Simple Summary
Epigenetic alterations strongly contribute to the development of various types of cancer, including blood cancers such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Unlike genetic mutations, epigenetic changes in cancer are reversible. Therefore, targeted modification of epigenetic regulators, such as histone deacetylases (HDACs), is under intense investigation. Here, we analyzed gene expression for all four classes of HDACs in AML patients compared to healthy controls. We observed significant overexpression of various HDACs, including the relatively unexplored HDAC class IIA members. To investigate the cellular consequences of HDAC inhibition, we treated AML cell lines with the class IIA HDAC inhibitor TMP269 and observed significant effects on the cellular proteome and the growth of AML cells. We further demonstrate that the combination of TMP269 and venetoclax results in enhanced cell apoptosis. Our work provides new data for the HDAC inhibitor TMP269 and suggests that TMP269 might be an alternative compound for polytherapy in AML.
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a hematopoietic malignancy characterized by altered myeloid progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. As in many other cancers, epigenetic transcriptional repressors such as histone deacetylases (HDACs) are dysregulated in AML. Here, we investigated (1) HDAC gene expression in AML patients and in different AML cell lines and (2) the effect of treating AML cells with the specific class IIA HDAC inhibitor TMP269, by applying proteomic and comparative bioinformatic analyses. We also analyzed cell proliferation, apoptosis, and the cell-killing capacities of TMP269 in combination with venetoclax compared to azacitidine plus venetoclax, by flow cytometry. Our results demonstrate significantly overexpressed class I and class II HDAC genes in AML patients, a phenotype which is conserved in AML cell lines. In AML MOLM-13 cells, TMP269 treatment downregulated a set of ribosomal proteins which are overexpressed in AML patients at the transcriptional level. TMP269 showed anti-proliferative effects and induced additive apoptotic effects in combination with venetoclax. We conclude that TMP269 exerts anti-leukemic activity when combined with venetoclax and has potential as a therapeutic drug in AML.
Keywords:
AML; HDAC; HDAC inhibitor; TMP269; RPL6; proliferation; venetoclax; azacitidine; apoptosis 1. Introduction
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is one of the most common malignant diseases of the hematopoietic system in adults, with a median age at diagnosis of 68 years [1]. AML is characterized by the altered proliferation and differentiation blockade of myeloid progenitor cells, which leads to the replacement of functional blood cells by non-functional leukemic blasts, resulting in a severely impaired hematopoietic system [2]. For several decades, the standard treatment for AML included high-dosage chemotherapy with or without subsequent allogeneic stem cell transplantation according to risk profile, age, and comorbidity as well as availability of adequate donors, or various low-dose palliative treatment regimens for patients incapable of withstanding such an aggressive treatment. Since 2017, several new drugs have emerged that revolutionized the treatment of AML [3,4]. One of the new promising drugs for patients not qualifying for high-dose chemotherapy is venetoclax. FDA approved since 2018, venetoclax induces rapid apoptosis of AML cells by inhibiting the anti-apoptotic protein B cell leukemia/lymphoma-2 (BCL-2). Venetoclax shows low efficacy as a monotherapy but is highly potent when used in combination with hypomethylating agents (HMAs) such as azacitidine and decitabine or chemotherapeutic agents such as cytarabine, resulting in synergistic anti-leukemic activity [5,6]. Even though the combination therapies of HMAs and venetoclax show a high success rate, clinical studies revealed that 1/3 of patients with newly diagnosed AML do not go into complete remission and/or become resistant to the drug treatment over time [7,8]. In particular, AML patients with monocytic differentiation (M5 AML according to the French-American-British (FAB) classification system) show little or no response to the combination of azacitidine and venetoclax [9]. Therefore, there is a strong need for new combination approaches with venetoclax to improve treatment efficacy.
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are enzymes that regulate gene expression by changing the acetylation state of N-terminal lysine residues of core histone proteins and of some non-histone proteins, including oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, transcription factors, chaperones, and other cell signaling molecules, thereby altering protein stability or biological function [10,11]. In many cancer types, the cellular acetylation homeostasis of the proteome is impaired due to dysregulation of HDACs [12,13], resulting in altered levels of cell proliferation, cell differentiation, and apoptosis [14]. These tumor-promoting effects can be antagonized by HDAC inhibitors, which block histone deacetylation and thereby inhibit cell proliferation and migration [15,16] and induce cell-cycle arrest [17] and apoptosis [18] of cancer cells. There are different types of HDAC inhibitors which are chemically grouped as hydroximates, benzamides, cyclic peptides, and aliphatic acids, and directly or indirectly block the active site pockets of HDACs; for example, hydroximates directly bind to the cofactor zinc [19,20]. HDAC inhibitors have already been shown to exhibit anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo in various types of cancer [21], including AML [20]. Similarly, non-selective inhibitors targeting all classes of HDACs such as vorinostat [22,23], panobinostat [24], and trichostatin A [25,26] as well as the class I selective inhibitor MS-275 (entinostat) [27,28] have been effective against AML cell lines, but often showed only limited anti-leukemic activity in clinical and preclinical trials, especially if used as monotherapy. Currently, little is known about the molecular mechanism and therapeutic effects of specific class IIA HDAC inhibitors and their combination with venetoclax in the context of AML [29].
In this study, we describe novel effects of the specific class IIA HDAC inhibitor TMP269 [30] on AML cell lines. We performed a proteomic and comparative bioinformatic analysis of AML cells treated with TMP269 and identified the specific downregulation of a set of proteins which are upregulated in AML patients compared to healthy controls at the gene expression level. Among the most significantly downregulated proteins are ribosomal proteins (RPs), annotated as active components of cytosolic ribosomes and functionally linked to the initiation of ribosomal protein translation. As a consequence, we demonstrate that TMP269 treatment dampens AML cell growth and cell proliferation. Strikingly, we provide evidence that the combination of TMP269 and venetoclax has additive apoptosis-inducing effects on AML cells in vitro.
We propose that TMP269 mediates its anti-leukemic effects by downregulation of cancer-associated RPs, which synergize with the anti-leukemic/pro-apoptotic effects of venetoclax. Based on our results, TMP269 in combination with venetoclax may provide a novel and potent polytherapy option for AML patients.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
TMP269, BML-210, and venetoclax were obtained from eubio (Vienna, Austria). MS-275 (entinostat) and bufexamac were purchased from Biozol (Eching, Germany). Azacitidine was obtained from Selleckchem (Houston, TX, USA). All compounds were dissolved in 100% DMSO and stored at −70 °C.
2.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
The human AML cell lines KG-1a, HL-60, OCI-AML3, MOLM-13, MOLM-14, and MV4-11 were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium (KG-1a, HL-60, MOLM-13, MOLM-14), Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium (IMDM) (MV4-11), or Minimum Essential Medium Eagle (MEM) (OCI-AML3), supplemented with 10% (HL-60, MOLM-13, MOLM-14, MV4-11) or 20% (KG-1a, OCI-AML3) heat-inactivated FBS, 1% L-glutamine, 1% penicillin, and streptomycin. Cells were kept at 37 °C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. All cell lines were obtained from the Leibniz-Institute DSMZ GmbH (https://www.dsmz.de accessed on 22 November 2022) with the following accession numbers: MOLM-13 (ACC 554), MOLM-14 (ACC 777), MV4-11 (ACC 102), HL-60 (ACC 3), OCI-AML3 (ACC 852), KG-1a (ACC 421).
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR)
Total RNA of cultured cells was extracted using TRI Reagent (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and reverse-transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA) with RevertAid H Minus M-MulV reverse transcriptase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). RT-PCR was performed with Luna® Universal Probe qPCR Master Mix (New England BioLabs® Inc., Ipswich, MA, USA) on the Rotor-Gene 3000 (Qiagen Instruments, Hombrechtikon, Switzerland). The amount of mRNA was normalized to the reference gene large ribosomal protein P0 (RPLP0). The relative mRNA expression was determined by calculating the difference between the cycle threshold of the gene of interest and the reference gene (ΔCT). The values are depicted as 2−ΔCT. The following primers (Sigma) were used: HDAC1: forward 5′- CTATCGCCCTCACAAAGCCAATGC -3′, reverse 5′- CAGCACTTGCCACAGAACCACCAG -3′; HDAC2: forward 5′- TGGACCCATCACCCAAGCAGTG -3′, reverse 5′- CCACAGGGAGGATGCCAGAACA -3′; HDAC3: forward 5′- TCGTGCTGGGTGGTGGTGGTTA -3′, reverse 5′- GATGCGGGTGCTGACATCTGGA-3′; HDAC8: forward 5′- ACGGCTCGATGCTGGACATACTTG -3′, reverse 5′- GTTGAGGATTTGTTGGATTCGGTGG -3′; HDAC4: forward 5′- CCCTGCAAATGGATGGCTTGTG -3′, reverse 5′- TGGAGACGGGAGCGGTTCTGTTA -3′; HDAC5: forward 5′- CGAAGTCAAAGGAGCCCACACCA -3′, reverse 5′- CCAGGCAAAGGCAGTTTGTAGGAG -3′; HDAC7: forward 5′- GTAGCAGCACGCCCGCATCA -3′, reverse 5′- AGCAAGGACACTGTCGGCAAGG -3′; HDAC9: forward 5′- GCGGTTGGCATGGATGGATTAGA -3′, reverse 5′- TGCTCAGGGTGGGTGGTGGAA -3′; HDAC6: forward 5′- ACTCATACTCCTGTGCCTGCCTGG -3′, reverse 5′- GCGGTGTTTCTGTTGAGCATAGCG -3′; HDAC10: forward 5′- GCCCTAGAGTCCATCCAGAGTGCC-3′, reverse 5′- GCAACAGCGGTGCGGACAGAG-3′; RPLP0: forward 5’- GGCACCATTGAAATCCTGAGTGATGTG -3’, and reverse 5’- TTGCGGACACCCTCCAGGAAG -3’.
