MiR-218-5p/EGFR Signaling in Arsenic-Induced Carcinogenesis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, siRNAs, Plasmids, and Reagents
2.2. Immunoblotting Assay
2.3. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR
2.4. Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.6. Colony Formation Assay
2.7. Wound Healing Assay
2.8. Transwell Migration Assay
2.9. Tube Formation Assay
2.10. Lentivirus Packaging and Viral Transduction
2.11. In Vivo Tumor Growth Assay
2.12. Immunohistochemical Staining for CD31
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Upregulation of EGFR and Its Downstream Targets and Downregulation of miR-218-5p in As-T Cells
3.2. MiR-218-5p Functioned as a Tumor Suppressor in As-T Cells to Negatively Regulate Cell Proliferation, Colony Formation, Cell Migration, and Tube Formation In Vitro
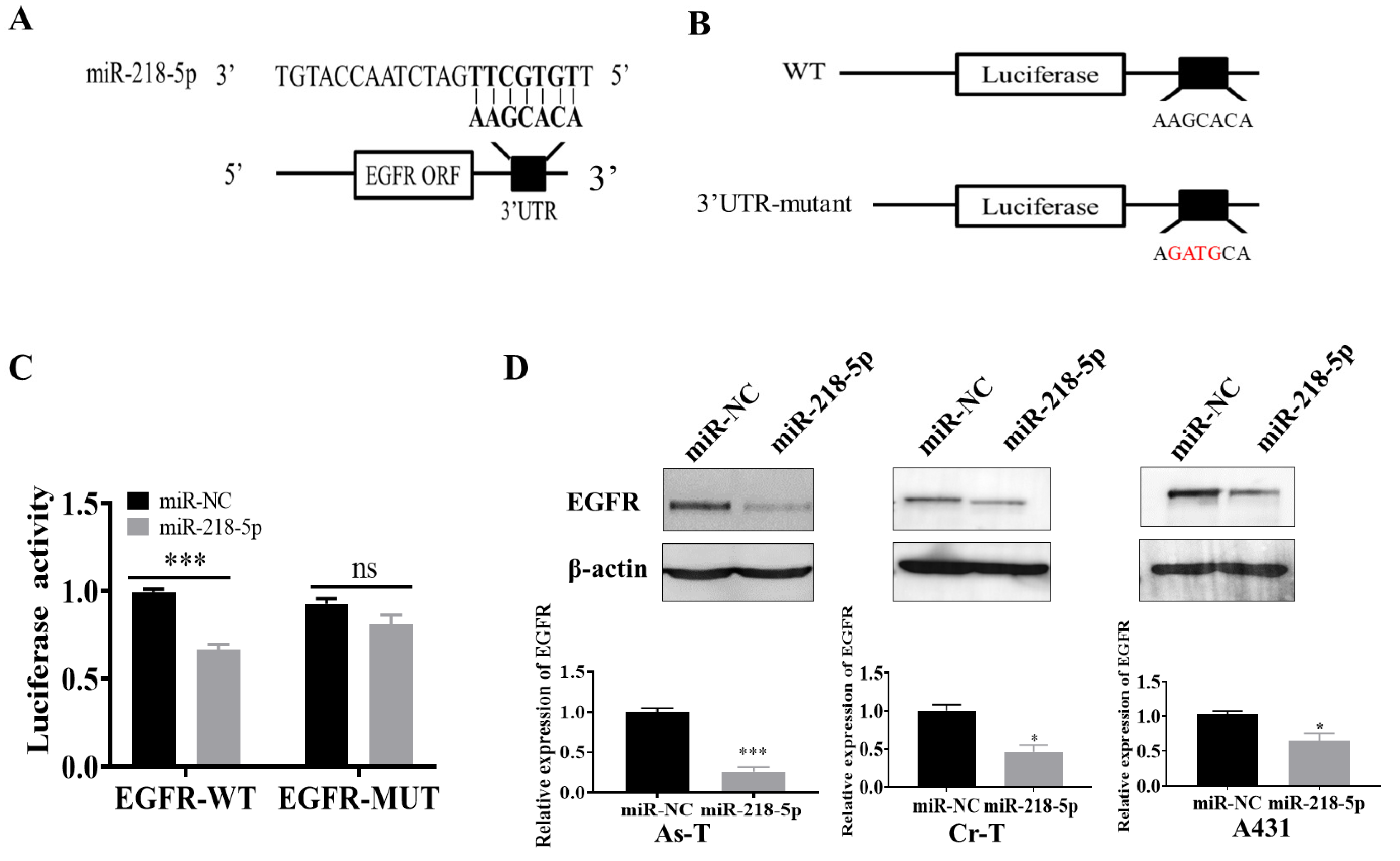
3.3. EGFR Was a Direct Target of miR-218-5p
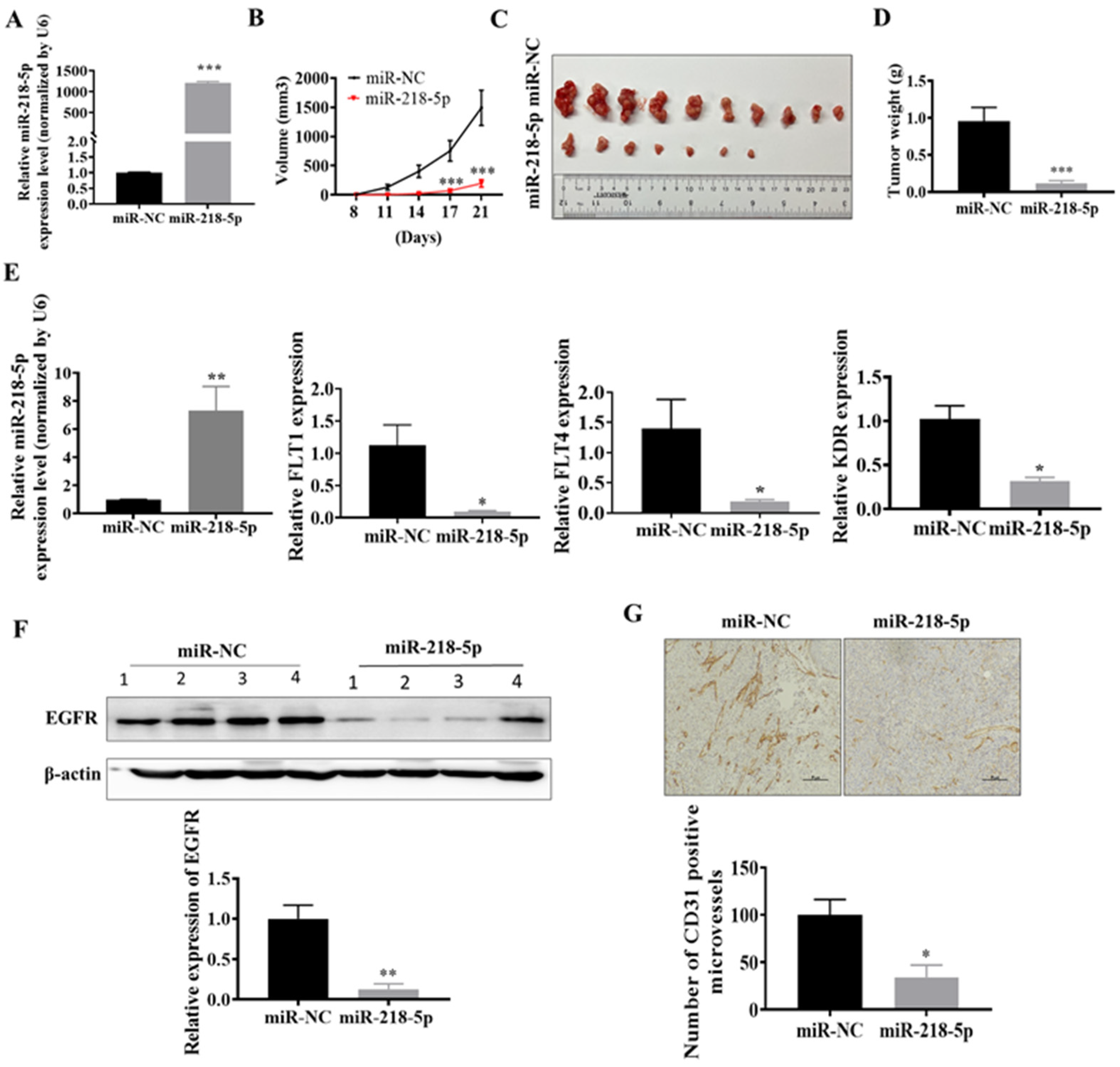
3.4. MiR-218-5p Inhibited As-T Cells-Induced Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis and Decreased EGFR Expression In Vivo
3.5. EGFR Forced Expression Recovered miR-218-5p-Inhibited Cell Proliferation, Colony Formation, Migration, and Tube Formation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vahter, M. Health effects of early life exposure to arsenic. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 102, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardach, A.E.; Ciapponi, A.; Soto, N.; Chaparro, M.R.; Calderon, M.; Briatore, A.; Cadoppi, N.; Tassara, R.; Litter, M.I. Epidemiology of chronic disease related to arsenic in Argentina: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straif, K.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A review of human carcinogens—Part C: Metals, arsenic, dusts, and fibres. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu-Yao, G.; Liu, L.-Z. Epigenetic Dysregulations in Arsenic-Induced Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayotte, J.D.; Medalie, L.; Qi, S.L.; Backer, L.C.; Nolan, B.T. Estimating the High-Arsenic Domestic-Well Population in the Conterminous United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12443–12454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Kuo, T.L.; Wu, M.M. Arsenic and cancers. Lancet 1988, 1, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, G.; Ferreccio, C.; Yuan, Y.; Bates, M.N.; Steinmaus, C.; Selvin, S.; Liaw, J.; Smith, A.H. Fifty-year study of lung and bladder cancer mortality in Chile related to arsenic in drinking water. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.H.; Hopenhayn-Rich, C.; Bates, M.N.; Goeden, H.M.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Duggan, H.M.; Wood, R.; Kosnett, M.J.; Smith, M.T. Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 1992, 97, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopenhayn-Rich, C.; Biggs, M.L.; Fuchs, A.; Bergoglio, R.; Tello, E.E.; Nicolli, H.; Smith, A.H. Bladder cancer mortality associated with arsenic in drinking water in Argentina. Epidemiology 1996, 7, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohel, N.; Persson, L.A.; Rahman, M.; Streatfield, P.K.; Yunus, M.; Ekström, E.C.; Vahter, M. Arsenic in drinking water and adult mortality: A population-based cohort study in rural Bangladesh. Epidemiology 2009, 20, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; States, J.C.; Ceresa, B.P. Chronic and acute arsenic exposure enhance EGFR expression via distinct molecular mechanisms. Toxicol. Vitro 2020, 67, 104925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, S.; Han, X.; Wang, Z. Anti-tumor activity of high-dose EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor and sequential docetaxel in wild type EGFR non-small cell lung cancer cell nude mouse xenografts. