In Vivo Detection of Circulating Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Breast Tumor Mouse Xenograft: Impact of Tumor Stroma and Chemotherapy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.3. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.4. Preparation of Liposomal Doxorubicin
2.5. Animal Studies
2.6. Blood Collection and Microsieve Filtration Processing
3. Results
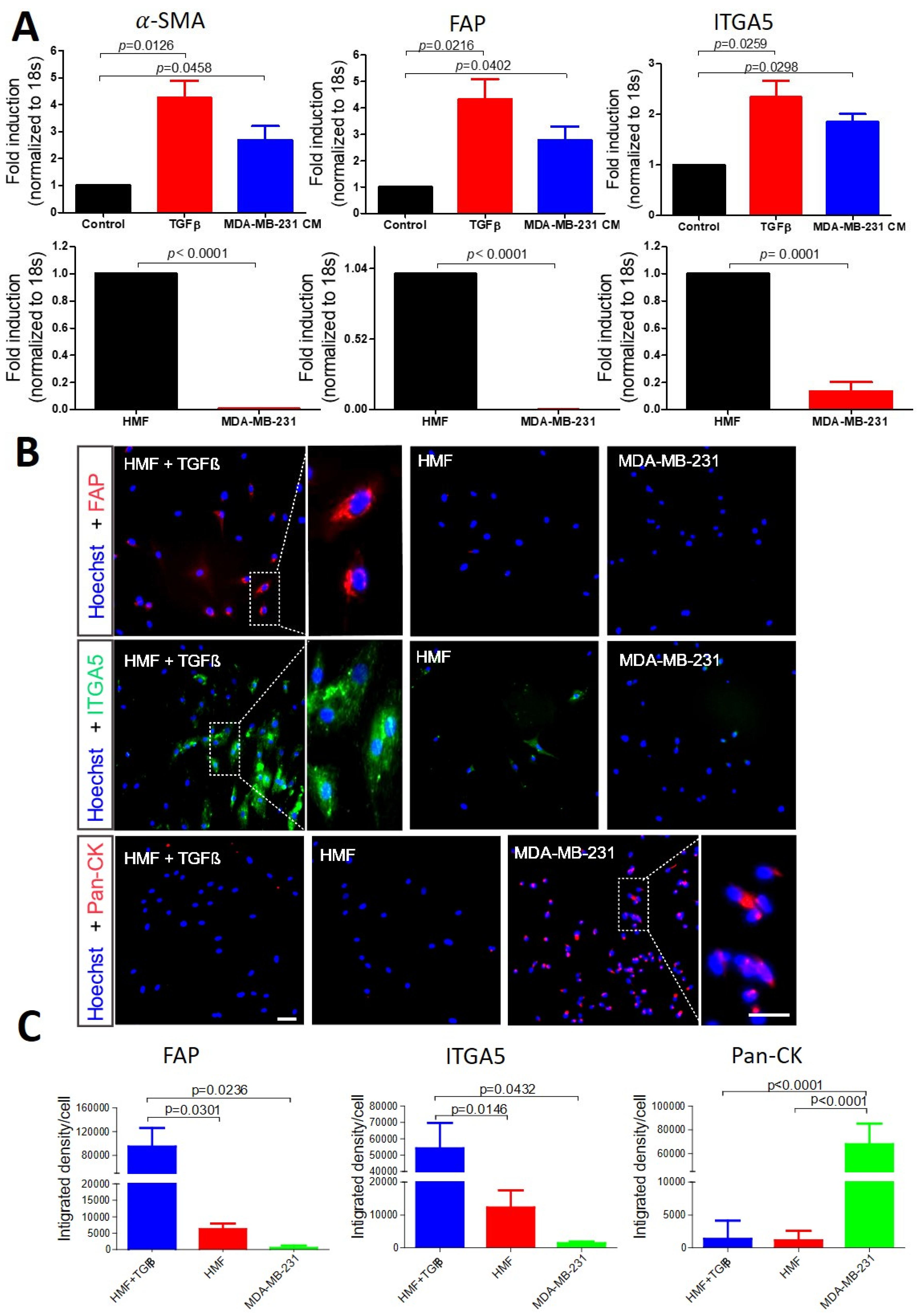
3.1. Selection of Biomarkers for Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Cancer Cell Identification
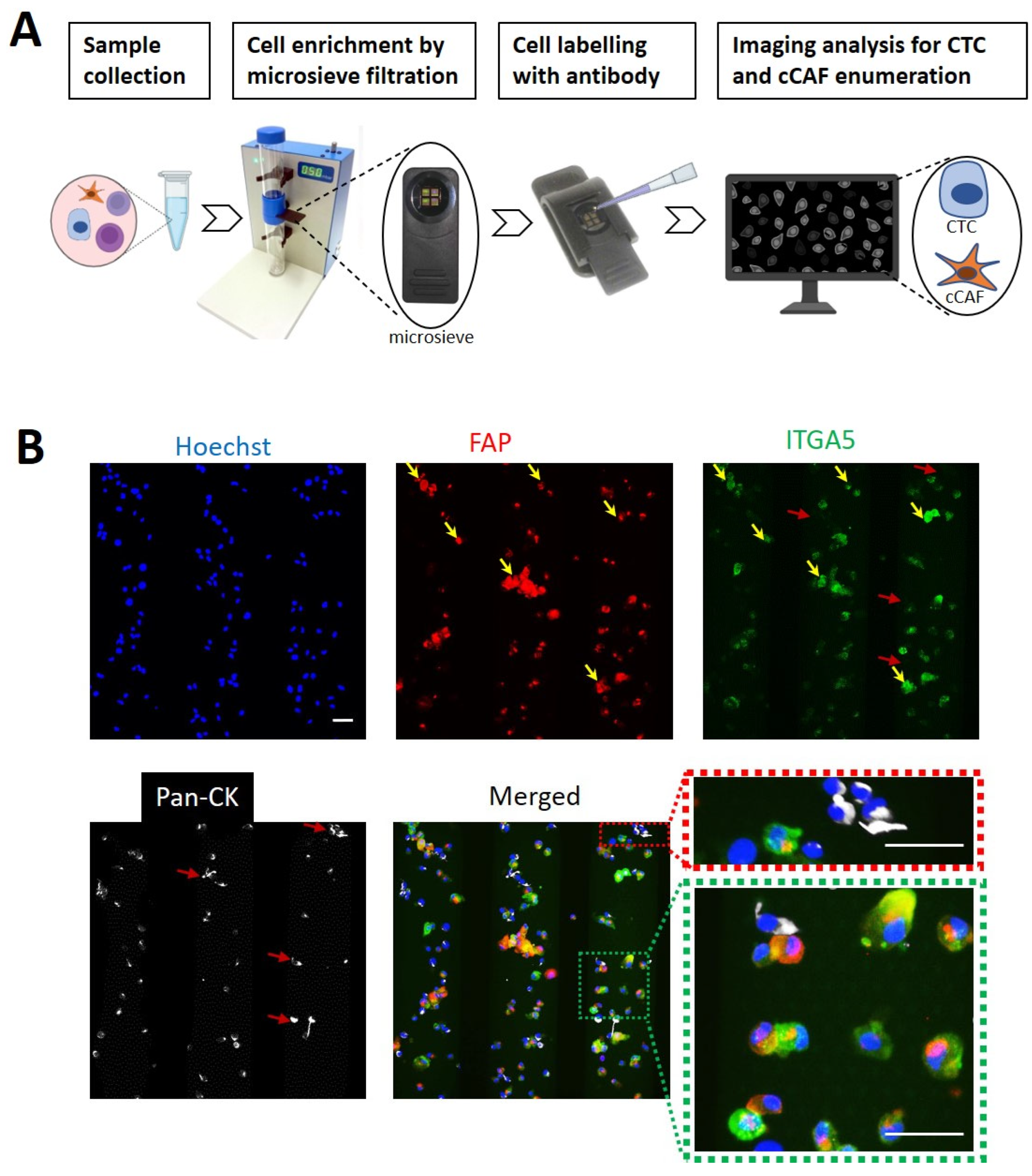
3.2. Identification of CAFs and Tumor Cells Using a Microsieve Platform
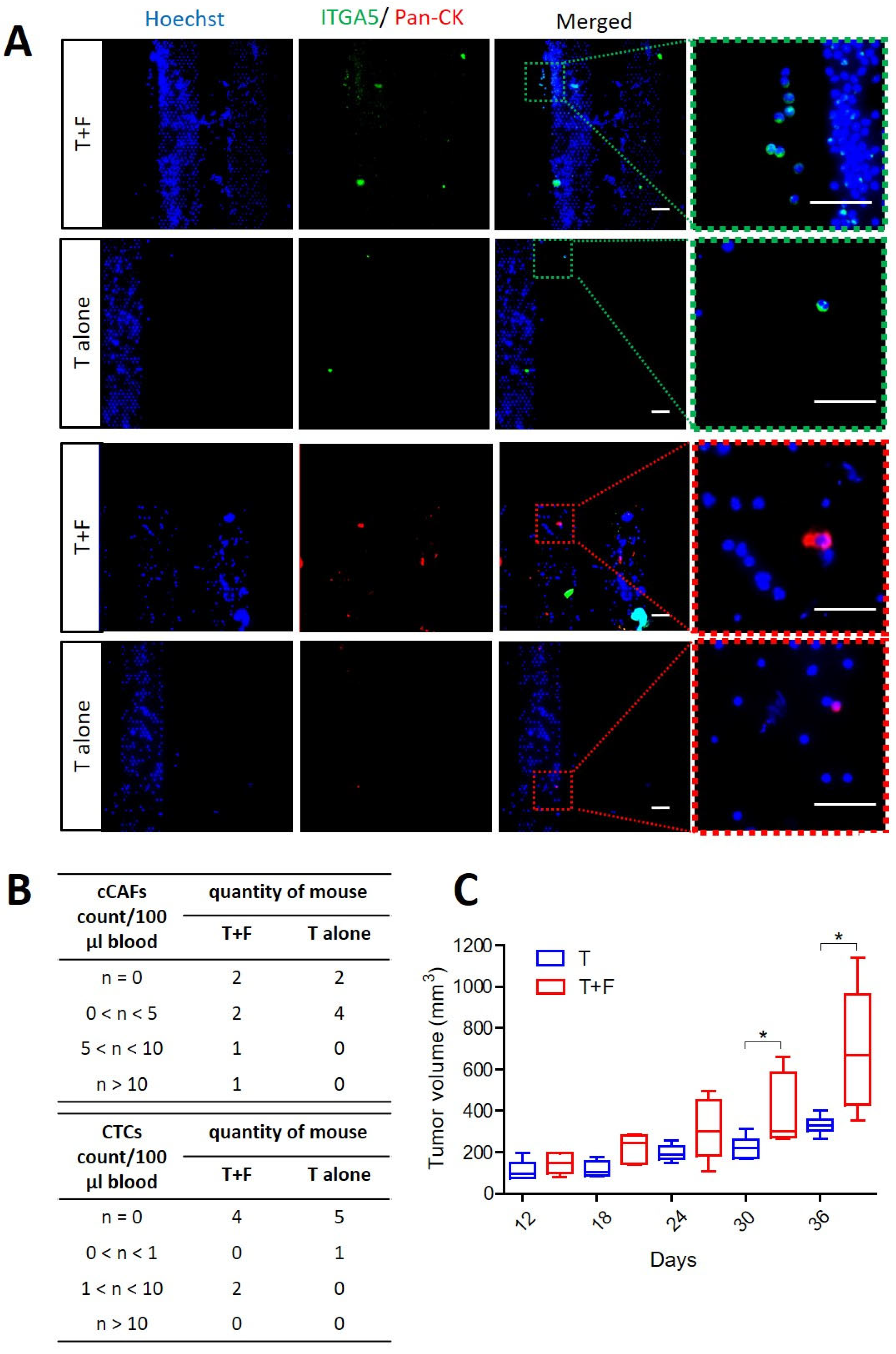
3.3. CAFs Promoting Tumor Growth and Supporting Dissemination of CTCs and cCAFs
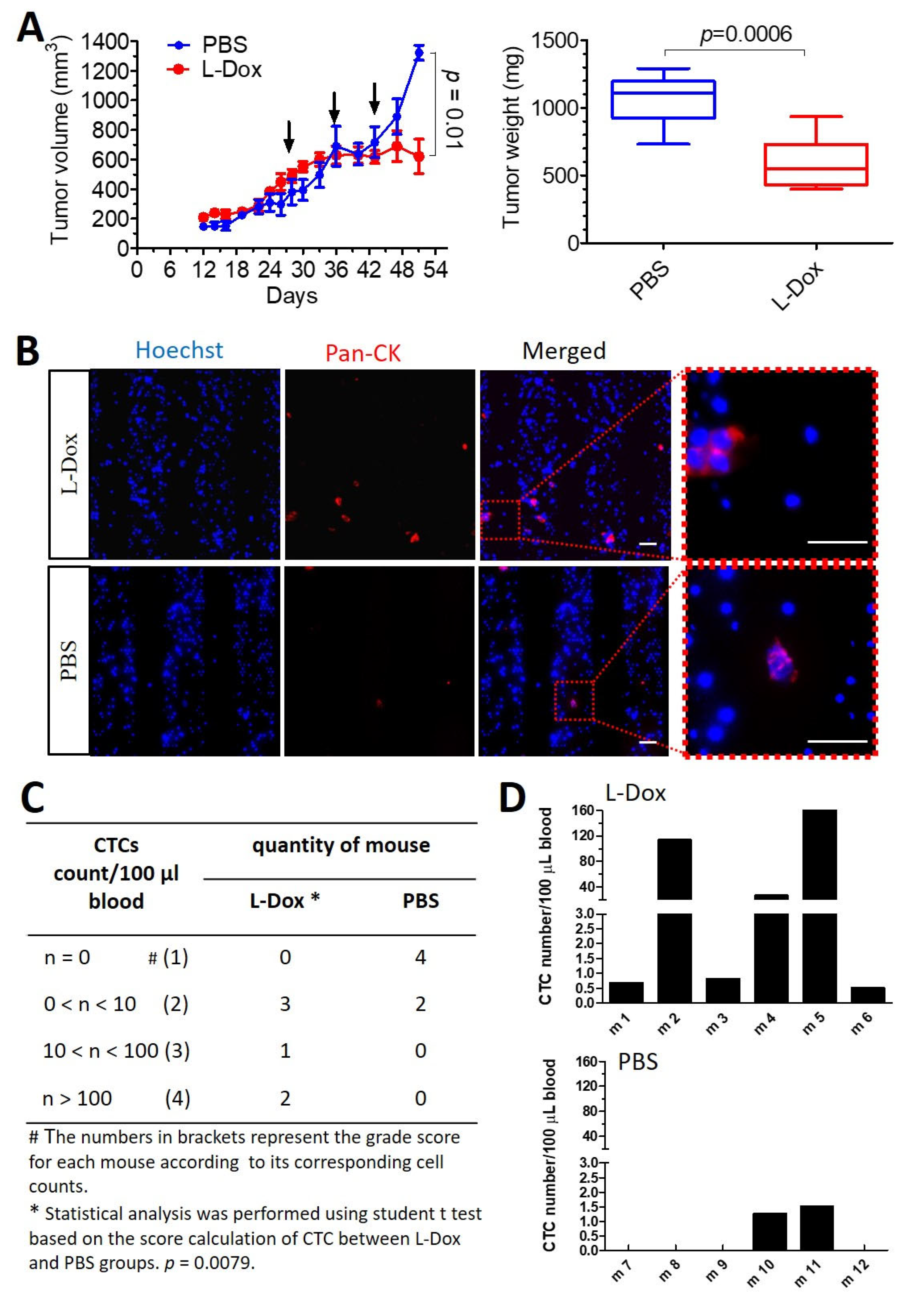
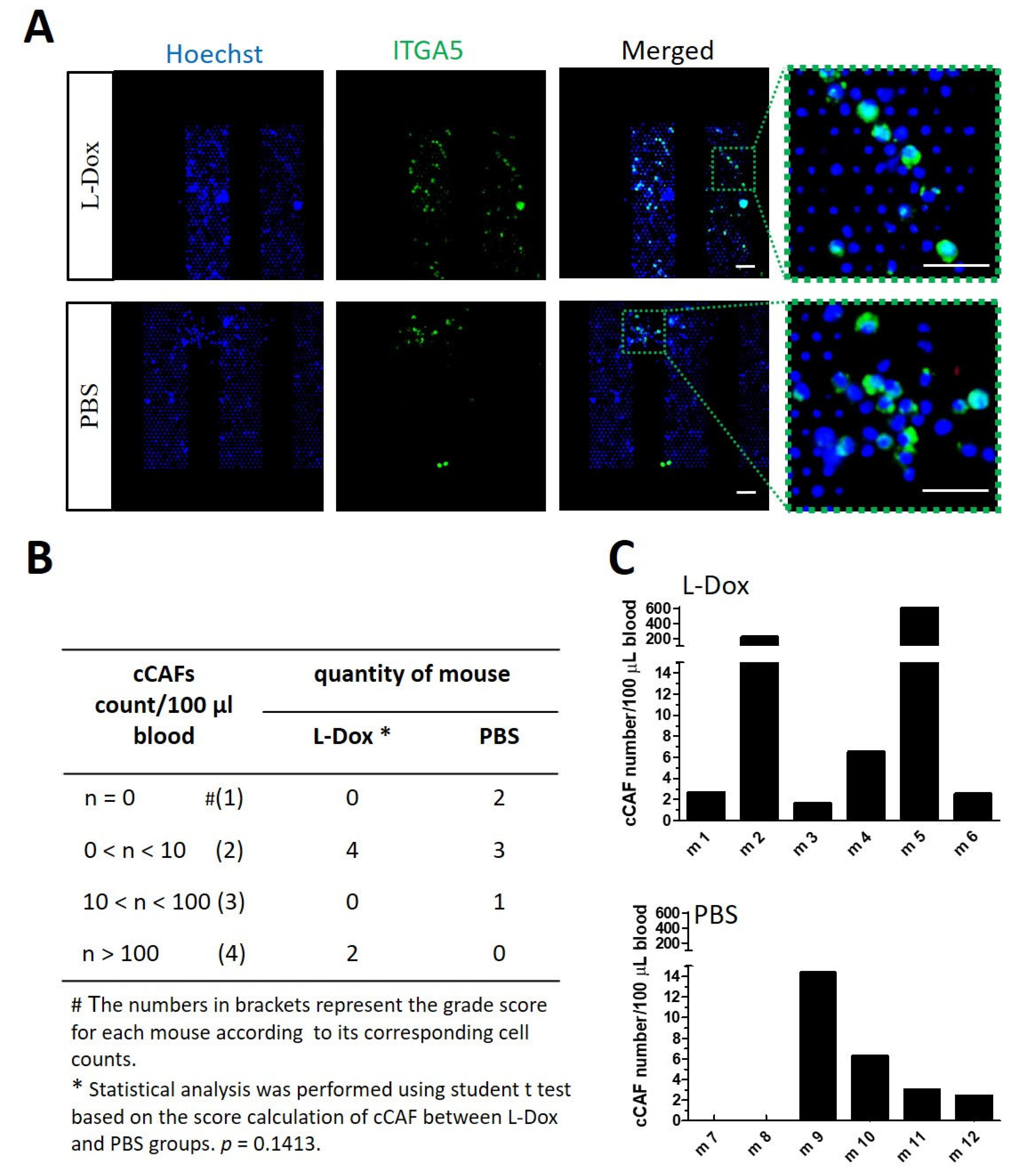
3.4. Chemotherapy Inducing More cCAFs and CTCs in Mice with Breast Tumors
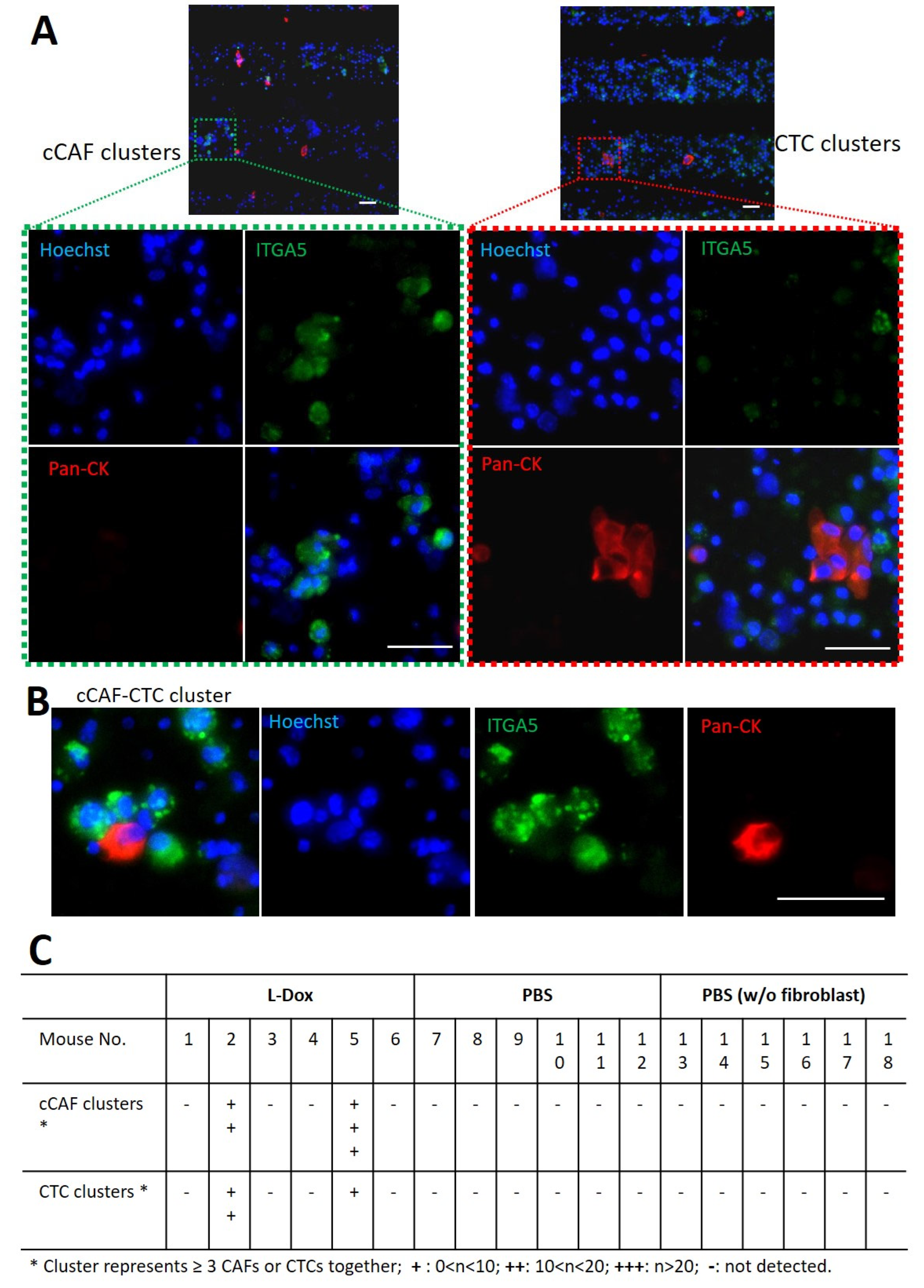
3.5. Detection of cCAFs and CTC Clusters in Blood from L-Dox-treated Mice with Breast Tumors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeiro, R.; Martínez-Pena, I.; López-López, R. Relevance of CTC clusters in breast cancer metastasis. In Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer Metastatic Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 93–115. [Google Scholar]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfried, T.N.; Huysentruyt, L.C. On the origin of cancer metastasis. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2013, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudineh, M.; Sargent, E.H.; Pantel, K.; Kelley, S.O. Profiling circulating tumour cells and other biomarkers of invasive cancers. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murlidhar, V.; Reddy, R.M.; Fouladdel, S.; Zhao, L.; Ishikawa, M.K.; Grabauskiene, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, J.; Chang, A.C.; Carrott, P. Poor Prognosis Indicated by Venous Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters in Early-Stage Lung CancersCirculating Tumor Cell Clusters in Early Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5194–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Sloane, R.; Priest, L.; Lancashire, L.; Hou, J.-M.; Greystoke, A.; Ward, T.H.; Ferraldeschi, R.; Hughes, A.; Clack, G. Evaluation and prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in patients with non–small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1556–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C. Relationship of circulating tumor cells to tumor response, progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W. Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bono, J.S.; Scher, H.I.; Montgomery, R.B.; Parker, C.; Miller, M.C.; Tissing, H.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.; Pienta, K.J.; Raghavan, D. Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.F.; Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Miller, M.C.; Matera, J.; Allard, W.J.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W. Circulating tumor cells at each follow-up time point during therapy of metastatic breast cancer patients predict progression-free and overall survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4218–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, D.G.; Duyverman, A.M.; Kohno, M.; Snuderl, M.; Steller, E.J.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Malignant cells facilitate lung metastasis by bringing their own soil. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21677–21682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Otero, N.; Clinch, A.B.; Hope, J.; Wang, W.; Reinhart-King, C.A.; King, M.R. Cancer associated fibroblasts confer shear resistance to circulating tumor cells during prostate cancer metastatic progression. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietras, K.; Östman, A. Hallmarks of cancer: Interactions with the tumor stroma. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.M.; Fusenig, N.E. Friends or foes—Bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W. CCR 20th anniversary commentary: Paving the way for circulating tumor cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2883–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Shen, L.; Luo, M.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y. Circulating tumor cells: Biology and clinical significance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andree, K.C.; Abali, F.; Oomens, L.; Passanha, F.R.; Broekmaat, J.J.; Kraan, J.; Mendelaar, P.A.; Sleijfer, S.; Terstappen, L.W. Self-seeding microwells to isolate and assess the viability of single circulating tumor cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magbanua, M.J.M.; Savenkov, O.; Asmus, E.J.; Ballman, K.V.; Scott, J.H.; Park, J.W.; Dickler, M.; Partridge, A.; Carey, L.A.; Winer, E.P. Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Hormone Receptor–positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients who Received Letrozole with or Without BevacizumabCTCs in HR+ Breast Cancer Treated with Hormone Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4911–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Wittner, B.S.; Stott, S.L.; Smas, M.E.; Ting, D.T.; Isakoff, S.J.