2.4. Cell Proliferation Analysis
Cells were labeled with a cell proliferation dye (eBioscience™ Cell Proliferation Dye eFluor™ 450, Invitrogen™, Waltham, MA, USA) diluted 1:5000 in PBS (final concentration: 2 µM). Then, 1 × 105 cells were seeded in 500 µL medium in a 48-well plate and treated with the desired concentrations of the appropriate HDAC inhibitors for 48 h. After harvesting, cells were manually counted using a Neubauer chamber and proliferation was assayed by flow cytometry on a BD FACS Canto II (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). Fixable viability dye eFluor780 (eBioscience) was used at 1:2000 to exclude dead cells. Results were analyzed using FlowJo analysis software (BD Biosciences).
2.5. Apoptosis Assay
Apoptosis was determined by staining the cells with Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit eFluor-450 and 7-AAD (eBioscience) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For titration of single drugs, MOLM-13 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of TMP269, azacitidine, or venetoclax for 24 h. For combinatory treatments, MOLM-13 or HL-60 cells were treated with 12.5 µM TMP269, 1 µM azacitidine, 25 nM venetoclax, or a combination thereof (TMP269 + venetoclax or azacitidine + venetoclax) for 24 h. Further, MOLM-13 cells were treated with 5 µM BML-210, 25 nM venetoclax, or a combination thereof (BML-210 + venetoclax) for 24 h. Cell viability and apoptosis were assessed by flow cytometry using a FACS Canto II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and the data were analyzed using FlowJo Software (BD Biosciences).
2.6. LDH Assay
MOLM-13 cells were treated with different concentrations of HDAC inhibitors for 48 h. Cytotoxicity was assessed by quantification of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release into cell supernatant by measuring the decrease in NADH absorbance at 340 nm. As a positive control, cells were lysed with 0.10% (v/v) Triton X-100 for 30 min prior to harvesting to achieve maximum LDH release.
2.7. Database Analysis
The public genome dataset GSE13159 from NCBI’s Gene Expression Omnibus (NCBI-GEO) was used to screen all HDAC classes and to compare the HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, HDAC8, HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC7, HDAC9, HDAC6, HDAC10, SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT3, SIRT5, SIRT6, SIRT7, and HDAC11 expression in AML patients to that in healthy individuals. In addition to HDACs, gene expression analysis of various other genes was performed. The dataset used is part of the MILE (Microarray Innovations in Leukemia) study research program and comprises whole-genome analysis data from 542 AML patients and 74 healthy donors of a total sample size of 2096 from 11 participating centers on three continents [31,32]. In all our analyses, we used only data from bone marrow samples. Datasets from the GEO database were imported using GEOparse (https://geoparse.readthedocs.io/ accessed on 12 December 2022) and the analysis was performed using Python.
2.8. Proteomics
Three batches of 1 × 106 MOLM-13 cells were treated with 12.5 µM TMP269 for 24 h. To analyze the proteome of the differentially treated MOLM-13 cells, label-free quantification (LFQ) was conducted. In short, the cells were lysed followed by proteolysis with trypsin and clean-up of the generated peptides by suspension trapping in an S-trap™ column (Protifi, NY, USA). Subsequently, the peptides were separated in a reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography system coupled to a quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Peptide spectra were acquired in data-dependent mode, whereby each scan cycle consisted of a full scan at a resolution setting of 70,000 at m/z 200, followed by 15 higher-energy collisional dissociation scans at 32% normalized collision energy at a resolution setting of 17,500 at m/z 200. The generated peptide spectra were processed utilizing MaxQuant 2.0.1.0 [33] with default settings for LFQ. For protein identification, a database from the Uniprot consortium [34] including only reviewed Swiss-Prot entries for Homo sapiens (Human) from 3 February 2022 was used applying a 1% false discovery rate and a reversed sequence decoy database. The obtained protein groups were further processed using the Perseus software platform [35]. More details are described in Supplementary Materials.
2.9. Bioinformatics
The identified protein groups were filtered to remove decoy hits as well as proteins that were only identified by site. Next, the LFQ intensities were log2-transformed and normalized by subtraction of the median. Protein abundances yielded by MaxQuant are shown as LFQ intensities, thus removing protein groups flagged as potential contaminants or as a hit to the reverse database [36]. Furthermore, no missing intensity measurements for any of the DMSO or the TMP269 replicates were required, and the associated UniProt accession numbers were proven to be valid. Protein differential abundance analysis was carried out with NormalyzerDE web interface v 1.14.0 [37]. After an initial round of MaxQuant protein intensity normalization methods evaluation, log2-transformed MaxQuant LFQ intensities were used as input for differential expression analysis, comparing the effect of cells treated with TMP269 to DMSO-treated controls. Here, the empirical Bayes approach Limma without covariates was chosen. The false discovery rate correction was performed according to Benjamini–Hochberg [38] and proteins were classified as differentially abundant if the so-corrected p-values were below 0.05. Proteins reported by MaxQuant were identified by UniProt accession numbers, and the corresponding gene symbols were derived by annotation mapping provided by the Ensembl database (release 107). Only proteins with a unique mapping were kept in the dataset. Principal component analysis was visualized with the plot_pca function from the DEP R package (v 1.18.0) [39] on variance stabilizing the transformed LFQ intensity data. Functional annotation was performed with clusterProfiler (v 4.4.4) [40]; enrichment representations were visualized with the barplot function called by clusterProfiler. Gene ontology terms were considered significantly enriched if the Benjamini–Hochberg adjusted p-value was less than 0.05. All analyses were performed in R (v 4.2.0) and Bioconductor (v 3.15). The String database (https://string-db.org/ accessed on 6 September 2022) was used to search for protein networks and physical protein interactions.
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
Western blots were prepared as previously described [41]. Cell lysates were prepared in NP40 sample buffer, containing 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X, 50 mM Tris pH 7.4, and 1 mM PMSF (protease inhibitor) and phosphatase inhibitor, diluted 1:4 with 4X Laemmli sample buffer (Bio-Rad, Vienna, Austria) containing 10% beta-mercaptoethanol. Samples were then separated on a 4–12% NuPAGE Bis-Tris gel (Invitrogen, Vienna, Austria) and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (0.45 µm). After blocking of non-specific binding sites with 5% skim milk for 1 h at room temperature (RT) under gentle agitation, the membrane was incubated with the appropriate primary antibody, prepared in 5% bovine serum albumin diluted in Tris-buffered saline containing 0.1% TWEEN20 (TBS-T) or 5% skim milk in TBS-T, overnight at 4 °C under gentle agitation. The membrane was then washed and incubated with the appropriate secondary antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for 1 h at RT under gentle agitation. After washing, the membrane was incubated with West Pico PLUS chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and detection was performed with a ChemiDoc Imager (Bio-Rad). The following primary antibodies were used according to the manufacturer’s instructions: anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys9) (C5B11) Rabbit mAb (#9649), anti-Histone H3 (D1H2) XP Rabbit mAb (#4499), and anti-β-Actin (13E5) Rabbit mAb (#4970, all from Cell Signaling Technology, Frankfurt, Germany). Quantification of protein levels from Western blots was performed with ImageJ and normalized to β-actin.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism 9 software. Comparisons of multiple groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. For comparison of two groups, the Mann–Whitney U test was used for non-parametric data. Data from at least three experiments are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or as indicated in the respective figure legend. p-values < 0.05 were considered significant (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001, ns = not significant).
3. Results
3.1. Increased Gene Expression of Specific Class I, Class IIA, and Class IIB HDAC Genes in AML Patients and Human AML Cell Lines
Dysregulation of HDACs is described as a hallmark in various cancer types [13]. To investigate which classes of HDACs are predominantly dysregulated in AML patients, we first screened the gene expression of all four classes of HDACs in AML patients compared to healthy controls (Figure 1A). We used the public dataset GSE13159 from NCBI’s Gene Expression Omnibus (NCBI-GEO). This dataset is part of the MILE (Microarray Innovations in Leukemia) study research program and comprises the whole-genome expression data of bone marrow and blood samples from 542 AML patients and 74 healthy donors [31,32]. For this analysis, only bone marrow samples were used and samples from peripheral blood were excluded. We observed significantly increased HDAC gene expression in samples from AML patients compared to healthy controls for HDAC1 and HDAC2 (class I HDACs, Figure 1B), as well as HDAC5, HDAC7, and HDAC9 (class IIA HDACs, Figure 1C), and HDAC6 and HDAC10 (class IIB HDACs, Figure 1D). Additionally, the gene expression of HDAC4 (class IIA) and of SIRT3, SIRT5, SIRT6, and SIRT7 (class III) were significantly reduced and HDAC11 (class IV) was significantly increased in AML patients compared to healthy controls (Supplementary Figure S1A).
