |||
| Total number of cycles | 273 | 444 | 460 | 578 | |
| Cisplatin delivery Number of cycles with cisplatin | 273 | 441 | 460 | 575 | |
| Number of cycles with full doses of cisplatin | 260 (95%) | 383 (87%) | 421 (92%) | 485 (84%) | 0.062 |
| Total dose (mg) Median (95% range) | 532 (215–603) | 720 (166–877) | 518 (128–607) | 689 (168–903) | 0.028 |
| Dose intensity (mg/m2/week) Median (95% range) | 22.6 (18.7–24.2) | 32.1 (21.3–35.6) | 23.0 (16.3–24.0) | 31.6 (21.8–35.8) | >0.9 |
| Relative dose intensity | 97% | 92% | 99% | 90% | |
| Time interval between randomization and surgery (days) Median (95% range) | 121 (90–149) | 121 (62–179) | 111 (48–164) | 118 (62–211) | 0.034 |
| Time interval between last course of chemotherapy and surgery (days) Median (95% range) | 51 (28.5–88.5) | 53.5 (27–93) | 47 (23–99.5) | 50 (23–145) | 0.4 |
| Relapses | ypT0N0 (n = 155) | ypTa/isN0 (n = 42) | ypT1N0 (n = 27) | ypT2N0 (n = 54) | ypT>2N0 (n = 60) | ypN+ (n = 55) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients (%) | 16 (10) | 3 (7.1) | 5 (18) | 15 (28) | 38 (63) | 43 (78) |
| Sites | ||||||
| Loco-regional (pelvis) | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 12 | 18 |
| Metastatic | 13 | 2 | 3 | 9 | 26 | 25 |
| Lung | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 12 | 9 |
| Liver | 4 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 11 |
| Bone | 6 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 9 |
| Other | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Variable | n | HR (CI 95%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | |||
| <60 | 47 | - | |
| 60–69 | 78 | 1.38 (0.48–3.99) | 0.5 |
| ≥70 | 30 | 2.02 (0.62–6.61) | 0.2 |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 126 | - | |
| Female | 29 | 0.43 (0.10–1.85) | 0.3 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | |||
| <18.5 | 4 | 1.42 (0.18–11.1) | 0.7 |
| 18.5–<25 | 41 | - | |
| 25–<30 | 74 | 0.36 (0.14–0.96) | 0.040 |
| ≥30 | 36 | 0.43 (0.14–1.38) | 0.16 |
| Body surface area (m2) | |||
| 0.15 (0.020–1.13) | 0.066 | ||
| Medical history | |||
| Tobacco | 121 | 0.92 (0.34–2.50) | 0.9 |
| Hypertension | 62 | 1.62 (0.70–3.74) | 0.3 |
| Coronary artery disease | 13 | 1.71 (0.51–5.78) | 0.4 |
| Diabetes | 7 | 2.48 (0.58–10.6) | 0.2 |
| Performance status | |||
| 0 | 113 | - | |
| 1 | 41 | 1.14 (0.45–2.91) | 0.8 |
| Biology at baseline | |||
| Hemoglobin | |||
| ≥12 g/dL | 142 | - | |
| <12 g/dL | 13 | 2.69 (0.91–7.95) | 0.074 |
| Neutrophil polynuclear cells | |||
| ≤7000/mm3 | 139 | - | |
| >7000/mm3 | 16 | 2.83 (1.04–7.67) | 0.041 |
| Creatinine clearance (mL/min) | |||
| ≥90 | 78 | - | |
| 60–89 | 68 | 1.33 (0.54–3.27) | 0.5 |
| 50–59 | 9 | 4.16 (1.12–15.4) | 0.033 |
| Histology at baseline | |||
| Central review | 113 | ||
| Urothelial carcinoma with divergence or subtypes > 10% | 63 | 1.24 (0.44–3.47) | 0.7 |
| Concomitant carcinoma in situ | 49 | 1.11 (0.40–3.06) | 0.8 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | 36 | 1.86 (0.67–5.13) | 0.2 |
| Perineural invasion | 7 | 1.07 (0.14–8.14) | >0.9 |
| Necrosis > 10% | 62 | 0.78 (0.28–2.15) | 0.6 |
| Treatment delivery (multivariate model) | |||
| Randomization arm | |||
| GC | 71 | - | |
| ddMVAC | 84 | 0.73 (0.19–2.84) | 0.6 |
| Cisplatin dose/cycle equivalence | |||
| for GC arm | |||
| ≥270 mg/m²/4 cycles | 55 | - | |
| <270 mg/m²/<4 cycles | 16 | 0.49 (0.06–4.00) | 0.5 |
| for ddMVAC arm | |||
| ≥410 mg/m²/6 cycles | 32 | - | |
| 340 to 410 mg/m²/5 cycles | 22 | 1.98 (0.44–8.85) | 0.4 |
| 270 to 340 mg/m²/4 cycles | 17 | 1.27 (0.21–7.59) | 0.8 |
| <270 mg/m²/< 4 cycles | 13 | 5.38 (1.28–22.54) | 0.021 |
| Clinical stage inferred by fibrosis on cystectomy (N = 99) | |||
| T2a | 17 | - | |
| T2b | 54 | 1.63 (0.36–7.45) | 0.5 |
| T3 | 28 | 1.24 (0.23–6.77) | 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Culine, S.; Harter, V.; Krucker, C.; Gravis, G.; Fléchon, A.; Chevreau, C.; Mahammedi, H.; Laguerre, B.; Guillot, A.; Joly, F.; et al. Refining the Characterization and Outcome of Pathological Complete Responders after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Lessons from the Randomized Phase III VESPER (GETUG-AFU V05) Trial. Cancers 2023, 15, 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061742
Culine S, Harter V, Krucker C, Gravis G, Fléchon A, Chevreau C, Mahammedi H, Laguerre B, Guillot A, Joly F, et al. Refining the Characterization and Outcome of Pathological Complete Responders after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Lessons from the Randomized Phase III VESPER (GETUG-AFU V05) Trial. Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061742
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuline, Stéphane, Valentin Harter, Clémentine Krucker, Gwenaelle Gravis, Aude Fléchon, Christine Chevreau, Hakim Mahammedi, Brigitte Laguerre, Aline Guillot, Florence Joly, and et al. 2023. "Refining the Characterization and Outcome of Pathological Complete Responders after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Lessons from the Randomized Phase III VESPER (GETUG-AFU V05) Trial" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061742
APA StyleCuline, S., Harter, V., Krucker, C., Gravis, G., Fléchon, A., Chevreau, C., Mahammedi, H., Laguerre, B., Guillot, A., Joly, F., Fontugne, J., Allory, Y., & Pfister, C., on behalf of the VESPER Trial Investigators. (2023). Refining the Characterization and Outcome of Pathological Complete Responders after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Lessons from the Randomized Phase III VESPER (GETUG-AFU V05) Trial. Cancers, 15(6), 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061742