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Wells, M.N.; Shah, A.M. Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in epithelial and mesenchymal composition. Science 2013, 339, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhu, D.; Tang, X.; Qiu, X.; Lu, D.; Li, B.; Lin, D.; Zhou, Q. Detection of circulating tumor cell molecular subtype in pulmonary vein predicting prognosis of stage i–iii non-small cell lung cancer patients. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamminga, M.; de Wit, S.; Schuuring, E.; Timens, W.; Terstappen, L.W.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Groen, H.J. Circulating tumor cells in lung cancer are prognostic and predictive for worse tumor response in both targeted-and chemotherapy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamminga, M.; Oomens, L.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Andree, K.C.; Tibbe, A.; Broekmaat, J.; Schuuring, E.; Terstappen, L.W.; Groen, H.J. Microsieves for the detection of circulating tumor cells in leukapheresis product in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rønnov-Jessen, L.; Petersen, O.W.; Koteliansky, V.E.; Bissell, M.J. The origin of the myofibroblasts in breast cancer. Recapitulation of tumor environment in culture unravels diversity and implicates converted fibroblasts and recruited smooth muscle cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Liu, T.; Yin, R. Biomarkers for cancer-associated fibroblasts. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuninty, P.R.; Bansal, R.; De Geus, S.W.; Mardhian, D.F.; Schnittert, J.; van Baarlen, J.; Storm, G.; Bijlsma, M.F.; van Laarhoven, H.W.; Metselaar, J.M. ITGA5 inhibition in pancreatic stellate cells attenuates desmoplasia and potentiates efficacy of chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barenholz, Y.C. Doxil®—The first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Lokerse, W.J.; Seynhaeve, A.L.; Koning, G.A.; Ten Hagen, T.L. Formulation and optimization of idarubicin thermosensitive liposomes provides ultrafast triggered release at mild hyperthermia and improves tumor response. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hagen, T.L.; Hossann, M.; Süss, R.; van Rhoon, G.C.; Eggermont, A.M.; Haemmerich, D.; Koning, G.A. Mild hyperthermia triggered doxorubicin release from optimized stealth thermosensitive liposomes improves intratumoral drug delivery and efficacy. J. Control. Release 2013, 168, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk-Draper, L.; Hall, K.; Griggs, C.; Rajput, S.; Kohio, P.; DeNardo, D.; Ran, S. Paclitaxel therapy promotes breast cancer metastasis in a TLR4-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5421–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingis-Velitski, S.; Loven, D.; Benayoun, L.; Munster, M.; Bril, R.; Voloshin, T.; Alishekevitz, D.; Bertolini, F.; Shaked, Y. Host response to short-term, single-agent chemotherapy induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and accelerates metastasis in mice. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6986–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, G.S.; Pastoriza, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Harney, A.S.; Entenberg, D.; Pignatelli, J.; Sharma, V.P.; Xue, E.A.; Cheng, E.; D’Alfonso, T.M. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy induces breast cancer metastasis through a TMEM-mediated mechanism. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan0026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rack, B.; Schindlbeck, C.; Jückstock, J.; Andergassen, U.; Hepp, P.; Zwingers, T.; Friedl, T.W.; Lorenz, R.; Tesch, H.; Fasching, P.A. Circulating tumor cells predict survival in early average-to-high risk breast cancer patients. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Otero, N.; Marshall, J.R.; Lash, B.; King, M.R. Chemotherapy-induced release of circulating-tumor cells into the bloodstream in collective migration units with cancer-associated fibroblasts in metastatic cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Z.; Shah, S.H.; Machlin, L.M.; Parajuli, R.; Miller, P.C.; Rawal, S.; Williams, A.J.; Cote, R.J.; Lippman, M.E.; Datar, R.H. Identification of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Circulating Blood from Patients with Metastatic Breast CancerIdentification of cCAFs from Metastatic Cancer Patients. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4681–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivello, F.; Matuła, K.; Piruska, A.; Smits, M.; Mehra, N.; Huck, W.T. Probing single-cell metabolism reveals prognostic value of highly metabolically active circulating stromal cells in prostate cancer. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Hu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, G.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, L. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast (CAF) Heterogeneity and Targeting Therapy of CAFs in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 655152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchou, J.; Zhang, P.J.; Bi, Y.; Satija, C.; Marjumdar, R.; Stephen, T.L.; Lo, A.; Chen, H.; Mies, C.; June, C.H. Fibroblast activation protein expression by stromal cells and tumor-associated macrophages in human breast cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2549–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Xing, S.; Xu, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, G. Evaluation of the circulating level of fibroblast activation protein α for diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Voisin, V.; Poon, S.; Karamboulas, C.; Bui, N.H.B.; Meens, J.; Dmytryshyn, J.; Ho, V.W.; Tang, K.H.; Paterson, J. Distinct fibroblast functional states drive clinical outcomes in ovarian cancer and are regulated by TCF21. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harigopal, M.; Kowalski, D.; Vosoughi, A. Enumeration and molecular characterization of circulating tumor cells as an innovative tool for companion diagnostics in breast cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Cebey-López, V.; Pereira-Veiga, T.; Martínez-Pena, I.; Abreu, M.; Abalo, A.; Lago-Lestón, R.M.; Abuín, C.; Palacios, P. Analysis of a real-world cohort of metastatic breast cancer patients shows circulating tumor cell clusters (CTC-clusters) as predictors of patient outcomes. Cancers 2020, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado, P.; Martínez-Pena, I.; Piñeiro, R. Dangerous liaisons: Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). Cancers 2020, 12, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.R.; Perez, M.J.; Munson, J.M. Docetaxel facilitates lymphatic-tumor crosstalk to promote lymphangiogenesis and cancer progression. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Medina-Saenz, K.; Miller, P.C.; Troness, B.; Spartz, A.; Sandoval-Leon, A.; Parke, D.N.; Seagroves, T.N.; Lippman, M.E.; El-Ashry, D. Heterotypic clustering of circulating tumor cells and circulating cancer-associated fibroblasts facilitates breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 189, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Jin, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, T.; Gong, C. Heterotypic CAF-tumor spheroids promote early peritoneal metastasis of ovarian cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, T.; Oomens, L.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Prakash, J. In Vivo Detection of Circulating Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Breast Tumor Mouse Xenograft: Impact of Tumor Stroma and Chemotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041127
Lu T, Oomens L, Terstappen LWMM, Prakash J. In Vivo Detection of Circulating Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Breast Tumor Mouse Xenograft: Impact of Tumor Stroma and Chemotherapy. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041127
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Tao, Lisa Oomens, Leon W. M. M. Terstappen, and Jai Prakash. 2023. "In Vivo Detection of Circulating Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Breast Tumor Mouse Xenograft: Impact of Tumor Stroma and Chemotherapy" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041127
APA StyleLu, T., Oomens, L., Terstappen, L. W. M. M., & Prakash, J. (2023). In Vivo Detection of Circulating Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Breast Tumor Mouse Xenograft: Impact of Tumor Stroma and Chemotherapy. Cancers, 15(4), 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041127