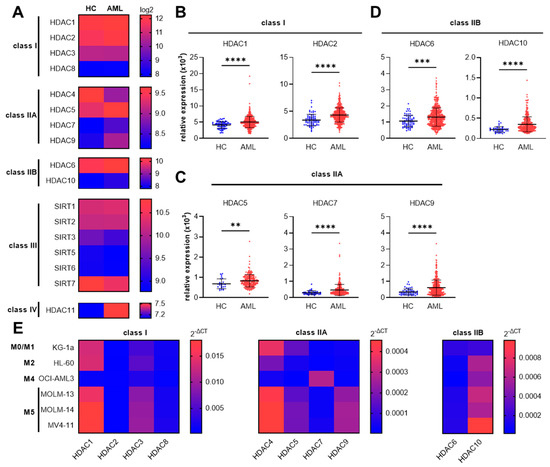
Figure 1.
HDAC gene expression in AML patients and AML cell lines. Specific class I and class II HDAC genes are overexpressed in AML patients. (A) Heat map (median) of genomic database analysis for class I–IV HDAC gene expression in AML patients (AML) compared to healthy controls (HC). Data are from the MILE study (Gene Expression Omnibus—GEO: GSE13159). Significantly overexpressed HDAC genes in AML patients compared to healthy controls included HDAC1 and HDAC2 for class I (B), HDAC5, HDAC7, and HDAC9 for class IIA (C), and HDAC6 and HDAC10 for class IIB (D). The dataset was imported using GEOparse from Python. Data are mean ± SD and were statistically analyzed by two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001. (E) Heat map of relative mRNA expression (2−ΔCT) of class I, class IIA, and class IIB HDAC gene members in different AML cell lines measured by RT-PCR (median of n = 4–5). Red color indicates high expression and blue color indicates low expression relative to the RPLP0 housekeeping gene.
Having shown that several class I and class IIA/IIB HDAC genes are overexpressed in AML patient samples, we sequentially aimed to investigate whether enhanced class I and class II HDAC gene expression can also be observed in different human AML cell lines. Thus, we monitored the class I and class II HDAC mRNA expression in six AML cell lines derived from patients of different FAB subtypes (M0–M5) (Figure 1E). While most of the tested HDAC genes are expressed in all AML cell lines, the expression levels of HDAC1 and HDAC3 (class I HDACs) but also HDAC4, HDAC5, and HDAC9 (class IIA HDACs), and HDAC10 (class IIB HDAC) are highly expressed in MOLM-13, MOLM-14, as well as in MV4-11 cells. All of these cell types are representative of the M5 FAB group, which is known to be the most aggressive AML subtype [42]. Therefore, for the experiments below, the MOLM-13 cell line was selected as a representative of the M5 AML subgroup and the HL-60 cell line was chosen as a representative of the M2 subgroup, which is the most abundant subtype in AML patients [43].
Taken together, these first results identify the increased HDAC gene expression of specific class I and class II HDACs in primary AML patient samples, an expression profile which is also retained in AML patient-derived cell lines.
3.2. TMP269 Treatment Downregulates Ribosomal Proteins Which Are Increased in AML Patients at the Gene Expression Level
Different HDAC inhibitors have been investigated in AML [20]. One of the best-studied class I HDAC inhibitors is MS-275, also known as entinostat [44,45]. MS-275 itself and in combination with other drugs exerts antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo, as demonstrated in different tumor models, including models for AML [27,46,47,48]. In contrast, data on the function of class IIA HDACs, as well as information on the molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential of class IIA HDAC inhibitors, are scarce. Therefore, in this study we focused on the novel selective class IIA HDAC inhibitor TMP269 [49] and its effects on different AML cell lines. TMP269 was already reported to have modest growth inhibitory effects and to enhance endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated apoptosis in multiple myeloma cell lines in combination with the protease inhibitor carfilzomib [50].
To better understand the molecular consequences of TMP269 administration, we performed differential proteomic analysis of MOLM-13 cells treated with 12.5 µM TMP269 or DMSO (solvent control, 0.1% as final concentration) for 24 h. The concentration of 12.5 µM TMP269 was chosen based on recently published data highlighting that >10 µM TMP269 produces strong inhibition of class IIA HDAC enzyme activity in a cell-free system [30] and anti-proliferative effects in, for example, urothelial carcinoma cell lines [51].
Our proteomic analysis generated a MaxQuant output file containing an initial 3647 protein groups. After removing those flagged as potential contaminants or as hits to the reverse database, as well as protein groups with missing abundance measurements, and filtering for valid UniProt accession numbers, 2025 protein groups remained for differential abundance analysis. The further removal of 49 protein groups matching more than a single gene and quantified proteins associated to multiple Uniprot IDs gave us a final set of 1976 proteins/genes for downstream analysis. This set contained 20 upregulated and 24 downregulated proteins/genes (significant at an adjusted p-value < 0.05 and no limitations on expression fold change).
Principal component analysis shows a clear separation of the replicates for the TMP269 or the DMSO treatment groups (Figure 2A). Forty-four proteins were significantly differentially expressed in TMP269-treated MOLM-13 cells compared to DMSO-treated cells (Figure 2B). According to their log2-fold changes, the top upregulated protein in TMP269-treated MOLM-13 cells was Malignant T-cell-amplified Sequence 1 (MCTS1), and the top downregulated protein was cell growth-regulating nucleolar protein (LYAR). The most significantly (adjusted p-value < 0.05) upregulated protein was mediator of cell motility 1 (MEMO1) and the most significantly downregulated protein was 60S ribosomal protein L6 (RPL6).
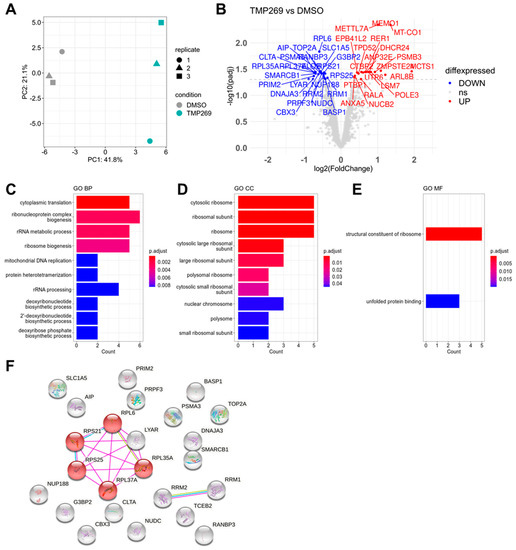
Figure 2.
Proteomics and functional annotation analysis. TMP269 treatment downregulates ribosomal proteins. MOLM-13 cells were treated with 12.5 µM TMP269. (A) Principal component analysis of TMP269 and DMSO groups. (B) Volcano plot of significantly upregulated (red) and downregulated (blue) proteins. Gene ontology (GO) analysis of significantly downregulated proteins showing the top 10 GO terms for biological processes (BP) (C), cellular components (CC) (D), and molecular functions (MF) (E). (F) String analysis of all proteins significantly downregulated by TMP269 treatment filtered for physical protein interactions. Red highlights ribosome-associated proteins RPS21, RPL6, RPL35A, RPL37A, and RPS25 (KEGG pathway for Ribosome).
Subsequently, we focused on proteins significantly downregulated by TMP269 treatment and performed gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis for the biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF). Our analysis revealed highly enriched GO terms for ribonucleoprotein complex biogenesis and cytoplasmic translation (Figure 2C), cytosolic ribosome (Figure 2D), and structural constituent of ribosome (Figure 2E). A complete list of all significantly differentially expressed proteins together with the full GO analysis is shown in Supplementary File S1. We entered the significantly downregulated proteins into the String database and filtered for physical interactions of these proteins. Consequently, we identified a core set of ribosomal proteins (RPs), including RPS21, RPS25, RPL35A, RPL37A, RPL6, and LYAR, that is downregulated by TMP269 treatment (Figure 2F).