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9134–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elghonaimy, E.A.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Youns, A.; Hussein, Z.; Nouh, M.A.; El-Mamlouk, T.; El-Shinawi, M.; Mostafa Mohamed, M. Secretome of tumor-associated leukocytes augment epithelial-mesenchymal transition in positive lymph node breast cancer patients via activation of EGFR/Tyr845 and NF-κB/p65 signaling pathway. Tumour. Biol. 2016, 37, 12441–12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiani, T.; Napolitano, S.; Della Corte, C.M.; Martini, G.; Martinelli, E.; Morgillo, F.; Ciardiello, F. Therapeutic value of EGFR inhibition in CRC and NSCLC: 15 years of clinical evidence. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.C.; Chiu, T.L. Tanshinone IIA decreases the protein expression of EGFR, and IGFR blocking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in gastric carcinoma AGS cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, R.; Gelardi, T.; Damiano, V.; Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G. Rational bases for the development of EGFR inhibitors for cancer treatment. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1416–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchowsky, A.; Klei, L.R.; Dudek, E.J.; Swartz, H.M.; James, P.E. Stimulation of reactive oxygen, but not reactive nitrogen species, in vascular endothelial cells exposed to low levels of arsenite. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobná, Z.; Jaspers, I.; Thomas, D.J.; Stýblo, M. Differential activation of AP-1 in human bladder epithelial cells by inorganic and methylated arsenicals. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonova, P.P.; Wang, S.; Hulderman, T.; Luster, M.I. c-Src-dependent activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by arsenic. Role in carcinogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2945–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Ortega, J.; Kim, C.; Huang, J.; Gu, L.; Li, G.M. Arsenic Inhibits DNA Mismatch Repair by Promoting EGFR Expression and PCNA Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14536–14541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, A.S.; Mason, R.A.; Memoli, V.; Duell, E.J. Arsenic activates EGFR pathway signaling in the lung. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 109, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V. microRNAs: Tiny regulators with great potential. Cell 2001, 107, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, E.C. Micro RNAs are complementary to 3’ UTR sequence motifs that mediate negative post-transcriptional regulation. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 363–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Ambros, V. An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 2001, 294, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Weinberg, R.A. Micromanagers of malignancy: Role of microRNAs in regulating metastasis. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miska, E.A. How microRNAs control cell division, differentiation and death. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.M.; Weiss, G.J. MicroRNAs and cancer: Past, present, and potential future. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 3655–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarogoulidis, P.; Petanidis, S.; Kioseoglou, E.; Domvri, K.; Anestakis, D.; Zarogoulidis, K. MiR-205 and miR-218 expression is associated with carboplatin chemoresistance and regulation of apoptosis via Mcl-1 and Survivin in lung cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.W.; Cheng, Y.W.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, H. Paxillin predicts survival and relapse in non-small cell lung cancer by microRNA-218 targeting. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10392–10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Ding, H.; Wang, W.; Liao, Z.; Fu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Chen, X. Tumor-suppressive miR-218-5p inhibits cancer cell proliferation and migration via EGFR in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 28075–28085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Tao, J.; Lu, Q. MicroRNA-218 inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting BMI-1. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 8015–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, C.; Xu, F.; Shen, W.; Geng, L.; Xie, F.; Dai, B.; Lu, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J. Overexpression of miR-218 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth through RET. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Wu, K.; Zeng, J.; Xu, S.; Mu, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, K.; Ma, Z.; Tian, J.; Shi, Q.; et al. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-218 inhibits tumor angiogenesis via targeting the mTOR component RICTOR in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8162–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.M.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Jiang, C.F.; Ge, X.; Li, D.M.; Wen, Y.Y.; Sun, H.R.; Pan, M.H.; Li, W.; et al. Downregulation of miR-218 contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in lung cancer by targeting Slug/ZEB2 signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Yang, P.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Shan, X.; Huang, R.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J. Survivin is a prognostic indicator in glioblastoma and may be a target of microRNA-218. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, B.; Kong, Y. MicroRNA-218-5p inhibit the migration and proliferation of pterygium epithelial cells by targeting EGFR via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 178, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xu, S.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, B.H.; Liu, L.Z. Chronic arsenic exposure and angiogenesis in human bronchial epithelial cells via the ROS/miR-199a-5p/HIF-1α/COX-2 pathway. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.L.; Jiang, Y.; Jing, Y.; He, J.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Liu, L.Z.; Jiang, B.H. Arsenite induces cell transformation by reactive oxygen species, AKT, ERK1/2, and p70S6K1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bayanbold, K.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Thorne, P.S.; Yang, H.; Jiang, B.