Next, we performed a comparative bioinformatic analysis of data from the above-mentioned MILE study and analyzed how many of the 44 significantly differentially expressed proteins are also differentially expressed at the transcriptional level in AML patients compared to healthy controls (Figure 3). We first focused on the proteins downregulated by TMP269 treatment and analyzed whether their respective genes are significantly overexpressed in AML patients. In this comparative analysis, we excluded all genes from the MILE study whose sample size was less than or equal to 460 for AML patients and less than or equal to 68 for healthy controls. Strikingly, we identified eight genes/proteins (AIP, NUDC, RPL35A, RPL37A, RPL6, RPS21, RPS25, and SMARCB1) that are overexpressed at the transcriptional level in AML patients but downregulated at the protein level upon TMP269 treatment in MOLM-13 cells (Figure 3A). Vice versa, we observed six overlapping genes/proteins (ANP32E, ANXA5, NUCB2, PSMB3, RER1, and TPD52) that are upregulated upon TMP269 treatment in MOLM-13 cells but are expressed at lower transcriptional levels in AML patients (Supplementary Figure S1B). String database analysis of the eight genes/proteins that are overexpressed in AML patients but downregulated upon TMP269 treatment revealed a similar core set of RPs including RPS21, RPS25, RPL35A, RPL37A, and RPL6, all of which are part of the KEGG pathway for Ribosome (Figure 3B, red). 3D structure analysis of the ribosome (PDB ID: 4V6X) further defined the location of these proteins within the ribosome. Whereas RPS21 and RPS25 are part of the 40S ribosomal subunit, RPL35A, RPL37A, and RPL6 are constituents of the large 60S ribosomal subunit (Figure 3C). A complete comparison of the proteomic data with the data from the MILE study and the significantly differentially expressed genes in AML patients are presented in Supplementary Data File S1.
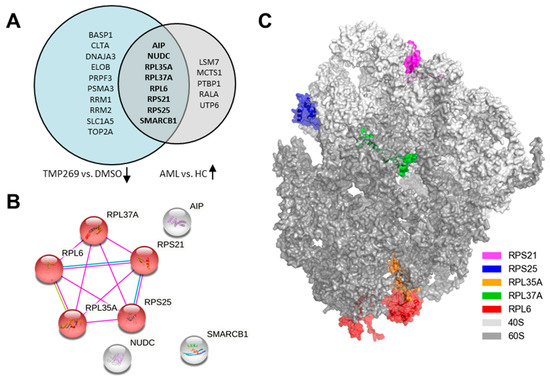
Figure 3.
Comparative bioinformatic analysis with the MILE study (Gene Expression Omnibus—GEO: GSE13159). TMP269 treatment downregulates ribosomal proteins which are increased in AML patients at the gene expression level. (A) Venn Diagram showing the intersection of 8 proteins downregulated by TMP269 (TMP269 vs. DMSO) which are overexpressed at the gene expression level in AML patients (AML vs. HC). (B) String analysis showing physical interactions of overlapping proteins/genes from the intersection in A. Red are proteins involved in the KEGG pathway for Ribosome. (C) 3D structure of the ribosome showing the large and small ribosomal subunits and the location of the proteins RPS21, RPS25, RPL35A, RPL37A, and RPL6.
Our data clearly demonstrate that the treatment of MOLM-13 cells with the class IIA HDAC inhibitor TMP269 downregulates RPs which are overexpressed at the transcriptional level in AML patients.
3.3. Inhibition of Class IIA HDACs by TMP269 Dampens AML Cell Growth and Reduces Cell Proliferation in a Concentration-Dependent Manner
Having shown that TMP269 treatment downregulates RPs, we next evaluated the cellular consequences of TMP269 treatment on AML cells. RPs are essential components of cytosolic ribosomes, involved in ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis, but RPs also have several extra-ribosomal functions implicated in tumorigenesis. For example, RPs can impact oncogenic pathways involved in cell proliferation, cell survival, cell-cycle progression, apoptosis, glycolysis, and metastasis in a variety of cancer types [52].
Initially, we investigated whether TMP269 and subsequent downregulation of RPs has anti-proliferative effects on AML cells in vitro. Additionally, we compared TMP269 to another selective class IIA HDAC inhibitor, BML-210 [53,54,55,56], to the class IIB inhibitor bufexamac [55], and to the well-studied class I HDAC inhibitor MS-275 [48,57,58,59] (Figure 4). We analyzed the effects of these different HDAC inhibitors on cell numbers and cell proliferation by treating MOLM-13 cells with increasing concentrations of the drugs (class IIA HDAC: TMP269 = 12.5–50 µM, BML-210 = 1–25 µM; class IIB HDAC: bufexamac = 2.5–12 µM; class I HDAC: MS-275 (entinostat) = 0.33–2.5 µM). Cell numbers were analyzed after 48 h by manual cell counting, and cell proliferation was analyzed by flow cytometry. The gating strategy for the cell proliferation assay is shown in Supplementary Figure S2A.
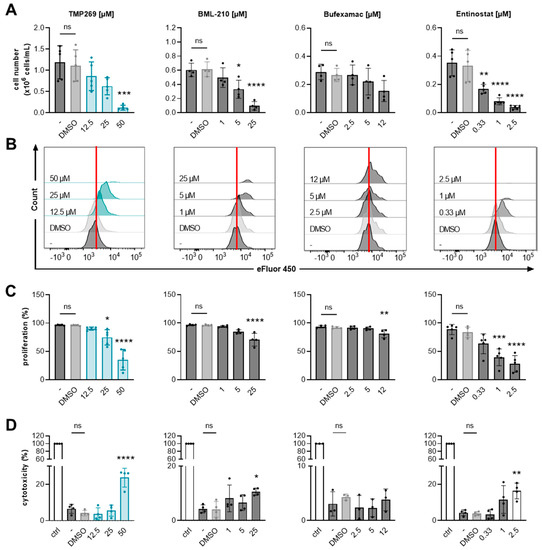
Figure 4.
Analysis of AML cell growth and cell proliferation upon treatment with different HDAC inhibitors. TMP269 reduces cell numbers and proliferation of AML cells. MOLM-13 cell numbers, cell proliferation, and cell cytotoxicity were analyzed upon treatment with the indicated concentrations [µM] of class IIA HDAC inhibitors TMP269 and BML-210, class IIB HDAC inhibitor bufexamac, and class I HDAC inhibitor entinostat (MS-275) for 48 h. (A) Cell numbers were evaluated using a Neubauer chamber (n = 4–5). (B,C) Proliferation of MOLM-13 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry, using the cell proliferation dye eFluor 450 (n = 4–5). Histograms of one representative out of 4–5 experiments are shown. The vertical red lines indicate proliferating cells in the DMSO control. (D) Cytotoxicity was measured by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay (n = 3–4). Data represent mean ± SD and were statistically analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post-hoc test, * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001. Stars indicate statistical significance compared to the DMSO treated group. ns = not significant. ctrl = control, cells lysed with 0.10% Triton X-100. - = uninduced, untreated cells. DMSO = solvent control, 0.1% DMSO as final concentration.
TMP269 treatment reduced MOLM-13 cell numbers in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 4A) and significantly reduced cell proliferation at a concentration of 25 µM compared to the DMSO-treated control (Figure 4B,C). TMP269 treatment at a 25 µM concentration resulted in significantly increased H3K9 acetylation compared to DMSO after 24 h of treatment (Supplementary Figure S1C). We further tested different concentrations of TMP269 for direct cytotoxic effects in our in vitro cell model system and began to observe cytotoxic effects, in terms of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, at 50 µM. Concentrations of 12.5 to 25 µM were well-tolerated by MOLM-13 cells (Figure 4D).
It has already been demonstrated that the class IIA HDAC inhibitor BML210 inhibits cell growth of AML cell lines by promoting apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in a dose- and time-dependent manner [54,60]. Accordingly, in our study, we observed a significant reduction in cell numbers (Figure 4A) as well as a reduction in cell proliferation (Figure 4B,C) upon treatment with 5 µM BML-210. BML-210 showed cytotoxic effects at a concentration of 25 µM (Figure 4D).
Additionally, we incubated MOLM-13 cells with the class IIB HDAC inhibitor bufexamac, which has already been investigated as a potential therapeutic agent against breast cancer [61]. However, bufexamac did not alter cell numbers significantly (Figure 4A) and we observed only a small reduction in MOLM-13 cell proliferation at 12 µM (Figure 4B,C). At 12 µM, bufexamac showed no signs of cytotoxicity (Figure 4D). The class I HDAC inhibitor entinostat (MS-275) produced the strongest reduction in cell number (Figure 4A) and cell proliferation (Figure 4B,C) in a concentration-dependent manner. Entinostat showed cytotoxicity at 2.5 µM (Figure 4D).
From these data, we conclude that TMP269 has anti-proliferative effects on AML cells comparable to BML-210 and entinostat treatment. We further validated the cell-growth inhibitory effects of TMP269 in three additional AML cell lines, i.e., MV4-11, HL-60, and OCI-AML, and observed a concentration-dependent reduction in cell numbers for all tested AML cell lines (Supplementary Figure S2B).
These data indicate that the class IIA HDAC inhibitor TMP269 is an interesting epigenetic drug and warrants further testing in new combinatory treatments for AML.
3.4. Combination Treatment of TMP269 with Venetoclax Has Additive Apoptotic Effects on AML Cells
Finally, we assessed whether TMP269 treatment and the observed downregulation of RPs have apoptotic effects or can even boost the apoptotic effects of the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax. We also analyzed if the combination of TMP269 with venetoclax is superior to the combination of venetoclax with azacitidine, which is the standard-of-care for AML patients not eligible to receive intensive chemotherapy [8,62]. We analyzed AML cell viability and apoptosis in MOLM-13 and HL-60 cells upon treatment with TMP269, azacitidine, venetoclax, or a combination of either TMP269 and venetoclax or azacitidine and venetoclax (Figure 5). We further treated MOLM-13 cells with BML-210, venetoclax, or a combination of BML-210 with venetoclax (Supplementary Figure S4). For cell death analysis, we used Annexin V and 7-AAD staining and flow cytometry to analyze the percentage of viable (Annexin V and 7-AAD double negative), early apoptotic (Annexin V positive and 7-AAD negative), and late apoptotic cells (Annexin V and 7-AAD double positive). The gating strategy for the cell death analysis is shown in Supplementary Figure S3A.
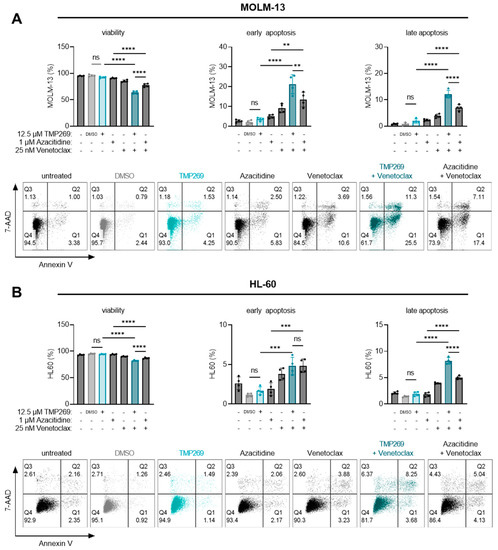
Figure 5.
The combination treatment of TMP269 plus venetoclax significantly increases AML cell death compared to azacitidine plus venetoclax. Cells were treated with 12.5 µM TMP269, 1 µM azacitidine, 25 nM venetoclax, or a combination thereof for 24 h. The percentage of MOLM-13 cells (A), or HL-60 cells (B) that were viable (Annexin V and 7-AAD double negative), early apoptotic (Annexin V positive and 7-AAD negative), or late apoptotic (Annexin V and 7-AAD double positive) was determined by staining for Annexin V and 7-AAD and flow cytometry analysis. Histograms of one representative out of 4 experiments are shown. Dots represent individual experiments (n = 4); bars represent mean ± SD and were statistically analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post-hoc test, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001. ns = not significant. - = uninduced, untreated cells. DMSO = solvent control, 0.1% DMSO as final concentration.
First, we evaluated the degree of cell death induced by different concentrations of TMP269, azacitidine, venetoclax, or BML-210 alone. TMP269 treatment started to induce early and late apoptosis at 25 and 50 µM concentrations (Supplementary Figure S3B). Azacitidine induced early and late apoptosis at 5 µM (Supplementary Figure S3C). As expected, venetoclax treatment resulted in a dose-dependent increase in early and late apoptosis already at 25 nM (Supplementary Figure S3D). BML-210 induced apoptosis at 25 µM (Supplementary Figure S3E). Next, we tested the additive effects by combining the different treatments. Based on these results and to avoid any masking effects by using too-high concentrations, MOLM-13 or HL-60 cells were treated with either 12.5 µM TMP269, 1 µM azacitidine, 25 nM venetoclax, or a combination thereof for 24 h (Figure 5).
Our results revealed that TMP269 at 12.5 µM alone does not reduce cell viability or induce apoptosis of MOLM-13 (Figure 5A) or HL-60 cells (Figure 5B). However, the viability of MOLM-13 cells (Figure 5A) decreased significantly while the percentage of early and late apoptotic cells increased significantly upon treatment with the combination of TMP269 plus venetoclax or azacitidine plus venetoclax compared to the respective single treatments. The same effects were observed in HL-60 cells (Figure 5B). Unexpectedly, in both AML cell lines, we observed that the combination of TMP269 plus venetoclax at given concentrations resulted in significantly reduced cell viability and significantly higher levels of apoptosis superior to azacitidine plus venetoclax (Figure 5A,B).
We also confirmed this additive apoptosis-inducing effect with the specific class IIA HDAC inhibitor BML-210 in combination with venetoclax (Supplementary Figure S4). Based on our results, we conclude that TMP269 exerts an additive apoptotic effect in combination with venetoclax and is superior to the combination of azacitidine plus venetoclax in AML cells.
In summary, our data demonstrate that specific class I and class II HDAC genes are overexpressed in AML patients. At the molecular level, the class IIA HDAC inhibitor TMP269 downregulates several different RPs. As a cellular consequence, TMP269 treatment has anti-proliferative and additive apoptotic effects when combined with venetoclax in different AML cell lines, suggesting that the combination of TMP269 plus venetoclax may have superior pro-apoptotic effects than the combination of azacitidine and venetoclax, which is already used to treat AML patients.
4. Discussion
AML is one of the most common and most aggressive myeloid malignancies, with a very poor 5-year overall survival rate [63]. This leukemia is characterized by altered myeloid progenitor cell proliferation, blocked cell differentiation, and resistance to apoptosis, which result in the replacement of functional blood cells by non-functional leukemic blasts [2,64]. AML is a very heterogenous disease, featuring both genetic mutations and epigenetic alterations as drivers of AML pathophysiology [65]. Most patients are 65 years or older when diagnosed with AML and are therefore not eligible for standard high-dose chemotherapy [66,67]. Consequently, these patients often receive low-dose chemotherapy and/or HMAs, but recently new drugs have been approved for this demographic [68]. For example, the pro-apoptotic agent venetoclax, which is a BCL-2 inhibitor, has been approved since 2018 and applied in combination with HMAs such as azacitidine or decitabine [69]. Despite these advances in AML treatment for older individuals, their overall 5-year survival rate is still only 10–15% [70]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop new treatment strategies and to find new combinations of drugs with strong anti-leukemic effects, which are also well-tolerated by older patients.
Cell proliferation and differentiation are tightly regulated processes depending on proper gene expression. Transcription factors regulate a number of hematopoesis-specific genes which are differentially expressed in different types of blood cancer, including AML. Recent evidence suggests that dysregulated epigenetic regulators also contribute to cancer progression [71]. Epigenetic regulators include DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), histone methyltransferases (HMTs), histone acetyltransferases (HATs), and HDACs, which are enzymes that modulate chromatin structure and thereby fundamentally regulate levels of gene expression [20,72]. In cancer, histone deacetylation results in transcriptional repression and silencing of tumor suppressor genes, thus favoring tumor progression [12,13]. In addition to HMAs such as azacitidine that are already used clinically in some AML patients who are not eligible for intensive chemotherapy [73], new HDAC inhibitors are currently under clinical development [20,74].
Altered expression levels of HDAC and related genes have been reported for different cancer types, including prostate cancer, liver cancer, colon cancer, breast cancer, and neuroblastoma [12]. However, in AML patients, altered expression levels of class I or class II HDACs are poorly described [75] and a detailed screen for differential gene expression of all classes of HDAC genes and their expression profiles in AML patients has not been reported so far.
Our work complements the existing data on dysregulated HDAC gene expression in AML patients. We screened the publicly available database from the MILE study for gene expression levels of all classes of HDAC genes in AML patients and compared them to healthy controls. We found specifically increased class I (HDAC1, HDAC2) and class II (HDAC5, HDAC7, HDAC9, HDAC6, HDAC10) HDAC gene expression in AML patients compared to healthy controls and also confirmed the expression of these genes in various AML cell lines, representative of different AML subtypes.
While considerable data are available on the beneficial effects of pan-HDAC inhibitors [20], less is known about the molecular and therapeutic function of specific class IIA inhibitors [76]. Here, we specifically investigated the class IIA HDAC inhibitor TMP269 and its effects on the cellular proteome, cell proliferation, and apoptosis in different AML cell lines. While data on TMP269 in the context of AML are scarce, TMP269 was pre-clinically tested in models for cardiovascular disease [30], urothelial carcinoma [51], and multiple myeloma [50]. In the latter study, TMP269 was reported to have modest growth inhibitory effects and to enhance ER stress-mediated apoptosis in multiple myeloma cell lines in combination with the protease inhibitor carfilzomib [49,50]. Kikuchi et al. showed that TMP269 enhances the pro-apoptosis activities of carfilzomib [50]. Likewise, we observed that TMP269 treatment in combination with venetoclax results in increased apoptosis rates. When used as a monotherapy, TMP269 did not induce apoptosis in AML cells at a concentration of 12.5 µM. Similar sensitizing effects are observed in patients who received the HMA azacitidine in combination with venetoclax. It was shown that azacitidine sensitizes AML cells for venetoclax-mediated apoptosis by inducing the pro-apoptotic molecule NOXA [77]. Similarly, we hypothesize that TMP269 treatment makes AML cells more vulnerable to venetoclax treatment, potentially by the downregulation of ribosomal proteins (RPs). The detailed mechanisms of how TMP269 makes AML cells more vulnerable to apoptosis need to be further investigated.