-H.; Liu, L.-Z. Redox sensitive miR-27a/b/Nrf2 signaling in Cr(VI)-induced carcinogenesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.F.; Liu, J.; Jiang, B.H.; Liu, L.Z. Human endothelial cells promote arsenic-transformed lung epithelial cells to induce tumor growth and angiogenesis through interleukin-8 induction. Aging 2022, 14, 2113–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satterlee, H.S. The arsenic-poisoning epidemic of 1900. Its relation to lung cancer in 1960—An exercise in retrospective epidemiology. N. Engl. J. Med. 1960, 263, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blot, W.J.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr. Arsenical air pollution and lung cancer. Lancet 1975, 2, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Lara, I.; Martínez-Castillo, M.; Quintana-Pérez, J.C.; Arellano-Mendoza, M.G.; Tamay-Cach, F.; Valenzuela-Limón, O.L.; García-Montalvo, E.A.; Hernández-Zavala, A. Arsenic exposure: A public health problem leading to several cancers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 110, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecci, F.; Cantini, L.; Metro, G.; Ricciuti, B.; Lamberti, G.; Farooqi, A.A.; Berardi, R. Non-small-cell lung cancer: How to manage EGFR-mutated disease. Drugs Context 2022, 11, 2022-4-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, W.A.; Veve, R.; Hirsch, F.R.; Helfrich, B.A.; Bunn, P.A., Jr. Epidermal growth factor receptor family in lung cancer and premalignancy. Semin. Oncol. 2002, 29, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Albanell, J. Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor in lung cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2002, 4, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grando, S.A. Connections of nicotine to cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X. Multiscale modeling reveals angiogenesis-induced drug resistance in brain tumors and predicts a synergistic drug combination targeting EGFR and VEGFR pathways. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.R. Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates gene transcription by acting as a protein kinase. Mol. Cell 2012, 45, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xia, Y.; Hawke, D.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Xing, D.; Aldape, K.; Hunter, T.; Alfred Yung, W.K.; Lu, Z. PKM2 phosphorylates histone H3 and promotes gene transcription and tumorigenesis. Cell 2012, 150, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Bamezai, R.N. Human pyruvate kinase M2: A multifunctional protein. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 2031–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Bamezai, R.N. Resveratrol inhibits cancer cell metabolism by down regulating pyruvate kinase M2 via inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofk, H.R.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Harris, M.H.; Ramanathan, A.; Gerszten, R.E.; Wei, R.; Fleming, M.D.; Schreiber, S.L.; Cantley, L.C. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature 2008, 452, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Li, D.; Zhao, D.; Lin, R.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zha, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; et al. Acetylation targets the M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase for degradation through chaperone-mediated autophagy and promotes tumor growth. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xia, Y.; Ji, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, J.; Huang, W.; Gao, X.; Aldape, K.; Lu, Z. Nuclear PKM2 regulates β-catenin transactivation upon EGFR activation. Nature 2011, 480, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Y.; Ji, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, F.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Aldape, K.; Cantley, L.C.; Lu, Z. ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of PKM2 promotes the Warburg effect. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xia, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Bu, W.; Zhang, L.; You, M.J.; Koh, M.Y.; Cote, G.; Aldape, K.; et al. EGFR-induced and PKCε monoubiquitylation-dependent NF-κB activation upregulates PKM2 expression and promotes tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Hu, H.; Chang, R.; Zhong, J.; Knabel, M.; O’Meally, R.; Cole, R.N.; Pandey, A.; Semenza, G.L. Pyruvate kinase M2 is a PHD3-stimulated coactivator for hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell 2011, 145, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Yan, Y.; Chai, H.; Chen, S.; Xiong, X.; Sun, D.; Yu, Y.; Deng, L.; Cheng, F. Pyruvate kinase M2 affects liver cancer cell behavior through up-regulation of HIF-1α and Bcl-xL in culture. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 69, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; Curtis, A.M.; Goel, G.; Lauterbach, M.A.; Sheedy, F.J.; Gleeson, L.E.; van den Bosch, M.W.; Quinn, S.R.; Domingo-Fernandez, R.; Johnston, D.G.; et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates Hif-1α activity and IL-1β induction and is a critical determinant of the warburg effect in LPS-activated macrophages. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.H.; Agani, F.; Passaniti, A.; Semenza, G.L. V-SRC induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and transcription of genes encoding vascular endothelial growth factor and enolase 1: Involvement of HIF-1 in tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 5328–5335. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, H.E.; Lo, J.; Johnson, R.S. HIF-1 alpha is required for solid tumor formation and embryonic vascularization. Embo J. 1998, 17, 3005–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, P.H.; Dachs, G.U.; Gleadle, J.M.; Nicholls, L.G.; Harris, A.L.; Stratford, I.J.; Hankinson, O.; Pugh, C.W.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates gene expression in solid tumors and influences both angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8104–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia, clonal selection, and the role of HIF-1 in tumor progression. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 35, 71–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadis, A.G.; Stisser, B.C.; Ghafar, M.A.; Burchardt, M.; Buttyan, R. Tumor hypoxia and the progression of prostate cancer. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2002, 3, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, Y.F.; Wang, C.S.; Xie, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Qian, Y.C.; Liu, W.T.; Wang, M.; Jiang, B.H. HB-EGF Activates the EGFR/HIF-1α Pathway to Induce Proliferation of Arsenic-Transformed Cells and Tumor Growth. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K. MicroRNA-218-5p affects lung adenocarcinoma progression through targeting endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductase 1 alpha. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 10061–10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Yang, J.; Luo, X. Long non-coding RNA MNX1-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion through targeting miR-218-5p/COMMD8 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Zeng, C.; Lu, X.; He, X.; Zhang, R.; Qiu, Q.; Zheng, G.; Jia, X.; Liu, H.; He, Z. miR-218 suppresses gastric cancer cell cycle progression through the CDK6/Cyclin D1/E2F1 axis in a feedback loop. Cancer Lett. 2017, 403, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Du, H.; Han, B.; Xia, G.; Shi, X.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, T. Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-218 inhibits trophoblast invasion by targeting LASP1: Implications for preeclampsia development. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 87, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.W.; Baxter, L.L.; Loftus, S.K.; Cronin, J.C.; Trivedi, N.S.; Borate, B.; Pavan, W.J. Distinct microRNA expression signatures are associated with melanoma subtypes and are regulated by HIF1A. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; He, J.; Li, F.; Yang, J.; Wei, J.; Cho, W.C.; Liu, X. Emerging Roles of MicroRNAs in EGFR-Targeted Therapies for Lung Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 672759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, M.; Ferragut Cardoso, A.; Al-Eryani, L.; Pan, J.; Kalbfleisch, T.S.; Srivastava, S.; Rai, S.N.; States, J.C. Dynamic alteration in miRNA and mRNA expression profiles at different stages of chronic arsenic exposure-induced carcinogenesis in a human cell culture model of skin cancer. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 2351–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Eryani, L.; Jenkins, S.F.; States, V.A.; Pan, J.; Malone, J.C.; Rai, S.N.; Galandiuk, S.; Giri, A.K.; States, J.C. miRNA expression profiles of premalignant and malignant arsenic-induced skin lesions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Islam, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.-Z. Epigenetic Regulation in Chromium-, Nickel- and Cadmium-Induced Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2022, 14, 5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Treatment Group | Number of Implantations | Number of Tumors |
|---|---|---|
| miR-NC | 10 | 10 |
| miR-218-5p | 10 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, R.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.-Z. MiR-218-5p/EGFR Signaling in Arsenic-Induced Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2023, 15, 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041204
Islam R, Zhao L, Zhang X, Liu L-Z. MiR-218-5p/EGFR Signaling in Arsenic-Induced Carcinogenesis. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041204
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Ranakul, Lei Zhao, Xiujuan Zhang, and Ling-Zhi Liu. 2023. "MiR-218-5p/EGFR Signaling in Arsenic-Induced Carcinogenesis" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041204
APA StyleIslam, R., Zhao, L., Zhang, X., & Liu, L.-Z. (2023). MiR-218-5p/EGFR Signaling in Arsenic-Induced Carcinogenesis. Cancers, 15(4), 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041204