Different types of HDAC inhibitors directly interfere with the active site of HDACs and, as a result, block deacetylation and foster acetylation of histones or non-histone related proteins [78]. With our proteomic analysis and comparative bioinformatic analysis on TMP269-treated MOLM-13 cells, we identified a core set of downregulated proteins, many of them RPs. Most interestingly, this set of proteins is also upregulated at the gene expression level in AML patients. RPs are not only important components of cytosolic ribosomes, they are also implicated in tumorigenesis via extra-ribosomal functions that interfere with a variety of oncogenic pathways involved in cell proliferation, cell survival, cell-cycle progression, apoptosis, glycolysis, or metastasis. For example, RPs can activate p53-dependent or -independent pathways, resulting in cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis [79]. Thereby, RPs contribute to cell transformation and are frequently dysregulated in a variety of different cancer types [52]. Defects in RPs result in ribosomopathies, and indeed, patients with ribosomopathies are at a higher risk of developing cancer later in life [79]. How RP dysregulation may impact AML is completely unknown.
Our proteomic analysis of TMP269-treated MOLM-13 cells revealed downregulation of the proteins LYAR (highest fold change) and RPL6 (most significant). LYAR is a cell growth-regulating protein and part of the 60S ribosomal subunit that is described to control protein translation [80]. In colorectal cancer, LYAR was shown to promote cancer progression [81]. Consistent with its nucleolar localization, LYAR is known to participate in the regulation of ribosomal gene transcription, rRNA processing, and ribosome biogenesis. LYAR is highly expressed in tumor cells and embryonic stem cells, which are cell types that increase the production of ribosomal proteins in order to support high rates of cell proliferation [82,83]. Overexpression of LYAR was shown to increase cell proliferation without altering the expression of the proto-oncogene c-Myc or the tumor suppressor p53 [83], and it enhances the proliferation and survival of neuroblastoma cells [84]. In non-small-cell lung cancer, expression of LYAR is associated with poor prognosis [85]. The function of LYAR in the context of AML is so far unknown. However, the results of the above-mentioned studies are in line with our own data presented here, as we observed the downregulation of LYAR in AML cells upon treatment with TMP269.
RPL6 is the most significantly downregulated protein in our proteomic analysis. RPL6 is a component of the large ribosomal subunit (60S) [86]. Ribosome biogenesis is essential for cell growth and cell proliferation. In the context of cancer, it was already shown that the expression levels of RPL6 are altered and that RPL6 monitors the level of tumor suppressor p53 in response to ribosomal stress [87]. In multidrug-resistant gastric cancer cells, RPL6 is upregulated and RPL6 overexpression correlates with lower overall survival in cancer patients [88]. In addition, in 2011, Wu et al. showed that the genetic downregulation of RPL6 in gastric cancer cells reduced its colony-forming ability in vitro, reduced cancer growth in vivo, and stopped cell-cycle progression via the downregulation of cyclin E [88]. Moreover, in lung cancer cells, downregulation of RPL6 inhibits cancer cell proliferation and migration and promotes cell apoptosis [89]. Furthermore, Zhang et al. showed that knockdown of RPL6 in lung cancer cells is accompanied by downregulation of BCL-2 and AKT signaling activators such as p-AKT and p-S6. Thereby, RPL6 downregulation leads to increased protein levels of pro-apoptotic molecules such as cleaved caspase-3 and BAX [89]. However, the role and function of RPL6 in AML are still largely unknown. In the present work, we demonstrated a link between RPL6 and AML, as the RPL6 gene is overexpressed in AML patients compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, the downregulation of RPL6 protein levels induced by TMP269 treatment is associated with increased AML cell apoptosis when the cells are additionally treated with venetoclax.
Our String analysis revealed that RPL6 directly interacts with other RPL proteins such as RPL35A, RPL37A, RPS21, and RPS25, which are also significantly downregulated by TMP269 treatment and upregulated at the gene expression level in AML patients.
RPS25 has recently been shown to play an essential role in the cap-independent initiation of translation, which suggests that RPS25 has an important general function in regulating protein translation [90]. The RPS25 gene was demonstrated to be overexpressed in human leukemia cells which exhibit chemotherapy resistance to adriamycin [91]. Furthermore, RPS25 was suggested to play a role in apoptosis [92] and cell-cycle arrest [93]. However, little is known about the role of RPS25 in the context of AML.
Another candidate to be investigated based on our proteome analysis is RPL35A, which was also downregulated upon TMP269 treatment but is upregulated at the transcriptional level in AML patients. In gastric cancer, RPL35A knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and migration, promoted apoptosis, and suppressed tumor growth [94]. Furthermore, overexpression of RPL35A was shown to inhibit cell death without affecting the levels of anti-apoptotic proteins such as BCL-2 and BCL-xL [95]. This indicates that RPL35A might also have direct anti-apoptotic, extra-ribosomal functions in cancer cells.
5. Conclusions
Although a significant proportion of AML patients can now be cured, studies on newer treatment options such as the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax revealed that patients can become resistant to this drug, resulting in lower survival rates [96]. Finding new drugs that might be combined with already existing drugs is key for increasing the overall survival of AML patients. Here, we showed that specific class I and class II HDAC genes are significantly overexpressed in AML patients compared to healthy controls and that combinatory treatment of AML cell lines with the class IIA HDAC inhibitor TMP269 and venetoclax leads to increased induction of cell apoptosis. The combination of TMP269 plus venetoclax might therefore be a new treatment option for AML patients.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers15041039/s1, Supplementary Materials and Methods for Proteomics; Supplementary Figure S1: HDAC gene expression in AML patients, comparative bioinformatic analysis with the MILE study (Gene Expression Omnibus—GEO: GSE13159) and H3K9 acetylation analysis; Supplementary Figure S2: Representative FACS plots for the gating strategy in the proliferation assay and treatment of different AML cell lines with increasing concentrations of TMP269; Supplementary Figure S3: Gating strategy for the apoptosis assay, and treatment of MOLM-13 cells with increasing concentrations of TMP269, azacitidine, venetoclax. and BML-210 for cell death analysis; Supplemenary Figure S4: The combination treatment of BML-210 plus venetoclax significantly increases AML cell death; Supplementary Data File S1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.U. and J.H.-H.; data curation, L.U., C.R., J.V. and E.K.; formal analysis, L.U., M.S.U., H.S., H.-H.D., T.N., C.R., J.V., E.K. and M.L.; funding acquisition, J.H.-H.; investigation, L.U., M.S.U., H.S., H.-H.D., T.N., C.R., J.V., E.K. and M.L.; resources, S.S., S.M.W., C.X.W. and C.G.H.; supervision, S.S., S.M.W., C.X.W., P.W.K., L.P., R.G., C.G.H., F.A. and J.H.-H.; validation, L.U., M.S.U., H.S., H.-H.D. and T.N.; visualization, M.S.U., H.S., J.V. and E.K.; writing—original draft, L.U. and M.S.U.; writing—review & editing, M.S.U., H.S., J.V., P.W.K., R.G., C.G.H. and J.H.-H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the County of Salzburg, Cancer Cluster Salzburg [grant number 20102-P1601064-FPR01-2017], the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) [grant number P33969], the Biomed Center Salzburg (project 20102-F1901165-KZP), the European Interreg V-A Italien-Österreich project EPIC (grant number ITAT1054), and by the Priority program ACBN, University of Salzburg.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- U.S. National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Dohner, H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Bloomfield, C.D. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daver, N.; Wei, A.H.; Pollyea, D.A.; Fathi, A.T.; Vyas, P.; DiNardo, C.D. New directions for emerging therapies in acute myeloid leukemia: The next chapter. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H. Emerging agents and regimens for AML. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, C.D.; Pratz, K.W.; Letai, A.; Jonas, B.A.; Wei, A.H.; Thirman, M.; Arellano, M.; Frattini, M.G.; Kantarjian, H.; Popovic, R.; et al. Safety and preliminary efficacy of venetoclax with decitabine or azacitidine in elderly patients with previously untreated acute myeloid leukaemia: A non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, A.H.; Strickland, S.A., Jr.; Hou, J.Z.; Fiedler, W.; Lin, T.L.; Walter, R.B.; Enjeti, A.; Tiong, I.S.; Savona, M.; Lee, S.; et al. Venetoclax Combined With Low-Dose Cytarabine for Previously Untreated Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Results From a Phase Ib/II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Pratz, K.; Pullarkat, V.; Jonas, B.A.; Arellano, M.; Becker, P.S.; Frankfurt, O.; Konopleva, M.; Wei, A.H.; Kantarjian, H.M.; et al. Venetoclax combined with decitabine or azacitidine in treatment-naive, elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Jonas, B.A.; Pullarkat, V.; Thirman, M.J.; Garcia, J.S.; Wei, A.H.; Konopleva, M.; Dohner, H.; Letai, A.; Fenaux, P.; et al. Azacitidine and Venetoclax in Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Pollyea, D.A.; Gustafson, A.; Stevens, B.M.; Minhajuddin, M.; Fu, R.; Riemondy, K.A.; Gillen, A.E.; Sheridan, R.M.; Kim, J.; et al. Monocytic Subclones Confer Resistance to Venetoclax-Based Therapy in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, D.M.; Walsh, L.A.; Chan, T.A. Driver mutations of cancer epigenomes. Protein Cell 2014, 5, 265–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, C.; Kumar, C.; Gnad, F.; Nielsen, M.L.; Rehman, M.; Walther, T.C.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science 2009, 325, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parbin, S.; Kar, S.; Shilpi, A.; Sengupta, D.; Deb, M.; Rath, S.K.; Patra, S.K. Histone deacetylases: A saga of perturbed acetylation homeostasis in cancer. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, S.; Panigrahi, D.P.; Praharaj, P.P.; Bhol, C.S.; Mahapatra, K.K.; Mishra, S.R.; Behera, B.P.; Jena, M.; Bhutia, S.K. Dysregulation of histone deacetylases in carcinogenesis and tumor progression: A possible link to apoptosis and autophagy. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3263–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chueh, A.C.; Tse, J.W.; Togel, L.; Mariadason, J.M. Mechanisms of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor-Regulated Gene Expression in Cancer Cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Horiuchi, A.; Kikuchi, N.; Hayashi, T.; Fuseya, C.; Suzuki, A.; Konishi, I.; Shiozawa, T. Type-specific roles of histone deacetylase (HDAC) overexpression in ovarian carcinoma: HDAC1 enhances cell proliferation and HDAC3 stimulates cell migration with downregulation of E-cadherin. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 1332–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Ali, A.; Khan, S.; Ibrahim, M.; Alshehri, M.A.; Thirupathi, A. Inhibition of HDACs Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Cell Migration of Gastric Cancer by Regulating E2F5 Targeting BCL2. Life 2021, 11, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrella, A.; D’Acunto, C.W.; Rodriquez, M.; Festa, M.; Tosco, A.; Bruno, I.; Terracciano, S.; Taddei, M.; Paloma, L.G.; Parente, L. Effects of FR235222, a novel HDAC inhibitor, in proliferation and apoptosis of human leukaemia cell lines: Role of annexin A1. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insinga, A.; Monestiroli, S.; Ronzoni, S.; Gelmetti, V.; Marchesi, F.; Viale, A.; Altucci, L.; Nervi, C.; Minucci, S.; Pelicci, P.G. Inhibitors of histone deacetylases induce tumor-selective apoptosis through activation of the death receptor pathway. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.Z. Histone deacetylase inhibition: An important mechanism in the treatment of lymphoma. Cancer Biol. Med. 2012, 9, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Jose-Eneriz, E.; Gimenez-Camino, N.; Agirre, X.; Prosper, F. HDAC Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2019, 11, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Seto, E. HDACs and HDAC Inhibitors in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, E.W.; Loaiza-Bonilla, A.; Juckett, M.; DiPersio, J.F.; Roy, V.; Slack, J.; Wu, W.; Laumann, K.; Espinoza-Delgado, I.; Gore, S.D.; et al. A phase 2 study of vorinostat in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.S.; Clarke, K.M.; Kettyle, L.M.; Thompson, A.; Mills, K.I. Decitabine-Vorinostat combination treatment in acute myeloid leukemia activates pathways with potential for novel triple therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 51429–51446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenk, R.F.; Krauter, J.; Raffoux, E.; Kreuzer, K.A.; Schaich, M.; Noens, L.; Pabst, T.; Vusirikala, M.; Bouscary, D.; Spencer, A.; et al. Panobinostat monotherapy and combination therapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: Results from two clinical trials. Haematologica 2018, 103, e25–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.T.; Kim, H.N.; Lee, I.K.; Nguyen-Pham, T.N.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.J.; Park, K.S.; Kook, H.; Kim, H.J. Improved therapeutic effect against leukemia by a combination of the histone methyltransferase inhibitor chaetocin and the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momparler, R.L.; Cote, S.; Momparler, L.F.; Idaghdour, Y. Epigenetic therapy of acute myeloid leukemia using 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine (decitabine) in combination with inhibitors of histone methylation and deacetylation. Clin. Epigenetics 2014, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, J.M.; Kettyle, L.M.; Sharpe, D.J.; Mulgrew, N.M.; Dickson, G.J.; Bijl, J.J.; Austin, P.; Mayotte, N.; Cellot, S.; Lappin, T.R.; et al. Entinostat prevents leukemia maintenance in a collaborating oncogene-dependent model of cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Stem. Cells 2013, 31, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gojo, I.; Jiemjit, A.; Trepel, J.B.; Sparreboom, A.; Figg, W.D.; Rollins, S.; Tidwell, M.L.; Greer, J.; Chung, E.J.; Lee, M.J.; et al. Phase 1 and pharmacologic study of MS-275, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in adults with refractory and relapsed acute leukemias. Blood 2007, 109, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giorgio, E.; Gagliostro, E.; Brancolini, C. Selective class IIa HDAC inhibitors: Myth or reality. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Kee, H.J.; Jin, L.; Ryu, Y.; Sun, S.; Kim, G.R.; Jeong, M.H. Inhibition of class IIa histone deacetylase activity by gallic acid, sulforaphane, TMP269, and panobinostat. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haferlach, T.; Kohlmann, A.; Wieczorek, L.; Basso, G.; Kronnie, G.T.; Bene, M.C.; De Vos, J.; Hernandez, J.M.; Hofmann, W.K.; Mills, K.I.; et al. Clinical utility of microarray-based gene expression profiling in the diagnosis and subclassification of leukemia: Report from the International Microarray Innovations in Leukemia Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2529–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmann, A.; Kipps, T.J.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Downing, J.R.; Shurtleff, S.A.; Mills, K.I.; Gilkes, A.F.; Hofmann, W.K.; Basso, G.; Dell’orto, M.C.; et al. An international standardization programme towards the application of gene expression profiling in routine leukaemia diagnostics: The Microarray Innovations in LEukemia study prephase. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willforss, J.; Chawade, A.; Levander, F. NormalyzerDE: Online Tool for Improved Normalization of Omics Expression Data and High-Sensitivity Differential Expression Analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate—A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Smits, A.H.; van Tilburg, G.B.; Ovaa, H.; Huber, W.; Vermeulen, M. Proteome-wide identification of ubiquitin interactions using UbIA-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 530–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauenlob, T.; Neuper, T.; Mehinagic, M.; Dang, H.H.; Boraschi, D.; Horejs-Hoeck, J. Helicobacter pylori Infection of Primary Human Monocytes Boosts Subsequent Immune Responses to LPS. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 847958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilha, S.L.; Souza, E.J.; Matos, M.C.; Domino, N.R. Acute myeloid leukemia: Survival analysis of patients at a university hospital of Parana. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 2015, 37, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basharat, M.; Khan, S.A.; Din, N.U.; Ahmed, D. Immunophenotypic characterisation of morphologically diagnosed cases of Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML). Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, E.; Dul, E.; Sung, C.M.; Chen, Z.; Kirkpatrick, R.; Zhang, G.F.; Johanson, K.; Liu, R.; Lago, A.; Hofmann, G.; et al. Identification of novel isoform-selective inhibitors within class I histone deacetylases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 307, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, A.; Volpari, C.; Filocamo, G.; Casavola, E.C.; Brunetti, M.; Renzoni, D.; Chakravarty, P.; Paolini, C.; De Francesco, R.; Gallinari, P.; et al. Crystal structure of a eukaryotic zinc-dependent histone deacetylase, human HDAC8, complexed with a hydroxamic acid inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15064–15069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Shin, T.; Verheul, H.; Hammers, H.; Sanni, T.B.; Salumbides, B.C.; Van Erp, K.; Schulick, R.; Pili, R. Synergistic in vivo antitumor effect of the histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 in combination with interleukin 2 in a murine model of renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4538–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, C.; Ikezoe, T.; Yang, J.; Takeuchi, S.; Koeffler, H.P.; Yokoyama, A. MS-275, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor with selectivity against HDAC1, induces degradation of FLT3 via inhibition of chaperone function of heat shock protein 90 in AML cells. Leuk. Res. 2008, 32, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess-Stumpp, H.; Bracker, T.U.; Henderson, D.; Politz, O. MS-275, a potent orally available inhibitor of histone deacetylases--the development of an anticancer agent. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1388–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobera, M.; Madauss, K.P.; Pohlhaus, D.T.; Wright, Q.G.; Trocha, M.; Schmidt, D.R.; Baloglu, E.; Trump, R.P.; Head, M.S.; Hofmann, G.A.; et al. Selective class IIa histone deacetylase inhibition via a nonchelating zinc-binding group. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, S.; Suzuki, R.; Ohguchi, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Lu, D.; Cottini, F.; Jakubikova, J.; Bianchi, G.; Harada, T.; Gorgun, G.; et al. Class IIa HDAC inhibition enhances ER stress-mediated cell death in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaletsch, A.; Pinkerneil, M.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Jaguva Vasudevan, A.A.; Wang, C.; Hansen, F.K.; Wiek, C.; Hanenberg, H.; Gertzen, C.; Gohlke, H.; et al. Effects of novel HDAC inhibitors on urothelial carcinoma cells. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khoury, W.; Nasr, Z. Deregulation of ribosomal proteins in human cancers. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20211577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayathilaka, N.; Han, A.; Gaffney, K.J.; Dey, R.; Jarusiewicz, J.A.; Noridomi, K.; Philips, M.A.; Lei, X.; He, J.; Ye, J.; et al. Inhibition of the function of class IIa HDACs by blocking their interaction with MEF2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 5378–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savickiene, J.; Borutinskaite, V.V.; Treigyte, G.; Magnusson, K.E.; Navakauskiene, R. The novel histone deacetylase inhibitor BML-210 exerts growth inhibitory, proapoptotic and differentiation stimulating effects on the human leukemia cell lines. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 549, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantscheff, M.; Hopf, C.; Savitski, M.M.; Dittmann, A.; Grandi, P.; Michon, A.M.; Schlegl, J.; Abraham, Y.; Becher, I.; Bergamini, G.; et al. Chemoproteomics profiling of HDAC inhibitors reveals selective targeting of HDAC complexes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savickiene, J.; Treigyte, G.; Borutinskaite, V.V.; Navakauskiene, R. Antileukemic activity of combined epigenetic agents, DNMT inhibitors zebularine and RG108 with HDAC inhibitors, against promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2012, 17, 501–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vire, B.; de Walque, S.; Restouin, A.; Olive, D.; Van Lint, C.; Collette, Y. Anti-leukemia activity of MS-275 histone deacetylase inhibitor implicates 4-1BBL/4-1BB immunomodulatory functions. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, S.C.; Rosato, R.R.; Kramer, L.B.; Dai, Y.; Rahmani, M.; Paik, D.S.; Czarnik, A.C.; Payne, S.G.; Spiegel, S.; Grant, S. The histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 interacts synergistically with fludarabine to induce apoptosis in human leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2590–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Yamashita, T.; Mariko, Y.; Nosaka, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Ando, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tsuruo, T.; Nakanishi, O. A synthetic inhibitor of histone deacetylase, MS-27-275, with marked in vivo antitumor activity against human tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4592–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borutinskaite, V.; Navakauskiene, R. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor BML-210 Influences Gene and Protein Expression in Human Promyelocytic Leukemia NB4 Cells via Epigenetic Reprogramming. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18252–18269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medler, T.R.; Craig, J.M.; Fiorillo, A.A.; Feeney, Y.B.; Harrell, J.C.; Clevenger, C.V. HDAC6 Deacetylates HMGN2 to Regulate Stat5a Activity and Breast Cancer Growth. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 994–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, E.M.; Abbott, D.; Amaya, M.; McMahon, C.; Schwartz, M.; Rosser, J.; Sato, A.; Schowinsky, J.; Inguva, A.; Minhajuddin, M.; et al. Venetoclax and azacitidine compared with induction chemotherapy for newly diagnosed patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 5565–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, E.S.; Stone, R.M. Novel therapy in Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): Moving toward targeted approaches. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2019, 10, 2040620719860645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estey, E.; Dohner, H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2006, 368, 1894–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, S.L.; Hassan, C.; Khunte, M.; Soldatenko, A.; Jong, Y.; Afshinnekoo, E.; Mason, C.E. Epigenetic Modifications in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Prognosis, Treatment, and Heterogeneity. Front. Genet 2019, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kouchkovsky, I.; Abdul-Hay, M. Acute myeloid leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2016 update. Blood Cancer J 2016, 6, e441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenberg, B.; Zittoun, R.; Kerkhofs, H.; Jehn, U.; Abels, J.; Debusscher, L.; Cauchie, C.; Peetermans, M.; Solbu, G.; Suciu, S.; et al. On the value of intensive remission-induction chemotherapy in elderly patients of 65+ years with acute myeloid leukemia: A randomized phase III study of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Leukemia Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1989, 7, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurdy, S.R.; Luger, S.M. Dose intensity for induction in acute myeloid leukemia: What, when, and for whom? Haematologica 2021, 106, 2544–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Cao, Y.; Sun, R.; Cheng, L.; Xiong, X.; Jin, X.; He, X.; Lu, W.; Zhao, M. Targeting Bcl-2 Proteins in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 584974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Andersson, T.M.; Rachet, B.; Bjorkholm, M.; Lambert, P.C. Survival and cure of acute myeloid leukaemia in England, 1971-2006: A population-based study. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Role of HDACs in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.A.; Kouzarides, T. Cancer epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell 2012, 150, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, A.C.; Dohner, H.; Pleyer, L.; Seymour, J.F.; Fenaux, P.; Dombret, H. Azacitidine in adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 116, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottamal, M.; Zheng, S.; Huang, T.L.; Wang, G. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in clinical studies as templates for new anticancer agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 3898–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Maddipoti, S.; Quesada, A.; Bohannan, Z.; Cabrero Calvo, M.; Colla, S.; Wei, Y.; Estecio, M.; Wierda, W.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; et al. Analysis of class I and II histone deacetylase gene expression in human leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 3426–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clocchiatti, A.; Florean, C.; Brancolini, C. Class IIa HDACs: From important roles in differentiation to possible implications in tumourigenesis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1833–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Cojocari, D.; Purkal, J.J.; Popovic, R.; Talaty, N.N.; Xiao, Y.; Solomon, L.R.; Boghaert, E.R.; Leverson, J.D.; Phillips, D.C. 5-Azacitidine Induces NOXA to Prime AML Cells for Venetoclax-Mediated Apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3371–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verza, F.A.; Das, U.; Fachin, A.L.; Dimmock, J.R.; Marins, M. Roles of Histone Deacetylases and Inhibitors in Anticancer Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Brajanovski, N.; Chan, K.T.; Xuan, J.; Pearson, R.B.; Sanij, E. Ribosomal proteins and human diseases: Molecular mechanisms and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, K.; Sugihara, Y.; Oshima, K.; Matsuda, T.; Nadano, D. Lyar, a cell growth-regulating zinc finger protein, was identified to be associated with cytoplasmic ribosomes in male germ and cancer cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2014, 395, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Jian, S.; Ding, Q.; Gu, W.; Yao, Y.; Ma, J.; et al. LYAR Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression by Upregulating FSCN1 Expression and Fatty Acid Metabolism. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 9979707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumikawa, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Yoshikawa, H.; Fujiyama, S.; Watanabe, A.; Aburatani, H.; Tachikawa, H.; Hayano, T.; Miura, Y.; Isobe, T.; et al. LYAR potentiates rRNA synthesis by recruiting BRD2/4 and the MYST-type acetyltransferase KAT7 to rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10357–10372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, N.; Yoshikawa, H.; Magae, S.; Ishikawa, H.; Izumikawa, K.; Terukina, G.; Suzuki, A.; Nakamura-Fujiyama, S.; Miura, Y.; Hayano, T.; et al. Human cell growth regulator Ly-1 antibody reactive homologue accelerates processing of preribosomal RNA. Genes Cells 2014, 19, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Atmadibrata, B.; Yu, D.; Wong, M.; Liu, B.; Ho, N.; Ling, D.; Tee, A.E.; Wang, J.; Mungrue, I.N.; et al. Upregulation of LYAR induces neuroblastoma cell proliferation and survival. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.N.; Ju, G.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.L.; Cai, W.; Zang, Q.W. LYAR promotes the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer and is associated with poor prognosis. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2021, 59, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zuo, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Ma, C.; Dong, M.Q.; Gao, N. Structural snapshots of human pre-60S ribosomal particles before and after nuclear export. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, X. Regulation of the HDM2-p53 pathway by ribosomal protein L6 in response to ribosomal stress. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Gou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jin, H.; Cui, L.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Wang, J.; Nie, Y.; Shi, Y.; et al. Downregulation of RPL6 by siRNA inhibits proliferation and cell cycle progression of human gastric cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, Q.; Han, Y.; Wen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, Y.; Xiao, F.; Liang, C. Downregulated RPL6 inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation and migration and promotes cell apoptosis by regulating the AKT signaling pathway. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhs, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Ismer, J.; Takaku, H.; Nashimoto, M.; Uchiumi, T.; Nakashima, N.; Mielke, T.; Hildebrand, P.W.; Nierhaus, K.H.; et al. Structural basis for the binding of IRES RNAs to the head of the ribosomal 40S subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5264–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Center, M.S. Regulation of ribosomal protein S25 in HL60 cells isolated for resistance to adriamycin. FEBS Lett. 1992, 298, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adilakshmi, T.; Laine, R.O. Ribosomal protein S25 mRNA partners with MTF-1 and La to provide a p53-mediated mechanism for survival or death. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4147–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, M.E.; Leal, J.F.; Lleonart, M.E.; Ramon, Y.C.S.; Carnero, A. Loss-of-function genetic screening identifies a cluster of ribosomal proteins regulating p53 function. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Sun, D.; Liao, Y.; Shang, K.; Lu, C. RPL35A is a key promotor involved in the development and progression of gastric cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, C.D.; Martinovsky, G.; Naumovski, L. Inhibition of cell death by ribosomal protein L35a. Cancer Lett. 2002, 180, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, A.N.; John, A.J.; Kaufmann, S.H. Resistance to venetoclax and hypomethylating agents in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Drug. Resist. 2021, 4, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).